
Hints of Independence in a Pre-scripted World:
On Controlled Usage of Open-domain Language Models for Chatbots in
Highly Sensitive Domains
Erkan Bas¸ar
1
, Iris Hendrickx
2
, Emiel Krahmer
3
, Gert-Jan de Bruijn
4,5
and Tibor Bosse
1
1
Behavioural Science Institute, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
2
Centre for Language Studies, Radboud University, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
3
Tilburg School of Humanities and Digital Sciences, Tilburg University, Tilburg, The Netherlands
4
Department of Communication Studies, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium
5
Faculty of Social and Behavioural Sciences, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Keywords:
Hybrid Conversational Agents, Task-oriented Dialogue Systems, Multi-turn Response Selection, Natural
Language Generation.
Abstract:
Open-domain large language models have progressed to generating natural-sounding and coherent text. Even
though the generated texts appear human-like, the main stumbling block is that their output is never fully pre-
dictable, which runs the risk of resulting in harmful content such as false statements or inflammatory language.
This makes it difficult to apply these models in highly sensitive domains including personal health counselling.
Hence, most of the chatbots for highly sensitive domains are developed using pre-scripted approaches. Al-
though pre-scripted approaches are highly controlled, they suffer from repetitiveness and scalability issues.
In this paper, we explore the possibility of combining the best of both worlds. We propose and describe in
detail a new, flexible expert-driven hybrid architecture for harnessing the benefits of large language models in
a controlled manner for highly sensitive domains and discuss the expectations and challenges.
1 INTRODUCTION
The attention for conversational agents (or chatbots)
has been on the rise in recent years. Technologi-
cal advancements allowed the development of chat-
bot applications in many domains, ranging from cus-
tomer services and entertainment, to smart personal
assistants. Health-related domains and counselling
also benefit from this technology for a number of rea-
sons. The chatbots are always accessible, have in-
finite patience, and can simultaneously interact with
multiple users (Krahmer et al., 2021). However,
personal health is a highly sensitive domain where
mishaps in the communication are not acceptable.
Counselling chatbots are required to be fair and non-
discriminatory against their users. As a result, cre-
ating engaging chatbots for highly sensitive domains
becomes a challenge.
Highly sensitive domain chatbots are often built
on pre-scripted methods (such as rules- and template-
based systems) and retrieval-based methods, because
these methods are highly controllable. They typically
operate on human-authored utterances. This lowers
the risk of uttering harmful content (such as false
statements or inflammatory language) to almost none.
However, the same feature makes them suffer from
repetitiveness and the lack of flexibility. These is-
sues decrease the user experience, especially during
long-term interactions where users can have multiple
sessions with the chatbot. In contrast, the latest open-
domain large language models can automatically gen-
erate coherent responses based on any given conver-
sation context. Yet their output is never fully pre-
dictable, and they contain the risk of generating harm-
ful content.
In this study, we address these problems by bridg-
ing the gap between the advancements in the natural
language generation (NLG) area and real-world coun-
selling chatbot applications. We focus on developing
personal health counselling chatbots with an attention
to long-term interactions, and explore the possibili-
ties of combining the flexibility of neural generation
models with the low-risk and structured advantages of
retrieval-based and pre-scripted chatbot models.
Ba¸sar, E., Hendrickx, I., Krahmer, E., de Bruijn, G. and Bosse, T.
Hints of Independence in a Pre-scripted World: On Controlled Usage of Open-domain Language Models for Chatbots in Highly Sensitive Domains.
DOI: 10.5220/0010914300003116
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2022) - Volume 1, pages 401-407
ISBN: 978-989-758-547-0; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
401

We introduce a hybrid approach consisting of
three state-of-the-art open-domain neural genera-
tion models (namely GPT-3, BERT, DialoGPT), a
novel retrieval-based approach using domain-specific
human-authored utterances, a dialogue state tracker,
and a neural response selection model which selects
the best fitting response from a set of both human-
authored and automatically generated candidates. We
expect the open-domain NLG models to add flexibil-
ity to the chatbot and prevent repetitiveness, while the
dialogue state tracker and retrieval-based model pro-
vide control similar to pre-scripted approaches.
2 OPEN-DOMAIN NEURAL
LANGUAGE GENERATION
Lately, arguably the most influential advancement
in the natural language processing (NLP) area has
been large-scale neural language modelling with deep
neural networks, or foundation models (Bommasani
et al., 2021), such as ELMo (Peters et al., 2018),
BERT (Devlin et al., 2019), and GPT (Brown et al.,
2020). These models have rapidly displayed a sig-
nificant increase in performance over the state-of-the-
art in a broad range of NLP tasks. With conspicuous
results, they have quickly gained the attention of the
NLP community and have reached various commer-
cial successes (such as Google using BERT for ma-
chine translation).
Typically, these large neural language models con-
sist of a special type of artificial neural network
architecture called Sequence-2-Sequence (Seq2Seq;
Sutskever et al. 2014). They typically incorporate bil-
lions of parameters and are trained on large corpora
in an unsupervised fashion, that is, without the re-
quirement of any labelling by human annotators (Gu-
rurangan et al., 2020). Because the training approach
is unsupervised, it is possible to include a massive
amount of data from various online sources, such as
Wikipedia and CommonCrawl, with minimal human
labour required. Hence, these neural language models
can create accurate grammatical and semantic repre-
sentations for words (known as word embeddings) by
analysing the context in which the words occur in the
training data (Mikolov et al., 2013; Peters et al., 2018;
Devlin et al., 2019). Later, these pre-trained language
models can be reused to generate word embeddings,
which are used as feature vectors in supervised train-
ing for downstream NLP tasks.
Seq2Seq neural networks are also suitable to be
trained as text-to-text natural language generation
models (Vinyals and Le, 2015). NLG is the task of au-
tomatically producing unstructured text in natural lan-
guages that humans can understand (Gatt and Krah-
mer, 2018), and the text-to-text approach only needs
unstructured text as their input. Previous studies show
that these neural generation models can produce very
natural and fluent utterances, leading to the creation
of human-like chatbots (Tao et al., 2018; Zhou et al.,
2020).
The main advantage of these neural generation
models is the flexibility to generate coherent and
unique responses to any given conversation context
(Yang et al., 2019). Likewise, writing domain spe-
cific rules or utterances is not required for these mod-
els, which reduces human labour for domain adapta-
tions. These features combined make neural genera-
tion models more attractive than traditional methods.
The underlying mechanisms of such models, how-
ever, are still based on statistical generalizations. This
results in generating stylistically intelligent-looking,
grammatically correct texts, but the models lack any
actual understanding or meaning behind what is gen-
erated (Floridi and Chiriatti, 2020). That is to say, the
way these models work is not concerned with whether
the generated content is semantically right or wrong.
Moreover, the generalization process may also result
in human biases, foul language usage, and hate speech
(Caliskan et al., 2017), because the models have been
trained on large corpora from the internet without any
interception from a human annotator. Consequently,
the models carry the risk of producing misinforming,
harmful and offensive content such as racist and sexist
slurs as well as implicit discriminatory text (Bender
et al., 2021; Schlesinger et al., 2018).
3 HIGHLY CONTROLLED
CHATBOTS
Many scientific projects focus on developing chatbots
for highly sensitive domains (Xu and Zhuang, 2020).
Most commercial implementations or real-world ap-
plications, however, tend to use traditional meth-
ods such as rule-based or retrieval-based approaches
(Chen et al., 2017; Gatt and Krahmer, 2018). The
main advantage of these approaches comes from the
use of human-authored utterances. In the retrieval-
based approach, the chatbot’s responses are selected
from corpora of utterances, based on their relevance
to the corresponding conversation context. In rule-
based systems, the dialogue flows are deterministic;
from the start of the conversation until the end, every
exchange with the chatbot is pre-scripted. These as-
pects not only make the chatbots speak with natural
human utterances, but they also make it easier to keep
them under control (Gatt and Krahmer, 2018).
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
402

On the one hand, traditional methods do not carry
any risk of exposing users to harmful contents be-
cause the responses are carefully crafted by humans.
On the other hand, these systems often have scala-
bility issues and labour-intensive domain adaptations.
Furthermore, due to the finite number of utterances,
dialogues with these chatbots may become repetitive.
Issues like repetition in conversations is disliked by
humans and can weaken the user engagement (See
et al., 2019). Consequently, users stop talking to the
chatbot after one session in a multi-session, long-term
setup.
In comparison, neural generation models do not
share the limited corpora and repetitiveness issues of
traditional approaches. However, the risk of harmful
content generation is an expensive problem for highly
sensitive domains. The currently most acclaimed of
these models, namely GPT-3 (Brown et al., 2020),
has been tested in medical support system scenarios.
It has produced convincingly well-written texts that
provide inconsistent and unreliable information, and
incidentally its suggestions become inappropriate for
medical applications (Rousseau et al., 2020). As a
result, we cannot yet fully embrace an uninterrupted
implementation of open-domain pre-trained genera-
tion models for chatbot applications in highly sensi-
tive domains.
4 HYBRID SOLUTION
We argue that the solution is a careful combination
of all approaches, in which the dialogue flow is de-
termined by domain experts. Previous studies (Yang
et al., 2019; Song et al., 2018) have demonstrated po-
tential benefits of combining retrieval and generation
approaches. Following these studies, we propose a
hybrid architecture consisting of (1) a retrieval model
based on human-authored utterances, (2) multiple
open-domain neural generation models pre-trained on
various online datasets, (3) a dialogue state tracker,
and (4) a neural response selection model trained on
manually annotated data.
Our proposed method starts with domain experts
who create clusters of chatbot utterances and assign
each cluster to a dialogue state. The retrieval model
is responsible for selecting the highest ranked utter-
ances, but only from the cluster corresponding to the
current dialogue state. Meanwhile, the neural gen-
eration models generate multiple response candidates
for the given conversation context. Then, the system
is completed with the response selection model, se-
lecting the best fitting candidate from a set of both
human-authored and generated response candidates.
For each conversation context, both human-
authored and automatically generated response can-
didates are taken into account, and the best fit-
ting response is uttered by the chatbot. However,
the dialogue state tracker contains a set of rules to
block the generation models under certain circum-
stances. For instance, at the end of each dialogue
state, human-authored utterances are prioritized to ac-
complish seamless transitions between the states.
The dialogue states and human-authored utter-
ances may provide the domain experts control over
the dialogue flow, similar to pre-scripted systems.
Meanwhile, the inclusion of generation models and
the possibility of delivering automatically generated
responses increase the variation of utterances. Like-
wise, they add the value of responding to unexpected
conversation contexts. Hence, with generation mod-
els, we explore the possibilities to counteract the main
limitations of pre-scripted systems, such as repeti-
tiveness and weak user engagement. Moreover, cur-
rent open-domain generation models are advanced
enough to provide the basic capabilities that are ex-
pected from chatbots in general, such as chit-chatting,
without any human-authoring. This means that the
labour of the domain experts is focused only on craft-
ing domain-specific utterances, without having to deal
with the chatbots’ capacity of handling basic interac-
tions.
Because of the highly sensitive nature of the per-
sonal health domain, the open-domain language mod-
els need to be constrained. From where we stand,
the extent to which this is necessary is an empirical
problem. Nonetheless, solving it is essential. We
hope to reduce the chance of mishaps by implement-
ing checks at 3 different places; (1) dialogue state
tracking, (2) harmful content filtering, and (3) neural
response selection. The monitoring by the dialogue
state tracker reduces deviations from the domain-
specific track. The harmful content filtering provides
a direct intervention to potentially harmful content as
soon as it is generated. Finally, the response selection
model is trained for selecting the response candidate
that is best fitting to the goals of the highly sensitive
domain, consequently, ignoring the harmful contents.
5 METHODOLOGY
Here we discuss the details of our proposed hybrid
framework for long-term multi-session counselling
chatbots. The framework consists of four modules,
explained below. The connection between these mod-
ules is displayed in Figure 1.
Hints of Independence in a Pre-scripted World: On Controlled Usage of Open-domain Language Models for Chatbots in Highly Sensitive
Domains
403
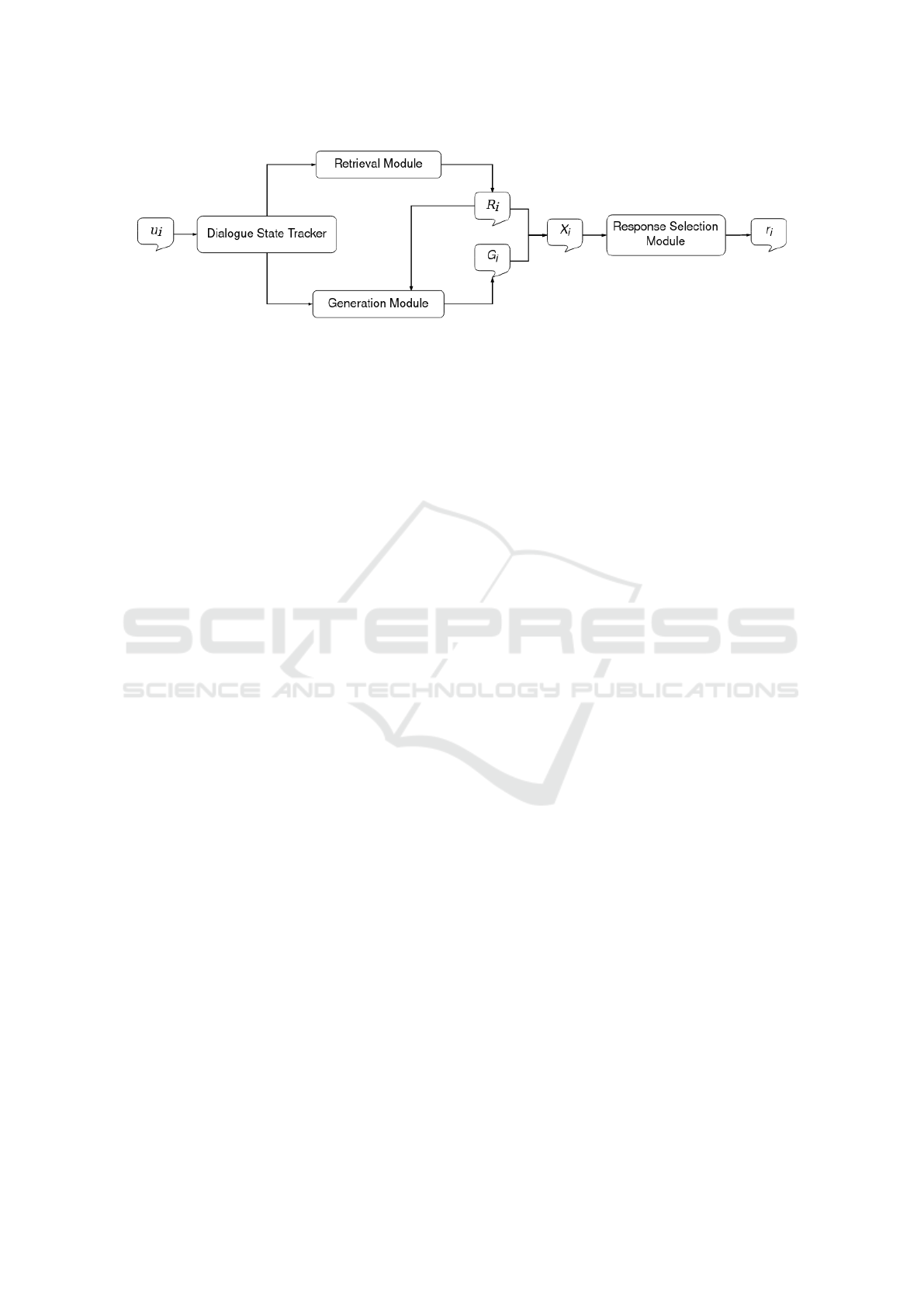
Figure 1: An overview of the pipeline within our proposed hybrid architecture.
• Dialogue State Tracker: This module is respon-
sible for tracking the progress of the dialogue.
Each state s ∈ S corresponds to a pre-defined ques-
tion, and possible reflections and follow-ups.
• Retrieval Module: This module focuses on re-
trieving a set of response candidates, from a pre-
constructed dataset, R, consisting of chatbot utter-
ances. The retrieval algorithm matches the con-
text u
i
of the i-th conversation, with pre-scripted
utterances, R
s
⊂ R, given the dialogue state s. It
then returns the highest ranked response candi-
dates set R
i
for the given context.
• Generation Module: We propose an ensemble
of three pre-trained open-domain generation mod-
els trained on a diversity of training data. Given
the conversation context, u
i
, each language model
generates multiple response candidates. After we
apply a filtering process to eliminate harmful con-
tent, the highest ranked candidates are collected in
a single set, G
i
.
• Response Selection Module: Given the gener-
ated and retrieved response candidates for the i-th
conversation, G
i
and R
i
, this module aims to select
the best response as the final chatbot output r
i
. To
do so, all candidates, X
i
= G
i
∪R
i
, are ranked with
a neural network trained on data obtained by man-
ual annotations.
5.1 Dialogue State Tracker
It is important for human counsellors to collect in-
formation about their patients during an interview.
Hence, these counsellors mostly ask questions at cer-
tain times, listen to the patient’s answers and follow
up by giving reflections on them. In this context, we
can define the relevant chatbot responses as correctly-
timed questions, and appropriate reflections on the
user answers. The dialogue state tracker is a rule-
based model that aims to replicate this highly orga-
nized aspect of human-human counselling.
The dialogue states, in this project, represent
micro-dialogues that we want the conversational
agent to conduct at one point in the conversation.
Each dialogue state, s ∈ S, has corresponding poten-
tial questions, reflections, and follow-ups. Assigning
at least one human-authored utterance to each state is
required to guide the dialogue flow. In the context of
counselling, we can expect a state to start with a coun-
selling question. For instance, the question “How
many cigarettes do you usually smoke in a day?” can
be asked with the hope that it initiates a discussion be-
tween the chatbot and the user on the user’s frequency
of smoking.
We control when a state ends and another begins
via the rules in the dialogue state tracker. We mon-
itor which states have been used in the conversation
and what user information is not available yet to de-
cide on the next dialogue state. Within a state, the
micro-dialogue between the chatbot and the user can
be as short as a single “question-answer-reflection”
triplet, or the reflection can be followed by more ex-
changes until the conversation reaches a limitation
preset. Moreover, we implement an intent classifier
to detect whether the user expresses explicit interest
in proceeding to the next state. If the limit is reached
or the user’s interest is detected, the chatbot proceeds
with the question of the next dialogue state.
5.2 Retrieval Module
The information retrieval-based conversational mod-
els aim to return the appropriate response to the user’s
final query from pre-constructed conversation cor-
pora. Unlike the common retrieval-based approaches,
the pre-constructed dataset in this project only con-
sists of conversational agent utterances which are
hand-crafted by the subject domain experts.
We divide the dataset into subsets corresponding
to the dialogue states. For a given dialogue state s,
there is a subset of the chatbot utterances, R
s
⊂ R,
containing the potential questions, reflections, and
follow-ups. The utterances in R
s
can only be pre-
sented to the user during the dialogue state s. Hence,
at the i-th conversation with a given dialogue state s,
the set of highest-ranked response candidates R
i
can
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
404

only be selected from the dialogue state utterances set
R
s
, and so making R
i
⊂ R
s
.
The retrieval of the utterance candidates set R
i
can
be performed by an information retrieval algorithm,
which is BM25 in our case. For each conversation
context u
i
during the dialogue state s, the retrieval al-
gorithm matches u
i
with the pre-scripted utterances
in the set R
s
. The retrieval algorithm then returns the
most relevant k number of utterances, R
i
.
5.3 Generation Module
The retrieval-based approach assumes that the appro-
priate response is pre-existing in the conversation cor-
pora. The generation-based approach, however, can
construct coherent and unique responses even for an
unseen conversational context. In this study, we ex-
plore the potential of 3 state-of-the-art pre-trained
open-domain neural generation models, namely GPT-
3, BERT, and DialoGPT.
In order to guide the pre-trained models to pro-
duce responses that are relevant and specific to the
conversation context, we implement a prompt gener-
ator that prepares the input to be given to the gener-
ation models. For each conversation context u
i
, the
prompt p
i
is generated from: (1) the combination of
the conversation context, u
i
, (2) the retrieved candi-
date utterances, R
i
, and (3) a selection of informa-
tion from the user database. Evidently, the pre-trained
models do not only take the conversation context into
account. Their generation process is also influenced
by the retrieved candidate utterances, R
i
, which are
hand-crafted by the domain experts. By this addition,
we anticipate that the generation models will adapt
to a style similar to the human experts (Song et al.,
2018).
In the long-term interaction setup, fitting the entire
dialogue history within the vector of the conversation
context u
i
would become unfeasible. To preserve the
coherence of the dialogue, we explore the outcomes
of feeding the generation models with a distilled ver-
sion of the history. Hence, we include a selection of
user information extracted from the dialogue.
As explained in Section 2, employing pre-trained
generation models without any precautions carries the
risk of exposing users to harmful contents. We accept
that we are unable to know and control what these
generations models may generate. Hence, we propose
to implement a classifier to detect harmful content
and eventually eliminate such cases from the response
candidate sets. We see this implementation as the first
necessary step towards keeping the pre-trained mod-
els in check, with the hope that the constrained setting
reduces the chance of mishaps.
Given the prompt p
i
for the i-th conversation, each
pre-trained model generates a response candidate set;
G
i
GPT 3
, G
i
BERT
, and G
i
DialoGPT
. We combine the sets of
response candidates to create the set of all generated
response candidates G
i
= G
i
GPT 3
∪ G
i
BERT
∪ G
i
DialoGPT
.
Finally, we remove the unwanted content detected by
the harmful content classifier from the response can-
didates set G
i
before the set is sent to the response
selection module.
5.4 Response Selection Module
For each i-th conversation, the retrieved response can-
didates R
i
and the generated response candidates G
i
are combined into the set of all response candidates
X
i
= R
i
∪ G
i
. The response selection module ranks all
response candidates in X
i
and returns the highest scor-
ing candidate r
i
as the final response which should be
uttered by the conversational agent.
Following previous work on domain-adapted
multi-turn response selection (Li et al., 2021; Gu
et al., 2020; Whang et al., 2020), we adopt a recur-
rent neural network approach based on the pre-trained
BERT model. The BERT model is mainly used to en-
code the utterances in the conversation context u
i
and
the response candidates in X
i
. The model is trained
with the next utterance prediction strategy on a corpus
that has been manually created by the domain experts.
Likewise, the BERT model is fine-tuned for domain
adaptation on the same dataset.
6 RELATED WORK
Chatbots in personal health-related domains typically
make use of pre-scripted approaches. He et al. (2022)
designed the dialogue flow of their smoking coun-
selling chatbot on the basis of commercial software
by using rules, human-authored utterances and intent
classifiers. Brixey et al. (2017) used a classifier to
select the highest ranked response candidate from a
database of linked questions and answers for their
HIV counselling chatbot. They addressed the repeti-
tion problem by randomly skipping the highest ranked
candidate. Likewise, Denecke et al. (2021) built their
mental health support chatbot on a system that re-
trieves response candidates from a human-authored
utterances corpus, based on their semantic and syn-
tactic similarities to the user input.
Recently, natural language generation approaches
have become popular for health-related chatbot ap-
plications and for other domains. Saha et al. (2021)
trained a variety of classifiers, based on a Seq2Seq ar-
chitecture and reinforcement learning applications, on
Hints of Independence in a Pre-scripted World: On Controlled Usage of Open-domain Language Models for Chatbots in Highly Sensitive
Domains
405

a manually annotated dialogue corpus for their mental
health chatbot application.
Methodology-wise, we follow the recent work
that has been done on hybrid retrieval-generation
models. Song et al. (2018) created an ensemble of a
retrieval-based model and a generation-based model.
They proposed multi-seq2seq as their generation-
based model, which incorporated the highest ranked
retrieval-based candidates into the generation process.
Likewise, Yang et al. (2019) proposed another hy-
brid retrieval-generation conversation model, where
the generation model also takes the relevant facts re-
trieved from external sources.
7 DISCUSSION
In the best-case scenario, the generation module pro-
duces responses that are more relevant and specific
to the conversation context than the human-authored
responses. This way, the response selection mod-
ule will favour the generated responses, resulting in
a unique experience per user. The human-authored
counselling questions are still enforced by the dia-
logue state tracker, but only at the beginning of each
state. The role of the domain experts becomes guiding
the dialogue by initiating the discussion points and
asking questions. They can set up the dialogue states
and author the first utterances, but the rest of the dia-
logue would consist of generated responses.
Ultimately, the performance of the system relies
on two properties; the performance of the generation
module and the performance of the response selection
module. In the case that only the generation mod-
ule underperforms, the generated responses would be
ignored by the response selection module, causing
the system to only follow the dialogue states and the
human-authored utterances. The chatbot would be-
come a pre-scripted chatbot with a retrieval-based re-
sponse selection.
If only the response selection module underper-
forms, the selection between the human-authored and
generated responses would be arbitrary. Given that
the dialogue state tracker is still in control of the di-
alogue flow and interrupts based on a limited num-
ber of exchanges, the chatbot could turn into its pre-
scripted version.
The case where both the generation module and
the response selection module underperform defines
our worst-case scenario. The response selection mod-
ule may not be able to distinguish an appropriate re-
sponse from a harmful one. Hence, combined with
an underperforming generation module, the risk of
harmful content exposure may reach levels that are
intolerable for highly sensitive domains.
We propose not replacing the pre-scripted dia-
logue flows completely, but enhancing them by in-
cluding open-domain NLG models. Hence, this sys-
tem does not reduce the labour of manually authoring
domain-specific utterances. Our proposed approach
can be seen as an improvement over pre-scripted chat-
bots in an attempt to counteract their main limita-
tions. From that perspective, it reduces the repetitive-
ness, increases the flexibility, and handles mundane
chatbot tasks without any human labour. Addition-
ally, we acknowledge that the current technological
advancements cannot fully replace a human counsel-
lor. Keeping that in mind, our efforts aim to create
a support system that people in need may hopefully
benefit from.
To understand how effective our approach is, we
plan to evaluate it by human evaluation methods, as
we prioritize understanding the engagement of our
chatbot with humans (Novikova et al., 2017; van der
Lee et al., 2021). We are going to conduct a user
study where we measure naturalness, relevance, con-
sistency, quality, and enjoyment. Naturalness will be
measuring how natural sounding the utterances are,
while relevance will be based on relevancy of the ut-
terances to their corresponding conversation contexts.
Finally, we will ask the users about the overall consis-
tency and quality of the entire conversation, alongside
how much they enjoyed talking to the chatbot.
8 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we present a new approach for develop-
ing multi-session long-term counselling chatbots for
highly sensitive domains such as personal health. We
explore the usage of open-domain NLG models to in-
crease enjoyability and to counteract the main limita-
tions of pre-scripted chatbots. Our proposed solution
is a hybrid approach that consists of a dialogue state
tracker, a retrieval module, three open-domain NLG
models, and a neural response selection module.
In taking this approach, we aim for the best of two
worlds: we expect the retrieval model and the dia-
logue state tracker to establish a controlled and effec-
tive dialogue flow, while the neural generation models
add variety and the flexibility to respond to any con-
versation context.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project is partly financed by the Dutch Research
Council (NWO) with project number 406.DI.19.054.
ICAART 2022 - 14th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
406

REFERENCES
Bender, E. M., Gebru, T., McMillan-Major, A., and
Shmitchell, S. (2021). On the dangers of stochastic
parrots: Can language models be too big? . In Proc.
of FAccT 2021.
Bommasani, R., Hudson, D. A., Adeli, E., Altman, R.,
Arora, S., von Arx, S., Bernstein, M. S., and et al.
(2021). On the opportunities and risks of foundation
models. CoRR.
Brixey, J., Hoegen, R., Lan, W., Rusow, J., Singla, K., Yin,
X., Artstein, R., and Leuski, A. (2017). SHIHbot:
A Facebook chatbot for sexual health information on
HIV/AIDS. In Proc. of the 18th Annual SIGdial Meet-
ing on Discourse and Dialogue. ACL.
Brown, T., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J. D.,
Dhariwal, P., Neelakantan, A., and et al. (2020). Lan-
guage models are few-shot learners. In NeurIPS.
Caliskan, A., Bryson, J., and Narayanan, A. (2017). Se-
mantics derived automatically from language corpora
contain human-like biases. Science.
Chen, H., Liu, X., Yin, D., and Tang, J. (2017). A survey on
dialogue systems: Recent advances and new frontiers.
SIGKDD Explor. Newsl.
Denecke, K., Vaaheesan, S., and Arulnathan, A. (2021). A
mental health chatbot for regulating emotions (sermo)
- concept and usability test. IEEE Transactions on
Emerging Topics in Computing.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K.
(2019). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional
transformers for language understanding. In Proc. of
the NAACL 2019: Human Language Technologies.
Floridi, L. and Chiriatti, M. (2020). Gpt-3: Its nature, scope,
limits, and consequences. Minds and Machines.
Gatt, A. and Krahmer, E. (2018). Survey of the state of the
art in natural language generation: Core tasks, appli-
cations and evaluation. JAIR.
Gu, J.-C., Li, T., Liu, Q., Ling, Z.-H., Su, Z., Wei, S., and
Zhu, X. (2020). Speaker-aware bert for multi-turn re-
sponse selection in retrieval-based chatbots. In Proc.
of the CIKM’20. ACM.
Gururangan, S., Marasovi
´
c, A., Swayamdipta, S., Lo, K.,
Beltagy, I., Downey, D., and Smith, N. A. (2020).
Don’t stop pretraining: Adapt language models to do-
mains and tasks. In Proc. of the 58th ACL.
He, L., Basar, E., Wiers, R., Antheunis, M., and Krah-
mer, E. (2022). Can chatbots support smoking ces-
sation? a study on the effectiveness of motivational
interviewing on engagement and therapeutic alliance.
Manuscript submitted for publication.
Krahmer, E., Bosse, T., and Bruijn, G.-J. (2021). Chatbots
and health: General. The International Encyclopedia
of Health Communication.
Li, L., Li, C., and Ji, D. (2021). Deep context modeling
for multi-turn response selection in dialogue systems.
Information Processing & Management.
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G., and Dean,
J. (2013). Distributed representations of words and
phrases and their compositionality. In Proc. of the
26th International NeurIPS.
Novikova, J., Du
ˇ
sek, O., Cercas Curry, A., and Rieser, V.
(2017). Why we need new evaluation metrics for
NLG. In Proc. of EMNLP 2017. ACL.
Peters, M. E., Neumann, M., Iyyer, M., Gardner, M., Clark,
C., Lee, K., and Zettlemoyer, L. (2018). Deep contex-
tualized word representations. In Proc. of NAACL.
Rousseau, A.-L., Baudelaire, C., and Riera, K.
(2020). Doctor gpt-3: Hype or reality?
https://www.nabla.com/blog/gpt-3/. Accessed:
2021-10-18.
Saha, T., Chopra, S., Saha, S., Bhattacharyya, P., and Ku-
mar, P. (2021). A large-scale dataset for motivational
dialogue system: An application of natural language
generation to mental health. In IJCNN 2021.
Schlesinger, A., O’Hara, K., and Taylor, A. S. (2018). Let’s
talk about race: Identity, chatbots, and ai. In ACM
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.
See, A., Roller, S., Kiela, D., and Weston, J. (2019). What
makes a good conversation? how controllable at-
tributes affect human judgments. In Proc. of NAACL:
Human Language Technologies. ACL.
Song, Y., Li, C.-T., Nie, J.-Y., Zhang, M., Zhao, D., and
Yan, R. (2018). An ensemble of retrieval-based and
generation-based human-computer conversation sys-
tems. In Proc. of IJCAI-18.
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., and Le, Q. V. (2014). Sequence to
sequence learning with neural networks. In NeurIPS.
Tao, C., Gao, S., Shang, M., Wu, W., Zhao, D., and Yan,
R. (2018). Get the point of my utterance! learning
towards effective responses with multi-head attention
mechanism. In Proc. of IJCAI-18.
van der Lee, C., Gatt, A., van Miltenburg, E., and Krahmer,
E. (2021). Human evaluation of automatically gener-
ated text: Current trends and best practice guidelines.
Computer Speech & Language.
Vinyals, O. and Le, Q. V. (2015). A neural conversational
model. In ICML Deep Learning Workshop.
Whang, T., Lee, D., Lee, C., Yang, K., Oh, D., and Lim,
H. (2020). An effective domain adaptive post-training
method for bert in response selection. In Proc. Inter-
speech 2020.
Xu, B. and Zhuang, Z. (2020). Survey on psychotherapy
chatbots. Concurrency and Computation: Practice
and Experience.
Yang, L., Hu, J., Qiu, M., Qu, C., Gao, J., Croft, W. B., Liu,
X., Shen, Y., and Liu, J. (2019). A hybrid retrieval-
generation neural conversation model. In Proc. of
CIKM’19. ACM.
Zhou, L., Gao, J., Li, D., and Shum, H.-Y. (2020). The
design and implementation of xiaoice, an empathetic
social chatbot. Computational Linguistics.
Hints of Independence in a Pre-scripted World: On Controlled Usage of Open-domain Language Models for Chatbots in Highly Sensitive
Domains
407
