
SpamFender: A Semi-supervised Incremental Spam Classification
System across Social Networks
Shengyuan Wen and Weiqing Sun
College of Engineering, University of Toledo, Toledo, Ohio, U.S.A.
Keywords: Social Spam, Online Learning, Incremental Learning, Data Scraping, Semi-supervised Learning, Label
Spreading.
Abstract: Social network users receive a large amount of social data every day. These data may contain malicious un-
wanted social spams, even though each social network has its social spam filtering mechanism. Moreover,
spammers may send spam to multiple social networks concurrently, and the spam on the same topic from
different social networks has similarities. Therefore, it is crucial to building a universal spam detection system
across different social networks that can effectively fend off spam continuously. In this paper, we designed
and implemented a tool Spam-Fender to facilitate spam detection across social networks. In order to utilize
the raw social data obtained from multiple social networks, we utilized a semi-supervised learning method to
convert unlabelled data into usable data for training the model. Moreover, we developed an incremental
learning method to enable the model to learn new data continuously. Performance evaluations demonstrate
that our proposed system can effectively detect social spam with satisfactory accuracy levels. In addition, we
conducted a case study on the COVID-19 dataset to evaluate our system.
1 INTRODUCTION
In modern society, online social networks have
become a necessity in human interactions. Especially
due to the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic,
people rely on online social networks to know what is
going on around them. In the meantime, spammers
have taken the opportunity to send out spam more
frequently. There are many messages, including
profanity, malicious links, bot users, fraudulent
reviews, on different social media. For example,
Facebook deleted 865 million posts and removed 583
million fake accounts in the first quarter of 2018
(Frenkel, 2018). The percentage of Twitter accounts
exhibiting social bot behaviours is between 9% and
15% (Newberg, 2017).
Thanks to the rapid development of machine
learning, spam detection systems are becoming more
and more sophisticated, but at the same time, there are
not much research works on the detection of social
spam. Although different social networks have their
social spam detection mechanisms, there is still a
large amount of social spam that can bypass the
detections and interfere with user activities. There are
various online social networks such as Facebook,
Twitter, Snapchat, and Pinterest. However, there are
no effective spam detection systems that can detect
across different online social networks. Also, social
spam detection relies on large data, but since the data
on the internet is raw and unlabeled, data labeling is
one of the issues that need to be addressed. Moreover,
due to time-sensitive nature of data on online social
networks, concept drift can make the detection
inaccurate. To solve these problems, we build an
online incremental learning social spam detection
system named SpamFender that can work across
different online social networks and continuously
fend off unwanted social spams. In particular, it can:
1) detect social spam across different social networks;
2) collect social data in an effective way; 3) propagate
labels to real social network unlabeled data; 4)
incrementally learn for the new social data; 5) detect
social data for spam and inform users timely.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 covers the related work. The design
methodology is described in Section 3. Section 4
presents the system implementation, evaluation, and
a case study about COVID-19 spam detection. And
finally, we conclude in Section 5.
388
Wen, S. and Sun, W.
SpamFender: A Semi-supervised Incremental Spam Classification System across Social Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0010840300003120
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2022), pages 388-395
ISBN: 978-989-758-553-1; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 RELATED WORK
With the increasing number of social network users,
people begin paying attention to social spam
detection. Social spam is featured by crossing
multiple platforms, with large volume, and ever-
increasing. For different social networks, spammers
may send social spam with similar content. When the
spam detector is not limited to a specific social
network, the detection efficiency and accuracy rate
will be significantly improved. Xu proposed spam
detection across online social networks (Xu et al.,
2016), Wang proposed a framework to detect social
spam in different social networks and websites (Wang
et al., 2011). Fakhraei proposed a collective spammer
detection method in evolving multi-relational social
networks (Fakhraei et al., 2015).
There is some research about incremental learning
for spam detection. Sheu et al. (2017) proposed an
efficient incremental learning mechanism for email
spam detection. Kho et al. (2019) proposed an
incremental learning method for spoof fingerprint
detection. Yang et al. (2017) proposed an incremental
laplacian regularization extreme learning machine for
online learning. Sanghani and Kotecha (2019)
proposed an incremental personalized E-mail spam
filter using a novel TFDCR feature. Peris and
Casacuberta (2019) proposed an online learning for
effort reduction in interactive neural machine
translation. Luo et al. (2020) developed an appraisal
of incremental learning methods. Guan and Zhu
(2005) proposed an incremental approach to genetic-
algorithms-based classification. Li et al. (2010)
proposed an incremental feature selection algorithm
for data stream classification. Polikar et al. (2001)
proposed an incremental learning algorithm for
supervised neural networks. However, previous
researches haven’t implemented a practical system to
detect social spam.
In addition, we also used real data collected from
multiple social networks. For data collection, a well-
known tool called Tweepy (Roesslein, 2021) can be
used to collect tweets. Another tool GetOldTweets
(Mottl, 2019) uses tweet crawling and can bypass the
two-week collection limit. Since the raw data is
unlabelled, we also adopted the Semi-Supervised
learning method to propagate the labels
automatically. Sedhai and Sun (2017) proposed a
semi-supervised spam detection method in the
Twitter stream. Whissell and Clarke (2011) proposed
a clustering method for semi-supervised spam
filtering. Chen et al. (2018) proposed a semi-
supervised clue fusion for spammer detection in Sina
Weibo. Imam et al. (2019) proposed a semi-
supervised learning approach for tackling twitter
spam drift. However, most of these approaches focus
on a single social network, unlike ours.
3 DESIGN METHODOLOGY
Based on the literature study, an ideal spam detection
system for online social networks should meet the
following requirements: 1) It should work across
multiple social networks seamlessly; 2) It should
work continuously; 3) It should have high spam
detection accuracy and efficiency; 4) It should require
minimal user configuration efforts.
3.1 System Design
The system architecture of SpamFender, as shown in
Fig. 1, is divided into two phases: the offline training
phase and the online learning phase.
In the offline training phase, we performed data
collection, labelling, pre-processing, cross-
validation, and then used multiple classification
algorithms for training and classification. For data
collection, we scraped real-world data across
different online social networks and then carried out
data pre-processing to facilitate natural language
classification. In particular, we removed punctuation
and stop words, performed tokenization and
lemmatization, and then applied term frequency–
inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) vectorization
(Ramos, 2003) to the data. For the model training, in
order to prevent overfitting, we used cross-validation
by dividing the dataset into ten subsets. A subset was
selected from 10 subsets as the test set in turn. At the
end of this offline phase, we tested and measured the
performance of the classification algorithms and
provided the trained models for the online learning
phase for real-time spam detection.
In the online learning phase, the real-world users’
social data from multiple social networks will be
collected using our self-developed tools and then go
through the data pre-processing, which is similar to
that used in the previous phase. After that, the
classification module will work on the processed data
by using the trained models. Finally, the users will be
notified of the posts as spam. In addition, we designed
an incremental learning system with label
propagation so that the model can be trained
continuously. The model can learn new social spam
features on social media in time and detect new social
spam.
SpamFender: A Semi-supervised Incremental Spam Classification System across Social Networks
389
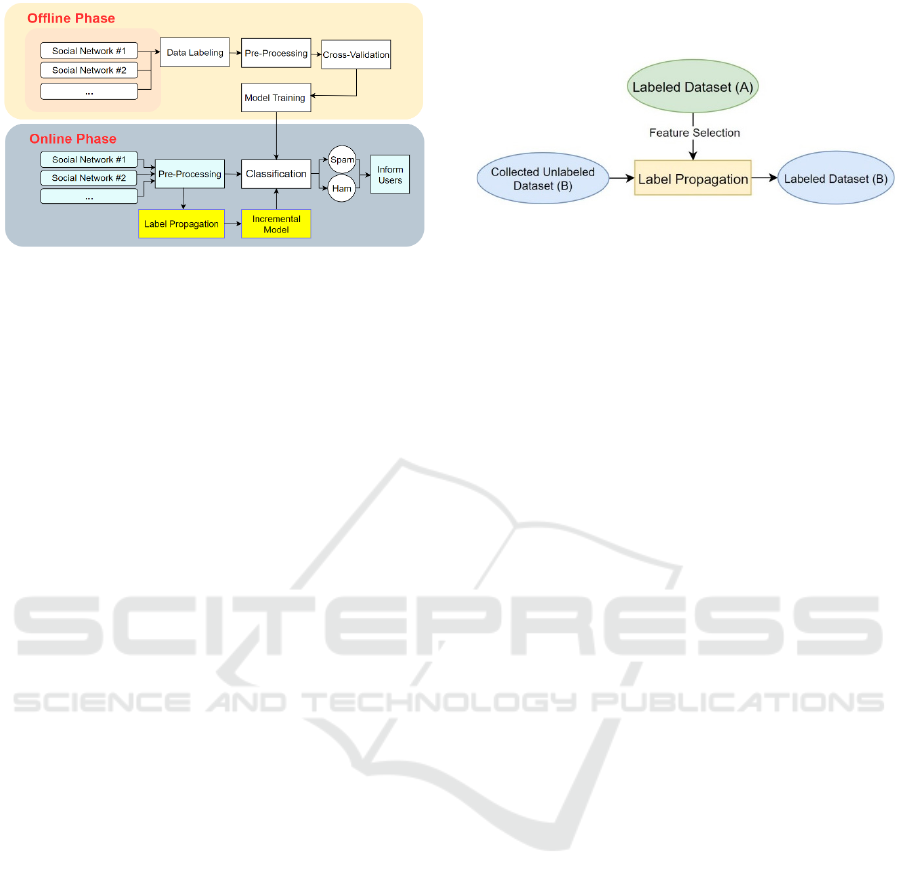
Figure 1: SpamFender Architecture.
3.2 Key Design Considerations
Now that we know the SpamFender architecture, it is
important to discuss a few key design components,
including incremental learning, semi-supervised
learning, and the support of multiple social networks.
3.2.1 Incremental Learning
Incremental learning can learn useful information
from new and incremental data. Meanwhile, it does
not require access to the original data that has been
used to train the model. Specifically, it has the ability
to continuously process the streaming flow of
information in the real world, retain or even integrate
and optimize old knowledge while adopting new
knowledge. The adoption of incremental learning is
instrumental in enabling SpamFender to detect social
spam in an adaptive and continuous manner.
3.2.2 Semi-supervised Learning
Labelled data is much harder to obtain than
unlabelled data. As the collected raw data is
unlabelled, there should be an efficient data labelling
method for preparing data for the training. The label
propagation algorithm is a commonly used semi-
supervised learning method in machine learning,
which is used to assign labels to unlabelled samples.
The label propagation algorithm constructs an edge-
weighted graph through the similarity of all samples,
and then each sample performs label propagation
between its neighbouring samples.
In the online learning phase, the streaming data
was cumulatively collected and converted to mini-
batch data. And after basic pre-processing, the mini-
batch data will be transformed into the label
propagation module where the previously labelled
social data would be pre-processed and selected high-
valued features will be used in label propagation. The
unlabelled social data will be converted to labelled
data after applying to label propagation, as shown in
Fig. 2.
Figure 2: Label Spreading in SpamFender.
3.2.3 Support of Multiple Social Networks
Due to the diversity of social networks, the same type
of social spam can be sent to more than one social
network by a spammer. And therefore, it would be
more cost-effective to consider multiple social
networks at the same time. We have therefore
collected data from more than one social network so
that our model is not limited to detecting social spams
in one social network, and we can input text data from
any social network into our model for detection. At
the same time, to further enhance our model's ability
to support multiple social networks, the training
dataset of the model is extended by collecting raw
data from different social networks and transforming
the raw data into the training dataset through label
propagation. The detection capability of the model is
also enhanced when the training data come from
various social networks.
4 IMPLEMENTATION AND
EVALUATION
We implement a prototype of SpamFender by
following the system architecture depicted in Fig. 1.
4.1 System Implementation
4.1.1 Data Collection and Processing
In our implementation, for the offline phase, we
developed data collection tools for both Twitter and
Facebook. For Twitter data collection, we made use
of a python library CollectOldTweet. It can bypass
Twitter API limitation that a developer can only
collect tweets data less than 2 weeks old. However,
the library can be easily detected by Twitter when
reaching the request sending limit. Hence, we used a
sleep timer to automatically pause the collection
module for 10 minutes. In this way, we collected
about 6,000 tweets on specific topics: bitcoin and
ICISSP 2022 - 8th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
390

news, and around 2,000 tweets in the chronological
order, as part of our initial training dataset. For
Facebook, we used an online collecting tool Netvizz
(UP2, 2015), and collected about 5,000 of the posts.
We then manually labelled this part of data and did
some exploratory analysis of it. The data collected in
this phase was also used in the online phase label
propagation processing as a learnable dataset.
After the data collecting process, we got a total of
13,721 data records, including 6,445 spam and 7,276
ham. The spam rate is 46.97% in our dataset, which
is close to the real-world ratio of around 40%.
Data processing is a must-do in natural language
classification. For punctuations and stop words
removing, we used String.punctuation which is a pre-
initialized constant in Python 3, a list of stop words
contained by NLTK (NLTK Team, 2021), and a
common natural language processing library. And
then we used re.split() function to split text into words
(tokens) and used .lower() function to convert them
into lower case. Lemmatization converts the different
forms of a word to its root word. Thus, they can be
analyzed as a single word. We adopted a WordNet
Lemmatizer in NLTK to lemmatize the sentences in
the dataset. Then we used a TF-IDF vectorizer
provided in scikit-learn to calculate the frequency of
words. After applying the TF-IDF vectorizer, the
content was transformed into a 5,000-column
frequency table.
4.1.2 Algorithm Selection
In our prototype, different classification algorithms
can be selected, such as Multinomial Naïve Bayes,
Bernoulli Naïve Bayes, Decision Tree, Random
Forest, Neural Network, SVC, Logistic Regression,
SGD Classifier, Passive-Aggressive Classifier, and
Perceptron. The algorithm with better performance
can be selected for the online learning phase to detect
social spam during real time. In this phase we used
10-fold cross-validation by dividing the entire
manually labelled dataset into 10 subsets, rotating 9
subsets as the training set and one data set as the test
set, taking the average of the ten results. In the later
sections we compared multiple performance metrics
of different algorithms. Meanwhile, the trained
models will be stored by using the Pickle package
(Kimbro et al, 2019) in the offline phase.
4.1.3 Online Learning
In the online phase, we used the Selenium (Stewart,
2021) package to simulate user actions and login
accounts to collect tweets and posts related to the
users. After the program is running, there will be a
Chrome window started with a Chromedriver
(Chromium, 2021) program pre-installed. Next,
Chrome is being controlled automatically to login to
an account with a preserved credential and scrape the
posts in the mini window. The program uses HTML
locators to download posts. The data scraped from
web pages was cleaned by the pre-processing
component. Finally, we used the Pickle package to
load the trained model to detect the spam. A
notification containing the spam post will be sent to
the user by using social networks API message
functions when a spam is detected.
4.1.4 Incremental Learning
For the incremental learning module, we make our
data collector periodically collect the social news data
from social networks. When the amount of data
reaches the threshold, the data will be batched into a
mini dataset. In the experimentation, we collected ten
batches with a total of 240,000 records. Natural
language pre-processing can reduce the data size and
classification time through punctuations and stop
words removing, tokenizing, lemmatization, and TF-
IDF. The mini dataset will then be annotated by label
propagation. In this module, we used the data
collected in the offline phase as an input learnable
labelled data set for label propagation and used the
label propagation method with the radial basis
function (RBF) kernel in scikit-learn. The dataset
labelled by propagation will be used in partial fit (to
reduce memory usage) to several incremental
learning algorithms: Multinomial Naïve Bayes,
Bernoulli Naïve Bayes, Perceptron, SGD Classifier,
and Passive-Aggressive Classifier. After each time
partial fit, every algorithm can predict the social spam
and then continuously learn the new data. Fig. 3
shows the incremental learning module architecture.
We will elaborate on the performances of different
algorithms in the evaluation section.
Figure 3: Incremental Learning Module Architecture.
4.2 System Evaluations
Our evaluation was performed by running
SpamFender on a PC workstation with Windows 10
64-bit Operating System, AMD Ryzen 1700X 8-Core
SpamFender: A Semi-supervised Incremental Spam Classification System across Social Networks
391

CPU @ 3.4GHz, and 24GB RAM. The evaluation
consists of two steps: offline phase evaluation and
online phase evaluation.
4.2.1 Offline Phase Evaluation
In the offline phase, we compared the performance of
several algorithms, including multinomial Naive
Bayes, decision tree, random forest, logistic
regression, support vector classification, basic neural
network, stochastic gradient descent classifier, and
passive-aggressive classifier. The metrics we used
include accuracy, precision, recall rate, AUC, and
running time in our experimentation. Accuracy is the
ratio of the number of samples correctly classified by
the classification model to the total number of
samples. Precision is the ratio of the number of
positive samples correctly classified by the model to
the total number of positive samples. The recall rate
is the ratio of the number of positive samples with the
correct classification of the model to the total number
of samples with the correct classification. The
receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and
area under the ROC curve (AUC) are the
conventional metrics for evaluating imbalanced
classification. The ROC curve of a good classification
model should be as close as possible to the upper left
corner of the square with area 1. ROC curve
illustrates the TPR (True Positive Rate) against the
FPR (False Positive Rate), and it is a good
performance measurement to show the trade-off
between sensitivity (TPR) and specificity (1-FPR). If
the curve is closer to the top left corner, it indicates
the classifier has good performance. On the other
hand, if the curve is closer to the 45-degree diagonal
line, it indicates it is less accurate. Fig. 4 shows ROC
curves of three algorithms used in our
experimentation. In particular, the AUC is the area
under the blue line for Random Forest.
Figure 4: ROC Curve & AUC.
Table 1 shows the detailed performance metrics
for the algorithms. All the values are averaged over
10 runs. Of all the algorithms we studied, Random
Forest has the best overall performance. Neural
Network also performed well, but the running time is
much longer than Random Forest. The precision of
the Random Forest is higher than Neural Network,
which means the Random Forest can identify more
positive samples than the Neural Network. Moreover,
the AUC of Random Forest is higher than the AUC
of Neural Network. The decision tree has a good
accuracy, but comparatively a poor precision, which
means there was a lot of spam that was not classified
properly. Due to the same reason, the recall rate of the
Decision Tree is not good as well. We can also see
that Multinomial Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression,
SGD Classifier, Passive-Aggressive Classifier have
comparatively poor accuracy. Because they are linear
models and the social spam feature is not in a linear
distribution, the performance of these three
algorithms is comparatively poor. Since Naive Bayes
uses a likelihood function to calculate word
probability and takes into account every relevant
word in the content, the Naive Bayes algorithms have
comparatively higher precision, i.e. identify positive
sample ability, than the other linear models.
Table 1: Algorithms Comparison in Offline Phase.
Algorithms Accuracy Precision Recall AUC Speed
(s)
Multinomial
Naïve Bayes
0.89458 0.94 0.87 0.87 0.012
Bernoulli
Naïve Bayes
0.87485 0.93 0.81 0.90 0.731
Decision
Tree
0.95551 0.825 0.79 0.87 0.195
Random
Fores
t
0.97678 0.96 0.93 0.98 0.316
Neural
Network
0.98162 0.93 0.95 0.96 40.24
SVC
0.88007 0.72 0.59 0.75 3.220
Logistic
Regression
0.92647 0.88 0.73 0.91 0.338
SGD
Classifie
r
0.86334 0.70 0.78
0.81 1.858
Passive-
Aggressive
Classifie
r
0.78046 0.66 0.83
0.82 1.011
Perceptron
0.88377 0.88 0.88
0.75 0.567
4.2.2 Online Phase Evaluation
For the online phase evaluation, we mainly focused
on the incremental learning module. In particular, we
tested five different algorithms: Multinomial Naive
Bayes, Bernoulli Naive Bayes, Passive-Aggressive
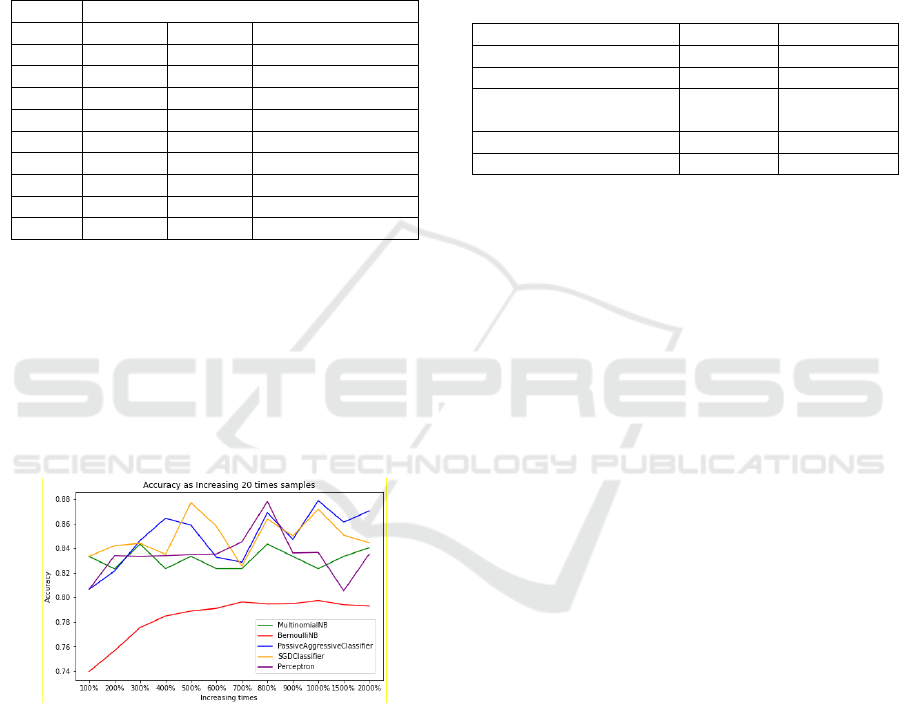
Classifier, SGD Classifier, and Perceptron. The result
was shown in Table 2 and Fig. 5. As we can see,
Multinomial Naive Bayes has a significant
improvement as the size of training samples
increases. Bernoulli Naive Bayes has a comparative
ICISSP 2022 - 8th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
392

higher accuracy and a slight improvement as training
samples increase. Passive-Aggressive Classifier,
SGD Classifier, and Perceptron have a minor
improvement as training samples increase. Because
Naive Bayes uses a likelihood function to calculate
word probability and takes into account every
relevant word in the content, they showed
comparatively better performance than the other three
algorithms.
Table 2: Incremental Algorithms Accuracy with Increasing
Sample Size.
Samples Increasing Percentage
100% 200% 300% 400% 500% 600%
Multinomial
Naive Bayes
0.800 0.830 0.860
0.872 0.879 0.881
Bernoulli
Naive Ba
y
es
0.875 0.878 0.881
0.879 0.883 0.882
Passive
Aggressive
Classifie
r
0.798 0.810
0.811 0.809 0.812 0.810
SGD
Classifie
r
0.801 0.815
0.822 0.817 0.809 0.821
Perceptron 0.788 0.802
0.792 0.791 0.795 0.800
Figure 5: Incremental Algorithms Accuracy with Increasing
Sample Sizes.
4.3 Case Study about COVID-19
In the pandemic period, people are working and
studying from home, and most of their
communication is online. At the same time, online
spams have grown exponentially. More than 300,000
unique online threats have been detected in three
months from the start of the coronavirus pandemic,
trying to take advantage of the coronavirus crisis and
our information about the pandemic and desire for an
end to this pandemic (Armstrong, 2020). Some
traditional spam detection has struggled to respond in
a timely manner. Therefore, we have taken the
opportunity to review our system as social spam has
emerged on social networks. We did a case study by
collecting coronavirus data on social networks and
evaluating our model.
4.3.1 COVID-19 Dataset
Starting from March 2020 to May 2020, we collected
around 10 million posts about COVID-19 on social
networks using the self-developed tools, and we
selected data from different time periods, about
800,000 in total, for this case study.
4.3.2 Label Propagation
We used the semi-supervised learning method to
obtain labels for the COVID-19 dataset.
First, we need to obtain a small number of labels
of data to propagate to unlabelled data. We manually
labelled 2000 posts; the percentage of social spam is
about 35% among those. Then we performed label
propagation. In this label propagation, we compared
two functions: Label Propagation function and Label
Spreading function. Label Propagation function uses
the raw similarity matrix constructed from the data
with no modifications. In contrast, Label Spreading
function minimizes a loss function that has
regularization properties, as such, it is often more
robust to noise. The algorithm iterates on a modified
version of the original graph and normalizes the edge
weights by computing the normalized graph
Laplacian matrix. There are two kernels for label
propagation. The radial basis function (RBF) kernel
will generate a fully connected graph, which is stored
in memory by a dense matrix. This matrix can be very
large, which, combined with the cost of performing
the matrix multiplication and iteration of the
algorithm, can cause a long runtime. On the other
hand, the K-nearest neighbor (KNN) kernel will
generate a sparse matrix that is more memory friendly
and can reduce the runtime significantly.
Due to the large amount of data in our experiment
and the fact that label spreading function slows down
much the processing speed when optimizing
robustness on noise. Therefore, we chose label
propagation function and KNN kernel with a faster
running speed.
We also improved the feature selection
component. In the previous label propagation, we
used all the features instead of selecting specific
features for propagating, which made the label
propagation process inefficient. And this time, due to
a significant increase in the amount of data, as natural
language feature extraction needs to vectorize the
words of the post to word frequency, there will be
expanded into thousands of features. In order to work
efficiently, we used the KBest feature selection
function in scikit-learn, and selected K features with
the highest scores, while the score calculation has
three functions: f_classif, mutual_info_classif, chi2.
SpamFender: A Semi-supervised Incremental Spam Classification System across Social Networks
393
We compared the results with different k values
and different score equations. As shown in Table 3,
we found that the score function using
mutual_info_classif has a much longer run time than
the other two. Finally, we selected Chi2 score
equation and k = 40, i.e., the 40 highest scoring
features were selected for propagation.
Table 3: KBest Accuracy Changes with Different Score
Function and K.
Accurac
y
K
chi2 f
_
classif mutual
_
info
_
classif
10 0.74 0.79 0.68
20 0.71 0.73 0.74
30 0.76 0.72 0.72
40 0.84 0.74 0.71
50 0.79 0.73 0.7
100 0.77 0.72 0.66
300 0.75 0.72 0.67
500 0.74 0.71 0.68
1000 0.74 0.73 0.65
4.3.3 Incremental Learning of COVID-19
Dataset
After the label propagation, we obtained 800,000 data
with labels. We then used the data for incremental
learning and tested the performance of different
algorithms. We split the dataset into a training dataset
and a test dataset at a ratio of 8:2. We set the training
set learning increment to 32000.
Figure 6: Incremental Algorithms Accuracy Changes in
COVID-19 Dataset.
From the trend shown in Figure 6, we can see that
the accuracy of the two naive Bayes methods has
lower values. And the accuracy of the other 3 linear
models is higher than the naive Bayes methods.
Among the three, the accuracy of the Passive
Aggressive Classifier shows an increasing trend as
more samples are learned. The highest accuracy
finally reached 0.8786. SGD Classifier and
Perceptron show a decreasing trend after the number
of samples learned reaches a threshold. Among them,
SGD Classifier reaches the highest accuracy, 0.8770,
after learning grows to 5 times the samples, after
which the accuracy hardly grows or even decreases
no matter how many samples are learned. And
Perceptron presents the highest accuracy, 0.8780,
when learning reaches 8 times the number of samples,
after which there is a significant decrease in accuracy
as increasing the number of samples is learned.
Table 4: Incremental Learning Algorithms Run Times for
the Case Study.
Al
g
orithms Trainin
g(
s
)
Prediction
(
s
)
Multinomial Naïve Bayes 5.022392 20.43906
Bernoulli Naïve Bayes 13.26481 64.57252
Passive Aggressive
Classifie
r
8.537352 16.02734
SGD 7.952496 15.37584
Perceptron 7.854932 16.69584
Table 4 demonstrates the running time of the 5
incremental algorithms. The time is obtained by
setting a timestamp before the start of the incremental
loop and setting a timestamp after the incremental
learning loop. Since each loop needs to do training
firstly and then prediction, the prediction time is not
easy to measure directly. Hence, we set two
timestamps to cover both the learning and prediction
process, and then subtract the learning time from the
total time to get the prediction time.
From Table 4, we can see that the overall time (for
both training time and prediction time) of Bernoulli
Naive Bayes is the longest. The overall runtime
performance of SGD classifier and Perceptron is very
similar. While the Passive Aggressive Classifier
showed a slightly longer training time and prediction
time. Multinomial Naïve Bayes learning time is the
shortest, but the prediction time is slightly longer.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this research, we develop a semi-supervised
incremental learning system SpamFender to detect
social spam to address the ever-growing spam issues
in different online social networks. Overall, the
experiments show that using label propagation to
obtain labels is the cost-effective method and
incremental learning can obtain an increase in
accuracy for continuous learning of new data. For the
future work, we will work on incorporating more
algorithms into different modules of our system.
ICISSP 2022 - 8th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
394

REFERENCES
Armstrong, M. (2020). The Online Coronavirus Threat.
statista.com. https://www.statista.com/chart/21286/
known-coronavirus-related-malicious-online-threats/
Chen, H., Liu, J., Lv, Y., Li, M. H., Liu, M., & Zheng, Q.
(2018). Semi-supervised clue fusion for spammer
detection in Sina Weibo. Information Fusion, 44, 22-32.
10.1016/j.inffus.2017.11.002
Chromium. (2021). ChromeDriver - WebDriver for
Chrome. https://chromedriver.chromium.org/
Fakhraei, S., Foulds, J., Shashanka, M., & Getoor, L.
(2015). Collective Spammer Detection in Evolving
Multi-Relational Social Networks. Paper presented at
the 1769-1778. 10.1145/2783258.2788606 http://
dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2788606
Frenkel, S. (2018). Facebook Says It Deleted 865 Million
Posts, Mostly Spam. New York Times (Online) https://
search.proquest.com/docview/2038688931
Guan, S., & Zhu, F. (2005). An incremental approach to
genetic-algorithms-based classification. IEEE
Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Part B,
Cybernetics, 35(2), 227-239. 10.1109/
TSMCB.2004.842247
Imam, N., Issac, B., & Jacob, S. M. (2019). A Semi-
Supervised Learning Approach for Tackling Twitter
Spam Drift. International Journal of Computational
Intelligence and Applications, 18(2), 1950010.
10.1142/S146902681950010X
Kho, J. B., Lee, W., Choi, H., & Kim, J. (2019). An
incremental learning method for spoof fingerprint
detection. Expert Systems with Applications, 116, 52-64.
10.1016/j.eswa.2018.08.055
Kimbro, L., Bicking, I., & Wick, L. (2019). Using Pickle,
https://wiki.python.org/moin/UsingPickle
Li, M., Wang, Y., & Cai, L. (2010). Incremental feature
selection algorithm for data stream classification.
Journal of Computer Applications, 30(9), 2321-2323.
10.3724/SP.J.1087.2010.02321
Luo, Y., Yin, L., Bai, W., & Mao, K. (2020). An Appraisal
of Incremental Learning Methods. Entropy (Basel,
Switzerland), 22(11), 1190. 10.3390/e22111190
Mottl, D. (2019). GetOldTweets3. https://pypi.org/project/
GetOldTweets3/
Newberg, M. (2017). As Many as 48 Million Twitter
Accounts Aren't People, Says Study. https://
www.cnbc.com/2017/03/10/nearly-48-million-twitter-
accounts-could-be-bots-says-study.html
NLTK Team (2021). Natural Language Toolkit. https://
www.nltk.org/#natural-language-toolkit
Peris, Á, & Casacuberta, F. (2019). Online learning for
effort reduction in interactive neural machine
translation. Computer Speech & Language, 58, 98-126.
10.1016/j.csl.2019.04.001
Polikar, R., Upda, L., Upda, S. S., & Honavar, V. (2001).
Learn++: an incremental learning algorithm for
supervised neural networks. IEEE Transactions on
Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Part C, Applications
and Reviews, 31(4), 497-508. 10.1109/5326.983933
Ramos, J. (2003). Using TF-IDF to Determine Word
Relevance in Document Queries.
Roesslein, J. (2021). Tweepy. https://docs.tweepy.org/en/
latest/
Sanghani, G., & Kotecha, K. (2019). Incremental
personalized E-mail spam filter using novel TFDCR
feature selection with dynamic feature update. Expert
Systems with Applications, 115, 287-299. 10.1016/
j.eswa.2018.07.049
Sedhai, S., & Sun, A. (2017). Semi-Supervised Spam
Detection in Twitter Stream. IEEE Transactions on
Computational Social Systems, 5(1), 169-175. 10.1109/
TCSS.2017.2773581
Sheu, J., Chu, K., Li, N., & Lee, C. (2017). An efficient
incremental learning mechanism for tracking concept
drift in spam filtering. PloS One, 12(2), e0171518.
10.1371/journal.pone.0171518
Stewart, S. Selenium automates browsers. That's it! ,
https://www.selenium.dev/
UP2. (2015). Collecting Facebook Data with Netvizz. http://
www.up2.fr/index.php?n=Main.Netvizz
Wang, D., Irani, D., & Pu, C. (2011). A social-spam
detection framework. Paper presented at the 46-54.
10.1145/2030376.2030382 http://dl.acm.org/
citation.cfm?id=2030382
Whissell, J., & Clarke, C. (2011). Clustering for semi-
supervised spam filtering. Paper presented at the 125-
134. 10.1145/2030376.2030391 http://dl.acm.org/
citation.cfm?id=2030391
Xu, H., Sun, W., & Javaid, A. (2016). Efficient spam
detection across Online Social Networks. Paper
presented at the 2016 IEEE International Conference
on Big Data Analysis (ICBDA), 1-6. https://doi.org/
10.1109/ICBDA.2016.7509829 https://
ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7509829
Yang, L., Yang, S., Li, S., Liu, Z., & Jiao, L. (2017).
Incremental laplacian regularization extreme learning
machine for online learning. Applied Soft Computing,
59, 546-555. 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.05.051
SpamFender: A Semi-supervised Incremental Spam Classification System across Social Networks
395
