
Integrating a Multi-Agent Smart Parking System using Cloud
Technologies
Milton Boos Junior
1 a
, Lucas Sakurada
1 b
, Paulo Leit
˜
ao
1 c
, Paulo Alves
1 d
, Gleifer Vaz Alves
2 e
,
Andr
´
e Pinz Borges
2 f
and Diego Roberto Antunes
2 g
1
Research Centre in Digitalization and Intelligent Robotics (CeDRI), Instituto Polit
´
ecnico de Braganc¸a, Braganc¸a, Portugal
2
Federal University of Technology - Paran
´
a (UTFPR), Campus Ponta Grossa, Paran
´
a, Brazil
Keywords:
Multi-Agent System, Cloud Architecture, Smart Parking.
Abstract:
Smart parking (SP) systems are becoming a solution to address the increasing traffic in major cities, which
are related to the traffic congestion, unnecessary time spent searching for parking spots, and, consequently,
environmental issues. These systems intend to help drivers that are searching for available parking spaces in a
given desired location. This paper presents a cloud-based solution to integrate a Multi-Agent System (MAS)
for SP, which enables the modularization, scalability and robustness of such large-scale systems. The MAS
abstraction is a suitable approach to represent the dynamic features of a SP, where multiple drivers arrive,
request, search, and leave the parking spots. The cloud services enable to scale up the use of a MAS, being
an intermediary in the communication between the MAS and the end user, providing a broad architecture that
involves database, asynchronous functions activated by events and real-time message exchange. The cloud
agent-based system was deployed in the parking of an University campus, where users driving bicycles and
cars can request and schedule parking slots that are managed in a distributed manner by the MAS. The obtained
results show the user friendly interaction with the system, the scalability of the system in terms of drivers and
parking spots, as well as the efficient management of the parking spots by the MAS system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the past few years, a considerable population
increase in large cities was noticed. According to
(United Nations, 2019), around 2050, the world’s ur-
ban population will reach 68%, exceeding the current
rate of 55%. As a result of this population growth,
these urban conglomerates tend to become messy and
disorganized over time, putting the management of
natural resources and energy at risk (Johnson, 2008).
The traffic in urban areas is greatly affected by
this disorganization. According to (IBM NewsRoom,
2011), approximately 30% of a city’s traffic is caused
by drivers actively searching for a parking spot. As
example, in London, drivers spend an average of 67
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9735-8249
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0145-1834
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2151-7944
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0100-8691
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5937-8193
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1716-8614
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7098-2597
hours a year looking for on-street and off-street park-
ings (Cookson and Pishue, 2017). This requires the
need to find solutions that reduce the time spent by
drivers on the roads and reducing traffic flow, re-
sources and emission of gases that are harmful to the
environment (Goetz, 2019). Although the creation
of new spaces facilitates the reduction of traffic con-
gestion, the ideal solution would be to facilitate the
search for available parking spots, which reduces sig-
nificantly the time spent in the traffic.
Smart parking technologies emerge to solve this
problem, allowing the better management of parking
spaces, quick rental of vacant spots, or even reserve
a space as needed in a private parking. Implemen-
tations in this field range from mobile applications,
that inform drivers about vacant spaces to park, to
the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to determine
the best parking spot for a given user according to
its needs. Most of the smart parkings are composed
of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), whose counter-
parts are computational processes such as software or
applications, and physical technologies such as sen-
sors and actuators, where both are integrated in the
Boos Junior, M., Sakurada, L., Leitão, P., Alves, P., Alves, G., Borges, A. and Antunes, D.
Integrating a Multi-Agent Smart Parking System using Cloud Technologies.
DOI: 10.5220/0010978300003179
In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2022) - Volume 1, pages 681-689
ISBN: 978-989-758-569-2; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
681

same network (Xu et al., 2018). Multi-Agent Sys-
tems (MAS) (Wooldridge, 2002) is seen as a suitable
approach to implement such smart CPS, based on a
collection of autonomous components that interact,
negotiate and coordinate efforts among themselves to
achieve their goals. Therefore, the system becomes
distributed and able to self-regulate in case of failures
or disruptions. In a Smart Parking Multi-Agent Sys-
tem (SPMAS), drivers and parking spots are seen as
agents, that communicate with each other to negoti-
ate the allocation of parking spots according to the
driver’s desires, namely the location, date and price.
This paper explores the integration of cloud tech-
nologies with MAS to implement a distributed smart
parking system, introducing flexibility to integrate
different modules, providing end-to-end security and
system decentralization. This cloud architecture also
integrates the user interface (UI) with the vehicle’s
drivers and the interface with the physical assets,
namely the controllers regulating the access to the
parking spots. The proposed approach extends a
previous MAS based smart parking system (Saku-
rada et al., 2019) that was implemented to manage
the parking of vehicles in an University campus, by
adding cloud computing functionalities to enable the
modularization, scalability and robustness of such
large-scale system.
2 TECHNOLOGICAL
APPROACHES FOR SMART
PARKING SYSTEMS
Currently, most of the smart parking solutions are im-
plemented by applications that aim to simplify the
search for parking spots by informing their location
using GPS (Global Positioning System) or allowing
some sort of digital payment for the used spots.
The system described in (Khanna and Anand,
2016) helps the users to know in real time the park-
ing spots availability, using mobile apps connected to
the Cloud. The system uses ultrasonic sensors con-
nected to an ESP8266 board to check if the parking
slot is occupied. The ESP8266 is connected to a pro-
cessing unit (Raspberry Pi) that transmits the gathered
data to the cloud using the MQTT (Message Queu-
ing Telemetry Transport) protocol. Due to its central-
ized approach, if the processing unit fails, the users
will not be able to search the available parking slots.
Another Cloud-based approach is presented in (Pandit
et al., 2019), which uses infrared sensors, to detect the
vehicles, connected to an Arduino board that captures
the data and sends to a specific cloud provider.
The system uses the HTTP protocol for the data
transmission and and allows the data reading in real
time.
Park King (Ajchariyavanich et al., 2019) is an In-
ternet of Things (IoT) based smart parking system in-
tegrated to a cloud in an University Campus. It uses
an IoT module for monitoring the parking spot avail-
ability and a Web application where users can reserve
a parking slot. To access the parking, users must read
the QR Code via the smartphone, generated by the
web application at the end of the reservation process,
and show it to the sensor that validates and allows the
vehicle to enter in the parking. A NodeMCU board
sends the data to a cloud database, which is used by
the system to display the data and to control reserva-
tions. As discussed earlier, this centralized approach,
based on a processing unit, can fail and external users
will not be able to search and reserve parking spots.
The smart parking management system described
in (Melnyk et al., 2019) aims to minimize the search
time for an empty spot in large car parkings and to
make the spot localization easier. It uses a mobile app
that communicates with the parking infrastructure us-
ing the MQTT protocol for requests, payment and no-
tifications. Although the system includes the payment
functionality, a dynamic pricing approach based on
location, demand or time is not provided. A parking
system based on wireless sensors that communicate
with a network router responsible to send the infor-
mation to a local server, which is responsible for syn-
chronizing information with an integrated cloud plat-
form, is proposed by (Mohammadi et al., 2019). End
users interact with the system through the cloud.
When using a centralized smart parking solution,
it is possible to notice the lack of scalability that can
lead to problems caused by the technical failure of
sensors, or precariousness in the negotiation and pric-
ing of spots that constantly depend on a central server.
Many of these solutions can solve certain problems
related to parking, but most do not present an ap-
proach that indeed makes use of smart based tech-
nology or yet fails to provide a decentralized solution
that mitigates the dependency of central node and the
need for responsiveness. The mentioned applications
only inform about the vacant parking spots and do not
consider any analytical knowledge.
Aiming to tackle the aforementioned issues,
MAS-based solutions provide the cooperation among
different components in a distributed way, where each
agent acts in an autonomous and decentralized way
to achieve a whole objective (Leit
˜
ao and Karnouskos,
2015). Different MAS-based approaches for smart
parking systems can be found in (Sakurada et al.,
2019; Pham et al., 2015; Castro et al., 2017). In
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
682

most of MAS-based approaches the cooperation be-
tween agents is carried out by the information shar-
ing and enforcing constraints using rule-based proce-
dures (Chieh-Chang Li et al., 2004). The ability to
operate even if one of the components fails due to the
malfunctioning is one of the benefits when using a
MAS technology within a smart parking architecture,
because it provides a distributed communication that
handles normalization of the system in such cases, as
well as multiple parallel requests.
A study was made to compare possible ap-
proaches to solve consensus problems in such dis-
tributed systems, and particularly addressing the ne-
gotiation strategies in an agent-based smart parking
system (Alves et al., 2019). Furthermore, the usage of
holonic agents in the MAS approaches applied to the
smart parking scenarios is also being explored, which
may have a higher capacity to deal with the failures
and higher scalability.
The incentive to technological advancement pro-
vides a better scenario for the implementation of a
smart parking in a context of large urban conglomer-
ates; however, an infrastructure that can support this
entire environment is necessary. Likewise, it is im-
portant to emphasize that the cost of IoT components,
e.g., sensors and microcontrollers, can be a decisive
factor when implementing a smart parking project.
Additionally, IoT systems provide a huge amount of
data traffic, which can be costly depending on the
number of users. Using local servers may not be a
choice that favors scalability, and it is extremely nec-
essary to take care of security factors, since a network
failure can cause serious damage.
In this context, Cloud computing is evolving as a
new computing model designed to offer dynamic and
on-demand computing environments for users, pro-
viding a fast, secure and customizable service (Hayes,
2008; Bharti and Goudar, 2012). Cloud can also com-
bine applications delivered as services over the Inter-
net, as well as the hardware and systems software in
the data centers that provide those services (Armbrust
et al., 2010). Based on these concepts, many applica-
tions have been developed using the services offered
by Cloud providers, which brings benefits related to
virtually unlimited data processing and storage re-
sources, and no investment needed with the mainte-
nance of the computational infrastructure.
On the one hand, there are some smart parking so-
lutions that use Cloud services but are not MAS-based
solutions. On the other hand, some MAS-based ap-
proaches for smart parking do not present the use of
Cloud technology to assure scalability and decentral-
ized services. The combination of these two worlds,
i.e. a MAS-based smart parking solution using Cloud
services, will bring significant benefits to scale up
some of the main MAS features like distribution, de-
centralization and autonomy.
3 CLOUD BASED SPMAS
ARCHITECTURE
The proposed solution is based on a cloud architecture
that integrates a MAS system that uses a society of
agents representing drivers and parking spots to man-
age the parking system operation, as seen in Figure 1.
The use of Cloud technology allows to provide scal-
able applications, better cost-benefit ratio and abstract
hardware specifications.
Figure 1: Cloud MAS Smart-Parking Architecture.
This architecture uses a three-tier approach:
Clients, who interact with the system via the web or
mobile app; the Cloud, which uses components to en-
sure user authentication, data storage and a scalable
real-time two-way communication in the system; and
the MAS, responsible for managing the entire parking
system in a distributed and intelligent way.
3.1 Multi-Agent System
The multi-agent smart parking system architecture
comprises a set of intelligent, autonomous and proac-
tive agents distributed along the edge and cloud com-
puting layers. Two types of agents were defined,
namely driver and spot agents, which offer more flex-
ibility, modularity, scalability and on-the-fly reconfig-
urability for smart parking solutions.
As seen in Figure 2, each parking spot has an
associated spot agent running in the edge computa-
tional layer, being a suitable approach by providing
autonomy and fast response to monitor each vacancy.
Moreover, the spot agents are interconnected with the
physical assets, namely sensors and actuators, aiming
to manage the access of the physical parking spots.
On the other hand, the driver agents, representing the
drivers, are accessed by an UI and are running in the
Integrating a Multi-Agent Smart Parking System using Cloud Technologies
683

cloud, taking advantage of more computational capa-
bilities, including, e.g., the possibility to embed more
robust AI algorithms for intelligent decision support.
Figure 2: Multi-agent Parking System Architecture.
The global functioning of the system emerges
from the interaction between the driver and spot
agents. For this purpose, the agents are endowed with
a set of behaviors to achieve their goals, particularly
the searching for available parking spots, negotiation
strategies, reservation process, and physical intercon-
nection. In this sense, driver agents can dynamically
and in real-time start a negotiation with several spot
agents to find and reserve a parking spot respecting
the specifications defined by the driver (e.g., location,
price and time). The spot agents are also enabled
to initiate the negotiation, recommending free park-
ing spots, e.g., by the inclusion of machine learning
techniques aiming to predict the occupancy of parking
spots, the analysis of the parking use history, the uti-
lization seasonality (e.g., work and vacation period)
and the usage forecast based on the weather forecast.
After the desired parking spot is reserved, the
driver can access the parking spot in the proper slot
of time. The interconnection between the spot agents
and the physical assets is essential to enable the ac-
cesses of the physical spots. In this sense, these cyber-
physical interactions should follow standards like the
recent IEEE 2660.1 (Leit
˜
ao et al., 2021), which rec-
ommends the best practices for integrating software
agents with low-level automation functions. For this
purpose, this interconnection follows a loosely cou-
pled interaction model based on the publish-subscribe
schema, providing the fundamental requirements for
the system’s proper functioning, where the time con-
straints are not critical, and the scalability and moni-
toring are much more significant for this application.
Furthermore, the architecture takes advantage of
holonic principles’ recursive capabilities to simplify
the development of large-scale smart parking systems
by building holarchies of driver and spot agents. In
this sense, a spot agent can be at the same time the
“whole”, e.g., representing a set of parking spots and
the “part”, e.g., representing a unique parking spot.
The same is applied for the driver agents, e.g., repre-
senting a company (set of drivers) and a unique driver.
Although an overview of smart parking systems
has been presented, this work focuses on the bene-
fits of the cloud technology to enhance and integrate
MAS solutions, particularly MAS-based smart park-
ing systems. Negotiation methods and principles of
holonic agents are out of the scope from this paper.
3.2 Specification of the Cloud
Architecture
A cloud solution must allow drivers to request reser-
vation allocations from the MAS, as well as check the
availability of parking spots in real time, providing
some essential services to the application. First of all,
the backend is constituted by a flexible Authentication
module responsible for the role management and ac-
cess control to the system’s resources. In this sense,
the driver’s requests, e.g., parking spot searches and
reservations, will only be executed if the user is au-
thenticated with the cloud provider.
Based on the data structuring model related to
parking systems provided by FIWARE (FIWARE,
2021), a platform that provides standardized data
models, it was possible to adapt to a document-based
database with NoSQL structure, using essential at-
tributes according to the model studied, as well as
adding new attributes that fit the project. In this ap-
plication, a document-based database is considered to
store information about each parking, as well as users
and their reservations. The main advantages of this
model are the flexibility for new data types in the fu-
ture and the scalability of the database by horizontal
partitioning (e.g. grouping by parking areas).
The back-end platform provides the direct con-
nection between the users and the Cloud service. It
provides fully scalable functionalities for user authen-
tication, storage in NoSQL databases, high perfor-
mance data management and a real-time engine for
notifications using the WebSocket protocol.
When considering the communication between
the MAS and the Cloud, the Publish-Subscribe model
provides the broadcast of real-time messages (e.g.,
using lightweight and performance protocols like
MQTT) for the multiple devices through several top-
ics, which are the central elements of the entire data
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
684
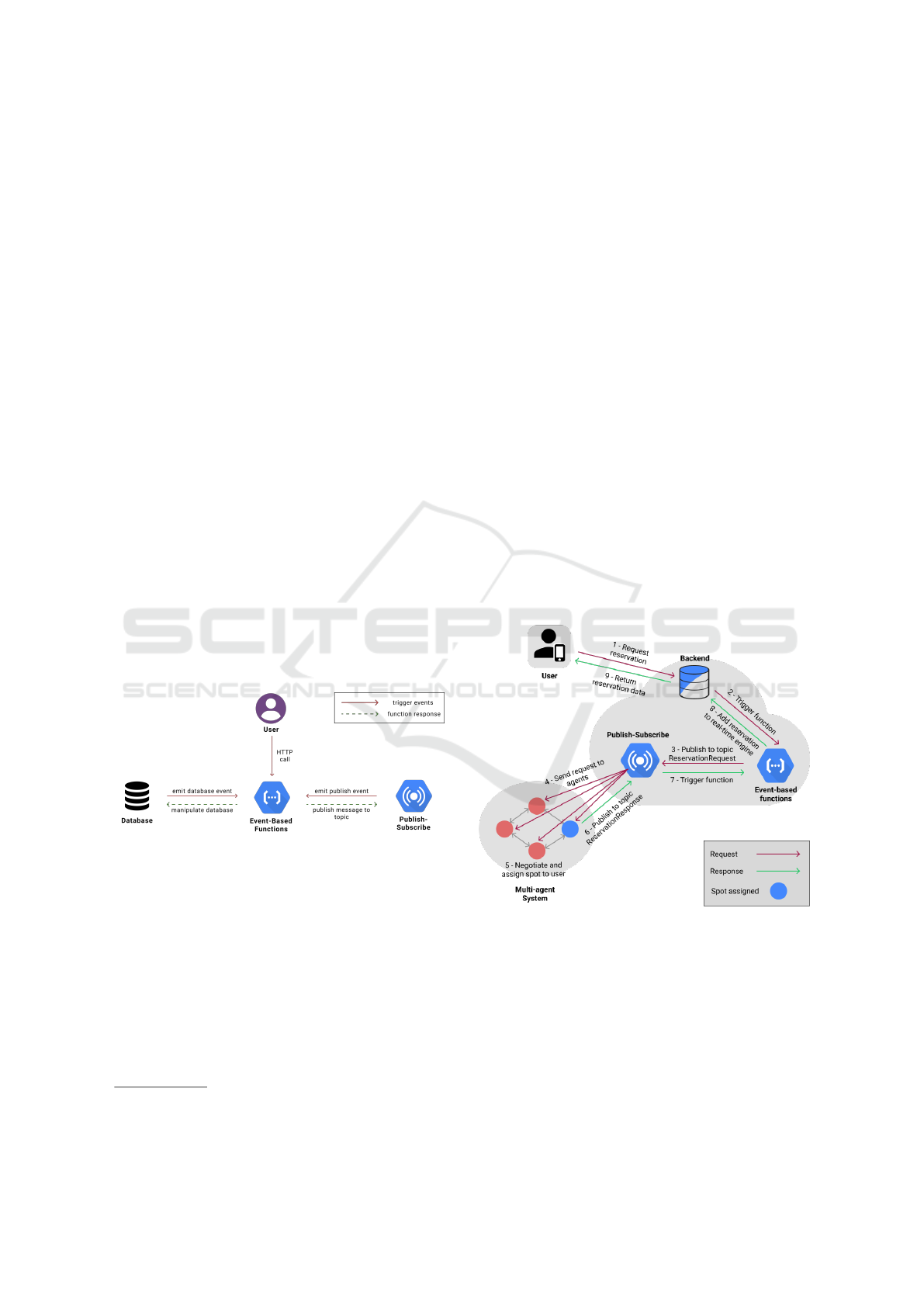
flow. To send a message to agents in the system, it
is necessary for the sender to simply publish a pay-
load containing the data in a topic. In a smart parking
MAS context, topics should cover scenarios in which
the target destination is either spot agents or drivers,
and cover features like search for available spots, re-
quest and finish a reservation, arriving and departing.
As soon as the message is published, the Cloud plat-
form will act as a message broker, transferring this
payload individually to all devices interested in the
topic through a subscription. This process is impor-
tant to maintain the scalability of the system, enabling
an end-user request (e.g. a search) to be delivered to
all agents in the system in a distributed manner.
There are occasions where a specific chunk of
code must be executed when a given event occurs in
the Cloud environment, such as adding data to the
database, or publishing a message on a topic, and to
prevent unwanted replication, functions triggered by
those events are used. Due to the execution based on
the occurrence of events, the use of this methodol-
ogy reduces the use of computational processing of
the server, as well as the need to periodically exe-
cute functions. Similar to the use of a cloud-based
Publish-Subscribe service, the use of an event-based
approach on the server enables the high scalability for
the system, since these functions enable the parallel
execution of multiple instances, providing great per-
formance in handling the requests
1
. Figure 3 shows
the possible events that can trigger these functions.
Figure 3: Event-based functions representation.
For the system operation and its integration with
the cloud platform, several use cases were defined.
User Authentication: Authentication methods are
used to provide secure access of users to the sys-
tem. Registration can be done through the identity
providers, phone numbers or simply by email and
password. The system assigns a unique identifier to
the user, which will be attached to every request. In
addition, a document is created with user’s personal
information in the database, where all the performed
actions are added, e.g., requesting reservations or en-
1
For example, the Google Cloud Functions service in
https://cloud.google.com/functions
tering and leaving spots. After this process is com-
pleted, the application must allow the user to access
the system using his credentials.
Search Available Spots: The application must of-
fer the option to search for available spots in a given
parking area. All spot agents receive the user’s re-
quest, but only available spots will respond informing
their status. Therefore, the driver agent receives the
responses from the spot agents about their availabil-
ity, displaying the identifier and coordinates of each
available spot.
Request Spot Reservation: It is the most important
functionality of the application, in which the user can
make a request for a reservation (see Figure 4), spec-
ifying parameters that impact on the MAS decision.
These parameters include the desired location, which
can vary depending on geography, and can be related
to sectors of an University or floors in a Shopping
Center, for example. Informing the type of vehicle
to be used is also important, so that the MAS assigns
the suitable spot for the corresponding type of vehi-
cle. Finally, the user needs to define the date and time
for the reservation as well as to inform which would
be the desired spot, the maximum acceptable distance
from the spot’s location and the maximum price that
the user is willing to pay.
Figure 4: Schema for requesting a spot.
Note that for the MAS system to come up with a
decision for the best parking spot, through the nego-
tiation among the driver and spot agents, it is neces-
sary that the user informs how much the chosen lo-
cation and price must weight in the agents’ decision.
Weights are mutually exclusive on a 100% scale, i.e.
when selecting 40% weight for one of them, the other
one necessarily correspond to 60%.
The communication flow of this functionality cov-
Integrating a Multi-Agent Smart Parking System using Cloud Technologies
685

ers the services provided in the cloud architecture,
firstly recording of data in the database, then activat-
ing an event-based function in the cloud, and finally
publishing the message in a Publish-Subscribe topic.
Enter and Leave Spot: The application must in-
clude the possibility to request to enter or exit the pre-
reserved spot, requiring the interaction with the MAS
system, and particularly with the physical hardware
of a parking spot. Once the spot reservation’s dura-
tion reaches the end, the application must remove the
user’s access to this functionality, so the user can no
longer interact and use it.
4 EXPERIMENTAL
IMPLEMENTATION
The designed cloud-based MAS architecture for
smart parking systems was experimentally imple-
mented and tested in a case study that considers the
bicycle parking system of the Polytechnic Institute of
Braganc¸a (IPB). The IPB parking system comprises
several sectors, where each one constitutes a set of bi-
cycle parking spots. The vacancies are available to
be used with mechanisms that guarantee the bicycle’s
safety and that enables verification for available spots.
4.1 Development of the MAS
The MAS-based smart parking system was developed
using the FIPA-compliant JAVA Agent DEvelopment
Framework (JADE) (Bellifemine et al., 2007), and
deployed in different computing layers, namely edge
and cloud layers. For this purpose, the spot agents
were deployed in Raspberry Pis at the edge level, and
the driver agents were deployed in the cloud, commu-
nicating with each other by using the TCP/IP protocol
encoded for the FIPA-ACL (Foundation of Intelligent
Physical Agents-Agent Communication Language).
The communication between the spot agents and the
physical assets was established using the MQTT pro-
tocol, where an exclusive Raspberry Pi was used as
an MQTT broker to support the cyber-physical in-
teractions. Furthermore, each physical asset com-
prises a logical control running in an ESP8266 mi-
crocontroller responsible for managing the access to
the parking spot, e.g., through a latch that will lock
the bicycle in the parking spot and release it after use.
4.2 Cloud Implementation
The cloud provider used in this work was the Google
Cloud Platform (GCP) and was configured based on
the West Europe location. The Cloud works through
the communication between modules such as the
backend, which is responsible for the communication
between the Client and the Cloud, event-based func-
tions for managing events and finally, the Publish-
Subscribe service being the bridge between the MAS
and Cloud. The Publish-Subscribe service was imple-
mented through the MQTT protocol.
The protocols used in this communication also in-
clude HTTP, where the client-side does not maintain
an active connection with server-side and data is ex-
changed by sending requests and receiving responses.
This type of protocol is used in most functionalities
when requesting to write or read a document from
the database, such as requesting a reservation, search
for spots, and search for history. On the other side,
a WebSocket is used for real-time message exchange
for situations where the client-side must wait for the
MAS response, such as spot availability, reservation
response, and arriving and departing confirmation.
4.3 Development of the User Interface
The React Native framework was used with the help
of Expo tools to build a mobile application that can
be natively compiled on Android and iOS platforms.
This application is focused on the driver, who must be
able to use the functionalities provided by the smart
parking system in an intuitive and effective way.
After the user authentication, the application re-
quests the available parking areas. Therefore, selec-
tive loading of only data close to the requested loca-
tion occurs, keeping the application light, responsive
and without making requiring significant bandwidth,
even with a large number of smart parking places reg-
istered in the system. Based on this, the user can
choose where to park, and when clicking on the mark-
ers at the home page (Figure 5A), a card is shown with
the name and image representing the parking (Fig-
ure 5B). The Check spots button allows to show the
spots that are currently available (Figure 5C).
To request the reservation allocation, the user se-
lects the search parameters, this request is recorded
in the database, activating a function in the cloud that
sends the request to the MAS through the Publish-
Subscribe service and the negotiation and decision
will take place between the agents. After the response
from the MAS, a card is displayed informing the pro-
posal and the user is able to accept or refuse it.
At the end of the reservation process, the applica-
tion schedules notifications, based on the 30 minutes
prior to the start and end of the reservation, to alert
the user about the reservation. As these are local no-
tifications, the user will be alerted even if the applica-
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
686

Figure 5: Process to search available spots.
Figure 6: Fragments of the UI to perform a reservation.
tion do not have access to the Internet. As shown in
Figure 6A, it is possible to observe more information
about the reservation, as well as open GPS applica-
tions with routes directly to the spot’s location. When
the current time is between the beginning and end of
the reservation, the action of entering the spot is made
available (Figure 6B), being communicated to MAS
in the same way as the reservation request.
5 ANALYSIS OF EXPERIMENTAL
RESULTS
The experimental tests were carried out using the
parking hosted in IPB, focusing the response time and
communication effectiveness for three functionalities
related to MAS, namely the search for available spots,
request for reservations, and entry or exit of spots.
There was no data communication loss reported
in any of the tests, and in all of them the informa-
tion from the mobile applications arrive in the MAS
system, and returned the expected result. This is due
to the Quality of Service (QoS) guaranteed by the
Publish-Subscribe service, which uses delivery recog-
nition methods for each subscriber.
Figure 7: Execution time for searching available spots and
requesting reservations.
In general, the application’s communication with
the back-end module was fast, proving efficiency in
cases with local and mobile network connection, and
flexible in case of connection loss. Fig. 7 shows the
average execution time of some system’s functionali-
ties, namely the search for available spots and the re-
quest for reservations. This execution time comprises
the time elapsed from the function call by the user ac-
tivation until the reception of the MAS response and
the visual presentation to the user. The tests were car-
ried out for scenarios comprising 10, 100 and 200
available parking spots. The execution time for the
reservation request functionality was constant, as it
does not depend on the number of spots available at
the moment. On the other hand, the execution time for
the search for spots increases with the raise of avail-
able spots, since the communication also increases.
Summing, the experimental tests clearly showed
that cloud technology is suitable to integrate such sys-
tems, particularly based on distributed components,
as MAS systems are, and provides a technological
solution to support scalability and robustness in such
systems. The used cloud platform approach also con-
tributes to increase authentication and security issues,
as well to integrate databases and UIs.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presented a cloud-based MAS architecture
for smart parking systems using Cloud computing
technologies to integrate the MAS system responsi-
ble for the spot allocation and the client-side modules.
Unlike other approaches, this option does not depend
on just one physical server, with Cloud computing al-
lowing an unlimited number of servers that act as an
unified system. The scalability and decentralization
of the system is guaranteed through the horizontal
scaling, which entails separating a sequential portion
Integrating a Multi-Agent Smart Parking System using Cloud Technologies
687

of the logic into smaller parts so that they can be per-
formed on several machines in parallel, increasing the
efficiency of large-scale processes. The security fac-
tor is satisfied by the Cloud service provider, which
abstract issues such as implementation of security
protocols, authentication tokens, and possible mali-
cious attacks. The communication between the MAS
and the Cloud was carried out through a Publish-
Subscribe service, which provided a simple integra-
tion between the system logic and physical compo-
nents. Event-based functions were used to provide
asynchronous and stable communication between the
various components of the Cloud. Finally, web and
mobile applications were developed to validate the
user’s interactivity with the system. The mobile app
for drivers was tested in a case study regarding a Uni-
versity campus, being promising, mainly considering
the successful communication between the users and
the MAS, as well as w.r.t the response time, scalabil-
ity and security issues. The implemented cloud based
MAS architecture proved to be flexible, capable of in-
corporating new smart parking modules and integrat-
ing different MAS systems.
Future work will be integrate intelligence algo-
rithms to support the negotiation process during the
allocation of parking spots to drivers. Regarding the
integration with the MAS, it can be explored features
that enable the agent management via a web interface.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work has been supported by FCT - Fundac¸
˜
ao
para a Ci
ˆ
encia e Tecnologia within the Project Scope:
UIDB/05757/2020.
REFERENCES
Ajchariyavanich, C., Limpisthira, T., Chanjarasvichai,
N., Jareonwatanan, T., Phongphanpanya, W., Wa-
reechuensuk, S., Srichareonkul, S., Tachatanitanont,
S., Ratanamahatana, C., Prompoon, N., and Pipattana-
somporn, M. (2019). Park King: An IoT-based Smart
Parking System. In IEEE International Smart Cities
Conference (ISC2), pages 729–734.
Alves, B. R., Alves, G. V., Borges, A. P., and Leit
˜
ao, P.
(2019). Experimentation of Negotiation Protocols for
Consensus Problems in Smart Parking Systems. In In-
dustrial Applications of Holonic and Multi-Agent Sys-
tems, LNCS 11710, pages 189–202. Springer.
Armbrust, M., Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A. D., Katz,
R., Konwinski, A., Lee, G., Patterson, D., Rabkin, A.,
Stoica, I., and Zaharia, M. (2010). A view of cloud
computing. Commun. ACM, 53(4):50–58.
Bellifemine, F., Caire, G., and Greenwood, D. (2007). De-
veloping multi-agent systems with JADE. John Wiley
& Sons.
Bharti, D. and Goudar, R. (2012). Cloud comput-
ing–research issues, challenges, architecture, plat-
forms and applications: A survey.
Castro, L. F. S. D., Alves, G. V., and Borges, A. P. (2017).
Using trust degree for agents in order to assign spots
in a Smart Parking. ADCAIJ: Advances in Dis-
tributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence Jour-
nal, 6(2):45–55.
Chieh-Chang Li, Shuo-Yan Chou, and Shih-Wei Lin (2004).
An agent-based platform for drivers and car parks ne-
gotiation. In IEEE International Conf. on Networking,
Sensing and Control, volume 2, pages 1038–1043.
Cookson, G. and Pishue, B. (2017). The Impact of Parking
Pain in the US, UK and Germany. INRIX Research.
FIWARE (2021). On Street Parking. https://fiware-
datamodels.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Parking/OnStreet
Parking/doc/spec/index.html. [Online; accessed
23-10-2021].
Goetz, A. R. (2019). Transport challenges in rapidly grow-
ing cities: is there a magic bullet? Transport Reviews,
39(6):701–705.
Hayes, B. (2008). Cloud computing. Commun. ACM,
51(7):9–11.
IBM NewsRoom (2011). IBM Global Parking Sur-
vey: Drivers Share Worldwide Parking Woes.
https://newsroom.ibm.com/2011-09-28-IBM-Global-
Parking-Survey-Drivers-Share-Worldwide-Parking-
Woes-1. [Online; accessed 23-10-2021].
Johnson, B. (2008). Cities, systems of innovation and eco-
nomic development. Innovation, 10(2-3):146–155.
Khanna, A. and Anand, R. (2016). Iot based smart parking
system. In 2016 International Conference on Internet
of Things and Applications (IOTA), pages 266–270.
Leit
˜
ao, P. and Karnouskos, S. (2015). Industrial Agents:
Emerging Applications of Software Agents in Industry.
Leit
˜
ao, P., Strasser, T., Karnouskos, S., Ribeiro, L., Bar-
bosa, J., and Huang, V. (2021). Recommendation of
Best Practices for Industrial Agent Systems based on
the IEEE 2660.1 Standard. In IEEE Int’l Conf. on In-
dustrial Technology (ICIT’21), pages 1157–1162.
Melnyk, P., Djahel, S., and Nait-Abdesselam, F. (2019). To-
wards a smart parking management system for smart
cities. In IEEE International Smart Cities Conference
(ISC2), pages 542–546.
Mohammadi, F., Nazri, G.-A., and Saif, M. (2019). A
real-time cloud-based intelligent car parking system
for smart cities. In 2nd IEEE Int’l Conf. on Infor-
mation Communication and Signal Processing, pages
235–240.
Pandit, S. N., Krishna, R. M., Akash, R., and Moharir, M.
(2019). Cloud based smart parking system for smart
cities. In International Conference on Smart Systems
and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), pages 354–359.
Pham, T. N., Tsai, M., Nguyen, D. B., Dow, C., and
Deng, D. (2015). A cloud-based smart-parking sys-
tem based on internet-of-things technologies. IEEE
Access, 3:1581–1591.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
688

Sakurada, L., Barbosa, J., Leit
˜
ao, P., Alves, G., Borges,
A. P., and Botelho, P. (2019). Development of agent-
based cps for smart parking systems. In Proc. of the
45th Annual Conf. of the IEEE Industrial Electronics
Society (IECON’19), pages 2964–2969.
United Nations (2019). World Urbanization Prospects: The
2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420). Department of
Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division,
New York: United Nations.
Wooldridge, M. (2002). An Introduction to MultiAgent Sys-
tems. Wiley.
Xu, H., Yu, W., Griffith, D., and Golmie, N. (2018). A
Survey on Industrial Internet of Things: A Cyber-
Physical systems perspective. IEEE Access, 6:78238–
78259.
Integrating a Multi-Agent Smart Parking System using Cloud Technologies
689
