
Boosting the Performance of Deep Approaches through Fusion with
Handcrafted Features
Dimitrios Koutrintzes
1
, Eirini Mathe
1,2
and Evaggelos Spyrou
1,3
1
Institute of Informatics and Telecommunications, National Center for Scientific Research - “Demokritos,” Athens, Greece
2
Department of Informatics, Ionian University, Corfu, Greece
3
Department of Computer Science and Telecommunications, University of Thessaly, Lamia, Greece
Keywords:
Human Activity Recognition, Multimodal Fusion.
Abstract:
Contemporary human activity recognition approaches are heavily based on deep neural network architectures,
since the latter do not require neither significant domain knowledge, nor complex algorithms for feature ex-
traction, while they are able to demonstrate strong performance. Therefore, handcrafted features are nowadays
rarely used. In this paper we demonstrate that these features are able to learn complementary representations
of input data and are able to boost the performance of deep approaches, i.e., when both deep and handcrafted
features are fused. To this goal, we choose an existing set of handcrafted features, extracted from 3D skeletal
joints. We compare its performance with two approaches. The first one is based on a visual representation
of skeletal data, while the second is a rank pooling approach on raw RGB data. We show that when fusing
both types of features, the overall performance is significantly increased. We evaluate our approach using a
publicly available, challenging dataset of human activities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is the problem
of identifying actions, activities or events that are per-
formed by humans. Typically, such approaches are
based on some sensorial input. Undoubtedly, the most
popular approach nowadays is to use video input, cap-
tured by one or more cameras. It is typically formu-
lated as a multi-class classification problem, i.e., of
outputting the class label of the performed activity. Its
areas of application are broad, including surveillance,
assisted living, human-machine interaction, affective
computing, etc. When approaching a HAR task, us-
ing a computer vision approach, one should select the
appropriate way to capture, represent, analyze and fi-
nally classify visual data to activities.
According to Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2016),
HAR may be divided into a) segmented recognition,
wherein the input video contains exactly one activity;
and b) continuous recognition, wherein the goal is to
detect and classify actions within a video, wherein
several parts may not contain actions, while start-
ing and ending points of actions should be detected.
Moreover, HAR may be further divided into 4 main
tasks, namely gesture, action, interaction and group
activity recognition. Actions require a significant
amount of time, contrary to gestures that are consid-
ered to be “instant” and may involve more body parts.
Interactions may take part either between a person and
some object, or between two persons. Group activi-
ties may be combinations of the above.
Earlier HAR approaches were based on the ex-
traction of handcrafted features from raw visual data.
These features are algorithmically extracted, capture
visual properties of postures and/or motion and are
used to train traditional machine learning approaches,
such as neural networks or support vector machines
(Schuldt et al., 2004). These approaches have been
criticized since they exhibit significant drop of per-
formance and lack of generalization when applied to
large-scale datasets. Moreover they are not robust to
viewpoint changes. Of course, as with every other
field of application, they require specific knowledge
of the domain of application. During the last few
years, they have been replaced by deep neural net-
work architectures. The latter do not require a feature
extraction step, since features are learnt within some
of their layers. Thus, raw data or simple data repre-
sentations have been replaced by this feature extrac-
tion step. Moreover, deep architectures exhibit higher
accuracies, that are typically increasing when they are
trained with larger datasets. Therefore, in many cases
370
Koutrintzes, D., Mathe, E. and Spyrou, E.
Boosting the Performance of Deep Approaches through Fusion with Handcrafted Features.
DOI: 10.5220/0010982700003122
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2022), pages 370-377
ISBN: 978-989-758-549-4; ISSN: 2184-4313
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

handcrafted features are considered to be obsolete and
are rarely used in research works.
The most popular deep approach that is applied
in the area of HAR is the one of Convolutional Neu-
ral Networks (CNNs). Note that since CNNs require
still images as their input, while activities are not in-
stant, i.e., may not be captured by a single image, typ-
ically an intermediate still representation that trans-
forms (moving) visual data to still images is required
(Wang et al., 2018). Visual data commonly comprise
of raw RGB and/or depth and/or skeletal sequences.
A depth sequence consists of the estimated depth of
each pixel within the scene. Skeletal data consist
of the 2D/3D positions of a set of skeleton joints,
over time. Therefore, the aforementioned intermedi-
ate representations are designed to capture both spa-
tial and temporal information regarding postures and
motion, reflected to color and/or texture properties of
their visual representation. Also, they often do not
require a significant amount of domain knowledge.
In this work, our goal is to demonstrate that hand-
crafted features may assist towards increasing the
accuracy of deep approaches, in the field of HAR.
More specifically, we evaluate two vision-based ap-
proaches: a) an approach that transforms skeletal data
into a pseudo-colored visual representation; and b) an
approach that is based on rank-pooling of raw RGB
data of consecutive video frames, producing “dy-
namic” images. Then we evaluate a set of handcrafted
features, initially proposed for the problem of arm
gesture recognition, which are herein applied to the
whole skeleton. Using an early fusion approach, we
fuse learnt features of both vision-based approaches
with the handcrafted ones and we demonstrate that
the latter are able to significantly boost their perfor-
mance.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows:
in section 2 we present related work in the field of
HAR, focusing on approaches that are based on skele-
tal data, on RGB data and on handcrafted features.
Then, in section 3 we present the skeletal data repre-
sentation that is used in this work, the three classifi-
cation approaches and the fusion one. The dataset we
use and the experimental results of our approach are
presented in section 4. Finally, conclusions are drawn
in section 5, wherein plans for future work are also
presented.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section we briefly present related work focus-
ing on HAR that is based on deep learning architec-
tures. More specifically, we focus on a) approaches
that are based on intermediate visual representations
of 3D motion of skeletal joints that are used with a
Convolutional Neural Network; b) approaches that
are based on the extraction of handcrafted features
from skeletal sequences and c) on approaches that are
based on fusion of learnt and handcrafted features.
2.1 Skeletal Motion Representations for
HAR
Skeletal motion image representations are used as in-
put in CNNs. In all approaches the motivation is to
create an artificial image, by mapping features to pixel
values. The result is either a grayscale or a pseudo-
colored image, whose color and texture properties
somehow reflect the spatial and temporal properties
of skeleton motion.
In the work of Hyunh-The et al. (Huynh-The
et al., 2020), two geometric features are extracted,
namely inter-joint distances and orientations, forming
vector representations which are then concatenated to
form images. Pham et al. (Pham et al., 2019) pro-
posed a similar representation, enhanced with an im-
age processing approach for contrast stretching, so
as to highlight textures and edges of the representa-
tion. Wang et al. (Wang et al., 2016) reflected direc-
tion of skeletal motion as hue and magnitude as satu-
ration, creating a representation for each body part.
Similarly, Li et al. (Li et al., 2017) generated im-
age representations based on inter-joint distances in
the three orthogonal planes (xy, yz and xz), and the
3D space (xyz), while Hou et al. (Hou et al., 2016)
used only the orthogonal planes, encoding temporal
variation of joints into hue values. To preserve not
only spatial, but also temporal features, Li et al. (Li
et al., 2017), apart from inter-joint features, also used
a Long-Short Term Memory network. Liu et al. (Liu
et al., 2019a) arranged skeleton joints in a 2D grid, en-
coded coordinate values and incorporated duration of
performed actions. To address view invariance, a 5D
representation has been proposed by Liu et al. (Liu
et al., 2019b), wherein spatial coordinates are com-
plemented with time and joint labels. In an effort to
preserve spatial relations between joints, Yang et al.
(Yang and Tian, 2014) incorporated skeleton graph in-
formation. Finally, Ke et al. (Ke et al., 2017) split the
skeleton into 5 parts and for each one they extracted
features which then were transformed into images.
2.2 Handcrafted Features
Handcrafted features are extracted from raw data us-
ing a predefined algorithm. Typical approaches in the
Boosting the Performance of Deep Approaches through Fusion with Handcrafted Features
371

field of HAR exploit angles between joints and joint
distances or properties of joint trajectories.
A 3D joint location histogram within a modified
spherical coordinate system has been proposed by
Xia et al. (Xia et al., 2012). Moreover, the authors
built posture vocabularies upon clustering of the his-
togram vectors. Similarly, Keceli and Can (Keceli
and Can, 2014) proposed histograms of angles and
displacements between a set of predefined joints in
the 3D space. Gowayyed et al. (Gowayyed et al.,
2013) used a histogram of oriented displacements, ex-
tracted under 3 viewpoints, so as to create 3D fea-
tures. Yang and Tian (Yang and Tian, 2014) com-
bined activity information including static pose, prop-
erties of motion and overall dynamics and combined
these three representations so as to create a compact
description of frames. Finally, Pazhoumand-Dar et al.
(Pazhoumand-Dar et al., 2015) first created relative
skeleton motion trajectories and then selected a sub-
set of these features using the longest common sub-
sequence algorithm.
2.3 Fusion Approaches
A few approaches for fusion of handcrafted features
with features learnt by a deep architecture have been
recently proposed in the field of HAR. Typically,
these approaches fuse features from the last pooling
layer of a CNN with the handcrafted ones by con-
catenating them into a single vector and then use a
traditional machine learning classifier, e.g., a support
vector machine for classification.
Khan et al. (Khan et al., 2020a) proposed fu-
sion of learnt features of a pre-trained CNN model,
namely the VGG19 architecture (Simonyan and Zis-
serman, 2014) and multiview handcrafted features
that are based on horizontal/vertical gradients and
directional features. In another work, Khan et al.
(Khan et al., 2020b) extracted motion, geometric and
shape features from regions of interest and fused
them with features of pre-trained AlexNet architec-
ture (Krizhevsky et al., 2012). Udeen and Lee (Ud-
din and Lee, 2019) extracted deep spatial features
of Inception-Resnet-v2 architecture (Szegedy et al.,
2017) and fused them with a novel feature descriptor
that captures spatio-temporal and shape features. In
previous work (Vernikos et al., 2019b) we trained a
CNN using a dataset for action recognition and used
it as feature extractor for a gesture recognition task,
upon fusing its learnt features with handcrafted inter-
joint distance and joint angle features.
HEAD
NECK
SHOULDERLEFT
SPINESHOULDER
ELBOWLEFT
WRISTLEFT
HANDLEFT
KNEELEFT
HANDTIPLEFT
THUMBLEFT
FOOTLEFT
ANKLELEFT
SPINEBASE
SHOULDERRIGHT
SPINEMID
ELBOWRIGHT
HIPLEFT
FOOTRIGHT
ANKLERIGHT
KNEERIGHT
HIPRIGHT
HANDTIPRIGHT
WRISTRIGHT
HANDRIGHT
THUMBRIGHT
Figure 1: Extracted human skeleton 3D joints using the
Kinect SDK.
3 PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data
As it has already been mentioned in Section 1, our
approach is based on skeletal joint motion informa-
tion. All techniques that are used and will be pre-
sented within this section use as their input 3D trajec-
tories of a set of human joints. We assume that these
joints have been extracted using the Microsoft Kinect
v2 camera, which consists of an RGB and depth cam-
era. More specifically, Kinect SDK is used to extract
and track in real time skeletal joint positions based
on captured RGB and depth data. For each joint, its
x, y and z coordinates per frame (i.e., over time) are
provided. Using Kinect v2, a set of 25 joints be-
comes available. Joints follow a graph-based hier-
archy; the whole skeleton is represented as a graph,
wherein joints correspond to nodes and are connected
by edges that follow the body structure. This repre-
sentation is illustrated in Fig. 1. The “SPINEBASE”
is considered as the root of the graph. Parent-child
relationship among pairs of joints is implied, e.g.,
“SPINESHOULDER” is the parent of “SHOULDER-
LEFT,” while “SHOULDERLEFT” is the parent of
“ELBOWLEFT” etc. Note that all approaches that we
shall later describe are also compatible to extracted
skeletons that follow a hierarchical structure. More-
over, in Fig. 2 we illustrate a sequence of frames de-
picting the activity kicking something with extracted
skeletons imposed on the raw RGB data.
3.2 Extracted Handcrafted Features
In this work we use a set of handcrafted features
that have been proposed by Paraskevopoulos et al.
(Paraskevopoulos et al., 2019). Although they have
ICPRAM 2022 - 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
372
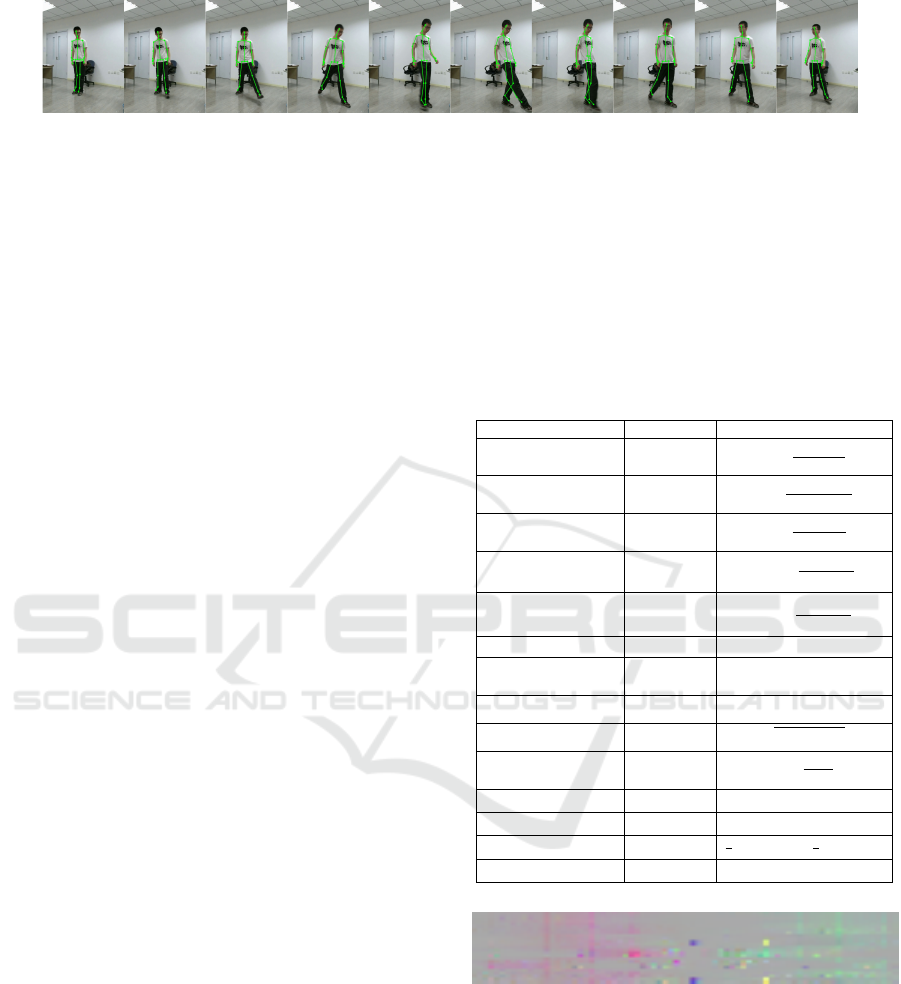
Figure 2: A sequence of an actor performing the activity kicking something. Extracted human skeleton 3D joints using the
Kinect SDK have been overlaid. Frames have been taken from the PKU-MMD dataset (Liu et al., 2017) and have been
trimmed for illustration purposes.
been initially designed for the problem of hand ges-
ture recognition, upon initial experimental evaluation
we ended up that they are appropriate for the problem
of HAR. These features assume a set of joints orga-
nized in a hierarchical structure, wherein a parent–
child relationship is implied. These joints move in a
3D space, over time. Therefore, they may be extracted
by the aforementioned set of skeletal sequences. At
the following we briefly present these features.
For a given joint J, let J
c
and J
p
be its child and
parent joints, respectively. Let F = {F
i
}, i = 1, 2, . . . N
denote the set of frames of a given video sequence
depicting an activity. Moreover, let v
J
i
be a vector
that corresponds to the 3D coordinates of J within F
i
.
More specifically, v
J
i
=
v
J
x,i
, v
J
y,i
, v
J
z,i
are the afore-
mentioned x, y and z coordinates. Also, let V
J
be
the set of all vectors v
J
i
. By B(V
J
) we denote the
3D bounding box of V
J
, by a
B(V
J
)
and b
B(V
J
)
the
lengths of its horizontal and vertical sides, respec-
tively. We summarize the extracted features in Table
1.
3.3 Pseudo-colored Images
Moreover, in order to use the skeletal information as
input to a CNN, we use the representation of Vernikos
et al. (Vernikos et al., 2019a). This representation
aims to capture inter-joint distances during an action
and use them to create pseudo-colors within an arti-
ficial RGB image. Note that it is based on the 3D
trajectories of skeletal joints. From the x, y and z co-
ordinates of each of the M available joints, a set of
3 · N signals is collected for a given video sequence
depicting an activity. To address the problem of tem-
poral variability between actions and between users, a
linear interpolation step is imposed, by manually set-
ting the duration of all video sequences equal to N
frames. From each sequence, coordinate differences
between consecutive frames are calculated, while x, y,
z coordinates correspond to R, G, B color channels of
the pseudo-colored image, respectively. More specif-
ically, the latter is created as follows:
Let x
i
(n) denote the x-position of the i-th joint in
the n-th frame. Let R denote the red channel of the
color image. The value of R(i, n) is calculated as:
Table 1: Proposed features, extracted from the skele-
tal joints. For features marked with
∗
, respective an-
gles a
pc
, b
pc
, c
pc
are calculated as: a
2
pc
=
v
J
x
− v
J
c
x
2
+
v
J
y
− v
J
c
y
2
, b
pc
= v
J
x
, c
2
pc
=
v
J
p
x
2
+
v
J
y
− v
J
p
y
2
. Note
that for the formulation of the triangle, a reference point
with coordinates (v
J
p
x,i
, 0, 0) is used. By d we denote the Eu-
clidean distance and F
J
is the number of frames for each
gesture, which is also used as a feature.
Feature name Frames involved Equation
Spatial angle F
2
, F
1
arccos
v
J
2
· v
J
1
v
J
2
·
v
J
1
Spatial angle F
N
, F
N−1
arccos
v
J
N
· v
J
N−1
v
J
N
·
v
J
N−1
Spatial angle F
N
, F
1
arccos
v
J
N
· v
J
1
v
J
N
·
v
J
1
Total vector angle F
1
, . . . , F
N
N
∑
i=1
arccos
v
J
i
· v
J
i−1
v
J
i
v
J
i−1
!
Squared total vector angle F
1
, . . . , F
N
n
∑
i=1
arccos
v
J
i
· v
J
i−1
v
J
i
v
J
i−1
!
2
Total vector displacement F
N
, F
1
v
J
N
− v
J
1
Total displacement F
1
, . . . , F
N
n
∑
i=1
v
J
i
− v
J
i−1
Maximum displacement F
1
, . . . , F
N
max
i=2,...,N
v
J
i
− v
J
i−1
Bounding box diagonal length F
1
, . . . , F
N
q
a
2
B(V
J
)
+ b
2
B(V
J
)
Bounding box angle F
1
, . . . , F
N
arctan
b
B(V
J
)
a
B(V
J
)
Initial angle F
1
]v
J
1
Ov
J
p
1
or ]v
J
1
Ov
J
c
1
Final angle F
N
]v
J
N
Ov
J
p
N
or ]v
J
N
Ov
J
c
N
Mean angle F
1
, . . . , F
N
1
N
∑
N
i=1
]v
J
i
Ov
J
p
i
or
1
N
∑
N
i=1
]v
J
i
Ov
J
c
i
Max angle F
1
, . . . , F
N
max
N
i=1
]v
J
i
Ov
J
p
i
or max
N
i=1
]v
J
i
Ov
J
c
i
Figure 3: The pseudo-colored image for the activity kicking
something that is illustrated in Fig. 2.
R(i, n) = x
i
(n + 1) − x
i
(n), where i = 1, . . . , N. Sim-
ilarly, B and G channels are constructed. As it is
exhibited, the way these pseudo-colored images are
formed, leads to preserving both the temporal and the
spatial properties of the skeleton trajectories. In Fig. 3
we illustrate a pseudo-colored image that corresponds
to the activity illustrated in Fig. 2.
Boosting the Performance of Deep Approaches through Fusion with Handcrafted Features
373

Figure 4: The dynamic image for the activity kicking some-
thing that is illustrated in Fig. 2.
3.4 Dynamic Images
The idea for the construction of dynamic images
(Bilen et al., 2016) is to represent a video sequence
as a ranking function S(•) of its frames F
1
, . . . , F
N
(Fernando et al., 2015). This function provides a fea-
ture vector ψ(F
i
) extracted from each video frame
F
i
. Let us denote by V
t
=
1
t
∑
t
i=1
ψ(F
t
) the time av-
erage of the aforementioned features from the first to
the t−th frame, wherein S(•) associates to each time
t a score S(t), given a set of parameters d that are
learned upon solving a convex optimization problem,
i.e., later frames obtain larger scores. Although ψ(•)
may be any feature extractor, Bilen et al. (Bilen et al.,
2016) opted for simply using raw RGB pixel values
and reported remarkable results. However, the most
important aspects of such an approach are a) d may
be interpreted as an RGB image; and b) this image is
obtained by rank pooling, thus it may be regarded as
a summary of the whole sequence. Note that the pix-
els in the produced dynamic images tend to focus on
salient information rather than the background, which
in our opinion makes them appropriate for the prob-
lem of HAR. In Fig. 4 we illustrate a dynamic image
that corresponds to the activity illustrated in Fig. 2.
3.5 Activity Classification
For classification of both pseudo-colored and dy-
namic images we use the same Convolutional Neural
Network that has been proposed and evaluated in our
previous work (Papadakis et al., 2019b), for a sim-
ilar HAR problem. More specifically, the first con-
volutional layer filters the 159 × 75 input activity im-
age with 32 kernels of size 3 × 3. The first pooling
layer uses max-pooling to perform 2 ×2 subsampling.
Then, the second convolutional layer filters the re-
sulting 76 × 34 image with 64 kernels of size 3 × 3,
followed by a second pooling layer, which also uses
max-pooling to perform 2 × 2 sub-sampling. A third
convolutional layer filters the resulting 36 × 15 im-
age with 128 kernels of size 3 × 3 and a third pool-
ing layer uses max-pooling to perform 2 × 2 sub-
sampling. Then, a flatten layer transforms the output
of the last pooling to a vector, which is then used as
input to a dense layer using dropout. Finally, a sec-
ond dense layer produces the output of the network.
For classification of the handcrafted features we used
a Support Vector Machine with linear kernel.
3.6 Fusion
As we have already mentioned, we use two distinct
feature extraction steps: a) handcrafted features, ex-
tracted by 3D joint motion; and b) deep features ex-
tracted using a CNN. The former are extracted using
the methodology described in section 3.2. The latter
consist of the learnt features, i.e., the dense layers of
the CNN are omitted. Both features are concatenated
into a single feature vector. For classification, they are
normalized and then upon a PCA step they are given
as input to an SVM.
4 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
4.1 Datasets
For the experimental evaluation of our approach we
used the PKU-MMD dataset (Liu et al., 2017). It is
a large-scale benchmark dataset that focuses on hu-
man action understanding. It contains approx. 20K
action instances from 51 action categories, spanning
into 5.4M video frames. For the data collection, 66
human subjects have been involved. Moreover, each
action has been recorded by 3 camera views, namely L
(left), M (middle) and R (right); fixed angles are used,
i.e., −45
◦
, 0
◦
and +45
◦
. Note, that the height of all
cameras is the same and remains fixed, while the area,
within which users perform actions is pre-determined.
The Microsoft Kinect v2 camera was used for all
recordings, and for each action instance the following
where provided: a) raw RGB video sequences depict-
ing one or more test subjects performing an action; b)
depth sequences, i.e., depth information of the afore-
mentioned RGB sequences; c) infrared radiation se-
quences of the aforementioned sequences; and d) ex-
tracted 3D positions of human skeleton joints.
4.2 Setup
Experiments were performed on a personal worksta-
tion with an Intel
TM
i7 5820K 12 core processor on
3.30 GHz and 16GB RAM, using NVIDIA
TM
Geforce
GTX 2060 GPU with 8 GB RAM and Ubuntu 18.04
ICPRAM 2022 - 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
374

Table 2: Experimental results of the proposed approach. P and R denote Precision and Recall, respectively. Also PC, DI and
HF denote the pseudocolored images (section 3.3), the dynamic images (section 3.4) and the handcrafted features (section
3.2), respectively.
Experiment
Viewpoint PC DI HF PC+DI PC+HF DI+HF PC+DI+HF
Train Test P R P R P R P R P R P R P R
Cross View
LR M 0.81 0.80 0.63 0.60 0.62 0.60 0.83 0.82 0.82 0.82 0.74 0.71 0.85 0.84
LM R 0.71 0.70 0.56 0.50 0.53 0.52 0.75 0.71 0.75 0.74 0.66 0.61 0.78 0.75
RM L 0.73 0.72 0.55 0.51 0.54 0.54 0.76 0.73 0.76 0.75 0.66 0.61 0.79 0.76
M L 0.61 0.60 0.54 0.47 0.52 0.51 0.70 0.64 0.68 0.68 0.65 0.57 0.74 0.70
M R 0.61 0.60 0.54 0.45 0.50 0.50 0.70 0.62 0.70 0.68 0.64 0.55 0.73 0.68
R L 0.53 0.52 0.35 0.30 0.47 0.46 0.58 0.50 0.63 0.61 0.51 0.43 0.63 0.57
R M 0.64 0.63 0.46 0.39 0.54 0.53 0.68 0.63 0.73 0.72 0.61 0.54 0.73 0.70
L R 0.53 0.52 0.40 0.31 0.46 0.44 0.60 0.52 0.61 0.59 0.54 0.46 0.65 0.59
L M 0.65 0.64 0.51 0.45 0.57 0.55 0.71 0.68 0.71 0.70 0.64 0.60 0.76 0.74
Cross Subject LRM LRM 0.73 0.72 0.69 0.68 0.58 0.57 0.82 0.81 0.76 0.75 0.76 0.75 0.83 0.82
Single View
L L 0.58 0.58 0.78 0.73 0.55 0.53 0.82 0.81 0.67 0.64 0.79 0.78 0.82 0.81
R R 0.53 0.54 0.77 0.74 0.56 0.53 0.80 0.78 0.67 0.66 0.79 0.78 0.82 0.80
M M 0.64 0.63 0.80 0.78 0.58 0.57 0.84 0.84 0.69 0.69 0.82 0.82 0.86 0.85
(64 bit). The deep architecture has been implemented
in Python, using Keras 2.2.4 (Chollet et al., 2018)
with the Tensorflow 1.12 (Abadi et al., 2016) back-
end. All data pre-processing and processing steps
have been implemented in Python 3.6 using NumPy,
SciPy and OpenCV.
4.3 Results
Our experiments are divided into 3 parts: a) ex-
periments under the same viewpoint (single-view),
wherein samples from the same camera viewpoint
are used for training and testing; b) experiments un-
der different viewpoints (cross-view), wherein sam-
ples from different camera viewpoints are used for
training and testing; and c) cross-subject experi-
ments, wherein actors are split into training and test-
ing groups, i.e., none participating in both groups.
The goal of cross view experiments is to evaluate
the robustness under simple transformations, such as
translation and/or rotation which are typical in real-
life applications and occur due to viewpoint changes
since cameras are still, while subjects move within a
space. Cross subject experiments aim to evaluate the
robustness of the approach in the case of intra-class
variations which in real-life situations may occur e.g.,
when a system is pre-trained and then used with dif-
ferent subjects and without any fine-tuning.
Experimental results are depicted in Table 2. For
each experiment we provide precision (P) and recall
(R) for each of the aforementioned parts of experi-
ments. As it may be observed, in almost every case
the fusion of the three approaches outperforms any
other approach or combination. Notably, handcrafted
features are able to boost the performance of every
other approach, upon fusion with them.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we demonstrated how handcrafted fea-
tures may be fused with learnt ones, in order to boost
the performance of classification within a human ac-
tivity recognition task. We experimentally demon-
strated that handcrafted features learn different data
representations than those learnt by deep architec-
tures, therefore, their fusion leads to increased per-
formance.
Among our future plans are to enhance the fused
approach by incorporating more modalities. Also we
would like to apply techniques such as data augmen-
tation (Papadakis et al., 2019a) transfer learning and
domain adaptation (Spyrou et al., 2020), which we be-
lieve may further increase performance. Finally, we
would like to evaluate our approach in larger datasets,
such as the NTU RGB+D120 (Liu et al., 2019b) and
in other HAR tasks, e.g., in gesture recognition and in
other domains such as surveillance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project has received funding from the Hellenic
Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI) and
the General Secretariat for Research and Technol-
ogy (GSRT), under grant agreement No 273 (Funding
Decision:GGET122785/I2/19-07-2018).
Boosting the Performance of Deep Approaches through Fusion with Handcrafted Features
375

REFERENCES
Abadi, M., Barham, P., Chen, J., Chen, Z., Davis, A.,
Dean, J., Devin, M., Ghemawat, S., Irving, G., Isard,
M., et al. (2016). Tensorflow: A system for large-
scale machine learning. In 12th {USENIX} sympo-
sium on operating systems design and implementation
({OSDI} 16), pages 265–283.
Bilen, H., Fernando, B., Gavves, E., Vedaldi, A., and Gould,
S. (2016). Dynamic image networks for action recog-
nition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on
computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 3034–
3042.
Chollet, F. et al. (2018). Keras: The python deep learn-
ing library. Astrophysics Source Code Library, pages
ascl–1806.
Fernando, B., Gavves, E., Oramas, J. M., Ghodrati, A., and
Tuytelaars, T. (2015). Modeling video evolution for
action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 5378–5387.
Gowayyed, M. A., Torki, M., Hussein, M. E., and El-
Saban, M. (2013). Histogram of oriented displace-
ments (hod): Describing trajectories of human joints
for action recognition. In Twenty-third international
joint conference on artificial intelligence.
Hou, Y., Li, Z., Wang, P., and Li, W. (2016). Skeleton op-
tical spectra-based action recognition using convolu-
tional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits
and Systems for Video Technology, 28(3):807–811.
Huynh-The, T., Hua, C.-H., Ngo, T.-T., and Kim, D.-S.
(2020). Image representation of pose-transition fea-
ture for 3d skeleton-based action recognition. Infor-
mation Sciences, 513:112–126.
Ke, Q., An, S., Bennamoun, M., Sohel, F., and Boussaid, F.
(2017). Skeletonnet: Mining deep part features for 3-
d action recognition. IEEE signal processing letters,
24(6):731–735.
Keceli, A. S. and Can, A. B. (2014). Recognition of basic
human actions using depth information. International
Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelli-
gence, 28(02):1450004.
Khan, M. A., Javed, K., Khan, S. A., Saba, T., Habib, U.,
Khan, J. A., and Abbasi, A. A. (2020a). Human ac-
tion recognition using fusion of multiview and deep
features: an application to video surveillance. Multi-
media tools and applications, pages 1–27.
Khan, M. A., Sharif, M., Akram, T., Raza, M., Saba, T., and
Rehman, A. (2020b). Hand-crafted and deep convo-
lutional neural network features fusion and selection
strategy: an application to intelligent human action
recognition. Applied Soft Computing, 87:105986.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. Advances in neural information processing
systems, 25:1097–1105.
Li, C., Hou, Y., Wang, P., and Li, W. (2017). Joint dis-
tance maps based action recognition with convolu-
tional neural networks. IEEE Signal Processing Let-
ters, 24(5):624–628.
Liu, C., Hu, Y., Li, Y., Song, S., and Liu, J. (2017). Pku-
mmd: A large scale benchmark for continuous multi-
modal human action understanding. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1703.07475.
Liu, J., Akhtar, N., and Mian, A. (2019a). Skepxels:
Spatio-temporal image representation of human skele-
ton joints for action recognition. In CVPR workshops.
Liu, J., Shahroudy, A., Perez, M., Wang, G., Duan, L.-Y.,
and Kot, A. C. (2019b). Ntu rgb+ d 120: A large-
scale benchmark for 3d human activity understanding.
IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine
intelligence, 42(10):2684–2701.
Papadakis, A., Mathe, E., Spyrou, E., and Mylonas, P.
(2019a). A geometric approach for cross-view human
action recognition using deep learning. In 2019 11th
International Symposium on Image and Signal Pro-
cessing and Analysis (ISPA), pages 258–263. IEEE.
Papadakis, A., Mathe, E., Vernikos, I., Maniatis, A., Spy-
rou, E., and Mylonas, P. (2019b). Recognizing human
actions using 3d skeletal information and cnns. In In-
ternational Conference on Engineering Applications
of Neural Networks, pages 511–521. Springer.
Paraskevopoulos, G., Spyrou, E., Sgouropoulos, D., Gian-
nakopoulos, T., and Mylonas, P. (2019). Real-time
arm gesture recognition using 3d skeleton joint data.
Algorithms, 12(5):108.
Pazhoumand-Dar, H., Lam, C.-P., and Masek, M. (2015).
Joint movement similarities for robust 3d action
recognition using skeletal data. Journal of Visual
Communication and Image Representation, 30:10–21.
Pham, H. H., Salmane, H., Khoudour, L., Crouzil, A.,
Zegers, P., and Velastin, S. A. (2019). Spatio–
temporal image representation of 3d skeletal move-
ments for view-invariant action recognition with deep
convolutional neural networks. Sensors, 19(8):1932.
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., and Caputo, B. (2004). Recognizing
human actions: a local svm approach. In Proceed-
ings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern
Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004., volume 3, pages 32–
36. IEEE.
Simonyan, K. and Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep con-
volutional networks for large-scale image recognition.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556.
Spyrou, E., Mathe, E., Pikramenos, G., Kechagias, K., and
Mylonas, P. (2020). Data augmentation vs. domain
adaptation—a case study in human activity recogni-
tion. Technologies, 8(4):55.
Szegedy, C., Ioffe, S., Vanhoucke, V., and Alemi, A. A.
(2017). Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact
of residual connections on learning. In Thirty-first
AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
Uddin, M. A. and Lee, Y.-K. (2019). Feature fusion of
deep spatial features and handcrafted spatiotempo-
ral features for human action recognition. Sensors,
19(7):1599.
Vernikos, I., Mathe, E., Papadakis, A., Spyrou, E., and My-
lonas, P. (2019a). An image representation of skeletal
data for action recognition using convolutional neural
networks. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM Interna-
ICPRAM 2022 - 11th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
376

tional Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related
to Assistive Environments, pages 325–326.
Vernikos, I., Mathe, E., Spyrou, E., Mitsou, A., Gian-
nakopoulos, T., and Mylonas, P. (2019b). Fusing
handcrafted and contextual features for human activ-
ity recognition. In 2019 14th International Workshop
on Semantic and Social Media Adaptation and Per-
sonalization (SMAP), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Wang, P., Li, W., Ogunbona, P., Wan, J., and Escalera, S.
(2018). Rgb-d-based human motion recognition with
deep learning: A survey. Computer Vision and Image
Understanding, 171:118–139.
Wang, P., Li, Z., Hou, Y., and Li, W. (2016). Action recog-
nition based on joint trajectory maps using convolu-
tional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 24th
ACM international conference on Multimedia, pages
102–106.
Xia, L., Chen, C.-C., and Aggarwal, J. K. (2012). View
invariant human action recognition using histograms
of 3d joints. In 2012 IEEE computer society con-
ference on computer vision and pattern recognition
workshops, pages 20–27. IEEE.
Yang, X. and Tian, Y. (2014). Effective 3d action recogni-
tion using eigenjoints. Journal of Visual Communica-
tion and Image Representation, 25(1):2–11.
Boosting the Performance of Deep Approaches through Fusion with Handcrafted Features
377
