
Analysis of the Involution Community Management in Emergency
Public Health Event based on an Evaluation Index Establishment and
Experimental Date Processing
Yicheng Peng
1a
and Yue Hu
2b
1
School of Politics and Public Administration, Soochow University, Xinghu street, Suzhou, China
2
School of Politics and Public Administration, Soochow University, Suzhou, China
Keywords: Involution, Index System, AHP, Public Health Emergencies, Emergency Management, Community
Governance.
Abstract: Though investigating the process of emergency prevention and control of public health emergencies in
community C of city R, province G during COVID-19 in 2020, the article overviews emergency management
in community C of city R, province G. The article identifies key elements in emergency government and
combines related elements to build an index system to evaluate the rationality and effectiveness of emergency
management in community C based on analytic hierarchy process. The article then collects data through
questionnaires in Likert 5-point scale from residents and conduct data processing in Spss software
c
to analyse
the emergency government. Through systematic evaluation and analysis, the article points out the existence
of involution of emergency management in the community governance caused by a combination of regular
management vulnerability and pressure for pandemic prevention and control.
1 INTRODUCTION
After the outbreak of the new crown pneumonia
epidemic, Community C, City R, G Province worked
overtime to ensure pandemic prevention and control
work. However, trapped by the poor local
development situation, imperfect governance system,
and the tight schedule of the epidemic prevention and
control task, the community’s good anti-epidemic
effect is based on high load, high pressure, high cost,
and low efficiency. On the surface, although it has a
certain effect, it is actually a kind of undeveloped
growth, that is, it has fallen into the predicament of
the involution of emergency management in the
prevention and control of public health emergencies.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9056-9652
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2191-3971
c
IBM® SPSS® Statistics is a powerful statistical software platform. It offers a user-friendly interface and a robust set of features that lets your organization quickly extract
actionable insights from your data.
2 RESEARCH REVIEW
2.1 Involution
"Involution" refers to the process in which an
organization is constrained by external expansion
conditions, but has neither mutational nor incremental
growth, and the internal system continues to become
more complex. The direct consequence is
organizational decline or organizational
ineffectiveness. The "involution" of an organization's
governance often manifests itself in the form of a high
pressure on the organization's staff due to the fine
structure and functional stability (Liu, Qiu 2004).
164
Peng, Y. and Hu, Y.
Analysis of the Involution Community Management in Emergency Public Health Event based on a Evaluation Index Establishment and Experimental Date Processing.
DOI: 10.5220/0011344500003437
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis (PMBDA 2021), pages 164-169
ISBN: 978-989-758-589-0
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
3.1 Sources of Materials
The purpose of this paper is to explore the dilemma
of involution of community emergency management
under public safety emergencies by taking the
practice of emergency management in Community C
as a cut-off point. In order to gain insight into the
situation of community C’s epidemic prevention and
control work, this paper, on the one hand, based on
volunteer practice, records and analyzes the
community C's pandemic prevention and control
work from December 2019 to May 2020 in R city, G
province, and conducts semi-structured interviews
with community workers.
3.2 Assessment of Emergency
Management of Community C
3.2.1 Study Assumptions
As far as this study is concerned, the target is the
community residents, so the residents can be regarded
as the "customers" of the community for epidemic
prevention and control, and satisfaction is the attitude
and psychological experience of the customers who
are satisfied with all aspects of the service after
comparing the gap between the actual value and
demand or expectation according to the cognitive
evaluation of the community epidemic prevention
and control. Thus, we can evaluate the
implementation effect of community outbreak
prevention and control services from the perspective
of customer satisfaction. The level of resident
satisfaction directly affects the effectiveness of
epidemic prevention and control. High-quality
community epidemic prevention and control services
can achieve a reasonable allocation of limited
resources, improve the efficiency of resource
utilization, and maximize the effect of epidemic
prevention and control. In this paper, the CSI method
is used to evaluate the fullness of farmers' policies,
but two assumptions need to be determined.
a) Community outbreak prevention and control
services are felt and perceived by residents (Wang,
Luo 2010).
b) Residents are free to express their judgment in
their entirety. That is, strategic behavior has less
impact on the CSI approach (in line with the
Brookshire fascite) through proper design of the
problem. It is also said that the resident's answers to
each question are consistent with the cumulative
normal distribution function.
3.2.2 Model Selection
An important objective of the resident satisfaction
survey is to measure the current level of satisfaction
of the rural residents. This article is rated using the
Likert 5-point scale and calculated using arithmetic
weighted average (Liu 2004):
=
=
n
i 1
ii
XWCSI
(1)
CSI in the formula: customer (residents)
satisfaction index;
W
i:
Weight of the first measurement indicator;
X
i
: Customer (Residents) evaluation of the ith
satisfaction indicator.
3.2.3 Weight Design of Indicators under
Analytic Hierarchy Process
According to customer satisfaction, emergency
management and other related theories, from the
community epidemic prevention measures, the
physical and mental health of residents, residents of
epidemic prevention activities, three aspects to build
residents' satisfaction evaluation of community
epidemic prevention services, see Table 1(Peng
2018). The evaluation section uses Likert 5-point
scale to score.
In this paper, based on the index system of related
studies, the hierarchical analysis method is used to
construct an index system for evaluating the
residents’ satisfaction of community pandemic
prevention and control in community C. The analytic
hierarchy process, proposed by Saaty, an American
operations researcher, is a decision making method
that decomposes the elements related to decision
making into levels such as objectives, criteria and
programs, on the basis of which qualitative and
quantitative analysis is carried out (Wang 2003).
There are four calculation methods i thins method,
and considering the realistic operability and data
characteristics, this study selects the arithmetic
average method (summation method) for the
calculation of questionnaire index weights, and the
calculation steps are: ① normalize the elements of
the judgment matrix by column; ② add the
normalized columns; ③ divide the summed vector
by n to obtain the weight vector(Deng, Zeng, Chen,
Zhao 2012).
Step 1: through two comparisons, to determine the
relative importance between the secondary indicators,
Analysis of the Involution Community Management in Emergency Public Health Event based on a Evaluation Index Establishment and
Experimental Date Processing
165

this paper refers to the 3/3 to 9/1 scale system to
determine the corresponding a
ij
value, to the second-
level indicator of the ratio of the more decisive
moment array, recorded as A,
namely:
(2)
The implication of a
ij
is that the weight of the i
indicator is a multiple of the importance of the j
indicator.
Step 2: Solve the weight w according to the A
matrix, remember ω=(ω
1
ω
2
ω
3
…ω
n
)
T
(2)
Calculate geometric mean
1062.0
2604.0
6333.0
Normalize by column
1047.0
2583.0
6370.0
Applying Row geometry mean and Normalization
right to A, identity λ
max.
13/15/1
313/1
531
105.0
258.0
637.0
=
3182.0
7848.0
9355.1
==
=
n
i
i
i
nw
Aw
n
1
max
)(
1
λ
3.0385 (3)
Step 3: Calculate the consistency ratio CR to
check the rationality of the constructed judgment
matrix A and the weight vector derived from it.
RI
CI
=CR
(4)
0193.0
13
30385.3
1-n
CI
max
=
−
−
=
−
=
n
λ
(5)
1.0037.0
52.0
0193.0
CR <===
RI
CI
(6)
Therefore, the degree of consistency of A is
relatively high, and the weight of the structure is
reasonable.
Similarly, the weight of the three-level indicator
can be set, the specific weight value is shown in Table
1.
Residents are the service objects of the
community. Their evaluation and perception of
community anti-pandemic work are important
indicators to measure the effectiveness of community
prevention and control. The perceptibility of
community pandemic prevention is based on
community residents' perceptions and satisfaction
with the various pandemic prevention activities in the
community, and the secondary indicators are
embedded in the three perspectives of emergency
management theory: prevention beforehand, handling
during the event, and evaluation afterwards, and are
assigned to different pandemic prevention activities
in the community. The physical and mental health is
based on the self-assessment of community residents'
physical and mental health in the absence of
confirmed or meaningful patients in the community.
The secondary indicators are weighted according to
physical and psychological categories. The pandemic
prevention behavior is the self-measurement of the
residents' self-prevention behavior in the community
activities based on the classification of the pandemic
prevention activities according to the emergency
management theory, and according to the coverage
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
166
and importance of the indicators in the situation of the
whole community against the pandemic. The
secondary indicators of pandemic prevention
behaviors and pandemic prevention concerns are
assigned weight. The weights of specific indicators is
shown in the table below.
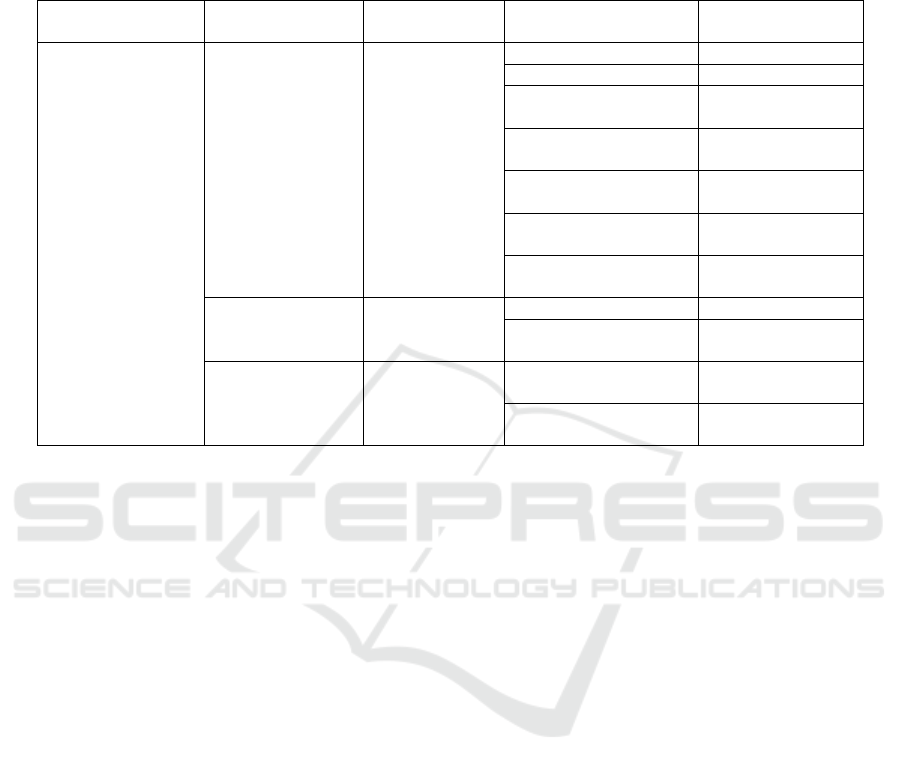
Table 1 Weight of indicators at each level of the questionnaire
First level
evaluation index
Second level
evaluation index
Weights
Third level evaluation
index
Weights
Satisfaction
Pandemic
prevention efforts
0.637
Publicit
y
0.111
Screening residents 0.435
Prevention work
attitudes
0.103
Residents' normal
service
0.043
Information
disclosure
0.043
Community
hygiene
0.205
Care for the
vulnerable
0.043
Physical and
mental health
situation
0.258
Physical health 0.5
Mental health 0.5
Residents'
pandemic
prevention
behavior
0.105
Anti-pandemic
b
ehavio
r
0.75
Concerns about the
p
andemic
0.25
4 RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS
4.1 Description of Emergency
Management of Community C
Community C has management challenges due to its
own characteristics. It has five resident groups under
its jurisdiction, and each resident group has a group
cadre for full-time integrated management. The
community also has a complex demographic
composition, with three ethnic groups living there,
making it difficult to manage. In terms of the
management of institutional mechanism, the low
incentive personnel management system caused by
low salary, low welfare and low threshold is difficult
to enhance stickiness to their own jobs among social
workers, thus threatening the effectiveness of
community governance. At the same time, the lack of
assessment mechanism will inevitably have a
negative impact on the effectiveness of community
prevention and control to a certain extent.
In addition, the COVID-19 led to high-volume,
high-stress epidemic prevention work of community
C: ① Suspected person identification ② Full
information collection③ Resumption of work and
schooling④Routine check of prevention⑤Normal
work.
4.2 Assessment of Emergency
Management of Community C
4.2.1 Data Source and Statistical Analysis
A total of 250 questionnaires were distributed to
residents in this survey, and 195 valid questionnaires
were recovered. The Likert's pentameter technique
and incorporating the indicator weighting system, a
five-level evaluation subset is used in the statistics of
scores. Date collected are processed by SPSS
software.
The scores assigned to the questionnaire
secondary indicators and questionnaire questions
were calculated to yield the primary indicators and
overall questionnaire scores as shown in Figure 1.
Analysis of the Involution Community Management in Emergency Public Health Event based on a Evaluation Index Establishment and
Experimental Date Processing
167

Figure 1: Overall questionnaire and Tier 1 indicator scores.
Referring to the literature, we choose 4 as the high
and low score boundary of this research, and we can
conclude that “Community pandemic prevention
efforts", "Physical and mental health situation" and
"Pandemic prevention behaviour" (He 2013). These
three first indicators have high scores, and the overall
score of the questionnaire is 4.47, which also belongs
to the high score range. This good score indicates that
the residents of Community C generally approve of
the anti-pandemic work of the social workers and that
the community anti-pandemic work has achieved
achievements.
4.2.2 Analysis of the Scores of Second Level
Evaluation Index under the Primary
Indicator
a) Community pandemic prevention efforts
The survey on residents’ perceptibility of community
pandemic prevention efforts was mainly evaluated in
seven dimensions, including publicity, screening
residents, prevention work attitudes, residents’
normal service, information disclosure, community
hygiene, care for the vulnerable etc. The indicator
aims to directly analyse the effectiveness of
community prevention and control work, and the
specific scores are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Scores for Second level evaluation index the
Community Community prevention efforts.
From this figure, it can be seen that the scores of
the above seven dimensions are all good, and the
residents of Community C highly approve of the work
of social workers in these aspects.
b) Physical and mental health
The survey on the physical and mental health of the
residents was conducted mainly in two aspects:
physical health and mental health. The long period of
closed homes during the pandemic had a negative
impact on the physical and mental health of residents,
so how to guide residents to maintain good physical
and mental health is also one of the important
indicators to examine the effectiveness of community
governance. As shown in Figure 3, the physical health
score of residents in Community C during the
pandemic was 4.41, and the mental health score was
4.37, which is a good score, and this good result could
not be achieved without the guidance of social
workers.
Figure 3: Scores for second level evaluation index Physical
and Mental Health Indicators of the Population.
c) Pandemic prevention behaviour
This indicator was established mainly to examine
whether residents have formed scientific and
reasonable pandemic prevention behaviors under the
guidance of community propaganda, including
insisting on wearing masks and opening windows for
ventilation, etc. In addition, it can also explore
whether residents pay attention to the pandemic
development situation in their own community, which
is a key cut-off point to measure the residents'
integration and sense of responsibility to the
community. From the analysis of the data, it is clear
that most of the residents in Community C said that
they insisted on scientific pandemic prevention
without the guidance of social workers, and it has
become a normal life style for the residents in the
community to pay close attention to the pandemic
development situation in their community.
4,4
4,39
4,6225
44,55
1.Pandemic prevention
efforts
2.Physical and mental
health situation
3.Residents' pandemic
prevention behavior
Total Questionnaire Score(4.47)
4,17
4,52
4,47
4,25
4,53
4,62
4,17
3,8 4 4,2 4,4 4,6 4,8
1.Publicity
2.Screening residents
3.Prevention work attitudes
4.ResideInformation…
5.Information disclosure
6.Community hygiene
7.Care for the vulnerable
Community Pandemic Prevention Effect
(4.39)
4,41
4,37
4 4,2 4,4 4,6 4,8 5
1.Physical health
2.Mental health
Physical and mental health
situation(4.39)
PMBDA 2021 - International Conference on Public Management and Big Data Analysis
168

Figure 4: Scores for Second level evaluation index
Pandemic prevention behaviour.
d) Summary of the results of the questionnaire
According to the analysis of the questionnaire data,
we can see that the pandemic prevention and control
work in Community C is recognized by the majority
of the residents, and the pandemic prevention and
control in Community C has achieved achievements
in this dimension. However, when combined with the
above, it is easy to see that behind this good result is
inefficiency and overload, and thus a clear dilemma
of involution, which is mainly due to the combination
of daily management system loopholes and
emergency pressure of public health emergencies.
5 CONCLUSIONS
However, due to the loopholes in the community
management system and the lack of capacity of the
social work team represented by the community
secretary, the community was unable to effectively
take time out from the increasingly heavy workload
to think about and improve the inefficient and
unreasonable work processes, and the work pressure
could not be effectively transformed into governance
performance. Therefore, even though the community
achieved remarkable governance performance, the
result was more based on the reverse incentive of the
institutional space rather than the community's own
spontaneous governance effectiveness, and such a
pushed anti-epidemic model was doomed to high
load, high pressure and low efficiency.
The logic behind the involution of community
epidemic fighting also creates a vicious circle in the
management system of Community C. Due to the
backward economic development and unsound
institutional environment, there is an obvious
mismatch between the incentive mechanism and
work pressure in Community C. The motivation and
initiative of social workers cannot be effectively
mobilized. The excessive pressure caused by the
tedious tasks in the public health emergencies and the
inefficient working methods of the actors made this
problem even more exposed, and when the pressure
gradually accumulated, the fatigue of the social
workers who were already lacking passion for their
work became more prominent, and the effectiveness
of governance further decreased. When the pressure
reaches a certain stage, the role of incentive
mechanism will be further weakened and the
enthusiasm of social workers will be further
weakened, and the inwardly-rolled dilemma will
come back again with a higher profile.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Soochow University's 2020 Jiangsu University
Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training
Program "Break the "involution" to "outside":
Research on the "involution" of community
emergency management" in public health
emergencies"" (project number 202010285070Y)
phased results, Supervisors: Professor Zhang Chen,
Professor Chen Jinhua.
REFERENCES
Deng, X., Li, J.M., Zeng, H.J., Chen, J.Y., Zhao, J.F. (2012).
Analysis of the Weight Calculation Method of Analytic
Hierarchy Process and Its Application Research. J.
Mathematics in Practice and Knowledge. 42, 93-100.
He, W.J., Cheng S. (2013). Research on beneficial
agricultural policies based on farmer satisfaction. J.
Journal of Northwest A&F University (Social Science
Edition). 02, 12-17.
Liu, S.D., Qiu, Z.Q. (2004). Analysis of the concept of
"involution". J. Sociology Studies. 05, 96-110.
Liu, X.Y., 2004. Customer satisfaction index model
research. China Finance and Economics Press. Beijing,
1
th
edition.
Peng,X.D. (2018). The basic theory of socialist emergency
management with Chinese characteristics in the new era
is summarized. Leadership Science. 27: 22-24.
Wang, Y. L., 2003. Systems Engineering. Machinery
Industry Press, Beijing, 1
th
edition.
4,65
4,54
44,55
1.Anti-pandemic
behavior
2.Concerns about
the pandemic
Residents' pandemic prevention behavior(4.60)
Analysis of the Involution Community Management in Emergency Public Health Event based on a Evaluation Index Establishment and
Experimental Date Processing
169
