
Cognitive Planning in Motivational Interviewing
Emiliano Lorini
1
, Nicolas Sabouret
2
, Brian Ravenet
2
, Jorge Fernandez
1
and C
´
eline Clavel
2
1
IRIT-CNRS, Toulouse University, France
2
Universit
´
e Paris-Saclay, CNRS, Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire des Sciences du Num
´
erique, Orsay, France
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence, Automated Planning, Motivational Interviewing, Human-computer Interaction, Health
Coaching.
Abstract:
This paper presents a cognitive planning model that implements the principles of motivational interviewing, a
counseling method used to guide people in adopting behavior changes. This planning system is part of a wider
dialogical architecture of artificial counseling agent. We present the formal model and planning problem. We
show how it can be used to plan for dialogue in the architecture. We illustrate its functionalities on a simple
example.
1 INTRODUCTION
Motivational Interviewing. Motivational inter-
viewing (for short MI) is a counseling method used
in clinical psychology for eliciting behavior change
(Lundahl and Burke, 2009). One crucial aspect of
MI consists in exploring the participant’s subjectivity
through open questions to identify her desires and
personal values (e.g., conformity, independence,
carefulness, etc.) (Miller and Rollnick, 2012). This
exploration allows the participant to become aware
of the inconsistency between her desires or personal
values (e.g., being in good health), and her current
behavior (e.g., not doing enough physical activity).
However, MI does not necessarily try to induce
beliefs about positive aspects of the behavior change
(e.g., most people are already aware that reasonable
physical activity is good for health and would like
to practice a sport regularly). It rather helps the
participant to identify the reasons why she did not
convert her mere desires (e.g., I would like to practice
a sport) into intentions (e.g., I commit to do sport
regularly) and reassures her that these limitations can
be overcome. To this aim, the counselor rephrases the
ideas expressed by the participant so as to provoke
reflections about the connection between her beliefs,
desires and intentions.
Several automated MI systems have been pro-
posed in recent times (da Silva et al., 2018; Kanaoka
and Mutlu, 2015; Lisetti et al., 2013; Olafsson et al.,
2019; Schulman et al., 2011). However, all these sys-
tems use predefined dialogue trees to conduct the MI.
In this paper, we propose a model based on cognitive
planning for driving MI in a human-agent interaction
system.
Cognitive Planning. Classical planning in artificial
intelligence (AI) is the general problem of finding a
sequence of actions (or operations) aimed at achiev-
ing a certain goal (Ghallab et al., 2004). It has been
shown that classical planning can be expressed in
the propositional logic setting whereby the goal to
be achieved is represented by a propositional formula
(Bylander, 1994). In recent times, epistemic planning
was proposed as a generalization of classical planning
in which the goal to be achieved can be epistemic,
i.e., the goal of inducing a certain agent to believe or
to know something (Bolander and Andersen, 2011;
L
¨
owe et al., 2011). The standard languages for epis-
temic planning are epistemic logic (EL) (Halpern and
Moses, 1992) and its dynamic extension, the so-called
dynamic epistemic logic (DEL) (van Ditmarsch et al.,
2007). A variety of epistemic logic languages and
fragments of DEL with different levels of expressivity
and complexity have been introduced to formally rep-
resent the epistemic planning problem and efficiently
automate it (see, e.g., (Muise et al., 2015; Muise
et al., 2021; Kominis and Geffner, 2015; Cooper et al.,
2016; Cooper et al., 2021)).
In a recent paper (Fernandez et al., 2021), cogni-
tive planning was introduced as a further generaliza-
tion of epistemic planning. In cognitive planning, it
is not only some knowledge or belief state of a target
agent that is to be achieved, but more generally a cog-
508
Lorini, E., Sabouret, N., Ravenet, B., Fernandez, J. and Clavel, C.
Cognitive Planning in Motivational Interviewing.
DOI: 10.5220/0010895400003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 2, pages 508-517
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
nitive state. The latter could involve not only knowl-
edge and beliefs, but also desires, intentions and,
more generally, motivations. The cognitive planning
(CP) approach is well-suited for modeling interaction
whereby an agent tries to trigger attitude change in
another agent through the execution of a sequence
of speech acts. CP takes into consideration resource
boundedness and limited rationality of the interlocu-
tor agent. This makes CP a very well-suited model for
implementing motivational interviewing in human-
machine interaction (HMI) applications in which an
artificial agent is expected to interact with a human
— who is by definition resource-bounded — through
dialogue and to induce her to behave in a certain way.
Motivational interviewing is composed of several
stages: prior to having the participant change her in-
tentions, one has to make her aware of the inconsis-
tencies between her desires and her actual behavior.
The artificial agent has both (i) a model of the hu-
man’s overall cognitive state, including her beliefs
and intentions, and (ii) a goal towards the human’s
mental attitudes, e.g., the goal of making the human
aware of the inconsistency between her desires and
her actual behavior. Given (i) and (ii), it tries to
find a sequence of speech acts aimed at modifying
the human’s cognitive state thereby guaranteeing the
achievement of its goal.
Outline. The aim of this paper is to explain how
to situate the cognitive planning module in a gen-
eral architecture of an artificial agent which is ex-
pected to interact with a human user through dialogue
and to motivate her to behave in a certain way or to
change/adopt a certain style of life through motiva-
tional interviewing methods. In Section 2, we provide
a birds-eye view of the architecture. In Section 3, we
present the formal framework on which the cognitive
planning approach is built. In Section 4, a variety of
cognitive planning problems are formalized. Section
5 is devoted to describe the belief revision module of
the architecture. Finally, in Section 6, the cognitive
planning problem is instantiated in a concrete exam-
ple of motivational interviewing between an artificial
agent and a human.
2 GENERAL ARCHITECTURE
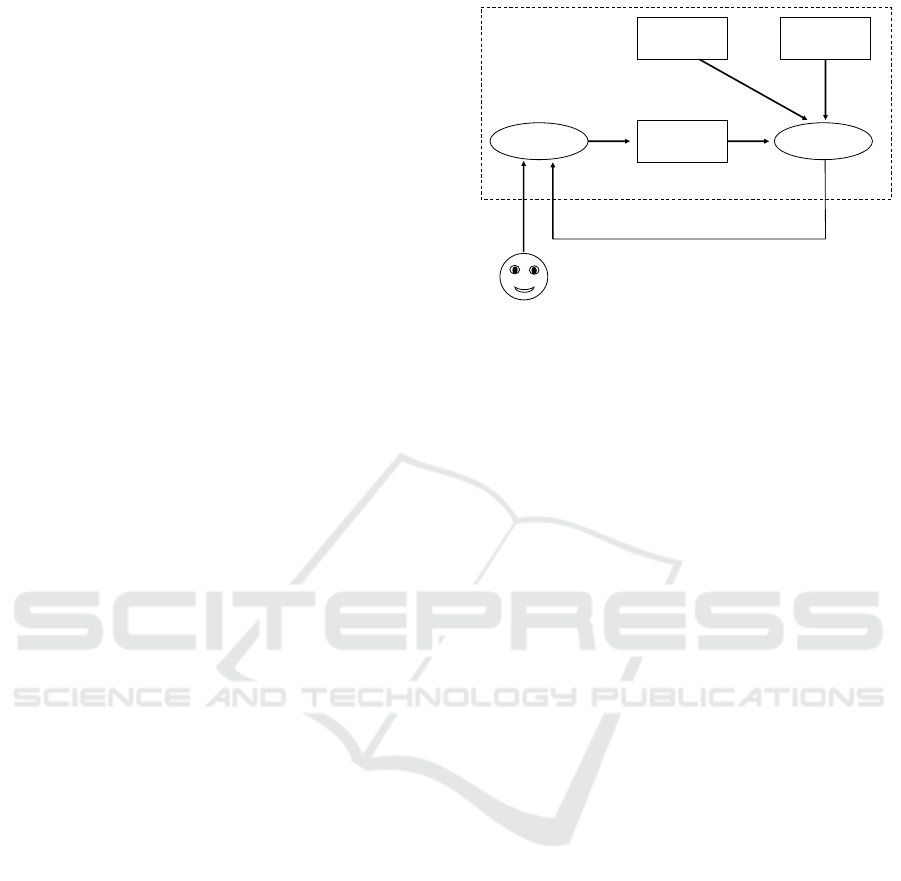
The general architecture of the system is detailed in
Figure 1.
Data Structures. The artificial planning agent, that
for simplicity we call the machine, is endowed with
three kinds of data structure: its belief base, the goal
Belief base
Belief base
revision
Planning
Goal
Speech act
repertoire
Act
Act
Machine
Human
Figure 1: General architecture.
to be achieved and the repertoire of speech acts (or
communicative actions) it can perform. We assume
the machine’s action repertoire includes two types of
speech act: assertions and questions. The machine
can have persuading goals, aimed at changing the hu-
man’s beliefs, or influencing goals, aimed at inducing
the human to form a certain intention or to behave
in a certain way. The machine’s belief base includes
both information about the environment and informa-
tion about the human’s overall cognitive state and its
way of functioning. In other words, the machine has
a theory of the human’s mind. The machine’s belief
base evolves during its dialogue with the human.
Interrogative and Informative Phase. The inter-
action between the machine and the human is struc-
tured in two phases the interrogative (or exploratory)
phase and the informative phase. In the interroga-
tive phase the machine gathers information about the
human’s cognitive state. This includes information
about the human’s beliefs, desires and preferences.
The interrogative phase is identified with a sequence
of questions by the machine to the human. The in-
formative phase is the core of the influence process.
In this phase, the machine performs a sequence of
assertions aimed at modifying the human’s cognitive
state (her beliefs and/or intentions). The interrogative
phase is propaedeutic to the informative phase. In-
deed, for the machine to be able to lead the human to
change her behavior, it must have information about
the human’s cognitive state. Such an information is
acquired during the interrogative phase. In this work,
we assume that the two phases are unified at the plan-
ning level: the machine includes in its plan not only
the assertions but also also the questions. In particu-
lar, the machine has to find a sequence of questions
followed by a sequence of assertions such that, for
some possible answer by the human, the composition
of the two sequences guarantees that the persuading
Cognitive Planning in Motivational Interviewing
509

or influencing goal will be achieved. It is reasonable
to assume that the machine first tries to find a plan
with only assertions. (why asking questions to the
human if what the machine knows about the human’s
cognitive state is already sufficient to persuade or in-
fluence her). However, in most cases, the machine
has uncertainty and lacks information about the hu-
man’s cognitive state so that it must ask questions to
the human before trying to induce her attitude change.
In Section 6, we will show how some aspects of the
motivational interviewing (MI) methodology can be
naturally captured in the two phases of the cognitive
planning approach.
Execution of the Plan. After having selected a
plan, the machine executes it. The machine can ei-
ther execute the entire plan or execute it one piece
after the other by waiting the reply of the human be-
fore executing the next piece. We assume that how
the plan is executed depends on the application un-
der consideration and on the type of speech act in the
plan to be executed. It is reasonable to suppose that
when executing the interrogative part of the plan, the
machine asks a single question at each step and waits
the answer by the human before moving to the next
question. After each question by the machine, the
human gives an answer and the machine expands or
revises, when necessary, its belief base accordingly.
Indeed, the information provided by the human in re-
sponse to the machine’s question can enrich the ma-
chine’s belief base with new facts about the environ-
ment (objective facts) or about the human’s cognitive
state (mental facts) or make the machine’s belief base
inconsistent. In the latter case, the machine must re-
vise its belief base after having incorporated the new
information.
3 FORMAL FRAMEWORK
In this section, we present the epistemic language on
which the cognitive planning approach is based. The
language is a two-agent fragment of the multi-agent
epistemic language presented in (Lorini, 2020). The
language distinguishes explicit from implicit belief:
an agent’s belief of explicit type is a piece of infor-
mation contained in the agent’s belief base, while a
belief of implicit type corresponds to a piece of infor-
mation that is derivable from the agent’s belief base.
Assume a countably infinite set of atomic proposi-
tions Atm and a finite set of agents Agt = {h, m}, with
h denoting the human and m the machine. The lan-
guage is defined in two steps. First, the language L
0
is defined by the following grammar in BNF:
α ::= p | ¬α | α
1
∧ α
2
| 4
i
α,
where p ranges over Atm and i ranges over Agt. L
0
is
the language for representing agents’ explicit beliefs.
The formula 4
i
α is read “agent i explicitly believes
that α”. Then, the language L extends the language
L
0
by a modal operator of implicit belief and a dy-
namic operator for belief expansion for the machine.
It is defined by the following grammar:
ϕ ::= α | ¬ϕ | ϕ
1
∧ ϕ
2
|
m
α | [+
m
α]ϕ,
where α ranges over L
0
. The formula
m
α is read
“agent m implicitly believes that α”. The formula
[+
m
α]ϕ is read “ϕ holds after agent m has privately
expanded its belief base with α”. The other Boolean
constructions >, ⊥, →, ∨ and ↔ are defined in the
standard way.
In L, both agent h and agent m have explicit be-
liefs but only agent m has implicit beliefs, and more-
over the latter are restricted to L
0
formulas of type
α. So there are no nested implicit beliefs for agent m.
Agent m is assumed to be the unique artificial agent in
the system which is endowed with unbounded reason-
ing and planning capabilities. The cognitive planning
problem will be modeled from agent m’s perspective.
The interpretation of language L exploits the no-
tion of belief base. While the notions of possible
state (or world) and epistemic alternative are primi-
tive in the standard semantics for epistemic logic (Fa-
gin et al., 1995), they are defined from the primitive
concept of belief base in our semantics. In particular,
a state is a composite object including a description
of both the agents’ belief bases and the environment.
1
Definition 1 (State). A state is a tuple B =
(B
h
, B
m
, V) where: for every i ∈ Agt, B
i
⊆ L
0
is agent
i’s belief base; V ⊆ Atm is the actual environment.
The set of all states is noted S.
Note that an agent’s belief base B
i
can be infi-
nite. The sublanguage L
0
(Atm, Agt) is interpreted
w.r.t. states, as follows:
Definition 2 (Satisfaction). Let B = (B
h
, B
m
, V) ∈ S.
Then:
B |= p ⇐⇒ p ∈ V,
B |= ¬α ⇐⇒ B 6|= α,
B |= α
1
∧ α
2
⇐⇒ B |= α
1
and B |= α
2
,
B |= 4
i
α ⇐⇒ α ∈ B
i
.
Observe in particular the set-theoretic interpreta-
tion of the explicit belief operator: agent i explicitly
believes that α if and only if α is included in its belief
base.
1
This is similar to the way states are modeled in the
interpreted system semantics for multi-agent systems (Lo-
muscio et al., 2017).
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
510

A model is defined to be a state supplemented with
a set of states, called context. The latter includes all
states that are compatible with the common ground
(Stalnaker, 2002), i.e., the body of information that
the agents commonly believe to be the case.
Definition 3 (Model). A model is a pair (B, Cxt),
where B ∈ S and Cxt ⊆ S. The class of all models
is noted M.
Note that we do not impose that B ∈ Cxt. When
Cxt = S then (B, Cxt) is said to be complete, since S
is conceivable as the complete (or universal) context
which contains all possible states. We compute agent
m’s set of epistemic alternatives from the agent m’s
belief base, as follows.
Definition 4 (Epistemic Alternatives). R
m
is the bi-
nary relation on the set S such that, for all B =
(B
h
, B
m
, V), B
0
= (B
0
h
, B
0
m
, V
0
) ∈ S:
BR
m
B
0
if and only if ∀α ∈ B
m
: B
0
|= α.
BR
m
B
0
means that B
0
is an epistemic alternative
for agent m at B. So m’s set of epistemic alternatives
at B includes exactly those states that satisfy all m’s
explicit beliefs.
Definition 5 extends Definition 2 to the full lan-
guage L. Its formulas are interpreted with respect to
models as follows. (We omit Boolean cases that are
defined in the usual way.)
Definition 5 (Satisfaction). Let B = (B
h
, B
m
, V) ∈ S
and (B, Cxt) ∈ M. Then:
(B, Cxt) |= α ⇐⇒ B |= α,
(B, Cxt) |=
m
ϕ ⇐⇒ ∀B
0
∈ Cxt, if BR
m
B
0
then (B
0
, Cxt) |= ϕ,
(B, Cxt) |= [+
m
α]ϕ ⇐⇒ (B
+
m
α
, Cxt) |= ϕ,
with B
+
m
α
= (B
+
m
α
h
, B
+
m
α
m
, V
+
m
α
), V
+
m
α
= V,
B
+
m
α
m
= B
m
∪ {α} and B
+
m
α
h
= B
h
.
According to the previous definition, agent m im-
plicitly believes that ϕ if and only if, ϕ is true at all
states in the context that m considers possible. More-
over, the private expansion of m’s belief base by α
simply consists in agent m adding the information α
to its belief base, while agent h keeps her belief base
unchanged.
A formula ϕ ∈ L is said to be valid in the class
M, noted |=
M
ϕ, if and only if (B, Cxt) |= ϕ for ev-
ery (B, Cxt) ∈ M; it is said to be satisfiable in M if
and only if ¬ϕ is not valid in M. Finally, given a fi-
nite Σ ⊂ L
0
, we say that ϕ is a logical consequence
of Σ in the class M, noted Σ |=
M
ϕ, if and only if,
for every (B, Cxt) ∈ M such that Cxt ⊆ S(Σ) we have
(B, Cxt) |= ϕ, with S(Σ) = {B ∈ S : ∀α ∈ Σ, B |= α}.
In (Fernandez et al., 2021), it is proved that the satisfi-
ability checking problem and the logical consequence
problem so defined are, respectively, NP-complete
and co-NP-complete.
4 PLANNING PROBLEMS
The cognitive planning problem is specified in the
context of the language L. It consists in finding a se-
quence of questions or informative actions for agent
m which guarantees that it believes that its goal α
G
is satisfied. As we emphasized above, agent m is as-
sumed to be an artificial agent which interacts with
the resource-bounded human agent h.
Informative Actions. Let Act
m
= {+
m
α : α ∈ L
0
}
be agent m’s set of belief expansion operations (or in-
formative actions) and let elements of Act
m
be noted
ε, ε
0
, . . . Speech acts of type ‘assertion’ are formalized
as follows:
assert(m,h,α)
def
= +
m
4
h
4
m
α.
The event assert(m,h,α) captures the speech act
“agent m asserts to agent h that α”. The latter is
assumed to coincide with the perlocutionary effect
(Searle, 1969, Sect. 6.2) of the speaker learning that
the hearer has learnt that the speaker believes that α.
2
We distinguish simple assertions from convincing ac-
tions:
convince(m,h,α)
def
= +
m
4
h
α.
The event convince(m,h,α) captures the action
“agent m convinces agent h that α”. We have
assert(m,h,α) = convince(m,h,4
m
α). We assume
‘to assert’ and ‘to convince’ correspond to differ-
ent utterances. While ‘to assert’ corresponds to the
speaker’s utterances of the form “I think that α is
true!” and “In my opinion, α is true!”, ‘to convince’
corresponds to the speaker’s utterances of the form “α
is true!” and “it is the case that α!”.
The previous abbreviations and, more generally,
the idea of describing speech acts of a communica-
tive plan performed by agent m with m’s private be-
lief expansion operations is justified by the fact that
we model cognitive planning from the perspective of
the planning agent m. Therefore, we only need to rep-
resent the effects of actions on agent m’s beliefs.
2
We implicitly assume that, by default, m believes that
h trusts its sincerity, so that h will believe that m believes
what it says.
Cognitive Planning in Motivational Interviewing
511

Questions. We consider binary questions by the
machine m to the human h of the form ?
m,h
α.
3
The
set of binary questions is noted Que
m
. Intuitively,
?
m,h
α is the utterance performed by agent m to agent
h of the form “Do you think that α is true?”. Let el-
ements of Que
m
be noted λ, λ
0
, . . . Each question is
associated with its set of possible answers. The an-
swer function A : Que
m
−→ 2
Act
m
is used to map each
binary question to its set of possible answers and is
defined as follows:
A
?
m,h
α
=
+
m
4
h
α, +
m
¬4
h
α
.
Answers to binary questions are noted ρ, ρ
0
, . . . The
operation +
m
4
h
α captures agent h’s positive answer
to agent m’s binary question ?
m,h
α (“I think that α is
true!”), while +
m
¬4
h
α captures agent h’s negative
answer (“I don’t think that α is true!”). Note that if
agent h answers negatively to the consecutive ques-
tions ?
m,h
α and ?
m,h
¬α, then she expresses her un-
certainty about the truth value of α .
We assume that the positive answer is the default
answer to a question. Indeed, when agent m asks
question ?
m,h
α, it wants to verify whether agent h en-
dorses the belief that α and presupposes that agent h
will answer positively to the question. In this perspec-
tive, the speaker expects a confirmation by the inter-
locutor. Thus, for notational convenience, we write
da(?
m,h
α) to denote the default answer +
m
4
h
α to
the question ?
m,h
α.
The following abbreviation defines a dynamic op-
erator capturing the necessary effects of agent m’s
question:
[λ]ϕ
def
=
^
ρ∈A(λ)
[ρ]ϕ,
with λ ∈ Que
m
. Note that, unlike the basic belief
expansion operator [+
m
α], the operator [λ] is non-
deterministic, as it represents the consequences of all
possible answers to question λ. In fact, while the for-
mula [+
m
α]¬ϕ ∨ [+
m
α]ϕ is valid in the class M, the
formula [λ]¬ϕ ∨ [λ]ϕ is not.
Executability Preconditions. The set of events in-
cludes both informative actions and questions, and is
defined as follows: Evt
m
= Act
m
∪ Que
m
. Elements
of Evt
m
are noted γ, γ
0
, . . . They have executability
preconditions that are specified by the following func-
tion: P : Evt
m
−→ L. We assume that an event γ can
take place if its executability precondition P (γ) holds.
We use the executability precondition function P
to define the following operator of possible occur-
3
In speech act theory, binary (yes-no) questions are usu-
ally distinguished from open questions.
rence of an event:
hhγiiϕ
def
= P (γ) ∧ [γ]ϕ,
with γ ∈ Evt. The abbreviation hhγiiϕ has to be read
“the event γ can take place and ϕ necessarily holds
after its occurrence”.
Informative and Interrogative Planning Problems.
We conclude this section with a formal specification
of two planning problems, informative planning and
interrogative planning.
Definition 6 (Informative Planning Problem). An in-
formative planning problem is a tuple hΣ, Op
inf
, α
G
i
where:
• Σ ⊂ L
0
is a finite set of agent m’s available infor-
mation,
• Op
inf
⊂ Act
m
is a finite set of agent m’s informa-
tive actions,
• α
G
∈ L
0
is agent m’s goal.
Informally speaking, an informative planning
problem is the problem of finding an executable se-
quence of informative actions which guarantees that,
at the end of the sequence, the planning agent m be-
lieves that its goal α
G
is achieved. Typically, α
G
is
a persuading or influencing goal, i.e., the goal of af-
fecting agent’s h cognitive state (including her beliefs
and intentions) in a certain way. A solution plan to
an informative planning problem hΣ, Op
inf
, α
G
i is a
sequence of informative actions ε
1
, . . . , ε
k
from Op
inf
for some k such that Σ |=
M
hhε
1
ii. . . hhε
k
ii
m
α
G
.
In an interrogative planning problem, the machine
can perform both informative actions and questions.
This problem is specified in the following definition.
Definition 7 (Interrogative Planning Problem).
An interrogative planning problem is a tuple
hΣ, Op
inf
, Op
quest
, α
G
i where:
• Σ ⊂ L
0
is a finite set of agent m’s available infor-
mation,
• Op
inf
⊂ Act
m
is a finite set of agent m’s informa-
tive actions,
• Op
quest
⊂ Que
m
is a finite set of agent m’s ques-
tions,
• α
G
∈ L
0
is agent m’s goal.
Intuitively, an interrogative planning problem is
the problem of finding a sequence of questions as a
means of understanding the interlocutor’s cognitive
state and, consequently, of being able to identify the
inconsistencies that she must be made aware of, via a
sequence of informative actions. In other words, the
sequence of questions serves the purpose of “explor-
ing” the interlocutor’s cognitive state and of building
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
512

a representation of it in order to being able to find a
plan to reach the motivational interviewing (MI) goal.
A strong solution plan to an interrogative planning
problem hΣ, Op
inf
, Op
quest
, α
G
i is a sequence of ques-
tions λ
1
, . . . , λ
m
from Op
quest
such that
Σ |=
M
hhλ
1
ii. . . hhλ
m
ii>,
and ∀ρ
1
∈ A(λ
1
), . . . , ∀ρ
m
∈ A(λ
m
), ∃τ
1
, . . . , τ
k
∈
Op
inf
such that
Σ |=
M
[ρ
1
]. . . [ρ
m
]hhτ
1
ii. . . hhτ
k
ii
m
α
G
.
A weak solution plan to an interrogative planning
problem hΣ, Op
inf
, Op
quest
, α
G
i is a sequence of ques-
tions λ
1
, . . . , λ
m
from Op
quest
such that
Σ |=
M
hhλ
1
ii. . . hhλ
m
ii>,
and ∃τ
1
, . . . , τ
k
∈ Op
inf
such that
Σ |=
M
[da(λ
1
)]. . . [da(λ
m
)]hhτ
1
ii. . . hhτ
k
ii
m
α
G
.
It is easy to verify that checking existence of a weak
solution for an interrogative planning problem (EWS-
INT problem) is reducible to checking existence of
a solution for an informative planning problem (ES-
INF problem). In (Fernandez et al., 2021) it was
proved that the ES-INF problem is in NP
NP
= Σ
P
2
.
Thus, we get the following complexity upper bound
for the EWS-INT problem.
Theorem 1. The EWS-INT problem is in NP
NP
= Σ
P
2
.
Checking existence of a strong solution for an in-
terrogative planning problem (ESS-INT problem) is
not comparable to the ES-INF problem or the EWS-
INT problem. Indeed, it requires to take all possible
answers to the questions and their possible ramifica-
tions into account. The EWS-INT problem considers
a single sequence of answers (the sequence of default
answers) instead.
5 BELIEF REVISION MODULE
In this section, we describe the belief revision module
of the architecture we sketched in Section 2. As we
emphasized above, such a module is necessary for up-
dating the machine’s belief base after the human has
replied to its questions.
Let L
PROP
be the propositional language built
from the following set of atomic formulas:
Atm
+
= Atm ∪ {p
4
i
α
: 4
i
α ∈ L
0
}.
Moreover, let tr
PROP
be the following translation
from the language L
0
defined in Section 3 to L
PROP
:
tr
PROP
(p) =p,
tr
PROP
(¬α) =¬tr
PROP
(α),
tr
PROP
(α
1
∧ α
2
) =tr
PROP
(α
1
) ∧ tr
PROP
(α
2
),
tr
PROP
(4
i
α) =p
4
i
α
.
For each finite X ⊆ L
0
, we define tr
PROP
(X) =
{tr
PROP
(α) : α ∈ X}. Moreover, we say that X
is propositionally consistent if and only if ⊥ 6∈
Cn
tr
PROP
(X)
, where Cn is the classical deduc-
tive closure operator over the propositional language
L
PROP
. Clearly, the latter is equivalent to saying that
V
α∈X
tr
PROP
(α) is satisfiable in propositional logic.
Let Σ
core
, Σ
mut
⊆ L
0
denote, respectively, the core
(or, immutable) information in agent m’s belief base
and the volatile (or, mutable) information in agent m’s
belief base. Agent m’s core beliefs are stable and do
not change under belief revision. On the contrary,
volatile beliefs can change due to a belief revision op-
eration . Moreover, let Σ
input
⊆ L
0
be agent m’s in-
put information set. We define Σ
base
= Σ
core
∪ Σ
mut
.
The revision of (Σ
core
, Σ
mut
) by input Σ
input
, noted
Rev(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
), is formally defined as follows:
1. if Σ
core
∪ Σ
input
is not propositionally consistent
then Rev(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
) = (Σ
core
, Σ
mut
),
2. otherwise, Rev(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
) = (Σ
0
core
, Σ
0
mut
),
with Σ
0
core
= Σ
core
and
Σ
0
mut
=
\
X∈MCS(Σ
core
,Σ
mut
,Σ
input
)
X,
where X ∈ MCS(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
) if and only if:
• X ⊆ Σ
mut
∪ Σ
input
,
• Σ
input
⊆ X ,
• X ∪ Σ
core
is propositionally consistent, and
• there is no X
0
⊆ Σ
mut
∪Σ
input
such that X ⊂ X
0
and
X
0
∪ Σ
core
is propositionally consistent.
The revision function Rev has the following effects on
agent m’s beliefs: (i) the core belief base is not modi-
fied, while (ii) the input Σ
input
is added to the mutable
belief base only if it is consistent with the core beliefs.
If the latter is the case, then the updated mutable be-
lief base is equal to the intersection of the subsets of
the mutable belief base which are maximally consis-
tent with respect to the core belief base and which
include the input Σ
input
.
4
This guarantees that belief
4
Note that the revision function Rev does not expand
agent m’s core belief set Σ
core
with the input information
set Σ
input
. It would be interesting to introduce a function
f
appr
: L
0
−→ {0, 1} which specifies for every formula α in
L
0
whether the information α is completely apprehensible
by agent m (i.e., f
appr
(α) = 1) or not (i.e., f
appr
(α) = 0).
Specifically, f
appr
(α) = 1 means that if agent m learns that
α is true then, as a consequence, it will firmly believe that
α is true thereby adding α not only to its set of muta-
ble beliefs but also to its set of core beliefs. The func-
tion f
appr
would allow us to define a variant of belief re-
vision according to which if Σ
core
∪ Σ
input
is proposition-
ally consistent, then the core belief set Σ
core
is expanded
by all formulas α in Σ
input
such that f
appr
(α) = 1, that is,
Σ
0
core
= Σ
core
∪ {α ∈ Σ
input
: f
appr
(α) = 1}.
Cognitive Planning in Motivational Interviewing
513

revision satisfies minimal change. The function Rev
is a screened revision operator as defined in (Makin-
son, 1997). The latter was recently generalized to the
multi-agent case (Lorini and Schwarzentruber, 2021).
Let Rev(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
) = (Σ
0
core
, Σ
0
mut
).
For notational convenience, we write
Rev
core
(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
) to denote Σ
0
core
and
Rev
mut
(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
) to denote Σ
0
mut
. Note
that, if Σ
base
is propositionally consistent, then
Rev
core
(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
) ∪ Rev
mut
(Σ
core
, Σ
mut
, Σ
input
)
is propositionally consistent too.
6 EXAMPLE
In this section, we illustrate the use of the cogni-
tive planning and belief revision module of the archi-
tecture with the aid of a human-machine interaction
(HMI) scenario. We assume m is a virtual coach-
ing agent which has to motivate the human agent h
to practice a physical activity. We suppose agent m
complies with the general principles of the theory of
motivational interviewing (MI) to find a persuasive
strategy aimed at changing the human’s attitude.
One of the central cornerstones of MI is the postu-
late that for eliciting behavior change in a person, she
has to become aware of the inconsistency between her
current behavior and her desires. In other words, she
has to recognize the fact that her current behavior will
prevent her from obtaining what she likes.
Let us assume the disjoint sets CondAtm, DesAtm
and ActAtm are subsets of the set of atomic proposi-
tions Atm. Elements of CondAtm are atoms specify-
ing conditions, while elements of DesAtm are atoms
specifying desirable properties, that is, properties that
agent h may wish to achieve (i.e., agent h’s possi-
ble desiderata). Finally, atoms in ActAtm are used to
describe agent h’s behavior. Specifically, we define
ActAtm = {does(h,a) : a ∈ Act}, where Act is a finite
a set of action names. The atom does(h,a) has to be
read “agent h behaves in conformity with the require-
ment a” or, simply, “agent h does action a”.
The sets of literals from CondAtm, DesAtm and
ActAtm are defined in the usual way as follows:
DesLit = DesAtm ∪ {¬p : p ∈ DesAtm},
CondLit = CondAtm ∪ {¬p : p ∈ CondAtm},
ActLit = ActAtm ∪ {¬p : p ∈ ActAtm},
Lit = DesLit ∪ CondLit ∪ ActLit.
We define LitSet = 2
Lit
and LitSet
0
= LitSet \ {
/
0}.
We moreover assume that the set of atomic propo-
sitions Atm includes one atom des(h, l) for each l ∈
DesLit standing for “agent h desires l to be true”.
For the sake of illustration, we suppose that Act =
{ps} where ps is the action (or requirement) “to prac-
tice regularly a sport or physical activity”. There-
fore, ActAtm = {does(h,ps)}. Moreover, DesAtm =
{dr, pw, lw, at, gh, st} and CondAtm = {ow, sl, co},
with the atoms having the following intuitive mean-
ing: dr: “agent h has dietary restrictions”; pw: “agent
h puts on weight”; lw: “agent h loses weight”; at:
“agent h is attractive”; gh: “agent h is in good health”;
st: “agent h is stressed”; ow: “agent h has an office
work”; sl: “agent h has a sedentary life style”; co:
“agent h is a commuter and spends quite some time in
the traffic everyday”.
The following abbreviation captures a simple no-
tion of necessity for X ∈ LitSet and l ∈ Lit:
nec(X, l)
def
=
^
l
0
∈X
l
0
→ l.
nec(X, l) has to be read “the facts in X will not be true
unless l is true” or more shortly “l is necessary for X”.
Agent m’s initial knowledge about agent h’s cog-
nitive state is specified by the following six abbrevia-
tions:
α
1
def
=
^
l∈Lit
4
h
nec({l}, l),
α
2
def
=
^
l∈Lit
4
h
nec(
/
0, l) ↔ 4
h
l
,
α
3
def
=
^
l∈Lit,X ,X
0
∈LitSet:X
0
⊆X
4
h
nec(X, l) →
^
l
0
∈X
0
4
h
l
0
→ 4
h
nec(X \X
0
, l)
,
α
4
def
=
^
l∈Lit,X ,X
0
∈LitSet:X⊆X
0
4
h
nec(X, l) →
4
h
nec(X
0
, l)
,
α
5
def
=
^
l∈Lit
des(h, l) ↔ 4
h
des(h, l)
∧
¬des(h, l) ↔ 4
h
¬des(h, l)
,
α
6
def
=
^
a∈Act
does(h, a) ↔ 4
h
does(h, a)
∧
¬does(h, a) ↔ 4
h
¬does(h, a)
,
Hypotheses α
1
-α
4
are general properties about agent
h’s conception of necessity. According to α
1
, agent
h believes that every fact is necessary for itself while,
according to α
2
, agent h believes a fact is true regard-
less of the circumstances if and only if she believes
that it is true. According to α
3
, if agent h believes
that l is necessary for the facts in X being true and
believes every fact in X
0
⊆ X, then she believes that l
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
514

is necessary for the facts in the remaining set X \ X
0
being true. According to α
4
, if X ⊆ X
0
and agent h be-
lieves that l is necessary for X then she believes that
l is necessary for X
0
as well. Hypotheses α
5
and α
6
capture agent h’s introspection over her desires (hy-
phothesis α
5
) and agent h’s perfect knowledge about
her actions and inactions (hyphothesis α
6
).
We moreover suppose that agent m has the follow-
ing information in its belief base capturing the neces-
sity relations between conditions, desirable properties
and actions:
α
7
def
= nec
{¬dr, ¬pw, sl}, does(h,ps)
∧
nec
{at, ¬dr}, does(h,ps)
∧
nec
{sl, gh}, does(h,ps)
∧
nec
{gh}, ¬st
∧
nec
{co, ow}, sl
.
For example, nec
{¬dr, ¬pw, sl}, does(h,ps)
means that practicing regularly a sport is necessary
for not having dietary restrictions and not putting
weight, while having a sedentary work style (i.e., a
person cannot pretend to not put weight and not have
dietary restrictions without practicing a sport, if she
has a sedentary work style).
The following abbreviation defines the concept of
agent h’s awareness of the inconsistency between the
actual state of affairs α and her desires:
AwareIncon(h, α)
def
=
_
X∈LitSet
^
l
0
∈X
des(h, l
0
)∧
4
h
nec(X, ¬α)∧ 4
h
α
.
According to the previous definition, agent h is aware
of the inconsistency between the actual state of affairs
α and her desires, noted AwareIncon(h, α), if she be-
lieves that the satisfaction of her desires is jeopardized
by the fact that α is true. More precisely, (i) agent h
believes that she will not achieve her desires unless α
is false and (ii) she believes that α is actually true.
We suppose that the pieces of information
α
1
, . . . , α
7
constitute agent m’s initial core belief base,
that is, Σ
core
= {α
1
, . . . , α
7
}. Moreover, we suppose
that agent m’s initial mutable belief base is empty,
that is, Σ
mut
=
/
0. We consider the planning problem
in which agent m tries to motivate agent h to practice
regularly a sport. To this aim, agent m tries to achieve
the following goal:
α
G
def
= ¬does(h,ps) → AwareIncon
h, ¬does(h,ps)
.
In other words, agent m tries to make it the case that
if agent h does not practice a sport, then she becomes
aware of the inconsistency between her actual desires
and the fact that she does not practice a sport.
Let X ⊆ DesLit, X
0
⊆ CondLit and
l ∈ ActLit ∪ CondLit. We assume agent m’s
action convince
m,h,nec(X ∪ X
0
, l)
to be con-
cretely realized through the utterance “since
condition X
0
holds, you will not satisfy your
desires X unless l is true!”. For example,
convince
m,h,nec(X ∪ X
0
, does(h,ps))
corresponds
to the utterance “since condition X
0
holds, you will
not satisfy your desires X unless you do action
ps!”, while convince
m,h,nec(X ∪ X
0
, ¬does(h,ps))
corresponds to the utterance “since condition X
0
holds, you will not satisfy your desires X unless you
refrain from doing action ps!”. For notational conve-
nience, we abbreviate convince
m,h,nec(X ∪ X
0
, l)
by !
m,h
(X,X
0
,l). We assume the following repertoires
of informative and interrogative actions for agent m:
Op
inf
=
!
m,h
(X,X
0
,l) : X ⊆ DesLit, X
0
⊆ CondLit
and l ∈ ActLit ∪ CondLit
,
Op
quest
=
?
m,h
des(h, l) : l ∈ DesLit
∪
?
m,h
l : l ∈ ActLit ∪ CondLit
,
with the following executability preconditions for
their elements:
P
!
m,h
(X,X
0
,l)
=
m
nec(X ∪X
0
, l)∧
^
l
0
∈X
des(h, l
0
) ∧
^
l
00
∈X
0
4
h
l
00
),
P
?
m,h
des(h, l)
=P
?
m,h
l
= >.
In other words, a question is always executable.
Moreover, agent m can perform the action
!
m,h
(X,X
0
,l) — i.e., “since condition X
0
holds,
you will not satisfy your desires X unless l is true!”
— only if (i) it believes that agent h desires every
fact in X to be true, (ii) it believes that agent h
believes every fact in X
0
, and (iii) it believes that l is
necessary for X when X
0
holds. Thus, by performing
the speech act !
m,h
(X,X
0
,l), agent m informs agent h
that, in view of the fact that condition X
0
holds, l is
necessary for the satisfaction of her desires X, since
it presupposes that agent h has indeed such desires
and believes that the condition holds.
We suppose that at every step k of the interac-
tion with agent h, agent m tries to find a solution for
the informative planning problem hΣ
k
base
, Op
k
inf
, α
G
i.
If it can find it, it proceeds with its execution and
then interaction stops. Otherwise, it tries to find a
weak solution for the interrogative planning problem
hΣ
k
base
, Op
k
inf
, Op
k
quest
, α
G
i. If it cannot find it, the
interaction stops. Otherwise, it executes the corre-
sponding sequence of questions and revises its be-
lief base according to agent h’s set of responses
Resp
k
h
. Then, it moves to step k + 1. We suppose
Cognitive Planning in Motivational Interviewing
515

that Σ
0
core
= Σ
core
, Σ
0
mut
= Σ
mut
, Op
0
inf
= Op
inf
and
Op
0
quest
= Op
quest
. Moreover,
Σ
k+1
core
=Rev
core
(Σ
k
core
, Σ
k
mut
, Resp
k
h
),
Σ
k+1
mut
=Rev
mut
(Σ
k
core
, Σ
k
mut
, Resp
k
h
),
Op
k+1
inf
=Op
k
inf
,
Op
k+1
quest
=Op
k
quest
\ Selected(Op
k
quest
),
where Selected(Op
k
quest
) is the set of questions in-
cluded in the interrogative plan selected at step k. We
remove them because we want to avoid that agent m
keeps asking the same question indefinitely.
Let us illustrate an example of interaction. At step
0, agent m cannot find a solution for the informative
planning problem. Thus, it decides to go with ques-
tions. It finds ?
m,h
does(h,ps) as solution for the in-
terrogative planning problem. We suppose agent h’s
response to agent m’s question is +
m
¬4
h
does(h,ps).
At step 1, again agent m cannot find a solution for the
informative planning problem. Thus, it moves to the
interrogative planning problem and finds the follow-
ing sequence of questions as a weak solution:
?
m,h
des(h, gh), ?
m,h
co, ?
m,h
ow.
Agent m executes the interrogative plan. We suppose
agent h’s set of responses to agent m’s questions at
step 1 is
+
m
4
h
des(h, gh), +
m
4
h
co, +
m
4
h
ow
.
Thus, at step 2, agent m can find a solution for
the informative planning problem. The solution is the
following sequence of assertive speech acts of length
2:
!
m,h
(
/
0,{co, ow},sl), !
m,h
{gh},{sl},does(h,ps)
.
Agent m executes the informative plan. The previous
interaction between agent m and agent h is illustrated
in Figure 2 in which every speech act is associated
with its corresponding utterance.
7 CONCLUSION
Let’s take stock. We have presented a model of cog-
nitive planning and shown that it can elegantly for-
malize some principles of the motivational interview-
ing (MI) methodology, a counseling method used in
clinical psychology for eliciting attitude and behavior
change in humans.
Directions of future work are manifold. An im-
portant strategy of MI consists in helping the partici-
pant to overcome the obstacles that prevent her from
converting her mere desires into intentions and then
into effective behavior. Some of these obstacles are of
cognitive nature. For example, the participant could
Speaker Utterance Speech act
m Do you practice ?
m,h
does(h,ps)
a sport regularly?
h I don’t +
m
¬4
h
does(h,ps)
m Do you wish ?
m,h
des(h, gh)
to be in good health?
h Yes +
m
4
h
des(h, gh)
m Do you spend quite ?
m,h
co
some time in the traffic
everyday as a commuter?
h Yes +
m
4
h
co
m Do you have ?
m,h
ow
an office work?
h Yes +
m
4
h
ow
m You spend quite some !
m,h
(
/
0,{co, ow},sl)
time in the traffic
everyday as a
commuter and you have
an office work. Therefore,
your life style is sedentary!
m Your life style is sedentary. !
m,h
{gh},{sl},
Therefore, you will not does(h,ps)
satisfy your desire to be
in good health unless you
practice a sport regularly!
Figure 2: Human-machine dialogue.
hesitate whether to start to practice a sport regularly
since she fears that practicing a sport increases the
risk of getting injured. In this situation, the coun-
selor can try to reassure the participant that her fear
is unfounded. More generally, it can try to make the
participant to revise her beliefs that a certain action
has negative consequences. Another cognitive ob-
stacle could be the participant’s belief that she does
not have the right capabilities and potential to change
her behaviour. The counselor can again try to make
the participant revise her belief by providing counter-
evidence. We plan to extend our analysis to these as-
pects of MI that we were neglected in the paper.
In future work, we also plan to experimentally val-
idate our approach to MI based on cognitive planning.
To this aim, we plan to implement the scenario de-
scribed in Section 6 and to evaluate the performance
of the artificial agent in its interaction with the human.
The work presented in this paper is part of a larger
project which is devoted to development of an artifi-
cial agent with persuasive capabilities which can pro-
mote positive behavior change in the human. The
next step of our investigation is to endow the artifi-
cial agent with multimodal communicative capabil-
ities which go beyond verbal behavior. As shown
in (Potdevin et al., 2021), non-verbal behavior in
communication including facial expressions is funda-
mental for increasing the machine’s believability and
trustworthiness thereby making the human more will-
ing to believe what the machine says.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
516

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Support from the ANR project CoPains “Cognitive
Planning in Persuasive Multimodal Communication”
(grant number ANR-18-CE33-0012) is gratefully ac-
knowledged.
REFERENCES
Bolander, T. and Andersen, M. B. (2011). Epistemic plan-
ning for single- and multi-agent systems. Journal of
Applied Non-Classical Logics, 21(1):9–34.
Bylander, T. (1994). The computational complexity of
propositional STRIPS planning. Artificial Intelli-
gence, 69(1-2):165–204.
Cooper, M. C., Herzig, A., Maffre, F., Maris, F., Perrotin,
E., and R
´
egnier, P. (2021). A lightweight epistemic
logic and its application to planning. Artificial Intelli-
gence, 298.
Cooper, M. C., Herzig, A., Maffre, F., Maris, F., and
R
´
egnier, P. (2016). Simple epistemic planning: gen-
eralised gossiping. In Proceedings of the 22nd Eu-
ropean Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI
2016), pages 1563–1564.
da Silva, J. G. G., Kavanagh, D. J., Belpaeme, T., Taylor,
L., Beeson, K., Andrade, J., et al. (2018). Experiences
of a motivational interview delivered by a robot: qual-
itative study. Journal of medical Internet research,
20(5):e7737.
Fagin, R., Halpern, J., Moses, Y., and Vardi, M. (1995).
Reasoning about Knowledge. MIT Press, Cambridge.
Fernandez, J., Longin, D., Lorini, E., and Maris, F. (2021).
A simple framework for cognitive planning. In Pro-
ceedings of the Thirty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Ar-
tificial Intelligence (AAAI-2021), pages 6331–6339.
AAAI Press.
Ghallab, M., Nau, D., and Traverso, P. (2004). Automated
planning: theory and practice. Morgan Kaufmann.
Halpern, J. Y. and Moses, Y. (1992). A guide to complete-
ness and complexity for modal logics of knowledge
and belief. Artificial Intelligence, 54(3):319–379.
Kanaoka, T. and Mutlu, B. (2015). Designing a motiva-
tional agent for behavior change in physical activity.
In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference
Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing
Systems, pages 1445–1450.
Kominis, F. and Geffner, H. (2015). Beliefs in multiagent
planning: from one agent to many. In ICAPS 2015,
pages 147–155. AAAI Press.
Lisetti, C., Amini, R., Yasavur, U., and Rishe, N. (2013). I
can help you change! an empathic virtual agent deliv-
ers behavior change health interventions. ACM Trans-
actions on Management Information Systems (TMIS),
4(4):1–28.
Lomuscio, A., Qu, H., and Raimondi, F. (2017). MCMAS:
an open-source model checker for the verification of
multi-agent systems. International Journal on Soft-
ware Tools for Technology Transfer, 19:9–30.
Lorini, E. (2020). Rethinking epistemic logic with belief
bases. Artificial Intelligence, 282.
Lorini, E. and Schwarzentruber, F. (2021). Multi-agent be-
lief base revision. In Proceedings of the 30th Interna-
tional Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJ-
CAI 2021). ijcai.org.
L
¨
owe, B., Pacuit, E., and Witzel, A. (2011). DEL planning
and some tractable cases. In Proceedings of the 3rd In-
ternational International Workshop on Logic, Ratio-
nality and Interaction (LORI 2011), pages 179–192.
Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Lundahl, B. and Burke, B. L. (2009). The effectiveness and
applicability of motivational interviewing: A practice-
friendly review of four meta-analyses. Journal of clin-
ical psychology, 65(11):1232–1245.
Makinson, D. (1997). Screened revision. Theoria, 63:14–
23.
Miller, W. R. and Rollnick, S. (2012). Motivational inter-
viewing: Helping people change. Guilford press.
Muise, C., Belle, V., Felli, P., McIlraith, S. A., Miller,
T., Pearce, A. R., , and Sonenberg, L. (2021). Effi-
cient multi-agent epistemic planning: Teaching plan-
ners about nested belief. Artificial Intelligence, 302.
Muise, C., Belle, V., Felli, P., McIlraith, S. A., Miller, T.,
Pearce, A. R., and Sonenberg, L. (2015). Planning
over multi-agent epistemic states: A classical plan-
ning approach. In AAAI 2015, pages 3327–3334.
AAAI Press.
Olafsson, S., O’Leary, T., and Bickmore, T. (2019). Co-
erced change-talk with conversational agents pro-
motes confidence in behavior change. In Proceedings
of the 13th EAI International Conference on Perva-
sive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, pages
31–40.
Potdevin, D., Clavel, C., and Sabouret, N. (2021). Virtual
intimacy in human-embodied conversational agent in-
teractions: the influence of multimodality on its per-
ception. Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces,
15(1):25–43.
Schulman, D., Bickmore, T., and Sidner, C. (2011). An in-
telligent conversational agent for promoting long-term
health behavior change using motivational interview-
ing. In 2011 AAAI Spring Symposium Series.
Searle, J. (1969). Speech acts: An essay in the philosophy of
language. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Stalnaker, R. (2002). Common ground. Linguistics and
Philosophy, 25(5-6):701–721.
van Ditmarsch, H. P., van der Hoek, W., and Kooi, B.
(2007). Dynamic Epistemic Logic. Kluwer Academic
Publishers.
Cognitive Planning in Motivational Interviewing
517
