
Steiner Tree-based Collaborative Learning Group Formation in Trust
Networks
Yifeng Zhou
1,2
, Shichao Lin
2
and Qi Zhao
2
1
School of Information Engineering, Nanjing Audit University, Nanjing, China
2
School of Computer Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, China
Keywords:
Group Formation, Collaborative Learning, Trust Network, Steiner Tree.
Abstract:
Group formation is one of the key problems for collaborative learning, i.e., how to allocate agents (learners)
to appropriate groups in order to improve the learning utility of the system. Previous works often focus
on investigating the potential factors that may influence the agent’s learning utility from the perspective of
intrinsic attributes of agents; however, the structural attributes of groups are rarely considered. Considering
that trust is an important interactive and cognitive attribute in collaborative learning, which can influence not
only the incentive of learners collaborating in a group but also the promotion of skills of agents in knowledge
sharing, this paper studies the collaborative learning group formation problem in trust networks. We propose
a Steiner tree-based group formation algorithm, which first allocates appropriate agents to groups as initiators
by considering the skill mastery and the strength of trust in the groups to guarantee the opportunities for skill
promotion and then select followers by searching locally in the trust network. Through experiments based on
real-world network datasets, we validate the performance of the proposed algorithm by comparing to several
benchmarks, e.g., the graph partitioning-based group formation algorithm and the simulated annealing-based
group formation algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Collaborative learning (CL), which is a paradigm
organizing the learning process by dividing agents
into multiple collaborative groups (Stahl et al., 2014;
Matazi et al., 2014), is often used in employee train-
ing programs in enterprise management. Under this
paradigm the employees’ necessary working skills
can be improved since employees can work under
the guidance of senior professional practitioners, and
can learn professional working skills from each other
(Zhang et al., 2017); it is critical for the growth of en-
terprise (Zhang et al., 2017). Intuitively, the results of
group formation could largely influence the learning
utility of each agent and further determine the util-
ity of the system. How to obtain an optimal group
formation solution has been considered to be of great
importance in CL area, which can be called the col-
laborative learning group formation (CLGF) problem.
There are many previous works trying to inves-
tigate potential factors that may influence the agent’s
learning utility in CL scenarios (Maqtary et al., 2019).
Most of them focus on the intrinsic attributes of
agents, e.g., the agent’s gender (Curs¸eu et al., 2018),
skill level (Graf and Bekele, 2006), learning style
(Abnar et al., 2012), etc. However, the structural at-
tributes of groups are rarely considered, except for
the communication constraint (Brauer and Schmidt,
2012) and the interaction cost (Zhang et al., 2017).
The structural attributes can be actually employed
to indicate whether a group is efficient for collab-
oration from the perspective of interaction structure
of a group. As an important interactive and cogni-
tive attribute, trust reflects the belief between people
(Granatyr et al., 2015) and plays an important role in
knowledge sharing (Evans et al., 2019); it can influ-
ence not only the incentive of learners being involved
into a collaboration group (Skinner, 2007), i.e., the re-
liability and efficiency of collaboration among agents,
but also the promotion of skills of agents in the CL
groups (Wickramasinghe and Widyaratne, 2012).
To this end, the trust network-aware collaborative
learning group formation (T-CLGF) problem is stud-
ied in this paper, aiming at achieving the group for-
mation solution that maximizes the learning utility of
system considering the effect of trust on the collabo-
ration of agents in groups. A trust network-aware col-
laborative learning model is first proposed which re-
Zhou, Y., Lin, S. and Zhao, Q.
Steiner Tree-based Collaborative Learning Group Formation in Trust Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0011078800003179
In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2022) - Volume 1, pages 243-250
ISBN: 978-989-758-569-2; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
243

flects the skill promotion of individuals (and groups)
involved in CL scenarios considering the group co-
hesion and the skill absorption in terms of the trust
network. The T-CLGF problem is then formally de-
fined according to the coalition structure generation
problem (Rahwan et al., 2015). Considering the
group formation constraint of the trust network, a
Steiner tree-based algorithm is proposed for the T-
CLGF problem, which firstly select appropriate ini-
tiators for each group by considering the skill mas-
tery and the strength of trust in the local trust net-
work for potential promotion of members’ skills, and
then select followers for each group by searching lo-
cally in the trust network based on a greedy strat-
egy. Through experiments on real-world datasets, the
performance of the proposed approach are validated
by comparing to several benchmark approaches, e.g.,
the graph partitioning-based algorithm, the simulated
annealing-based algorithm and the trust-network con-
strained random algorithm.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Section II, we present the trust network-
aware collaborative learning group formation (T-
CLGF) problem. In Section III, we introduce the
Steiner tree-based group formation algorithm for the
T-CLGF. Then in Section IV, we present experimental
results that validate our models. Finally, we conclude
our paper and discuss the future work in Section V.
2 PROBLEM FORMULATION
We formalize the trust network-aware collaborative
learning group formation problem in this section.
Collaborative Learning Trust Network: Let
S = {s
1
,s
2
,...,s
m
} be a set of skills. The collaboravie
learning trust network is defined as T N = (A,E,W),
where A = {a
1
,a
2
,...,a
n
} is a finite set of learners
in the collaborative learning system each element of
which is associated with a vector of skill mastery
P
i
= {p
1
i
, p
2
i
,..., p
m
i
} (∀p
k
i
∈ P
i
, p
k
i
∈ [0,1]), and E is
two-element subsets of A called edges of T N rep-
resenting the collection of trust between learners, in
which e
i j
∈ E is associated with a weight w
i j
(∀w
i j
∈
W,w
i j
∈ (0,1]) representing the direct trust (obtained
from direct experience of interaction (Granatyr et al.,
2015)) between learners a
i
and a
j
.
The learners in the system will be divided into
multiple groups in collaborative learning, i.e., the
learner set A will be split into several subsets. The
edges within a group is a subset of E representing the
direct trust relationships among group members. It’s
worth noting that the trust from a learner to another in
a group can be influenced by other group members in
collaborative learning process considering the effect
of trust propagation and aggregation. The trust re-
lationship, called collaborative trust actually can be
built through the aggregation of the direct trust and
indirect trust (Granatyr et al., 2015) assessed through
paths along other group members.
Collaborative Learning Group: G
x
=
(A
G
x
,T
G
x
), where A
G
x
represents the set of learners in
the group G
x
, T
G
x
represents the two-element subsets
of A
G
x
indicating the collaborative trust between
group members within G
x
.
Due to the effect of knowledge sharing and diffu-
sion (Maleszka, 2019) (or group synergy) in the pro-
cess of collaborative learning, group members usu-
ally have a positive trust tendency, that is, they tend to
trust others through trust propagation. The collabora-
tive trust from one learner to another in G
x
can be as-
sessed by trust propagation and aggregation with pos-
itive bias, which is defined as
trust
G
x
(a
i
,a
j
) =
max
∏
e
uv
w
uv
, ∀{e
uv
} ∈ P(a
i
,a
j
)
i 6= j
0, i = j
(1)
where P(a
i
,a
j
) is the set of all the paths from learner
a
i
to a
j
in group G
x
, e
uv
is the set of edges represent-
ing direct trust along the path.
Completing a collaborative learning phase, the
mastery level of a certain type of skill of each learner
in a group has the opportunity to be improved be-
cause of the interactions among group members that
will facilitate the knowledge and experience sharing.
The improvement of skill mastery of learners can be
mainly determined by the following three aspects: a)
Group cohesion: collaborative trust of a group has a
great influence on the cohesion of the group that re-
flects the communication efficiency and knowledge
sharing opportunities within the group; group mem-
bers are more likely to put in more effort in collab-
orative activities in a group with higher group cohe-
sion. b) Group skill mastery: the improvement space
of a learner is positively related to the gap between
the skill mastery of the group and itself. The group
skill mastery can be indicated by some experts hold-
ing highest skill mastery level in the group, since we
take the CL scenario of hierarchical-structured skills
in this paper (Zhang et al., 2017). c) Learner trust
on the group: the extent of a learner’s trust on the CL
group determines the possibility of accepting specific
knowledge concepts and improving the correspond-
ing skill mastery. The last two factors are personal-
ized for each group member, while the first factor is
homogeneous for the group.
Skill Mastery Improvement of Learners in CL:
the improvement of learner a
i
’s mastery of skill s
k
in
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
244

group G
x
after a CL phase can be represented as
imp(a
i
,G
x
,s
k
) = Coh
G
x
(p
k
G
x
− p
k
i
)trust(a
i
,G
x
) (2)
where Coh
G
x
∈ [0, 1] is the cohesion level of G
x
and
trust(a
i
,G
x
) ∈ [0,1] is the trust of learner a
i
on G
x
.
Expert-led CL (ELCL): there are some members
acting as experts for teaching or training in the group.
For each skill there is a corresponding expert, that is,
the group member with the highest skill mastery level
in the group (a member can be the expert of mul-
tiple types of skill in a group). Meanwhile, expert
members also act as learners, developing other types
of skill through collaborative learning. Let Exp
x
=
{Exp
1
x
,Exp
2
x
,...,Exp
m
x
} be a set of experts of group
G
x
for each type of skill where Exp
x
∈ G
x
, and Exp
k
x
be the expert of G
x
on skill s
k
: a) The group cohesion
distinguished by skill type can be determined by the
average of collaborative trust of learners to the expert
of each type of skill, which is represented as Coh
k
G
x
=
∑
a
i
∈G
x
trust
G
x
(a
i
,Exp
k
x
)/(|A
G
x
| − 1); b) According to
the hierarchical-structured of skills, the group skill
mastery of s
k
is represented by the skill mastery of
the expert Exp
k
x
, p
k
G
x
= max
a
i
∈G
x
{p
k
i
},A
G
x
⊆ A. c)
The learner trust of a
i
on the group G
x
of skill type s
k
is also represented by the collaborative trust of a
i
on
the expert Exp
k
x
, trust(a
i
,G
x
) = trust
G
x
(a
i
,Exp
k
x
).
Skill Mastery Improvement of Learners in
ELCL: the improvement of learner a
i
’s mastery of
skill s
k
in group G
x
after a expert-led collaborative
learning can be represented as
imp(a
i
,G
x
,s
k
) =
∑
a
i
∈G
x
trust
G
x
(a
i
,Exp
k
x
)
|A
G
x
| − 1
· (p
k
G
x
− p
k
i
) ·trust
G
x
(a
i
,Exp
k
x
)
(3)
Learning Utility of CL Groups: the learning
utility of a CL group G
x
is the sum of the learning
utility of group members A
G
x
, which is represented
as:
U
G
x
=
∑
a
i
∈A
G
x
∑
s
k
∈S
imp(a
i
,G
x
,s
k
) (4)
Trust Network-aware Collaborative Learning
Group Formation (T-CLGF) Problem: given a col-
laborative learning trust network T N with |A| = d ·
q for some integer q, finding a collection of non-
overlapping groups G
∗
= {G
1
,G
2
,...,G
d
} over T N
with the optimal learning utility:
G
∗
= arg max
G
{
∑
G
x
∈G
U
G
x
} (5)
where for any G
i
,G
j
∈ G, with i 6= j, A
G
i
∩ A
G
j
=
∅ (i.e., no learner is in more than one group),
∪
G
i
∈G
A
G
i
= A (i.e., a learner is at least in one group),
and ∀G
i
∈ G,|A
G
i
| = |A|/d where |A| and |A
G
i
| indi-
cate the number of learners in T N and group G
i
re-
spectively.
3 COLLABORATIVE LEARNING
GROUP FORMATION
ALGORITHM
We present a Steiner tree-based group formation algo-
rithm for T-CLGF in this section, which follows the
initiator-follower group formation architecture, i.e.,
firstly select appropriate agents from T N to form the
initiator set for each CL group, and then select follow-
ers (i.e., the other group members) locally for each
group in a greedy manner.
3.1 Steiner Tree-based Initiator
Assignment
In order to increase the group skill mastery of the
skills in S and guarantee the collaborative trust levels
as well as the connectivity of trust among the group
members, the initiator assignment algorithm first con-
structs an enhanced trust network H covering all the
skills in the skill set S according to the approach pre-
sented in (Lappas et al., 2009), and then builds the
skill Steiner tree for each group considering the skill
mastery of agents and the trust among them (each ver-
tices of the skill Steiner tree is an agent in the set of
initiators of a group). The Steiner tree-based initiator
assignment is presented in Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: IntiatorAssignment algorithm for
the T-CLGF problem.
Input: Trust network TN(A,E,W); the
individuals’ skill vectors
P = {P
1
,...,P
n
}; the skills’ vector
S = {s
1
,...,s
m
}; the group number d;
the specified group size q.
Output: A collection of non-overlapping
groups G = {G
1
,...,G
d
}
1 H ← EnhanceGraph(T N,P,S)
2 for i ← 1 to d do
3 X
H
← SteinerTree(H,X
0
,q)
4 G
i
← X
H
\X
0
To build the enhanced trust network H, first, for
each skill in S a skill node needs to be added to
the trust network T N; Then the leaders of each skill
(learners with the highest skill mastery) should be
connected to the skill node. Intuitively, for each skill,
Steiner Tree-based Collaborative Learning Group Formation in Trust Networks
245

the learner whose skill mastery ranks in the top d can
be one of the leaders; in this case, the set of lead-
ers in T N can be represented as I
T N
. However, when
constructing the skill Steiner tree, learners along the
paths between leaders need to be added to ensure the
connectivity of trust network among group members.
Hence, under the constraint of the limited group size,
the selection conditions of leader need to be relaxed.
Leader Selection Redundancy:
r =
|
S
|
− R
T N
|
S
|
− 1
(6)
where S is the set of skills that can be mastered by
learners, R
T N
is the average number of skills mastered
by the original leaders in I
T N
. R
T N
is represented as
R
T N
=
d
|
S
|
|
I
T N
|
(7)
where d is the number of groups to be formed. Note
that R
T N
∈ [1, |S|], and the redundancy r ∈ [0,1]; the
closer R
T N
is to 1, the greater the cost of building
Steiner tree, and the less Steiner tree that can cover
all skill nodes in H.
We don’t present the detailed algorithm for the en-
hanced trust network construction (EnhanceGraph)
in initiator assignment due to space limitation. The
main idea is based on the algorithm introduced in
(Lappas et al., 2009). It is important to note that
by considering the leader selection redundancy r, the
number of leaders should be (1 + r) ∗ d.
Distance Between a Learner and a CL Group
in H: the distance between a learner (or a node) a
i
to
a CL group represented as X
0
here is defined as
Dist(a
i
,X
0
) = min
a
j
∈X
0
Dist(a
i
,a
j
)
(8)
where Dist(a
i
,a
j
) is the distance between two learn-
ers a
i
and a
j
. Dist(a
i
,a
j
) can be represented as
Dist(a
i
,a
j
) = min
∑
{
e
uv
}
[1 −
1
2
(w
uv
+ w
vu
)],
∀
{
e
uv
}
∈ P
T N\
S
G
x
∈G
Gx
(a
i
,a
j
)
(9)
where e
uv
is the set of edges representing direct trust
along a path between a
u
to a
v
, P
T N\
S
G
x
∈G
Gx
(a
i
,a
j
) is
the set of all the feasible paths from learner a
i
to a
j
.
Here a feasible path from learner a
i
to a
j
means the
path does not contain any node in G
x
except a
i
and a
j
.
On the basis of the greedy heuristic for Steiner tree
(Takahashi et al., 1980), we propose a Steiner tree al-
gorithm for the initiator assignment of T-CLGF prob-
lem, which is presented in Algorithm 2. The algo-
rithm adds the skill nodes and the nodes along the
paths between the skill nodes to the set X
0
in turn.
Specifically, it chooses the skill node v
∗
with the min-
imum distance from the group Dist(v
∗
,X
0
) (line 3)
Algorithm 2: SteinerTree algorithm for the T-
CLGF problem.
Input: Enhanced trust network H; the skill
nodes X
0
; the specified group size q.
Output: Group X
0
⊆ A
1 X
0
← v,where v is a random node from X
0
2 while X
0
\X
0
6= ∅ do
3 v
∗
← arg min
u∈X0\X
0
Dist(u,X
0
)
4 if Path(v
∗
,X
0
) 6= ∅ and
|{X
0
∪ Path(v
∗
,X
0
)}\X
0
| ≤ q then
5 X
0
← X
0
∪ Path(v
∗
,X
0
)
6 else
7 break
8 if |X
0
| = 1 then
9 X
0
← {v
0
}, where v
0
is an available leader
connected with v
and the nodes along the path Path(v
∗
,X
0
) achieving
the minimum distance Dist(v
∗
,X
0
) (line 4-5) in each
round. If v∗ does not exist or the number of members
in X’ exceeds q after joining the new nodes, the algo-
rithm stops building the Steiner tree (line 6-7). More-
over, if there is only one skill node and no other nodes
in the Steiner tree, an available leader of any skill is
returned (line 8-9).
3.2 Greedy Follower Selection
In order to guarantee the learning utility of each
group while ensuring the connectivity of trust among
group members, the follower selection algorithm se-
lects members for each group in turn by searching the
local environments of the initiators in T N in a greedy
manner until all the agents in TN attend in the groups,
which is presented in Algorithm 3.
Neighbors of the CL Group: the set of neighbors
of a CL group G
x
is represented as
N(G
x
) =
a
i
|a
i
∈ A \ G
x
,∃a
j
∈ A
G
x
,e
i j
∈ E
(10)
where a
i
is a neighbor of G
x
and a
j
is a learner in G
x
.
Because of the different size of Steiner trees
formed in the initiator assignment step, the groups
are first aligned through greedy selection (line 1-10).
The algorithm sorts the groups in ascending order ac-
cording to the number of neighbors, and the group
with fewest neighbors choose follower first. After
this operation, all the groups G
x
∈ G become the same
size. Then, each group takes turns to select members
through greedy selection (line 11-23). Each group can
only greedily choose one follower from neighbors in
each round; and the order of each round of selection is
determined by the number of neighbors of each group,
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
246

Algorithm 3: GreedySelection algorithm for the
T-CLGF problem.
Input: Trust network TN(A,E,W); the
individuals’ skill vectors
P = {P
1
,...,P
n
}; the skills’ vector
S = {s
1
,...,s
m
}; the group number d;
the specified group size q.
Output: A collection of non-overlapping
groups G = {G
1
,...,G
d
}
1 maxSize ← max
G
i
∈G
|A
G
i
|
2 sort G by the number of group’s neighbors in
ascending order
3 for i ← 1 to d do
4 di f ← maxSize − |A
G
i
|
5 for j ← 1 to di f do
6 V ← {u|u ∈ N(G
i
),∀G
x
∈ G, G
x
∩ u =
∅}
7 if V = ∅ then
8 break
9 v
∗
← arg max
u∈V
U(G
i
∪ u)
10 G
i
← G
i
∪ v
∗
11 while true do
12 count ← 0
13 sort G by the number of group’s neighbors
in ascending order
14 for i ← 1 to d do
15 if |A
G
i
| ≥ q then
16 continue
17 V ← {u|u ∈ N(G
i
),∀G
x
∈ G, G
x
∩ u =
∅}
18 if V 6= ∅ then
19 v
∗
← arg max
u∈V
U(G
i
∪ u)
20 G
i
← G
i
∪ v
∗
21 count ← count +1
22 if count = 0 then
23 break
24 for i ← 1 to d do
25 while |A
G
i
| < q do
26 V ← {u|u ∈ A,∀G
x
∈ G, G
x
∩ u = ∅}
27 v
∗
← arg max
u∈V
U(G
i
∪ u)
28 G
i
← G
i
∪ v
∗
the group with fewest neighbors choose follower first.
Finally, due to the constraints of the trust network,
some groups may not have available neighbors when
the group size is smaller than the specified value q.
For these groups, the algorithm selects the learners
who bring the highest learning utilities for each group
from the remaining available learners in T N (line 24-
28).
4 EXPERIMENTS AND
ANALYSES
4.1 Experimental Settings
There are two real-world datasets used in the exper-
iments: 1) the research institution membership net-
work (Yin et al., 2017)(Leskovec et al., 2007) with
1005 nodes and 68430 edges (marked as N1). The
edges in the original dataset consist of the mail trans-
fer relationships between members and the depart-
mental colleague relations. We assume that there
are interactions between nodes that have any of these
relationships, i.e., the members have connections if
and only if there is a mail transfer relationship be-
tween them or they belong to the same department.
Since members of each department are interconnected
with each other and the departments are connected
by e-mail relations, this network has obvious com-
munity structure. 2) the student friendship network
(Sapiezynski et al., 2019) with 851 nodes and 12834
edges. The edges are friendship relations among
students collected from Facebook (marked as N2).
We also conduct experiments on the random network
(Bollob
´
as and B
´
ela, 2001), and the small world net-
work (Watts and Strogatz, 1998), investigating the
effect of network density on the performance of the
presented algorithm. In the experiments, the edge
weights are generated randomly range from 0 to 1,
and the number of skills is set to 5. The initial skill
mastery of the learner is generated by the beta (4, 4)
distribution, which is a continuous probability distri-
bution defined in the interval (0, 1), and the expecta-
tion of beta (4, 4) is 0.5.
We evaluate the performance of the presented
Steiner tree-based (ST) group formation algorithm
compared with the following benchmark approaches.
• Graph partitioning-based (GP) algorithm
(Karypis, 1997; METIS, 2021; Karypis and
Kumar, 1998b): the GP algorithm is able to
split a graph into several connected components.
Let agents in T N be the vertices of a graph,
and the direct trust relationships in T N be the
edges, the GP algorithm can be used to solve the
collaborative learning group formation problem.
This algorithm can ensure the connectivity of
each collaborative learning group, considering
that the connectivity of a group has a great impact
Steiner Tree-based Collaborative Learning Group Formation in Trust Networks
247
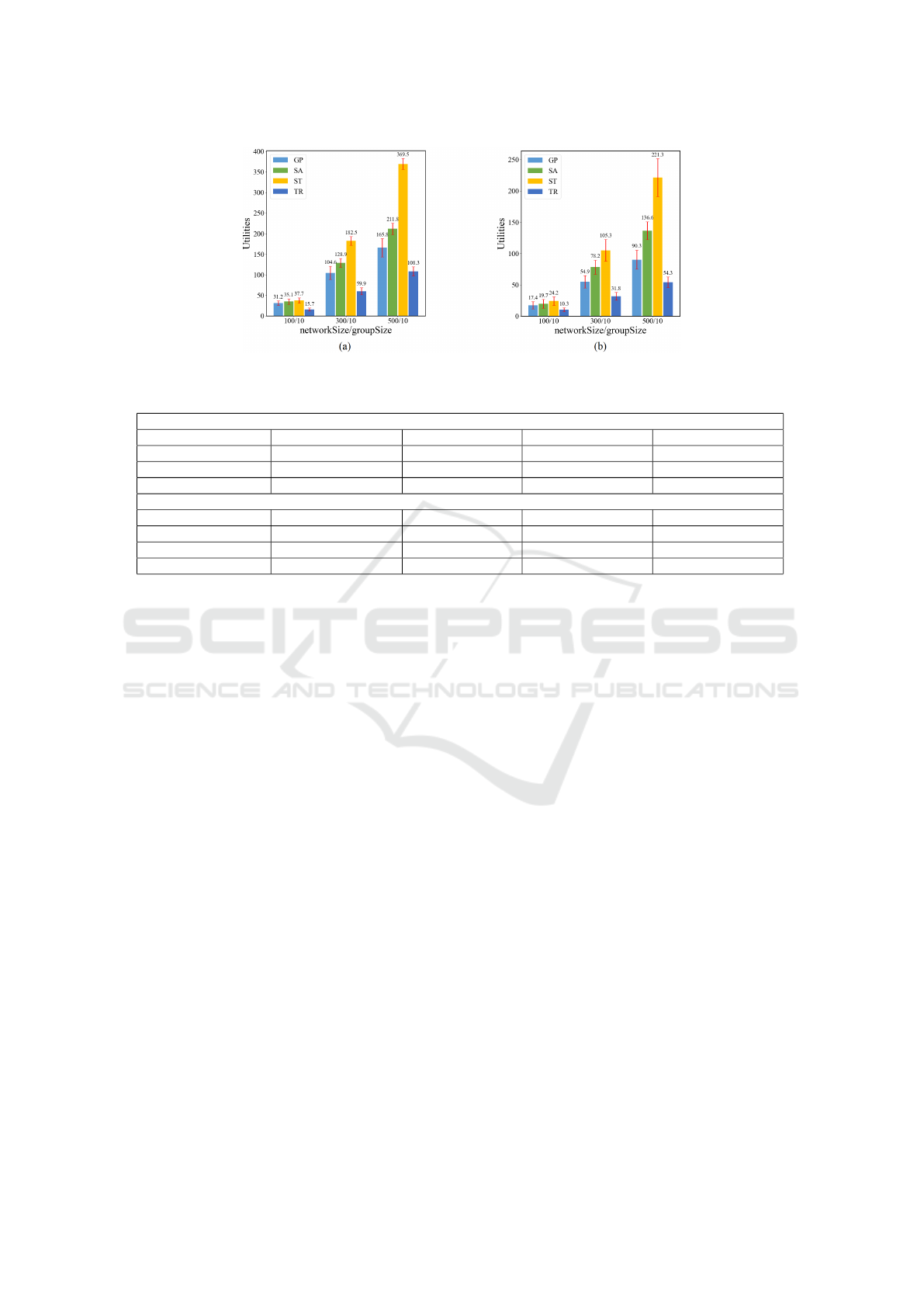
Figure 1: Learning utilities of CL groups in the network N1(a) and N2(b).
Table 1: Running time of algorithms in the network N1 and N2 (s).
Network N1
Network/Group Size GP SA ST TR
100/10 0.054±6.960e-4 34.679±13.925 0.738±5.0069e-2 0.0578±2.7423e-3
300/10 0.1759±1.700e-3 48.6867±16.6237 13.319±0.5750 0.24055±6.3046e-3
500/10 0.30996±1.6323e-3 53.9094±12.5364 57.401±2.2445 0.50464±1.0701e-2
Network N2
Network/Group Size GP SA ST TR
100/10 0.05322±6.09593-4 81.2871±36.2385 0.45856±7.1254e-2 0.05229±2.2329e-3
300/10 0.16927±5.6813e-3 150.389±39.3495 6.77763±0.9683 0.1988±6.3734e-3
500/10 0.29062±1.4750e-3 187.978±50.2311 28.4208±3.6787 0.38074±5.8080e-3
on the learning utility of the group. The tool used
in this article is METIS (Karypis, 1997; METIS,
2021). METIS realizes both the multi-level
k-way division (Karypis and Kumar, 1998b) and
the multi-level recursive division (Karypis and
Kumar, 1998a). Since METIS with multi-level
k-way division can guarantee the connectivity of
subgraphs, we adopt this tool for the T-CLGF
problem.
• Simulated Annealing-based (SA) algorithm
(Kein
¨
anen, 2009): the SA group formation
algorithm is a representative heuristic algorithm
which can be applied to large-scale group forma-
tion problems in multi-agent systems. The SA
algorithm starts by randomly selects a feasible
group structure G, and then generates a neighbour
group structure G
0
of G at each iteration. If the
utility of the newly generated group structure G
0
is better than G, G
0
will be adopted; otherwise,
there is still a certain probability that G
0
will be
adopted, which is controlled by a temperature
parameter that will decrease after each iteration.
Through a series of experiments of SA, we
use 1 as the initial temperature and 0.99 as the
annealing rate in the following experiments
• Trust-network constrained random (TR) algo-
rithm: the random group formation algorithm can
naturally achieve the heterogeneity of groups to
some extent, i.e., it can guarantee the group learn-
ing utilities to a certain extent, with a low com-
putation complexity. The random group forma-
tion algorithm is extended to match the scenario
of the collaborative learning trust network consid-
ered in this paper. Firstly, it randomly selects the
initial agents for all the groups; then it continues
to randomly select agents to join the groups from
the neighbor agents who have direct trust relation-
ships with the group members.
4.2 Results and Analyses
The experiments are conducted on the research
institution membership network N1 (Yin et al.,
2017)(Leskovec et al., 2007) and the student friend-
ship network N2 (Sapiezynski et al., 2019). For each
simulation with different network sizes (100, 300 and
500), the agents and the network among them are
generated from the original network randomly, and
the group size is set to 10, i.e., each group has 10
members. For the research institution membership
network N1, the mastery of each skill an agent mas-
tered is generated by the beta (4, 4) distribution and
is independent of each other. For the student friend-
ship network N2, it is assumed that there is a cor-
relation between the mastery of skills for a student
in such a learning environment in a university. For
example, for a student with a high cognitive level,
he/she may have a high mastery of the skills to be
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
248

Figure 2: Learning utilities of CL groups in the ER network and the small-world network.
mastered, and vice versa. Hence, for N2, this pa-
per generates a mastery baseline mb
i
for each stu-
dent through the distribution of beta(4, 4), and the
mastery of each skill is randomly generated from
[max{0,mb
i
− 0.1},min{mb
i
+ 0.1,1}].
Fig.1 and Table 2 show the results of learning util-
ities and average running time of the algorithms in
networks N1 and N2, respectively. From the results,
it can be observed that the learning utility of the ST
algorithm is significantly better than the benchmarks.
The main reason is that the ST algorithm can divide
the agent set in the network hierarchically and allo-
cate the agents into groups more properly, and it can
also guarantee the network connectivity among mem-
bers in the groups. In addition, it can be observed
that the performance advantage of the ST algorithm
increases with the increase of network scale (the num-
ber of agents increases from 100 to 300 and then to
500). The learning utility of the SA algorithm is infe-
rior to the ST algorithm but better than the GP and TR
algorithms. Note that, the ST algorithm is much faster
than the SA algorithm in most cases, but in some spe-
cial situations such as the cases where the network
size is 500, the SA algorithm may take less running
time, the potential reason is that the neighbor partition
can be found quickly in each iteration and the number
of iterations is limited in large-scale dense networks
like N1 and N2. The learning utilities obtained by the
GP and TR algorithms are significantly worse than
that of the ST and SA algorithms but with lower run-
ning time; the main reason is that the GP algorithm ig-
nores the member attributes in group formation, while
the TR algorithm only performs local search of the
trust networks. Moreover, it can be found that the ST
algorithm performs well in both the situation where
the mastery of each skill an agent mastered is inde-
pendent of each other (N1) and the situation where
there is a correlation between the mastery of skills for
an agent (N2). Therefore, it can be concluded that the
ST algorithm has significant advantages in the collab-
orative learning utility compared with the benchmarks
in real world networks N1 and N2, and the advantage
is increasing with the increase of the network scale.
Moreover, in order to investigate the influence of
network density on the algorithm performance, ex-
periments on the ER random network (Bollob
´
as and
B
´
ela, 2001) and the WS small-world network (Watts
and Strogatz, 1998) are conducted and the results are
shown in Fig. 2. The trust networks generated consist
of 300 agents, and the group size is set to 10; the mas-
tery of each skill an agent mastered is generated by
the beta (4, 4) distribution and is independent of each
other. From the results, the ST algorithm can obtain
the highest learning utility of the system for different
settings of network average degree; the performance
of the SA algorithm is superior to the GP and TR
algorithms in most cases; and the TR algorithm get
the lowest cooperative learning utility of the system.
When the average degree of network is low, the per-
formance gap between these algorithms is small; but
as the network size increases, the performance gap
between the algorithms increases significantly.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper first formalizes the collaborative learning
group formation problem in trust networks(T-CLGF),
considering the influence of trust on not only the in-
centive of learners collaborating in a group but also
the promotion of skills of agents in knowledge shar-
ing; and this paper then proposes a Steiner tree-based
group formation algorithm to solve the T-CLGF prob-
lem, which first allocates appropriate agents to groups
as initiators by considering the skill mastery and the
strength of trust in the groups to guarantee the oppor-
tunities for skill promotion and then select followers
by searching locally in the trust network.
We validate the performance of the proposed algo-
rithm by comparing with the graph partitioning-based
algorithm, the simulated annealing-based algorithm
and the trust-network constrained random algorithm
Steiner Tree-based Collaborative Learning Group Formation in Trust Networks
249

through experiments. From the results, it can be con-
cluded that our algorithm has significant advantages
in the learning utility of the system compared with the
benchmark algorithms and has an practical running
time. Moreover, considering some other collaborative
learning scenarios, e.g., the non-expert led scenarios,
we plan to extend the group formation problem and
our algorithm to these scenarios in our future work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Sci-
ence Foundation of China (No.61807008, 61806053,
61932007, 62076060, and 61703097) and the Nat-
ural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of
China (BK20180369, BK20180356, BK20201394,
and BK20171363).
REFERENCES
Abnar, S., Orooji, F., and Taghiyareh, F. (2012). An evolu-
tionary algorithm for forming mixed groups of learn-
ers in web based collaborative learning environments.
In 2012 IEEE international conference on technology
enhanced education (ICTEE), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Bollob
´
as, B. and B
´
ela, B. (2001). Random graphs. Num-
ber 73. Cambridge university press.
Brauer, S. and Schmidt, T. C. (2012). Group formation
in elearning-enabled online social networks. In 2012
15th international conference on interactive collabo-
rative learning (ICL), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Curs¸eu, P. L., Chappin, M. M., and Jansen, R. J. (2018).
Gender diversity and motivation in collaborative
learning groups: the mediating role of group dis-
cussion quality. Social Psychology of Education,
21(2):289–302.
Evans, M. M., Frissen, I., and Choo, C. W. (2019). The
strength of trust over ties: Investigating the relation-
ships between trustworthiness and tie-strength in ef-
fective knowledge sharing. Electronic Journal of
Knowledge Management, 17(1):pp19–33.
Graf, S. and Bekele, R. (2006). Forming heterogeneous
groups for intelligent collaborative learning systems
with ant colony optimization. In International confer-
ence on intelligent tutoring systems, pages 217–226.
Springer.
Granatyr, J., Botelho, V., Lessing, O. R., Scalabrin, E. E.,
Barth
`
es, J.-P., and Enembreck, F. (2015). Trust and
reputation models for multiagent systems. ACM Com-
puting Surveys (CSUR), 48(2):1–42.
Karypis, G. (1997). Metis: Unstructured graph partitioning
and sparse matrix ordering system. Technical report.
Karypis, G. and Kumar, V. (1998a). A fast and high qual-
ity multilevel scheme for partitioning irregular graphs.
SIAM Journal on scientific Computing, 20(1):359–
392.
Karypis, G. and Kumar, V. (1998b). Multilevel k-way par-
titioning scheme for irregular graphs. Journal of Par-
allel and Distributed computing, 48(1):96–129.
Kein
¨
anen, H. (2009). Simulated annealing for multi-agent
coalition formation. In KES International Symposium
on Agent and Multi-Agent Systems: Technologies and
Applications, pages 30–39. Springer.
Lappas, T., Liu, K., and Terzi, E. (2009). Finding a team of
experts in social networks. In Proceedings of the 15th
ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowl-
edge discovery and data mining, pages 467–476.
Leskovec, J., Kleinberg, J., and Faloutsos, C. (2007).
Graph evolution: Densification and shrinking diame-
ters. ACM transactions on Knowledge Discovery from
Data (TKDD), 1(1):1–41.
Maleszka, M. (2019). Application of collective knowledge
diffusion in a social network environment. Enterprise
Information Systems, 13(7-8):1120–1142.
Maqtary, N., Mohsen, A., and Bechkoum, K. (2019). Group
formation techniques in computer-supported collabo-
rative learning: A systematic literature review. Tech-
nology, Knowledge and Learning, 24(2):169–190.
Matazi, I., Messoussi, R., and Bennane, A. (2014). The de-
sign of an intelligent multi-agent system for support-
ing collaborative learning. In 2014 9th International
conference on intelligent systems: Theories and appli-
cations (SITA-14), pages 1–8. IEEE.
METIS (2021). http://glaros.dtc.umn.edu/gkhome/views/
metis.
Rahwan, T., Michalak, T. P., Wooldridge, M., and Jennings,
N. R. (2015). Coalition structure generation: A sur-
vey. Artificial Intelligence, 229:139–174.
Sapiezynski, P., Stopczynski, A., Lassen, D. D., and
Lehmann, S. (2019). Interaction data from the copen-
hagen networks study. Scientific Data, 6(1):1–10.
Skinner, E. (2007). Building knowledge and community
through online discussion. Journal of Geography in
Higher Education, 31(3):381–391.
Stahl, G., Koschmann, T., and Suthers, D. (2014).
Computer-supported colaborative learning. In The
cambridge handbook of the learning sciences, pages
479–500.
Takahashi, H. et al. (1980). An approximate solution for the
steiner problem in graphs.
Watts, D. J. and Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynam-
ics of ‘small-world’networks. nature, 393(6684):440–
442.
Wickramasinghe, V. and Widyaratne, R. (2012). Effects of
interpersonal trust, team leader support, rewards, and
knowledge sharing mechanisms on knowledge shar-
ing in project teams. VINE, 42(2):214–236.
Yin, H., Benson, A. R., Leskovec, J., and Gleich, D. F.
(2017). Local higher-order graph clustering. In
Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD international
conference on knowledge discovery and data mining,
pages 555–564.
Zhang, J., Yu, P. S., and Lv, Y. (2017). Enterprise employee
training via project team formation. In Proceedings
of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Web
Search and Data Mining, pages 3–12.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
250
