Towards a More Reliable and Reproducible Protocol of Source Camera
Recognition
Alexandre Berthet, Chiara Galdi and Jean-Luc Dugelay
Department of Digital Security, Eurecom, Sophia Antipolis, France
Keywords:
Digital Image Forensics, Camera Recognition, Verification Protocol, Deep Learning, Convolutional Neural
Network, Siamese Neural Network, Dresden Image Database, SOCRatES.
Abstract:
Source digital camera recognition is an important branch of digital image forensics, which aims at authenti-
cating cameras from the captured images. By analysing the noise artifacts left on the images, it is possible to
recognize the label: brand, model and device of the camera (e.g. Nikon - NikonD70 - NikonD70 of Alice).
Camera recognition is increasingly difficult as the label become more precise. In the specific case of source
camera recognition based on deep learning, literature has widely addressed recognition of the camera model,
while the recognition of the instance of the camera (i.e. device) is currently under-studied. Moreover, we have
identified a lack of protocols for performance assessment: state-of-the-art methods are usually assessed on
databases that have specific compositions, such as the Dresden Image database (74 cameras of 27 models).
However, using only one database for evaluation does not reflect reality, where it may be necessary to anal-
yse different sets of devices that are more or less difficult to classify. Also, for some scenarios, verification
(1-to-1) is better suited to camera recognition than identification (1-to-N). Based on these elements, we pro-
pose a more reliable and reproducible protocol for verification of the source camera made of three different
levels (basic, intermediate and advanced) of increasing difficulty, based on camera labels (brand, model and
device). State-of-the-art methods are tested with the proposed protocol on the Dresden Image Database and
on SOCRatES. The obtained results prove our assumptions, with a relative drop in performance, up to 49.08%
between the basic and advanced difficulty levels. Our protocol is able to assess the robustness of methods
for source camera recognition, as it tests whether they are really able to correctly classify cameras in realistic
contexts.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the rise of digital technologies and social net-
works, images have become a predominant way of
communication. In fact, improvements in digital
camera technology, especially for those embedded in
smartphones, have had a significant impact on the
digital world. In 2020, more than 1.12 trillion pho-
tos were taken worldwide
1
. The rise of images as a
communication media has also led to the misuse of
cameras and smartphones for collecting covert videos
and illegal contents. In the latter case, it is extremely
important to have tools to reliably associate an im-
age with illegal content to the correct source camera.
This research field is referred to as source digital cam-
era recognition. Source camera recognition (SCR)
provides tools to analyse images in order to authen-
1
https://blog.mylio.com/how-many-photos-will-be-
taken-in-2021-stats
ticate their origin. In this field, cameras are defined
and classified according to three labels: brand, model,
and device. Recognition is achieved by analysing the
camera’s artifacts, which correspond to the traces left
by the camera hardware and software when a digital
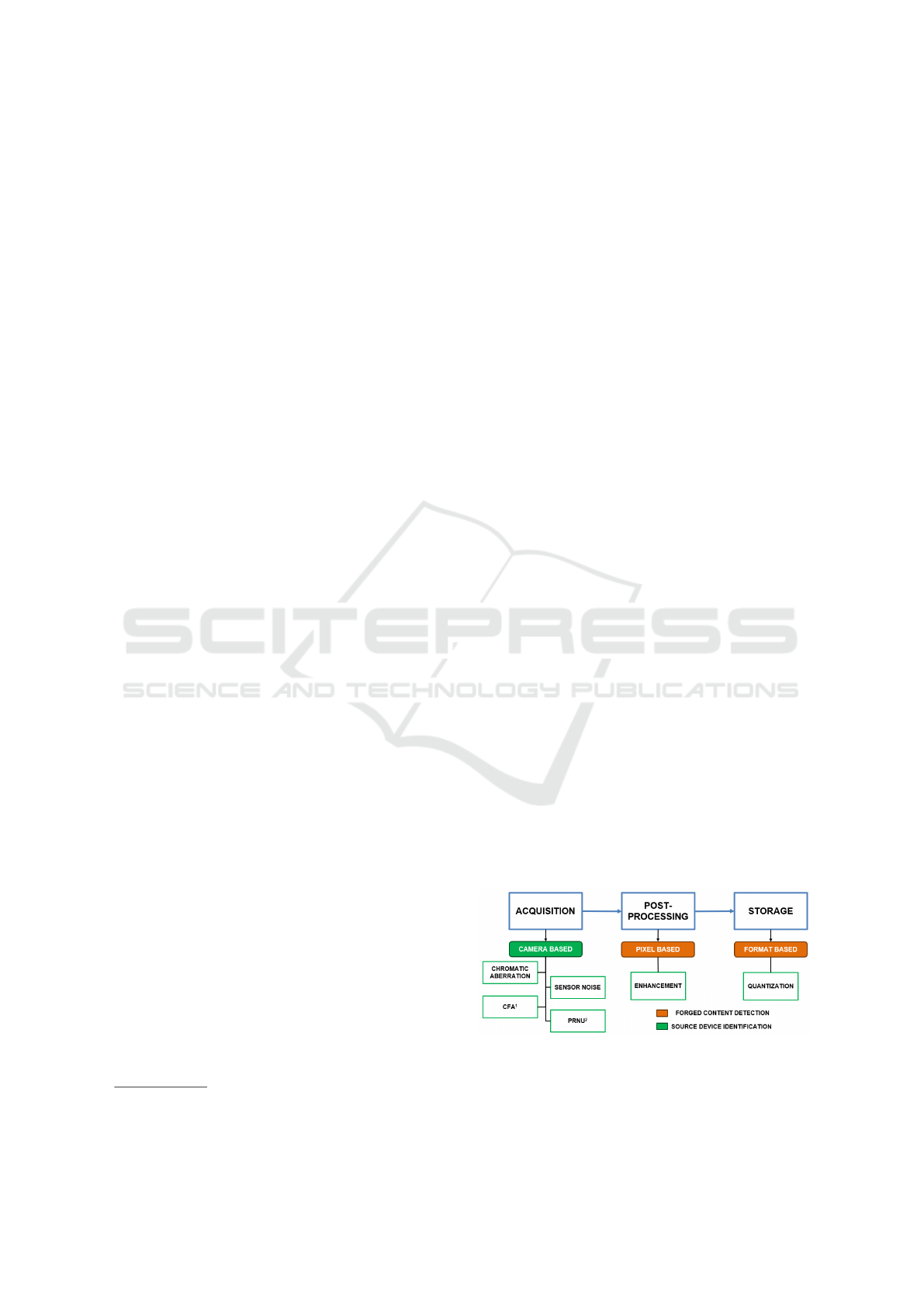
image is created (Fig. 1).
Figure 1: Diagram of artifacts coming from the image
creation pipeline that can be used for source camera
recognition.
1
Color Filter Array;
2
Photo Response Non-
Uniformity.
Berthet, A., Galdi, C. and Dugelay, J.
Towards a More Reliable and Reproducible Protocol of Source Camera Recognition.
DOI: 10.5220/0010912900003122
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2022), pages 745-752
ISBN: 978-989-758-549-4; ISSN: 2184-4313
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
745

The ensemble of such artifacts is often referred to
as camera fingerprint, as for the human fingerprint,
which allows identifying a person. The camera fin-
gerprint is composed of different elements, such as
the features created by the color filter array (CFA)
(Celiktutan et al., 2006; Long and Huang, 2006),
or the chromatic aberration, due to imperfections in
the lens (Choi et al., 2006; Van et al., 2007). An-
other important component of the camera fingerprint
is the so-called ”sensor noise” (Geradts et al., 2001) or
the ”photo response non-uniformity” (PRNU) (Lukas
et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2008), which is due to
imperfections in the silicon wafer during the sensor
manufacturing. Such imperfections cause a different
pixel sensibility to light, generating a distinctive pat-
tern unique for each camera. Finally, traces resulting
from image enhancement (Tsai and Wu, 2006; Khar-
razi et al., 2004) or JPEG quantization (Farid, 2006),
are also used for camera recognition. With the de-
velopment of deep learning (DL) in the last decades,
deep architectures have been adopted in the state of
the art (SOTA), such as convolutional neural networks
(CNNs) (Krizhevsky et al., 2017) or two-stream net-
works (Berthet et al., 2021) and Siamese Neural
Networks (SNNs) (Mayer and Stamm, 2018; Mayer
and Stamm, 2020), which are particularly known for
their robustness. Several articles (Bayar and Stamm,
2017a; Bayar and Stamm, 2017b; Bayar and Stamm,
2018) have been released on the use of constrained
CNNs for source camera recognition, which integrate
a layer specifically designed to extract the camera fin-
gerprint. In fact, DL methods for digital image foren-
sics require a preprocessing module to extract relevant
artifacts that are overshadowed by the image content
(Berthet and Dugelay, 2020).
Most of these DL-based approaches recognize the
source camera based on its model - a task referred to
as camera model recognition in the literature. How-
ever, this task is not sufficient in most scenarios where
the set of cameras under consideration contains at
least two cameras of the same model. In this case,
the recognition of the source camera must be based
on the specific features associated with the device
- which we will refer to as camera device recogni-
tion. The literature on SCR shows the increasing dif-
ficulty of classifying the camera according to the la-
bels: brand, model, and device - where the brand is
the easiest and the device the most difficult to classify.
This problem comes from camera fingerprints, which
are more likely to be close to one another for cameras
of the same brand and model. In the literature, DL-
based methods have widely addressed camera model
recognition, while camera device recognition is still
under-studied. The few papers addressing camera
device recognition, however, do not fully address
the problem of close camera fingerprints. Further-
more, the evaluation protocol adopted by these meth-
ods is that of identification (1-to-N) and the database
mostly used in their experiments is the Dresden im-
age database (Gloe and B
¨
ohme, 2010). The following
problems in this respect are identified: (i) the 1-to-
1 verification protocol might be more appropriate in
some cases. When we want to know if an illegal pic-
ture has been captured by a certain device, we will
compare it with the fingerprint of that device; (ii) the
distribution of cameras in the database (e.g. number
of cameras for each model) is not controlled. There-
fore, the different levels of difficulty of classification
are not highlighted because they depend on the dis-
tribution of cameras; (iii) using only one database for
testing means having always the same exact composi-
tion of cameras, which is not representative of real life
since, for example, more than 1.6 billion capturing de-
vices were sold in 2020 (cameras
2
and smartphones
3
).
Thus, many possible combinations of devices should
be taken into account by using a protocol that includes
a mechanism for randomising the selection of devices.
Based on these elements, we decided to focus our
work on the verification protocol (1-to-1) and on a
controlled selection of cameras, so that the distribu-
tion is not dependent on the selected database distri-
bution. We propose a reliable and reproducible pro-
tocol to fully evaluate state-of-the-art methods. This
protocol consists of three levels of difficulty, namely
basic, intermediate and difficult, that correspond re-
spectively to the selection of cameras according to
three camera characteristics: brand, model and de-
vice. To the best of our knowledge, this article pro-
poses the first protocol for verification to comprehen-
sively assess SCR methods. The reminder of the ar-
ticle is structured as follows: Section 2 presents rel-
evant methods from the SOTA dealing with camera
device recognition. In Section 3, we explain the moti-
vation for our article as well as the proposed protocol.
The experimental evaluation is described in Section
4 with a special metric specifically designed to assess
the impact of difficulty levels. Finally, we provide our
conclusions in Section 5.
2 RELATED WORK
Regarding traditional approaches for source digital
camera recognition (i.e. not based on DL), the most
2
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1172711/forecast-
of-digital-camera-sales-volume/
3
https://www.statista.com/statistics/263437/global-
smartphone-sales-to-end-users-since-2007/
ICPRAM 2022 - 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
746

Table 1: Confusion matrix for camera identification ac-
cording to their model. Performances in the original pa-
pers are assessed over 27 models in total. Here, only the
performances for some selected models that share the same
brand are reported.
Method Chen17 Ding19 Zhao20
Camera model CI55 CI70 CI55 CI70 CI55 CI70
Canon Ixus 55 56% 38% 76.5% 23.5% 90% 9%
Canon Ixus 70 6% 87% 0.6% 99.4% 4% 96%
Camera model ND70 ND70s ND70 ND70s ND70 ND70s
Nikon D70 58% 39% 69.6% 29.5% 64% 35%
Nikon D70s 42% 56% 53.2% 44.1% 41% 58%
Overall Accuracy 94.73% 97.1% 96.1%
used and efficient ones are based on sensor pattern
noise (SPN) analysis, first introduced by Lukas et al.
in 2006 (Lukas et al., 2006), and improved by sev-
eral works in the following years. This method is
based on the analysis of noise residuals. The chal-
lenge today is thus to further improve the camera
device recognition performance by using DL, which
has greatly improved the performance of many im-
age processing tasks so far. In the following, we
present the literature on camera device recognition
with DL, analysing their architecture and evaluation
protocol,which is based on identification (1-to-N).
The work presented in (Chen et al., 2017), ad-
dresses multiple classification along three experi-
ments to provide performance for each label: brand,
model, and device. Their method is based on the
residual neural network (ResNet) (He et al., 2016),
which is a network that incorporates skipping connec-
tions in its layers. The idea is to keep low-level fea-
tures while convolutional layers process the images
to obtain high-level features. By combining both,
the final output is more comprehensive and includes
more information to recognize camera fingerprints.
They achieved an identification accuracy of 99.12%,
94.73%, and 45.81% for brands, models, and devices,
respectively.
In the two following works, multiple classification
is also addressed with a very similar protocol, as they
produce predictions for the three labels (brand, model
and device) with only one experiment. In (Ding et al.,
2019), a preprocessing module is used, which exploits
a concatenation of three high-pass filters and of the
original image to obtain more diversity in the fea-
tures. The network is made of three parts that are built
with three ResNet blocks followed by a classification
layer to identify a single label: first the brand, then the
model, and finally the device. The ResNet blocks are
made of two consecutive convolutional layers in par-
allel with a single convolutional layer, for the extrac-
tion of high- and low-level features. They obtained an
accuracy of 99.6%, 97.1%, and 52.4% for the identi-
fication of brands, models, and devices, respectively.
Table 2: Confusion matrix for camera device identifica-
tion. Performances in the original papers are assessed over
74 devices. Here, only the values for some selected de-
vices are reported. Accuracy is averaged over three devices
per model. Bold font indicates performance values that are
larger or smaller than the overall accuracy.
Camera model Chen17 Ding19 Zhao20
FujiFilm FinePixJ50 48.14% 49% -
Olympus Mju-1050SW - 43.33% -
Sony DSC-T77 - 77.67% 64%
Samsung NV15 - - 47%
Casio EX-Z150 - - 35%
Overall Accuracy 45.81% 52.4% 47.5%
The authors of (Zhao et al., 2020) propose a
method based on the combination of a ResNet in par-
allel with a set of convolution layers, which extract
camera attributes and the relevant information of the
image neighborhoods, respectively. They use a re-
cursive method with a classification in cascade: the
predictions are given with consecutive sub-classifiers
(first brand, then model, and finally device). The sub-
classifier can affect the parent-classifier to drop some
features that are invalid for sub-classification. They
achieved an identification accuracy of 99.4%, 96.1%,
and 47.5% for brands, models, and devices, respec-
tively.
In these state-of-the-art articles, evaluations have
been conducted by identification (1-to-N) and have
shown that recognition is increasingly difficult for de-
vices sharing the same brand and the same model,
making camera device recognition the most challeng-
ing task (note the drop in performance even up to
half when classifying brands or models vs. devices).
Regarding recognition of devices sharing the same
brand, the difficulty in classifying them is confirmed
by observing Tab. 1, which reports a part of the con-
fusion matrices from state-of-the-art methods (Chen
et al., 2017; Ding et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2020) (pre-
sented in section 2) for some camera models. In fact,
the performance of camera model recognition is lower
for cameras of the same brand. Regarding the diffi-
culty of performing camera device recognition com-
pared to camera model recognition, Tab. 2 reports
the results from the same SOTA methods as before,
but this time used for device classification. The ta-
ble shows the mean accuracy for some camera mod-
els, which has been computed over three devices per
model. The table also reports the overall classification
accuracy that is much lower than for model classifica-
tion (see Tab. 1 overall accuracy for comparison).
The drop in performance between the two tasks
(model and device identification) is surely due in part
to the number of classes on which to classify the cam-
eras, which is usually higher for device than model
Towards a More Reliable and Reproducible Protocol of Source Camera Recognition
747
(i.e. usually in a dataset there are more different cam-
era devices than different camera models). It is known
that in DL, the accuracy and the number of classes are
inversely correlated. This drop is also due to the fact
that cameras of the same brand and model have close
camera fingerprints, which is further analysed in the
next section.
3 PROPOSED PROTOCOL
3.1 Close Camera Fingerprints
The literature has shown that camera recognition is
increasingly difficult, as cameras of the same brand
or model have close digital features. The problem of
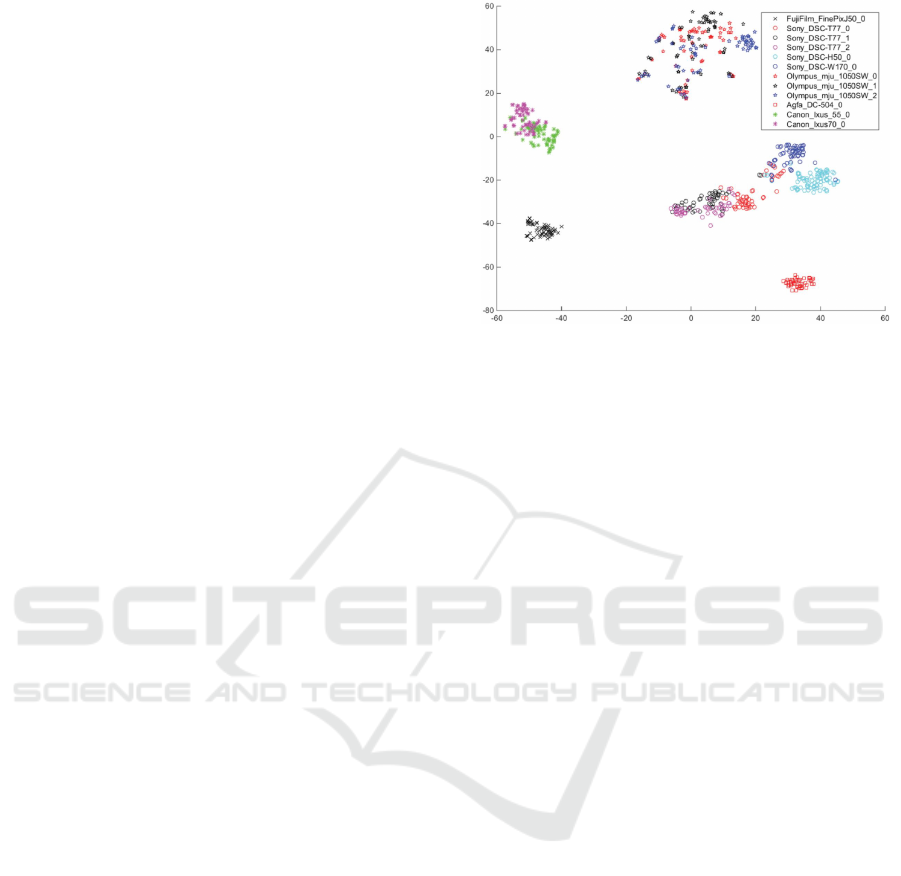
close camera fingerprints is well illustrated in (Ding
et al., 2019) by a visualization plot of the features
extracted with t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Em-
bedding (t-SNE) (Fig. 2). This visualization high-
lights the similarity of camera features based on their
brand and model. For example, the cameras Olym-
pus mju 1050SW are quite difficult to group together.
This chart also shows that cameras of the same model
can still be differentiated, such as the Sony DSC-T77,
whose features can be grouped for each camera of
that model. Although this issue of close camera fin-
gerprints has been mentioned in the literature of DL
based SCR methods, especially via the confusion ma-
trix analysis, it has never been fully addressed. In par-
ticular, SOTA methods are always evaluated by iden-
tification (1-to-N) on an entire database, which does
not showcase the challenge of camera fingerprint sim-
ilarity. In fact, in such type of evaluation the dis-
tribution of cameras is often, if not all the time, not
controlled. Therefore, cameras of the same model (or
brand) are mixed with many other models (brands)
and the difficulty of classification may differ from one
database to another. To overcome this problem, we
propose to adopt a protocol that uses camera selection
to create sets with a control distribution of cameras.
The camera selection allows controlling the presence
of cameras with close digital fingerprints, and thus
controlling the difficulty of classification. Moreover,
the protocol that we propose in the following subsec-
tions is based on 1-to-1 verification, as we believe that
verification is more likely to be used in future applica-
tions (e.g. in police investigation). That is, to distin-
guish Bob’s iPhone 11 from Alice’s iPhone 11 rather
than recognizing it within a random group of smart-
phones.
Figure 2: Visualization of the similarity of different cam-
eras in the feature space t-SNE (Ding et al., 2019). (stars)
Olympus; (circles) Sony; (asterisk) Canon; (cross) Fuji;
(square) Agfa.
3.2 Verification Protocol
Verification has been already adopted in some works
on SCR. For example, the authors of (Mandelli et al.,
2020) use a Siamese neural network (SNN) for device
recognition, by evaluating camera fingerprint similar-
ity between pairs of images. SNN is an architecture
that has been quite used for SCR and particularly in
model classification. The network is composed of two
twin sub-networks whose weights are updated iden-
tically. They have trained one part of the network
with coherent pairs and the other with non-coherent
pairs. The noise residual of an image associated with
a device d
i
is combined with PRNUs from the same
device d
i
and a dissimilar device d
j
to create coher-
ent and non-coherent pairs, respectively. The PRNU
is obtained from a large set of images from each de-
vice to obtain a more robust and reliable pattern. The
idea is to extract and then compare the PRNU using
the two streams of the network, which output each
an encoding of the input image (e.g. a vector of size
1024). The network works in tandem on two different
input images to compute comparable output vectors.
Instead of “which class does the image come from”,
SNNs answer the question “Are the two images from
the same class?”. We can draw a parallel with bio-
metric recognition saying that single-stream networks
perform 1-to-N comparison, and thus identification,
while two-stream networks, such as SNNs, perform 1-
to-1 comparison, and thus verification. In fact, source
camera recognition is even sometimes referred to as
hardwaremetry (Galdi et al., 2015). One major ad-
vantage of using SNN is that, once trained, they are
able to establish if two images come from the same
class, even for unseen classes. The purpose is to deter-
ICPRAM 2022 - 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
748

mine if two images are coming from the same camera
or not. One of the SOTA methods that we analyse in
the following is based on SNN, and thus naturally en-
tails assessment by means of verification. In addition,
we propose to evaluate single-stream SOTA methods
with a protocol for verification. To do this, the encod-
ing of an image calculated by the neural network is
extracted before the network performs classification
and compared with other encodings in a 1-to-1 com-
parison by Euclidean distance.
3.3 Cameras Selection
Traditionally, the evaluation of SCR methods is per-
formed on the entire database without any particu-
lar camera selection strategy. However, using the
whole database as it is does not take into account
the problem of close camera fingerprints. Ideally,
the databases for camera recognition should contain
a large and balanced number of cameras of the same
model, otherwise it would not be clear whether a
method is actually classifying the camera according
to camera model recognition or camera device recog-
nition. As a parallel with biometric recognition, it
would be like having a database made of only young
women and elderly men, how to establish if the model
indeed recognizes the gender rather than the age? In
practice, the currently available databases have a very
limited number of cameras sharing the same model.
The protocol that we proposed is based on a selection
of cameras that allows defining subsets of the exist-
ing datasets to test SOTA methods according to dif-
ferent levels of difficulty. The selection strategy aims
at selecting pairs of cameras for the 1-to-1 compari-
son. We have to ensure that when the pairs are cre-
ated, they reflect the need to test the network against
different levels of difficulty, which increase with the
amount of cameras with close camera fingerprints. To
confirm the problem of increasing difficulty of clas-
sification from brand to device, we propose to create
three levels: i) with only cameras of different brands
(basic); ii) with only cameras of the same brand and
different models (intermediate); iii) with only cam-
eras of the same brand and model (advanced). Even
among these difficulty levels, some cameras could be
easier to classify than others, as the confusion ma-
trices showed in the section 2: the method of (Zhao
et al., 2020) was able to well distinguish Canon Ixus
55 from Canon Ixus 70, whereas it was not the case
for Nikon D70 and Nikon D70s. As verification is
performed with pairs of images, these difficulty lev-
els will represent the different dissimilar pairs (see
Fig. 3). The problem of database distribution is fixed
thanks to the controlled selection of pairs of images
according to the three difficulty levels.
Figure 3: Diagram illustrating difficult and classical
dissimilar pairs. (Red) Advanced; (Blue) Intermediate;
(Green) Basic.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The protocol with our proposed selection of cameras
is applied to four different SOTA methods to have
a comprehensive analysis of SCR that suffer from
the problem of classifying devices with close cam-
era fingerprints. From the camera device recogni-
tion methods described in Section 2, we selected the
most efficient one (Ding et al., 2019). We also chose
two methods for camera model recognition, which
were re-trained to perform camera device recogni-
tion instead, to test other architectures as well. Both
methods are based on constrained CNNs (Bayar and
Stamm, 2017a; Bayar and Stamm, 2018): the first one
is the basic constrained CNN, introduced by Bayar et
al., and the second one integrates enhanced prepro-
cessing. Finally, a method based on SNN (Mayer
and Stamm, 2020) is also selected in order to test
the possible higher robustness of SNNs. The study
is conducted on two databases, chosen for their dif-
ferent features: SOCRatES and the Dresden Image
database. In the case of methods originally designed
for identification, the architecture is adapted to verifi-
cation by removing the classification layer and com-
paring the output feature vectors (or encodings) with
Euclidean distance.
4.1 Databases
SOCRatES: SOurce Camera REcognition on Smart-
phones, is an image and video database especially de-
signed for source camera recognition on mobile de-
vices. SOCRatES is currently one of the databases
for source digital camera recognition with the largest
number of different cameras. It is made up of about
9,700 images and 1000 videos captured with 101 dif-
ferent smartphones of 15 different makes and about
Towards a More Reliable and Reproducible Protocol of Source Camera Recognition
749

Table 3: Details of the databases: the brand, model and
the number of devices; Some devices are on the same line
(e.g. S3 and S3 Neo).
Dresden Image Database
AgfaPhoto Canon Nikon
DC-504 1 Ixus 55 1 Coolpix S710 5
DC-733s 1 Ixus 70 3 D70/D70s 2/2
DC-830i 1 PS A640 1 D200 2
Sensor 505-X/530s 1/1 Casio FujiFilm
Sony EX-Z150 5 FinePix J50 3
DSC-H50 2 Pentax Samsung
DSC-T77 4 Optio A40 4 L74wide 3
DSC-W170 2 Optio W60 1 NV15 3
Kodak Panasonic Rollei
M1063 5 DMC-FZ50 3 RCP-7325XS 3
Ricoh Olympus Praktica
Capilo GX100 5 1050SW 5 DCZ 5.9 5
Total brand 14 Total model 27 Total device 74
SOCRatES
Apple Asus HTC
iPhone 4s 3 Zenfone 2/3 3/1 One M8 1
iPhone 5/5s 1/2 Huawei Lenovo
iPhone 5c 6 P7/P8 Lite 1 S60 1
iPhone 6/6s/6s plus 8/3/1 Motorola Acer
iPhone 7 3 Moto G/G3 3/2 Liquid E700 1
iPhone SE 1 Moto X-Style 1 OnePlus
iPad Mini 2 1 X Play 1 X/One 1/1
Samsung LG Nokia
S3/S3 Neo 1/2 G3/G4 4/2 Lumia 635/930 1/1
S4/S4 mini 2/1 Nexus 5X/5 2/1 Wiko
S5/S5 mini 4/1 Spirit LTE 1 Rainbow 4G/Up 4G 1/1
S6/S6 Edge 1/1 K10 4G 1 Highway 4G 1
S7 Edge 2 Sony Birdy 4G 1
Core Max/Prime 1/2 Xperia Z/Z1 1/1 Vernee
Grand Plus/Prime 1/1 Xperia Z3/Z5 3/1 Thor 1
A3/A510 2/1 Xperia T3/E3/M4 1/1/1 Meizu
J7/Note 4 2/1 NEX-VG20 1 M3 Note 1
Total brand 15 Total model 62 Total device 101
60 different models. The acquisition has been per-
formed in uncontrolled conditions (Galdi et al., 2019).
The Dresden Image database (Gloe and B
¨
ohme,
2010) is perhaps the most popular database in the
field of digital image forensics. It is composed of
more than 14,000 images of various indoor and out-
door scenes that were captured by 74 cameras of 27
different models. Tab. 3 gives an overview of the
distribution of both databases. A difference can al-
ready be made in terms of models per brand: there is
an over-presence of Apple and Samsung cameras in
SOCRatES compared to other brands, while in Dres-
den the distribution is more uniform. Moreover, there
is another specificity at the device level: most of the
cameras have a single device in SOCRatES whereas
in Dresden only few cameras are represented with
only one device. Thus, these two databases have re-
ally different compositions of cameras, which high-
lights the problem of using only one database for eval-
uation. Moreover, this specificity of composition will
probably have consequences on the results.
4.2 Evaluation
For the evaluation with the protocol presented in 3,
the creation of the datasets has required two steps:
to establish a dataset of patches and then of pairs of
patches. First, we cropped each image from both
databases by a window of size 128 × 128 pixels.
Table 4: Results of camera device verification on Dres-
den and SOCRatES for four SOTA methods. The re-
ported metric is the area under the curve of the receiver op-
erating characteristic in percentage: AuC*100. Drop mea-
sures the relative drop in performance between the basic and
the advanced levels of difficulty.
Methods Ding19 Bayar18 Bayar17 Mayer20
Selection SOCRatES
Basic 67.5% 81.4% 82.4% 97.4%
Intermediate 66.6% 77% 78% 92.5%
Advanced 62.5% 69.5% 68.5% 76.2%
Drop (%) 7.4 14.62 16.87 22.39
Selection Dresden
Basic 59.9% 87.8% 89.9% 97.8%
Intermediate 58.9% 71.1% 74.9% 75.2%
Advanced 50.5% 50.3% 50.3% 49.8%
Drop (%) 15.69 42.71 44.05 49.08
Then, we picked these patches according to their
brightness, as dark and saturated areas are not optimal
for the extraction of sensor noise. We selected 2.7M
and 630K patches from the Dresden and SOCRatES
databases, respectively. We split both datasets in three
subsets (60:20:20), corresponding to training, valida-
tion, and testing, respectively. Training and valida-
tion sets are used to train the SOTA networks follow-
ing their original protocols, as indicated in the corre-
sponding papers. The datasets for each difficulty level
are created with the testing subset according to their
respective selection of pairs. The code used for gen-
erating the image patches and the different selection
of pairs of images is made available online
4
for re-
producibility.
The performances of the SOTA methods are re-
ported in terms of area under the curve of the receiver
operating characteristic (ROC AuC), which plots the
true positive rate (T PR =
T P
T P+FN
) against the false
positive rate (FPR =
FP
FP+T N
, where TP = True Posi-
tives, TN = True Negatives, FP = False Positives, and
FN = False Negatives. An additional metric is used
to show the relative drop in performance between the
basic and the advanced levels of difficulty. This met-
ric is defined as:
drop =
(AuC
BASIC
− AuC
ADVANCED
)
AuC
BASIC
∗ 100 (1)
The higher the AuC value, the better the classifi-
cation capability of the method. The lower the drop
value, the more robust the classification method.
As our camera selection strategy has a part of
randomness, the Monte Carlo method (Kroese et al.,
2014) for random sampling is adopted. Therefore,
4
https://gitlab.eurecom.fr/imagingsecuritypublic/
eurecom difficultdeviceevaluationprotocol
ICPRAM 2022 - 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
750

Figure 4: Visualization of the similarity of different cell-
phones in the feature space t-SNE (Ding et al., 2019).
(circle) iPhone; (square) Xiaomi; (asterik) Samsung; (star)
Huawei.
over 50 repetitions of our protocol are performed,
and the average scores are compute. The results are
presented in Tab. 4. The method of (Ding et al.,
2019) presents the best results in terms of relative
drop, meaning that the results are more stable over
the three difficulty levels, whatever database is used
for evaluation. The robustness of this method proba-
bly comes from its architecture as (Ding et al., 2019)
is designed to perform multiple classification (i.e.
brand, model, and device). On the contrary, the other
SOTA methods have better performances for the ba-
sic and intermediate levels, but the drop for the ad-
vanced level is larger. Meaning that they fail the
test to see if they can really distinguish between in-
dividual devices. The method of (Bayar and Stamm,
2018), with enhanced processing, shows more robust-
ness compared to (Bayar and Stamm, 2017a) (without
enhancement). Overall, the results obtained for the
advanced experiments, in particular on the Dresden
dataset, are far from what one should expect. In fact,
for verification (1-to-1), a score of 50% correspond
to a random classifier. Our protocol shows that the
current SOTA methods are not able to perform verifi-
cation for cameras with close digital fingerprints.
Overall, the SOTA methods are more robust
when camera device verification is conducted on
SOCRatES than on Dresden: relative drop twice
less. This is due to their different characteristics:
SOCRatES is really diverse with a camera/model ra-
tio of 1,63 while Dresden has a ratio of 2,74. More-
over, the graph in Fig. 4, which presents the feature
space t-SNE for some smartphones in SOCRatES,
shows that clusters can be more easily established
for each camera compared to the ones from Dresden.
This can explain the different decrease in performance
between Dresden and SOCRatES. However, even if
smaller, the drop of performances on SOCRatES is
detected too thanks to the protocol with our selection
of cameras. This selection highlights close camera
fingerprints, providing a more reliable assessment of
source camera verification. Especially, if the perfor-
mance decreases too much from one difficulty level to
another, it means that the method is not able to clas-
sify according to the valid characteristic (e.g. model
for intermediate and device for advanced). Therefore,
efficient methods should obtain stable performance in
each level of difficulty. Moreover, the higher the per-
formance, the better (N.B. 50% means random classi-
fication.)
5 CONCLUSION
This article addresses source camera verification, and
particularly the issue of correctly classifying cam-
eras according to different difficulty levels. Four se-
lected SOTA methods are tested on the Dresden Im-
age Database and on SOCRatES. These datasets are
selected because very different from each other in
both the devices used for image acquisition, cam-
eras for the Dresden database and smartphones for
SOCRatES, and their different number of classes per
label (brand, model, and device). The protocol of
evaluation uses three different strategies for selection
of cameras to showcase the increasing difficulty of
classifying cameras: (i) only different brands; (ii)
same brand and different models; (iii) same brand
and same model. The results reveal a drop of perfor-
mances for the tested SOTA methods in the advanced
scenario (i.e. cameras of the same model), partic-
ularly on the Dresden database. Moreover, thanks
to this protocol, the gap between the basic and the
advanced levels confirms the problem of robustness
of the SOTA methods over different distributions of
cameras in the dataset. Therefore, the contributions of
this article are the definition of a new reliable and re-
producible evaluation protocol to assess source cam-
era recognition methods, the analysis and explanation
of the problems related to the evaluation protocols
used in the literature, and the proposal of solutions to
fix them. Future works on this subject could include
the definition of a standard acquisition protocol to cre-
ate databases that allow to reliably assess methods for
source camera recognition that takes into account the
issue of close camera fingerprints.
Towards a More Reliable and Reproducible Protocol of Source Camera Recognition
751

ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the DEFACTO (Auto-
mated detection of digital images falsifications) con-
sortium (UTT, Eurecom and Surys), which partici-
pated in the French challenge DEFALS (DEtection of
FALSifications in images and videos).
REFERENCES
Bayar, B. and Stamm, M. C. (2017a). Augmented con-
volutional feature maps for robust cnn-based cam-
era model identification. In 2017 IEEE International
Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pages 4098–
4102.
Bayar, B. and Stamm, M. C. (2017b). Design principles of
convolutional neural networks for multimedia foren-
sics. In Media Watermarking, Security, and Forensics.
Bayar, B. and Stamm, M. C. (2018). Towards open set cam-
era model identification using a deep learning frame-
work. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on
Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP),
pages 2007–2011.
Berthet, A. and Dugelay, J.-L. (2020). A review of data pre-
processing modules in digital image forensics meth-
ods using deep learning. In 2020 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Visual Communications and Im-
age Processing (VCIP), pages 281–284.
Berthet, A., Tescari, F., Galdi, C., and Dugelay, J.-L.
(2021). Two-stream convolutional neural network
for image source social network identification. In
2021 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW),
pages 229–237.
Celiktutan, Avcibas, Sankur, Ayerden, and Capar (2006).
Source cell-phone identification. In 2006 IEEE 14th
Signal Processing and Communications Applications,
pages 1–3.
Chen, M., Fridrich, J., Goljan, M., and Lukas, J. (2008).
Determining image origin and integrity using sensor
noise. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics
and Security, 3(1):74–90.
Chen, Y., Huang, Y., and Ding, X. (2017). Camera model
identification with residual neural network. In 2017
IEEE International Conference on Image Processing
(ICIP), pages 4337–4341.
Choi, K., Lam, E., and Wong, K. (2006). Source cam-
era identification using footprints from lens aberra-
tion. Proceedings of the SPIE, 6069.
Ding, X., Chen, Y., Tang, Z., and Huang, Y. (2019). Cam-
era identification based on domain knowledge-driven
deep multi-task learning. IEEE Access, 7:25878–
25890.
Farid, H. (2006). Digital image ballistics from jpeg quanti-
zation.
Galdi, C., Hartung, F., and Dugelay, J.-L. (2019). Socrates:
A database of realistic data for source camera recog-
nition on smartphones. In ICPRAM.
Galdi, C., Nappi, M., and Dugelay, J.-L. (2015). Combin-
ing hardwaremetry and biometry for human authen-
tication via smartphones. In Murino, V. and Puppo,
E., editors, Image Analysis and Processing — ICIAP
2015, pages 406–416, Cham. Springer International
Publishing.
Geradts, Z., Bijhold, J., Kieft, M., Kurosawa, K., Kuroki,
K., and Saitoh, N. (2001). Methods for identification
of images acquired with digital cameras. In SPIE Op-
tics East.
Gloe, T. and B
¨
ohme, R. (2010). The dresden image
database for benchmarking digital image forensics. J.
Digit. Forensic Pract., 3:150–159.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016). Deep resid-
ual learning for image recognition. In 2016 IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
(CVPR), pages 770–778.
Kharrazi, M., Sencar, H., and Memon, N. (2004). Blind
source camera identification. In 2004 International
Conference on Image Processing, 2004. ICIP ’04.,
volume 1, pages 709–712 Vol. 1.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2017). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. Commun. ACM, 60(6):84–90.
Kroese, D. P., Brereton, T. J., Taimre, T., and Botev, Z. I.
(2014). Why the monte carlo method is so impor-
tant today. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Compu-
tational Statistics, 6:386–392.
Long, Y. and Huang, Y. (2006). Image based source cam-
era identification using demosaicking. In 2006 IEEE
Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, pages
419–424.
Lukas, J., Fridrich, J., and Goljan, M. (2006). Digital cam-
era identification from sensor pattern noise. IEEE
Transactions on Information Forensics and Security,
1(2):205–214.
Mandelli, S., Cozzolino, D., Bestagini, P., Verdoliva, L.,
and Tubaro, S. (2020). Cnn-based fast source de-
vice identification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters,
27:1285–1289.
Mayer, O. and Stamm, M. C. (2018). Learned forensic
source similarity for unknown camera models. In
2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics,
Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pages 2012–
2016.
Mayer, O. and Stamm, M. C. (2020). Forensic similarity
for digital images. IEEE Transactions on Information
Forensics and Security, 15:1331–1346.
Tsai, M.-J. and Wu, G.-H. (2006). Using image features to
identify camera sources. In 2006 IEEE International
Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Process-
ing Proceedings, volume 2, pages II–II.
Van, L. T., Emmanuel, S., and Kankanhalli, M. S. (2007).
Identifying source cell phone using chromatic aberra-
tion. In 2007 IEEE International Conference on Mul-
timedia and Expo, pages 883–886.
Zhao, M., Wang, B., Wei, F., Zhu, M., and Sui, X. (2020).
Source camera identification based on coupling cod-
ing and adaptive filter. IEEE Access, 8:54431–54440.
ICPRAM 2022 - 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
752
