
Modeling Context-aware Systems: A Conceptualized Framework
Achiya Elyasaf
a
and Arnon Sturm
b
Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Israel
Keywords:
Modeling, Context, Context-aware Systems, Conceptual Framework, Benchmark.
Abstract:
Context-aware systems keep on emerging in all of our daily activities. Context, which can be a location, a user,
an actual activity, or physical conditions, plays a major role in such systems. Actually, everything we refer
to in our systems can be considered as context. To cope with this new situation, mechanisms for managing
context were devised, including frameworks and programming languages. However, modeling languages that
address the notion of context are rare. In this paper, we aim at framing and further defining the requirements for
context modeling languages. Such a conceptualized framework sets the ground for designing and evaluating
modeling languages for context-aware systems. We demonstrate a possible use of the proposed framework
through the evaluation of CO-LSC, a context-oriented modeling language.
1 INTRODUCTION
Context-aware systems are all around us and are
actually involved in every domain of our daily
socio-technological life, for example, in health
care (Bricon-Souf and Newman, 2007), in educa-
tion (Ireri et al., 2018), and in ambient intelligent sys-
tems (Ramos et al., 2011). Such systems sense their
environment and their internal state and adapt their
behavior accordingly. Thus, both the environment
and the internal state can be considered as context.
Environmental context can be location, temperature,
or user attributes, and internal context, i.e., the sys-
tem state, can be a combination of objects’ properties
or sequences of operations. Thus, a context is an ab-
straction of certain circumstances that are of interest
to the system and plays a major role in designing such
systems, as it facilitates situational information (Dey
et al., 2000).
As it appears that everything can be con-
sidered as a context, various context-oriented,
context-based, and context-aware techniques have
emerged, including Context-Oriented Programming
(COP) (Hirschfeld et al., 2008), context-oriented be-
havioral programming (Elyasaf, 2021; Elyasaf et al.,
2019), and modeling facilities (Sindico and Grassi,
2009). Nevertheless, these studies address context to
a limited extent and only focus on certain aspects of it.
One prominent reason for this gap is that the context
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4009-5353
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4021-7752
definition, and the requirements from it, are still quite
vague and there is no consensus of what a context is.
Is it external or internal? Is it a set of information or
processes? Is it static or dynamic?
With the vast knowledge of context-aware systems
and context-oriented techniques that emerged during
the last two decades, we believe it is time to clarify
the requirement for context modeling and further con-
ceptualize the notion of a context along with its many
facets. Specifically, we wish to describe the relation-
ships between the context of the system and its be-
havior, and how the data aspects and the behavioral
aspects of the system interact and influence one an-
other.
Various attempts to conceptualize context have
been suggested (Cabrera et al., 2017; Bettini et al.,
2010).Yet, these refer mainly to the structure and con-
text types neglecting the relationship to the system be-
havior.
The contribution of this paper is two-folded. First,
we provide a concise and clear view of a context for
the purpose of modeling context-aware systems. Sec-
ond, we define a framework that can be used for ana-
lyzing and developing context-oriented modeling lan-
guages (and techniques).
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2
we revisited the requirements for context modeling
language, review studies that aim at similar goals as
ours, i.e., framing the notion of context, and refer to
existing context modeling languages. In Section 3 we
present a case study that serves us for demonstrat-
26
Elyasaf, A. and Sturm, A.
Modeling Context-aware Systems: A Conceptualized Framework.
DOI: 10.5220/0010818200003119
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development (MODELSWARD 2022), pages 26-35
ISBN: 978-989-758-550-0; ISSN: 2184-4348
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

ing the context conceptual framework we suggest in
Section 4. In Section 5 we demonstrate potential use
of the framework, i.e., use it as a benchmark to ex-
amine a specific context-oriented modeling language.
Finally, in Section 6 we conclude and refer to further
framework utilization.
2 RELATED WORK
To set a conceptualized framework for context model-
ing we begin with setting the requirements. In doing
so, we refer to existing studies, such as (Bettini et al.,
2010) and to the experience we gained in context-
aware systems. In the following, we list the require-
ments we gathered. A context-oriented modeling lan-
guage should:
• Handle the heterogeneity of context information
sources.
• Capture the relationships between contexts and
system behaviors.
• Refer to past states of the system.
• Deal with the uncertainty of both data and behav-
ior.
• Facilitate reasoning in detecting problems in the
model and during execution.
• Manage the complexity of context.
In light of these requirements, we start with re-
viewing studies related to context conceptualization
and then refer to specific modeling languages.
2.1 Conceptualizing Context
When referring to context conceptualization there are
two major directions. One refers to metamodels and
the other to ontology specification. We first be-
gin with analyzing metamodels followed by ontology
studies.
Referring to service-oriented computing, a meta-
model that emphasizes the structure of contextual en-
tities and also refers to the system behaviors that are
determined by the context is presented (Vieira et al.,
2011). It refers to both static and dynamic aspects
of context-sensitive systems. The approach taken ad-
dresses the handling of many information sources and
captures the relationships between context and behav-
ior via contextual graph. Nevertheless, it neglects past
states, uncertainty, the management of contexts, and
reasoning.
In the case of service adaptation, a metamodel is
proposed for conceptualizing context-aware systems
(Peinado et al., 2015). While the metamodel includes
the notion of context, its abstraction is limited and
mainly refers to the system architecture rather than
modeling contexts and their binding to the system be-
haviors. Past states, uncertainty, and reasoning are
also neglected.
Domain-specific languages are also means for ad-
dressing context modeling, for example via a UML
profile for context modeling (Simons, 2007). Such a
profile includes a static view of a system and refers
to contexts as classes. It addresses the notion of dif-
ferent information sources, yet the other requirements
set above are mostly neglected. The metamodel of the
language is centered around the notion of an entity
that is assigned with a context. It further elaborates
on various types of contexts including physical (e.g.,
time, speed), environmental (e.g., distance, location),
computational (e.g., network traffic, hardware status),
personal (e.g., age, gender, preferences), social (e.g.,
law, rules, roles, friends), and task (e.g., activities that
need to be performed or are already being executed)
that set the context landscape. It refers to informa-
tion sources and to various properties of a context.
However, the relationship to the system behavior, un-
certainty, past states, and reasoning features are not
explicated.
A model–based approach for context-aware sys-
tems is suggested in (L
´
opez-Jaquero et al., 2016). It
is centered around a goal-oriented approach and thus
the main entity that considers the context for its oper-
ation is a task. A task in that metamodel consists of
contexts that comprise context elements which are ac-
tually data information in the form of attributes, that
are monitored to identify a context. The metamodel
also includes resources that support awareness. In ad-
dition, the paper presents a context metamodel that
further elaborates the context components that corre-
spond to either the static or dynamic aspects of a con-
text. Here again, the operation of a context, i.e., its
activation and execution implications are ignored (in-
cluding references to past states, reasoning, and un-
certainty).
A comprehensive framework for model-driven
development of context as a service is presented
in (Moradi et al., 2020). The authors introduce var-
ious viewpoints on context and its related aspects.
In particular, they refer to modeling context-aware
objects, high-level contexts, situations, context ele-
ments, context sources, and changes in context. In
addition to the above, the resulting metamodel also
consists of derivation rules according to which con-
texts are created. However, the framework focuses on
context execution and provides little evidence for its
specification (including reference to past states, rea-
soning, and uncertainty).
Modeling Context-aware Systems: A Conceptualized Framework
27

Following two surveys (Bettini et al., 2010; Cabr-
era et al., 2017) dealing with ontology with respect to
context modeling, the authors emphasize two issues:
context information model and reasoning techniques,
see for example, (Brings. et al., 2018; Ejigu et al.,
2007; Aguilar et al., 2018). In that sense, ontology-
based approaches focus on the system/context struc-
ture and facilitate reasoning capabilities, yet these ne-
glect the behavioral aspect. The context information
is classified following a pre-defined ontology, thus,
sometimes it limits the flexibility of the context infor-
mation model.
2.2 Context-Oriented Modeling
Techniques
Various context-oriented modeling techniques were
devised. For example, Context-Oriented Domain
Analysis (CODA) adds the notion of context on top
of feature diagrams to model software requirements
(Desmet et al., 2007). The approach mainly refers
to the system structure and functionality, yet the ac-
tual behaviors are not elaborated. As it utilizes feature
models reasoning is also applicable.
Context modeling can also be modeled using
states (Yue et al., 2017). In that case, each state
represents a context instance with values of several
attributes. The transitions between the contexts de-
scribe the system behavior. Nevertheless, it seems
that describing context instances using that approach
may result in states explosion.
Context Modeling Language (CML) was also de-
vised for the purpose of developing context-aware
systems (Henricksen and Indulska, 2006). The lan-
guage focuses on the context information and the re-
lationships among that information. It neglects the
binding to the system behavior, yet it facilitates rea-
soning.
The search we performed for context-oriented
modeling reveals that the modeling needs for context-
aware systems are addressed only to a limited extent.
It seems that no comprehensive language that takes
into account the overall needs exist and there is also
a need to define such requirements. In this paper, we
aim at addressing the latter.
Summary. Back to the requirements, we set be-
fore, it seems that the majority of the approaches
address the context information (static) model to a
large extent. In some cases, reasoning capabilities
are also provided. However, most approaches neglect
the binding of the context to behavior, the past sys-
tem state, the uncertainty, and the management of the
context complexity. We believe that a major reason
for that is the lack of conceptualizing these aspects.
Thus, in this paper, we aim at framing the notion of
context, its components, and the semantics that need
to be taken care of.
3 THE TRAINING SYSTEM
As mentioned before, in this paper, we propose a
framework for conceptualizing context. To clarify
the definitions and the concepts of this framework,
we demonstrate them via a training-system case study
that we now describe. The system allows trainers to
plan the training for their trainees and adapt the plans
to various situations and circumstances. A simplified
(class) model of such a system is depicted in Figure 1
and the basic training behavior is depicted in Figure 2.
A trainer selects a training type for the trainee and
executes it, where each training is composed of one
or more activities. Note that we deliberately omit the
many details of the models (such as relationship types
and multiplicities, as well as exact navigation across
objects) as these are of limited importance for this pa-
per.
Naturally, this basic training behavior might re-
quire some adjustments, depending on the context.
For example, the actual training has to be adjusted for
senior trainees or be rescheduled upon bad weather
(Figure 3).
4 CONCEPTUALIZING
CONTEXT
A context according to Dey is “any information that
can be used to characterize the situation of an entity.
An entity is a person, place, or object that is consid-
ered relevant to the interaction between a user and an
application, including the user and application them-
selves” (Dey et al., 2000). Such a definition which is
adopted in many studies is too vague and refers only
to some facets of a context.
In this paper, we propose to further refine the def-
inition of context and refer to its components, opera-
tions, and states. To do that, we devise a metamodel
and a life cycle of a context, based on related stud-
ies and experience we gained in context-oriented sys-
tems.
4.1 Preliminaries
The Word ‘Context’. Generally, when describing
systems, the term “context” is used in two different
MODELSWARD 2022 - 10th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
28
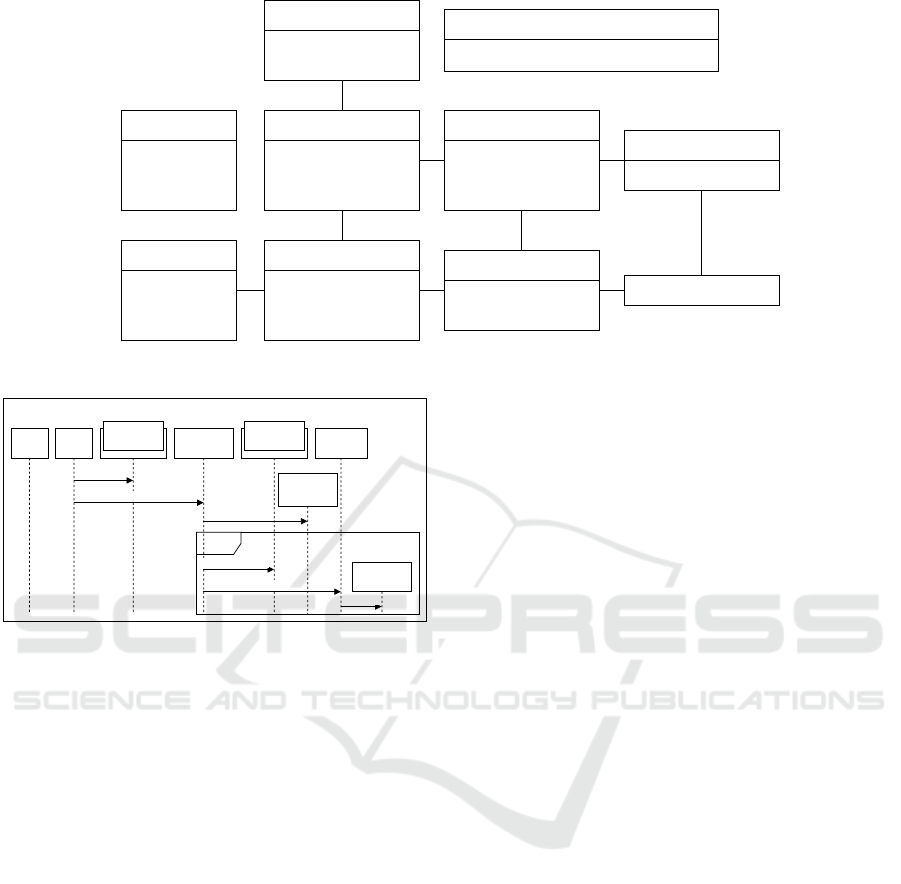
Trainer
name
expertise
TrainingType
duration
location
levelOfDifficulty
ActualTraining
date
location
levelOfDifficulty
Trainee
age
status
experience
Weather
temprature
wind
humidity
ActivityType
name
description
levelOfDifficulty
ActualActivity
repetition
weight
Equipment
EquipmentType
name
CivilCondition
status:{regular, lockdown, partial}
Figure 1: The class diagram of the training system.
Title: A regular training session
loop
tr:
Trainer
:Object
TrainingType
t1:
TrainingType
:Object
ActivityType
at1:
ActualTraining
a:
ActivityType
create
pick(te):t1
execute()
chooseByOrder():a
execute()
aa1:
ActualActivity
create()
te:
Trainee
Figure 2: The default training behavior.
ways:
• System Context — the internal and environmen-
tal state of the system. For example, the system
context in the training system includes the state of
all system objects (that also represent the environ-
ment) and the state of the executing behaviors.
• Behavior Context — the context of each of the
system’s behaviors. Such a context is a projec-
tion of the system context in view of the specific
behavior. For example, “During a lockdown, all
training sessions must be held virtually, i.e., via
Zoom. Thus, only indoor activities are permitted
and these should require only equipment that is
available at the trainee location.” In such a case
the ”during lockdown” is the context that matters
for the training behavior. It is important to stress
that contexts only affect the system behaviors.
As the two meanings of context may confuse,
some paradigms use different terms for each mean-
ing. In context-oriented programming, for example,
the term context refers to the system context, while
the term layer refers to the context of a behavioral as-
pect (Hirschfeld et al., 2008). We believe that there
is no difference between the two, and artificially sep-
arating them may be confusing even more. Thus, in
the proposed meta-model we refer to the system con-
text as a composition of other contexts that combine
many simple and complex elements, where each con-
text corresponds to a different behavioral aspect of the
system.
Separation of Concerns. Many times, several be-
haviors are bound to the same context, as in the case
of the “bad weather” context, where both the fol-
lowing behaviors are bound to it — “Suspend active
training when the weather gets bad” and “Reschedule
training before it starts when weather is bad” (Fig-
ure 3b). Similarly, multiple conditions can lead us to
determine that we are in the context of bad weather,
such as weather forecast; sensors data; or even a se-
quence of events, like three sequential sensor read-
ings. The proposed metamodel and life cycle sup-
port this separation of concerns between “what to do
in context x”, i.e., the system behavior, and “when is
context x active”, i.e., the context information model.
Context Data. Furthermore, when describing
context-dependent behaviors, we encapsulate the
relevant data for specific behavior in the context. For
example in Figure 3a, given the context “a training
session with a senior trainee”, the actual adjustment
may rely on the age of the trainee. Such data is
encapsulated within the context.
Inter-context Relationship. Different contexts
may relate to other contexts in different ways. The
relations can be structural, temporal, and dependency.
Another type of relation is priority, which defines the
priority of context-dependent behaviors, based on the
priority of the context that they are bound to. The
use of priorities is one of the approaches for handling
contradicting behaviors.
Modeling Context-aware Systems: A Conceptualized Framework
29

loop
tr:
Trainer
:Object
TrainingType
t1:
TrainingType
:Object
ActivityType
at1:
ActualTraining
a:
ActivityType
create
pick(te):t1
execute()
chooseByOrder():a
execute()
aa1:
ActualActivity
create()
adjust()
te:
Trainee
Title: Adjust activities for senior trainees
(a) Adjust activities in the context of a senior trainee.
tr:
Trainer
:Object
TrainingType
pick(te):t1
te:
Trainee
w:
BadWeather
cancel()
reschedule()
Title: Reschedule training before it starts when weather is
bad
(b) Reschedule training in the context of bad
weather.
Figure 3: Context-dependent behavioral variations of Figure 2.
4.2 The Context Metamodel
To cope with the above definitions we devise the
metamodel presented in Figure 4. In the following,
we explain the various components of a context, ex-
plicate their rationale, and demonstrate these via the
training system.
Generally, each behavior in a system is bound to
a context, meaning that the behavior is relevant only
when the context preconditions are met. Of course, a
context-independent behavior is a special case of the
general behavior, where the context is always active
(e.g., the context “the system is running”).
Context. An information that refers to elements and
their activities. A context is defined by its precondi-
tions and the data that it encapsulates. For example,
the context “a training session with a senior trainee”
(Figure 3a) is active whenever a session with a senior
trainee is started. The preconditions in this example
are both behavioral (something happens) and struc-
tural (constraints on the Trainee element). The data
of this context is a specific training session with a se-
nior trainee, meaning that it encapsulates structural
elements that are relevant for this context, such as
Trainee, Trainer, Training Type, and ActualTraining.
Each system behavior (behavioral element) is bound
to a specific context, recall that unbound behavior is
a private case of general behavior, and whenever the
context’s preconditions are met, the system behavior
starts running, with the relevant context data given as
a parameter for the behavior. For example, as men-
tioned before, the actual age of a trainee might affect
the required adjustment.
Context Type. Context has a type. It can be static,
i.e., predefined and constant, such as a specific loca-
tion, like a training studio. It can also be dynamic,
that is, the structure of the context is defined, yet it
is populated during run time, such as the Weather. It
can also be behavioral, that is, refers to a sequence of
operations, such as three Actual Training in a Week.
The context type is not explicated in the metamodel,
yet, it is derived from the elements that define it.
Simple Context. A simple context is an atomic
piece of information or an action. For example, the
location of the training, a trainee at a certain age/age
range, and the weather, when referring to information.
When referring to an action or a behavior, a context
can be, for example, running, swimming, functional
exercise, or on the way (for training).
Complex Context. A complex context consists of
multiple other contexts. For example, the “training
session” context consists of the following simple con-
texts: Trainee, Trainer, Training Type, and Actual-
Training. The “training session with a senior trainee”
consists of the complex context “training session” and
the simple context “a senior trainee”. This is, of
course, only one way to model such contexts.
Inter-context Relationship. Different contexts
may have various types of relationships among
them. In the following we elaborate on common
relationships we identified:
• Structural, including Association and General-
ization. Association refers to cases in which a
context in associated with another context. For
example, an ActualTraining is associated with an
MODELSWARD 2022 - 10th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
30
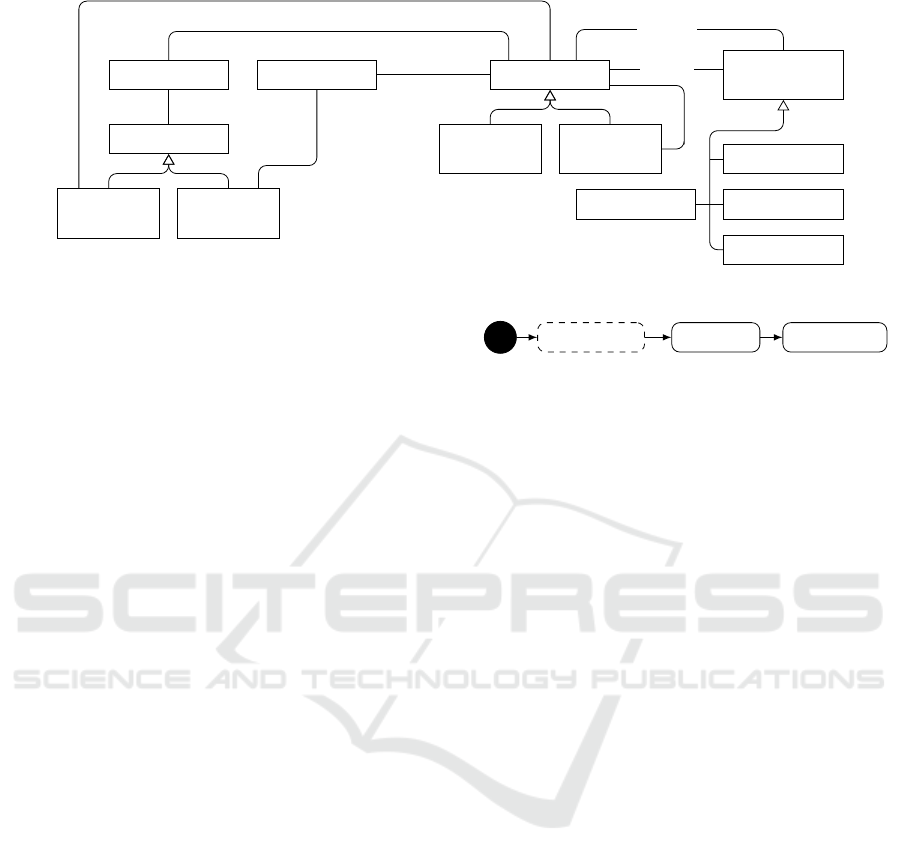
Context
Simple
Context
Complex
Context
Data
Precondition
Element
Behavioral
Element
Structural
Element
Inter-Context
Relationship
Dependency
Temporal
Structural
Priority
n
1
1
target
n
source
1
n
n
n
encapsulates
n n
n
1
n
n
n
bound
1
Figure 4: A context metamodel.
ActualTrainee. Generalization refers to cases in
which a context may be refined. For example,
the VirtualTraining context and PhysicalTraining
context are both refinements of the Training con-
text. In that case, it means that all properties, con-
straints, dependencies, and relationships that refer
to the Training context are applied to the other two
unless specified otherwise.
• Context Dependency. Context dependency
refers to cases when one context relies on another
one. For example, every actual training depends
on the Weather context, though not necessarily
vice versa.
• Context Temporal. The context temporal rela-
tionship refers to temporal relationships between
contexts. For example, the period between two
Actual Trainings should be at least 24 hours.
• Context Priority. In some cases, several contexts
are simultaneously active, which may result in
several active context-dependent behaviors. This
may be problematic if two contradicting behav-
iors are active at the same time. For example,
the context of a specific activity within a training
requires X repetitions, yet in another context in
which the Trainee fails in accomplishing the goal,
the number of repetitions should be reduced by
30%. There are many ways to overcome such
contradictions, for example, by defining the pri-
ority of each context of behavior. While priorities
may be dangerous, as they require a cross-aspect
perspective on the system, it is still a popular op-
tion, as in the case of rule-based systems, which
is why we include this type of relation. Yet, other
solutions may be more robust to constant changes,
such as explicitly defining the behavior when the
two contexts are simultaneously active.
Specification Activation Deactivation
Figure 5: The context life cycle.
4.3 The Context Life Cycle
Another important observation we had is that context
has both a type (its specification) and occurrences (in-
stances). Thus, the life cycle of a context can be sum-
marized as appears in Figure 5.
Context Specification: refers to its definition. The
activity is dashed since it is usually done before the
system runs, though it can also be done during run
time, in cases of self-adaptive systems.
Context Activation: refers to the instantiation of a
context, based on its preconditions. Meaning that the
system tracks the elements’ state (i.e., the state of the
system) and the set of context preconditions. At the
moment that some elements become to a state that re-
sembles the elements’ state of context preconditions
– then the context is instantiated. In the case of the
training system, the identification of the bad-weather
context occurs when the temperature actually drops
below zero.
Once a new context instance is generated, the be-
haviors that are bound to this context take place. In
the case of the training system, the behavior in Fig-
ure 3b takes place whenever the bad-weather context
is active.
Context Deactivation: refers to the point in which
a context is not relevant anymore. So, in the case of
the above example, due to heating devices, the tem-
perature crosses zero and the training should get back
to normal. This should also affect the system’s opera-
tion.
Modeling Context-aware Systems: A Conceptualized Framework
31

In this case, the active behaviors that are bound to
the bad-weather context, are either immediately ter-
minated, or they may perform a “cleanup” action be-
fore terminating, such as: gracefully ending the cur-
rent activity before returning to normal.
4.4 Reflection over the Metamodel
Here again, we review the devised metamodel in
light of the requirements set in Section 2. In the
metamodel, we did not elaborate on the context in-
formation. To cope with heterogeneous information
sources, such information can be associated with the
context element. Relationships are explicitly defined
in the metamodel. References to past states can be
accomplished by the behavioral aspect specified in
the metamodel. The complexity is dealt with through
the context hierarchy and its relationships. Applying
reasoning capabilities depends on the implementation
approach and uncertainty can be handled by the bind-
ing and priority mechanisms.
5 UTILIZING THE PROPOSED
FRAMEWORK
In this section, we aim at demonstrating the usage of
the framework we suggested. For that purpose, us-
ing the framework, we examine an existing context-
aware modeling technique based on live-sequence
charts (LSC) (Harel and Marelly, 2003), an extension
of message-sequence charts (MSC) with the ability to
specify possible and mandatory behaviors of reactive
systems (Harel and Pnueli, 1985), as well as forbid-
den behavior. LSC has execution semantics that al-
lows for synthesizing the model and verifying its cor-
rectness (Harel et al., 2010; Harel and Marelly, 2003).
Elyasaf et al. proposed an extension to LSC (CO-
LSC) that allows for subjecting charts to context and
demonstrated it on a case study of a smart-home sys-
tem (Elyasaf et al., 2018). Specifically, they pro-
posed to handle contextual data in terms of a rela-
tional data model, where preconditions are specified
as ‘select’ queries, and any change to the contextual
data is done using ‘update’ queries. The charts can
be bound to one or more contexts, represented as the
queries’ names. They also presented translational se-
mantics to the LSC semantics and implemented them
in a tool that enables the execution and verification of
the charts. According to these semantics, whenever
the context preconditions are met (i.e., there is a new
answer to the query), a new live copy of the chart is
created, with the context’s data encapsulated as a pa-
rameter for the chart.
<<device>>
AirCondition
<<device>>
SmartLight
<<device>>
MotionDetector
Office Restroom Kitchen
Emergency
Building
Room
hasPerson:bool
Figure 6: The contextual-data schema of (Elyasaf et al.,
2018).
Figure 6 depicts the schema of the contextual data
of the smart home application and Table 1 presents
the definition of contexts, i.e., the names of the con-
texts, their preconditions, and the definition of the
context encapsulated data. We note that the queries’
elements are all structural, and while it may seem that
the preconditions are using structural elements only,
it is not the case, as depicted in Figure 7. The chart
on the left is bound to the context of “Nonempty-
Room”, specifying that whenever a room becomes
nonempty, then the lights should be turned on, and
when the context ends (deactivated) – they should be
turned off (allowing for performing “cleanup” actions
when the context becomes deactivated). The chart on
the right demonstrates how the NonemptyRoom is ac-
tivated/deactivated based on the detection of a mo-
tion. While the NonemptyRoom precondition is de-
fined by a structural element, the state of this element
is controlled by a behavioral element – the chart in
Figure 7b.
The charts in Figure 7 demonstrate the separation
of concerns between the specification of what to do
in a nonempty room, and the specification of how
we know that a room is nonempty using the update
queries appear in Table 2.
Finally, Figure 8 depicts the use of a complex con-
text. In CO-LSC there is no explicit composition
of contexts, but rather implicit composition within a
query.
In the following we discuss the inter-context rela-
tionships support in CO-LSC:
1. Structural — In CO-LSC there are no explicit re-
lationships among contexts. Nevertheless, such
relationships can be expressed via the query op-
erators. For example, an association can be spec-
ified using additional phrases of a query. Gener-
alization can be specified by adding conditions to
further refine the query results.
2. Dependency and Temporal — since CO-LSC is
MODELSWARD 2022 - 10th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
32

Table 1: Context Definition of (Elyasaf et al., 2018).
ID Context Name Pre-Conditions Encapsulated Data
1 Room r ∈ Room Room
2 Emergency e ∈ Emergency Emergency
3 NonemptyRoom r ∈ Room: r.hasPerson Room & Person
Name: Turn lights on/off in
nonempty rooms
Context: r ∈ NonemptyRoom
r.light r
setOn()
ended(“NonemptyRoom”)
setOff()
(a) Binding charts to dynamically created context.
Name: Activate/deactivate “NonemptyRoom”
based on motion detection
Context: r ∈ Room
r r.mSensor
motionDetected()
execute(“Mark room as nonempty”, r)
motionStopped()
execute(“Mark room as empty”, r)
(b) Execute ‘update’ queries to activate/deactivate context(s).
The gears lifeline denotes a contextual data controller that
allows for querying and updating the system context.
Figure 7: The smart-home system of (Elyasaf et al., 2018). Charts are bound to contexts Room and NonemptyRoom.
Table 2: Context Initiation of (Elyasaf et al., 2018).
ID Context Name Operation
1 Mark room as nonempty r.hasPerson = true
2 Mark room as empty r.hasPerson = false
Name: Lights During Emergency
Context: r ∈ Room, e ∈ Emergency
r.light r
setOff()
Forbid
Figure 8: A Complex context, binding to more than one
simple context.
provided with execution semantics, these relation-
ships exist during execution and verification. For
example, the contexts EmptyRoom and Nonemp-
tyRoom are temporally related, as they cannot
be simultaneously active. Thus dependency and
temporal relations are specified in the behavioral
charts. Furthermore, reasoning techniques can be
applied to the model for extracting the implicit
temporal and dependency relationships.
3. Priority — CO-LSC supports priorities for events
through the mechanism of smart play-out (execu-
tion) (Harel et al., 2010; Harel et al., 2002). If
a certain behavior in a specific context requires
a higher priority than another, then it is possi-
ble to prioritize the events of the first. Yet, CO-
LSC does not provide an idiom for prioritizing all
the behaviors that are bound to a specific context.
While it is technically possible to create such an
idiom, it might not be safe to prioritize a context
with all the current and future behaviors that are
bound to it. In addition, CO-LSC does not support
the prioritization of contexts.
4. Life Cycle Support — CO-LSC supports the
entire context life cycle. Contexts are speci-
fied using queries and are activated and deacti-
vated based on the system behavior and the update
queries.
To conclude, it seems that CO-LSC provides com-
prehensive support for context-aware systems. How-
ever, it can benefit from explicit references to the con-
text core elements.
6 SUMMARY
This paper proposes a framework for supporting the
evaluation of context-oriented development methods
(i.e., modeling techniques and programming lan-
guages). It conceptualizes and explicates the build-
ing blocks of context-aware systems. Such a frame-
work can be used for evaluating existing development
methods (as we demonstrated in this paper) and for
Modeling Context-aware Systems: A Conceptualized Framework
33

the development of new ones.
We do not claim that the framework is complete,
yet it certainly can serve as a starting point for bench-
marking of context-oriented development methods.
For that reason, we suggest adopting the framework
with caution as more refinements may emerge. In
future work, we wish to continue to examine the
proposed framework and further examine context-
oriented/aware programming/modeling approaches.
REFERENCES
Aguilar, J., Jerez, M., and Rodr
´
ıguez, T. (2018). Cameonto:
Context awareness meta ontology modeling. Applied
Computing and Informatics, 14(2):202–213.
Bettini, C., Brdiczka, O., Henricksen, K., Indulska, J.,
Nicklas, D., Ranganathan, A., and Riboni, D. (2010).
A survey of context modelling and reasoning tech-
niques. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 6(2):161–
180. Context Modelling, Reasoning and Management.
Bricon-Souf, N. and Newman, C. R. (2007). Context aware-
ness in health care: A review. International Journal
of Medical Informatics, 76(1):2–12.
Brings., J., Daun., M., Hildebrandt., C., and T
¨
orsleff.,
S. (2018). An ontological context modeling frame-
work for coping with the dynamic contexts of cyber-
physical systems. In Proceedings of the 6th Inter-
national Conference on Model-Driven Engineering
and Software Development - MODELSWARD,, pages
396–403. INSTICC, SciTePress.
Cabrera, O., Franch, X., and Marco, J. (2017). Ontology-
based context modeling in service-oriented comput-
ing: A systematic mapping. Data and Knowledge En-
gineering, 110:24–53.
Desmet, B., Vallejos, J., Costanza, P., De Meuter, W., and
D’Hondt, T. (2007). Context-oriented domain anal-
ysis. CONTEXT’07, page 178–191, Berlin, Heidel-
berg. Springer-Verlag.
Dey, A. K., Abowd, G. D., et al. (2000). The context
toolkit: Aiding the development of context-aware ap-
plications. In Workshop on Software Engineering for
wearable and pervasive computing, pages 431–441.
Citeseer.
Ejigu, D., Scuturici, M., and Brunie, L. (2007). An
ontology-based approach to context modeling and rea-
soning in pervasive computing. In Proceedings of
the Fifth IEEE International Conference on Pervasive
Computing and Communications Workshops, PER-
COMW ’07, page 14–19, USA. IEEE Computer So-
ciety.
Elyasaf, A. (2021). Context-Oriented Behavioral Pro-
gramming. Information and Software Technology,
133:106504.
Elyasaf, A., Marron, A., Sturm, A., and Weiss, G. (2018).
A Context-Based Behavioral Language for IoT. In
Regina Hebig and Thorsten Berger, editor, CEUR
Workshop Proceedings, volume 2245, pages 485–494,
Copenhagen, Denmark. CEUR-WS.org.
Elyasaf, A., Sadon, A., Weiss, G., and Yaacov, T. (2019).
Using Behavioral Programming with Solver, Con-
text, and Deep Reinforcement Learning for Play-
ing a Simplified RoboCup-Type Game. In 2019
ACM/IEEE 22nd International Conference on Model
Driven Engineering Languages and Systems Compan-
ion (MODELS-C), pages 243–251. IEEE.
Harel, D., Kugler, H., Marelly, R., and Pnueli, A. (2002).
Smart Play-out of Behavioral Requirements. In
Aagaard, M. and O’Leary, J. W., editors, Formal
Methods in Computer-Aided Design, 4th Interna-
tional Conference, FMCAD 2002, Portland, OR, USA,
November 6-8, 2002, Proceedings, volume 2517 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 378–398.
Springer.
Harel, D., Maoz, S., Szekely, S., and Barkan, D. (2010).
PlayGo: Towards a Comprehensive Tool for Scenario
Based Programming. In ASE’10 - Proceedings of the
IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated
Software Engineering, pages 359–360.
Harel, D. and Marelly, R. (2003). Come, Let’s Play:
Scenario-Based Programming Using LSCs and the
Play-Engine. Springer Science & Business Media.
Harel, D. and Pnueli, A. (1985). On the Development of
Reactive Systems. In Logics and models of concurrent
systems, pages 477–498. Springer.
Henricksen, K. and Indulska, J. (2006). Develop-
ing context-aware pervasive computing applications:
Models and approach. Pervasive and Mobile Comput-
ing, 2(1):37–64.
Hirschfeld, R., Costanza, P., and Nierstrasz, O. M. (2008).
Context-oriented programming. Journal of Object
technology, 7(3):125–151.
Ireri, B. N., Wario, R. D., and Mwingirwa, I. M. (2018).
Choosing and adapting a mobile learning model for
teacher education. In Handbook of Research on Dig-
ital Content, Mobile Learning, and Technology Inte-
gration Models in Teacher Education, pages 132–148.
IGI Global.
L
´
opez-Jaquero, V., Rodr
´
ıguez, A. C., Teruel, M. A., Mon-
tero, F., Navarro, E., and Gonzalez, P. (2016). A
bio-inspired model-based approach for context-aware
post-wimp tele-rehabilitation. Sensors, 16(10):1689.
Moradi, H., Zamani, B., and Zamanifar, K. (2020). Caasset:
A framework for model-driven development of con-
text as a service. Future Generation Computer Sys-
tems, 105:61–95.
Peinado, S., Ortiz, G., and Dodero, J. M. (2015). A meta-
model and taxonomy to facilitate context-aware ser-
vice adaptation. Computers & Electrical Engineering,
44:262–279.
Ramos, C., Marreiros, G., and Santos, R. (2011). A sur-
vey on the use of emotions, mood, and personality
in ambient intelligence and smart environments. In
Handbook of Research on Ambient Intelligence and
Smart Environments: Trends and Perspectives, pages
88–107. IGI Global.
Simons, C. (2007). Cmp: a uml context modeling profile
for mobile distributed systems. In 2007 40th Annual
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences
(HICSS’07), pages 289b–289b. IEEE.
MODELSWARD 2022 - 10th International Conference on Model-Driven Engineering and Software Development
34

Sindico, A. and Grassi, V. (2009). Model driven devel-
opment of context aware software systems. In Inter-
national workshop on context-oriented programming,
pages 1–5.
Vieira, V., Tedesco, P., and Salgado, A. C. (2011).
Designing context-sensitive systems: An integrated
approach. Expert Systems with Applications,
38(2):1119–1138.
Yue, S., Smith, R., and Yue, S. (2017). A state-based ap-
proach to context modeling and computing. In 2017
IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence Comput-
ing, Advanced Trusted Computed, Scalable Comput-
ing Communications, Cloud Big Data Computing,
Internet of People and Smart City Innovation (Smart-
World/SCALCOM/UIC/ATC/CBDCom/IOP/SCI),
pages 1–6.
Modeling Context-aware Systems: A Conceptualized Framework
35
