
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test
Design and Execution
Igor Ernesto Ferreira Costa
a
and Sandro Ronaldo Bezerra Oliveira
b
Graduate Program in Computer Sciense, Institute of Exact and Natural Sciences,
Federal University of Pará Belém, Pará, Brazil
Keywords: Exploratory Test, Syllabus, Software Test Education.
Abstract: Exploratory Testing has become increasingly widespread in the industry, one of the reasons being the need
to use agile approaches in the quality assurance process. In this context, it was observed that many
professionals in the area are hardly able to apply this approach with systematic procedures because they
understand it as an informal strategy. From a literature review carried out, a great potential for research was
identified, focusing on the education of Exploratory Test Design and Execution. Therefore, this study
presents the process of building a systematic teaching-learning approach to support the Exploratory Tests
Design and Execution, training students to obtain skills, theoretical and practical knowledge relevant to the
industry. For this, a mapping of assets involving the curricula was carried out: training reference for
undergraduate courses in computing from SBC (Brazilian Computer Society), Computer Science Curricula
from ACM/IEEE and the practical guide from TMMi (Test Maturity Model integration), analyzing the
process area of Test Design and Execution. In addition, interviews were conducted with professionals to
identify tools, work products and techniques used to make a teaching-learning approach adherent to industry
practices and guidelines for theoretical knowledge in the academic context. Therefore, this work provides a
set of skills favorable to teaching Exploratory Test Design and Execution, encouraging academic program
managers and professors to use the knowledge generated to help them build disciplines containing a
systematic application of exploratory testing.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2503-4077
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8929-5145
1 INTRODUCTION
The need for quick delivery of products and services
has led to a growth in the more agile software
development process. Consequently, new testing
approaches, considered agile in the specialized
literature, have become protagonists in the industry
so that products and services are offered with quality
as they develop (Gregory and Crispin, 2015). In this
context, the use of Exploratory Testing (ET) has
been quite widespread in the industry as observed by
Elgrably and Oliveira (2017), however it is still
understood by many professionals in the field as an
informal approach, without any structured and
organized procedures, thus not supporting test
process management activities (Pfahl et al., 2014;
Bach, 2015).
Against this, it was observed by the authors,
from a literature review, that few activities related to
the application of ET are carried out in the test
design phase. Mostly, the application of only
execution activities, correlating them to the software
development cycle was noticed (Costa and Oliveira,
2020).
For this, the importance of a process with well-
structured procedures is highlighted, as when it is
aligned with guidelines prescribed in international
and/or national (in Brazil) standards or good practice
guides, it tends to be carried out systematically. This
can make it possible to reach a very significant level
of effectiveness in discovering defects, as these
documents are organized records of market
experiences, uniting theory and practice (Crespo et
al., 2004; Naik and Tripathy, 2008).
From this, this work aims to present a teaching-
learning approach directed to the activities of Design
and Execution of ET. This approach is divided into
teaching units, aimed at the systematic application of
Costa, I. and Oliveira, S.
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution.
DOI: 10.5220/0010955300003182
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2022) - Volume 2, pages 303-315
ISBN: 978-989-758-562-3; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
303

ET and based on constant practices and sub-
practices in the Test Design and Execution process
area, prescribed in TMMi. About the syllabus and
subjects that served as a reference for the
construction of this approach, the Training
Benchmark (RF) for Undergraduate Courses in
Computing provided by the SBC and the guidelines
contained in Computer Science (CS) Curricula
provided by the Association for Machinery and the
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineer
(ACM/IEEE) were used.
In this context, this work has the following
Research Question (PQ): How to develop an
approach that adopts teaching guidelines for
Exploratory Test Design and Execution, which
develops knowledge and skills in students relevant
to the software industry?
In addition to this introductory section, this paper
is structured as follows: Section 2 presents the
theoretical foundation, Section 3 presents some
related works, Section 4 presents the research
methodology, Section 5 presents the assets mapping,
Section 6 presents the interview carried out with
professionals/experts, Section 7 presents an
evaluative discussion on the proposal of this paper,
Section 8 presents a proposed Syllabus and Section
9 presents the conclusions and future work.
2 THEORETICAL FOUNDATION
This section presents concepts of Exploratory Testing
and a description of the reference curricula addressed
in this work.
2.1 Exploratory Testing
It is an experience-based testing approach, in which
the tester spontaneously and freely designs and runs
tests based on their acquired knowledge, prior
exploration of the test item, including previous test
results (ISO/IEC/IEEE, 2013; Bach, 2004; Kaner,
2008). ET is defined as learning, test design, and
concurrent execution, that is, tests are not defined in
advance in a test plan, but are dynamically designed,
executed, and modified. The effectiveness of ET
depends on the tester's knowledge, which can be
gained from many resources, for example, product
behavior observed during testing, familiarity with
the application or application domain, the platform,
the failure process, the types of incidents already
detected, and the risk associated with a particular
product (Swebok, 2014).
For Gregory and Crispin (2009), ET is an agile
testing approach that can be applied in a targeted way
to what is proposed in the Agile Testing Quadrant by
Huttermann (2011). In which the tests are subdivided,
raising the participation and subsequent quality of the
professional who performs them.
It is emphasized that Bach (2015) defining that
such a test approach consists of evaluating a product
by learning about it from exploration and experiment-
tation, including to some degree: questioning, study,
modeling, observation, inference, among others.
This work is based on the concept defined by
Bach (2015), who also argues that the ET is a formal
and structured approach, which exemplifies by
analogy with the case of taxi racing, where the client
does not request the race plan for trust the intentions
and competence of taxi drivers. The same happens to
the use of ET, where the tester trusts the implicitly
adopted exploration strategies. Toward this end,
Micallef et al. (2016) identified in their studies that
testers apply many exploration strategies implicitly
depending on the level of education.
According to Suranto (2015), the flexibility of ET
is a very significant factor in the testing process, as it
can be applied at any stage of the software lifecycle.
In this context, Bach (2000) states that due to some
deficiencies that affect process management,
management techniques emerged, such as Session-
Based Test Management (SBTM), Thread-Based
Test Management, Risk-Based Test Management.
These management techniques propose more
structured procedures to provide a systematic
application of ET, considering factors relevant to the
effectiveness of the testing process.
2.2 Test Design and Execution from
TMMi
The TMMi structure for all process areas is composed
of general and specific objectives, practices, and sub-
practices, in addition there are work products for each
practice. Among the many areas, Test Design and
Execution has the proposal to improve the capacity of
the test process during the activities of design, test
execution and analysis from the establishment of
architectural technical specifications, performing a
structured test execution process as well as managing
incidents at closure (Van Veenendaal, 2018).
The structured testing implies the application of
test design techniques with the possibility of using
tools. These test design techniques are used to derive
and select test conditions and test cases from design
requirements and specifications. A test case consists
of the description of input values, preconditions,
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
304

expected results and postconditions. All this
information is implemented as test procedures, which
are specific test actions. Among such information, the
specific test data required are essential to allow the
execution of test procedures in an organized way
(Van Veenendaal, 2018).
All these Test Design and Execution activities
follow the testing approach defined in the test plan. In
this way, specific test project techniques are based on
the product level and risks identified in the planning.
Finally, test execution activities are all about
discovering, reporting, and evaluating incidents aimed
at closure. It is emphasized that all incidents found
must be reported through an incident management
system and communication to stakeholders must be
carried out through established protocols (Van
Veenendaal, 2018).
2.3 Computer Science (CS) Curricula
and Computing Curricula (CC)
from ACM/IEEE
The ACM and IEEE computing society has made
great efforts to establish international curriculum
guidelines for undergraduate computing programs in
recent decades. Due to the growth and diversification
of the computing area, the curriculum recommend-
dations also grew covering Computer Engineering,
Information Systems, Information Technology,
Software Engineering and Computer Science.
These guidelines are regularly updated to keep
computer curricula up to date and relevant. Samples
of courses and programs are presented to provide
more concrete guidance related to the curriculum
structure and the development of numerous
institutional contexts (ACM/IEEE, 2013).
They established principles to the curriculum of
Computing courses that are about skills expected
from students. The principles define how a curriculum
must be designed to provide the ability of graduates to
be flexible to work in many subjects, that is, it must
prepare students for a variety of professions and,
above all, identify the skills and knowledge that
students should possess, while providing greater
flexibility in the selection of topics.
In the CS-Curricula of 2013 three levels of
knowledge description are established, which are
organized in: Core Tier 1, Core Tier 2 and Elective
(ACM/IEEE, 2013). While in the Computing
Curricula (CC) 2020 new paradigms for computer
education are presented, including emphasizing the
need to have teaching-learning aligned with industry
practices, also citing systematic ways of evaluating
learning, as well as the possible use from active
methodologies to pedagogical practices to improve
student engagement (ACM/IEEE, 2020).
2.4 Training Referential for the
Graduation Course in Computing
from SBC
The SBC has been fundamental in recent decades in
relation to computer education in Brazil, as it has
always brought up discussions on how undergraduate
courses should be conducted. The SBC has
participated in commissions for the elaboration of
Reference Curriculums or discussed the forms of
evaluation of these courses together with the Ministry
of Education in Brazil. In this context, it is
emphasized that from these curricula and discussions
emerged the National Curriculum Guidelines (DCNs),
which were approved in November 2016, through
Resolution No. 05 of 11/16/2016 (SBC, 2017).
These discussions related to the teaching of
computing at the undergraduate level take place at
many events (congress, workshop, forum,
symposium, etc.) organized by the SBC. From these
discussions and preliminary studies, it created the
"Computer Training Benchmarks" (RFs) for each of
the courses contained in the DCNs: Computer
Science, Computer Engineering, Software
Engineering, Degree in Computing and Information
Systems, including technological graduation. It is
noteworthy that the RFs are aligned with the DCNs
(SBC, 2017).
For each RF of the courses, there is: a presentation,
a brief history of the course or the reference curricula
of the course, the benefits that the course offers to
society, aspects related to the professional training of
the course, the profile of the graduate indicating
expected competences, the training axes, as well as
the competences and contents that make up the FRs
for the course, the relationships of the competences
described in the FRs with the determinations of the
DCNs, considerations on internships, complementary
activities and work course completion, the teaching
and learning methodology, the legal requirements for
the course and, finally, the thanks to several people
who somehow contributed to the construction of that
curriculum (SBC, 2017).
The methodology for preparing the RFs adopts a
competence-oriented approach expected from the
course graduate related to the contents involved in a
given competence. Thus, the RFs were structured to
understand that the expected profile for the graduate
determines the general objective of the course,
decomposed into different formation axes. The
training axes aim to train graduates in generic skills.
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution
305

To achieve each competence, several derived
competences are listed, which determine the need to
be developed in specific content (SBC, 2017).
3 RELATED WORKS
Initially, there was a search in the specialized
literature on approaches focusing on teaching-
learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution
and no work was identified. However, two similar
works were identified on: i) building a curriculum
for broad teaching of software testing, and ii) a
gamified algorithm teaching approach.
In this case, Elgrably and Oliveira (2020) present
a study program designed to be applied face-to-face
to software testing, based on results obtained in a
specialized literature review and asset mapping.
These authors used the documents with guidelines
for processes applied in industry (TMMi and
SWEBOK) and academic (RF-SBC and CS-
Curricula of ACM/IEEE), identifying more at the
level of definition of concepts. If differentiated from
that, this present work did not use SWEBOK
(Software Engineering Body of Knowledge), as it
was more directed to practical activities of Test
Design and Execution, instead of trying to observe
different concepts about the same technique.
In the work of Quaresma and Oliveira (2018), a
gamified teaching framework aimed at the curricular
component of algorithms and equivalent was
proposed. The elaboration of this framework was
based on a systematic literature review. It is noted
that the authors are based on specialized literature,
but do not use national and/or international
curricular inputs.
Therefore, there are some similarities with the
other works when observing the analysis inputs to
carry out the asset mapping, aiming to develop a
teaching-learning approach. However, the
differential of this work is that it focuses on
theoretical and practical activities of Design and
Execution of Exploratory Tests, which will support
the development of a teaching plan containing more
practical subjects that are essential for the systematic
application of ET in the industry.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In first step, the Thematic was identified, where the
definition of the subject to be studied was carried out
based on a literature review, discovering a great
potential for studies in the context of Exploratory
Test Design and Execution education (Costa and
Oliveira, 2020). For this, the great importance of
identifying both the inputs for a documental analysis
of curriculum guidelines was perceived, as well as
investigating in the industry the tools, techniques
and work products used to support the preparation of
a teaching plan, directed to the corresponding
subject, with practical applications relevant to the
industry and adhering to curriculum guidelines.
In the asset mapping step, input for analysis was
identified, where the RF-SBC, CS-Curricula of
ACM/IEEE and TMMi were selected. The first two
for presenting national and international curriculum
guidelines, respectively, and the last one for having
a process area that deals specifically with the
structured and systematic application of Test Design
and Execution. From this, a mapping of assets was
carried out based on the identification and cross-
analysis of information in the curriculum guidelines
and in the application, guide referring to assets
relevant to the activities of Design and Test
Execution, in general.
In the interview step, the target audience was
defined, establishing that the participants should be
professionals in software testing accredited by a
national (Brazilian) and international institution, or
professionals who had professional certification in
TMMi, with experience in process improvement of
test, to be able to obtain answers relevant to the
elaboration of a teaching plan for Exploratory Test
Design and Execution involving practical subjects
closer to reality.
From that, there was a definition of the questions,
which were established based on the Test Design
and Execution process area prescribed in TMMi,
which contains established practices based on the
experiences of several professionals. Finally, there
was the application of interviews and data analysis,
with interviews being carried out remotely with each
professional interviewed. Subsequently, the analysis
and summarization of data took place.
Therefore, at the step of construction of the study
program, there was a definition of general
competences that a student needs to acquire, which
were established from the mapping and based on the
competences present in the RF-SBC and CS-
Curricula. Subsequently, there was the construction
of the study program, where there was the
organization, structuring and documental record of
the teaching-learning approach.
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
306

5 ASSET MAPPING
In the mapping, curricular assets aimed at the
teaching and learning of Test Design and Execution
were established, which provided support for the
elaboration of an approach on these activities. For
this, there was first the definition of the theme to be
research, which occurred through a literature review
and selection of inputs (guides, curricula) to be
analyzed. In this context, the following were used
for analysis: i) the TMMi, with specific attention to
the Test Design and Execution process area, ii) the
RF-SBC, being observed for the Software
Engineering and Computer Science course, and iii)
the “CS-Curricula 2013” of the ACM/IEEE, being
observed the Software Engineering course (Costa
and Oliveira, 2021a).
In the mapping, 13 assets and 110 items of assets
adhering to the guidelines prescribed in the
international and national curriculum for Test
Design and Execution were identified, involved in a
correspondence at two levels, as follows: a) Training
axes (RF-SBC) and knowledge areas (ACM/IEEE)
related to the TMMi Test Design and Execution
process area, b) Derived competences and contents
(RF-SBC), as well as topics and learning outcomes
(ACM/IEEE), which were related to the specific
goals, specific practices and sub-practices of the
TMMi process area, which is the focus of this work
(Costa and Oliveira, 2021a).
The mapping made it possible to observe the
main competences expected by the egress in
undergraduate courses in computing defined at
national and international level, referring to the
context of Test Design and Execution (Costa and
Oliveira, 2021a).
6 INTERVIEWS WITH
PROFESSIONALS
The interviews were conducted with implementing
professionals and/or evaluators of MPT.Br
(Brazilian Software Testing Process Improvement)
and TMMi, and with professionals without
accreditation, but working in the Software Testing,
mainly in process improvement. The goal was to
identify tools, techniques and/or methods, and work
products relevant to ET Design and Execution
activities used by professionals in the industrial
context and that adhere to the practices and goals
contained in the TMMi (Costa and Oliveira, 2021b).
First, pairs validated the questions established
during the interview to certify that there was a
coherent relationship with the TMMi Test Design
and Execution practices, as well as the assessment of
the target audience and the guidelines established for
the execution of the interview from the application
of the review.
After the review, interviews were carried out
remotely with each participating professional.
Therefore, data were consolidated in a graph to
facilitate the visualization.
The results were organized into three groups: 1)
identification of participants, 2) identification of
tools, techniques and/or models, and work products
in the ET Design, and 3) identification of tools,
techniques and/or models, and work products in the
ET Execution. Thus, in group “1” all participants
had more than 5 years of experience in Software
Testing and with the ET approach, having their first
contact with ET in the workplace or studying on
their own. In group "2" the Testlink and Jira tools
were the most used to support Design activities, with
risk analysis being the most cited technique for
activities of identification and prioritization of
conditions and test data, also serving as a
complement to the application of ET (Costa and
Oliveira, 2021b).
As for the work products, the most cited were the
use of the test plan and results of previous test runs
in which the ET was applied. In group “3”, the
Mantis and Jira tools were most mentioned to
support test management and execution. Regarding
execution techniques, the use of ET with manual and
automated strategy is noted, and regarding work
products, the Incident Report and Matrix were the
most cited. It is noted that a tool serves several
activities related to ET Design and Execution, with
risk analysis as a widely used technique and incident
reports being important in the analysis to make
decisions regarding the test process (Costa and
Oliveira, 2021b).
7 SYLLABUS EVALUATION
The results of the Peer Review are presented in
Table 1, with an identifier (ID) being assigned to
each change request, a category to which the request
belongs, the item to be adjusted, the comment
justifying the reason for the adjustment and the
suggestion of improvement. In this case, it is
mentioned that the categories are: High Technician
(TA), indicates that a problem was found in an item
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution
307
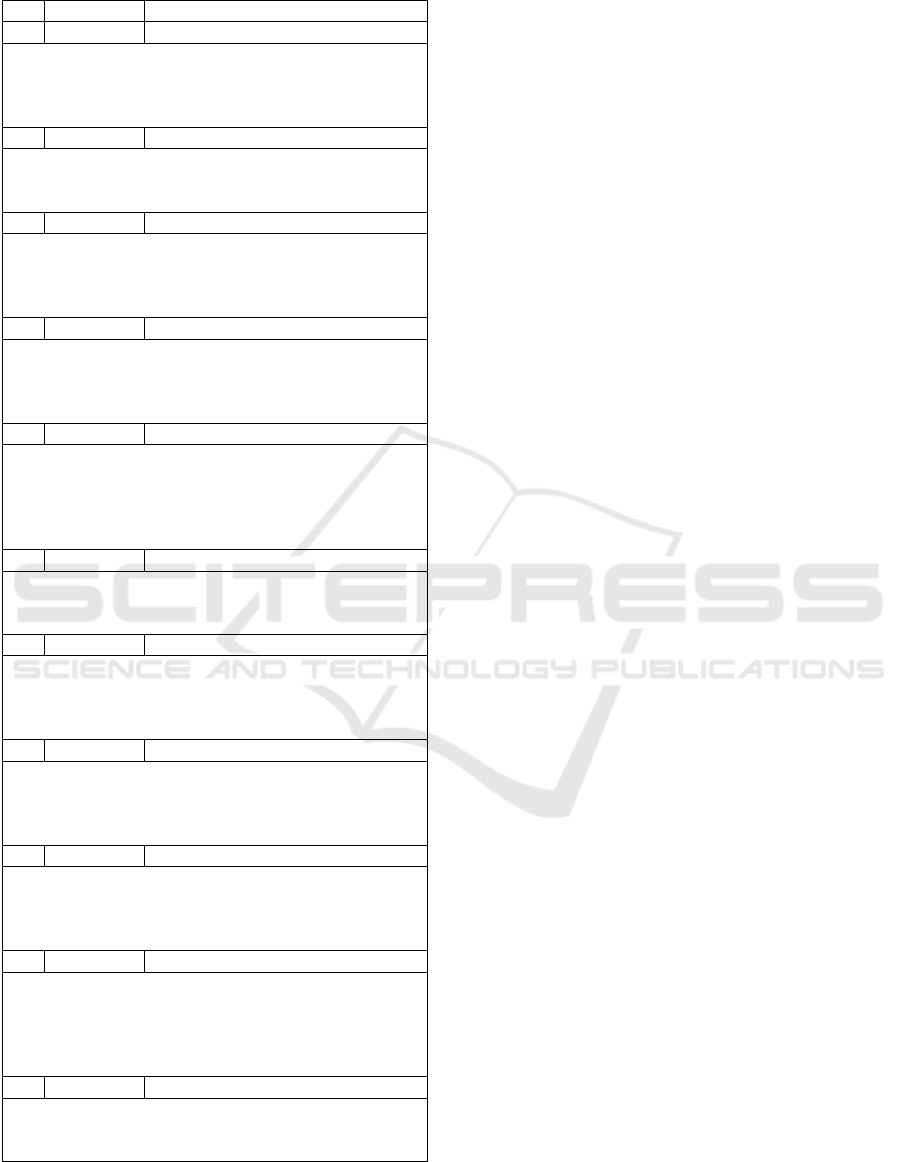
Table 1: Peer Review Adjustment Items.
ID Cate
g
or
y
Item
1 E Teachin
g
A
pp
roach
Comment: There are words and grammatical and
spelling errors throughout the text.
Suggestion: Fix these errors and replace the words
with more formal texts.
2 E Introduction
Comment: No reference was made to the mapping of
curriculum assets.
Su
gg
estion: Include asset ma
pp
in
g
.
3 TB Com
p
etences and Teachin
g
Units
Comment: Competences and Teaching Units are
comprehensive for any type of test.
Suggestion: Customize these competences for
Ex
p
lorator
y
Tests.
4 TB Sub
j
ect Plannin
g
Comment: The origin of the definition of Teaching
Units was not specified.
Suggestion: Define that the Teaching Units maintained
com
p
liance with the TMMi.
5 E Descri
p
tion of Teachin
g
Units
Comment: There is no reference from where the
elements that make up the description of the Teaching
Units were extracted.
Suggestion: Reference the base work to describe the
teaching units.
6 E Learning Level Element
Comment: There is no reference from where the
Learning Level elements were extracted.
Suggestion: Reference Bloom's Revised Taxonomy.
7 TB Ex
p
ected Results in Teachin
g
Units
Comment: The expected results of the teaching units
are not objectively detailed.
Suggestion: Be clearer and more objective, detailing
the expected results of the teaching units.
8 TB Learnin
g
Levels of Teachin
g
Units
Comment: Some levels of learning are not aligned
with expected results.
Suggestion: Review the alignment between learning
levels and expected results for each teaching unit.
9 E Teaching Strategies
Comment: There is no reference to the use of possible
tools commonly used in the industry.
Suggestion: Reference the work that analyzes tools
used in industry.
10 TA Selection of Pedagogical Practices
Comment: The selection of pedagogical practices used
for the administration of teaching units was not
justified.
Suggestion: Inform the references used for a selection
of
p
eda
g
o
g
ical
p
ractices.
11 TB Teachin
g
Unit Detail
Comment: Some learning levels detailed in each
teaching unit are not in line with its description.
Su
gg
estion: Review this ali
g
nment.
that, if not changed, will compromise the
considerations, Low Technician (TB), indicates that
a problem was found in an item that it would be
convenient to change, Editorial (E), indicates that an
error in current language was found or that the text
could be improved, Questioning (Q), indicates that
there were doubts about the content of the
considerations, General (G), indicates that the
comment is general regarding the considerations.
It is noteworthy that all adjustments requested by
the expert were implemented by the author of this
study, which enabled the elaboration of a program of
studies that adhered to the curricula obtained as
inputs and the practices prescribed in the TMMi.
8 SYLLABUS
It is mentioned that it is widely known in society
that there is no single form or even a single model of
education. However, the academic and professional
community joins efforts to develop study programs
involving many topics related to the computing,
which may be sufficient to promote skills and
abilities to students in order to prepare them for the
labor market. This fact is evidenced in the CS-
Curricula, RF-SBC and in the current CC2020, as
they present structured curriculum guidelines that
seek to develop the cognitive potential of graduates,
in line with the theory of the area and practical
knowledge in the industry. In this context, Higher
Education Institutions (HEIs) remain adherent to
these study programs, as they use them as a
fundamental basis for preparing their course syllabi
(ACM/IEEE, 2013; ACM/IEEE, 2020; SBC, 2017).
Through the new update of the curriculum
(CC2020) of the ACM/IEEE, this work underwent
new revisions to keep in line with the new
approaches, syllabus and especially the skills
expected of graduates of the undergraduate course in
computing. The importance of keeping the syllabus
of the computing always up to date is highlighted, in
order to adapt to the rapid and recurrent changes in
the area and in the teaching of computing in general,
in addition to meeting the needs of the software
industry. This continuous development of teaching-
learning syllabus must be constant, as new skills are
also required from students, especially in the labor
market. Thus, the forms and contents must be
updated considering perspectives of providing
autonomy to students, obtaining outstanding
participation and prominence in the current world
scenario.
To build a good curriculum, in (Harnish et al.,
2011) the authors mention that it is interesting to
involve eight learning components: (1) basic
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
308

information about the course and contact
information, (2) course purpose, including goals and
objectives, (3) instructor teaching philosophy and
beliefs, (4) course assignments and schedule, (5)
required and optional materials, including textbooks
and supplemental reading, such as newspapers, (6)
methods of instruction and course delivery, (7)
assessment procedures, and (8) learning resources
for students. This work addresses the first three
topics mentioned by Harnish et al. (2011), since the
authors chose to separate the syllabus aimed mainly
at the construction of knowledge units and a
teaching plan partially using this program.
Therefore, based on the results obtained from the
mapping and the interviews, the construction of a
approach began, organized in a teaching unit for the
Design and Execution of Exploratory Tests,
according to the analyzed inputs. In this context, it is
important to highlight, initially, the importance of
Bloom's Revised Taxonomy in this work.
8.1 Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy
In all expected results, for each teaching unit, the
expected level of cognitive ability was defined. In
this case, Bloom's Revised taxonomy was used,
which presents a model that classifies the different
levels of human cognition of thinking, learning and
understanding. The use of this taxonomy aims to
facilitate the exchange of questions about
Exploratory Test Design and Execution, in addition
to helping in the planning, organization and control
of learning objectives. It is noteworthy that over the
years this taxonomy has been revised to meet new
contexts. Thus, the new update is called Revised
Bloom's Taxonomy, where, in part, it maintains an
original structure, however it is more adequate to
support the new learning approaches, consequently,
it has the perspective of extracting the maximum
benefit from educational goals (Ferraz and Belhot,
2010; Anderson and Krathwohl, 2001).
Therefore, Bloom's Revised Taxonomy is divided
into two dimensions: knowledge and the cognitive
process. The possible capabilities of the knowledge
dimension and associated verbs are: (i) Factual
Knowledge, where the student must be able to
master the basic content so that he can perform tasks
and solve problems, (ii) Conceptual Knowledge,
where the student must be able to understand the
interrelationship of the basic elements in a more
elaborate context, so the simple elements need to be
connected for the formation of knowledge, (iii)
Procedural Knowledge, where the student must be
able to involve the knowledge of achieving an
objective using methods, criteria, algorithms and
techniques, thus the abstract knowledge is
stimulated, and (iv) Metacognitive Knowledge,
where the student must be aware of the breadth and
depth of the knowledge acquired, so there is a
relationship with the knowledge previously
assimilated to solve a given problem. On Fig. 1 are
possible capabilities of the cognitive and verbs.
On the other hand, the possible capabilities of the
cognitive process dimension and associated verbs
are: (i) Remember, where the student must recognize
and reproduce ideas and learned content, (ii)
Understand, where the student must relate a
connection between the new and previously acquired
knowledge and must be able to explain it in their
own words, (iii) Apply, where the student must
know how to relate the execution of a knowledge
procedure in a specific or new situation, (iv)
Analyze, where the student must relate the
understanding of the relevant and irrelevant parts of
a given knowledge and the understanding and
correlation between different parts of knowledge, (v)
Assess, where the student must be able to make
judgments based on criteria and standards pertaining
to acquired knowledge, (vi) and Create, where the
student must be able to develop new and original
ideas, products and methods, using previously
acquired knowledge and skills.
8.2 Parameters for the Construction of
the Teaching and Learning
Approach
At this step of the research, the appropriate
components were established in the definition of a
generic program, which includes: the prerequisites,
the program objectives, the guiding questions, the
syllabus of each teaching unit, the proposition of
problems, the results to be obtained, the expected
level of learning and the additional topics to be
addressed in each teaching unit. Furthermore, it is
crucial to define a teaching strategy (plan), that is, to
create an application instance from this approach,
however this will be a future activity, not addressed
in this work.
The purpose of this study program is to promote
the teaching of Exploratory Test Design and
Execution involving many practical activities
identified in the industry and being adherent to the
corresponding TMMi process area. Table 2 shows
the generic construction of the syllabus with the
characteristics of each component (Elgrably and
Oliveira, 2020; Furtado and Oliveira, 2019).
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution
309
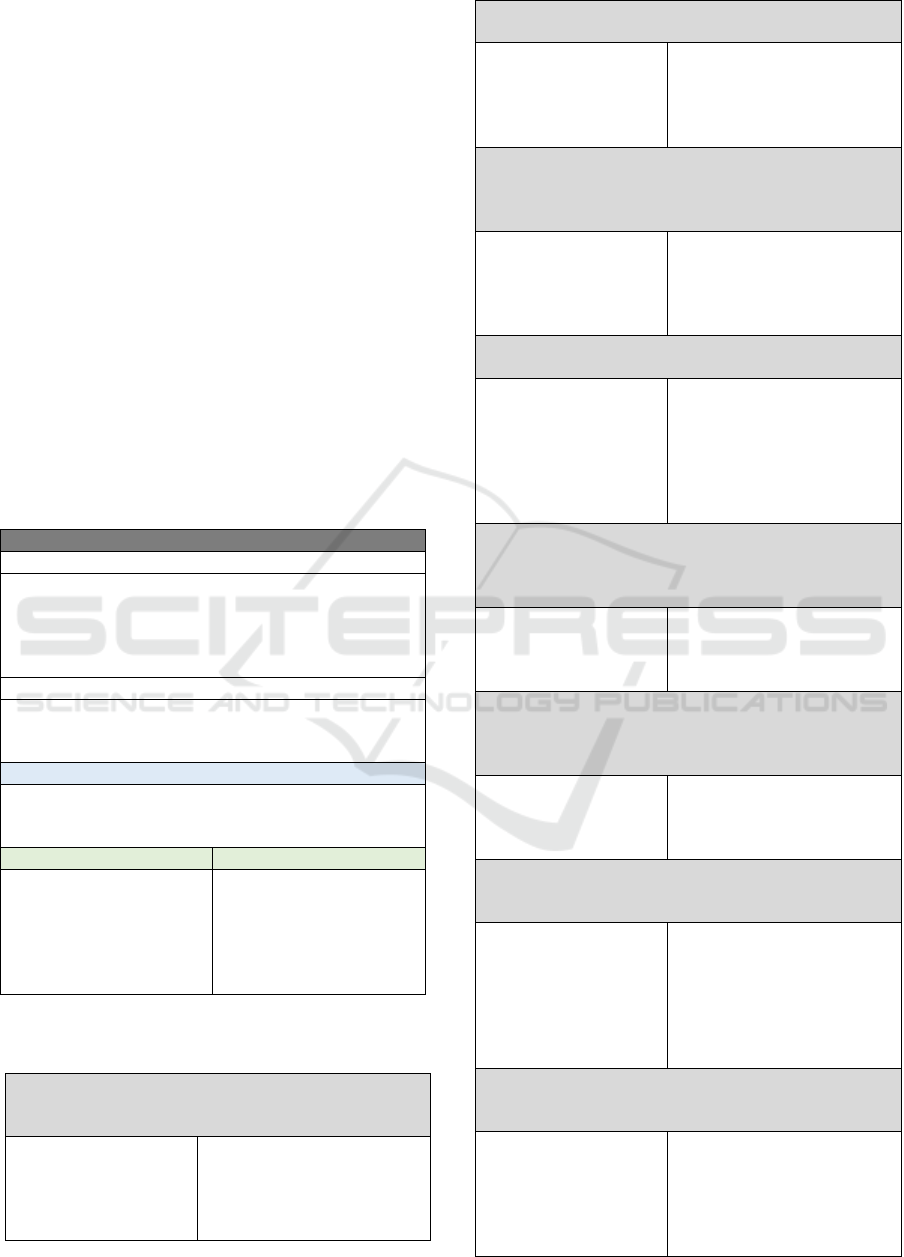
8.3 Learning Units Adhering to
Exploratory Test Design and
Execution
In principle, there was the analysis and identification
of competences that a Software Engineer needs to
perform activities related to Software Test Design
and Execution, being adherent to the specific
practices defined in the corresponding process area
of TMMi. From this, the expected general
competences for the students who graduated from
the teaching-learning process about Design and
Execution of the proposed Exploratory Test were
established. This definition was based on
competences prescribed in the RF-SBC and CS-
Curriculum of the ACM/IEEE, being analyzed from
a mapping of assets contained in these curricula,
presented in Section 4. In Table 3 the general
competences (CG) and the correlation with the
aforementioned curricula are presented.
Table 2: Generic Construction of the Teaching Unit.
Teaching Unit
Prerequisites
These are the subjects or teaching units that can facilitate
learning if they are previously attended by students and
serve as the basis for the subject addressed in this
teaching unit. It is advisable to indicate the reference
curriculum that was used.
Guiding Questions
These are questions asked to students during the
beginning of each unit, which aim to start the discussion
of the to
p
ic.
Programmatic Content (CP)
These are the contents to be taught in the curricular unit,
in view of the skills foreseen for the didactic unit.
Mapping was used to create learning topics.
Ex
p
ected Results Level of Learnin
g
It is what the student must
be able to learn and
perform after learning
accumulated in the unit,
always of an evolutionary
nature.
Each of these expected
results is associated with a
certain level of cognitive
ability and knowledge
dimension of the revised
Bloom's Taxonomy.
Table 3: General competences adopted and corresponding
area in RF-SBC, CS-Curricula and CC.
CG1. Employ methodologies that aim to ensure quality
criteria throughout the exploratory test design and
execution step for a computational solution.
RF-SBC:
i) Computer Science:
Systems Development.
ii) Computer Science:
S
y
stems De
p
lo
y
ment.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/Tools and Environments
ii) SE/Software Design
iii) SE/ Software Verification
and Validation
CG2. Apply software maintenance and evolution
techni
q
ues and
p
rocedures usin
g
the ET a
pp
roach.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Management
and Process.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/Software Evolution
ii) SE/Tools and Environments
iii) SE/ Software Verification
e Validation
CG3. Manage the exploratory test approach involving
basic management aspects (scope, time, quality,
communication, risks, people, integration, stakeholders
and business value).
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Management
and Process.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/ Software Verification e
Validation
ii) SE/ Software Project
Mana
g
ment
CG4. Apply techniques for structuring application
domains characteristics in the exploratory test approach.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Requirements,
Analysis and Design.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/Tools and Environments
ii) SE/Software Design
iii) SE/ Software Verification
e Validation
iv) SE/ Requirement
En
g
ineerin
g
CG5. Apply techniques and procedures for identifying
and prioritizing test conditions (with a focus on
exploratory testing) based on requirements and work
p
roducts generated during software design.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Requirements,
Analysis and Design.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/ Requirement
Engineering
ii) SE/ Software Design
CG6. Apply software model analysis techniques to
enable traceability of test conditions and test data (with a
focus on exploratory testing) to requirements and work
p
roducts.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Requirements,
Anal
y
sis and Desi
g
n.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/ Requirement
Engineering
ii
)
SE/ Software Desi
g
n
CG7. Apply theories, models and techniques to design,
develop, implement and document exploratory testing
for software solutions.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Requirements,
Analysis and Design.
ii) Software Engineering:
Software Construction
and Testing.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/Tools and Environments
ii) SE/Software Design
iii) SE/ Software Verification
e Validation
CG8. Apply validation and verification techniques and
procedures (static and dynamic) using exploratory
testing.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Construction
and Testing.
ii) Software Engineering:
Software Quality.
CS-Curricula / CC:
i) SE/ Software Verification e
Validation
ii) SE/ Software Project
Management
iii) SE/ Software Testing
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
310

Table 3: General competences adopted and corresponding
area in RF-SBC, CS-Curricula and CC (cont.).
CG9. Preemptively detect software failures on systems
from the exploratory test application.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Quality.
CS-Curricula:
i) SE/ Software Verification e
Validation
CG10. Perform integrative testing and analysis of
software components using ET in collaboration with
customers.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Quality.
CC:
i) SE/ Software Testing
CG11. Conduct exploratory testing using appropriate
testing tools focused on the desirable quality attributes
specified by the quality assurance team and the
customer.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Construction
and Testing.
CC:
i) SE/ Software Testing
CG12. Plan and drive the process for designing test cases
(charters) for an organization using the ET approach.
RF-SBC:
i) Software Engineering:
Software Requirements,
Analysis and Design.
CC:
i) SE/ Software Testing
Table 4 presents the curriculum proposal for the
first teaching unit, where CP 1.1 was defined to
provide the basic reference on the activity of
analysis of base work products to support the
Exploratory Test Design. CP 1.2, aims to provide
sufficient learning for deriving exploratory test
conditions from the application of pre-established
test design techniques during the test analysis
activity (CP 1.1). For CP 1.3, the goal is to provide a
basic reference on the strategies for applying the
exploratory test process in a systematic way.
In Teaching Unit I, it is pointed out that the many
subjects were established from the interviews,
discussed in Section 5, as they are related to the need
to involve important fundamentals to form a
theoretical basis necessary to apply such concepts in
practice, while the subjects about use of test design
techniques and prioritization aspects were identified
in the mapping and interview. The use of
exploratory test management techniques and the use
of work products were specifically defined from the
interview. Furthermore, it is mentioned that the
general competences of the unit are CG1, CG4,
CG5, CG6 and CG7.
Table 4: Teaching Unit I.
TEACHING UNIT I - EXPLORATORY TEST
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
Prerequisites
ACM/IEEE: (SE) Software Engineering
SBC: Software En
g
ineerin
g
Guiding Questions
Q1. How to identify which tests (focus on exploratory
testing) are best suited for certain contexts? (CP1 - 1.1)
Q2. What exploratory test management techniques
might be best suited to ensure the effectiveness and
organization of the exploratory test process? (CP1 - 1.1,
1.3)
Q3. How to apply a set of design techniques to identify
test conditions and test procedures, both exploratory?
(CP1 - 1.1, 1.2)
Q4. What criteria are suitable for prioritizing test condi-
tions and test procedures, both exploratory? (CP1 - 1.2)
Q5. What aspects are analyzed for the strategic
definition of an ex
p
lorator
y
test
p
rocess?
(
CP1 - 1.3
)
Programmatic Content
1.1 Introduction to Exploratory Test Analysis
1.1.1. Concepts of agile quality and testing
1.1.2. Test Fundamentals
1.1.3. Test Types, Techniques and Levels
1.1.4. Appropriate work products for the analysis and
identification of test conditions adhering to the test
objective
1.1.5. Introduction to Test Design Techniques
1.1.6. Introduction to exploratory test management
techni
q
ues
(
Session-
b
ased and Threa
d
-
b
ased
)
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student must understand the
basics of software quality and
testing, including the exploratory
testing approach. In addition to
understanding the test design
techni
q
ues to be used.
Remember /
Factual
Understand /
Conceptual
The student must be able to
establish a list of suitable work
products for analysis and
identification of test conditions
and test
p
rocedures.
Remember /
Factual
Understand /
Conceptual
Programmatic Content
1.2 Introduction to the Exploratory Test Design
1.2.1. Practical application of test design techniques
1.2.2. Analysis Aspects for Test Condition
Prioritization and Test Procedures
1.2.3. Practical application of prioritization technique
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student should be able to
identify the test coverage to be
achieved with test design
techniques being aligned with
established test conditions.
Apply / Conceptual
Analyze /
Conceptual
Evaluate /
Procedural
The student should be able to
understand and apply design
technique prioritizing test
conditions and testin
g
p
rocedures.
Understand /
Conceptual
Apply / Conceptual
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution
311

Table 4: Teaching Unit I (cont.).
TEACHING UNIT I - EXPLORATORY TEST
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
Programmatic Content
1.3 Definition of Strategy for Application of the
Exploratory Testing Process
1.3.1. Introduction to the software development cycle
1.3.2. Introduction to the agile testing process (focus on
exploratory testing)
1.3.3. Analysis aspects relevant to the test process
aligned with the test objective
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student must understand and
differentiate the development
c
y
cles discussed.
Understand /
Conceptual
The student must be able to
define an adequate testing
process according to the analysis
performed.
Apply / Procedural
Analyze /
Procedural
Evaluate /
Conceptual
In Table 5, two syllabuses are presented, in which
CP 2.1 is intended to provide a deeper knowledge
both about the application of techniques for
developing test cards according to the pre-
established test conditions, as well as possible
verification criteria intended to support decision
making for further testing. CP 2.2, on the other hand,
aims to provide sufficient knowledge to understand
and correlate the test strategies with established test
charts and provide the student with the ability to
prepare an adequate execution schedule.
In Teaching Unit II, good practices and
exploration strategies were established based on
interviews with professionals in the field. In this
context, from the mapping, it was possible to
establish the verification criteria in initial tests and
development of the agenda. The general
competences of the unit are CG5 and CG7.
Table 5: Teaching Unit II.
TEACHING UNIT II - IMPLEMENTATION OF
EXPLORATORY TEST PROCEDURES
Prerequisites
ACM/IEEE: (SE) Software Engineering
SBC: Software En
g
ineerin
g
Guiding Questions
Q1. How to develop test charts (charters) suitable for
certain contexts? (CP2 - 2.1)
Q2. How to identify suitable criteria for verification of
initial tests? (CP2 - 2.1)
Q3. What exploration techniques might be better suited
to achieving efficiency according to the test charts?
(CP2 - 2.1, 2.2)
Q4. How to develop a sticky test execution schedule
with the predefined test charts? (CP2 - 2.1, 2.2)
Programmatic Content
2.1 Implementation of Preparatory Procedures for
Exploratory Testing
2.1.1. Technique and best practices for writing test
cards
2.1.2. Identification of initial test verification criteria
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student must understand
and apply good practices for
writin
g
test letters.
Understand /
Conceptual
A
pp
l
y
/ Conce
p
tual
The student must be able to
analyze and establish
verification criteria for initial
tests.
Understand /
Conceptual
Analyze / Conceptual
Apply / Conceptual
Programmatic Content
2.2 Introduction to Exploration Strategies and Test
Execution Schedule Development
2.2.1. Exploration techniques
2.2.2. Test Execution Schedule Development
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student must be able to
understand the exploration
techniques and relate them to
the test cards.
Remember / Factual
Understand /
Conceptual
Analyze / Conceptual
The student must be able to
analyze criteria to enable him
to develop a suitable test
execution schedule.
Apply / Procedural
Analyze / Procedural
Evaluate / Conceptual
Create / Conce
p
tual
In Table 6, two syllabuses are presented, in which
CP 3.1 aims to provide a practical knowledge of
exploratory testing, using exploration strategies and
the use of procedures prescribed in the technique,
which provides the structuring of the application
form of this agile test approach. CP 3.2, on the other
hand, aims to provide the understanding and
application of good practices in the field of incident
recording and cause analysis of these incidents, in
addition to establishing good incident
communication practices.
In Teaching Unit III, the subjects are more
focused on the execution of the exploratory test,
involving everything that has been identified and
projected in the previous units. Thus, most issues
were established based on interviews with
professionals in the area, for example, the
establishment of the application of good practices
for the systematic execution of tests, recording and
analysis of incidents. From the mapping, it was
possible to identify the strong need for maintenance
of work products. The general competences of the
unit are CG2, CG8 and CG9.
Table 7 presents two syllabuses, CP 4.1, which
aims to provide a practical knowledge for
conducting incident report reviews, how to prepare
test summary reports following good practices for
effective communication with stakeholders and
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
312

Table 6: Teaching Unity III.
TEACHING UNIT III - EXPLORATORY TEST
EXECUTION
Prerequisites
ACM/IEEE: (SE) Software Engineering
SBC: Software En
g
ineerin
g
Guiding Questions
Q1. How to systematically apply exploratory testing
considering predefined test cards and selected
exploration techniques? (CP3 - 3.1)
Q2. How to apply best practices for recording
incidents? (CP3 - 3.2)
Q3. How to apply best practices for incident cause
analysis? (CP3 - 3.2)
Q5. How to apply good work product maintenance
practices to ensure bidirectional traceability between
requirements, test cards and test procedures from test
results?
(
CP3 - 3.1, 3.2
)
Programmatic Content
3.1 Systematic Application of Exploratory Testing
3.1.1. Practical Execution of Exploratory Testing using
Structured Exploration Techniques
3.1.2. Practical execution of ET usin
g
SBTM.
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student must understand
and apply ET adhering to pre-
defined test charts and
selected exploration strategy
in an ad hoc manner.
Understand /
Conceptual
Apply / Procedural
The student must understand
and apply exploratory testing
following structured
procedures inherent to SBTM
Understand /
Conceptual
Apply / Conceptual &
Procedural
Analyze / Procedural
Programmatic Content
3.2 Introduction to Incident Recording and Cause
Analysis
3.2.1. Applying good incident recording practices
3.2.2. Application of good incident analysis practices
3.2.3 Application of good work product maintenance
p
ractices as per test results
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student should be able to
understand and apply good
practices in recording and
analyzing the cause of
incidents.
Remember / Factual
Understand /
Conceptual
Apply / Procedural
Anal
y
ze / Procedural
The student must be able to
analyze changing criteria or
impacts from the test results
to enable them to maintain a
bidirectional traceability of
the work
p
roducts.
Apply / Procedural
Analyze / Procedural
Evaluate / Conceptual
Create / Conceptual
understand possible appropriate incident remediation
actions. CP 4.2, on the other hand, is intended to
provide the ability to analyze the testing process
using essentially the lessons learned and data
collected on factors that directly and indirectly
influence this process.
In Teaching Unit IV, the review and
communication strategy were established based on
mapping and interviews with professionals in the
area. It is emphasized that the possibility of using
tools was observed in the mapping, while the
interviews identified which tools are commonly
used. From the interviews, it was possible to
establish good practices to improve the process. The
general competences of the unit are CG2 and CG3.
Table 7: Teaching Unit IV.
TEACHING UNIT IV - TEST AND INCIDENT
PROCESS MANAGEMENT
Prerequisites
ACM/IEEE: (SE) Software Engineering
SBC: Software En
g
ineerin
g
Guiding Questions
Q1. How to apply exploratory test session report review
best practices? (CP4 - 4.1)
Q2. How to use good practices for communicating
incidents to stakeholders? (CP4 - 4.1)
Q3. How to apply improvements in the testing process
considering the lessons learned and the communication
strate
g
ies defined?
(
CP4 - 4.1, 4.2
)
Programmatic Content
4.1 Introduction to Incident Management
4.1.1. Report Review Practice Exploratory Test
Sessions
4.1.2. Good practices for communicating incidents to
stakeholders
4.1.3. Introduction to Incident Management Tools
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student should be able to
understand and apply good
practices in reviewing reports
and writing test reports.
Understand /
Conceptual
Apply / Conceptual
& Procedural
The student must understand
and apply proper procedures
for reporting incidents to
stakeholders.
Understand /
Conceptual
Apply / Procedural
Analyze / Procedural
Programmatic Content
4.2 Introduction to Test Process Management
4.2.1. Analysis of lessons learned for exploratory
testing process management
4.2.2. Best Practices for ET Process Improvement
Expected Results Level of Learning
The student must be able to
analyze the lessons learned to
apply proper procedures to the
exploratory test process
management
Remember / Factual
Understand /
Conceptual
Apply / Procedural
Analyze / Procedural
The student should be able to
analyze and apply
improvements in the ET process
by observing the impacts of
chan
g
e.
Apply / Procedural
Analyze / Procedural
Evaluate /
Conceptual
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution
313

9 CONCLUSION
This work presented a program of studies on the
activities of Design and Execution of Software
Exploratory Testing, composed of didactic units
developed with a view to supporting students'
learning in such activities and preparing them for the
professional market. Regarding the research
question, the syllabus established from reference
guides, quality model and data from professionals in
the area used in the software industry made it
possible to generate teaching units strongly adherent
to industry practices in a systematic way, which they
received a favorable opinion by the expert.
Therefore, the teaching-learning syllabus is the
main contribution of this work, which seeks to
indicate contents that can develop knowledge, skills
and competences aligned with the process area
discussed in this work. It is emphasized that the
teaching units were based on different knowledge
areas, but all related to Test Design and Execution,
with a focus on the systematic application of
exploratory testing, aiming to create a content
integration in an evolutionary way of knowledge to
contribute to learning from the students.
In the future, the focus will be on the
construction of a teaching plan for Exploratory Test
Design and Execution, involving activities very
close to reality in the software industry. This
instance must present teaching procedures, support
materials that can stimulate learning, as well as the
use of active learning methods to then be applied in
undergraduate classes in computing. In addition,
avaluate quantitative and qualitative this approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Coordination for
the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel
(CAPES) in Brazil for the financial support for
granting an institutional PhD scholarship.
REFERENCES
ACM/IEEE (2013). Computer Science Curricula 2013.
ACM and IEEE Computer Society. USA.
ACM/IEEE (2020). Computing Curricula: Paradigms for
Global Computing Education. ACM and IEEE
Computer Society. USA.
Anderson, W., Krathwohl, D. (2001). A Taxonomy for
Learning Teaching and Assesing: A Revision of
Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives.
Longman.
Bach, J. (2015). History of Definitions of ET. SATISFICE:
Software Testing For Serious People.
Bach, J. (2000). Session-Based Test Management.
Software Testing and Quality Engineering Magazine.
Bach, J. (2004). Exploratory Testing. The Testing
Software Engineer. 2nd ed., Den Bosch: UTN.
Crespo, A., Silva, O., Borges, C., Salviano, C., Junior, M.,
Jino, M. (2004). A Methodology for Software Testing
in the Context of Process Improvement. SBQS. Brazil.
Costa, I and Oliveira, S. “An Evidence-Based Study on
Automated Exploratory Testing”. 17th CONTECSI.
Brazil. 2020.
Costa, I. and Oliveira, S. “An Asset Mapping in the ACM
/ IEEE and SBC Curriculum to the Test Design and
Execution of the TMMi”. (FIE). 2021a.
Costa, I. and Oliveira, S. “A study on assets applied in
design and execution activities of exploratory test to
be used in teaching-learning: A survey
application”. (FIE). 2021b.
Elgrably, I., Oliveira, S. (2020). Construction of a syllabus
adhering to the teaching of software testing using agile
practices. FIE’20.
Elgrably, I., Oliveira, S. (2017). The Importance of
Application of Agile Tests in the Software Industry:
An Exploratory Approach Using Interview. 14th
CONTECSI. Brazil.
Ferraz, A., Belhot, R. (2010). Bloom's taxonomy:
theoretical review and presentation of the instrument's
adjustments to define instructional objectives. Gest.
Prod. São Carlos, vol. 17, no. 2.
Furtado, J., Oliveira, S. (2019). A Methodology to
Teaching Statistical Process Control in Computer
Courses. 13th ENASE.
Gregory, J., Crispin, L. (2015). More Agile Testing:
Learning Joureys for the Whole and Team. Addison-
Wesley Professional: USA.
Gregory, J., Crispin, L. (2009). Agile Testing: A Pratictal
Guide for Testers and Agile Teams. Addison-Wesley
Professional: USA.
Harnish, R., O’Brien McElwee, R., Slattery, J., Frantz, S.,
Haney, M., Shore, C., Penley, J. (2011). Creating the
foundation for a warm classroom climate: Best
practices in syllabus tone. APS Observer, 24.
Huttermann, M. (2011). Agile Record. The Magazine for
Agile Developers and Agile Testers.
ISO/IEC/IEEE 29119-1 (2013).
Software and systems
engineering, Software testing, Part 1, Concepts and
definitions. Geneve.
Kaner, C. (2008). A Tutorial in Exploratory Testing.
QUEST.
Micallef, M., Porter, C., Borg, A. (2016). Do Exploratory
Testers Need Formal Training? An Investigation
Using HCI Techniques. IEEE. - 9th ICSTW.
Naik, K., Tripathy, P. (2008). Software Testing and
Quality Assurance: Theory and Practice. John Wiley
& Sons, Inc.
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
314

Pfahl, D., Mantila, M., Yin, H., Much, J. (2014). How is
Exploratory Testing Used?: A state of the Practice
Survey. ESEM’14. Torino, Italy.
Quaresma, J., Oliveira, S. (2018). A Gamified Framework
for Teaching and Learning a Subject of Algorithms or
Equivalents. Nuevas Ideas en Informática Educativa,
Chile.
SWEBOK (2014). Guide to the Software Engineering
Body of Knowledge V3.0. IEEE Computer Society.
Suranto, B. (2015). Exploratory Software Testing in Agile
Project. IEEE. - International Conference on
Computer, Communication, and Control Technology,
Malaysia.
Sociedade Brasileira de Computação – SBC (2017).
Training Benchmarks for Undergraduate Computer
Courses. Brazil.
Van Veenendaal, E. (2018). Test Maturity Model
integration – TMMi: Guidelines for Test Process
Improvement. Produced by TMMi Foundation.
A Syllabus to Support Teaching and Learning of Exploratory Test Design and Execution
315
