
Identifying Problematic Gamblers using Multiclass and Two-stage
Binary Neural Network Approaches
Kurt Dylan Buttigieg
a
, Mark Anthony Caruana
b
and David Suda
c
University of Malta, Malta
Keywords: Artificial Neural Networks, Bayesian Neural Networks, Problematic Gambling.
Abstract: Responsible gaming has gained traction in recent years due to the harmful nature of compulsive online
gambling and the increased awareness on the unfavourable consequences arising from this type of gambling.
In Malta, legislation passed in 2018 places the onus of responsibility on online gaming companies has made
studying this problem even more important. The focus of this research paper is to apply multistage and two-
stage artificial neural networks (ANN), and two-stage Bayesian neural networks (BNN), to the responsible
gaming problem by training models that can predict the gambling-risk of a player as a multiclass classification
problem. The models are trained using data from gambling session histories provided by a gaming company
based in Malta. These models will then be compared using different performance metrics. It is shown that,
while all approaches considered have their strengths, multiclass artificial neural networks perform best in
terms of overall accuracy while the two-stage Bayesian neural network model performs best in classifying the
most important class, the one where the players have a high risk of becoming problematic gamblers, and also
second best at classifying the medium risk class.
1 INTRODUCTION
The inception of the internet introduced new issues to
the gambling industry. Due to the harmful nature of
online gambling, responsible gaming gained
popularity in recent years, together with the
awareness regarding the unfavourable consequences
arising from gambling, especially the addiction of
gambling. Griffiths (2003) was amongst the first to
study gamblers’ behaviours in both traditional and
online forms of gambling. The paper studies the
accessibility, anonymity, affordability, and
convenience of internet gambling and noted that
problematic gamblers use the internet to further
satisfy their addiction. The author also mentions that
online gambling is incredibly dangerous considering
its convenient nature. Peller et al. (2008) mentioned
that to broaden studies on problematic online
gambling behaviour and the effect it has on one’s
health, one needs to study actual player data. Griffiths
et al. (2009) suggest that it may be more likely that
online gambling leads to problematic gambling rather
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7861-7479
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9033-1481
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0106-7947
than offline gambling such as casinos. Hayer and
Meyer (2010) suggested, from preliminary scientific
evidence, that online gamblers are at greater risk of
becoming problematic gamblers than ordinary casino
or betting parlour gamblers. They argued that more
research should be conducted and favoured an
increase in effective measures which protect
gamblers. Furthermore, they concluded that
temporary self-exclusion measures to online
gambling sites yield positive psycho-social effects. A
study by McCormack & Griffiths (2012) showed that
even players themselves feel that the online element
of gambling, when compared to offline gambling,
causes more obsession and this form of gambling
increases social problems. Hubert & Griffiths (2018)
concluded that, although there were some
resemblances, online compulsive gamblers
demonstrate different characteristics when compared
to offline compulsive gamblers. The latter are more
prone to depression, feel more emotional while
gambling and experience frequent suicidal thoughts.
336
Buttigieg, K., Caruana, M. and Suda, D.
Identifying Problematic Gamblers using Multiclass and Two-stage Binary Neural Network Approaches.
DOI: 10.5220/0010821100003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 3, pages 336-342
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

There have been a number of studies that made
use of machine learning techniques in the field of
responsible gaming. Braverman (2010) used a k-
means cluster analysis approach to identify clusters in
a dataset of 48,114 people who opened an account
with an online betting service provider. The analysis
identified four subgroups, in which one of the groups
is a cluster of gamblers that are at a higher risk for
reporting gambling-related problems. Philander
(2013) compared different data mining procedures,
with the aim of identifying gamblers at a high risk of
becoming problematic gamblers. A sample of online
live action sports betting data was used and different
classification and regression algorithms were applied
to identify which methods are better at achieving the
objective. Percy et al. (2016) applied logistic
regression, Bayesian networks, neural networks and
random forests to predict self-exclusion – these
models had very comparable results after applying
data balancing, with Bayesian networks being the
most superior in terms of accuracy and sensitivity.
Furthermore, Ukhov et al. (2020) utilise a gradient
boosting approach to identify the most important
traits of the casino and sports gambling groups,
finding distinct traits between the two. To the
authors’ knowledge, Bayesian neural networks
(BNN) has not been used for the identification of
problematic gamblers, though these have been used
in a variety of other applications. The aim is to see if
this approach yields any added benefits to the
standard ANN approach.
In this study, the problem will be tackled using
two-stage artificial neural networks, both in their
classical and Bayesian form. These techniques shall
be used to create models that can predict whether a
gambler is problematic or has a high risk of becoming
a problematic gambler by using historical session
data. The aim is to classify gamblers using 4-level
multiclass classifiers: minimal-risk, low-risk,
medium-risk and high-risk. As defined by Braverman
(2010) and Percy et al. (2016), there are four variables
which assist in classifying a player as problematic or
not: the number of bets, the amount of money bet, the
total winnings, and the number of active days. These
variables then yield the four important factors that,
depending on their degree, signify the extent of
problematic gambling behaviour, which are the
trajectory (total amount bet), frequency (days active),
intensity (how regularly the gambler places bets on
active days), and variability (the standard deviation of
the amount of money gambled) of the gambler. These
1
https://github.com/buttigiegkurt/responsible-gaming-
paper/blob/main/variablelist.pdf
four factors, together with similar behavioural
variables to those mentioned by Adami et al. (2013)
and Ukhov et al. (2020), and several other variables,
will be included in the analysis. In total 74 variables
are considered (see link in footnote
1
).
2 METHODOLOGY
In the methodology, multiclass artificial neural
networks and two-stage artificial and Bayesian neural
networks are considered. To keep a similar
framework throughout, only one hidden layer shall be
considered in the models. Artificial neural networks
(ANN) need no introduction. An important parameter
that shall require considering for ANN is the penalty
parameter for L
2
-norm regularisation 𝜑 which is
intended to regulate overfitting: 𝜑=0 means no
regularisation while larger values correspond to more
regularisation. Further theoretical detail on ANN can
be found in Courville et al. (2015). For ANN variable
selection shall also be implemented through variable
importance in some of the models. For variable
importance, Gevrey et al. (2003) introduced a method
which calculates the variable importance depending
on the absolute value of the weights. This method
gives the importance of a variable expressed in terms
of a percentage, with the most important variable
having an importance of 100%, and shall be used in
the application for calculating the importance of the
variables in the neural network models. In the
application, only variables with importance higher
than 50% will be kept.
The Bayesian approach to neural networks shall
also be considered. BNN offer automatic complexity
control, that is, regularisation coefficients which are
selected using data, and also the possibility of using
prior information for the hyperparameters. Automatic
complexity control helps in avoiding overfitting even
with highly complex models – this was tested by
Sharaf et al. (2020) where the authors concluded that
while there was the danger of overfitting the data with
ANN, the problem as not present in BNN. In this
paper, the focus shall be on the binary BNN setup
found in Liang et al. (2018). Consider the indicator
variables defined by
𝐼
()
=
1
0
if connection from input unit 𝑖 to hidden unit 𝑟 exists
otherwise
,
𝐼
()
=
1
0
if connection from hidden unit 𝑟 to output unit exists
otherwise
,
𝐼
()
=
1
0
if connection from input unit 𝑖 to output unit exists
otherwise
.
Identifying Problematic Gamblers using Multiclass and Two-stage Binary Neural Network Approaches
337

Then the neural network can be written as:
𝑦
(
𝒙,𝒘
)
=𝜓
()
∑
𝐼
()
𝑤
𝑥
+
∑
𝐼
()
𝑤
𝑧
(1)
where 𝑝 is the number of input variables, 𝐷 is the
number of nodes in the hidden layer, and 𝑧
=
𝜓
()
∑
𝐼
()
𝑤
𝑥
. Note that in equation (1), the
term
∑
𝐼
()
𝑤
𝑥
which is not typically present in
ANN includes the connections from the input to the
output units thus skipping the hidden layer. Also note
that the bias terms have been included as part of the
summations, by starting the summations from 0 rather
than 1. In this case, 𝑥
=1.
Next, the sets which specifies the structure and
weights of the Bayesian neural network can be
defined. Let
𝛤=𝐼
()
,𝐼
()
,𝐼
()
:𝑖=0,1,…,𝑝,𝑟=1,2,…,𝐷
denote the set which specify the structure of the
Bayesian neural network and let
𝛩
𝚪
={𝑤
,𝑤
,𝑤
:𝐼
(
)
=1,𝐼
(
)
=1,𝐼
(
)
=1: 𝑖
=0,1,…,𝑝,𝑟=1,…,𝐷}
denote the set which specifies the connection weights
associated with the BNN. Let
|
𝛤
|
denote the network
size, that is, the number of connections which have
their indicator equal to 1. Then the prior for 𝛩
is a
normal distribution with a zero vector mean and
covariance matrix 𝑉
, which has dimension
|
𝛤
|
×
|
𝛤
|
, and the prior for 𝛤 is the probability mass
function
𝜋
(
𝛤
)
of 𝛤 satisfying
𝜋
(
𝛤
)
∝ 𝜆
|
|
(
1−𝜆
)
|
|
𝐼
(
1≤
|
𝛤
|
≤𝑟̅
,𝛤∈𝒢
)
(2)
where 𝑛 is the number of observations in the training
set, 𝐾
=
(
𝑝+1
)(
𝐷+1
)
+𝐷 is the total number of
connections between all the units in the neural
network when all the indicator variables are equal to
1, 𝑟̅
is the maximum network size allowed in
simulation,
𝜆
is the optimal prior hyperparameter
and 𝒢 is the set of all valid neural networks. In other
words, (2) can be considered to be Binomial with
parameters 𝐾
and 𝜆
.
For variable selection, Liang et al. (2018) made
use of the marginal inclusion probability approach.
The marginal inclusion probability approach,
explained in Barbieri et al. (2004), is a measure of
how likely a variable is in the true model. The
marginal inclusion probability approach can also be
used when selecting the network connections. The
same theory applies and all those connections which
have a marginal probability greater than 0.5 are
included in the BNN model. The actual number of
connections in the network, as well as the
corresponding number of hidden units, shall be
calculated automatically using the marginal inclusion
probability criterion. Furthermore, the optimal prior
hyperparameter 𝜆
is determined by specifying a
candidate set of 𝑚 values, and using K-fold cross-
validation. The 𝜆
for which the best likelihood is
obtained is then chosen. Finally, the algorithm for
generating posterior samples is an MCMC type
algorithm called the pop-SAMC algorithm.
This
algorithm operates by fine-tuning a parameter 𝜽
based on previous samples. By doing so, the
algorithm penalizes the most visited subregions and
rewards the ones less visited and thus escapes from
local traps, in which the Gibbs and the Metropolis-
Hastings algorithms are known to be vulnerable for.
The Pop-SAMC Algorithm, first published in Liang
et al. (2018), is now presented.
Pop-SAMC Algorithm:
Let 𝔊 be the sample space of 𝛩
and 𝑘 a constant.
Suppose that the posterior mass function of the BNN
can be written as ℎ
(
𝛩
)
=𝑘𝛶
(
𝛩
)
, where 𝛶
(
∙
)
is a
function of the connection weights. Partition 𝔊 into 𝑠
partitions defined as 𝑃𝑎𝑟
,𝑃𝑎𝑟
,…,𝑃𝑎𝑟
. Let 𝝎=
(
𝜔
,𝜔
,…,𝜔
)
denote the sampling frequencies for
each of the subregions, which satisfy the constraints
𝜔
>0 ∀𝑖 and
∑
𝜔
=1 . Let 𝜩
=
𝛩
()
,…,𝛩
()
denote the population of samples
simulated at iteration 𝑡, where 𝑁 is the population
size. Let 𝜏∈[1,2), 𝜏
∈(0,1) and denote
{
𝑎
:𝑡=
1,2,…
}
as a positive and non-increasing sequence
which satisfies the following conditions:
𝑎
=∞,
𝑎
−𝑎
𝑎
=𝑂
(
𝑎
)
,
𝑎
√
𝑡
<∞.
In general, set 𝑎
=
for some 𝑡
>0 and 0.5 <
𝜍<1. One iteration of the algorithm consists of the
following two steps:
1. (Population Sampling) For 𝑙=1,…,𝑁,
simulate a sample 𝛩
()
by running, for one
step, the Metrapolis-Hastings algorithm
which starts with 𝛩
()
and admit the
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
338
stationary distribution ℎ
(
𝛩
)
∝
∑
(
)
,
𝐼
(
𝛩
∈𝑃𝑎𝑟
)
, where 𝜃
=
𝜃
,
,…,𝜃
,
is the working parameter.
Denote the population of the new samples by
𝜩
=𝛩
()
,…,𝛩
()
.
2. ( 𝜃-updating) Firstly denote a vector 𝜻
()
made up of 𝑠 indicators 𝜻
(
)
=
𝐼𝛩
(
)
∈
𝑃𝑎𝑟
,…,𝐼𝛩
(
)
∈𝑃𝑎𝑟
, and let
𝑯
(
𝜃
,𝜩
)
=
∑
𝜻
(
)
𝝎
. Now, set
𝜃
= 𝜃
+𝑎
𝑯
(
𝜃
,𝜩
)
.
In this study, apart from considering a multiclass
ANN approach, a two-stage ANN and BNN approach
shall also be implemented, particularly to check
whether these yield better predictions. In particular,
the BNN that will be studied can only be implemented
in a binary setting, and hence the two-stage approach
for tackling the multiclass problem is essential. This
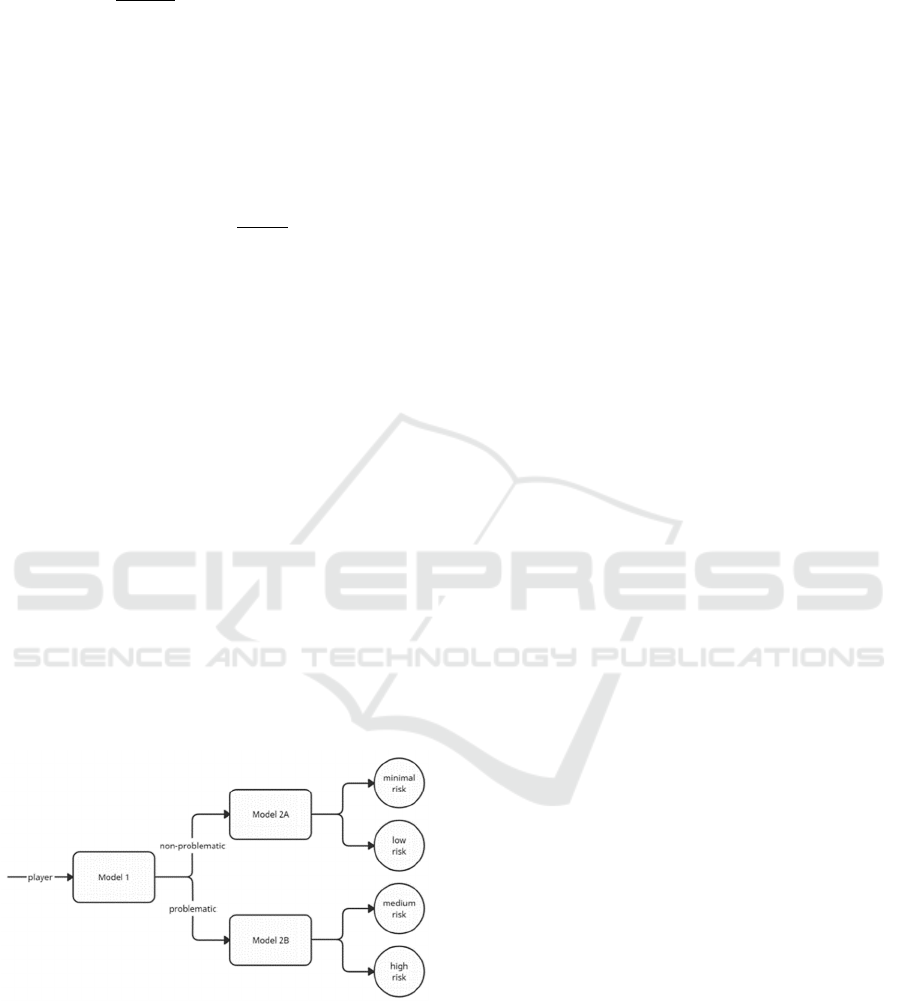
approach is described as follows. Initially, a model is
trained, denoted Model 1, which will predict whether
a gambler is classified as problematic or non-
problematic. Then, another independent model is
trained, denoted Model 2A, which classifies a non-
problematic gambler as minimal-risk or low-risk by
taking the actual class of the gamblers as reference,
i.e., only observations which have an actual class of
minimal-risk or low-risk are taken for training.
Similarly, a new model denoted Model 2B is trained,
which classifies a problematic gambler as medium-
risk or high-risk. A graphical representation of this is
given by Figure 1.
Figure 1: A graphical representation of the two-stage binary
model.
In the next section, the procedure of implementing
two-stage binary ANN and BNN, and multiclass
ANN to the responsible gambling problem shall be
described.
3 APPLICATIONS
The dataset considered consists of 30706
observations. It was discovered that a number of
observations had the same player ID due to the fact
that the same player can be assessed multiple times
by a responsible gaming agent. These duplicate
observations were removed, keeping the observations
with lowest number of days since last activity. A total
of 1829 duplicate observations have been removed,
leaving 28877 observations in the dataset.
Since the dataset used for this analysis consists of
both categorical and continuous data, SMOTE-NC
will be used to oversample the minority classes in the
training set. Python’s imblearn library (see Lemaître
et al., 2017) has been designed to deal with
imbalanced datasets and will be used for data
balancing since it has SMOTE-NC available. For
more information on SMOTE-NC, see Chawla et al.
(2002). It is known that neural networks perform
better with standardized data - see e.g. Shanker et al.
(1996). Thus, before creating the models, the data
used for both for all models has been centred and
scaled. The programming language R was used for
the data analysis, where the nnet package (see Ripley
and Venables., 2021) was used to implement artificial
neural networks and the BNN package (see Jia et al.,
2018) was used for implementing Bayesian neural
networks. To assess the performance of the models,
the MAE (the average absolute distance between the
predicted category and the actual category for
multiclass problems) and accuracy shall be used.
For ANN, the two-stage binary model uses the
sigmoid function for both the hidden and output
activation functions, the cross-entropy function as the
error function and the BFGS algorithm as the
optimisation algorithm to minimise this error
function. For further reading on the BFGS algorithm,
see Kelley (1999). This is done for all the three
models, that is, models 1, 2A and 2B. The same grid
search method will be used to find the optimal
parameters. The three models will be considered
separate and the grid search shall be used separately
for the three models. The sets specifying the different
number of hidden units 𝐷 and penalty parameter 𝜑
will be taken as {1,2,3,…,24,35} and
{0,0.1,0.2,…,0.9,1} respectively. This gives a total
of 35 × 11 = 385 different models for each of model
1, model 2A and model 2B. For each of these models,
5-fold cross validation will be used, where the
distributions of the classes over the different folds
will be kept equal. The optimal model for model 1 is
the one with 33 hidden units and a weight decay of
0.9, giving an MAE of 0.1539. The optimal model for
Identifying Problematic Gamblers using Multiclass and Two-stage Binary Neural Network Approaches
339

model 2A is the one with 23 hidden units and a weight
decay of 0.9, giving an MAE of 0.1458. The optimal
model for model 2B is the one with 35 hidden units
and a weight decay of 1, giving an MAE of 0.0886.
Next, the optimal model for model 1 shall be used to
predict gamblers on the testing set, which are then
predicted as minimal-risk, low-risk, medium-risk or
high-risk using the optimal models for 2A and 2B,
depending on their predicted class in model 1. The
two-stage binary model achieved an MAE of 0.5107
and an accuracy of 61.28%.
Variable importance is also considered on each of
the three optimal models, new models shall be trained
using just the variables with an importance greater
than 50%. The ratio of the number of days with at
least one denied deposit over the total number of
active days in the past thirty days was the most
important feature for model 1. For models 2A and 2B,
the average of the number of increases in the deposit
limit per active day for the last seven days and the
standard deviation of the total daily session time per
active day are the most important variables
respectively. For the top 5 most important variables
for each model refer to Table 1. The two-stage binary
model with variable selection has an accuracy of
62.06% and an MAE of 0.5035, a marginal
improvement in performance over the model without
variable importance. This shows that although
variable importance reduces the number of variables
in the models, better accuracy can still be obtained,
possibly due to further reducing overfitting in the
models.
Table 1: The five most important variables for each of the
three models in the two-stage binary artificial neural
network model (refer to variables list for full description of
each variable).
For the multiclass version of ANN, the sigmoid
function shall be used as the hidden activation
function and the softmax function for output
activation. In this case, 𝐷 shall be selected from
{1,2,3,…,24,40} and 𝜑 from
{0,0.1,0.2,…,0.9,1}. 5-fold cross validation will be
used once again. The best model is attained at 39
hidden units with a weight decay of 0.7, giving an
MAE of 0.3709. An MAE of 0.5164 is obtained, with
an accuracy of 61.7%. When considering variable
importance, this model is refitted and an MAE of
0.4919 and accuracy of 62.95% is obtained. In this
case, the variable representing the lowest number of
days since the last activity was the most important
one. For the top 20 most important variables refer to
Table 2.
Table 2: The twenty most important variables in the
multiclass artificial neural network model
(refer to variables
list for full description of each variable).
The two-stage binary model using BNN is finally
assessed. The two-stage binary BNN model uses the
tanh function as the hidden activation function and
the sigmoid function as the output. The 𝜆
’s
evaluated for each model will be from the set
{0.005,0.01,…,0.05} for each of models 1, 2A and
2B. For model 1, the optimal 𝜆
is found to be 0.015,
while for model 2A and 2B it is found to be 0.01 and
0.005 respectively. The best performing model with
25000 iterations, 5000 iterations and 50000 iterations
for models 1, 2A and 2B respectively – this yields an
MAE or 0.536 and an accuracy of 60.2%.
The MAE and accuracy for the different models
are summarised in Table 3 - it can be seen that the
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
340
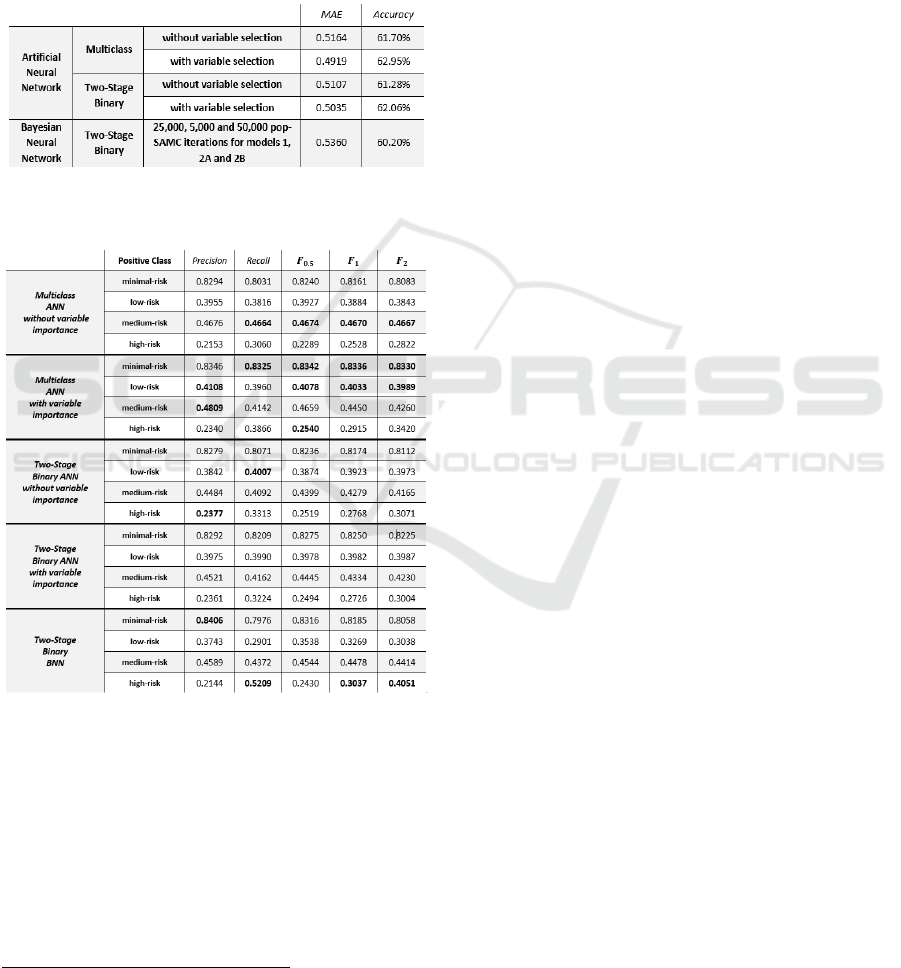
multiclass neural network model with variable
selection performed best in both. The two-stage
binary model with variable selection obtained close
results to the multiclass model, indicating that the
models with variable selection are better than the ones
without, showing that overfitting may be an issue.
Two-stage BNN’s performance is slightly inferior to
ANN, though not considerably.
Table 3: Comparing models in terms of MAE and accuracy.
Table 4: Testing model performance metrics using the one-
vs-all approach.
However, in these types of problems, accuracy is
not necessarily the most important measure, and what
needs to be considered is how well the models predict
higher risk categories, including the higher risk
classes, in particular the high-risk class. For this
reason, a one-vs-all approach is implemented to
check the performance of multiclass classifiers, i.e.,
setting a class as the positive class while setting the
other classes as the negative class. This reduces the
problem to a binary one, and thus binary performance
2
https://github.com/buttigiegkurt/responsible-gaming-pa
per/blob/main/variableimportance.pdf
metrics can be used such as precision, recall and the
𝐹
metrics – these are presented in Table 4. The
multiclass ANN model with variable selection
performed best in most of the metrics for the minimal
and low risk classes. However, the multiclass ANN
without variable selection performed best in
classifying the medium risk class, with BNN ranking
second best. The BNN model performed considerably
better than other models in classifying the high-risk
class, as a recall score of 0.5209 was obtained. This is
further shown by 𝐹
and 𝐹
metrics as the BNN
model obtained the best score with values of 0.3037
and 0.4051 respectively. This is of particular interest,
as detection of the high-risk class is of utmost
importance, while falsely classified lower risk
gamblers are less problematic.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, it is concluded that BNN have been
more successful for predicting higher risk categories,
while multiclass ANN have performed better for
overall accuracy. Variable selection through
evaluating variable importance has, in the majority of
cases, been useful in improving accuracy. While this
has to be done via an extra procedure in ANN, this is
automatic in BNN where any unuseful connections
are automatically severed (see link in footnote for the
variables used in the BNN
2
). BNN have also proved
to be quite a computationally intensive procedure to
run, especially to determine the optimal 𝜆
’s, which
in total took more than 400 hours to run on a
workstation with an i7vPro 8
th
Gen processor. One
limitation which was experienced in the modelling is
the use of only single hidden layer neural networks in
the BNN package. The effect of the addition of extra
hidden layers could thus not be studied.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We wish to express our gratitude to LeoVegas
Gaming PLC in Sliema (Malta) for providing the data
in this study and, in addition, their support and their
insightful perspectives on the research topic.
Identifying Problematic Gamblers using Multiclass and Two-stage Binary Neural Network Approaches
341

REFERENCES
Adami, N., Benini, S., Boschetti, A., Canini, L., Maione, F.,
Temporin, M. (2013). Markers of unsustainable gaming
for early detection of at-risk online gamblers.
International Gambling Studies. 13, 188-204.
Barbieri, M., Berger, J. (2004). Optimal predictive model
selection. Annals of Statistics. 32(3), 870-897.
Braverman, J., Shaffer, H. (2010). How do gamblers start
gambling: identifying behavioural markers for high-
risk internet gambling. European Journal of Public
Health. 22, 273-278.
Chawla, N., Bowyer, K., Hall, L., & Kegelmeyer, P. (2002).
SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 16, 321-
357.
Courville, A., Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y. (2015). Deep
Learning, The MIT Press. London, 2
nd
edition.
Gevrey, M., Dimopoulos, I., Lek, S. (2003). Review and
comparison of methods to study the contribution of
variables in artificial neural network models.
Ecological Modelling. 160(30), 249-264.
Griffiths, M. (2003). Internet gampling: issues, concerns,
and recommendations. Cyber Psychology and
Behaviour. 6(6), 557-568.
Griffiths, M., Wardle, H., Orford, J., Spreston, K., Erems,
B. (2009). Sociodemographic correlates of internet
gambling: Findings from the 2007 British ambling
prevalence survey. Cyber Psychology and Behaviour.
12(2), 199-202.
Hayer, T., Meyer, G. (2010). Self-exclusion as a harm
minimization strategy: evidence for the casino sector
from selected European countries. Journal of Gambling
Studies. 27(4), 685-700.
Hubert, P., Griffiths, M. (2018). A comparison of online
versus offline gambling harm in Portuguese
pathological gamblers: An empirical study.
International Journal of Mental Health Addiction. 16,
1219-1237.
Jia, B., Liang F., Gentleman, R., Ihaka, R., The R Core
Team. (2018). Package ‘BNN’ (Version 1.0.2). CRAN
R-Project.
Kelley, C. T. (1999). Iterative Methods for Optimization.
Frontiers in Applied Mathematics, 18, 71-86.
Lemaître, G., Nogueira, F., Aridas, C. K. (2017).
Imbalanced-learn: a python toolbox to tackle the curse
of imbalanced datasets in machine learning. The
Journal of Machine Learning Research. 18(1), 559–
563.
Liang, F., Li, Q., Zhou, L. (2018). Bayesian neural
networks for selection of drug sensitive genes. Journal
of the American Statistical Association. 113(523), 955-
972.
McCormack, A., Griffiths, M. D. (2012). Motivating and
inhibiting factors in online gambling behavior: A
grounded theory study. International Journal of Mental
Health and Addiction. 10, 39-53.
Percy, C., Franca, M., Dragicevic, S., Garcez, A. (2016).
Predicting online gambling self-exclusion: An analysis
of the performance of supervised machine learning
methods. International Gambling Studies. 16(2), 1-18.
Peller, A., Laplante, D., Shaffer, H. (2008). Parameters for
safer gambling behaviour: examining the empirical
research. Journal of Gambling Studies. 24, 519-534.
Ripley, B., Venables, W. (2021). Package ‘nnet’ (Version
7.3-16). CRAN R-Project.
Philander, K. (2013). Identifying high-risk online gamblers:
a comparison of data mining procedures. International
Gambling Studies. 14(1), 53-63.
Shanker, M., Hu, M. Y., & Hung, M. S. (1996). Effect of
data standardization on neural network training.
Omega, 24, issue 4, 385–397.
Sharaf, T., Williams, T., Chehade, A., Pokhrel, K. (2020).
BLNN: An R package for training neural networks
using Bayesian inference. SoftwareX. 11, 100432.
Ukhov, I., Bjurgert,, J., Auer, M., Griffiths, M. (2020).
Online problem gambling: a comparison of casino
players and sports bettors via predictive modelling
using behavioral tracking data. Journal of Gambling
Studies. 37, 887-897.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
342
