
Real-time Arabic Sign Language Recognition based on YOLOv5
Sabrina Aiouez
1
, Anis Hamitouche
2
, Mohamed Sabri Belmadoui
2
, Khadidja Belattar
3
and Feryel Souami
1
1
Computer Science Department, University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene,16000, Algiers, Algeria
2
Computer Science Department, University of Algiers 1 Benyoucef Benkhedda, 16000, Algiers, Algeria
3
Department of Fundamental Computer Sciences and their Applications,
Constantine 2 University, 25000, Constantine, Algeria
Keywords:
Deep Learning, Real-time Detection, Arabic Sign Langage, YOLOv5, Faster R-CNN, Hand Gesture.
Abstract:
Sign language is the most common communication mode of deaf and mute community. However, hearing
people do not generally know this language. So, an automatic sign langage recognition is required to facilitate
and better understand interactions with such people. However, one of the main challlenges in this field is the
real-time sign recognition. That is why, deep learning-based object detection models can be used to improve
the recognition performance (in terms of time and accuracy). In this paper, we present a real-time system
that allows the detection and recognition of hand postures intended for the Arabic sign language alphabet. To
do so, we constructed a dataset of 28 Arabic signs containing around 15,000 images acquired with different
sizes of hands, lighting conditions, backgrounds and with/without accessories. We then trained and tested
different variants of YOLOv5 on the constructed dataset. The conducted experiments on our ArSL real-time
recognition system show that the adapted YOLOv5 is more effective than Faster R-CNN detector.
1 INTRODUCTION
Object detection in images and real-time streaming is
an essential process in various computer vision ap-
plications such as hand gesture recognition. Indeed,
this technology is gaining increased attention driven
by Human Machine Interface advances.
One of the most interesting applications of ges-
ture recognition is in sign language recognition field.
While sign language, like any common communica-
tion language, consists of a set of structured hand ges-
tures, used in the deaf community. However, hearing
people do not always master sign language. Thereby,
a human interpreter is usually needed. Then, the de-
velopment of automatic real-time systems that can
recognize sign language, helps communicate and un-
derstand better with hearing impaired.
In the earlier works on sign language recognition,
the hand was equipped with instrumented gloves.
Such devices are designed to capture hand motions
and provide recognition-related information includ-
ing in particular position and the orientation (Zafrulla
et al., 2011; Oz and Leu, 2011; Dipietro et al., 2008).
That is more expensive and intrusive than computer
vision based recognition methods, which have been
adopted in the last years. Using computer vision sys-
tems, images (or video streams) of visual gestures and
signs are acquired via webcam or smartphone cam-
era.They are very practical and have lower cost.
In this respect, we distinguish manual and non-
manual gestures for sign language recognition pur-
poses. The manual gestures involve using hands.
Whereas, the non-manual gestures consist of body
poses, head tilting, shoulder raising as well as facial
expressions.
Each country has its own sign language. How-
ever, the alphabet of Arabic Sign Language (ArSL) is
unique for all Arab countries. ArSL alphabet is made
up of set of letters; each letter is represented by a hand
gesture. This alphabet is used to spell out words by
hand (fingerspelling) that don’t have associated sign
(place names, people’s names, object’s names). It has
been reported that ArSL is the most difficult recog-
nition task among other foreign sign languages due
to its unique structure and complex grammar (Abdel-
Fattah, 2005). Figure 1 shows the 28 ArSL alpha-
bet letters. We can see some similarities within cer-
tain sign classes. For instance, the letters “Ta” and
“Tha”, “Dal” and “Thal” ,”Ra” and “Zay”,“Ayn” and
“Ghayn” are visually very similar. This is due to the
Aiouez, S., Hamitouche, A., Belmadoui, M., Belattar, K. and Souami, F.
Real-time Arabic Sign Language Recognition based on YOLOv5.
DOI: 10.5220/0010979300003209
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering (IMPROVE 2022), pages 17-25
ISBN: 978-989-758-563-0; ISSN: 2795-4943
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
17

limited degrees of freedom of the hand and possible
hand gestures. Hence, recognizing and discriminating
each letter is a challenging problem.
Figure 1: The 28 arabic sign language alphabet (Almasre
and Al-Nuaim, 2017).
In this paper, we used the YOLOv5 object detector
to resolve the real-time Arabic sign language recog-
nition. Furthermore, we compared the adapted model
YOLOv5s (smallest) against Faster R-CNN. The rest
of the paper is organized as follows. In section 2, we
review ArSL approaches. In section 3, we detail the
adapted solution. Then, we present and discuss the
experimental results obtained by our system using a
15088 images dataset in section 4. Finally, we con-
clude the paper in section 5.
2 RELATED WORKS
Performing ArSL recognition has been the focus of
many researchers. Previous works include the ap-
proach proposed by Assaleh and Al-Rousan (As-
saleh and Al-Rousan, 2005), where they used colored
gloves marked with six different colors at six regions
(on the five fingertips and the wrist). The recognition
process includes image segmentation, feature extrac-
tion and ArSL recognition stages. The input image is
segmented. The next stage consists of computing the
relative position and orientation of the fingertips with
respect to the wrist and to each other, based on the
segmented image. The last stage ; alphabet recogni-
tion is accomplished through a polynomial classifier.
The proposed approach achieves a recognition rate of
93.41% on a collected dataset of 2323 samples.
Alzohairi et al. (Alzohairi et al., 2018) were in-
vestigated different visual descriptors for ArSL recog-
nition problem. The best results were obtained with
Histograms of Oriented Gradients (HOG) feed to a
one versus all soft-margin SVM classifier. The de-
veloped system achieves an accuracy of 63.56% on a
collected dataset of 1800 images.
Another work in that class of approaches is that
of Tharwat et al. (Tharwat et al., 2015) in which
they used the SIFT (Scale Invariant Features Trans-
form) descriptor to extract robust features of the input
ArSL image. This is followed by the LDA (Linear
Discriminant Analysis)-based dimensionality reduc-
tion for getting an improved recognition accuracy us-
ing the selected features as input. The authors used
a database of 210 gray level ArSL images and con-
sidered 30 Arabic letters. The recognition rate of the
proposed method is estimated around 99,5%.
In (Dahmani and Larabi, 2014), the authors com-
bined Tchebichef moments, the Hu moments and ge-
ometric features for SVM based sign classification.
The stated moments were computed from the outline
and internal contours of the hand, while the geomet-
ric features were derived from the convex hull that
encloses the hand shape.The best combination yields
a 96,88% recognition rate on Treisch hand postures
database.
Most of ArSL recognition methods reported in the
literature make use of geometric features based on
finger configuration and orientation of the segmented
hand in the feature extraction stage. According to the
reference (Tharwat et al., 2015), the authors experi-
mented multiple configurations of SIFT parameters to
obtain the suitable results. Furthermore, in (Alzohairi
et al., 2018) and (Dahmani and Larabi, 2014), differ-
ent descriptors were investigated and/or combined to
select the relevant ones for ArSL recognition. We can
also notice that the recognition performance is related
to a meticulous choice of the hand descriptors.
Hence, to better deal with the complexity (among
classes) of the ArSL dataset, an automatic feature ex-
traction process would be more suitable to solve the
hand gesture recognition problem. The relevant ex-
tracted features can lead to an enhanced separability
between classes of the ArSL dataset.
In the last years, the development of deep learn-
ing and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) (Jiao
et al., 2019; Krizhevsky et al., 2012) has made great
progress in artificial intelligence field. The CNN is
able to perform relatively complex tasks particularly
object detection (Wu et al., 2017; Ranjan et al., 2017;
Hu et al., 2017; Yin et al., 2013; Han et al., 2014).
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
18
The main benefit of such a model is that it automati-
cally detects the relevant features without any human
supervision.
Several approaches based on CNN were proposed
in sign language recognition for foreign languages
(Goswami and Javaji, 2021; Yang and Zhu, 2017).
For Arabic sign language context, the authors of
(Alani and Cosma, 2021) employed CNN architec-
ture for ArSL classification. They revealed the ef-
fectiveness of the SMOTE oversampling method to
increase the accuracy on the used dataset. The max-
imum classification accuracy of the adapted ArSL-
CNN model is 97.29% on ArSL2018 dataset (Latif
et al., 2019).Transfer learning was also applied in (El-
Badawy et al., 2017; Islam et al., 2018; Bheda and
Radpour, 2017; Bantupalli and Xie, 2018; Rao et al.,
2018) for sign language recognition.
In (Alawwad et al., 2021), the authors used Faster
R-CNN detector which is associated with ResNet and
VGG-16 models. Faster R-CNN is a two stages de-
tector (Ren et al., 2015). In the first stage, it proposes
candidate object bounding boxes using Region Pro-
posal Network. In the second stage, the image fea-
tures are extracted by RoIPool (RoI Pooling) oper-
ation from each candidate box for the classification
and bounding-box regression tasks. The proposed
method achieves a recognition rate of 93% on a col-
lected dataset of 15,360 images.
In real-time, it is highly essential to have a model
that can process the images and recognize the signs
very fast at the speed of streaming images. In this
respect, YOLO (You Only Look Once) is one of the
most powerful real-time CNN architectures. It is one
stage-object detector where bounding box prediction
and object classification are performed in one pass.
In order to investigate the performance of
YOLOv5 for real-time ArSL recognition system, dif-
ferent variants were applied. Hence, in this work, we
constructed realistic (with different acquisition con-
ditions) data-set of 28 categories representing Arabic
alphabet letters. Furthermore, we adapted Yolov5 de-
tector, which is compared against Faster R-CNN (in
terms of recognition precision and inference speed).
3 THE ADAPTED SOLUTION
Our goal is to develop an efficient real-time system
to detect and recognize hand gestures of the ArSL
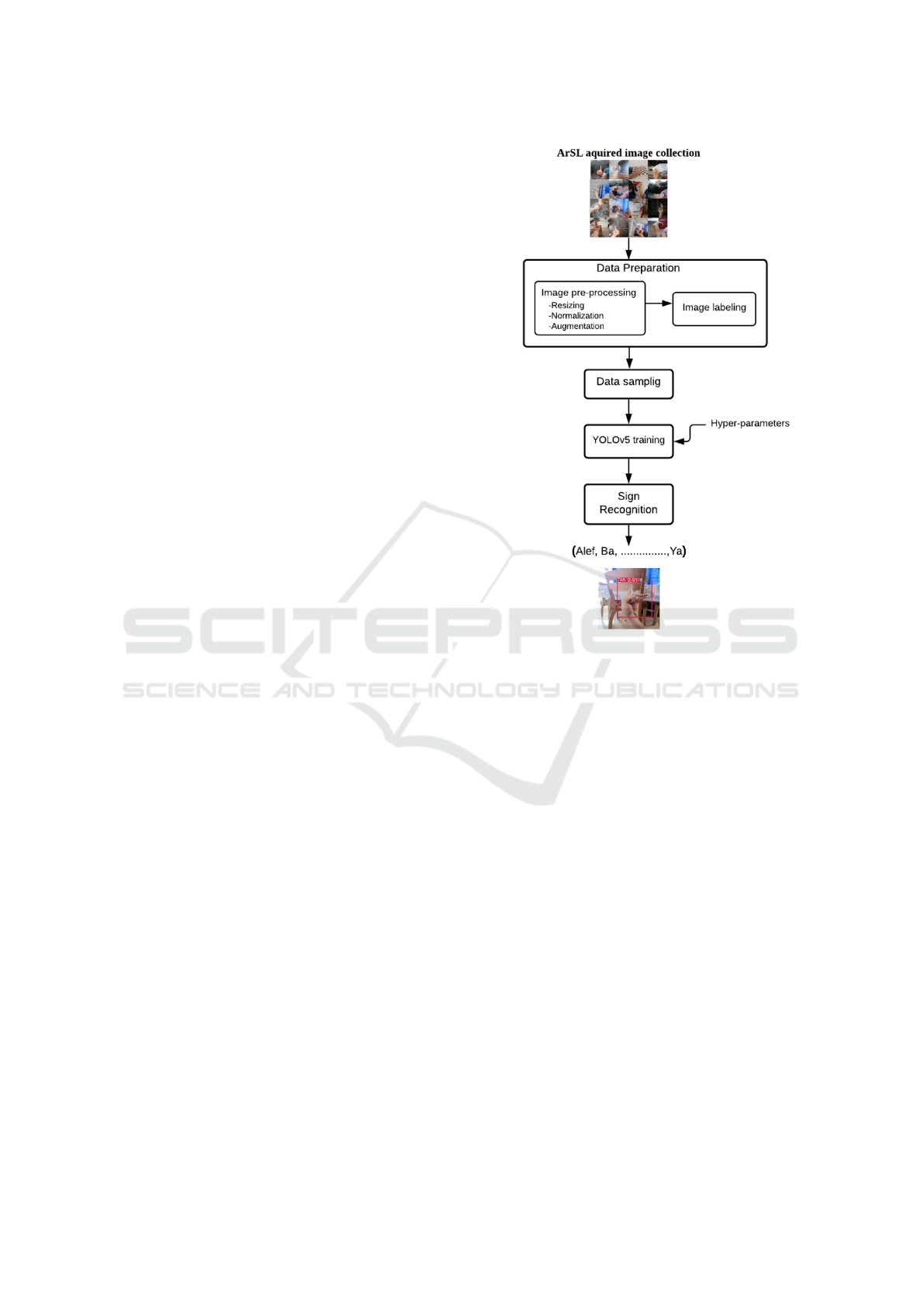
alphabet from images and video streams. The Fig-
ure 2 illustrates the overall YOLOv5 system for ArSL
recognition. The involved stages are detailed in the
following sections.
Figure 2: YOLOv5 system for ArSL recognition.
3.1 Data Preparation
Before feeding the acquired hand gesture images into
YOLOv5 architecture, we should prepare the col-
lected images. For that purpose, we performed data
preprocessing and image annotation using Roboflow
website tools (www.roboflow.com).
3.1.1 Dataset Pre-processing
In dataset pre-processing step, we first resized the ac-
quired images to 416 × 416 pixels (the size that the
YOLOv5 is designed to take). Then, we performed
data normalization.
Indeed, the real-world recognition applications
can be generally constrained by the low-quality of
the aquired data, small datasets or uneven unbalanced
data class problems. To this end, a data augmentation
is necessary before recognition.
According to (Dodge and Karam, 2016), the blurred
and noisy images affect the generalization perfor-
mance of the adapted deep learning model. That’s
why we introduced Gaussian blur and salt and pepper
noise to the original input images. As seen in Table 3,
we set the amount of the random gaussian blur from
Real-time Arabic Sign Language Recognition based on YOLOv5
19

0 up to 1 pixel, which means that the Gaussian kernel
size is equal to 3x3. While the percent of the affected
pixels by the noise is up 5%.
Moreover, affine image transformation and color
modification are the most polpular methods for data
augmentation, since they are fast and allow to ob-
tain a tolerant model against some specific variations
(Mikołajczyk and Grochowski, 2018). In this context,
we used rotation and grayscale tranformations.
Table 1: Data augmentation.
Technique Data augmentation factor
Gaussian blur up to 1 pixel
Salt and pepper noise up to 5% of the pixels
Grayscale transformation 25% of images
Rotation between -20° and + 20°
In this respect, we expanded the size of the orig-
inal dataset of 5600 RGB images (with around 200
images per class) to 15088 images (with around 540
images per class).
3.1.2 Dataset Annotation
Data annotation is an essential step in object detec-
tion task. Each image in the dataset was labeled with
its corresponding sign of the Arabic alphabet. Bound-
ing box annotation was also performed to define the
location of the target object. So, the bounding box
around the hand gesture can be determined by the co-
ordinates of the upper left corner (x,y), and specified
by its width and height. All the labels were saved in
xml files.
3.2 Data Sampling
Training and testing YOLOv5 involve image sam-
pling. We randomly splited the image dataset into
training, validation and test sets containing 80%,
10%, 10% of the sign data, respectively. We selected
these partition values according to some conducted
tests.
3.3 Training based YOLOv5 Model
In the proposed system, the Arabic sign language
recognition process is modeled as a regression prob-
lem. It is aimed to predict bounding boxes and class
probabilities of the requested input sign image. In this
work, we adapted YOLO detector. Various versions
of this model have been published : YOLOv1 (Red-
mon et al., 2016), YOLOv2 (Redmon and Farhadi,
2017) and YOLOv3 (Redmon and Farhadi, 2018).
In 2020, two major versions of YOLO have been
released named YOLOv4 (Bochkovskiy et al., 2020),
YOLOv5(https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5).
Each new version has a boosted performance (in-
ference speed and mAP score) compared to its
predecessor.
The YOLO algorithm applies a single neural net-
work to the input image. The latter is divided into
SxS grids. Each grid cell detects the object defined
by its center. The output of the algorithm is a vec-
tor computed for each grid cell (i.e object), containing
the predicted bounding box (width, hight), confidence
score of having an object and number of classes. The
network architecture of YOLOv5 is shown in Figure
3 (Yolov5, 2020).
Figure 3: The network architecture of YOLOv5.
According to the Figure 3, YOLO consists of three
main blocks:
• Backbone: is a CNN architecture used for the
feature extraction.
• Neck: is a series of network layers that aggregate
the features formed in the backbone.
• Head: is the final layer of the network in which
the detection happens in one stage, with three
(18×18, 36×36, 72×72) levels of granularity. This
enables multi-scale (Redmon and Farhadi, 2018)
object recognition, targeting at objects with vari-
ous sizes. One-stage detectors make the predic-
tions for object localization and classification at
the same time. In contrast, two-stage detectors de-
couple the object localization (based region pro-
posal) and classification for each bounding box.
Major improvements in YOLOv5 includes:
(1) In backbone module, YOLOv5 incorporates
Cross Stage Partial Network (Wang et al., 2020)
into Darknet. The model parameters and FLOPS
(Floating-point Operations Per Second) are re-
duced, which decrease the model size, while
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
20

enhancing its speed. By adjusting the width
and depth of the BottleneckCSP module, differ-
ent models (with different sizes and inference
time) can be obtained, such as YOLOv5small,
YOLOv5medium, YOLOv5large, and YOLOv5-
extraLarge. However, the deployment of the small
version in embedded and mobile devices would be
more convenient for real-time recognition appli-
cations.
(2) In neck module, YOLOv5 applied PANet (Liu
et al., 2018) to generate feature pyramids. The lat-
ter helps improving the precision of object recog-
nition.
(3) YOLOv5 is on PyTorch implementation, while all
the previous models used the DarkNet implemen-
tation.
(4) In terms of performance, YOLOv5 is much faster
(high inference time), more accurate (improved
mAP) and smaller (reduced parameters) model
compared to the stated versions.
In the training step, transfer learning is required to
generate YOLOv5 recognizer. The idea is as follows:
• Pre-train the source model (in our case, YOLOv5
neural network) on COCO dataset (Lin et al.,
2014) including 80 classes.
• Create a target model that has the same configura-
tion of the source model except the output layer.
• Add an output layer to the target model.
• Train the target model on the training ArSL im-
age set (including 28 classes), which allows fine
tuning the parameters of the first layers and opti-
mizing from scratch the parameters of the added
output layer). During the training, YOLOv5 uses
a loss function which is the sum of a localization
loss and a classification loss.
Transfer learning (Pan and Yang, 2009) has the ad-
vantages of requiring much less training data (than a
CNN trained from scratch) and retraining quickly the
adapted model on new data.
3.4 ArSL Recognition
Once the YOLOv5 model is generated, it is used to
make inference on ArSL image test set. The recog-
nition output is bounding box coordinates around the
hand gesture, the corresponding class and the confi-
dence score of the hand gesture.
4 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
All experiments are carried on Google Colaboratory
(called also Colab) platform, which is a free cloud
service for deep learning applications. Colab provides
NVIDIA Tesla (k80, T4, P4 and P100) GPU of about
12.8 GB memory.
4.1 Dataset Description
To achieve high performance when performing deep
learning, it is required to use large scale datasets.
However, most of the available datasets are of small
size such as (Hemayed and Hassanien, 2010) or
constructed with uniform backgrounds (Latif et al.,
2019). In response to these issues, a new database
was established, which is freely available for inter-
ested researchers
1
.
It contains 5600 static posture images of size
720x960 pixels. It has up to 28 sign classes acquired
from two different signers (hand size, and skin tone)
via a mobile smartphone. The posture images were
recorded under different realistic (uncontrolled) con-
ditions, i.e varying position, lighting, and with in-
door/outdoor background. Figure 4 shows some sam-
ple images representing the letter “Ba”.
Figure 4: Image samples of letter Ba.
4.2 Empirical Hyper-parameter
Settings
The hyper-parameters of the YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m,
YOLOv5l and Faster R-CNN models, are set as ex-
posed in Table 2. The adapted tuning of the models is
based on extensive tests.
Table 2: Empirical hyper-parameter values.
Model YOLOv5l YOLOv5m YOLOv5s Faster R-CNN
Learning rate 0.01 0.01 0.015 0.001
Batch size 24 16 16 24
Max epochs 50 50 60 60
Optimizer SGD SGD SGD SGD
Activation function SiLu SiLu SiLu SiLu
1
https://www.kaggle.com/sabribelmadoui/arabic-sign-
language-unaugmented-dataset
Real-time Arabic Sign Language Recognition based on YOLOv5
21

4.3 Evaluation Metrics
In the performed experiments, we are interested in
evaluating the adapted real-time Arabic sign language
recognition models in terms of the mean Average Pre-
cision (mAP) and FPS (Frame-Per-Second), which
are described in the following:
• Intersection over Union. To compute the mAP,
we use Intersection over Union (IoU) metric. It is
defined as the intersection between the predicted
and ground truth bounding boxes divided by their
union. The IoU values vary from 0 to 1. The high
score of IoU, means more overlapping between
the predicted and ground truth bounding boxes B1
and B2, respectively.
IoU =
B1 ∩ B2
B1 ∪ B2
(1)
• Precision: represents the proportion of positive
predictions that were correctly identified.
precision =
T P
T P + FP
(2)
In object detection problems , a correct prediction
(TP) is calculated based on a fixed IoU threshold.
• Recall: is the ratio of positive samples correctly
detected by the model.
precision =
T P
T P + FN
(3)
• Mean Average Precision (mAP): In order to cal-
culate mAP, first, we need to calculate Average
Precision (AP) per class which corresponds to the
area under the Precision–Recall curve. For a given
class, APs could be computed at different IoU
thresholds. In this case, we take the mean of AP
over different thresholds. Once the AP per class
(object category) is gotten, we can measure the
mean Average Precision by averaging the AP val-
ues over all classes. with Api is the average preci-
sion of the ith class and N is the number of classes.
mAP =
1
N
N
∑
i=1
AP
i
(4)
• Frame-Per-Second: called FPS for short, is a
unit that defines how fast the object detection
model processes the input images and recognizes
the desired output. It consists of the number of
frames that occur each second. The higher FPS
value is, the faster the recognition would be.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 3 reports the results obtained using the consid-
ered models: YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, and YOLOv5l.
These models achieve comparable detection accuracy.
We observe that YOLOv5-large yields the best recog-
nition precision, recall and mAP@.5 values (99.5%,
99.4%, 99.4%, respectively) compared to YOLOv5-
small and YOLOv5-medium.
Table 3: Performance of YOLOv5 model on ArSL.
Models Precision Recall mAP@.5 mAP@[.5:.95]
YOLOv5s 99.2% 99.4% 99.3% 85.9%
YOLOv5m 99.2% 99.2% 99.3% 87.75%
YOLOv5l 99.5% 99.4% 99.4% 87.2%
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the loss func-
tion evolution during the training of YOLOv5L and
YOLOv5s, respectively.
From the plots of loss, we can observe that the
YOLOv5l model achieves at 50th epoch, for bound-
ing box prediction and classification tasks, values of
0.0199, 0.020 respectively on the training set. In
YOLOv5s, the loss function for bounding boxes pre-
diction decreases to reach 0.0229 at the 60th epoch,
in the training phase. Whereas, validation loss keeps
decreasing over the epochs reaching value of 0.0086
at the 60th epoch. The classification loss of the vali-
dation set converges to 0.00064 at the 60th epoch.
In order to select the best-suited YOLOv5 model
for real-time ArSL recognition, we also computed the
speed recognition of them in terms of Frames Per Sec-
ond (FPS).
From Figure 7, we can see that YOLOv5s can
perform ArSL recognition with the highest speed. It
gives FPS of 121. While YOLOv5m has a speed of
92 FPS. The lowest value (i.e 72 FPS) is that yielded
by YOLOv5l.
As it recognized that YOLOv5s is the lightweight
version compared to YOLOv5m and YOLOv5l. It
gives faster inference time, while it yields a sat-
isfactory mAP in comparison with YOLOv5m and
YOLOv5l models.
So, YOLOv5s model would be more suitable for
real-time ArSL hand posture recognition. Similarly,
the recognition performance of the YOLOv5s was
compared to Faster R-CNN model.
Regarding the development of Faster R-CNN, we
used the X101-FPN model provided by Detectron2
library. This models presents the best accuracy rate
on ImageNet dataset (Wu et al., 2019). As we can
observe from Table 4, YOLOv5s outperform Faster
R-CNN in terms of mAP and FPS. We present in the
Figure 8 the results obtained after applying YOLOv5s
on some test images.
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
22
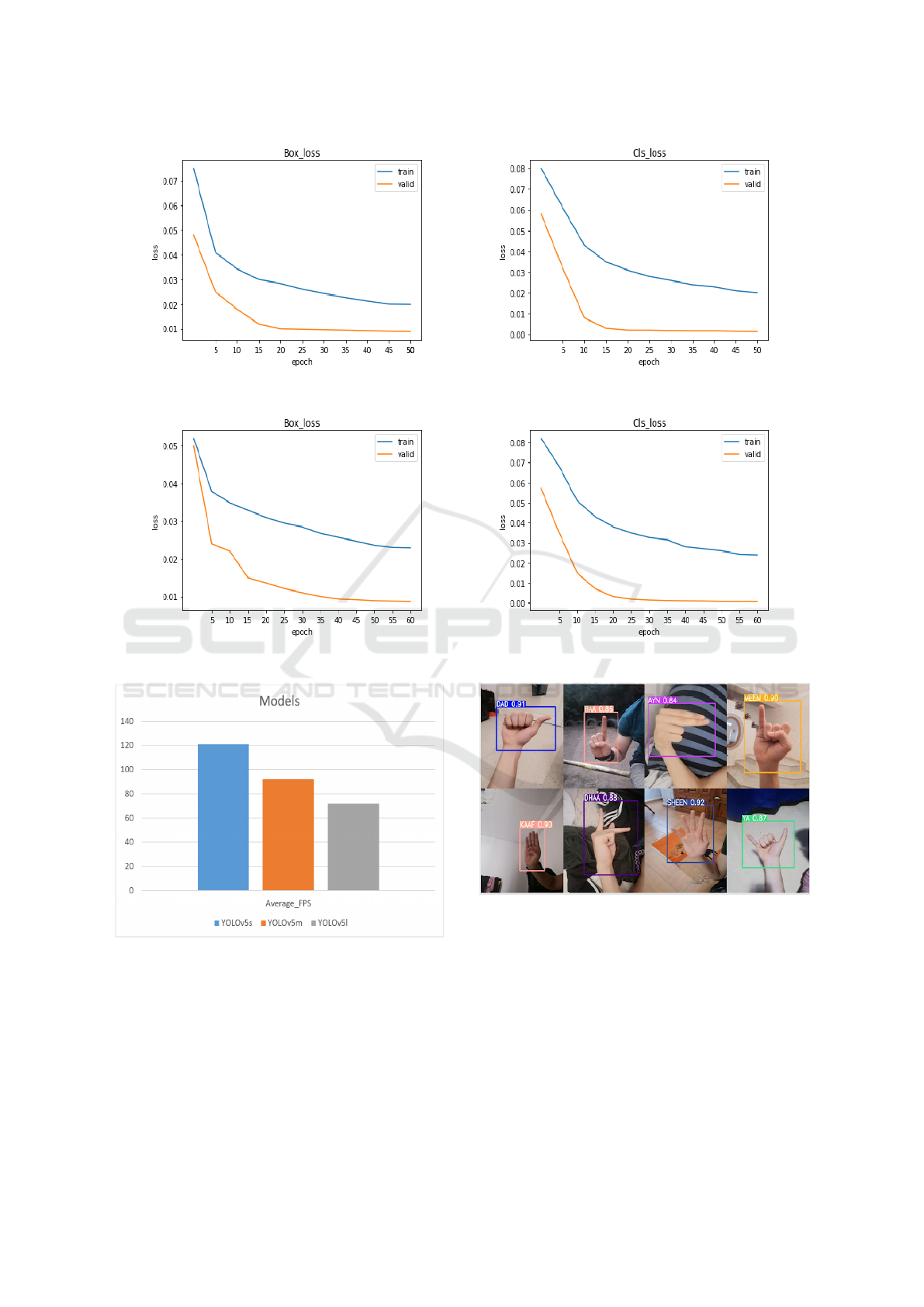
Figure 5: YOLOv5l loss evaluation. (a) bounding box prediction, (b) Sign classification.
Figure 6: YOLOv5s loss evaluation. (a) bounding box prediction, (b) Sign classification.
Figure 7: Inference time.
Consequently, the experiments conducted in this
research confirmed the potential of YOLOv5 to rec-
ognize the Arabic sign language efficiently.
Figure 8: ArSL recognition results on test images.
6 CONCLUSION
A real-time Arabic sign language hand posture recog-
nition system based on YOLOv5 is proposed in this
paper. To do so, we trained and tested YOLOv5s,
YOLOv5m and YOLOv5l models. In order to eval-
uate YOLOv5, we created a dataset containing more
than 15000 sign images including 28 classes. The
ArSL recognition results were very satisfying both in
Real-time Arabic Sign Language Recognition based on YOLOv5
23
Table 4: Performance comparison.
Models Model parameters Inference time Average FPS mAP@.5 mAP@[.5:.95]
YOLOv5s 7.5 millions 0.007s to 0.01s 121 99.3% 85.9%
Faster R-CNN 105 millions 0.55s 1.8 98.7% 81.38%
terms of inference time and mAP. We also performed
a comparative study with Faster R-CNN. The results
showed that YOLOv5 has an overall better perfor-
mance. As perspectives, it seems interesting to de-
velop real-time ArSL recognition system in mobile
applications based YOLOv5s. Moreover, we need
to further experiments to enhance the performance of
YOLOv5s. It would be also interesting to compare
YOLOv5s against YOLOX-Tiny (Ge et al., 2021).
REFERENCES
Abdel-Fattah, M. A. (2005). Arabic sign language: a per-
spective. Journal of deaf studies and deaf education,
10(2):212–221.
Alani, A. A. and Cosma, G. (2021). Arsl-cnn: a convolu-
tional neural network for arabic sign language gesture
recognition.
Alawwad, R. A., Bchir, O., and Ismail, M. M. B. (2021).
Arabic sign language recognition using faster r-cnn.
Almasre, M. A. and Al-Nuaim, H. (2017). The performance
of individual and ensemble classifiers for an arabic
sign language recognition system. INTERNATIONAL
JOURNAL OF ADVANCED COMPUTER SCIENCE
AND APPLICATIONS, 8(5):307–315.
Alzohairi, R., Alghonaim, R., Alshehri, W., Aloqeely, S.,
Alzaidan, M., and Bchir, O. (2018). Image based ara-
bic sign language recognition system. International
Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applica-
tions (IJACSA), 9(3).
Assaleh, K. and Al-Rousan, M. (2005). Recognition of ara-
bic sign language alphabet using polynomial classi-
fiers. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Pro-
cessing, 2005(13):1–10.
Bantupalli, K. and Xie, Y. (2018). American sign language
recognition using deep learning and computer vision.
In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data
(Big Data), pages 4896–4899. IEEE.
Bheda, V. and Radpour, D. (2017). Using deep convolu-
tional networks for gesture recognition in american
sign language. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.06836.
Bochkovskiy, A., Wang, C.-Y., and Liao, H.-Y. M. (2020).
Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detec-
tion. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.10934.
Dahmani, D. and Larabi, S. (2014). User-independent
system for sign language finger spelling recognition.
Journal of Visual Communication and Image Repre-
sentation, 25(5):1240–1250.
Dipietro, L., Sabatini, A. M., and Dario, P. (2008). A survey
of glove-based systems and their applications. Ieee
transactions on systems, man, and cybernetics, part c
(applications and reviews), 38(4):461–482.
Dodge, S. and Karam, L. (2016). Understanding how image
quality affects deep neural networks. In 2016 eighth
international conference on quality of multimedia ex-
perience (QoMEX), pages 1–6. IEEE.
ElBadawy, M., Elons, A., Shedeed, H. A., and Tolba, M.
(2017). Arabic sign language recognition with 3d con-
volutional neural networks. In 2017 Eighth Interna-
tional Conference on Intelligent Computing and In-
formation Systems (ICICIS), pages 66–71. IEEE.
Ge, Z., Liu, S., Wang, F., Li, Z., and Sun, J. (2021). Yolox:
Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv e-prints, pages
arXiv–2107.
Goswami, T. and Javaji, S. R. (2021). Cnn model for ameri-
can sign language recognition. In ICCCE 2020, pages
55–61. Springer.
Han, J., Zhang, D., Cheng, G., Guo, L., and Ren, J. (2014).
Object detection in optical remote sensing images
based on weakly supervised learning and high-level
feature learning. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience
and Remote Sensing, 53(6):3325–3337.
Hemayed, E. E. and Hassanien, A. S. (2010). Edge-based
recognizer for arabic sign language alphabet (ars2v-
arabic sign to voice). In 2010 International Computer
Engineering Conference (ICENCO), pages 121–127.
IEEE.
Hu, Q., Wang, P., Shen, C., van den Hengel, A., and Porikli,
F. (2017). Pushing the limits of deep cnns for pedes-
trian detection. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and
Systems for Video Technology, 28(6):1358–1368.
Islam, S., Mousumi, S. S. S., Rabby, A. S. A., Hossain,
S. A., and Abujar, S. (2018). A potent model to recog-
nize bangla sign language digits using convolutional
neural network. Procedia computer science, 143:611–
618.
Jiao, L., Zhang, F., Liu, F., Yang, S., Li, L., Feng, Z., and
Qu, R. (2019). A survey of deep learning-based object
detection. IEEE access, 7:128837–128868.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. Advances in neural information processing
systems, 25:1097–1105.
Latif, G., Mohammad, N., Alghazo, J., AlKhalaf, R., and
AlKhalaf, R. (2019). Arasl: Arabic alphabets sign
language dataset. Data in brief, 23:103777.
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., and Belongie, S. e. a. (2014). Mi-
crosoft coco: Common objects in context. In Euro-
pean conference on computer vision, pages 740–755.
Springer.
Liu, S., Qi, L., Qin, H., Shi, J., and Jia, J. (2018). Path ag-
gregation network for instance segmentation. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision
and pattern recognition, pages 8759–8768.
Mikołajczyk, A. and Grochowski, M. (2018). Data augmen-
tation for improving deep learning in image classifica-
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
24

tion problem. In 2018 international interdisciplinary
PhD workshop (IIPhDW), pages 117–122. IEEE.
Oz, C. and Leu, M. C. (2011). American sign language
word recognition with a sensory glove using artificial
neural networks. Engineering Applications of Artifi-
cial Intelligence, 24(7):1204–1213.
Pan, S. J. and Yang, Q. (2009). A survey on transfer learn-
ing. IEEE Transactions on knowledge and data engi-
neering, 22(10):1345–1359.
Ranjan, R., Patel, V. M., and Chellappa, R. (2017). Hy-
perface: A deep multi-task learning framework for
face detection, landmark localization, pose estimation,
and gender recognition. IEEE transactions on pattern
analysis and machine intelligence, 41(1):121–135.
Rao, G. A., Syamala, K., Kishore, P., and Sastry, A. (2018).
Deep convolutional neural networks for sign language
recognition. In 2018 Conference on Signal Processing
And Communication Engineering Systems (SPACES),
pages 194–197. IEEE.
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., and Farhadi, A.
(2016). You only look once: Unified, real-time object
detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 779–
788.
Redmon, J. and Farhadi, A. (2017). Yolo9000: better, faster,
stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 7263–
7271.
Redmon, J. and Farhadi, A. (2018). Yolov3: An incremental
improvement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.02767.
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., and Sun, J. (2015). Faster
r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region
proposal networks. Advances in neural information
processing systems, 28.
Tharwat, A., Gaber, T., Hassanien, A. E., Shahin, M. K.,
and Refaat, B. (2015). Sift-based arabic sign language
recognition system. In Afro-european conference for
industrial advancement, pages 359–370. Springer.
Wang, C.-Y., Liao, H.-Y. M., Wu, Y.-H., Chen, P.-Y., Hsieh,
J.-W., and Yeh, I.-H. (2020). Cspnet: A new backbone
that can enhance learning capability of cnn. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer
vision and pattern recognition workshops, pages 390–
391.
Wu, B., Iandola, F., Jin, P. H., and Keutzer, K. (2017).
Squeezedet: Unified, small, low power fully convo-
lutional neural networks for real-time object detection
for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE
conference on computer vision and pattern recogni-
tion workshops, pages 129–137.
Wu, Y., Kirillov, A., Massa, F., Lo, W.-Y., and Girshick,
R. (2019). Detectron2. 2019. URL https://github.
com/facebookresearch/detectron2, 2(3).
Yang, S. and Zhu, Q. (2017). Continuous chinese sign
language recognition with cnn-lstm. In Ninth In-
ternational Conference on Digital Image Processing
(ICDIP 2017), volume 10420, page 104200F. Interna-
tional Society for Optics and Photonics.
Yin, X.-C., Yin, X., Huang, K., and Hao, H.-W. (2013).
Robust text detection in natural scene images. IEEE
transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelli-
gence, 36(5):970–983.
Yolov5 (2020). Overview of model structure about
YOLOv5 · issue #280 · ultralytics/yolov5 . accessed
2021-11-01.
Zafrulla, Z., Brashear, H., Presti, P., Hamilton, H., and
Starner, T. (2011). Copycat: An american sign lan-
guage game for deaf children. automatic face & ges-
ture recognition and workshops (fg 2011). In 2011
IEEE International Conference.
Real-time Arabic Sign Language Recognition based on YOLOv5
25
