
A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm using Progressive Alignment and
Consistency based Approach for Multiple Sequence Alignments
Vitoria Zanon Gomes
1 a
, Matheus Carreira Andrade
1 b
, Anderson Rici Amorim
2,1 c
and Geraldo Francisco Doneg
´
a Zafalon
1,3 d
1
Department of Computer Science and Statistics, Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP), Rua Crist
´
ov
˜
ao Colombo, 2265,
Jardim Nazareth, S
˜
ao Jos
´
e do Rio Preto - SP, 15054-000, Brazil
2
Department of Computer and Digital Systems Engineering, Universidade de S
˜
ao Paulo (USP) - Escola Polit
´
ecnica,
Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, Travessa 3, 158, Butant
˜
a, S
˜
ao Paulo - SP, 05508-010, Brazil
3
Department ICET, Universidade Paulista, Avenida Presidente Juscelino Kubitschek de Oliveira, s/n, Jardim Tarraf II,
S
˜
ao Jos
´
e do Rio Preto-SP, 15091-450, Brazil
Keywords:
Bioinformatics, Multiple Sequence Alignment, Genetic Algorithm, Hybrid Multiple Sequence Alignment.
Abstract:
The multiple sequence alignment is one of the most important tasks in bioinformatics, since it allows to analyze
multiple sequences at the same time. There are many approaches for this problem such as heuristics and meta-
heuristics, that generally lead to great results in a plausible time, being among the most used approaches.
The genetic algorithm is one of the most used methods because of its results quality, but it had a problematic
disadvantage: it can be easily trapped in a local optima result, not being able to reach better alignments. In
this work we propose a hybrid genetic algorithm with progressive and consistency-based methods as a way to
smooth the local optima problem and improve the quality of the alignments. The obtained results show that
our method was able to improve the quality of AG results 2 a 27 times, smoothing the local maximum problem
and providing results with more biological significance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to the increasing importance of Next Generation
Sequencing (NGS) techniques, the amount of biolog-
ical data is in constant growth nowadays (Amorim
et al., 2018; Bawono et al., 2017), leading to a cres-
cent need to faster and more accurate biological anal-
ysis, so the computational support became essential to
help on those biological tasks (Baxevanis et al., 2020).
At the begining, pairwise alignment algorithms
were created, aligning two sequences at once.
Needleman and Wunsch (1970) created an algorithm,
known as Needleman-Wunsch algorithm, able to gen-
erate the optimal alignment for the given sequences
by dynamic programming (DP). However, if the input
has three or more sequences the execution time grows
prohibitively due the use of DP and the nature of the
problem. The so-called multiple sequence alignment
(MSA) is an NP-Complete (Non-Polynomial) prob-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4176-566X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1670-266X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7862-7530
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2384-011X
lem (Wang and Jiang, 1994), which means that, until
now, there is no deterministic method able to find the
optimal solution for it in a polynomial time, that is, a
reasonable execution time (the P versus NP problem)
(Cook, 2006).
So, the development of MSA algorithms came as a
way to analyze many sequences simultaneously (Ba-
wono et al., 2017) through a stochastic approach, be-
ing able to produce results with relevant biological
significance in a timely manner (Nute et al., 2019). A
MSA algorithm rearranges DNA or protein sequences
through gap insertions, following a predefined crite-
ria (Bawono et al., 2017; Edgar and Batzoglou, 2006)
as a way to maximize the similar residues that are
matched (Mount, 2001).
There are many approaches to perform MSA, such
as progressive alignment (Lassmann, 2020; Sievers
and Higgins, 2018; Thompson et al., 1994), Fast-
Fourier Transform (Katoh et al., 2002, 2019), simu-
lated annealing (Correa et al., 2012; Kim et al., 1994),
Tabu Search (Riaz et al., 2004), artificial bee colony
(Rubio-Largo et al., 2016), genetic algorithm (GA)
(Gondro and Kinghorn, 2007; Kaya et al., 2016),
Gomes, V., Andrade, M., Amorim, A. and Zafalon, G.
A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm using Progressive Alignment and Consistency based Approach for Multiple Sequence Alignments.
DOI: 10.5220/0011082900003179
In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2022) - Volume 2, pages 167-174
ISBN: 978-989-758-569-2; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
167

among others.
Progressive alignment is the base of many well-
known tools, such as the Clustal family (Sievers and
Higgins, 2018; Thompson et al., 1994), Kalign (Lass-
mann, 2020) and MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004), and it’s
very fast when compared with other methods (Rubio-
Largo et al., 2016). However, a great accuracy is not
guaranteed since errors occurred in the first steps of
the algorithm can not be repaired, causing error prop-
agation (Bawono et al., 2017; Gondro and Kinghorn,
2007; Rubio-Largo et al., 2016).
GA, on the other hand, does not have this disad-
vantage, since it is an iterative algorithm (Gondro and
Kinghorn, 2007), which means that errors occured in
a certain iteration can be repaired in the next one (Ba-
wono et al., 2017).
The Genetic Algorithm is a sthocastic method in-
spired by the evolution theory (Amorim et al., 2021;
Chowdhury and Garai, 2017). It is also a population-
based method, where the individuals represent a can-
didate solution for the problem (Kaya et al., 2016). In
each generation, these individuals are exposed to mu-
tation and recombination operators (Lee et al., 2008)
and evaluated by a fitness function, so the best indi-
viduals will produce a offspring and the worst ones
are discarded (Kaya et al., 2016).
The GA is frequently used for solving MSA prob-
lems (Chowdhury and Garai, 2017) since the qual-
ity and biological significance from its results tends
to be better when compared to progressive methods
(Gondro and Kinghorn, 2007). SAGA (Notredame
and Higgins, 1996) and MSA-GA (Gondro and
Kinghorn, 2007) are well known tools that apply GA
for MSA. The first one has 22 complex operators for
mutation and recombination, but even getting good
results, further studies shown that the complexity of
the operators does not influence on the quality of the
final result (Thomsen and Boomsma, 2004). The sec-
ond one, on the other hand, is a simpler version of
GA, being able to produce great results when com-
pared to other well known tools, such as Clustal W
(Gondro and Kinghorn, 2007).
However, the GA also has its disadvantages. Due
to its greedy nature, the algorithm can be trapped in
a local optima result, which means that the solution
is nott the global optima and could be improved (Lee
et al., 2008).
Thus, this work aims to develop a new hy-
brid approach using the progressive alignment and a
consistenc-based heuristic, so we can improve even
more the GA-based tools results, avoiding the local
optima problem without increasing prohibitively the
computational cost of the method.
This work is organized as follows: in section 2, the
Multiple Sequence Alignment is explained, in section
3 the related works are shown, in section 4 we de-
scribe the materials used and show our methodology,
in section 5 we show the tests and discuss about the
obtained results and in section 6, we show our con-
clusions.
2 MULTIPLE SEQUENCE
ALIGNMENT
As mentioned before, a Multiple Sequence Alignment
is the rearrange of sequences following a pre-defined
criteria. Given a set of sequences S =
{
s1, s2, ..., sn
}
defined over an alphabet
∑
, where
∑
= {A, T, C, G}
for DNA sequences and
∑
= {A, C, D, E, F, G, H,
I, K, L, M, N, P, Q, R, S, T, V, W, Y} for protein se-
quences, a MSA is a set S’ =
{
s1
0
, s2
0
, ..., sn
0
}
defined
over an alphabet
∑
’ where
∑
’ =
∑
∪ (−), which is the
gap symbol (Rubio-Largo et al., 2016). A gap repre-
sents insertions and/or deletions on the sequences.
In a practical way, a MSA is a matrix, where the
rows represent the sequences and the columns repre-
sent the aligned bases. This matrix is generated by
the insertion of gaps along the sequences following a
given criteria, not allowing columns with only gaps,
equaling the sequences length and optimizing quality
metrics.
3 RELATED WORKS
The local optima problem in GA is well-known in the
literature, and many published works try to resolve
it. Lee et al. (2008) describes the GA-ACO: a hybrid
GA with Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) algorithm,
which helps GA to escape from local optima, improv-
ing the quality of the results. But, since ACO has
a greater computational cost than other approaches,
like the progressive ones, the total computational cost
of GA-ACO becomes exorbitant (Rubio-Largo et al.,
2016).
Nonetheless, recent works show that hybrid differ-
ent heuristics and metaheuristics is important. Chat-
terjee et al. (2019) use the Chemical Reaction Opti-
mization (CRO) algorithm to help GA to achieve bet-
ter results. The CRO is executed at the end of every
GA generation, looking for alignments better than the
current population. Even with good results achieved,
producing better results in 47% when compared to
other well-known tools, the authors warned that the
method has some difficulties when dealing with less
similar sequences.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
168

Figure 1: An example of multiple sequence alignment.
Zafalon et al. (2021) also describe a hybrid ap-
proach to solve the GA local optima problem us-
ing Kalign (Lassmann, 2020), a progressive approach.
The method was able to get better results when com-
pared to GA by itself, but the authors describe that
the method still having some difficulties when deal-
ing with less similar sequences, suggesting that other
heuristics could help to improve even more the align-
ments.
Rubio-Largo et al. (2016) used a hybrid-
progressive approach to solve the local optima prob-
lem too, but this time in the Artificial Bee Colony al-
gorithm (ABC). Due to its evolutionary nature, the
ABC have the same disadvantage as GA, so the
Kalign tool (Lassmann, 2020) is applied to execute
a local search in stagnated bees (individuals) as a way
to improve the quality of the results at a viable run
time. The authors show that the method got better
results when compared to the existing GA tools for
MSA, and its results are statistically relevant in rela-
tion to other well-known tools.
Once the less similar sequences generally implies
noisy alignments, the hybridization with consistency-
based methods may overcome this drawback. As
we can see, Amorim et al. (2015) use the COF-
FEE, a consistency-based function (Notredame et al.,
1998), instead of the Weighted Sum-of-Pairs (WSP)
in MSA-GA tool (Gondro and Kinghorn, 2007). The
results obtained with the COFFEE objective function
were better than the results with WSP, and improve-
ments on this method can be seen in Amorim et al.
(2018).
Do et al. (2005) proposed a new approach called
ProbCons to the MSA problem, using consistency as
its objective function. It works creating a guide tree
using probability matrices and the consistency func-
tion, so the progressive alignment can be executed,
resulting in more accurate and statistically relevant
alignments in relation to other tool.
Thus, a hybrid approach is a effective way to deal
the local optima problem, and when combined with a
consistency based method it may result in alignments
with better quality and smooth any difficulties that
might occur due to the use of progressive alignment.
4 THE PROPOSED METHOD
4.1 MSA-GA
The MSA-GA tool was chosen as the GA in this work
due its simplicity when compared to other GA tools
and for the quality of its results that are better than the
most used MSA methods such as Clustal W (Gondro
and Kinghorn, 2007).
The execution starts initializing the population. It
can be done by pre-alignment files or based in pair-
wise alignment with the Needleman-Wunsch algo-
rithm (Needleman and Wunsch, 1970). Then, each
individual is evaluated with the WSP, the worst ones
will be discarded and the best ones will be exposed to
genetic operators: crossover and mutation, as a way
to diversify the population and to possibly produce
better individuals.
The crossover operators work using two individu-
als to generate an offspring. The MSA-GA uses two
of these operators: horizontal recombination and ver-
tical recombination. Both operators define cut points
on both parents, separating them in two parts, and
combine their parts into new alignments, but the first
one defines a horizontal cut point and the second one
a vertical cut pont.
The mutation operators modify a individual align-
ment, creating a new individual. MSA-GA uses three
mutation operators to optimize gap positions: gap
opening, that selects randomly a position and inserts
a block of gaps into the sequence; gap extension, that
selects a block of gaps and adds a gap at its end; and
gap reduction, that deletes a gap from a block of gaps
selected randomly.
After that, we have a new population and the in-
dividuals are evaluated by the WSP again. Each it-
eration follows these steps until a pre-defined criteria
is reached, such as a limit of iterations or a certain
individual score. 2 shows the MSA-GA execution.
A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm using Progressive Alignment and Consistency based Approach for Multiple Sequence Alignments
169

Knowing that, our method will be executed after
the tournament end, modifying the new population
before the next tournament begins.
4.2 First Refinement Step: Local
Realignment with Kalign
As a way to smooth the local optima, the local realign-
ment with a progressive method is executed when the
GA reaches n iterations without any improvement in
the best individual, which is the individual with best
score (evaluated by WSP), being n a user-defined pa-
rameter. Initially, a portion of the best individual
is randomly selected to be realigned by Kalign. Its
length is also randomly defined over an interval be-
tween 5%-25% of the individual size, since Rubio-
Largo et al. (2016) showed that this interval is effi-
cient for a local refinement. Then, the gaps of this
portion are removed and it is written in a fasta file
that is the input for Kalign.
After the realignment, the output file produced by
Kalign is read and the sequences portions are rein-
serted at the original individual, replacing the old por-
tion. Then, the new individual has its score evaluated,
and if there is any improvement, it replaces the best
individual on the GA population, and the execution
continues. Figure 3 shows how this step works.
Despite the good results obtained with the first
step by itself, it may have some difficulties when deal-
ing with less similar sequences due to the propagation
error problem from the progressive method. Looking
for solve that while improving even more the quality
of the GA results and solving its local optima prob-
lem, a second step is added to the hybrid method.
4.3 Second Refinement Step: A
Consistency-based Realignment
As shown in section 3, a consistency-based approach
helps to achieve better alignments without significant
disadvantages, so this work added to the hybrid GA
a second step as a way to deal with less similar se-
quences, smoothing the local optima problem even
more: the realignment of the worst individual using
the T-COFFEE
1
tool (Notredame et al., 2000). T-
COFFEE is an open-source package for MSA, and it
is well known by the quality of its results, the reason
why it was chosen as the consistency-based method
for this work.
This routine is executed at the end of the genera-
tion after n iterations, being n a user-defined param-
eter. However, unlike the first refinement step of our
1
http://www.tcoffee.org/
algorithm, it does not use the non improvement con-
dition, and it works with the worst individual in the
population. We show in Figure 4 the execution of the
consistency-based realignment step. Basically, we ex-
ecute the processes as follows:
1. First of all, the search for the worst individual in
the population takes place. The routine starts by
checking the population score array and finding
the smallest value. Then, its index leads to its
respective individual in the population. If there
is more than one individual with the same worst
score, then the first found is the chosen one.
2. After that, the selected individual has its gaps
deleted and it is written in a new file. This file
is used as the input to T-COFFEE, which will re-
align this individual, creating a new alignment as
the output.
3. Back in the GA, the output file is read, and the
WSP function evaluates the new individual. If
there is any improvement when compared to the
original individual, the new one replaces it, and
the GA execution continues, starting a new gener-
ation. If the new alignment has a score better than
the actual best score, it becomes the best individ-
ual in the population.
If both steps are going to be executed in a same
generation, the progressive method is processed first,
followed by the consistency method.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5.1 Benchmark and Test Parameters
In this work, we used the test cases from BAliBase
(Thompson et al., 2005). This benchmark contains
sequences sets, organized in different families with
different characteristics, such as biological similarity
and size. BAliBase also contains the reference align-
ments, so we can compare the obtained results with
the ideal ones.
We have executed cases from RV11, RV12, RV20,
RV30, RV40 and RV50 families. The first one con-
tains sequence sets with less than 20% of similarity;
the second one is related to sequences sets which at
least two sequences are between 20% and 40% simi-
lar; the third one contains sequence sets with similar-
ity between 20% and 40%; the fourth one is related
to sets with, at least, one divergent sequence; the fifth
one contains sequence sets with more than 40% of
similarity, but less than 20% when compared to the
other families; last but not least, the sixth one is re-
lated to sequences with many insertions.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
170
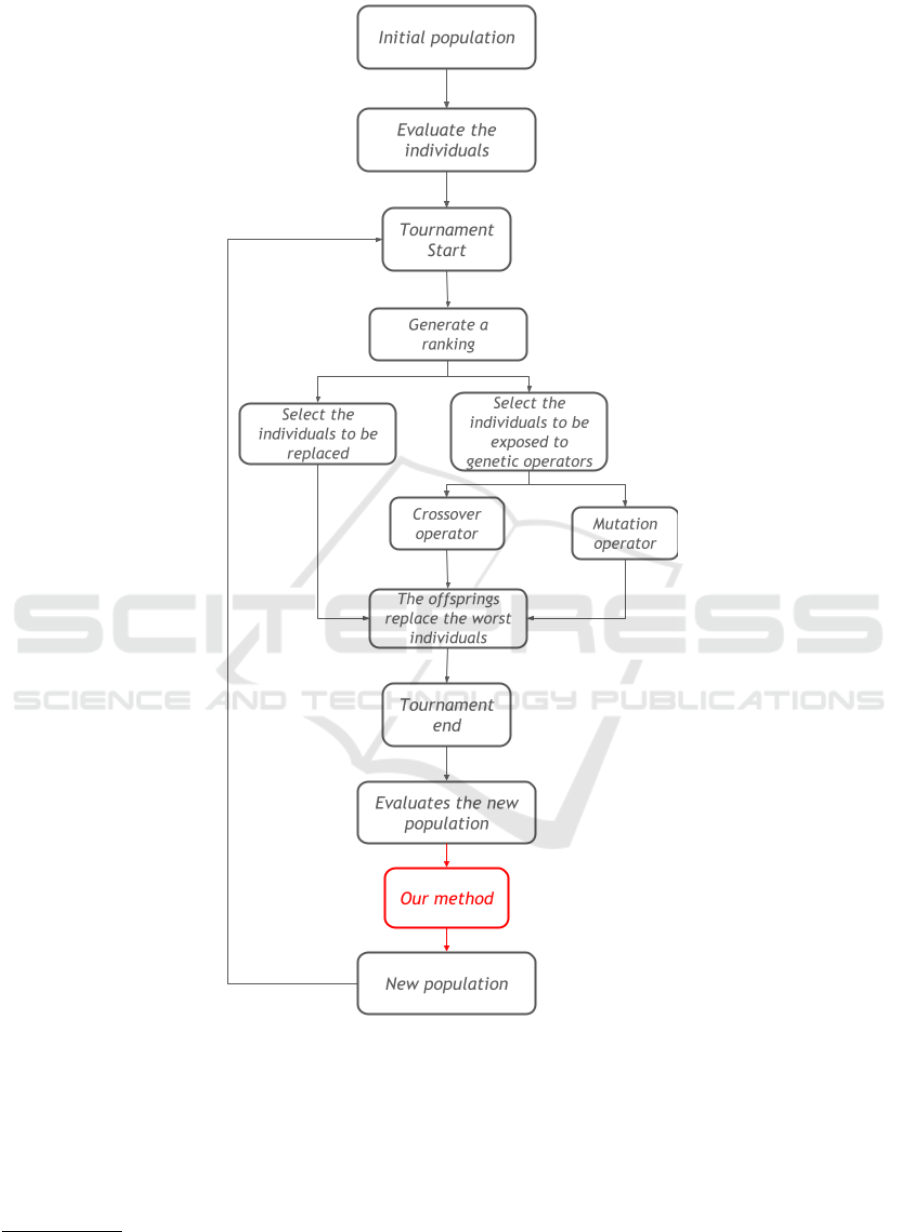
Figure 2: Flowchart of MSA-GA execution.
To measure the quality of the results, we used the
Qscore tool
2
to calculate the Q (Quality) and TC (to-
tal column) scores, which are metrics related to the
biological significance of the alignment when com-
pared to the reference alignment. The scores values
are between 0 and 1, so the greater the score, more
2
https://www.drive5.com/qscore/
biologically significant is the alignment and better the
produced MSA.
All the tests were executed using a computer with
Windows 10 Home 64 bits, Intel Core i7-8565U CPU
4.60GHz processor and 12GB of RAM. The parame-
ters of MSA-GA were the default values described by
Gondro and Kinghorn (2007) and the n parameter for
both progressive and consistency refinement routines
A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm using Progressive Alignment and Consistency based Approach for Multiple Sequence Alignments
171
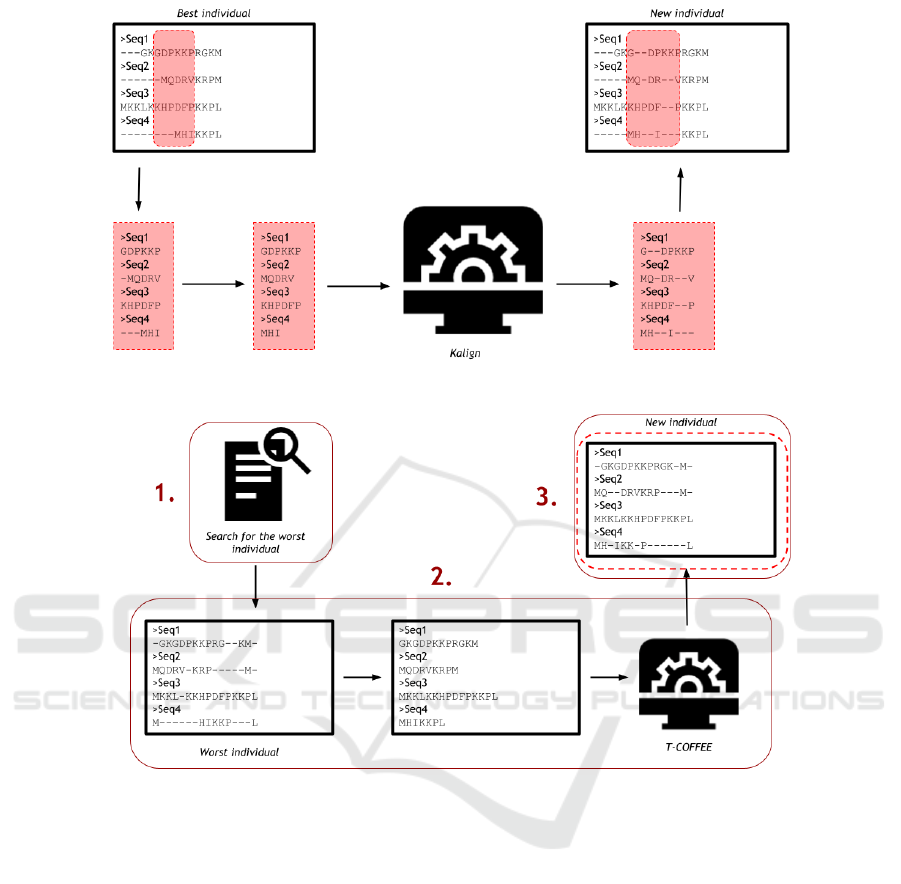
Figure 3: The local realignment using Kalign.
Figure 4: The realignment using T-COFFEE.
was 500.
5.2 Results
Due to the stochastic nature of GA, each test case was
executed five times and the average value was calcu-
lated. The results were compared with the original
MSA-GA and three well-known tools: Kalign (Lass-
mann, 2020), Clustal Omega (Sievers and Higgins,
2018) and MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004).
In Table 1 the average values of Q score for each
family are presented. We can notice that our hybrid
method has a better performance in five of the six
families, being the family RV30 the one where Clustal
Omega performed better, but yet our method aver-
age value in this family has less than 5% of differ-
ence compared to the Clustal Omega values. When
comparing to the original MSA-GA, our method is
able to increase the quality of the final alignments in
290%, suggesting that the changes proposed in this
work were effectively able to smooth the maximum
local problem.
We can see in Table 2 the average TC scores for
all the families. This time, our method was able to
increase the AG results in 2769% in compare with
the original one, showing that the proposed method is
able to refine the alignments and even beat the well-
known tools in most cases.
We can observe in Table 3 and Table 4 the aver-
age standard deviation calculated for all tools and all
families from BAliBase. The method proposed in this
work has the least average standard deviation, which
indicates a better statistical consistency when com-
pared to the others.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
172

Table 1: Q scores obtained for all families of BAliBase.
RV11 RV12 RV20 RV30 RV40 RV50 Average
MSA-GA 0.2375 0.3497 0.3082 0.2657 0.3569 0.3261 0.2989
Kalign 0.6397 0.8873 0.9230 0.8020 0.8947 0.8643 0.8352
Clustal Omega 0.6359 0.8910 0.9265 0.8723 0.9073 0.8680 0.8502
MUSCLE 0.6033 0.8960 0.8845 0.8290 0.8977 0.9010 0.8352
Our method 0.6904 0.9130 0.9500 0.8330 0.9120 0.8963 0.8658
Table 2: TC scores obtained for all families of BAliBase.
RV11 RV12 RV20 RV30 RV40 RV50 Average
MSA-GA 0.0971 0.0893 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0135 0.0221
Kalign 0.4376 0.8045 0.5640 0.5830 0.6780 0.5363 0.6006
Clustal Omega 0.4473 0.8167 0.6435 0.7147 0.7500 0.5502 0.6537
MUSCLE 0.3349 0.8177 0.2760 0.5843 0.7147 0.5605 0.5605
Our method 0.4649 0.7147 0.6545 0.5093 0.7277 0.6007 0.6120
Table 3: Average Standard Deviation of Q score for each tool.
MSA-GA Kalign Clustal Omega MUSCLE Our Method
Average Standard Deviation 0.1300 0.1080 0.1083 0.1158 0.0945
Table 4: Average Standard Deviation of TC score for each tool.
MSA-GA Kalign Clustal Omega MUSCLE Our Method
Average Standard Deviation 0.2102 0.2115 0.2095 0.2564 0.2093
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work we presented a new hybrid method for
multiple sequence alignment, combining both pro-
gressive and consistency-based techniques to smooth
the local maximum problem in AG and increase the
quality of the results. The Kalign tool was used
to perform a local realignment when the algorithm
shows stagnation signs, and the T-COFFEE tool re-
align globally individuals that would be discarted
from the population as a way to avoid degradation that
may result from the use of a progressive approach,
since it is known for its difficult when dealing with
less similar sequences.
The results shown that the given hypothesis was
correct, since the hybrid proposed AG was able to ob-
tain results 2 a 27 times better than the original one,
indicating the smooth of the local maximum problem.
Our method also was able to beat the quality of align-
ments realized by well-known tools 5 out of 6 times,
encouraging its use in situations when the quality of
the result is prioritized over the execution time.
We propose, as future work, combining the ad-
vantages of hybridization techniques with parallel ap-
proaches as a way to obtain a better execution time,
balancing the quality/time ratio.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank S
˜
ao Paulo Research
Foundation (FAPESP) for the financial support,
under grant 2019/00030-3, Universidade Paulista
(Unip/ICET) to partially support this research un-
der grant number 7-03-1169/2021, and Coordenac¸
˜
ao
de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de N
´
ıvel Superior -
Brasil (CAPES) for the partial financial support.
REFERENCES
Amorim, A. R., Neves, L. A., Val
ˆ
encio, C. R., Roberto,
G. F., and Zafalon, G. F. D. (2018). An approach
for coffee objective function to global dna multiple se-
quence alignment. Computational biology and chem-
istry, 75:39–44.
Amorim, A. R., Zafalon, G. F. D., de Godoi Contessoto, A.,
Val
ˆ
encio, C. R., and Sato, L. M. (2021). Metaheuristics
for multiple sequence alignment: a systematic review.
Computational Biology and Chemistry, page 107563.
Amorim, A. R., Zafalon, G. F. D., Neves, L. A., Pinto, A.,
Val
ˆ
encio, C. R., and Machado, J. M. (2015). Improve-
ments in the sensibility of msa-ga tool using coffee ob-
jective function. In Journal of Physics: Conference Se-
ries, volume 574, page 012104. IOP Publishing.
A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm using Progressive Alignment and Consistency based Approach for Multiple Sequence Alignments
173

Bawono, P., Dijkstra, M., Pirovano, W., Feenstra, A., Abeln,
S., and Heringa, J. (2017). Multiple sequence alignment.
In Bioinformatics, pages 167–189. Springer.
Baxevanis, A. D., Bader, G. D., and Wishart, D. S. (2020).
Bioinformatics. John Wiley & Sons.
Chatterjee, S., Hasibuzzaman, M., Iftiea, A., Mukharjee,
T., Nova, S. S., et al. (2019). A hybrid genetic algo-
rithm with chemical reaction optimization for multiple
sequence alignment. In 2019 22nd International Confer-
ence on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT),
pages 1–6. IEEE.
Chowdhury, B. and Garai, G. (2017). A review on multi-
ple sequence alignment from the perspective of genetic
algorithm. Genomics, 109(5-6):419–431.
Cook, S. (2006). The p versus np problem. The millennium
prize problems, pages 87–104.
Correa, J. M., de Melo, A. C. M. A., Jacobi, R. P., and
Boukerche, A. (2012). Parallel simulated annealing for
fragment based sequence alignment. In 2012 IEEE 26th
International Parallel and Distributed Processing Sym-
posium Workshops & PhD Forum, pages 641–648. IEEE.
Do, C. B., Mahabhashyam, M. S., Brudno, M., and Bat-
zoglou, S. (2005). Probcons: Probabilistic consistency-
based multiple sequence alignment. Genome research,
15(2):330–340.
Edgar, R. C. (2004). Muscle: multiple sequence align-
ment with improved accuracy and speed. In Proceed-
ings. 2004 IEEE Computational Systems Bioinformatics
Conference, 2004. CSB 2004., pages 728–729. IEEE.
Edgar, R. C. and Batzoglou, S. (2006). Multiple se-
quence alignment. Current opinion in structural biology,
16(3):368–373.
Gondro, C. and Kinghorn, B. P. (2007). A simple genetic
algorithm for multiple sequence alignment. Genetics and
Molecular Research, 6(4):964–982.
Katoh, K., Misawa, K., Kuma, K.-i., and Miyata, T. (2002).
Mafft: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence align-
ment based on fast fourier transform. Nucleic acids re-
search, 30(14):3059–3066.
Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J., and Yamada, K. D. (2019). Mafft
online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive
sequence choice and visualization. Briefings in bioinfor-
matics, 20(4):1160–1166.
Kaya, M., Kaya, B., and Alhajj, R. (2016). A novel multi-
objective genetic algorithm for multiple sequence align-
ment. International Journal of Data Mining and Bioin-
formatics, 14(2):139–158.
Kim, J., Pramanik, S., and Chung, M. J. (1994). Multiple
sequence alignment using simulated annealing. Bioinfor-
matics, 10(4):419–426.
Lassmann, T. (2020). Kalign 3: multiple sequence align-
ment of large datasets.
Lee, Z.-J., Su, S.-F., Chuang, C.-C., and Liu, K.-H. (2008).
Genetic algorithm with ant colony optimization (ga-aco)
for multiple sequence alignment. Applied Soft Comput-
ing, 8(1):55–78.
Mount, D. W. (2001). Bioinformatics. In Bioinformatics,
pages 564–564.
Needleman, S. B. and Wunsch, C. D. (1970). A general
method applicable to the search for similarities in the
amino acid sequence of two proteins. Journal of molec-
ular biology, 48(3):443–453.
Notredame, C. and Higgins, D. G. (1996). Saga: sequence
alignment by genetic algorithm. Nucleic acids research,
24(8):1515–1524.
Notredame, C., Higgins, D. G., and Heringa, J. (2000).
T-coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multi-
ple sequence alignment. Journal of molecular biology,
302(1):205–217.
Notredame, C., Holm, L., and Higgins, D. G. (1998). Cof-
fee: an objective function for multiple sequence align-
ments. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 14(5):407–
422.
Nute, M., Saleh, E., and Warnow, T. (2019). Evaluating
statistical multiple sequence alignment in comparison to
other alignment methods on protein data sets. Systematic
biology, 68(3):396–411.
Riaz, T., Wang, Y., and Li, K.-B. (2004). Multiple sequence
alignment using tabu search. In Proceedings of the sec-
ond conference on Asia-Pacific bioinformatics-Volume
29, pages 223–232.
Rubio-Largo,
´
A., Vega-Rodr
´
ıguez, M. A., and Gonz
´
alez-
´
Alvarez, D. L. (2016). Hybrid multiobjective artificial
bee colony for multiple sequence alignment. Applied Soft
Computing, 41:157–168.
Sievers, F. and Higgins, D. G. (2018). Clustal omega for
making accurate alignments of many protein sequences.
Protein Science, 27(1):135–145.
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G., and Gibson, T. J. (1994).
Clustal w: improving the sensitivity of progressive mul-
tiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting,
position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice.
Nucleic acids research, 22(22):4673–4680.
Thompson, J. D., Koehl, P., Ripp, R., and Poch, O.
(2005). Balibase 3.0: latest developments of the multi-
ple sequence alignment benchmark. Proteins: Structure,
Function, and Bioinformatics, 61(1):127–136.
Thomsen, R. and Boomsma, W. (2004). Multiple sequence
alignment using saga: investigating the effects of oper-
ator scheduling, population seeding, and crossover op-
erators. In Workshops on applications of evolutionary
computation, pages 113–122. Springer.
Wang, L. and Jiang, T. (1994). On the complexity of multi-
ple sequence alignment. Journal of computational biol-
ogy, 1(4):337–348.
Zafalon, G. F. D., Gomes, V. Z., Amorim, A. R., and
Val
ˆ
encio, C. R. (2021). A hybrid approach using progres-
sive and genetic algorithms for improvements in multi-
ple sequence alignments. In 23rd International Confer-
ence on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2021),
volume 2, pages 384–391. SciTePress.
ICEIS 2022 - 24th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
174
