
An Image Quality Assessment Method
based on Sparse Neighbor Significance
Selcuk Ilhan Aydi
Institute of Science, Faculty of Computer Engineering, Gebze Technical University, Turkey
Keywords:
Image Quality Assessment, Sparse Coding, Human Visual System.
Abstract:
In this paper, the image quality assessment problem is tackled from a sparse coding perspective, and a new
automated image quality assessment algorithm is presented. Specifically, the input image is first divided into
non-overlapping blocks and sparse coding is used to reconstruct a central sub-block using the neighboring
sub-blocks as dictionaries. The resulting 2D sparse vectors from each neighboring sub-block, are devised
as significance maps that are then used in similarity measures between the reference and distorted images.
The proposed method is compared against various recently introduced shallow and deep methods across four
datasets and multiple distortion types. The experimental results that have been obtained show that it possesses
a strong correlation with the Human Visual System and outperforms its counterparts.
1 INTRODUCTION
Image quality assessment (IQA) is a difficult task due
to the not yet fully understood Human Visual System
(HVS). The HVS has a complex behavior during the
process of rating the quality of visual content. Over
the past few decades, many objective image quality
assessment methods have been developed. IQA mod-
els may be categorized as full-reference (FR-IQA),
reduced-reference (RR-IQA), and no-reference (NR-
IQA). In the case of FR-IQA, the reference version of
the distorted image is available, while only partial in-
formation is provided in the second category. In the
case of NR-IQA, the reference image is unavailable.
The present study focuses on the first case.
Two main IQA strategies have met with wide ac-
claim by the scientific community (Wang and Bovik,
2006). The first is the error sensitivity paradigm,
where an error signal is obtained, which is assumed
to be a quality measurement. The primitive methods
using error sensitivity, including mean squared error
(MSE), peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), do not cor-
relate well with the HVS (Wang and Bovik, 2006).
Another difficulty concerns distinguishing distortion
types with the same error value. The second ap-
proach, known as structural similarity index (SSIM)
(Zhou Wang et al., 2004), is based on the assumption
that the HVS focuses on structural information (Wang
et al., 2002). It is motivated by the internal mecha-
nism of the HVS, where hierarchical pre-processing
is known to be conducted in order to extract progres-
sively more complex object-level information (Wang
and Bovik, 2006).
In both approaches, the main challenge consists
of dealing with the different types of distortions that
may lead to various divergent or convergent results
in terms of quality scores (Wang and Bovik, 2006).
In this paper, an IQA method based on sparse cod-
ing called Sparse Significance Image Quality Mea-
sure (SSIQM) has been developed, that deals explic-
itly with structural distortion types.
Recently, sparse coding has been a promising ap-
proach in the domain of image quality assessment
(Guha et al., 2014; Li et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2017). It
also has a strong consistency with the HVS.
The perception of the scene by the HVS has the
following procedures. The continuous stream of vi-
sual stimuli projected on retina is transmitted to the
primary visual cortex (V1) through the Lateral Genic-
ulate Nucleus (LGN) for the abstraction process. The
extensive experiments show that the underlying pro-
cess of the brain is heavily based on reducing the re-
dundancy presents in the visual stimuli and not only
the visual cortex but also the other parts of the brain
are involved in this process. If it is assumed that for
each image the weights of each neuron is different
then utilizing the weights of each neuron in the IQA
is feasible to implement an IQA method. Such a be-
havior of the HVS can be well modelled using sparse
coding, in the sense of atoms in the dictionary have
different weights and corresponds to different signifi-
cance.
Specifically sparse coding represents a signal via
a linear combination using a set of basis functions
34
Aydi, S.
An Image Quality Assessment Method based on Sparse Neighbor Significance.
DOI: 10.5220/0011058700003209
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering (IMPROVE 2022), pages 34-44
ISBN: 978-989-758-563-0; ISSN: 2795-4943
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

and their corresponding coefficients and is widely ac-
cepted as a process related to the cognitive behavior
of the HVS (Olshausen and Field, 1996; Olshausen
and Field, 1997; Comon, 1994; Bell and Sejnowski,
1995; Lee et al., 1999; A. Hyv
¨
arinen and E. Oja,
2010). Sparse Feature Fidelity (Chang et al., 2013)
and Adaptive Sub-Dictionary Selection Strategy (Li
et al., 2016) learn dictionaries to represent any dis-
torted image in linear relation with sparse vector and
employ this sparse coefficients in the calculation of
objective quality of the distorted image.
In addition to the idea of using sparse coding in
IQA, the neighboring blocks are also considered in
the design of SSIQM. From the perspective of biol-
ogy, a phenomenon known as visual agnosia (Farah,
2004), refers to the impairment of the visual stimuli in
the process of recognition of objects. In general, there
exist two types of agnosia, including apperceptive ag-
nosia and associative agnosia. In the former, patients
can recognize the local features of the visual informa-
tion projected on the retina. However, patients cannot
correctly perceive the adjacent features that are con-
tributing to the actual structure of the visual object.
As a result, considering the neighboring blocks in the
IQA problem is crucial and consistent with the visual
perception of the HVS.
Furthermore, many pieces of research support the
fact that the use of neighboring blocks is an important
approach in visual recognition (Khellah, 2011; Qian
et al., 2013). In (Khellah, 2011), the author employ-
ees a pixel-based similarity map, is constructed by
utilizing the dominant neighborhood structure for tex-
ture classification. In (Qian et al., 2013), the authors
aim to use a relationship between the center pixel and
its neighboring pixels, is defined by linear representa-
tion coefficients determined using ridge regression in
the problem of face recognition.
In this paper, an IQA method based on sparse cod-
ing called Sparse Significance Image Quality Mea-
sure (SSIQM) has been developed, that deals explic-
itly with structural distortion types. SSIQM takes into
account the relationship of the neighboring blocks in
terms of sparse significance.
This article’s contributions can be summarized as
follows:
1. A novel FR-IQA method, adopting sparse feature
vectors is proposed; the sparse vectors are ex-
tracted via dynamic dictionaries constructed from
normalized pixel intensities of image patches
(neighboring blocks of the center block), instead
of using fixed over-complete orthogonal dictio-
naries. Moreover, gradient information, known
to be well-correlated (Xue et al., 2014) with the
HVS is also exploited. Also, on the contrary of
alternative approaches, the proposed SSIQM does
not require input image sanitation as preprocess-
ing.
2. This approach assumes that the neighboring
blocks may affect the perceptual quality of the
center block and this implicit relation between the
neighboring and center blocks may be reveled by
sparse coding. Hence, the sparse significance re-
lation between the center block and its neighbors
are investigated. Instead of comparing the ref-
erence and distorted images directly, a similarity
metric is developed processing on sparse signif-
icance maps. These maps are constructed in a
novel manner; the center block is used as the sig-
nal of interest and the neighbour blocks are uti-
lized as dictionaries. The sparse feature vectors
are then considered as the feature sets to be used
in the quality assessment.
In the remainder of this article, first an overview of
related studies (Section 2), including sparse based
methods, are provided. Next, in Section 3 the details
of the proposed method are presented. Then, in Sec-
tion 4 the results of an extensive set of experiments
are discussed. The article concludes with Section 5
where future directions of research are provided.
2 RELATED WORKS
The approaches addressing the FR-IQA problem,
can be divided into three main categories: error-
sensitivity, structural similarity and information the-
oretic (Wang and Bovik, 2006).
2.1 Error Sensitivity based Methods
The methods under this category measure the errors
between reference and distorted images via known
features of the HVS. There are several methods based
on the concept of error sensitivity, e.g. Perceptual Im-
age Distortion (PID) (Teo and Heeger, 1994), Noise
Quality Index (NQM) (Damera-Venkata et al., 2000)
and, Visual Signal-to-Noise Ratio (VSNR) (Chandler
and Hemami, 2007), operating on the contrast sen-
sitivity function, luminance adaptation, and contrast
masking features of the HVS to deal with the IQA
problem.
Most Apparent Distortion (MAD) (Larson and
Chandler, 2010) assumes that the HVS has a different
sensitivity to the different degrees of distortion in im-
ages. The basic assumption is that the HVS tends to
be sensitive to the distortions in relatively more qual-
ity images, whereas the HVS looks for image content
An Image Quality Assessment Method based on Sparse Neighbor Significance
35

in low-quality images. By following this hypothesis,
MAD proposes two models simulating the underlying
mechanism of the HVS and finally provides a distor-
tion measure.
The Visible Differences Predictor (VDP) (Daly,
1992) looks for the probability of difference between
two images. VDP produces a probability-of-detection
map between the reference and distorted image. The
map is utilized in the subsequent stages to obtain a
final quality score.
Watson’s DCT model (Watson, 1993) is based on
DCT coefficients of local blocks. It first divides the
image into DCT sub-blocks and calculates a visibility
threshold for each coefficient in each sub-block. The
DC coefficients of DCT blocks are then normalized
by the average luminance. The model also addresses
the contrast/texture masking determined by all the co-
efficients within the same block. In the next stage, the
errors are normalized between the reference and dis-
torted image. At the final phase, the errors and fre-
quencies are pooled together, and a final quality score
is obtained.
2.2 Structural Information based
Methods
As far as structural information is concerned, the
milestone method might be the Structural Similarity
Index (SSIM) that incorporates luminance, contrast,
and structural information as a feature set to evaluate
the distorted image’s quality perceived by the HVS.
Many extensions to SSIM have been proposed, such
as Multiscale SSIM (M-SSIM) (Wang et al., 2003)
and Information content weighted SSIM (IW-SSIM)
(Wang and Li, 2011).
The Gradient Similarity-based FR-IQA method
(GSM) (Zhu and Wang, 2011) uses four directional
high-pass filters to calculate the variations in con-
trast/structural information in images. Another exam-
ple in this category, considering the fact that the HVS
tends to be sensitive to low level features at key lo-
cations such as edges (Stevens, 2012), the Riesz Fea-
ture Similarity index (Zhang et al., 2010) employs the
Riesz transform to characterize local structures in an
image at edges formed by Canny operator. In addition
to that, the frequency domain is essential in quality
assessment algorithms. A representative method that
deals with frequency is the Feature Similarity index
(FSIM) (Zhang et al., 2011), which uses phase con-
gruency and gradient magnitude as complementary
features to detect visual quality in images. Phase con-
gruency is utilized as a weighting function to provide
single similarity for each sub-block, supporting the
fact that the phase information is more important than
the gradient magnitude. Another method that uses
phase and gradient components is the Visual Saliency
Index (VSI) (Zhang et al., 2014). Phase information
is used to calculate visual saliency with some priors
and, the gradient magnitude is obtained by the Scharr
gradient operator.
In addition to these methods, gradient variation in-
formation has been an important feature to be consid-
ered in the quality problem (Liu et al., 2011). Gra-
dient Magnitude Similarity Deviation (GMSD) (Xue
et al., 2014) assumes that gradients have a more
meaningful variation to image distortions and, this
behavior may point out the quality of an image per-
ceived by the HVS.
Structural Contrast Quality Index (SC-IQ) (Bae
and Kim, 2016) has been recently proposed and, it
deals well with various structural distortion types and
has been developed on top of the Structural Contrast
Index (SCI) (Bae and Kim, 2014). SCI can detect per-
ceived distortion for many different distortion types.
It defines the structural distortion as the ratio of struc-
tureness and contrast intensity, where the structure-
ness is defined as the kurtosis of the magnitudes of
DCT AC coefficients, and contrast intensity is defined
as the ratio of mean and square of N, where N is the
height (= width) of NxN DCT block. By following
this index, SC-IQ employs SCI as a feature in the de-
sign of IQA method. In addition to that, SC-IQ de-
vises chrominance values to reflect the effect of the
color components on perceived quality (Zhang et al.,
2011) (Zhang et al., 2014). Moreover, to reflect the
contrast sensitivity function (CSF) of the HVS, SC-
IQ introduces three frequency domain measures by
comparing contrast energy values in high frequency,
middle frequency and low frequency.
2.3 Information Theoretic based
Methods
From the perspective of this category, image qual-
ity assessment is treated as an information fidelity
problem. The basic idea is to model a communica-
tion channel between the image distortion process and
the visual perception process. This approach seeks
the answer to the question: how much information is
shared between the reference and distorted image?
A representative and successful implementation
in this category, Visual Information Fidelity (VIF)
(Sheikh and Bovik, 2006), quantifies the perceived
information present in the reference image and the
amount of this reference information extracted from
the distorted image. These two measures are com-
bined, and the VIF index is proposed as the model
output. This model is an extension of its former
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
36

method Information Fidelity Criterion (IFC) (Sheikh
et al., 2005).
2.4 Sparse Coding based Approaches
In the field of image quality assessment, many effec-
tive approaches attempt to mimic the HVS. Some of
them use structural information and integrate this in-
formation with sparse coding techniques to give some
meaningful weights to extracted structural features
and blocks. However, sparse coding-based methods
generally waste time in the training stage to learn dic-
tionaries from the reference image set. Moreover,
training on the dictionary is very specific to the used
dataset. In this section, a review of such methods is
presented.
In the first method, Sparse Feature Fidelity
(Chang et al., 2013), the weighting matrix is learned
by machine learning and, the resulting matrix is used
to find the sparsest feature map by using Independent
Component Analysis (ICA). The calculated sparse
features are utilized as a feature set to be used in qual-
ity assessment. Sparse Feature Fidelity (SFF) also
combines luminance correlation with sparse feature
to enhance the correlation with the HVS.
In the second method, Adaptive Sub-Dictionary
Selection Strategy (Li et al., 2016) firstly, an over-
complete visual dictionary which is used to represent
the reference image in the feature extraction phase, is
learned by utilizing a set of natural images. The dis-
torted image is represented by the sub-dictionary that
is obtained from the over-complete dictionary used
in the representation of the reference image. More-
over on this, to enhance the performance of the pro-
posed method, a number of auxiliary features includ-
ing, contrast, color and luminance are employed to be
able to reflect the HVS behavior more precisely.
The third method, Kernel Sparse Coding Based
Metric (Zhou et al., 2021) approaches the IQA from
a nonlinear perspective to better reveal the structures
which provide an effective representation of image
patches. In addition to that, sparse coding coefficients
and reconstruction error are utilized to construct a fi-
nal quality score. However, this approach has many
parameters and computationally inefficient.
In the fourth method, Sparseness Significance
Ranking Measure (Ahar et al., 2018), the general idea
is to rank Fourier components by their significance to
provide a quality metric. The Fourier basis are used as
complete-dictionaries for sparse coding and a ranking
mechanism is provided. A sparse analysis of AC and
DC components is performed and pooled to calculate
a final quality score.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
3.1 Sparse Coding
Sparse coding represents a given signal in a linear
combination of two components: the first is a dic-
tionary or weight vector, the latter is the sparse fea-
ture vector (Wang et al., 2015). In other words, the
main goal is to find a set of basis functions having
linear combinations with sparse features. Generally
speaking, a sparse feature vector/matrix has mostly
zero components, pointing out its sparsity. A given
signal, x, present in a high dimensional space R
m
, can
be represented using D ∈ R
m×n
, with n atoms as
x = Ds (1)
where D is a dictionary of atoms extracted or learned
and s is a sparse feature vector. The sparsest vector
s can be found by solving the following optimization
problem
min
s
kDs − xk
2
2
+ λksk
1
(2)
where λ is an adjustment parameter to balance be-
tween reconstruction error and sparsity. The l
1
-norm
denoted by k.k
1
, counts the number of zero elements
in sparse vector. If D is properly chosen then, s tends
to have values of zero or close to zero.
3.2 SSIQM
SSIQM consists of two pipelines executing in par-
allel to each other. The first pipeline constructs the
sparse significance maps while the second pipeline
deals with gradient information extraction for each
sub-block. The outputs of the underlying pipelines
are pooled at the final phase, producing quality score.
Preprocessing stage converts the RGB color space to
grayscale and a unity-based min-max normalization
is employed to rescale the intensity values to scale the
range in [0, 1]. In addition to that, the input images are
down-scaled to a fixed size of 128×128 by perform-
ing interpolation for the sake of computational com-
plexity. The experimental results show that directly
converting from RGB to grayscale produces more ef-
ficient results. To sum up, SSIQM can be shown as
SSIQM = F(I
r
,I
d
,β,γ,θ) (3)
where β and γ are the weights of sparse significance
map and gradient similarity scores, respectively, θ
points to internal parameters including window size
and sparse coding parameters. I
r
and I
d
denote
the reference and distorted images, respectively. An
overview of SSIQM is illustrated in Fig.1.
In the first pipeline, the input image is divided into
15×15 blocks and then each block is divided into five
An Image Quality Assessment Method based on Sparse Neighbor Significance
37
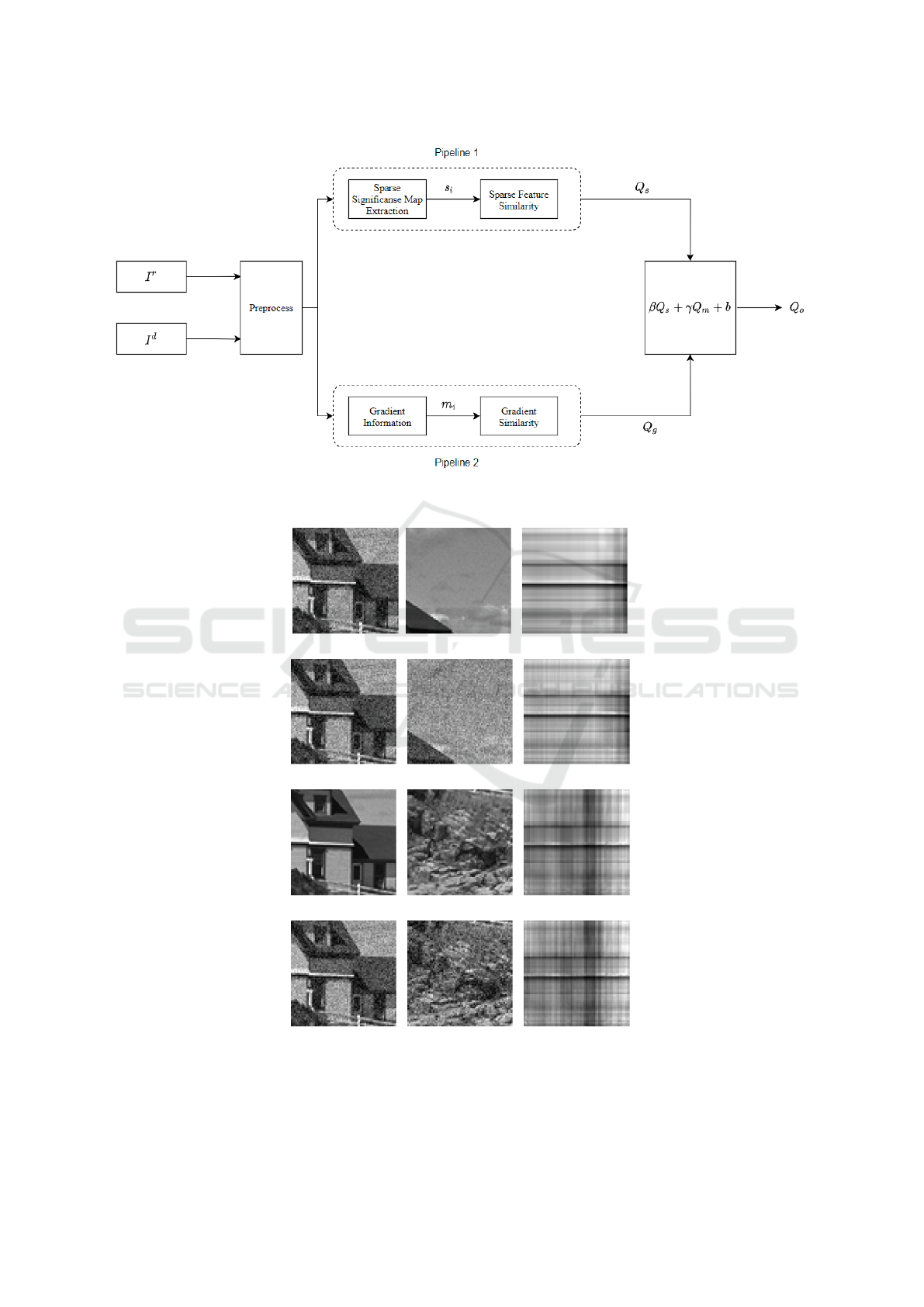
Figure 1: General SSIQM design, having two parallel pipelines calculating gradient and sparse significance maps. The global
quality scores produced by pipelines are pooled in the last step, offering an objective quality score.
(a) (b) (c)
(d) (e) (f)
(g) (h) (i)
(j) (k) (l)
Figure 2: Reference and distorted local blocks, and their corresponding north, south and significance maps. a and d are the
same reference center local blocks, g and j are the the same distorted center local blocks, b and e are the north local blocks
of the reference and distorted local blocks, h and k are the north and south local blocks of the reference and distorted local
blocks. The latest column c, f, i and l are the sparse significance maps of the pair of center and its neighbour local blocks.
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
38

sub-blocks. Each sub-block consists of the center c
i
,
i∈{1,...,M} and its 4-neighbors n
i, j
, j∈{1, 2, 3, 4}.
Each n
i, j
block is used as D in (2). The center block
is used as the signal of interest, x, in (2) and, a sparse
coding algorithm A(c,n) is utilized to obtain sparse
vectors. For each center block, c
i
, four sparse signif-
icance maps are constructed using the sparse vectors,
S
j
, resulting a set of pairs of (n
i, j
,S
j
). Final sparse
significance maps are then, forwarded to a local sim-
ilarity function, providing the local quality for each
pair. In this study, a well-known structural similarity
measure is adapted as the local quality function
q(x
i
,y
i
) =
2x
i
2y
i
+ δ
x
i
2
+ 2y
i
2
+ δ
(4)
where x
i
and y
i
are the two image patches and δ
used to avoid zero division. The resulting normalized
global similarity Q
s
between the reference and dis-
torted significance maps can be derived from equation
4 as
Q
s
= 1/M
M
∑
i=1
S
r
i
S
d
i
+ δ
S
r
i
2
+ S
d
i
2
+ δ
(5)
where S
r
i
and S
d
i
are the significance maps of the
i − th center block extracted from the reference and
distorted images, respectively. This final normal-
ized score represents the global similarity in terms of
sparse significance.
The reason of using direct pixel values is in order
to find a relationship in the pixel domain in terms of
sparse significance. Since SSIQM does not prioritize
representing a signal in a lower dimensional space,
the neighbouring local blocks are used as complete
dictionaries. On the other hand, a frequency level
dictionary might also be used such as, DCT or FFT
components. In this situation, a relationship may be
captured in the frequency domain, which is however
out of the scope of this work.
A number of sparse significance maps and the cor-
responding dictionaries with the center local blocks
are illustrated in Fig.2. The sparse significance maps
are shown in the last column for each pair of center
and its neighbour block. The distortion type used in
Fig.2 is additive gaussian noise. Whiter pixels in the
significance maps represent a strong weight whereas
darker pixels exhibit weak weight for each atom in the
dictionary.
In Fig.2, each column in the significance maps
represent a weight vector for each column in the dic-
tionaries/neighbour blocks. It can be observed that
the significance maps have a correlation with the sim-
ilarity between the center and neighbour blocks. In
other words, the sparse coding algorithm uses almost
all the atoms in the dictionary to be able to recon-
struct the original image when the pixel-level similar-
ity between the center and neighbour block is lower.
Noticeably, the significance maps are sensitive to the
distortions as it is depicted in Fig.2(c), 2(f) and 2(i),
2(l), where the variations in the maps are quite visible.
There are many sparse coding algorithms imple-
mented and ready to use in literature. In this paper,
threshold is selected as sparse coding algorithm de-
noted by A(c,n), implemented in (Pedregosa et al.,
2011) that squashes to zero all coefficients of sparse
vector less than the given threshold.
In the second pipeline, the magnitude information
is extracted from the reference and distorted images.
We used the Robert’s cross edge detector to find the
edges which correlates to the HVS relatively better
compared to the Sobel filter according to our experi-
ments. The magnitude P can be shown as
P =
q
g
x
2
+ g
y
2
(6)
where g
x
and g
y
are the direction in both axis. The
normalized magnitude map m produced by equation
6, is then divided into 15×15 blocks. The magnitude
similarity, Q
m
, for each block extracted from the ref-
erence and distorted image is then calculated as
Q
m
= 1/M
M
∑
i=1
m
r
i
m
d
i
+ δ
m
r
i
2
+ m
d
i
2
+ δ
(7)
where m
r
i
and m
d
i
are i − th local block magnitude
maps of the reference and distorted images, respec-
tively.
In the latest stage, Q
s
and Q
m
are pooled to pro-
vide a final objective quality score Q
o
for the given
distorted image. Both quality scores have their own
weights in the pooling stage as
Q
o
= βQ
s
+ γQ
m
+ b (8)
In equation 8, b is used to avoid zero quality score.
Instead of determining β, γ and b by ad-hoc methods,
Support Vector Regression (SVM) is used to obtain
more effective results.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
This section presents the performance analysis and re-
sults gathered from different experiments conducted
on well-known subjective datasets; TID2008 (Pono-
marenko et al., 2009), TID2013 (Ponomarenko et al.,
2015), CSIQ (Larson and Chandler, 2010) and LIVE
(Sheikh et al., 2006), and a set of comparisons are
demonstrated with a number of state-of-the-art IQMs.
TID2008 has 1700 distorted images, 25 reference
images, having 17 distortion types with 4 levels.
An Image Quality Assessment Method based on Sparse Neighbor Significance
39

Table 1: Comparison of SSIQM vs. seven state of the art IQMs on four datasets with five performance metrics.
Method Criteria
TID2013 TID2018 LIVE CSIQ
PSNR
SRCC 0.754 0.672 0.819 0.887
PRCC 0.732 0.641 0.800 0.897
KRCC 0.548 0.453 0.617 0.685
RMSE 22.90 21.65 28.19 29.94
SSIM (Zhou Wang et al., 2004)
SRCC 0.728 0.694 0.874 0.890
PRCC 0.735 0.679 0.713 0.807
KRCC 0.535 0.500 0.687 0.695
RMSE 3.700 3.687 0.291 0.322
MS-SSIM (Wang et al., 2003)
SRCC 0.799 0.769 0.877 0.918
PRCC 0.770 0.734 0.665 0.826
KRCC 0.597 0.567 0.687 0.742
RMSE 3.659 3.634 0.334 0.336
VIFp (Sheikh and Bovik, 2006)
SRCC 0.538 0.594 0.869 0.886
PRCC 0.538 0.523 0.858 0.890
KRCC 0.432 0.439 0.677 0.790
RMSE 4.032 4.040 0.187 0.163
FSIMc (Zhang et al., 2011)
SRCC 0.869 0.902 0.919 0.899
PRCC 0.849 0.845 0.776 0.827
KRCC 0.686 0.718 0.748 0.709
RMSE 3.644 3.609 0.356 0.356
GMSD (Xue et al., 2014)
SRCC 0.810 0.896 0.909 0.947
PRCC 0.859 0.868 0.866 0.938
KRCC 0.644 0.714 0.730 0.796
RMSE 4.502 4.430 0.510 0.095
UQI (Zhou Wang and Bovik, 2002)
SRCC 0.707 0.567 0.786 0.589
PRCC 0.530 0.418 0.450 0.419
KRCC 0.505 0.393 0.579 0.420
RMSE 3.616 3.576 0.441 0.354
SSIQM proposed
SRCC 0.883 0.890 0.914 0.937
PRCC 0.790 0.794 0.679 0.855
KRCC 0.702 0.711 0.728 0.772
RMSE 7.770 7.709 11.05 11.22
Table 2: Comparison of SSIQM vs. ten state of the art FR/NR CNN Based IQMs on three datasets with two performance
metrics.
Method Criteria
TID2013 LIVE CSIQ
H-IQA (Lin and Wang, 2018)
SRCC 0.790 0.982 0.885
PRCC 0.880 0.982 0.910
AIGQA (Ma et al., 2021)
SRCC 0.871 0.960 0.885
PRCC 0.893 0.957 0.952
BPSQM (Pan et al., 2018)
SRCC 0.862 0.973 0.927
PRCC 0.885 0.963 0.952
DB-CNN (Zhang et al., 2018)
SRCC 0.816 0.968 0.874
PRCC 0.865 0.971 0.915
BIECON (Kim and Lee,
2016)
SRCC 0.717 0.958 0.946
PRCC 0.762 0.960 0.959
DIQA (Kim et al., 2018)
SRCC 0.825 0.975 0.884
PRCC 0.850 0.977 0.915
CaHDC (Wu et al., 2020)
SRCC 0.862 0.965 0.903
PRCC 0.878 0.964 0.914
DSIR-IQA (Liang et al.,
2021)
SRCC 0.782 0.967 0.820
PRCC 0.816 0.969 0.878
DMIR-IQA (Liang et al.,
2021)
SRCC 0.796 0.967 0.823
PRCC 0.821 0.971 0.881
SSIQM proposed
SRCC 0.883 0.914 0.937
PRCC 0.790 0.679 0.855
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
40
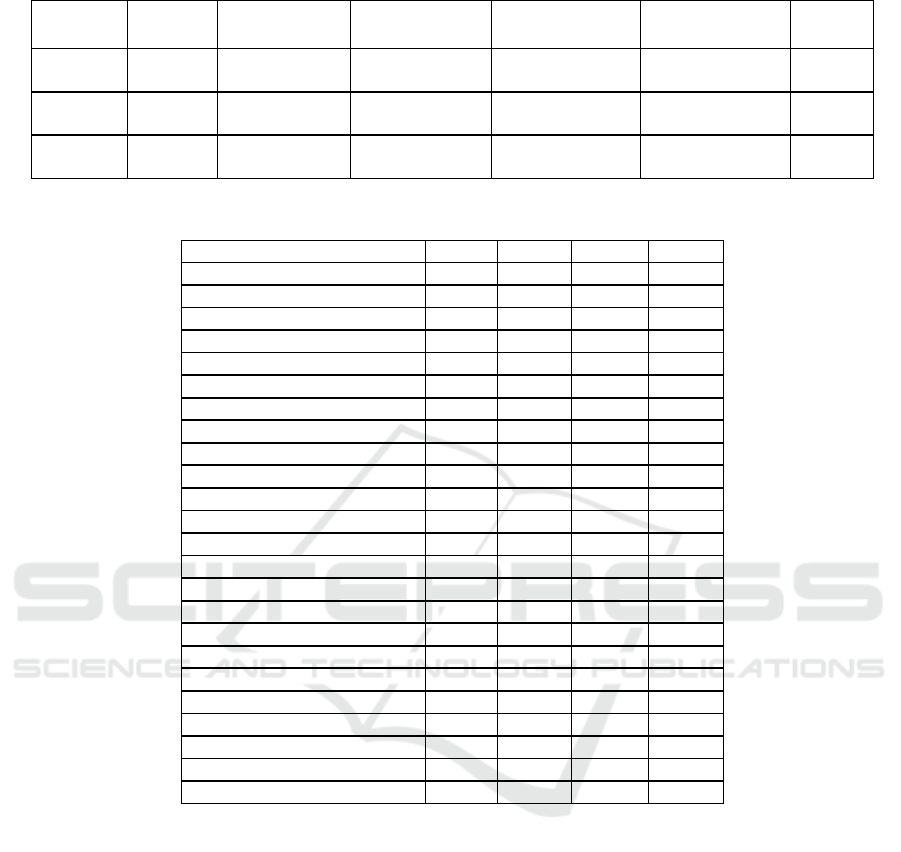
Table 3: Comparison of SRCC of CNN Based Models and SSIQM in cross dataset test.
Trained Tested
AIGQA
(Ma et al., 2021)
DIQA
(Kim et al., 2018)
DSIR-IQA
(Liang et al., 2021)
DMIR-IQA
(Liang et al., 2021)
SSIQM
proposed
TID2013
LIVE 0.886 0.904 0.879 0.880 0.914
CSIQ 0.823 0.877 0.856 0.867 0.937
LIVE
TID2013 0.698 0.922 0.878 0.891 0.883
CSIQ 0.847 0.915 0.903 0.922 0.937
CSIQ
LIVE - 0.926 0.936 0.947 0.914
TID2013 - 0.923 0.906 0.907 0.883
Table 4: Performance of SSIQM on individual distortions of TID2013.
Type SRCC PRCC KRCC RMSE
Additive Gaussian noise 0.938 0.850 0.759 7.693
Noise in color components 0.876 0.866 0.683 7.260
Spatially correl. Noise 0.920 0.857 0.737 7.697
Masked noise 0.827 0.747 0.632 7.310
High frequency noise 0.928 0.878 0.748 7.626
Impulse noise 0.885 0.795 0.700 8.361
Quantization noise 0.906 0.773 0.721 7.536
Gaussian blur 0.974 0.876 0.862 7.878
Image denoising 0.963 0.890 0.840 7.431
JPEG compression 0.948 0.918 0.793 7.762
JPEG2000 compression 0.960 0.887 0.832 8.023
JPEG transm. Errors 0.887 0.822 0.656 7.67
JPEG2000 transm. Errors 0.889 0.779 0.701 8.005
Non ecc. patt. Noise 0.785 0.701 0.535 7.130
Local block-wise dist 0.613 0.561 0.433 8.687
Mean shift 0.592 0.539 0.409 3.690
Contrast change 0.429 0.575 0.297 5.997
Change of color saturation 0.478 0.305 0.329 8.334
Multipl. Gauss. Noise 0.911 0.842 0.727 7.787
Comfort noise 0.924 0.861 0.755 7.471
Lossy compr. of noisy images 0.941 0.868 0.783 7.742
Image color quant. w. dither 0.921 0.809 0.748 7.672
Chromatic aberrations 0.884 0.826 0.720 7.365
Sparse sampl. and reconstr 0.966 0.874 0.836 7.890
TID2013 dataset has 3000 distorted images, 25 ref-
erence images, and 24 distortion types with 5 levels.
CSIQ has 866 distorted images, 30 reference images
with 6 distortion types in 5 levels. On the other hand,
the LIVE dataset has 779 distorted images based on
29 references that are subjected to 5 different distor-
tion types at different distortion levels.
The experiments conducted in this section consist
of two categories: comparing SSIQM with statisti-
cal and CNN-based methods. In addition, the perfor-
mance of SSIQM on different distortion types is stud-
ied. It is assumed that an ideal IQA method should en-
sure a correlation with the HVS without any internal
layer between objective and subjective scores. That
is why, any logistic regression method between ob-
jective and subjective scores has not been performed
in this study. Since this paper focuses on structural
degradation, contrast and mean shift distortion types
are excluded from all experiments.
In the first experiment, PSNR, SSIM (Zhou Wang
et al., 2004), MS-SSIM (Wang et al., 2003), VIF
(Sheikh and Bovik, 2006), FSIMc (Zhang et al.,
2011), GMSD (Xue et al., 2013) and UQI (Zhou
Wang and Bovik, 2002) are compared to the pro-
posed method SSIQM in terms of correlation with
the HVS. All these methods are implemented and
performed with their default values. To be able to
evaluate the performance of each IQMs four metrics
are employed, including Pearson’s linear correlation
coefficient (PLCC), Spearman rank-order correlation
coefficient, Kendall rank-order correlation coefficient
(KRCC), and root mean squared error (RMSE).
The overall performance of SSIQM is shown in
Table 1 with seven alternative methods and four met-
An Image Quality Assessment Method based on Sparse Neighbor Significance
41

rics on four datasets. The most successful results are
highlighted in bold. From Table 1, on TID2013, it can
be observed that SSIQM has superior performance
over the other full reference IQA methods specifically
in terms of prediction accuracy while FSIMc shows
a better monotonic performance than SSIQM in this
dataset. Moreover, RMSE is higher than SSIQM and
PSNR. This is mainly due to the fact that SSIQM
does not have an optimized pooling strategy. On
the TID2008 dataset, although GMSD and FSIMc
have a higher correlation, SSIQM presents a com-
petitive performance in terms of prediction accuracy.
On the other hand, SSIQM has a worse PRCC score.
The proposed method has competitive performance
against SSIM, MS-SSIM, FSIMc, and GMSD on the
LIVE dataset. On CSIQ, SSIQM is not at the first
rank, however, it exhibits a competitive prediction ac-
curacy and a fair level of PRCC.
When deep models are trained on one dataset they
can produce good results if the test dataset is the same
as the training set that has the same distortion types.
Moreover, cross dataset tests show the real generaliza-
tion of deep models where they are trained on dataset
X and evaluated on dataset Y. However, the general
challenging problem is the lack of dataset to be used at
the training phase which leads to over-fitting in most
of the cases if the number of parameters of the deep
model is relatively big enough. To tackle down this
problem, most of the papers use augmentation tech-
niques to increase the number of items in a dataset
that will help avoid the over-fitting problem. This
may provide some performance improvement but lo-
cal qualities and their importance are not distributed
uniformly in most of the distortion types.
In the second experiment of setup, SSIQM is com-
pared against CNN based methods including, H-IQA
(Lin and Wang, 2018), AIGOA (Ma et al., 2021),
BPSQM (Pan et al., 2018), DB-CNN (Zhang et al.,
2018), BIECON (Kim and Lee, 2016), DIQA (Kim
et al., 2018), CaHDC (Wu et al., 2020), DSIR-IQA
and DMIR-IQA (Liang et al., 2021). The overall per-
formance of each deep model is illustrated in Table 2,
showing only SRCC and PRCC scores and compar-
ing them with SSIQM. All the models are trained and
validated in the same dataset in each row. It is pos-
sible to notice that SSIQM has a superior prediction
accuracy on TID2013 while its SRCC is competitive
to others. On LIVE and CSIQ, deep models generally
have higher performance whereas SSIQM performs
well and its accuracy is promising.
Furthermore, the cross dataset test is conducted to
measure the power of SSIQM on LIVE, CSIQ, and
TID2013 databases. For this experiment the com-
mon distortion types among the three databases are
selected including, GB, WN, JPEG, and JPEG200
and the methods used including, AIGQA, DIQA,
DSIR-IQA, and DMIR-IQA. Table 3 demonstrates
the SRCC results of cross dataset test. It can be ob-
served that SSIQM performs best when deep models
are trained on TID2013 and tested with other datasets.
DIQA has a better generalization capability compared
to other deep models. Training on LIVE and vali-
dating on other datasets gives better scores for DIQA
while other models follow a stable graph. On the
other hand, SSIQM’s performance is the best in the
CSIQ dataset compared to others. When the training
dataset is CSIQ, deep models have higher prediction
accuracy than SSIQM.
Each distortion type has its own effect on differ-
ent aspects of an image that potentially may alter the
perception of the scene by the HVS. To determine the
performance of SSIQM on variety of distortions an
experiment is conducted and the results are shown in
Table 4. It can be seen that, SSIQM has a strong cor-
relation in a wide range of distortion set in TID2013.
It performs best in structural and non-color distortions
while its performance is not sufficient in mean shift,
contrast change, change of color saturation and local
block-wise distortion and the corresponding rows are
in bold. Since SSIQM only relies on two extracted
features it does not address all kinds of degradation,
however, the performance on failed distortions might
be enhanced by adding new features which are im-
portant for the perception of the HVS. The underly-
ing features might be sensitive to color components,
contrast information, and light adaptation.
5 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, it can be established that the pro-
posed method works well with most of the distortion
types except mean shift and contrast. To be able to
determine the performance of the proposed method
we conducted intensive experiments where SSIQM is
first compared with the most successful statistical FR-
IQA methods. Furthermore, SSIQM’s performance is
compared with deep models on different datasets via
cross dataset tests. Since each distortion has different
effects on perceptual quality SSIQM’s performance
on each distortion type has been measured. From
the experiments we can conclude that our proposed
method has a good correlation with HVS on many
distortion types. Its performance is very competitive
with a simple design when its counterparts are con-
sidered.
A further study would be adding more features
considering the aspects of HVS to provide a more
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
42

robust IQA method on all the distortion types and
databases. It is also possible to integrate the sparse
significance maps with the modern deep models. Fi-
nally, we would like to remark that SSIQM shows a
well moderate correlation with the HVS and holding
the promise to evaluate the images in a robust and ef-
fective manner when it is used in video codecs and
applications that consider image quality.
REFERENCES
A. Hyv
¨
arinen, J. K. and E. Oja, J. W. (2010). Independent
component analysis. New York, NY, 62(3):412–416.
Ahar, A., Barri, A., and Schelkens, P. (2018). From sparse
coding significance to perceptual quality: A new ap-
proach for image quality assessment. IEEE Transac-
tions on Image Processing, 27(2):879–893.
Bae, S.-H. and Kim, M. (2014). A novel generalized dct-
based jnd profile based on an elaborate cm-jnd model
for variable block-sized transforms in monochrome
images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
23(8):3227–3240.
Bae, S.-H. and Kim, M. (2016). A novel image quality as-
sessment with globally and locally consilient visual
quality perception. IEEE Transactions on Image Pro-
cessing, 25(5):2392–2406.
Bell, A. J. and Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). An information-
maximization approach to blind separation and blind
deconvolution. Neural computation, 7(6):1129–1159.
Chandler, D. M. and Hemami, S. S. (2007). Vsnr: A
wavelet-based visual signal-to-noise ratio for natural
images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
16(9):2284–2298.
Chang, H.-W., Yang, H., Gan, Y., and Wang, M.-H. (2013).
Sparse feature fidelity for perceptual image quality as-
sessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
22(10):4007–4018.
Comon, P. (1994). Independent component analysis, a new
concept? Signal processing, 36(3):287–314.
Daly, S. J. (1992). Visible differences predictor: an algo-
rithm for the assessment of image fidelity. In Hu-
man Vision, Visual Processing, and Digital Display
III, volume 1666, pages 2–15. International Society
for Optics and Photonics.
Damera-Venkata, N., Kite, T. D., Geisler, W. S., Evans,
B. L., and Bovik, A. C. (2000). Image quality as-
sessment based on a degradation model. IEEE trans-
actions on image processing, 9(4):636–650.
Farah, M. J. (2004). Visual agnosia. MIT press.
Guha, T., Nezhadarya, E., and Ward, R. K. (2014). Sparse
representation-based image quality assessment. Sig-
nal Processing: Image Communication, 29(10):1138–
1148.
Khellah, F. M. (2011). Texture classification using domi-
nant neighborhood structure. IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing, 20(11):3270–3279.
Kim, J. and Lee, S. (2016). Fully deep blind image quality
predictor. IEEE Journal of selected topics in signal
processing, 11(1):206–220.
Kim, J., Nguyen, A.-D., and Lee, S. (2018). Deep cnn-
based blind image quality predictor. IEEE trans-
actions on neural networks and learning systems,
30(1):11–24.
Larson, E. C. and Chandler, D. M. (2010). Most appar-
ent distortion: full-reference image quality assessment
and the role of strategy. Journal of electronic imaging,
19(1):011006.
Lee, T.-W., Girolami, M., and Sejnowski, T. J. (1999). Inde-
pendent component analysis using an extended info-
max algorithm for mixed subgaussian and supergaus-
sian sources. Neural computation, 11(2):417–441.
Li, L., Cai, H., Zhang, Y., Lin, W., Kot, A. C., and Sun,
X. (2016). Sparse representation-based image quality
index with adaptive sub-dictionaries. IEEE Transac-
tions on Image Processing, 25(8):3775–3786.
Liang, D., Gao, X., Lu, W., and Li, J. (2021). Deep blind
image quality assessment based on multiple instance
regression. Neurocomputing, 431:78–89.
Lin, K.-Y. and Wang, G. (2018). Hallucinated-iqa: No-
reference image quality assessment via adversarial
learning. In 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 732–741.
Liu, A., Lin, W., and Narwaria, M. (2011). Image quality
assessment based on gradient similarity. IEEE Trans-
actions on Image Processing, 21(4):1500–1512.
Liu, Y., Zhai, G., Gu, K., Liu, X., Zhao, D., and Gao,
W. (2017). Reduced-reference image quality assess-
ment in free-energy principle and sparse representa-
tion. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 20(2):379–
391.
Ma, J., Wu, J., Li, L., Dong, W., Xie, X., Shi, G., and Lin,
W. (2021). Blind image quality assessment with active
inference. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
30:3650–3663.
Olshausen, B. A. and Field, D. J. (1996). Emergence
of simple-cell receptive field properties by learn-
ing a sparse code for natural images. Nature,
381(6583):607–609.
Olshausen, B. A. and Field, D. J. (1997). Sparse coding
with an overcomplete basis set: A strategy employed
by v1? Vision research, 37(23):3311–3325.
Pan, D., Shi, P., Hou, M., Ying, Z., Fu, S., and Zhang, Y.
(2018). Blind predicting similar quality map for image
quality assessment. In Proceedings of the IEEE con-
ference on computer vision and pattern recognition,
pages 6373–6382.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer,
P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos,
A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., and
Duchesnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning
in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
12:2825–2830.
Ponomarenko, N., Jin, L., Ieremeiev, O., Lukin, V., Egiazar-
ian, K., Astola, J., Vozel, B., Chehdi, K., Carli, M.,
Battisti, F., and Jay Kuo, C.-C. (2015). Image database
An Image Quality Assessment Method based on Sparse Neighbor Significance
43

tid2013: Peculiarities, results and perspectives. Signal
Processing: Image Communication, 30:57 – 77.
Ponomarenko, N., Lukin, V., Zelensky, A., Egiazarian, K.,
Carli, M., and Battisti, F. (2009). Tid2008-a database
for evaluation of full-reference visual quality assess-
ment metrics. Advances of Modern Radioelectronics,
10(4):30–45.
Qian, J., Yang, J., and Xu, Y. (2013). Local structure-based
image decomposition for feature extraction with ap-
plications to face recognition. IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing, 22(9):3591–3603.
Sheikh, H., Sabir, M., and Bovik, A. (2006). A statisti-
cal evaluation of recent full reference image quality
assessment algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing, 15(11):3440–3451.
Sheikh, H. R. and Bovik, A. C. (2006). Image information
and visual quality. IEEE Transactions on Image Pro-
cessing, 15(2):430–444.
Sheikh, H. R., Bovik, A. C., and De Veciana, G. (2005). An
information fidelity criterion for image quality assess-
ment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Transactions
on image processing, 14(12):2117–2128.
Stevens, K. A. (2012). The vision of david marr. Perception,
41(9):1061–1072.
Teo, P. and Heeger, D. (1994). Perceptual image distortion.
In Proceedings of 1st International Conference on Im-
age Processing, volume 2, pages 982–986 vol.2.
Wang, Z. and Bovik, A. C. (2006). Modern image quality
assessment. Synthesis Lectures on Image, Video, and
Multimedia Processing, 2(1):1–156.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., and Lu, L. (2002). Why is image
quality assessment so difficult? In 2002 IEEE Inter-
national conference on acoustics, speech, and signal
processing, volume 4, pages IV–3313. IEEE.
Wang, Z. and Li, Q. (2011). Information content weighting
for perceptual image quality assessment. IEEE Trans-
actions on Image Processing, 20(5):1185–1198.
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E. P., and Bovik, A. C. (2003). Mul-
tiscale structural similarity for image quality assess-
ment. In The Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on
Signals, Systems & Computers, 2003, volume 2, pages
1398–1402. Ieee.
Wang, Z., Yang, J., Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Huang, T. S., Liu,
D., and Yang, Y. (2015). Sparse coding and its appli-
cations in computer vision. World Scientific.
Watson, A. B. (1993). Dct quantization matrices visually
optimized for individual images. In Human vision, vi-
sual processing, and digital display IV, volume 1913,
pages 202–216. International Society for Optics and
Photonics.
Wu, J., Ma, J., Liang, F., Dong, W., Shi, G., and Lin, W.
(2020). End-to-end blind image quality prediction
with cascaded deep neural network. IEEE Transac-
tions on Image Processing, 29:7414–7426.
Xue, W., Mou, X., Zhang, L., and Feng, X. (2013). Percep-
tual fidelity aware mean squared error. In 2013 IEEE
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
705–712.
Xue, W., Zhang, L., Mou, X., and Bovik, A. C. (2014).
Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly ef-
ficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Transac-
tions on Image Processing, 23(2):684–695.
Zhang, L., Shen, Y., and Li, H. (2014). Vsi: A visual
saliency-induced index for perceptual image quality
assessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
23(10):4270–4281.
Zhang, L., Zhang, L., and Mou, X. (2010). Rfsim: A fea-
ture based image quality assessment metric using riesz
transforms. In 2010 IEEE International Conference
on Image Processing, pages 321–324.
Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Mou, X., and Zhang, D. (2011).
Fsim: A feature similarity index for image quality as-
sessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
20(8):2378–2386.
Zhang, W., Ma, K., Yan, J., Deng, D., and Wang, Z. (2018).
Blind image quality assessment using a deep bilinear
convolutional neural network. IEEE Transactions on
Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 30(1):36–
47.
Zhou, Z., Li, J., Quan, Y., and Xu, R. (2021). Image quality
assessment using kernel sparse coding. IEEE Trans-
actions on Multimedia, 23:1592–1604.
Zhou Wang and Bovik, A. C. (2002). A universal im-
age quality index. IEEE Signal Processing Letters,
9(3):81–84.
Zhou Wang, Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., and Simoncelli,
E. P. (2004). Image quality assessment: from error
visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions
on Image Processing, 13(4):600–612.
Zhu, J. and Wang, N. (2011). Image quality assessment
by visual gradient similarity. IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing, 21(3):919–933.
IMPROVE 2022 - 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Vision Engineering
44
