
Project Ranking with Uncertainty using Multicriteria Decision Method
and Fuzzy
Guilherme A. Barucke Marcondes
a
National Institute of Telecommunications, Inatel, Av. Joao de Camargo, 510, Santa Rita do Sapucai, Brazil
Keywords:
Project Selection, Multicriteria Decision Methods, TOPSIS, Uncertainty, Fuzzy.
Abstract:
Decision-makers are frequently faced with the task of picking projects to be carried out. Generally, there
aren’t enough resources to fund all of them. Because numerous criteria to be examined at the same time in
this task, decision requires the assistance of a tool or approach. Multi-Criteria Decision-Making strategies
can be helpful. However, as with all project estimation, uncertainty must be addressed. Using the TOPSIS
method and fuzzy numbers, this article presents a way for incorporating uncertainty in project selection. It is
exemplified by the application of selection method over a set of 11 real projects.
1 INTRODUCTION
The selection of projects is a prevalent problem in
businesses. Due to the fact that they must share re-
sources, which are typically few and insufficient to
run them all at the same time (Agapito et al., 2019;
Dutra et al., 2014; Lee et al., 2020). The decision-
makers must then choose a subset of them from
among the candidates for execution (Abbassi et al.,
2014). There are numerous approaches for making
this selection, with ranking being one of them. Rank-
ing is a useful tool that allows a choice based on
structured forms of comparison, especially if objec-
tive criteria are specified, with the goal of better align-
ing with the companies’ market objectives and desires
(Perez and Gomez, 2014).
When applying formal methods for project se-
lection, the chances of success in execution for the
company increase (Dutra et al., 2014). Because, the
choice for the correct project portfolio may avoid the
waste of resources, which are scarces (Abbassi et al.,
2014; Agapito et al., 2019).
This kind of decision, generally, is complex,
once several criteria must be considered simultane-
ously (Tzeng and Huang, 2011). Specially for R&D
projects, whose results, if not expected, may nega-
tively impact the company’s future (Lee et al., 2020).
To deal with this type of choice, a Multicrite-
ria Decision Method (MCDM) may support the se-
lection of project portfolio, because it is a tool for
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8062-4347
helping in complex engineering problems. Some of
them offer the possibility of a final ranking, indicat-
ing the alternatives in order of preference (Mavrotas
and Makryvelios, 2021; Wallenius et al., 2008). Pref-
erence Ranking Organization Method for Enrichment
Evaluation II (PROMETHEE II), VIseKriterijum-
ska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR),
Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to
Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) and Elimination Et Choix
Traduisant la R
´
ealit
´
e II (ELECTRE II) (Martins and
Marcondes, 2020) are examples of MCDM. Sadi-
Nezhad (2017) states their applications has been
growing in academic publications.
However, as the decision must be made based on
estimates, since uncertainty is inherent and unavoid-
able in this process (Bohle et al., 2015). Which in-
dicates that it must be considered in the decision, as
it can change the results obtained (Marcondes, 2021;
Marcondes et al., 2017).
PMI (2021) presents an alternative to deal with
uncertainty in estimation, using three-points. With
it, instead of a single estimated value, decision must
be made based on three (worst-case, most likely and
best-case), using some approach to dealing with vari-
ation, as Monte Carlo simulation or fuzzy numbers
(Deng, 2014; Marcondes, 2021; Wang, 2015).
Fuzzy numbers provide a convenient concept
when working with imprecise numerical quantities,
allowing for their proper representation and arith-
metic manipulation (Deng, 2014). They are widely
used in a variety of applications for handling practical
challenges of many types in imprecision real-world
Marcondes, G.
Project Ranking with Uncertainty using Multicriteria Decision Method and Fuzzy.
DOI: 10.5220/0010804900003117
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2022), pages 131-136
ISBN: 978-989-758-548-7; ISSN: 2184-4372
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
131

contexts (Deng, 2014).
Marcondes (2021) proposed a way to deal with
uncertainty in project selection using three-point es-
timation, ELECTRE II method and Monte Carlo sim-
ulation. This work proposes a change using fuzzy
numbers relative preference relation, as presented
by Wang (2015), to deal with uncertainty, instead
of Monte Carlo simulation, and the use of TOP-
SIS method (instead of ELECTRE II). The selection
method was adapted and numerical example was done
over the same set of projects, allowing a comparison
between both results.
The uncertainty addressed in this work is the one
introduced in the estimation process, naturally, due to
the error in values attributed to the decision criteria for
each alternative. The example presented could have
been done with other MCDMs. TOPSIS was chosen
because it is one of the most used in the literature.
The remaining of this paper is organized as fol-
low: Section 2 presents the principles of multicriteria
decision methods, detailing TOPSIS; the importance
of uncertainty in project selection problems and fuzzy
numbers comparison is presented in Section 3; Sec-
tion 4 proposes a method for selecting projects con-
sidering uncertainty; which is exemplified by a real
problem in Section 5; Section 6 concludes the work.
2 MULTI-CRITERIA DECISION
METHODS
When only one criterion is used to choose among
alternatives, the process is relatively simple, as se-
lecting the ones with the highest scores is all that
is required. When more than one criterion is used,
the decision becomes more difficult since the criteria
must be examined simultaneously and, in some situa-
tions, there may be a conflict among them (Tzeng and
Huang, 2011).
According to research, the usage of Multi-criteria
Decision Methods (MCDM) in project selection is in-
creasing (Sadi-Nezhad, 2017). These strategies allow
one to order multiple options based on a variety of
factors and then choose the best ranked. Technique
for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution
(TOPSIS) is an MCDM able to generate a final rank-
ing of the alternatives, comparing them with the ideal
and non-ideal solutions. It is presented in the se-
quence.
2.1 Technique for Order Preference by
Similarity to Ideal Solution
(TOPSIS)
TOPSIS is a multi-criteria method for assessing and
comparing the performance of potential solutions.
The best option is the one that is the most similar to
the ideal solution and the least similar to the non-ideal
solution. For each criterion must be given a weight
based on the importance to the decision-maker (Mar-
tins and Marcondes, 2020; Tzeng and Huang, 2011).
The TOPSIS method is executed by the steps
described below (Martins and Marcondes, 2020;
Tzeng and Huang, 2011).
Step 1 - Calculate the normalized r
i j
in the deci-
sion matrix:
r
i j
=
f
i j
q
∑
m
j=1
f
2
i j
(1)
where:
j is the alternative ( j = 1, ..., m)
i is the selection criteria (i = 1, ..., n)
f
i j
is the value assigned to the alternative j in the
criterion i
Step 2 - Calculate the weighted ς
i j
for each r
i j
in
normalized decision matrix:
ς
i j
= w
i
r
i j
(2)
where:
w
i
is the weight of i
th
criterion;
∑
n
i=1
w
i
= 1.
Step 3 - Determine the ideal and negative solution:
ς
∗
= (max
j
)ς
i j
| j ∈ J
0
, (min
j
)ς
i j
| j ∈ J
00
(3)
ς
−
= (min
j
)ς
i j
| j ∈ J
0
, (max
j
)ς
i j
| j ∈ J
00
(4)
where:
J
0
associated with positive impact criteria;
J
00
associated with negative impact criteria.
Step 4 - Use Euclidean distance to calculate sep-
aration measures (D
∗
j
and D
−
j
separations from the
ideal and negative solutions, respectively):
D
∗
j
=
s
n
∑
i=1
(ς
i j
− ς
∗
i
)
2
(5)
ICORES 2022 - 11th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
132
D
−
j
=
s
n
∑
i=1
(ς
i j
− ς
−
i
)
2
(6)
Step 5 - Calculate the relative proximity of the
ideal solution:
C
∗
j
=
D
−
j
D
∗
j
− D
−
j
(7)
Step 6 - Organize alternatives in ascending order
of preference, taking into account the growing value
of C
∗
j
. It is feasible to determine the best alterna-
tive using this ranking of preferences. (Opricovic and
Tzeng, 2004).
3 UNCERTAINTY WITH FUZZY
Fuzzy numbers are useful for arithmetically manag-
ing imprecise numerical quantities and decision mak-
ers’ subjective preferences in a variety of decision-
making circumstances. Because of imprecision inher-
ent in human decision-making, they are widely used
in a variety of applications for handling practical chal-
lenges of many types in real-world contexts (Deng,
2014).
As a result, comparing and ranking fuzzy num-
bers becomes a significant challenge that must be an-
swered sufficiently in decisions under uncertainty. It’s
difficult and time-consuming to compare and evalu-
ate fuzzy numbers in order to determine their overall
ranking in a specific context. This is due to the fact
that in many practical scenarios, fuzzy numbers, as
represented by the possibility distribution (member-
ship functions), often overlap. It might be difficult
to tell whether one fuzzy number is larger or smaller
than another in a given setting, especially when the
two fuzzy values are close (Deng, 2014).
One way to deal with uncertainty is using the
three-point estimate (worst-case, most likely and best-
case), as suggested by PMI (2021). The three es-
timated values indicate the direct use of triangular
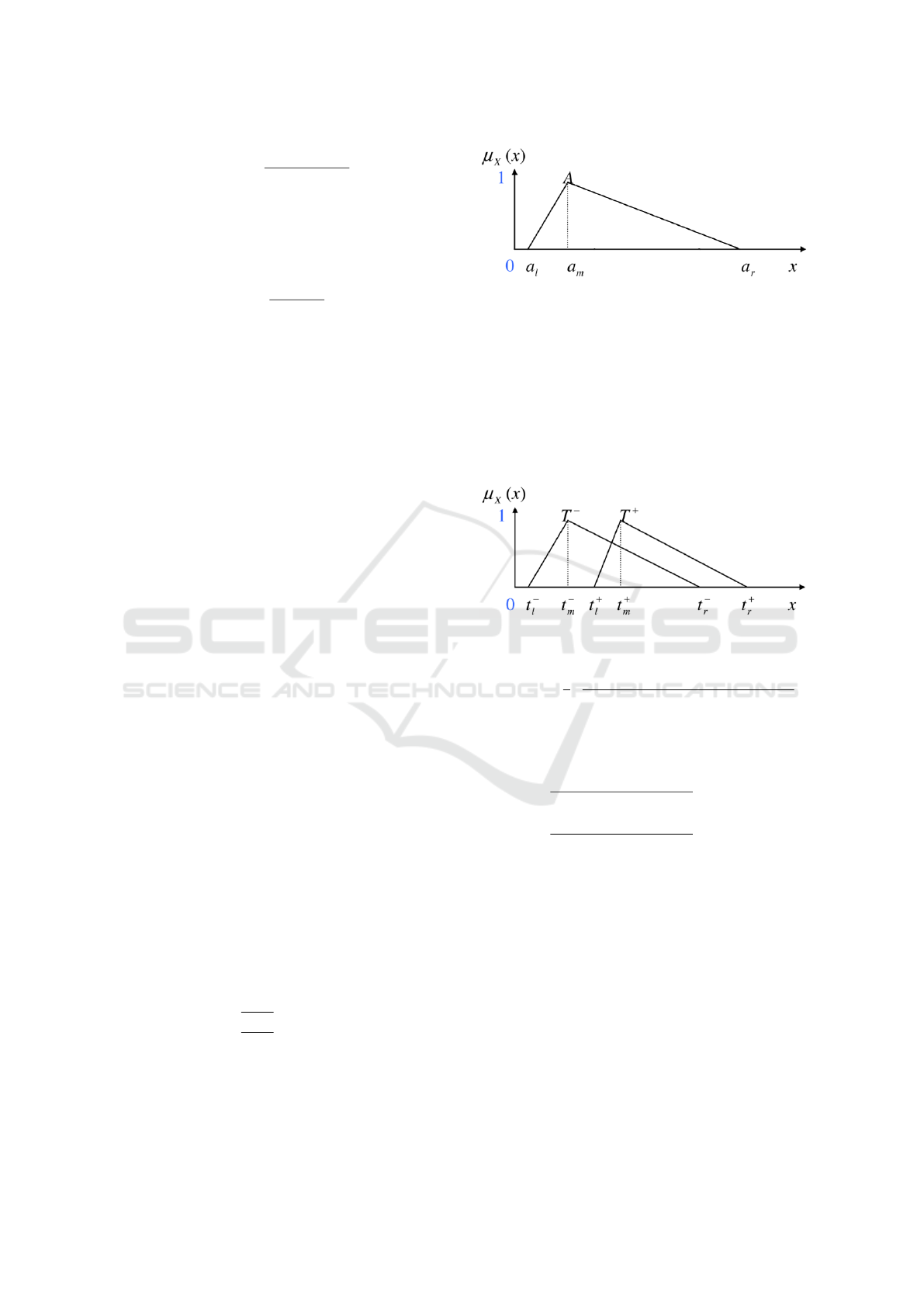
fuzzy numbers. A triangular fuzzy number A is one
with the following membership function µ
A
, graphi-
cally represented in Figure 1 (Wang, 2015):
µ
A
=
x−a
l
a
m
−a
r
a
l
6 x 6 a
m
a
r
−x
a
r
−a
m
a
m
6 x 6 a
r
0 otherwise
(8)
Wang (2015) concluded that two generic trian-
gular fuzzy numbers, as presented in Figure 2, may
be compared by a fuzzy preference relation P, with
Figure 1: The membership function of triangular fuzzy
number A - Adapted from (Wang, 2015).
membership function µ
P
(A, B), representing prefer-
ence degree of A over B. However, this compari-
son is complex in terms of time when dealing with
k fuzzy numbers, due to pair-wise comparison. The
proposal is, in a set of k triangular fuzzy numbers
S = {X
1
, X
2
, ..., X
j
}, compare X
j
= (x
jl
, x
jm
, x
jr
), j =
1, 2, ..., k, with the average
¯
X = ( ¯x
l
, ¯x
m
, ¯x
r
), as pre-
sented in Equation 9 (Wang, 2015):
Figure 2: The membership functions of triangular fuzzy
numbers T
+
and T
−
(Wang, 2015).
µ
P
∗
(X
j
,
¯
X) =
1
2
(x
jl
− ¯x
r
) + 2(x
jm
− − ¯x
m
) + (x
jr
− ¯x
l
)
2
k
T
S
k
(9)
where:
if t
+
sr
> t
−
sr
:
k
T
s
k
=
(t
+
sl
−t
−
sr
)+2(t
+
sm
−t
−
sm
)+t
+
sr
−t
−
sl
2
if t
+
sr
< t
−
sr
:
k
T
s
k
=
(t
+
sl
−t
−
sr
)+2(t
+
sm
−t
−
sm
)+t
+
sr
−t
−
sl
2
+ 2(t
−
sr
−t
+
sl
)
t
+
sl
= max{x
jl
}
t
+
sm
= max{x
jm
}
t
+
sr
= max{x
jr
}
t
−
sl
= min{x
jl
}
t
−
sm
= min{x
jm
}
t
−
sr
= min{x
jr
}
j = 1, 2, ..., s
At the end, one has s µ
P
∗
(X
k
,
¯
X) values, represent-
ing preference degree of X
k
over
¯
X in S (Wang, 2015).
Allowing a proportional comparison among s triangu-
lar fuzzy numbers.
Project Ranking with Uncertainty using Multicriteria Decision Method and Fuzzy
133
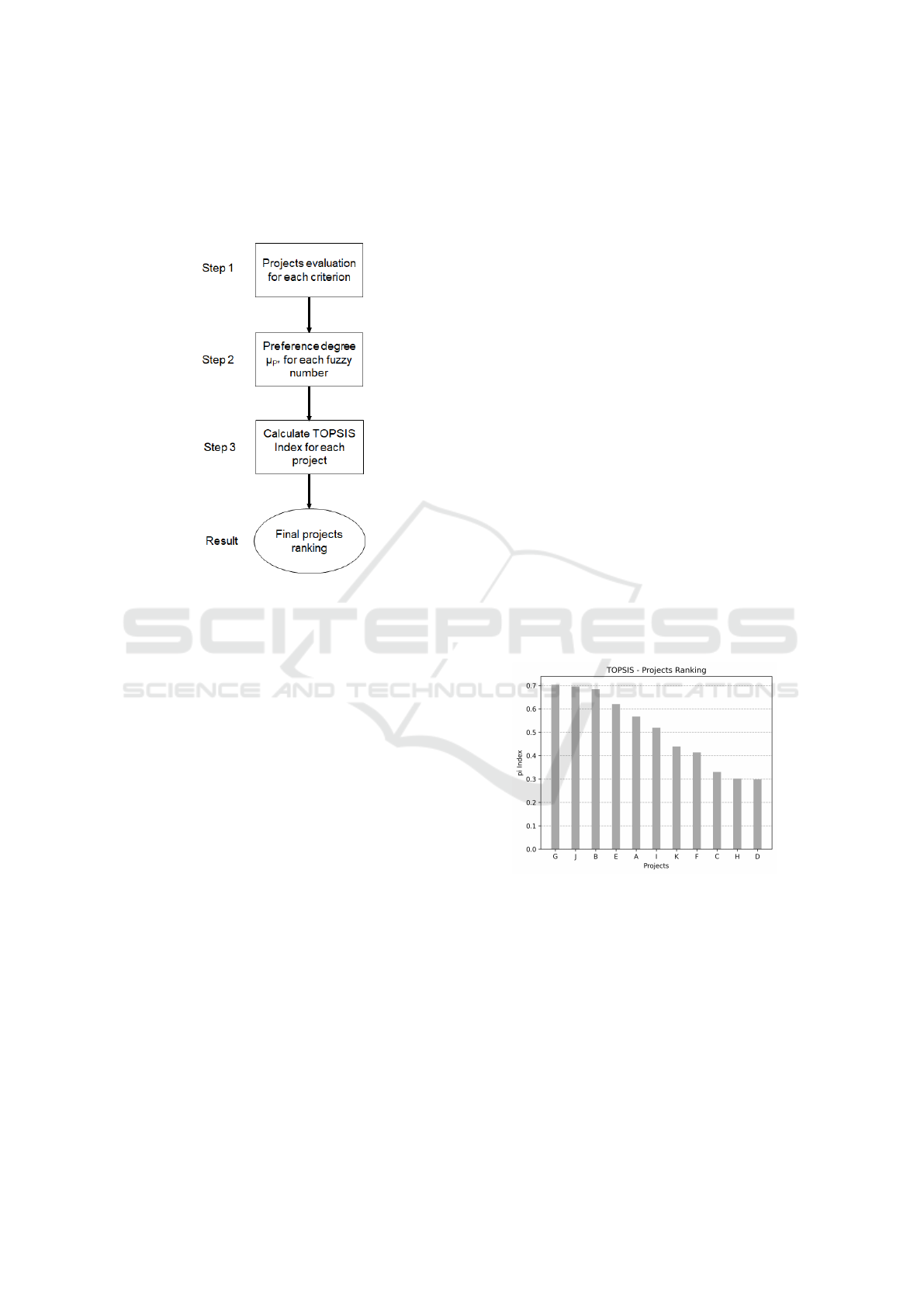
4 PROPOSED METHOD
The proposed method for this work indicates three
steps for a final projects ranking, as presented in Fig-
ure 3.
Figure 3: Proposed method flow.
At Step 1, for each selected criterion i (i =
1, 2, ..., n), the projects are evaluated by specialists.
They receive values, in a predefined range (from 1 to
10, for instance), representing the relative importance
of the project in the scenario. These values are estab-
lished using three-point estimation. As a result in this
step, each project has three estimated values for each
criterion i, forming a triangular fuzzy number. That
is, k ( j = 1, 2, ..., k representing each project) triangu-
lar fuzzy numbers for each criterion i.
Uncertainty in project ranking process is dealt in
Step 2. For the n criteria, all k projects’ fuzzy num-
bers are compared among each other, using Equation
9. It generates new values, representing the relative
preference degree of project j related to the others, in
the same criterion i.
In the last step (Step 3), TOPSIS method is ap-
plied, indicating the final projects’ ranking, from
the best option to the worst (based on the selection
criteria). Decision-maker may choose the selected
projects, to companies’ portfolio for execution.
To better represent the importance of the criteria
in the decision, they can be associated with weights,
which will be considered when defining the ranking.
5 NUMERICAL EXAMPLE
The method proposed in Section 4 was applied over
a set of 11 real R&D software development projects
(the same set of Marcondes (2021)). All the projects
were evaluated by three experts in market and soft-
ware development. The criteria were the same used
in Marcondes (2021).
• C1 - Return/risk rate (weight - 0,4): a ratio be-
tween the estimated return and the associated risk
(from 1 - the lowest to 10 - the highest);
• C2 - Competitiveness improvement (weight -
0,3): the capacity of project for improving com-
pany competitiveness (from 1 - the lowest to 10 -
the highest);
• C3 - Market potential (weight - 0,2): the capac-
ity of project for improving market share or mar-
ket insertion (from 1 - the lowest to 10 - the high-
est);
• C4 - Degree of innovation (weight - 0,1): how
innovative the project is (from 1 - the lowest to 10
- the highest).
The final goal were the selection of three projects
to be executed by the company, being the best placed
in the final ranking. They would be the most aligned
with the defined strategy.
Figure 4: Projects Ranking - With Uncertainty - Fuzzy Ap-
proach.
The result obtained with the execution of the
method was the selection of projects G, J and B,
which were the ones that obtained the best position in
the final ranking. Comparing this result with the se-
lection presented in Marcondes (2021), it can be seen
that the selected projects were the same considering
the uncertainty scenario and using the Monte Carlo
simulation. Considering the whole ranking, all the
projects kept the same position.
ICORES 2022 - 11th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
134
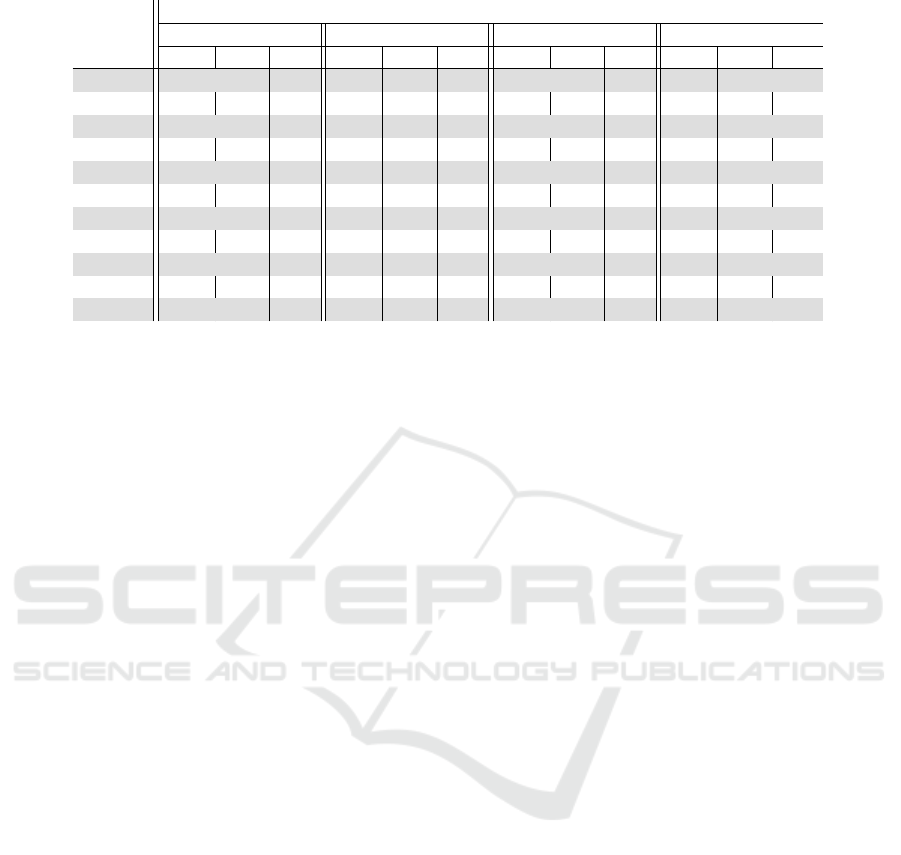
Table 1: Projects Characteristics.
Criteria
C1 C2 C3 C4
Project
WC ML BC WC ML BC WC ML BC WC ML BC
A 8 10 10 2 3 4 1 2 4 2 3 5
B 7 8 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 7 8
C 1 2 4 4 6 7 3 5 6 3 4 5
D 1 1 2 1 2 3 7 9 10 9 10 10
E 3 5 6 6 9 10 8 10 10 5 6 7
F 5 6 7 2 3 6 1 2 3 1 2 4
G 5 7 9 5 7 8 5 7 9 8 9 10
H 2 3 4 4 5 6 2 3 5 2 3 4
I 7 8 9 1 1 3 4 6 7 5 7 8
J 6 9 10 8 9 10 1 2 3 3 4 5
K 2 3 5 7 8 10 1 1 2 3 5 7
6 CONCLUSIONS
The selection of projects in companies is necessary,
due to the scarcity of resources and difficulty in ex-
ecuting all the candidates that present themselves.
Thus, using formal mechanisms for selecting projects
for execution (project portfolio) is important for better
application of resources, maintaining strategic objec-
tives.
Since several factors must be taken into considera-
tion simultaneously in the selection, the application of
Multi-Criteria Decision Methods can be useful. Many
of them allow ranking of options, comparing prede-
fined criteria.
Like any process that involves decisions about fu-
ture situations, uncertainty is present. The decision
maker should consider it.
This work presents a way of selecting projects that
uses the TOPSIS Multi-Criteria Decision Method. To
address uncertainty, the proposal uses fuzzy triangular
numbers and a means of comparing them.
The result was compared with that presented in a
previous work, indicating the same subset of projects
to be selected. This assessment should be made more
broadly and considering other examples. But it indi-
cates the coherence of the method used with the one
that deals with uncertainty through the Monte Carlos
simulation.
As future works, new experiments with other ex-
amples of project selection and the application of
other multi-criteria decision methods can be consid-
ered, in addition to TOPSIS.
REFERENCES
Abbassi, M., Ashrafi, M., and Tashnizi, E. S. (2014). Select-
ing balanced portfolios of R&D projects with inter-
dependencies: A cross-entropy based methodology.
Technovation, 34(1):54–63.
Agapito, A. O., Vianna, M. F. D., Moratori, P. B., Vianna,
D. S., Meza, E. B. M., and Matias, I. O. (2019). Us-
ing multicriteria analysis and fuzzy logic for project
portfolio management. Brazilian Journal of Opera-
tions & Production Management, 16(2):347–357.
Bohle, F., Heidling, E., and Schoper, Y. (2015). A new ori-
entation to deal with uncertainty in projects. Interna-
tional Journal of Project Management, 34(7):1384–
1392.
Deng, H. (2014). Comparing and ranking fuzzy numbers
using ideal solutions. Applied Mathematical Mod-
elling, 38(5-6):1638–1646.
Dutra, C. C., Ribeiro, J. L. D., and de Carvalho, M. M.
(2014). An economic-probabilistic model for project
selection and prioritization. International Journal of
Project Management, 32(6):1042–1055.
Lee, S., Cho, Y., and Ko, M. (2020). Robust optimiza-
tion model for R&D project selection under uncer-
tainty in the automobile industry. Sustentability,
12(23):773–788.
Marcondes, G. A. B. (2021). Multicriteria decision method
for project ranking considering uncertainty. In In-
ternational Conference on Operations Research and
Enterprise Systems - ICORES.
Marcondes, G. A. B., Leme, R. C., Leme, M. S., and
da Silva, C. E. S. (2017). Using mean-Gini
and stochastic dominance to choose project portfo-
lios with parameter uncertainty. The Engineering
Economist, 62(1):33–53.
Martins, D. T. and Marcondes, G. A. B. (2020). Project
portfolio selection using multi-criteria decision
methods. In IEEE International Conference on Tech-
nology and Entrepreneurship – ICTE.
Mavrotas, G. and Makryvelios, E. (2021). Combining mul-
tiple criteria analysis, mathematical programming
and monte carlo simulation to tackle uncertainty in
Project Ranking with Uncertainty using Multicriteria Decision Method and Fuzzy
135

research and development project portfolio selec-
tion: A case study from greece. European Journal
of Operational Research, 291(2):794–806.
Opricovic, S. and Tzeng, G.-H. (2004). Compromise solu-
tion by mcdm methods: A comparative analysis of
vikor and topsis. European Journal of Operational
Research, 156(2):445–455.
Perez, F. and Gomez, T. (2014). Multiobjective project port-
folio selection with fuzzy constraints. Annals of Op-
erations Research, 236:1–23.
PMI (2021). A Guide to the Project Management Body of
Knowledge. Project Management Institute, Atlanta,
EUA, 7 edition.
Sadi-Nezhad, S. (2017). A state-of-art survey on project
selection using mcdm techniques. Journal of Project
Management, 2(1):1–10.
Tzeng, G. H. and Huang, J. J. (2011). Multiple attribute de-
cision making: methods and applications. Chapman
and Hall/CRC.
Wallenius, J., Dyer, J. S., Fishburn, P. C., Steuer, R. E.,
Zionts, S., and Deb, K. (2008). Multiple criteria de-
cision making, multiattribute utility theory: Recent
accomplishments and what lies ahead. Management
Science, 54(7):1336–1349.
Wang, Y.-J. (2015). Ranking triangle and trapezoidal fuzzy
numbers based on the relative preference relation.
Applied Mathematical Modelling, 39(2):586–599.
ICORES 2022 - 11th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
136
