
An Approach to Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence for the
Internet of Things
Tariq Alsboui
a
, Hussain Al-Aqrabi
b
, Richard Hill
c
and Shamaila Iram
d
School of Computing and Engineering, University of Huddersfield, U.K.
Keywords:
Internet of Things (IoT), Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), IOTA Tangle, Masked Authenticated
Messaging (MAM), Privacy.
Abstract:
In the Internet of things (IoT), security and privacy issues are a fundamental challenge determining the suc-
cessful implementation of many IoT applications. Distributed ledger technology (e.g., Blockchain) offers a
great promise to solve these issues. Blockchain-based solutions support security and privacy, yet they involve
significant energy due to mining, low throughput, and computational overhead that is not acceptable for IoT
resource-constrained devices. In this paper, we propose a scalable Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence
approach (PPDI) by leveraging the IOTA technology. IOTA is an emerging distributed ledger technology that
allows for zero fees transactions for the IoT. The proposed PPDI aims to address the privacy issues in the IoT
by using the IOTA Masked Authenticated Messaging (MAM) protocol. MAM ensures privacy by encrypting
and granting permission to authorized users to access data. This paper presents a healthcare scenario that
demonstrate how IOTA MAM can be used to address the privacy issue in the IoT. The experimental results
clearly show that the IOTA MAM is a feasible solution that can be used to solve privacy related issues in the
IoT domain.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Internet of Things (IoT) is considered to be an
enabling technology for several applications. It con-
nects physical objects together with the main aim of
exchanging data with other systems over the Internet
to enable communications between these objects (At-
zori et al., 2010), also referred to as Cyber-Physical
Systems (CPS) (Cares et al., 2019).
The elements of IoT applications include: (1)
sensing to perceive the environment; (2) communica-
tion for efficient data transfer between objects, and (3)
computation, which is performed to generate useful
information from the raw data.
IoT systems have already enhanced the quality of
life by turning cities into smart cities (Perera et al.,
2017), homes into smart homes (Doan et al., 2018),
and campuses into smart campuses (Angelis et al.,
2015). The research reports estimate the rapid growth
of IoT, i.e., in the order of 125 billion devices con-
nected to the Internet in 2030 (Cisco, 2016; Gartner,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6004-3756
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1920-7418
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0105-7730
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0217-500X
2013; Research, 2013). Therefore, this will present
many challenges with regard to data volume, velocity,
timely processing, privacy and scalability (Al-Aqrabi
et al., 2019; Alsboui et al., 2020a).
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is an
emerging development that shares data among dif-
ferent participants deployed over various locations all
over the world. This technology provides several ben-
efits to various IoT applications. DLT is being in-
vestigated by many researchers across the world as
a promising solution to the challenges of IoT, such
as scalability, energy-efficiency, security, and pri-
vacy (Alsboui et al., 2020a; Fan et al., 2019; Alsboui
et al., 2019).
In this paper, we propose a privacy-preserving
distributed intelligence approach using the IOTA
Masked Authenticated Messaging (MAM) (See Sec-
tion 2 for Further details) as a suitable solution to
tackle the privacy, and scalability issues for IoT ap-
plications. MAM is a second layer data communica-
tion protocol used to authenticate, and encrypt data
streams through the use of a mixture of modes, such
as public, private, and restricted.
Contributions: In this paper, we propose a sys-
tem architecture for IoT, called Privacy-Preserving
174
Alsboui, T., Al-Aqrabi, H., Hill, R. and Iram, S.
An Approach to Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence for the Internet of Things.
DOI: 10.5220/0011056400003194
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security (IoTBDS 2022), pages 174-182
ISBN: 978-989-758-564-7; ISSN: 2184-4976
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Distributed Intelligence Approach (PPDI). This ap-
proach addresses privacy realted issues in IoT, whilst
supporting the popular proof-of-work (PoW) mecha-
nism in an energy-efficient way. The key contribu-
tions can be summarised as follows:
• A Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence ar-
chitecture that ensures privacy by using IOTA
MAM protocol with a mixture of modes.
• Evaluation of an existing Proof of Work (PoW)
offloading mechanism for efficacy with regard to
energy efficiency and transaction throughput;
• Preliminary experimental results to verify the ef-
fectiveness and scalability of the proposed ap-
proach.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Sec-
tion 2 presents an overview of the IOTA technology
and a detailed description of the masked authenti-
cated messaging. Section 3 presents the recent re-
search efforts in distributed intelligence in the IoT do-
main. In Section 4, we describe our proposed privacy-
preserving distributed intelligence for the IoT. Sec-
tion 5 considers a healthcare application scenario in
the context of the proposed privacy preserving ap-
proach. Section 6 presents an implementation of the
proposed approach and analysis of the results. Fi-
nally, in Section 7, we conclude the paper and discuss
future work.
2 IOTA PLATFORM: AN
OVERVIEW
IOTA’s tangle architecture is an evolving DLT plat-
form aimed at addressing transaction costs, mining
and scalability issues (in the context of Blockchain
technology) (Zhang and Jacobsen, 2018), that are re-
lated to IoT. The architecture of a Tangle (Serguei,
2017), which is central to IOTA, a DAG that offers a
potentially scalable IoT-enabled applications. IOTA
technology offers the necessary privacy for IoT ap-
plications. In the context of transactions, IOTA may
promote IoT interactions. This approach radically
changes the overall design, development, implemen-
tation and management process of IoT systems.
2.1 The Tangle
The IOTA Tangle was developed to cope with the re-
quirements of IoT applications such as privacy, and
security. Tangle is built upon a Directed Acyclic
Graph (DAG), which is considered to be the ledger
that stores transactions. The Tangle is the data
structure that consists of a collection of sites and
edges (Serguei, 2017). In order to issue a transaction
by a node, the node should work to approve two pre-
vious transactions. Choosing the two previous trans-
actions is done by using the tip selection technique
whereby default is the Markov Chain Monte Carlo
(MCMC) technique (Serguei, 2017). The main aim
of the tangle network is to make all the transactions to
be confirmed and to make all the unconfirmed trans-
actions to confirmed transactions, the MCMC tech-
nique is executed n number of times. Genesis is the
first transaction of the network, which is approved di-
rectly or indirectly by the other transactions.
It is possible to securely store information within
the Tangle, or even spread larger amounts of informa-
tion across multiple bundled or linked transactions.
This particular type of structure also enables high
scalability of transactions. According to the IOTA
foundation (Serguei, 2017), the more activity in the
Tangle, the faster transactions can be confirmed.
2.2 Masked Authentication Messaging
IOTA offers a second layer of data communication
called Masked Authenticating Messaging (MAM).
MAM is responsible for masking, authenticating, and
encrypting data streams. Consequently, data streams
are broadcasted and retrieved through the Tangle as
zero fee transactions. Given these properties, MAM
fulfills an important need in which integrity and pri-
vacy are required.
Every MAM data transaction is linked with an ad-
dress in which a user can refer to the transaction. Data
transactions would be transmitted using the MAM
protocol at any point in time, but a small amount of
Proof of Work (PoW) is needed in order to broad-
cast data streams to the IOTA network. Transaction
data broadcasted using MAM are linked together in
chronological order. Furthermore, a signature of the
user is attached to all MAM data streams. This en-
sures that subscribers are required to verify the au-
thenticity of the user. By adopting MAM, users will
certainly ensure safety when exchanging data to the
Tangle.
MAM transactions can be broadcasted and fetched
from the IOTA Tangle, by communicating with a fully
functional node. This indicates that an IoT device will
be able to transmit encrypted data streams using the
IOTA MAM protocol.
2.2.1 MAM Privacy and Encryption Modes
MAM enables encryption to occur through several
modes including: public, private, and restricted. In
An Approach to Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence for the Internet of Things
175

public mode, the user uses the tree’s root as the ad-
dress of the transaction that the message is published
to. A user will be able to decode it by using the ad-
dress of the message. Public mode enables any user to
read the content of the data, but it adds immutability
and data integrity.
In the case of private mode, there is an added level
of security that controls the access in order to be able
to read the content of the transaction data. It enables
access to users who have only the hash of the channel
key. The users would request the tangle for the hash
of the channel key. Then, it would enable them to
decode the transaction data by using the channel key.
Figure 1: The Process of Publishing Transaction Using Re-
stricted Mode.
In the case of restricted mode, it adds an autho-
rization key to the private mode. The address used
to attach to the network is the hash of the authoriza-
tion key and the Merkle root. It also offers granular
access to users who have the secret key. Therefore,
access would be revoked from users if needed. If the
secret key change, the new authorized key is required
and should be distributed to the users that needs to
gain access to the data. Fig. 1 describes the process
of sending transactions using the restricted mode. In
our implementation, we focus on the public mode, to
ensure authenticity, and data integrity, as well as the
restricted mode to enable granular access to data.
3 RELATED WORK
There has been sustained research into distributed
intelligence approaches for IoT over the last few
years. In a recent publication (Alsboui et al., 2021),
the authors classified distributed intelligence tech-
niques into five categories depending on the factors
that support distributed functionality and data acquisi-
tion: cloud-computing, mist-computing, distributed-
ledger-technology, service-oriented-computing and
hybrid. For a comprehensive and recent literature re-
view, we refer the interested readers to (Alsboui et al.,
2021) and the references therein. Such research ef-
forts focused on developing distributed intelligence
approaches for IoT. However, there has been little at-
tention on addressing the privacy issue.
Recently, a computing paradigm called Edge
Mesh is being suggested in (Sahni et al., 2017) to al-
low distributed intelligence in IoT. Decision-making
task is distributed through the network among de-
vices, instead of data being transmitted directly to a
central location for processing. Combining the use of
both computation and data, tasks are exchanged with
Edge Mesh through a network of routers and edge de-
vices. The architecture of Edge Mesh comprises of
several devices. First of all, the end devices are con-
cerned with actuation and sensing purposes. Second,
edge devices can be used to process and connect end
devices. Third, routers are being utilized to transmit
data. Finally, the cloud is increasingly being used to
perform advanced analysis of data. The incorpora-
tion of Edge Mesh could bring various benefits such
as increased scalability, improved security. However,
some will have a concern over privacy and security,
but how privacy can be accomplished is not taken into
account. Also, the architecture lacks support for inter-
operability.
In (Klonoff, 2017), the authors applied fog com-
puting as a means to support distributed intelligence
by setting up an architecture that is made up of three
layers. The sensing layer is concerned with the trans-
mission of data to the upper layer. A fog layer plays
the role of data processing transferred from the sen-
sor nodes. The cloud computing layer is used for the
heavy processing of data. The system is suitable for
timely response applications and is energy efficient
since processing is performed near the data source.
It also provides support for interoperability. How-
ever, the approach lacks support for other IoT tech-
nical challenges such as scalability, and privacy.
Most recently, the authors in (Alsboui et al.,
2020a) proposed a distributed intelligence approach
called Mobile Agent Distributed Intelligence Tangle-
based approach (MADIT) that adopts the IOTA tan-
gle. The approach supports distributed intelligence
at two levels including high-level and low-level. At
the high-level, a Tangle based architecture is used to
deal with transaction data, while the low-level, em-
ploys a mobile agent to cater for node level commu-
nications. The proposed approach is scalable, energy-
efficient, and eliminates redundant data. However, the
approach lacks support for privacy, which is outlined
as future work.
Another recent approach is introduced by the au-
thors in (Alsboui et al., 2020b) in support of dis-
tributed intelligence. The approach mainly solves
some of the IoT technical challenges such as scala-
bility, energy-consumption, and decentralization. A
PoW enabled server is used to deal with heavy com-
putation tasks on behalf of constrained IoT devices.
The proposed approach is scalable, energy-efficient,
IoTBDS 2022 - 7th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
176
and decentralized. However, security and elimination
of redundant data are not considered. Also, they out-
line to develop a schema to deal with privacy issues
as part of their future work.
In comparison to the above, the research in (Rah-
man and Rahmani, 2018) suggested an AI-based dis-
tributed intelligence solution. The solution incorpo-
rates the use of both cloud based and edge controller
to enable distribute intelligence. To be specific, it has
been shown that the cloud-based controller is capa-
ble of providing intelligence at a high level. The edge
controller is designed to support intelligence at a low
level. The advantages of their research are reduc-
ing response time and loosening rules requirements.
However, the approach lacks a mechanism which al-
lows offline capability and privacy preserving.
The authors in (V
¨
ogler et al., 2015) introduced
The LEONORE system to support distributed intel-
ligence. LEONORE is built up using a service-
oriented architecture and supports several applica-
tion components in large-scale IoT deployments.
The LEONORE framework works according to two
phases push-based and pull-based. The pull-based
is responsible to independently propose a run time
method, while provisioning of push-based, responsi-
ble for providing control for the application by pro-
viding software updates and maintains security. The
proposed framework is energy-efficient, and scalable.
However, offline-capability, security, and privacy are
not well supported (Al-Aqrabi et al., 2020).
A distributed intelligence approach that adopts the
IOTA protocol is proposed in (Fan et al., 2019). It
establishes an infrastructure network for smart home
paying a particular attention to ensure scalability. All
of the home IoT nodes in the system are linked with
neighbouring nodes to exchange information and en-
sure synchronization with the ledger. The approach is
only suitable for small scale applications, and would
lead to higher energy to be consumed in all nodes
since PoW computation is performed on local IoT
nodes. The approach does not support a schema to
deal with privacy.
Table 1 compares the selected most recent dis-
tributed intelligence approaches and presents compar-
isons in regards to energy-efficiency, scalability, secu-
rity, and privacy of each approach.
From the table we can see that privacy is a crit-
ical challenge in distributed intelligence approaches.
Meanwhile, Most of the distributed intelligence ap-
proaches focuses on solving the energy-consumption,
and scalability. Our work adopts the IOTA Masked
Authenticated Messaging (MAM) protocol as a solu-
tion to solve the privacy issue.
4 PRIVACY-PRESERVING
DISTRIBUTED INTELLIGENCE
APPROACH
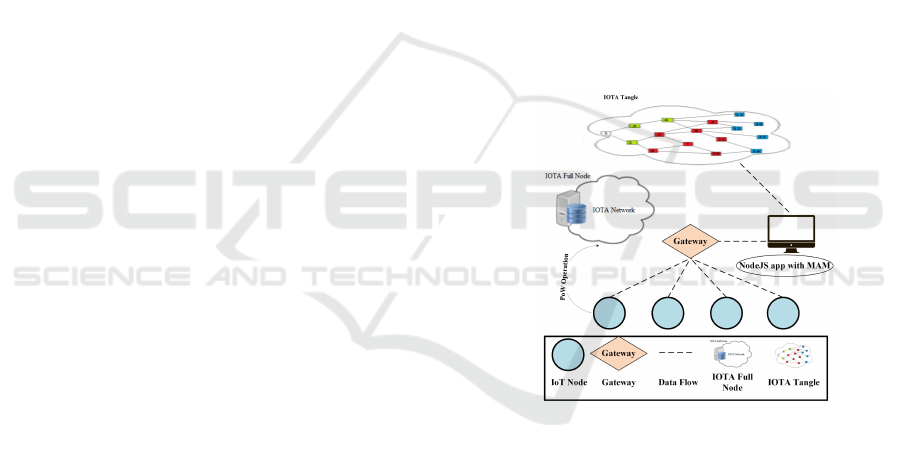
Fig. 2 presents an abstract view of the system ar-
chitecture of the proposed Privacy-Preserving Dis-
tributed Intelligence approach (PPDI). It describes all
relevant components including IoT devices, transac-
tion data flow, Node JS with MAM, Gateway, and
PoW computation server. The IoT devices are respon-
sible for sending transaction data using MAM client
and transmits transaction data to a receiver, which is
the gateway. The gateway is connected to the Inter-
net and transmits transactions data to a server, which
runs the Node JS Masked Authenticated Messaging
(MAM) application. The Node JS MAM is responsi-
ble for sending transaction data to the IOTA Tangle.
For example, the transaction data flow from IoT de-
vices (e.g., dash lines) represents the way how trans-
action data is transmitted to the IOTA Tangle using
MAM.
Figure 2: The Proposed Privacy-Preserving Distributed In-
telligence Approach (PPDI).
The PoW enabled server is responsible for per-
forming heavy computation tasks on behalf of con-
strained IoT devices.
The flowchart of the proposed PPDI approach is
shown in Fig. 3. First, the MAM state is initialized
using the main Tangle provider. After MAM state is
initialized, its patched with the Proof of Work (PoW)
for performing the PoW, which patches MAM sate
with the PoW Provider. Then, the channel mode is
set to restricted on the MAM state. Once this step is
completed, the payload is created and prepared to be
transferred to the main Tangle. Then, the PoW is per-
formed on the PoW provider. Once the PoW is com-
pleted, the payload will be attached to the main Tan-
gle. In order for users to be able to access healthcare
records, the root ID and the correct secret key should
An Approach to Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence for the Internet of Things
177
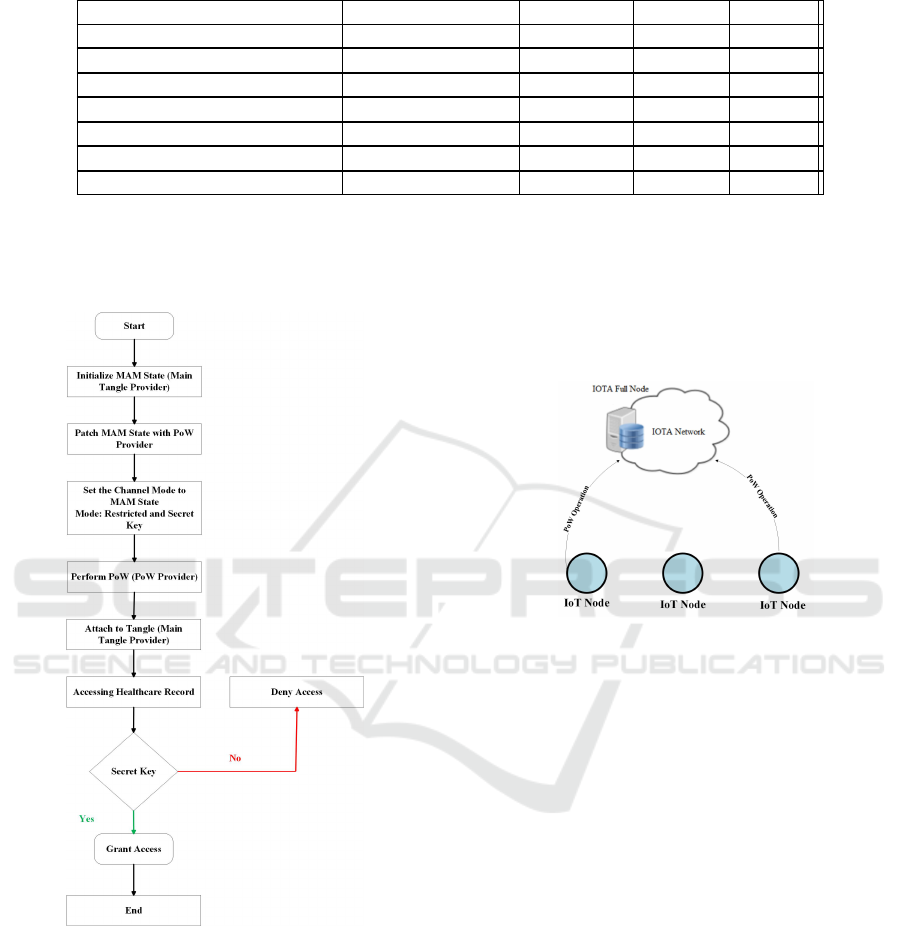
Table 1: Comparisons Among Distributed Intelligence (DI) Approaches.
DI Approaches Energy-Efficiency Scalability Security Privacy
(Sahni et al., 2017) X X X X
(Klonoff, 2017) X X X X
(Alsboui et al., 2020a) X X X X
(Alsboui et al., 2020b) X X X X
(Rahman and Rahmani, 2018) X X X X
(V
¨
ogler et al., 2015) X X X X
(Fan et al., 2019) X X X X
be provided. Consequently, If the correct secret key
is provided, grant access to that user otherwise deny
access.
Figure 3: Flowchart of the basic PPDI approach.
4.1 PoW Offloading
There are two types of offloading including: data
offloading and computation offloading. The former
refers to the use of novel network techniques to trans-
mit mobile data originally planned for transferring
via cellular networks. The latter refers to offloading
heavy computation tasks to reserve resources (Zheng
et al., 2020). Fig. 4 illustrates the PoW computation
offloading mechanism used in the PPDI approach. It
shows how constrained IoT devices in terms of power
are able to offload the PoW computation to a node
with higher resources to save energy consumption.
The selected node is an IOTA full node, which is re-
sponsible for performing the PoW as described in Fig.
4.
Figure 4: PoW Computation Offloading in PPDI Approach.
The aim of offloading is to save total energy con-
sumption or overall task execution time, or both of
them. A proof of work (PoW) is a piece of data that
is calculated by using trial and error to meet certain
requirements. The key to PoW is that it is difficult to
perform but easy to verify. Since MAM transaction
data requires a small amount of a PoW to be com-
puted, we offload the PoW computation to a node with
higher resources in order to save energy consumption
of IoT devices.
In particular, we address the issue of privacy and
scalability by adapting the IOTA MAM protocol. We
have presented the proposed approach in view of the
system architecture, and the role of the PoW compu-
tation offloading technique employed.
5 PPDI APPROACH: AN
APPLICATION SCENARIO
This section of the paper describes the proposed PPDI
approach in the context of IoT healthcare application
scenario. In healthcare, IoT devices are responsible
IoTBDS 2022 - 7th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
178

for collecting health data such as heart rate, blood
pressure, and temperature from patients (Zhang et al.,
2018). Distributed Ledger Technology plays an im-
portant role in healthcare scenarios as it offers sig-
nificant features, such as immutability, decentraliza-
tion, security, privacy, and transparency, which even-
tually will overcome pressing issues in healthcare sys-
tems (McGhin et al., 2019). The efficiency and effec-
tiveness of healthcare systems depend on the interop-
erability, and data access management. Interoperabil-
ity enables software applications and several technol-
ogy platforms to establish a secure communication,
exchange data, and utilize the exchanged data across
healthcare organizations.
Data access management is required in health-
care applications and therefore, when a transaction is
recorded in the IOTA network, MAM allows trans-
action to be encrypted and enables authorized users
to access the data. Through the storage of the data
on the IOTA Tangle, doctors, nurses, patients or any
other authorized user or device can control access to
the data. When a user requests access to the personal
information of a particular patient’s, the application
checks their credentials and then either grants or de-
nies access to the data accordingly. It is important
to note that accessing healthcare records is based on
the secret key, which in turns does not disclose any
private information to unauthorized users of the sys-
tem. In conclusion, the use of IOTA technology and
in particular MAM to manage access to data ensures
that authorized users will be able to access data when
needed, while guaranteeing that private information
cannot be accessed by unauthorized users of the sys-
tem.
IOTA MAM offers the opportunity to encrypt,
mask, and enable access to healthcare records with
a mixture of modes, while the IOTA Tangle is used to
handle transactions data in an efficient way.
6 IMPLEMENTATION, RESULTS
AND ANALYSIS
In this section, we present our preliminary experimen-
tal results and an evaluation of the proposed PPDI ap-
proach in terms of privacy, and scalability. In addi-
tion, we provide analysis and discussion of the results.
6.1 Environment Setup
The implementation of our proposed approach
is based on Node JS. The functionality related
to IOTA addresses, transactions, broadcasting,
and multi-signatures has been implemented using
iota.lib.js (Foundation, 2018), the official JavaScript
library of the IOTA Distributed Ledger Technology
that enables issuing and fetching transactions. We
have used the IOTA Devnet as clients, which in par-
ticular communicates with IOTA full node
1
to issue
and fetch MAM transactions data. Another IOTA full
node was deployed on a local server dedicated for per-
forming the Proof of Work (PoW) operations.
Our implementation focuses on the public and re-
stricted modes of MAM. Public mode ensures authen-
ticity, and data integrity, while restricted mode pro-
vides users with the ability to gain access to the data
using the secret key. This is particularly useful for
healthcare applications where permissions to access
data is needed.
6.2 Results and Analysis
Fig. 5 shows the result of sending transaction data to
the Tangle using the public mode. It also shows the
output of fetching masked transaction data in which
the user would only require the root, which is the en-
cryption and decryption key. The transaction data sent
using public mode ensures authenticity and data in-
tegrity i.e., confirming that the data is coming from
a particular IoT device. The Public mode uses the
root as the address of the transaction that contains the
MAM message (channel ID). Consequently, any user
can find and decrypt the message in a public mode.
Figure 5: Publishing Transaction Data from IoT devices
Using Public Mode.
Sending Transactions with Restricted Mode:
Fig. 6 shows the result of publishing transactions data
using the restricted mode.
Access Right Authorization: Restricted mode
enables granular access control to transactions and
provides inherent privacy to the transaction data
stored on the Tangle. It only allow users who have
the secret key to decode the transaction data. Fig.
7 demonstrates the granular access control over the
transaction data stored on the Tangle. It also shows
1
https://nodes.devnet.iota.org
An Approach to Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence for the Internet of Things
179
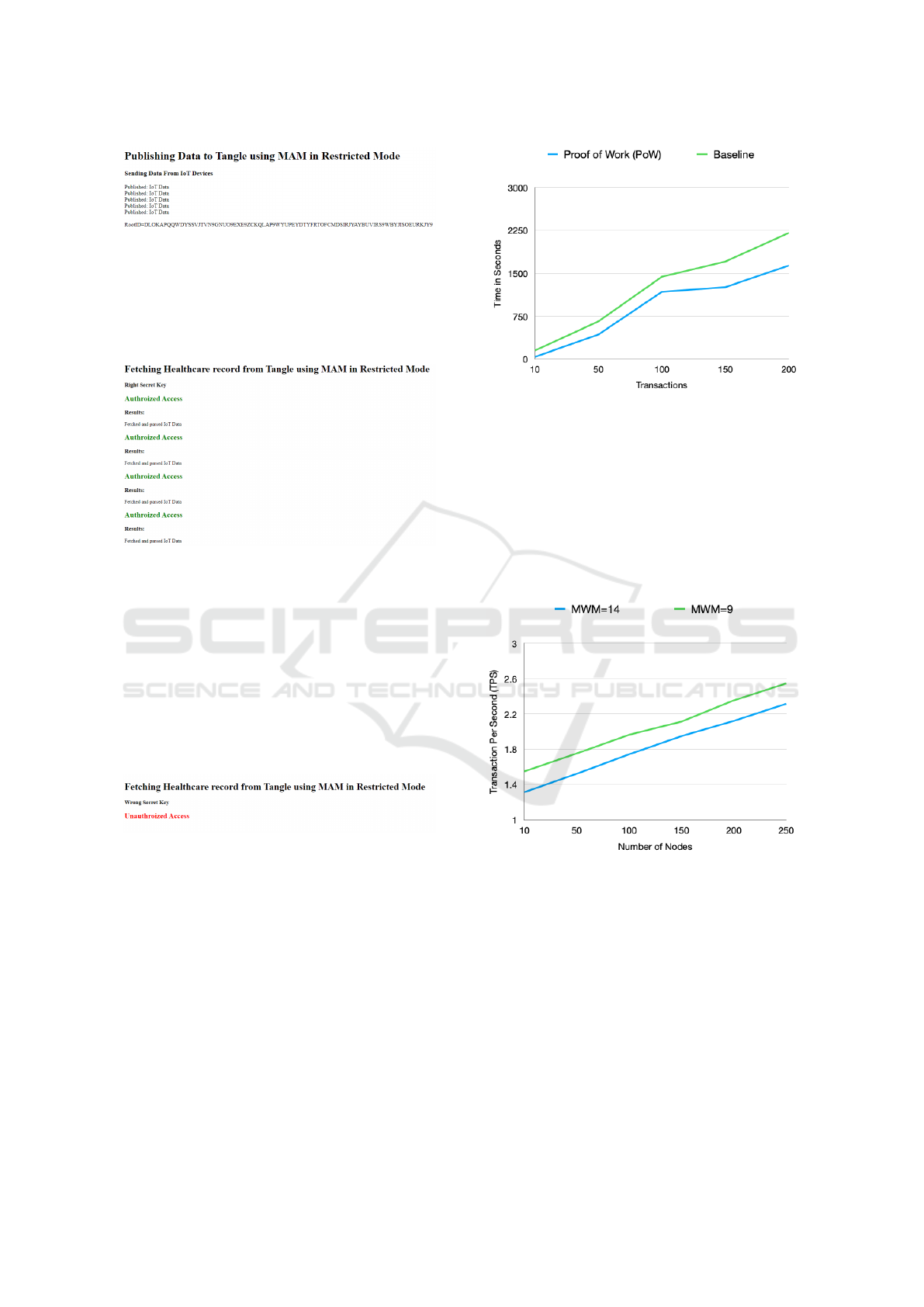
Figure 6: Publishing Transactions Data from IoT de-
vices Using Restricted Mode.
that when a user fetches transaction data with the cor-
rect secret key, access will be authorized, and a user
is allowed to decrypt the transaction data. Therefore,
access will be authorized.
Figure 7: Accessing Transaction Data with Right Secret
Key (Authorized Access).
Unauthorized Access: Fig. 8 demonstrates the
use of restricted mode when providing the wrong se-
cret key. A user who has the wrong secret key will
be unable to access the transaction data stored on the
Tangle. It also shows that when a user is attempt-
ing to fetch the transaction data with the wrong secret
key, access will be unauthorized. This is particularly
useful in healthcare applications for data access man-
agement.
Figure 8: Accessing Transaction Data with Wrong Se-
cret Key (Unauthorized Access).
PoW Execution Time: Fig 9 shows the result of
the execution time when offloading the PoW com-
pared to the baseline. As it can be seen that when
the number of sent transactions are 100, the execution
time of the PoW reaches 1177.5 second and the base-
line reaches 1440.1 second. This is because the PoW
is being offloaded to a dedicated node with higher re-
sources, while in the baseline the PoW is computed
on the same node.
Scalability: Fig 10 shows the result of the PPDI
approach in terms of scalability with different Min-
imum Weight Magnitude (MWM) settings, and dif-
ferent number of nodes. it is clear that as the num-
Figure 9: PoW Execution Time Compared to the Base-
line.
ber of nodes increases, the Transaction Per Second
(TPS) transaction speed increases linearly. Conse-
quently, the transaction speed has a good linear scala-
bility when the number of nodes increases. As it can
be seen that when 100 nodes are sending transactions,
the average TPS reaches 1.543 tx/s when the MWM
is set to 14, while the average TPS reaches 1.764 tx/s
when the MWM is set to 9.
Figure 10: Scalability in Tangle with 250 Nodes.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we have addressed the issue of privacy
in IoT by using the IOTA distributed ledger tech-
nology. In particular, we have employed the MAM
protocol using a mix of modes, such as public and
restricted, to grant granular access to data. In or-
der to achieve privacy and ensure scalability, an ap-
proach to privacy preserving distributed intelligence,
called PPDI, has been proposed. Restricted and pub-
IoTBDS 2022 - 7th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
180

lic modes are implemented to ensure data authentic-
ity, integrity as well as in what form the data should
be and who can gain access to it all of which privacy
related issues (Alsboui et al., 2021).
This paper is not the result of a completed project,
but the exposition of the start of one. We feel that this
area of research is pertinent to internet of things, and
in this paper we have taken initial steps towards inte-
grating IOTA MAM to enable distributed intelligence
in the internet of things.
There are a number of interesting directions for fu-
ture work. Firstly, we plan to thoroughly investigate
the saving in energy consumption with the PoW com-
putation offloading mechanism. Secondly, we plan
to develop an interactive model and access control
mechanisms that enables the users to access health-
care records (Atlam et al., 2018; Florea, 2018).
Thirdly, we plan to investigate the possibilities of
integrating the IOTA MAM with cloud computing
infrastructure to build a model that supports multi-
party authentication (Al-Aqrabi and Hill, 2018). Fi-
nally, we plan to design and develop a complete hy-
brid distributed intelligence framework that tackles
all of the IoT technical challenges including, scala-
bility, energy-efficiency, security, and privacy by in-
tegrating components from various technologies and
demonstrate it is applicability, and efficiency to sev-
eral real-world IoT application scenarios including
smart transportation system.
REFERENCES
Al-Aqrabi, H. and Hill, R. (2018). Dynamic multiparty
authentication of data analytics services within cloud
environments. 2018 IEEE 20th International Con-
ference on High Performance Computing and Com-
munications; IEEE 16th International Conference on
Smart City; IEEE 4th International Conference on
Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS),
pages 742–749.
Al-Aqrabi, H., Johnson, A. P., Hill, R., Lane, P., and Als-
boui, T. (2020). Hardware-intrinsic multi-layer se-
curity: A new frontier for 5g enabled iiot. Sensors,
20(7):1963.
Al-Aqrabi, H., Pulikkakudi Johnson, A., Hill, R., Lane, P.,
and Liu, L. (2019). A multi-layer security model for
5g-enabled industrial internet of things. In 7th In-
ternational Conference on Smart City and Informa-
tization (iSCI 2019), Guangzhou, China, November
12-15, 2019, Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
Switzerland. Springer International Publishing AG.
Alsboui, T., Qin, Y., and Hill, R. (2019). Enabling dis-
tributed intelligence in the internet of things using the
IOTA tangle architecture. In Ramachandran, M., Wal-
ters, R. J., Wills, G. B., Mu
˜
noz, V. M., and Chang,
V., editors, Proceedings of the 4th International Con-
ference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security,
IoTBDS 2019, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, May 2-4,
2019, pages 392–398. SciTePress.
Alsboui, T., Qin, Y., Hill, R., and Al-Aqrabi, H. (2020a).
Enabling distributed intelligence for the internet of
things with IOTA and mobile agents. Computing,
102(6):1345–1363.
Alsboui, T., Qin, Y., Hill, R., and Al-Aqrabi, H. (2020b).
Towards a scalable IOTA tangle-based distributed in-
telligence approach for the internet of things. In
Arai, K., Kapoor, S., and Bhatia, R., editors, Intelli-
gent Computing - Proceedings of the 2020 Comput-
ing Conference, Volume 2, AI 2020, London, UK, 16-
17 July 2020, volume 1229 of Advances in Intelligent
Systems and Computing, pages 487–501. Springer.
Alsboui, T., Qin, Y., Hill, R., and Al-Aqrabi, H. (2021).
Distributed intelligence in the internet of things: Chal-
lenges and opportunities. SN Comput. Sci., 2(4):277.
Angelis, E. D., Ciribini, A., Tagliabue, L., and Paneroni,
M. (2015). The brescia smart campus demonstrator.
renovation toward a zero energy classroom building.
Procedia Engineering, 118:735–743.
Atlam, H. F., Alassafi, M. O., Alenezi, A., Walters, R. J.,
and Wills, G. B. (2018). XACML for building ac-
cess control policies in internet of things. In Mu
˜
noz,
V. M., Wills, G. B., Walters, R. J., Firouzi, F., and
Chang, V., editors, Proceedings of the 3rd Interna-
tional Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and
Security, IoTBDS 2018, Funchal, Madeira, Portugal,
March 19-21, 2018, pages 253–260. SciTePress.
Atzori, L., Iera, A., and Morabito, G. (2010). The internet of
things: A survey. Computer Networks, 54(15):2787–
2805.
Cares, C., Sep
´
ulveda, S., and Navarro, C. (2019). Agent-
Oriented Engineering for Cyber-Physical Systems:
Helping Teachers Develop Research Informed Prac-
tice, pages 93–102.
Cisco (2016). Internet of things at a glance. (1).
Doan, T. T., Safavi-Naini, R., Li, S., Avizheh, S., K., M. V.,
and Fong, P. W. L. (2018). Towards a resilient smart
home. In Proceedings of the 2018 Workshop on IoT
Security and Privacy, IoT S&P ’18, pages 15–21,
New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Fan, C., Khazaei, H., Chen, Y., and Musilek, P. (2019).
Towards a scalable dag-based distributed ledger for
smart communities. In 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum
on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), pages 177–182.
Florea, B. C. (2018). Blockchain and internet of things
data provider for smart applications. In 2018 7th
Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing
(MECO), pages 1–4.
Foundation, I. (2018). Iota javascript api library. (visited on
1-08-2021).
Gartner (2013). Gartner says the internet of things installed
base will grow to 26 billion units by 2020. (1).
Klonoff, D. C. (2017). Fog computing and edge comput-
ing architectures for processing data from diabetes de-
vices connected to the medical internet of things.
An Approach to Privacy-Preserving Distributed Intelligence for the Internet of Things
181

McGhin, T., Choo, K.-K. R., Liu, C. Z., and He, D. (2019).
Blockchain in healthcare applications: Research chal-
lenges and opportunities. Journal of Network and
Computer Applications, 135:62–75.
Perera, C., Qin, Y., Estrella, J. C., Reiff-Marganiec, S., and
Vasilakos, A. V. (2017). Fog computing for sustain-
able smart cities: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv.,
50(3):32:1–32:43.
Rahman, H. and Rahmani, R. (2018). Enabling distributed
intelligence assisted future internet of things con-
troller (fitc). Applied Computing and Informatics,
14(1):73 – 87.
Research, A. (2013). More than 30 billion devices will wire-
lessly connect to the internet of everything in 2020.
(1).
Sahni, Y., Cao, J., Zhang, S., and Yang, L. (2017). Edge
mesh: A new paradigm to enable distributed intelli-
gence in internet of things. IEEE Access, 5:16441–
16458.
Serguei, P. (2017). The tangle. (1).
V
¨
ogler, M., Schleicher, J., Inzinger, C., Nastic, S., Sehic,
S., and Dustdar, S. (2015). Leonore – large-scale pro-
visioning of resource-constrained iot deployments.
Zhang, K. and Jacobsen, H. (2018). Towards depend-
able, scalable, and pervasive distributed ledgers with
blockchains. In 2018 IEEE 38th International Con-
ference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS),
pages 1337–1346.
Zhang, P., Schmidt, D. C., White, J., and Lenz, G. (2018).
Chapter one - blockchain technology use cases in
healthcare. In Raj, P. and Deka, G. C., editors,
Blockchain Technology: Platforms, Tools and Use
Cases, volume 111 of Advances in Computers, pages
1–41. Elsevier.
Zheng, T., Wan, J., Zhang, J., Jiang, C., and Jia, G. (2020).
A survey of computation offloading in edge comput-
ing. In 2020 International Conference on Computer,
Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS),
pages 1–6.
IoTBDS 2022 - 7th International Conference on Internet of Things, Big Data and Security
182
