
Formal Concept Analysis Applied to a Longitudinal Study of COVID-19
Paulo Lana, Cristiane Nobre, Luis Zarate and Mark Song
Instituto de Ci
ˆ
encias Exatas e Inform
´
atica, Pontif
´
ıcia Universidade Cat
´
olica de Minas Gerais, Brazil
Keywords:
Formal Concept Analysis, Triadic Concept Analysis, Association Rules, Implications, COVID-19.
Abstract:
The COVID-19 pandemic, and consequently the difficulty of obtaining feedback on the effectiveness of con-
tamination prevention methods, has caused an increased need to produce a relevant and consistent analysis
from collected data. Through Formal Concept Analysis, applying the triadic approach, called Triadic Con-
cept Analysis (TCA), it is possible to evaluate the correlation between prevention measures and the number
of contaminated people by performing concept extraction and implication rules. The advantage of using this
method is the possibility of correlating the waves, which allows us to explain and understand the evolution of
the data over the collection waves, helping us draw a more assertive conclusion from the data analyzed. This
paper uses the data collected from the 2020 National Population Survey of Nigeria to depict how Nigerian
society’s essential and everyday behaviors impacted the evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic in that country.
The results obtained from this research can assist governments, and public entities in developing better public
policies to combat highly infectious diseases. Furthermore, it provides practical evidence of how TCA can be
applied, bringing benefits to different areas and fields of science.
1 INTRODUCTION
Formal Concept Analysis (FCA) (Wille, 1982) was
introduced in 1982 by Rudolf Wille as a derivation
of concept hierarchy from a set of objects and their
properties. The main objectives are to extract and rep-
resent knowledge in an efficient way that aids and cor-
roborates decision-making from database analysis.
On the fundamental theorem of triadic concepts
and contexts, Wille (1982), providing considerable
contributions to the intelligent and adequate database
modeling for the extraction of triadic concepts, devel-
oped the Triadic Concept Analysis (TCA).
The developed work has shown that FCA’s qual-
itative concept data analysis capability can be com-
bined with a more quantitative approach, investigat-
ing data correlations that are not a priori visible or
easy to link.
The main benefit of choosing to use TCA in this
research is in the correlation between different peri-
ods of data collection, represented by the longitudinal
base analyzed here.
As we will further explain in the theoretical foun-
dation, triadic rules consist of a context formed from
a quadruple T = (G, M, B,Y ) where G, M, B are, re-
spectively, sets of objects, attributes, and conditions
belonging to the ternary relation Y ⊆ (G × M × B).
This relation is interpreted as: object g has attribute
m under condition b.
Thus, in any longitudinal databases, the advantage
of using an analysis such as TCA is to make it possi-
ble to explain the evolution of variables between col-
lection waves, clarifying possible causes of change,
such as temporal behaviors, impacts of external fac-
tors, assisting in a more accurate conclusion of the
data analyzed.
In this work, Triadic Formal Analysis is applied to
behavioral data collected from a society widely im-
pacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, specifically the
society of Nigeria. Through this analysis it is possible
to generate knowledge, portraying within the popula-
tion context of this country, the relationship between
basic hygiene and public health actions that can in-
terfere in the contamination and dissemination of the
disease.
The analysis of behavioral relations such as wash-
ing hands with soap, the use of masks in public, the
need for medical treatment, and the frequency of chil-
dren/adolescents with school activities that can affect
the spread of COVID-19 is made, helping in indirect
actions that aim at the containment and prevention of
contamination.
The data collected and analyzed bring about com-
plex relationships due to the variety of question cat-
148
Lana, P., Nobre, C., Zarate, L. and Song, M.
Formal Concept Analysis Applied to a Longitudinal Study of COVID-19.
DOI: 10.5220/0011036000003179
In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2022) - Volume 1, pages 148-154
ISBN: 978-989-758-569-2; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

egories and possible answers, the number of inter-
viewees, and the several collection waves carried
out. However, after a refinement, they can be ex-
plored, through the Formal Analysis of Triadic Con-
cepts (TCA), to obtain results derived from several
combinations that optimize actions and health poli-
cies adopted to fight the pandemic.
The result intended with this study is the applica-
tion of the TCA in a questionnaire of basic public hy-
giene and health behaviors. Thus, this work brings as
a result rules (implications) regarding the behavior of
society by means of health policies and the evolution
of the pandemic.
Such results can direct, corroborate and open pos-
sibilities for taking actions that add value, either
by optimizing the flow of data in a given network
or by increasing confidence in decision making for
strengthening or weakening of certain policies to fight
pandemics and diseases.
This work is structured by presenting a brief intro-
duction to Triadic Formal Concept Analysis (TCA).
After the TCA introduction, the database processing
steps are described, alongside the results of the meth-
ods applied. At the end of this work, over the con-
clusion of the analysis, the contributions of the study
are revelead as to how critical gaps could be filled
on information that can be used by the Nigerian gov-
ernment. This is relevant to assist the development
of public policies to mitigate the negative impacts of
COVID-19 on its population.
2 BACKGROUND
Formal Concept Analysis (FCA) is a mathematical
formalism that deals with data represented in two di-
mensions, relating objects and their attributes. Triadic
Formal Concept Analysis (TCA) extends FCA, trans-
forming the binary relation into a ternary considera-
tion by introducing a dimension called condition or
mode, establishing a link between objects, attributes,
and conditions.
This approach allows the identification of factors
related to object changes over time. Moreover, the tri-
adic approach contributes to databases from longitu-
dinal studies by considering the time factor as a con-
dition for analyzing the variation of the relationship
between objects and attributes. In this way, the triadic
implication rules also explore the temporal evolution
of the relations studied.
Thus, with the results from the TCA, it is possi-
ble to indicate points of improvement and failure re-
garding the impacts from health policies and the dis-
covery of previously unnoticed relationships. Never-
theless, the gains for the increase in the quality of life
and health of the population, in general, are countless,
even if we consider only the impacts coming from the
discoveries of new relations and correlations.
Formal Concept Analysis involves different com-
ponents such as: Formal Context, formal concept, and
rules.
A formal Context K is a triple K = (G, M, I),
where G is a set of objects, M is a set of attributes and
I is the incidence relation (I ⊆ G × M) that assigns an
object certain characteristics.
K = (G, M, I) (1)
I ⊆ G × M (2)
If an object (g ∈ G) and an attribute (m ∈ M ) are
in relation I, this is represented by ((g,m) ∈ I) or gIm
and is interpreted as the object g has the attribute m.
From a set of objects A ⊆ G, coming from a for-
mal context K, it is interesting to recognize which at-
tributes B ⊆ M are shared by all objects in A. Anal-
ogously, determine for a set B ⊆ M, which objects
A ⊆ G have in common the attributes defined in B.
The search for these answers leads to derivation oper-
ators, which are formally defined as:
A
0
:= {m ∈ M | gIm ∀ g ∈ A} (3)
B
0
:= {g ∈ G | gImIm; ∀ m ∈ B} (4)
From K, it is possible to extract association rules
dependent on elements in a set of M. An association
between attributes of M is a pair (X, Y), X, Y ∈ M,
receiving the notation X → Y. Association rules, in
turn, reveal frequent patterns in data.
From FCA, we extend the definition to encom-
pass a third dimension resulting in a triadic context
T , which is now a quadruple T = (G, M, B, Y ) where
G, M, B are, respectively, sets of objects, attributes
and conditions pertaining to the ternary relation Y ⊆
(G × M × B). This relation is interpreted as: object g
has attribute m under condition b.
Table 1 presents a triadic context similar to the one
analyzed in this paper.
T = (G, M, B, Y ) (5)
Y ⊆ (G × M × B) (6)
Table 1: Example of triadic context.
Cicle 1 Cicle 2 Cicle 3
Obj p1 p2 p3 p1 p2 p3 p1 p2 p3
1 x x x x x x x
2 x x x x x
3 x x
4 x x x x x x
5 x x x x x
6 x x x x x
One can describe two types of triadic associa-
tion rules that can be extracted from the context
Formal Concept Analysis Applied to a Longitudinal Study of COVID-19
149

K := (G, M, B, Y ) (Biedermann, 1997): Biedermann
Conditional Attribute Association Rule (BCAAR) and
Biedermann Attributional Condition Association Rule
(BACAR) (Zhuk et al., 2014).
The BCAAR rule is represented by: (R → S) C,
where R, S ⊆ M and C ⊆ B. That is, each object pos-
sessing all attributes in R also possesses all attributes
in S under a condition C, with one support (sup.) and
one confidence (conf.).
The BACAR rule is represented by: P → Q N
(sup.,conf.), where P, Q ⊆ B and N ⊆ M. That is, ev-
ery object under the conditions in P will also be under
the conditions in Q on attribute N, with one support
(sup.) and one confidence (conf.).
The support corresponds to the proportion of ob-
jects in the subset g ∈ G that satisfy the implication
P → Q, relative to the total number of objects |G| of
the formal context K (Equation 7) where (
0
) corre-
sponds to the derivation operator.
Support(P → Q) =
|(P ∪ {Q})
0
|
|G|
(7)
Confidence corresponds to the ratio of objects g ∈
G that contain P, which also contain Q, to the total
number of objects |G| (Equation 8).
Con f (P → Q) =
|(P ∪ {Q})
0
|
|P
0
|
=
Support(P → Q)
Support(P)
(8)
3 RELATED WORKS
This paper utilizes the Formal Analysis of Triadic
Concepts, and the approach and rationale for this un-
derstanding are applied through a practical and the-
oretical bias. Related work on this research topic is
presented below.
Wei et al. (2018) analyzed the Triadic approach of
Formal Concept Analysis (TCA), from four aspects:
(i) basics of triadic concept analysis, (ii) triadic impli-
cations and triadic association rules, (iii) triadic factor
analysis, and, (iv) triadic fuzzy concept analysis.
The addition offered by Konecny and Osicka
(2010) on the theoretical research and the seek sub-
sidies for applications of TCA, aims to better under-
stand the general approach on TCA and its fundamen-
tals. (Konecny and Osicka, 2010) discusses Triadic
Concept Analysis (TCA), presenting it as an exten-
sion of Formal Concept Analysis (FCA), dyadic case,
through the optic of conditions, besides just weight-
ing on objects and attributes relations.
The work of Ganter and Obiedkov (2004) head to-
wards a more practical bias of the research on Tri-
adic Concept Analysis, considering the various im-
plications of its use in multiple scenarios. The work
addresses the various possibilities of defining impli-
cations of a triadic formal context. Due to the vast
different interests one can have for a given triadic con-
text, the authors aim to present compact descriptions
and incorporate them into an algorithm that generates
implications from triadic contexts. Examples of this
variety of interests in a triadic context is the work pre-
sented in Silva et al. (2017), where social networks
interactions are in focus, and in Ferreira et al. (2017),
in which molecular biology challenges are faced.
Kis et al. (2016) reveals the development of a tool
that provides a visualization for dyadic and triadic
concepts, focusing on a navigation paradigm for tri-
adic contexts. The authors take into consideration
the complex contexts of application of Triadic Con-
cept Analysis, given the importance of the existence
of methods and procedures for the development and
improvement of analyses.
Biedermann (1997), also presents contexts and
ways of applying Triadic Concept Analysis. The
work is dedicated to explain different types of infor-
mation and knowledge that can be read in triadic di-
agrams. These labeled line diagrams graphically rep-
resent the conceptual structure of triadic contexts that
can be represented as three-dimensional. The author
discusses throughout the paper how one should inter-
pret such diagrams and how such dyadic conceptual
structures can be determined within the triadic dia-
grams.
Bringing fundamentals and subsidies for the de-
termination of Triadic Concept Analysis guidelines in
various scenarios and circumstances, similiar to Ana-
nias et al. (2019), Dau and Wille (2000) developed a
study on modal applications for the understanding of
triadic contexts, having as perspective the triadic con-
text as sets of formal objects, formal attributes and
formal conditions, along with the formalization of the
ternary relation, indicating when an object has an at-
tribute under a certain condition.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Database
The database used in this paper was obtained from the
COVID-19 National Longitudinal Phone Survey 2020
(Nigeria COVID-19 NLPS), a survey applied on indi-
viduals residing in Nigeria, conducted by the National
Bureau of Statistics (NBS), an affiliate of the Federal
Government of Nigeria and produced by the World
Bank.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
150

The survey, which collects data monthly, aims to
monitor the socio-economic effects of the pandemic
COVID-19 with real-time evolution. The study is part
of the World Bank’s Living Standards Measurement
Survey program to provide support to countries to
help mitigate the spread and impact of the new coro-
navirus disease.
The data collection is done through several tele-
phone calls to households located throughout Nigeria.
Each month, Nigerian households across the country
are asked about topics that are likely to be affected by
COVID-19 restrictions. Thus, the Nigeria COVID-19
NLPS intends to monitor the socio-economic effects
of the COVID-19 pandemic that will contribute to the
development of policies that will mitigate the negative
impacts on the population.
This paper performs the triadic analysis applied to
this base, using data collected in 3 waves of monthly
interviews, which had as areas of interest (i) access to
basic services, (ii) behavior, (iii) education, and (iv)
access to medical treatment.
The survey was conducted with 1,800 individuals
who are components and residents of the population
of Nigeria, aged eighteen (18) years and above.
In order to analyze the areas of interest mentioned,
four questions were selected related to areas of behav-
ior and status in society, such as: washing hands with
soap, use of mask in public, need for medical treat-
ment, and frequency of children and adolescents with
school activities.
The resulting analysis will allow us to associate
such behaviors with the spread of COVID-19 and the
socioeconomic impacts on the country.
The first wave of Nigeria COVID-19 NLPS tele-
phone interviews considered for the present work was
conducted between June 2 and 16, 2020. The second
took place between July 2-16, 2020, and the third be-
tween the dates of August 9-24, 2020.
To bring the intended result in the present paper,
relating the behavioral results of the Nigeria COVID-
19 NLPS survey to the spread of COVID-19 during
June, July, and August 2020 in Nigeria, the base Nige-
ria: Coronavirus Pandemic Country Profile was used,
which determines the estimate of the effective repro-
duction rate (R) of COVID-19. The reproduction
rate represents the average number of new infections
caused by a single infected individual.
The aforementioned statistics and survey Nige-
ria: Coronavirus Pandemic Country Profile, was con-
ducted by Our World in Data. The database provided,
in addition to the many linked graphs, uses the com-
plete set of data on confirmed cases and deaths from
Johns Hopkins University (JHU) and the European
Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC).
This Johns Hopkins University dataset is main-
tained by the Center for Systems Science and Engi-
neering (CSSE). Since January 22, 2020, it has pub-
lished updates on confirmed cases and deaths for all
countries and updates its data several times a day. The
data used from this database comes from the govern-
ment, national and subnational agencies in Nigeria.
4.2 Methods
To achieve the goal of the paper, it was necessary to
perform data transformation in a triadic context, us-
ing the Nigeria COVID-19 NLPS database as input
to the concept extraction algorithm. To do this, the
following process was carried out:
1) A preprocessing of the base was performed.
Relevant and consistent questions were filtered and
selected between the collection waves. After selecting
the questions, the respective answers were discretized
according to each context, so that there was no in-
terference in the configuration and purpose of each
question.
2) Grouping the preprocessed data into their
waves. After preparing the questions and discretizing
the answers, the data from each wave were grouped in
the same table, keeping the reference of each wave for
later interpretation of the implication rules generated.
3) For the rule generation the Lattice Miner 2.0
tool was used, a data mining prototype developed un-
der the supervision of Professor Rokia Missaoui by
the LARIM research laboratory of the Universit
´
e du
Qu
´
ebec (Missaoui and Emamirad, 2017). It is a public
domain Java platform whose main functions include
all the low-level operations and structures to represent
and manipulate input data, structures, and association
rules. The platform allows the generation of clusters,
called formal concepts, and association rules, includ-
ing logical implications, given a binary relationship
between a collection of objects and a set of attributes
or properties.
Among the functions made available by Lattice
Miner 2.0, this work focuses on the use of the
rules proposed by Biedermann (1997), these are:
Biedermann Conditional Attribute Association Rule
(BCAAR) and Biedermann Attributional Condition
Association Rule (BACAR).
The first, BCAAR, takes the form (A1 →
A2)C(sup, con f ), where A1, A2 ⊆ M and C ⊆ B. This
rule indicates that every time A1 occurs in the condi-
tions C, then A2 also occurs, with support sup and
confidence conf. The second rule used is BACAR,
which takes the form (C1 → C2)A(sup, con f ), where
C1, C2 ⊆ B and A ⊆ M, that is, every time C1 occurs
for all attributes in A, then for the condition C2, there
Formal Concept Analysis Applied to a Longitudinal Study of COVID-19
151

is an occurrence of the same attributes, with support
sup and confidence conf.
5 RESULTS
From the triadic analysis performed on the database,
it was possible to relate how the various basic,
everyday behaviors of the Nigerian population can
affect the spread of COVID-19.
Considering:
w1: Collection wave 1 conducted in June 2020;
w2: collection wave 2 conducted in July 2020, and
w3: Collection wave 3 carried out in August 2020.
We could obtain the follwing rules:
BCAAR Implication Rules
1 : (B → D) w1 [sup = 53, 6% con f = 68, 5%]
2 : (B → A) w3 [sup = 70, 7% con f = 92, 4%]
3 : (B → D) w3 [sup = 50, 5% con f = 66, 0%]
4 : (A → D) w2 [sup = 51, 0% con f = 58, 8%]
5 : (A → B) w2 [sup = 74, 6% con f = 86, 0%]
6 : (D → B) w1 [sup = 53, 6% con f = 84, 1%]
7 : (A → B) w3 [sup = 70, 7% con f = 85, 7%]
8 : (A → D) w3 [sup = 52, 8% con f = 64, 1%]
9 : (D → A) w2 [sup = 51, 0% con f = 89, 1%]
10 : (B → A) w2 [sup = 74, 6% con f = 94, 0%]
11 : (D → B) w3 [sup = 50, 5% con f = 83, 2%]
12 : (D → A) w3 [sup = 52, 8% con f = 87, 1%]
For this research, the questions asked to the
nigerian population were:
A: Washing hands with soap after going in public;
B: Wearing a mask in public;
C: Need for medical treatment in the last 7 days;
D: Children and adolescents with school activi-
ties;
The value of 50% was used as lower limits of
support and confidence in the generation of the
BCAAR implication rules. With the results in hand,
for interpretation and exposition in this paper, we
kept the 50% for support and considered only the
rules above 75% confidence.
From rule 5 it can be seen that during wave 2 (w2,
conducted in June), 74.6% of the individuals inter-
viewed who took care to wash their hands with soap
in public (A) also took precautions by wearing masks
(B). Note that of those who washed their hands in
public, 86.06% certainly wore masks.
From rule 9, it is observed that during collection
wave 2, in June 2020, 51% of the individuals living
with children and adolescents with school activities
(D) were careful to wash their hands after going in
public (A). Of these respondents, 89.1% were sure to
wash their hands with soap after going out in public.
From the generated rule 10, 74.6% of individuals
who wore a mask in public (B), 94.5% were associ-
ated with washing their hands with soap after going
out in public (A), in wave 2.
It is observed by rule 11, through the data col-
lected during wave 3 (August 2020), that 50.5% of the
interviewed individuals live with children and adoles-
cents with school activities (D). Of this percentage,
it is perceived that 83.2% were certain to have worn
masks in public (B).
The aforementionted rules implies a direct re-
lationship between individuals who washed their
hands after going out in public, who also used masks
in public, and in which families kept children and
adolescents with school activities, during July and
August.
BACAR Implication Rules
1 : (w1 → w3) B [sup = 64, 5% con f = 82, 5%]
2 : (w1 → w2) B [sup = 63, 5% con f = 81, 1%]
3 : (w3 → w1) B [sup = 64, 5% con f = 84, 3%]
4 : (w3 → w2) B [sup = 61, 1% con f = 79, 9%]
5 : (w2 → w3) A [sup = 71, 5% con f = 82, 5%]
6 : (w3 → w2) A [sup = 71, 5% con f = 86, 8%]
7 : (w2 → w1) B [sup = 63, 5% con f = 80, 0%]
8 : (w2 → w3) B [sup = 61, 1% con f = 77, 0%]
9 : (w1w3 → w2) B [sup = 52, 4% con f = 81, 2%]
10 : (w1w2 → w3) B [sup = 52, 4% con f = 82, 5%]
11 : (w2w3 → w1) B [sup = 52, 4% con f = 85, 7%]
Similarly applied to the BCAAR rules, no rules
were generated with support and confidence lower
than 50%. Also, as with the previous interpretation,
only rules with percentages above 50 support and 75
confidence were taken into account.
From rule 1, it can be seen that among the 64.5%
of individuals interviewed who had taken precautions
by wearing masks in public (B) in wave 2, in June
2020, 82.5% continued to wear their masks in wave
3, in August of the same year.
It is observed from rule 2 that among the 63.5%
individuals who were wearing masks in public (B) in
wave 2, in June 2020, 81.1% maintained the same
protective behavior in wave 2, the following month,
in July.
Also, employing rule 8, it is possible to iden-
tify that of the 61.1% of respondents who adhered to
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
152
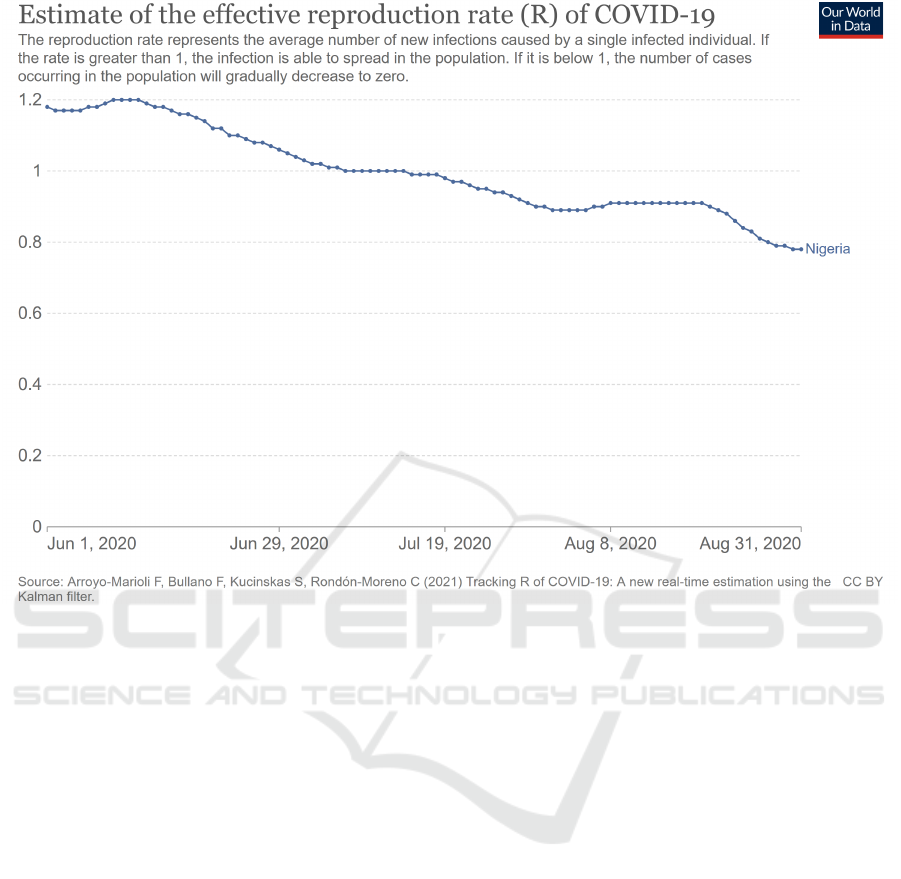
Figure 1: Covid Rate.
wearing masks in July 2020 (wave 2), 77.0% contin-
ued wearing the masks in public also in the subse-
quent month, during wave 3.
Finally, from rule 10, it is noted that 52.4% of
the interviewed individuals who were wearing masks
in public continuously between the months of June
and July 2020 (w1 and w2), 82.5% continued with the
protection method during the month of August of the
same year (w3).
It is possible to observe that the behavior of indi-
viduals who used a mask in June, in the wave w1, was
maintained during July and August, waves w2 and w3
respectively. Rule 5 also enforces basic service access
behavior:
5 : (w2 → w3) A [sup = 71.5%; con f = 82.5%]
Using rule 5, it can be seen that of the 71.5% in-
dividuals who followed the recommendation to wash
their hands with soap after going in public in July
2021 (w2), 82.5% maintained this good practice in
August (w3).
When comparing such implication rules with the
results found in Nigeria (Figure 1): Coronavirus Pan-
demic Country Profile survey on the estimation of the
effective reproduction rate (R) of COVID-19, we can
observe that during June, July, and August, there was
a decrease in R rate:
It is possible to infer, when compiling such
databases, that the adherence of individuals in public
policies to basic behavioral services, such as wearing
masks and washing hands after going public, had an
impact in preventing the spread of new cases of infec-
tion by an individual contaminated by COVID-19.
Yet another interpretation we can draw from
BCAAR rules 5, 9, 10, 11, we find that keeping chil-
dren and adolescents in school activities may have
assisted in the adherence of families to the public
health recommendations put forth by the government
of Nigeria.
Thus, by analyzing these implications, it is possi-
ble to generate practical results, increasingly reliable,
to support the construction of mitigatory and pre-
ventive actions and policies for the contamination of
COVID-19, helping the government to obtain greater
adherence of the population in restrictive actions with
low socioeconomic impact and that have positive re-
sults in combating COVID-19.
Formal Concept Analysis Applied to a Longitudinal Study of COVID-19
153

6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
The intention of the work, after careful selection of
the results, is to understand the importance of the ex-
tracted knowledge on mortality rates, infection rates,
and the number of cases of COVID-19 during the col-
lection period.
In addition, the research seeks to highlight the
contrasts of the results obtained with information
from the Nigeria: Coronavirus Pandemic Country
Profile” database, maintained and updated daily by
the organization ”Our World In Data”.
This database provides statistical information
about the progression of COVID-19, with data such
as the number of deaths, number of confirmed cases,
mortality rate, and number of tests performed.
Thus, in face of the proposed analyses, the present
work aimed to expand the applicability of the Triadic
Concepts Analysis.
It turned out to be an efficient and useful approach
to find aspects not easily identified at first, related to
several contexts of knowledge areas, as health and so-
cial information related to pandemics, diseases, and
social behaviors.
Such results, by bringing correlations between
population behaviors and dissemination of diseases,
can be very useful in the basis and rationale for
making government decisions of great impact on the
health of the world population.
The study, therefore, by performing the complex
analysis of data not directly linked, finding their cor-
relation, can help governments and public entities to
develop better public policies to combat highly infec-
tious diseases and promote sanitation.
Thus, it is expected that several areas of study and
scenarios will benefit from this methodology in their
investigations and analysis, relying on the data inter-
pretation enabled through TCA.
REFERENCES
Ananias, K., Neves, J., Ruas, P. H., Z
´
arate, L., and Song,
M. (2019). Manipulating triadic concept analysis con-
texts through binary decision diagrams.
Biedermann, K. (1997). How triadic diagrams represent
conceptual structures. In Lukose, D., Delugach, H.,
Keeler, M., Searle, L., and Sowa, J., editors, Concep-
tual Structures: Fulfilling Peirce’s Dream, pages 304–
317, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Dau, F. and Wille, R. (2000). On the modal understanding
of triadic contexts.
Ferreira, L., Pinto, C., Dias, S., Nobre, C., and Z
´
arate, L.
(2017). Extraction of conservative rules for translation
initiation site prediction using formal concept analy-
sis.
Ganter, B. and Obiedkov, S. (2004). Implications in tri-
adic formal contexts. In Wolff, K. E., Pfeiffer, H. D.,
and Delugach, H. S., editors, Conceptual Structures
at Work, pages 186–195, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Kis, L. L., Sacarea, C., and Troanca, D. (2016). Fca tools
bundle - a tool that enables dyadic and triadic concep-
tual navigation. In FCA4AI@ECAI.
Konecny, J. and Osicka, P. (2010). General approach to
triadic concept analysis. In CLA.
Missaoui, R. and Emamirad, K. (2017). Lattice miner
2.0: A formal concept analysis tool (2017. In Sup-
plementary Proceedings of ICFCA’2017, page 91–94,
Rennes.
Silva, P., Dias, S., Brand
˜
ao, W., Song, M., and Z
´
arate, L.
(2017). Formal concept analysis applied to profes-
sional social networks analysis.
Wei, L., Qian, T., Wan, Q., and Qi, J. (2018). A re-
search summary about triadic concept analysis. In-
ternational Journal of Machine Learning and Cyber-
netics, 9(4):699–712.
Wille, R. (1982). Restructuring lattice theory: An approach
based on hierarchies of concepts. In Rival, I., edi-
tor, Ordered Sets, pages 445–470, Dordrecht. Springer
Netherlands.
Zhuk, R., Ignatov, D., and Konstantinova, N. (2014). Con-
cept learning from triadic data. Procedia Computer
Science, 31:928–938.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
154
