
Applying Simulation in Teaching Selected Courses in Business
Informatics with the FlexSim Platform
Aleksander Binsztok
a
, Beata Butryn
b
Katarzyna Hołowińska
c
, Mieczysław L. Owoc
d
and Małgorzata Sobińska
e
Department of Business Intelligence in Management, Wroclaw University of Economics and Business,
Komandorska, Wroclaw, Poland
mieczyslaw.owoc@ue.wroc.pl, malgorzata.sobinska@ue.wroc.pl
Keywords: Education, Simulation Processes, Industry 4.0, New Technologies, Active Teaching, FlexSim, Business
Informatics.
Abstract: Using simulation in various sectors as a tool to predict and design processes is very common. The popularity
of such solutions is growing, and even in the education field, this kind of tool can be an interesting form of
enriching classes. Today, education requires a constant search of methods and instruments that stimulate
students' engagement. Active teaching methods ensure students' activities through their creativeness and
reactiveness during educational processes. The research aims to investigate the role and usability of
simulation, which in turn can be a crucial component of the active teaching method. Education in the Business
Informatics area relates to computer technologies and management skills. Our proposals presented in the
paper cover both mentioned areas, the simulation of defined business models and the development of
applications useful in certain phases of managerial procedures. The application of simulation techniques in
education is considered a vital teaching instrument, which allows preparing adequate education, directs
students to the proper attitude, motivates them to learn, inspires them and enables their development. This
article attempts to fill the research gap by describing the usability of such tools.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the biggest challenges of modern education is
to attract students research and allow them to progress
in the extension of their professional skills. It also
matters as a way of preparing alternative solutions to
defined problems. In addition, all these mentioned
aspects are typical of active learning. So, looking for
innovative and attractive methods of teaching, we
decided to analyse the usability of simulation in
teaching selected courses in the Business Informatics
major. The Business Informatics major covers
different areas of education; apart from general
economic knowledge, the studies provide graduates
with practical skills in the use of software tools
supporting business processes. Students obtain,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5643-4172
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4992-3044
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2811-4889
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1578-6934
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9080-4322
methods and techniques of analysis and
design of
information systems, business applications, database
technology, design and development of mobile
applications and methods of project management.
The problems solved by students as part of case
studies will enable them to gain analytical skills,
flexibility and self-fulfillment of tasks as business
informatics professionals (2022, March 08).
The research goal is to investigate the role of
simulation in preparing certain projects essential in
practical education in selected courses in the major
discussed. There are many platforms supporting
simulation in teaching; FlexSim seems to be useful as
an example in line with this approach. However, this
platform is dedicated to preparing individual models,
and it is worth analysing how students elaborating
330
Binsztok, A., Butryn, B., Holowinska, K., L. Owoc, M. and Sobi
´
nska, M.
Applying Simulation in Teaching Selected Courses in Business Informatics with the FlexSim Platform.
DOI: 10.5220/0011084300003182
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2022) - Volume 1, pages 330-337
ISBN: 978-989-758-562-3; ISSN: 2184-5026
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

solutions tend and are able to cooperate, how they
may share their results and what level of efficiency is
reached in simulations prepared by students’ teams.
The paper is organized as follows. After an
overview of the state-of-the-art current and available
research (in the next section), short characteristics of
the platform are presented. Then, two cases of
applying FlexSim in two courses are demonstrated. In
these cases, we aimed to detect how the applied
platform is equipped with mechanisms and measures
useful in monitoring students’ activities during their
work on models. Finally, a discussion of the obtained
results with conclusions is described. There is a
tangible research gap in the knowledge of using
simulation tools in business informatics, in our
opinion.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The use of simulation techniques in education is
considered an important teaching tool; it makes it
possible to create a reality adequate to the level of
education, directs the student to the appropriate
attitude, motivates to them learn, inspires them, and
enables their development (Bock and Wiener. 2017).
Simulation-based education refers to the use of
simulation software, tools, techniques and serious
games to enrich learning processes (Ibezim., Asogwa,
2020); (Campos, Nogal, Caliz, Juan, 2020). Games
based on simulation offer challenges and autonomy
for students while involving them more in cognitive
processes. This format is especially attractive for
students who are keen on intensive intellectual effort
(Chernikova, Heitzmann, Stadler, Holzeberger,
Seidel, Fischer, 2020).
The largest number of articles related to
simulation modeling concerns ecological modeling.
However, as recent studies show, simulation
modeling has shifted to healthcare issues (Story,
Yukhymenko-Lescroart, Deitz, 2020). Therefore, it is
most
often used for teaching in the field of medicine.
Distinguished simulation methods defined criteria
and steps that need to be applied when designing a
simulation course as well as developing a skills
checklist to ensure that simulation is successfully
applied to medical education (Jadrić, Mijač , Ćukušić,
2020). Interactive methods based on computer
simulation bring the expected results in improving
communication knowledge and self-efficacy among
medical students and are well received by them
(Heeseung, Ujin, Ye, Chanhee, 2020). In the case of
educating students in other fields of study, there are
fewer examples of the use of simulations.
Simulation techniques are also successfully used
in sports (Eshama, 2020) or in simulating business
processes and designing information systems
(Emerson, Dunn, Takito, 2020). Previous studies
indicate different models of games and simulations
and usually refer to the tools used and provide their
detailed description. Business process management
focuses on various methods, techniques, or
frameworks, such as the business process model and
notation (BPMN), identification, simulation,
evaluation, the improvement (ISEI) method, process
based on events, event-driven simulation modeling,
educational process management (EPM) structure,
social network analysis (SNA), agent-based
simulation and TOGAF (The Open Group
Architecture Framework), rapid analysis and design
(RAD), educational process management (EPM) and
the serious game-based method for business process
management (Paul, Serano, 2004).
Simulation models fully or partially simulate real
processes or systems. Introducing them into the
student learning process enables students to find
themselves in a variety of realistic circumstances
when real practice is unavailable. They can try their
hand at running a software development company or
carrying out various business processes (Bosilj,
Vuksic, Tomicic-Pupek, Bach, 2018).
Teachers are under increasing pressure to
empower students to directly apply what they are
learning. It is forced by the development of ICT; also,
it is required by both students and the industries in
which they will work. Implementing business
simulations that put students at the center of different
scenarios allows them to make their own decisions
about real-world business problems (Vakaliuk,
Kontsedailo, Antoniuk, Korotun, Mintii, Pikilnyak,
2020).
Publications in this thematic area indicate the
following:
• Simulations provide a wide range of practical
possibilities/options, enhanced by using the
latest technology.
• A higher level of authenticity is related to a more
precise design of the simulation-based learning
environment.
Simulations offer one of the most effective ways
to design learning environments in higher education.
The combination of simulation in teaching with the
latest technologies is an area that is still relatively
little explored. The research gap is to test usability by
using simulation methods in the learning process in
Business Informatics field.
Applying Simulation in Teaching Selected Courses in Business Informatics with the FlexSim Platform
331

3 FlexSim AS A SIMULATION
PLATFORM
FlexSim is software dedicated to modeling,
developing, visualizing, simulating and monitoring
processes and activities in companies or
organizations. It is used as a tool to perform tasks
consisting of 3D simulations, model layout, model
building, model analysis and optimizations (2022,
March 09). Due to its realistic 3D graphics and
complex reports (dashboards can be customized), it is
easy to find a problem in the process and prepare
suitable solutions. FlexSim is widely used in a variety
of industries , from manufacturing to warehousing, by
supporting decision-making and answering even the
most difficult questions connected with processes.
The most important benefits of using Flexsim are
(Nordgren, 2013):
• Reducing business risks by using a virtual
environment that can be precisely reproduced
exactly as in reality to check how particular
scenarios work in practice.
• The analysis of cases and scenarios which are
more than data in basic spreadsheets.
• Possibilities of implement ingvery realistic 3D
visualizations.
• Optimization of the system before
implementation in real life, which saves time
and money.
FlexSim is a very useful tool to create a variety of
simulations. Building models include identifying
objects and flows between elements in general
structures. A 3D model is built in the main panel,
which is the main workspace.
Figure 1: Initial interface supporting Simulation in
FlexSim.
Users can construct their models by choosing
fixed resources from the menu bar, e.g. Source,
Queue, Processor, Sink, Combiner, Separator,
MultiProcessor and Basic FR, and put elements in the
field designated for the model.
Figure 2: List of categories useful in creating simulations
with FlexSim.
All fixed resources have a specific function (e.g.,
source, which makes flow items with intervals and
implements them to the model, queue, supplies items,
etc.) In addition, users can also use the tasks executers
menu bar, which is list of categories dedicated to
performing tasks such as transporting flow items or
operating machines. The most popular kind of task
executer is Operator, which in the simulation can
represent an employee. The Main Menu encloses all
tools and commands which can be used while
creating a simulation model mainly connected with
the administration of the file. The toolbar provides
fast access to the most popular commands and tools.
The Simulation Control bar includes commands and
tools which are necessary to run the simulation and
regulate simulation time (2022, March 08).
The architecture of the FlexSim software makes
the creation of 3D models and simulations simple and
intuitive, but in complex projects, there are
possibilities of using many variants of the simulation,
also changing the execution time for particular
processes, or changing the time of starting the
triggers. What is important, FlexSim allows users to
choose ready-made solutions and tools or use full
customization.
4 SIMULATION OF BUSINESS
MODELS USING FlexSim
Taking into account the fact that the FlexSim
software allows for intuitive mapping and
optimization of advanced processes that take place in
the analyzed industry, it is possible to use this tool in
very different areas of production, logistics and
services. For this reason, this part of the article will
focus on the potential of simulation and the FlexSim
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
332

tool in the context of conducting classes at an
economic university in the field of Business
Informatics.
The authors will provide a short description of
two subjects/courses which, due to their nature, seem
to be particularly
predisposed to use FlexSim tools
during their implementation and propose example
scenarios for conducting classes.
The courses in question are Digitalization of
Business Models and E-business in the Age of
Industry 4.0.
The Digitalization of Business Models course
covers, among others, such issues as
entrepreneurship, organization and planning in
business, organizational structures, business model
analysis, market research and branding, opportunity
detection, positive persuasion in practice, social
responsibility and ethics, team building in the modern
companies, motivation in modern companies and
information gathering.
The teaching methods used so far are
presentations, discussions, case studies, managerial
games, active forms of movement ("ice-breakers" and
"energizers" stimulating more effective interpersonal
communication), team exercises and heuristic
techniques (activating creative solving of problem
situations) and exercises with the use of video
cameras (optional).
During the course, students carry out a research
project, whose topic is: “Project preparation –
Digitalization of Business Models”. The student's
task is to develop a model. They should also find
examples of interesting business solutions based on a
literature review and their observations.
During the classes on the subject “E-business in
the era of Industry 4.0”, students learn about the
concept of “Industry 4.0”, including the
distinguishing factors and consequences of the fourth
industrial revolution. In addition, they learn in detail
the concepts of the e-business model: conditions for
the development of this type of model, the impact of
ICT on the challenges posed by this type of business,
legal aspects of the functioning of e-business and
aspects related to knowledge sharing and relationship
management in selected e-business models. In
addition, they learn about the fundamental principles
of creating an e-business model and develop their
concepts of e-business models.
The teaching methods used so far in the classes
are lecture, seminar lecture and exercises: group
work, presentations and discussion. Students of this
course carry out a research project covering the
following:
• development (in a team) of a concept of an e-
business model with assumptions and
justification/comments on the selection of
individual elements of the model;
• preparation of a multimedia presentation on
the developed concept.
Considering the above information, it is possible
to propose making the classes in these courses more
attractive by introducing simulations as an element of
the didactic process, which will make it possible to
better illustrate the functioning of selected elements
of the business reality, including aspects such as the
functioning of specific elements of the business
model (e-business), which depend on different
variables. It can be, for example, a customer service
process in an online store as a key process within one
of the canvas business model elements called “key
processes”. Using the FlexSim simulation tool would
present the different possible paths/runtimes of the
process and show where the weak points are, and
then, with some changes, observe the difference and
possibly make further modifications. Students/future
managers would learn which elements/activities
within the simulated processes are more sensitive
and/or influencing the remaining process links and
the result, and which are of little importance or can
even be eliminated from the process without
compromising the final result. Taking into account
the fact that FlexSim is easy to use because, thanks to
a very extensive library of 3D objects, it is possible to
accurately reproduce the analyzed business process,
there is a chance to use this tool to conduct classes
with students that related to various types of
simulations of business activities – e.g.
manufacturing of goods on the production line,
logistic work in the warehouse or the customer
service process in a trading company (see Fig. 3 and
Fig.4 – Model and Results of Customer Service
Simulation in FlexSim). All this, in turn, would allow
the final result to develop flexible and easy-to-
configure statistics of processes, which, in turn,
would allow the visualization of fully digital business
models in modern companies. Therefore, the use of
this tool to conduct classes for students learning the
subjects "Digitalization of Business Models" and "E-
business in the Age of Industry 4.0", where lectures
and exercises are mainly based on the concept of
Maximilian Bock and Martin Wiener (Table 1), could
turn out to be the optimal solution in didactic
processes.
Applying Simulation in Teaching Selected Courses in Business Informatics with the FlexSim Platform
333

Table 1: Digital BM Taxonomy.
Dimension Characteristics
Digital
offering
Digital products Digital services
Human services and
complementary
digital services
Physical products
and complementary
digital services
Physical products
with embedded
digital technology
Digital
experience
Personalization Engagement Community building
Digital
platform
Internal integration Supplier integration Partner integration
Inbound customer
integration
Outbound customer
integration
Data analytics
Process and product data Customer data (Free) external data
Digital
pricing
Demand-based pricing Supply-based pricing Consumption-based pricing
Table 2: The three components of a digital business model. An example for a commercial company selling music products
via the Internet.
Content
What is
consumed?
Information
Product information, price and use details, etc.
Example: information about a given artist and other artists and music, charts,
album reviews, comments from music experts and critics, links to various social
networking sites, music fan clubs, up-to-date information on concerts and other
cultural events.
Product
Digital products such as CDs, e-books, e-saver accounts, movies, software, online
meetings with musicians, conferences
Experience
How is it
packaged?
Customer
Experience
The experience can include customer-facing digitized business processes,
community and customer input, expertise for informed decision making,
recommendations, tools and interface; for example, each login to the system based
on a subscription may be associated with the strengthening of ties between system
users. Here, there can be an exchange of content between customers, i.e. they can
exchange their insights in the area of different musical tastes, impressions about the
music purchased or feelings from music events and other cultural events.
Platform
How is it
delivered?
Internal Other business processes, customer data, technology
External
Software available only to users of a given system, open public networks, business
partners
Example:
A global music platform adapted locally; highly developed system architecture
with global access to various content related to the sphere of music and culture;
modular design and global and local content exchange.
A very interesting solution could then be the
combination of the above concept of building a digital
business model based on the three components of the
digital business model proposed by P.Weill and
S.Woerner. Based on 3 elements: content, experience
and platform (Table 2), it is possible to create an
attractive value proposition for the client, which
could constitute aninteresting concept, providing
inspiration for the future of the visualization of
business processes during classes.
The above example of the functioning of a digital
music store in combination with the use of the
FlexSim tool could be an interesting source of
observation for students. They could introduce
various variables into the system, such as, for
example, the number of participants in the platform,
various reviews and opinions, information on planned
concerts and other cultural events, as well as many
other variables, thanks to which they could simulate
changes in revenues in such a trading company or also
study how relationships with potential and real
customers change.
The first simulation dedicated to the course
Ebusiness in the Age of Industry 4.0. is presented in
Fig. 3. Real objects existing in customer service
(recently performed online) are mapped as Fixed
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
334

Resources in our model, so:
• CustomerOrders represent the Source category
in this model,
• Ordering and NewCustomers play the role of
supported Queue,
• main actions are performed by Processors
(AccountCreation, Catalogue overviewing,
defining Basket content, and finally Payments),
and
• final results of order processing (Failed,
NotServed, Waited, and Served orders) are
represented as Sink objects.
Figure 3: Model of Customer Service Simulation using
FlexSim.
Relationships between particular objects,
supported by setting parameters for the defined
resources, were created to analyze the results of such
defined simulation. This version of simulation
reflects typical processes present in Customer Service
models and should be extended in more advanced
research. Before starting the simulation, a specialized
dashboard was created consisting of selected objects
to be analyzed and types of expected charts
demonstrating the results of simulation – see Fig. 4.
Figure 4: Results of Customer Service Simulation using
FlexSim.
The presented charts inform about different
aspects of Customer Service including all phases of
customer order processing, staytime (customers’
Catalogue reviewing), and the efficiency of the
determined processors according to the defined
parameters for particular objects. The platform is very
flexible in terms of objects defined in the model and
the preparation of dashboards illustrating the
simulation process of customer services.
Summing up, it is very easy to model and make
the simulation of more or less complex business
processes for managers. Thus, students are able to
experiment by creating business models, perform
simulations of different processes as well as visualize
obtained results.
5 MODELING OF PROCESSING
DATABASE TRANSACTION
SUPPORTED BY FlexSim
The next group of courses which can be supported by
simulation tools is strictly connected with the
technological aspects of the Business Informatics
major. IT people and students have many developed
platforms useful in modeling information systems,
designing applications and programming software.
However, preparing many variants of the final
applications and simulation of data processing in
more complex computer systems is still a big
challenge for software developers and IT managers.
One of such problems, essential in all information
systems, is the simulation of database transactions
typical of all events-oriented and analytical-based
applications. The proposed simulation is prepared for
the Databases course, one of the very fundamentals in
Business Informatics.
The simplified version of the model presenting
database transaction processing is shown in Fig. 5.
The main components of the model are as follows:
• Transactions representing Source from the
Fixed Resources categories,
• DirectAccess and Authorization belongingto
the Queue category; we assume that some
database transactions should be additionally
verified using a specialized processor while
the others can obtain direct access to databases
servers,
• The list of Processors responsible for the
defined group of transactions (respectively for
performed queries and generating reports and
more complex tasks: DBServer0, DBServer1,
DBServer2, and DBMultiServer),
Applying Simulation in Teaching Selected Courses in Business Informatics with the FlexSim Platform
335
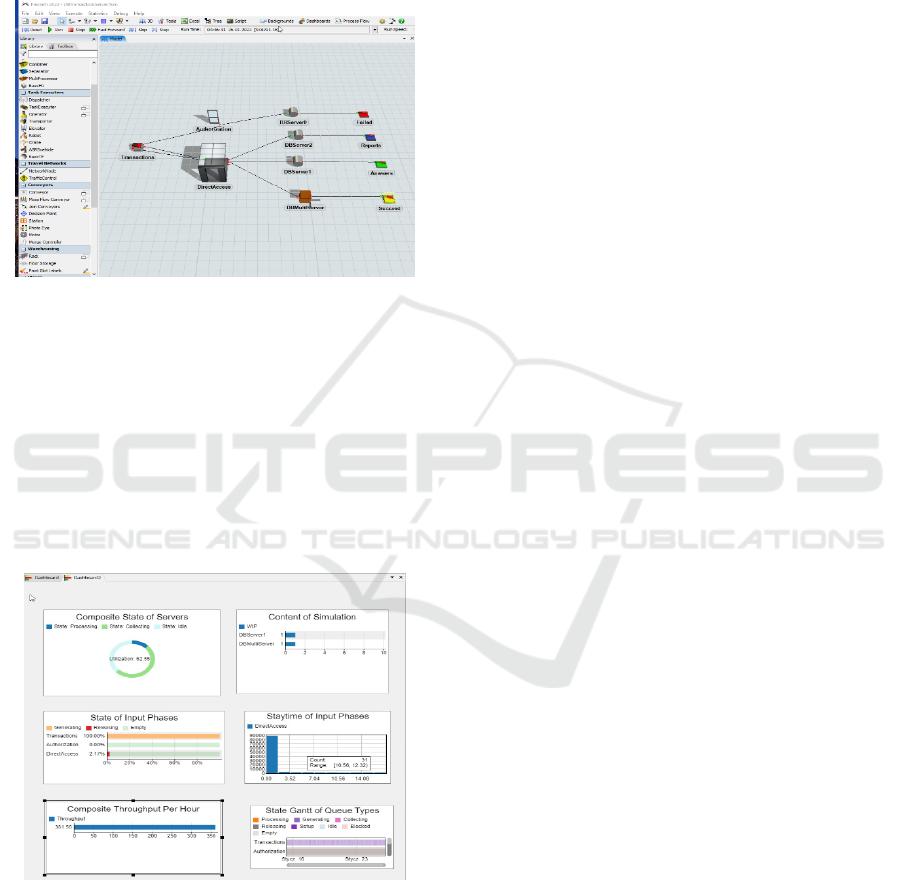
• Outputs of database transaction processing
representing Sink category diversified on
Failed, Succeed, Reports,and Answers results.
All these components were precisely defined by
setting adequate parameters and connected via
determined ports.
Figure 5: Model of DB Transaction Processing Simulation
using FlexSim.
As previously, before starting the simulation
process, separate dashboard should be created
containing monitored objects with the definition of
chart types prepared for a different analysis of the
ongoing processes. Compared to the previous
simulation, new aspects of simulation have been
explored; for example State Gantt of Queue Types or
Composite Throughput per Hour visualizations. The
results of this simulation are depicted in Fig. 6.
Figure 6: Results of DB Transaction Processing Simulation
using FlexSim.
Also, the presentation of technological aspects
can be multi-folded and created in a very flexible
way. Students can be activated by providing different
parameters of the model components and in addition
defining several dashboards supporting different
methods of monitoring particular servers. In the case
of discovering bottlenecks in transaction processing,
additional servers can be added or parameters
guaranteeing better efficiency can be applied.
Database transaction processing can be visualized
using many ways; simulation of real operations
performed in many sectors creates the opportunity for
students to understand the complexity of all processes
served by database machines.
6 CONCLUSIONS
It must be assumed that the more simulations would
be carried out in the classroom, the more proficient
students could become in assessing various processes.
In addition, the use of the FlexSim tool is an
opportunity to increase the activity and involvement
of students during classes, thus making them a
modern form of activity that is attractive for young
people whose life and work are already inextricably
linked with ICT tools. Teaching in faculties such as
Business Informatics should be supported even more
by the latest ICT technologies. Simulations and
games properly designed in the FlexSim tool (tailored
to the needs of selected classes) could be an important
element increasing the attractiveness of the course,
and above all, students’ satisfaction with interactive
classes. In the future, it is planned to use the FlexSim
tool to analyze and assess to what extent classes using
simulation affect student behavior, i.e., whether, for
example, they increase student involvement during
classes, develop creativity, increase the number of
ideas generated, improve the flow of data/information
between team members, etc.
It has turned out that active teaching methods are
not the optional solution but an inseparable element
of today's education. Further research will be
performed on more complex models which use
monitoring tools that enable the registration of user
behavior, i.e., time of work, kinds of undertaken
activities, number of logins, etc., and analytics of the
obtained data, as well as evaluate the usefulness of the
prepared tool and conclude other functions or
improvements that can be introduced to optimize the
work with the tool.
REFERENCES
Bock M., Wiener M., Towards a Taxonomy of Digital
Business Models – Conceptual Dimensions and
Empirical Illustrations, Thirty-Eighth International
Conference on Information Systems, South Korea 2017
CSEDU 2022 - 14th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
336

Bosilj V., Vuksic K., Tomicic-Pupek K., Bach M.P.,
Simulation based business processes analysis in higher
education institutions, DOI:10.23919/MIPRO.20
18.8400229 Conference: 41st International Convention
on Information and Communication Technology,
Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO),
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326707678_
Simulation_based_business_processes_analysis_in_hi
gher_education_institutions, May 2018.
Campos N., Nogal M., Caliz C., Juan A.A., Simulation-
based education involving online and on-campus
models in different European Universities,
International Journal of Educational Technology in
Higher Education volume 17, Article number: 8 (2020).
Chernikova O., Heitzmann N., Stadler M., Holzeberger D.,
Seidel T., Fischer F., Simulation-Based Learning in
Higher Education: A Meta-Analysis, Review of
Educational Research, https://doi.org/10.3102/00346
54320933544, June 15, 2020.
Emerson F., Dunn E., Takito M. Y., Journal of Strength and
Conditioning Research, Volume 34 Issue9-p2557-2564
doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000002727, September
2020.
Eshama S. S., How to apply Simulation-Based Learning in
Medical Education? Iberoamerican Journal of
Medicine, Iberoam J Med, vol.2, n2, p.79-86, 2020.
Heeseung C., Ujin L., Ye S.J., Chanhee K., Efficacy of the
computer simulation-based, interactive communication
education program for nursing students, Elsevier, Nurse
Education Today, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.20
20.104467, Volume 91, August 2020.
Ibezim N. E., Asogwa A. N, Computer Simulation Model
Effect on Students’ Academic Achievement in
Computer Logic, International Journal of Management,
11(8), 2020, pp. 58-71.
Jadrić M., Mijač T., Ćukušić M., Text Mining the Variety
of Trends in the Field of Simulation Modeling
Research, Perspectives in Business Informatics
Research, 19th International Conference on Business
Informatics Research, BIR, Vienna, September 2020,
pp. 143-158,
Nordgren B., FLEXSIM: Focusing on Problem Solving,
Proceedings of the 2013 Winter Simulation Conference
R. Pasupathy, S.-H. Kim, A. Tolk, R. Hill, and M. E.
Kuhl, eds
Paul R. J., Serano A., Simulation for business processes and
information systems design Proceedings - Winter
Simulation Conference, 2:1787-1796vol.2
DOI:10.1109/WSC.2003.1261634, January 2004.
Story W. K., Yukhymenko-Lescroart M. A., and Deitz
G.D., Understanding Student Preferences: Improving
Outcomes in Computer Simulation Experiential
Learning Activities, Journal for Advancement of
Marketing Education, Volume 28, Issue 1, Spring 2020.
Vakaliuk T. A., Kontsedailo V.V, Antoniuk D.S., Korotun
O.V., Mintii I.S., Pikilnyak A.V., Using game simulator
Software Inc. in the Software Engineering education,
https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.01127, November 2020.
Weill P., Woerner S. L., Optimizing Your Digital Business
Model, MIT Sloan Management Review, Spring 2013,
VOL. 54, NO.3, pages: 71-77
https://www.ue.wroc.pl/kandydaci/21358/business_inform
atics.html
https://docs.flexsim.com/en/19.2/FlexSimUI/OverviewUse
rInterface/
https://www.flexsim.com/flexsim/
Applying Simulation in Teaching Selected Courses in Business Informatics with the FlexSim Platform
337
