
User Profiling: On the Road from URLs to Semantic Features
Claudio Barros and Perrine Moreau
Data Science Direction, M
´
ediam
´
etrie, 70 rue Rivay, Levallois-Perret, France
Keywords:
Text Mining, URLs, User Profiling, Feature Engineering, Topic Extraction, Semantics.
Abstract:
Text data is undoubtedly one of the most rich and peculiar source of information there is. It can come in many
forms and require specific treatment based on their nature in order to create meaningful features that can be
subsequently used in predictive modelling. URLs in particular are quite specific and require adaptations in
terms of processing compared to usual corpora of texts. In this paper, we review different ways we have used
URLs to create meaningful features, both by exploiting the URL itself and by scrapping its page content. We
additionally attempt to measure the impact of the addition of different groups of features created in a predictive
modelling use case.
1 INTRODUCTION
M
´
ediam
´
etrie is the entity in charge of audience
measurement in France. For this purpose, we possess
multiple panels of individuals, including one dedi-
cated to measuring the Internet audience, which is
representative of the French internet user population.
Thanks to this panel, we have surf data, as well as the
characteristics of the individuals who originated it.
The surf data consists of logs containing a timestamp,
a user ID and a visited URL.
Table 1: Example of surf data.
ID Panelist Timestamp
133121 2021-05-06 12:03:42
133121 2021-05-06 12:37:01
509666 2021-05-06 22:16:18
URL
https://www.doctolib.fr/vaccination-covid-19/paris
https://www.lemonde.fr/actualite-en-continu/
https://www.750g.com/macarons-chocolat-r79291.htm
On the other hand, we receive data from clients
who own websites or groups of websites. This data
also contains user IDs and the associated surf on the
websites, but no information on the characteristics of
people surfing. In order to have a better understand-
ing of their audiences, our clients are interested in
the socio-demographic profile of their websites’ vis-
itors, their home composition, their purchase intents
or their behaviours and interests. To predict these, we
have proposed a machine learning model based on our
panel. The inputs of the model include features cre-
ated from the visited URLs.
In this paper we review different ways we have
used URLs in order to create features that can be in-
terpreted by algorithms. Throughout the paper, the
data we used as illustration comes from our panel’s
PC surf data from May 2021. This corresponds to
more than 8 million logs and over 1.8 million distinct
URLs. In section 2, we focus on feature creation by
exploiting the raw URLs. In section 3, we scrap the
URLs with the intent of adding content and context
into the equation. Section 4 consists of an evaluation
of the impact of each group of features created in a
predictive modelling use case. Finally, we draw some
conclusions and provide some critical analysis of our
work in section 5.
2 URL-BASED FEATURES
Here we focus on exploiting the raw URLs in or-
der to create features. Throughout our researches,
the perimeters of domains we studied were usually
made up of news, cooking, cinema, videogames and
forum French-speaking websites. The correspond-
ing URLs contained the associated page titles in most
cases which made it possible for us to use them as is.
The features created based on the raw URLs can be
split into 3 groups:
• keyword presence dummies
Barros, C. and Moreau, P.
User Profiling: On the Road from URLs to Semantic Features.
DOI: 10.5220/0011139900003269
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications (DATA 2022), pages 227-235
ISBN: 978-989-758-583-8; ISSN: 2184-285X
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
227

• topic inference and clustering
• word rarity inference and clustering
2.1 Domain and Keyword Presence
Dummies
As a starting point we created the most simple fea-
tures we possibly could, which consists in checking if
the raw URLs belong to a specific domain or contain
some predefined basic keywords. The list of domains
was built by taking the top 11 to 60 domains with
most distinct visitors. We considered the top 10 do-
mains too widely visited to be discriminative (Google
or Instagram for example) and therefore decided to
cut them from the list.
As for the keywords, these included the French
words for health, news, economy, cook and sport
amongst others.
Table 2 provides an illustration of these features.
Table 2: Dummy features.
URL
1 https://www.doctolib.fr/vaccination-covid-19/paris
2 https://www.lemonde.fr/actualite-en-continu/
3 https://750g.com/macarons-chocolat-r79291.htm
Dummy actu Dummy covid
1 0 1
2 1 0
3 0 0
Dummy lemonde.fr Dummy fnac.com
1 0 0
2 1 0
3 0 0
2.2 Topic Inference and Clustering
The following idea consisted in creating groups of
URLs.
2.2.1 URL Processing
In order to do this, we started by processing the URLs
and transform them into a list of stemmed tokens by
performing the following steps:
1. Tokenisation: URLs are separated on non-
alphabetical characters in order to obtain lists of
words.
https://www.lemonde.fr/ecologie/transition-
ecologique/article/2020/11/23/ville-
autosuffisante-reve-ou-realite 6060816 179.html
⇓
https www lemonde.fr ecologie
transition ecologique article ville
autosuffisante reve ou realit html
2. Cleaning: this included a number of handmade
rules and choices based on our findings:
• domain names removed since it could have a
heavy influence on the upcoming clustering
• extensions (php, html, pdf...), www and http(s)
removed
• tokens shorter than 2 characters removed
• tokens containing 4 or more consecutive vowels
removed
• tokens starting or ending with 2 same letters re-
moved (with some exceptions)
https www lemonde.fr ecologie
transition ecologique article ville
autosuffisante reve ou realit html
⇓
ecologie transition ecologique article
ville autosuffisante reve realite
3. Stemming: this aims to standardise some com-
mon family words by reducing them to the same
stem. Because we are working on URLs, which
might not be the cleanest text data to start with,
we thought doing this was more suitable.
ecologie transition ecologique article
ville autosuffisante reve realite
⇓
transit ecolog articl vill autosuffis
rev realit
Although some of these rules might seem particu-
larly specific, the goal of this was to reduce the num-
ber of residual, meaningless tokens which could intro-
duce noise going forward. These rules could, without
a doubt, be improved and remain always highly de-
pendant on the language (in our case, French, since
we were working on a perimeter of French-language
sites).
2.2.2 Word Embedding
At this point, we have a corpus of stemmed URLs. We
make the assumption that these URLs can be inter-
preted as short documents and proceed to create word
embeds with the popular word2vec technique. Let’s
review some parameters we used:
• Word2vec allows us to chose between a Con-
tinuous Bag Of Words (CBOW) or a Skip-gram
model. We chose to run a Skip-gram model which
DATA 2022 - 11th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
228

seemed more suited to our needs since it tends to
allow for words with different spellings to be con-
sidered close if used in similar contexts.
• The number of neurons in the hidden layer rep-
resents the dimension of the output word vectors,
which is a hyperparameter of the model. Tuning
this can be quite complex, and after some test-
ing with different values, we ended up setting it
to 300, which yields decent clusters.
• We chose to arbitrarily ignore all words appearing
less than 20 times in our corpus of URLs in an at-
tempt to, once again, remove some parasite words
which would probably be poorly represented as
vectors anyways.
• The initial task the Skip-gram model is meant to
achieve is to determine the probabilities of each
word of the vocabulary being in the neighbour-
hood of a given input word. This implies defining
a context window, which will translate what we
mean by neighbourhood. Considering the nature
of our corpus and how small our documents are,
we set the context window to 2.
After training a Skip-gram model on our corpus,
we obtained a vector for each word of our vocabulary.
Here are 2 examples:
v
articl
=
0.603775
0.243117
0.050973
.
.
.
−0.132890
0.039507
v
f ranc
=
0.165156
0.156861
0.162746
.
.
.
0.143844
−0.065017
2.2.3 From Word Embeds to URL Clusters
Having a set of numerical values to represent a word
greatly eases the process of creating clusters of URLs.
In order to achieve this, we started by crafting clusters
of words by performing an agglomerative hierarchical
classification on the word vectors with Ward’s method
for the linkage. We automated the choice of the num-
ber of clusters b between an interval Km, MJ given as
input (for our matter, this ranged between 40 and 60
clusters) by maximising the double differentiation of
the descending intra-class inertia series w
i
:
b = argmax
i∈Km,MJ
(w
i+1
− w
i
) − (w
i
− w
i−1
) (1)
URLs being groups of words, we can represent
them as a distribution of the previous word clusters:
https://www.lemonde.fr/transition-
ecologique/article/2020/11/23/ville-autosuffisante-
reve-ou-realite 6060816 179.html
⇓
transit → Cluster 22
ecolog → Cluster 22
articl → Cluster 35
vill → Cluster 29
autosuffis → Cluster 22
rev → Cluster 6
realit → Cluster 35
⇓
43%
C. 22
14%
C. 29
29%
C. 35
14%
C. 6
We interpret these distributions as if they were
vectors. This means we can compute distances be-
tween URLs using them, and therefore create clusters.
For this purpose, we used the K-means algorithm.
Similarly to the previous word clustering, we auto-
mated the choice of the number of clusters c between
an interval Jn, NK given as input (here, this ranged be-
tween 90 and 110 clusters to account for combina-
tions of words from different clusters) by maximis-
ing the silhouette score. This score varies from -1
to 1, with a score close to 1 indicating that the clus-
ters are well-separated from each other. Below you
can find some URLs put together with some trans-
lations/explanations to help overcome the barrier of
language:
• Cluster 27: This cluster centers on Japanese
anime and manga. Some examples of URLs:
– http://www.mavanimes.co/kono-yo-no-hate-de-koi-wo-utau-
shoujo-yu-no-15-vostfr/
– https://anime-flix.net/episodes/my-hero-academia-3x13/
– https://attaquetitans.com/manga/shingeki-no-kyojin-scan-115/
– https://www.crunchyroll.com/fr/tokyo-revengers/episode-4-return-
811112
• Cluster 45: The focus here is clearly food, with
recipes of all sorts (vanilla flan, Portuguese bean
stew, blueberry and raspberry dragees, ...). Some
examples of URLs:
– http://www.chocodic.com/708-myrtilles-framboises-et-
mirabelles.html
– http://www.lesfoodies.com/1958/recette/feijoada-cassoulet-
portuguais
– https://chefsimon.com/gourmets/gourmandises/recettes/flan-a-la-
vanille
– https://cookidoo.fr/recipes/recipe/fr-FR/r729986
• Cluster 101: Mainly tutorials and advice revolv-
ing around vegetable and fruit culture and garden-
ing. Some examples of URLs:
– http://www.jardicom.fr/p/jardin-deco-eolienne
– https://fr-fr.bakker.com/products/4x-plantes-purif-air-melange
User Profiling: On the Road from URLs to Semantic Features
229

– https://fr.wikihow.com/amender-un-sol-argileux
– https://potagerdurable.com/potager-semer-planter-mai
2.3 Word Rarity Inference and
Clustering
The backbone of this following idea is quite similar
to the previous one, the main difference being how we
represent words as numeric values. The URL process-
ing here is the same as seen before. Furthermore, this
section’s methodology is partly inspired by Olivier
Grisel’s, Lars Buitinck’s and Chyi-Kwei Yau’s code
provided in (Olivier Grisel, 2017).
2.3.1 TF-IDF
TF-IDF (Term Frequency - Inverse Document Fre-
quency) is a method used to give a weight to each
word in each document. This weight will be higher
when:
• the word is frequent in the document in focus
(TF). In practice, this can usually be a raw word
count per document (which we used for our data),
or a logarithmically scaled word count if need be.
• few documents possess this word (IDF). This is
translated by computing, for each word of the vo-
cabulary:
IDF(w
j
) = log
N + 1
df
j
+ 1
, j ∈ {1, . . . ,V } (2)
with:
– V the size of the vocabulary ;
– N the size of the corpus (or number of docu-
ments) ;
– df
i
the number of documents containing the
word w
i
.
The product of both terms gives the final TF-IDF
score for a word in a document:
TF-IDF(d
i
, w
j
) = TF(d
i
, w
j
) × IDF(w
j
), (3)
i, j ∈ {1, . . . , N} × {1, . . . ,V }
This method gives us a representation of each doc-
ument within our vocabulary space. Nevertheless, us-
ing this matrix directly is complicated given the size
of the vocabulary of a corpus (more than 25000 to-
kens). Factorising this matrix will therefore be needed
going forward.
2.3.2 Non-negative Matrix Factorisation
Matrix factorisation is used as a means to reduce di-
mensionality by finding a latent space in which our
input matrix A of dimensions N ×V (the TF-IDF ma-
trix) is factorised into 2 matrices W and H of dimen-
sions N × K and K ×V respectively. Additionally, be-
cause every element of A is positive, we chose to run
a non-negative matrix factorisation (NMF), which has
proven to be most effective in topic extraction like we
are trying to do.
A
(N×V )
≈ W
(N×K)
H
(K×V )
The output matrix W provides a representation of
each document in the latent space of dimension K.
This is a hyperparameter which, similarly to the num-
ber of neurons of the hidden layer of the Skip-gram
model, is complex to tune. After testing several val-
ues, we ended up choosing K = 50.
2.3.3 From NMF to Word and URL Clusters
With a representation of the documents in a smaller,
exploitable space, we proceeded with the same logic
as in the previous section to create word clusters (be-
tween 40 and 60), followed by URL clusters (between
90 and 110).
From our findings, we observed that most word
clusters created with TF-IDF and NMF were com-
posed of a single or few words, unlike the word clus-
ters created with the Skip-gram model. We conse-
quently felt the two methods were complementary,
since on one side we could obtain general topics,
while on the other having some very specific subjects
(focused around few words most of the time). Be-
low you can find some URLs put together with some
translations/explanations to help overcome the barrier
of language:
• Cluster 34: All kind of small ads or offers. Some
examples of URLs:
– https://gensdeconfiance.com/fr/annonce/608697d036864
– http://www.encheres-publiques.com/annonces/vente-maison-
irigny-30987.html
– https://www.leboncoin.fr/ventes immobilieres/1562218012.htm
– https://www.ouestfrance-immo.com/annonce/html
• Cluster 78: Mostly informative pages or wikis.
Some examples of URLs:
– https://animalcrossing.fandom.com/fr/wiki/Mathilda
– https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Louvre
– https://fr.wiktionary.org/wiki/silex
– https://bulbapedia.bulbagarden.net/wiki/Cuvette (Ability)
• Cluster 79: Gathering of contest pages. Some
examples of URLs:
DATA 2022 - 11th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
230

– https://jeu.maisonsdumonde.com/concours/0/5P33o/
– https://www.carrefour.fr/jeux-concours
– https://www.monnaiedeparis.fr/fr/jeu-concours-harry-potter
– https://www.prepamag.fr/concours/main.html
3 CONTENT-BASED FEATURES
The second idea to use URLs for the prediction of
users characteristics is to process and analyse content
of web pages. In fact, we want to establish a connec-
tion between the web pages visited by an user and its
interests. To make this, we decide to not only process
the URL itself but to use the text content of the web
page associated. The recovery of texts from URLs is
possible with a web scraping method that is described
in the following sections.
3.1 Web Content Extraction
3.1.1 Data Preprocessing
From URLs visited by panelists, we create a set of
unique URLs, to process each one only once. A first
cleaning is already made at this point. Indeed, some
URLs of specific categories such as weather, humour
or dating are considered accurate enough. Some oth-
ers do not contain a lot of relevant text content like
personal spaces and search engine homepages, or re-
quire a connection like social networks. These kinds
of URLs represents 25% of the data set, they are re-
moved from it.
3.1.2 Web Scraping
Web scraping is a method that allows to collect struc-
tured data on websites from an URL. It works in two
steps: a HTTP request to a target website and then the
extraction of the data. The source code of the web
page is written in HTML with tags, so we have access
easily to a specific part of the page that we want to
get. This universal structure allows to automate the
process for a huge number of web pages. We limit the
web scraping to textual data and to get a maximum of
information on each web page, we decide to keep the
following tags:
• The name of the document: <title>
• The section titles: <h1> to <h6>
• The various paragraphs of the web page: <p>
All URLs of the data set do not return a result
with the web scraping because some websites block
the collect of data on their web pages. Other issues
can be encountered due to technical errors (web page
not found, refused access, server error etc.). In that
case, the URL is removed from the data set (17.5% is
concerned).
3.1.3 Text Processing
Text contents collected are not usable as is. We need
to process them with text mining methods to uni-
formise them. To operate it, we decide to only keep
texts written in french. Each text is transformed by
the following steps:
1. Tokenisation: words are separated on spaces and
punctuation to obtain a list of words.
Let’s take an example of a translated sentence in a
web page.
”Presidential election in Chile: historic victory
for leftist candidate Gabriel Boric.”
⇓
Presidential election in Chile :
historic victory for leftist
candidate Gabriel Boric .
2. Tagging: grammatical tags are assigned to each
word. This step allows to pool together some
words like proper nouns.
Presidential → adj election → noun
in → prep Chile → pr noun : → punct
historic → adj victory → noun
for → prep leftist → adj
candidate → noun
Gabriel Boric → pr noun . → punct
3. Cleaning: numbers and punctuation are removed
thanks to tags such as some stop-words.
Presidential → adj election → noun
Chile → pr noun historic → adj
victory → noun leftist → adj
candidate → noun
Gabriel Boric → pr noun
4. Lemmatisation: base forms of words are re-
turned.
On the example, we finally get the following list.
presidential election chile historic
victory leftist candidate
Gabriel Boric
Texts are kept if they contain at least 2 words:
20% of the URLs are removed because not enough
text have been found on the web page, or because it
is not written in french. In the end, 50% of the data
User Profiling: On the Road from URLs to Semantic Features
231

set of distinct URLs remains.
The text processing allows to get the vocabulary
of the corpus. The vocabulary is defined by every dis-
tinct word of every web page analysed, and with it,
we can create the term-document matrix. In our case,
a document is equivalent to a web page. So this ma-
trix contains the number of occurrences of each word
on each web page. It is very large and contains a lot
of zeros.
3.2 Theme Creation
In order to extract subjects that are likely to interest
users from visited websites, we create groups based
on contents of all web pages scraped and processed.
These groups are made with a statistical model.
3.2.1 Topic Modeling
A Topic Model is a probabilistic method to reinterpret
texts with a mathematical form, to compute distance
between them, classify them or group them as we
want. We use here Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA).
With this method, we initialise a number of groups
(called topics) expected. The algorithm is based on
the term-document matrix: it processes each word of
each document. For fixed word w and document d, it
makes the following computations.
• The probability having topic t ∈ T in the docu-
ment d.
p
t,1
= P(T = t|D = d) (4)
• The probability having the word w in topic t ∈ T .
p
t,2
= P(W = w|T = t) (5)
For a topic t, the normalised multiplication of these
results gives the probability that the topic t generates
word w in document d. To assign a topic to word w, a
random sampling of a binomial distribution is made,
with the probabilities obtained for every topic as
parameters. Repeating this allows to stabilise topic’s
allocations.
Latent Dirichlet Allocation creates groups from
web pages and especially from words appearing on
it. In the end, we get every topic and the list of words
associated with their probabilities’ distribution. We
can analyse the topics among themselves (Figure 1)
and their composition (Figure 2).
From these results, we can average probabilities of
words which are on a web page to get the distribution
of topics on the web page (Table 3).
It is essential to note that topic models don’t give
any guarantee on the interpretability of topics created.
Figure 1: PyLDAvis animation with the distribution of top-
ics created with Principal Component Analysis. The more
the point is big, the more the topic is frequent in the corpus
of web pages. Two points nearby on the graph means that
their vocabulary is close.
Figure 2: PyLDAvis animation with the list of words (trans-
lated into English) in a topic example. Red color represents
the frequency of words in the topic, and blue color the fre-
quency of words in all the corpus.
3.2.2 Relevance of the Model
To get the best possible results, we make several tests
of LDA models. We can vary:
• The number of topics expected. The more this
number is high, the more topics are likely to be
precise, but sometimes too specific. On the con-
trary, a low number of topics will produce general
groups that can contain various subjects in itself.
• The size of the vocabulary. We decide to set min-
imum and maximum thresholds of occurrences in
the vocabulary. Words too occasional or exces-
sively common could affect the model.
We decide to keep default values for other parameters
of LDA model.
To evaluate a LDA model, and in particular choose
the optimal number of topics, we compute some met-
rics. First, perplexity allows to see the behaviour of
the model on unseen data since it is based on a test set
of documents D
test
.
DATA 2022 - 11th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
232

Table 3: Example of distribution in n topics created with
LDA on our 3 previous examples.
URL
https://www.doctolib.fr/vaccination-covid-19/paris
https://www.lemonde.fr/actualite-en-continu/
https://www.750g.com/macarons-chocolat-r79291.htm
Topic n°1 Topic n°2 ... Topic n°n
0.32 0.08 ... 0.01
0.00 0.20 ... 0.13
0.67 0.01 ... 0.09
perplexity(D
test
) = exp
−
∑
M
d=1
log p(w
d
)
∑
M
d=1
N
d
(6)
M represents the number of documents in the test
set, w
d
the words in document d and N
d
the number
of words in document d.
A low score indicates a best performance of gen-
eralisation of the model. However, a known limit is
that optimising for perplexity may not yield human
interpretable topics.
The coherence score in topic modeling is used to
measure how interpretable topics are to humans.
C
UMass
(w
i
, w
j
) = log
D(w
i
, w
j
) + 1
D(w
i
)
(7)
D(w
i
, w
j
) indicates how many times words w
i
and
w
j
appear together in documents, D(w
i
) is how many
time word w
i
appear alone.
The global coherence of the topic is the average
score on the top N words which describe the topic.
The greater the score is, the better is the coherence.
After trying multiple LDA models with different
parameters, we compare the perplexity and coherence
scores to choose the best model: in our case, it creates
50 topics, and the size of the vocabulary is 1136
words (words must appear on at least 2% of the web
pages of the corpus).
Distribution of probabilities of URL on topics will
be used as features in a model to predict a target,
which is detailed in section 4. It has to be noted that
topics are groups of words that we consider as themes
people can be interested in or not, but here the topics
are not always interpretable for humans.
Figure 3: Examples of words (translated into English) form-
ing topics quite easily interpretable by humans.
Figure 4: Words (translated into English) forming a topic
hard to interpret.
4 IMPACT OF THE ADDITION OF
THESE FEATURES
In this section, we propose to learn a model on the
created features to observe their impact in applica-
tion. The considered target of the model is the socio-
demographic category Woman aged between 25 and
49 years old. Target value is 1 if the panelist is part of
the category, 0 otherwise.
4.1 Input Data Creation
First, we decide to limit the perimeter to 7 days of
web navigation of panelists, which represents roughly
2 million logs (with nearly 400000 belonging to the
target).
Since the target is user-wise, we need to summarise
each panelist’s surf on the period in order to get a
unique value for every feature. The rule chosen de-
pends on the feature’s type:
• Domain and keyword presence dummies as
well as URL clusters are transformed as a per-
cent of logs by user.
• Word clusters and Topics on content are aver-
aged by user.
After this aggregation, we have 459 features for a
User Profiling: On the Road from URLs to Semantic Features
233
total of 8993 rows as the number of users (1829 in tar-
get). On table 4 you shall find the number of features
for each group.
Table 4: Number of features per group.
Group Features #
G1 Domain and keyword features 96
G2 Topic cluster features 152
G3 Word rarity cluster features 161
G4 Content features 50
TOTAL 459
The data is split in two sets to learn the models on
80% of the panelists and test them on the remaining
20%. This division is made with a draw by stratifica-
tion according to the target.
4.2 Modeling
We decide to run several models, each one consider-
ing one or several groups of the features created in
order to evaluate the impact of each group. Table 5
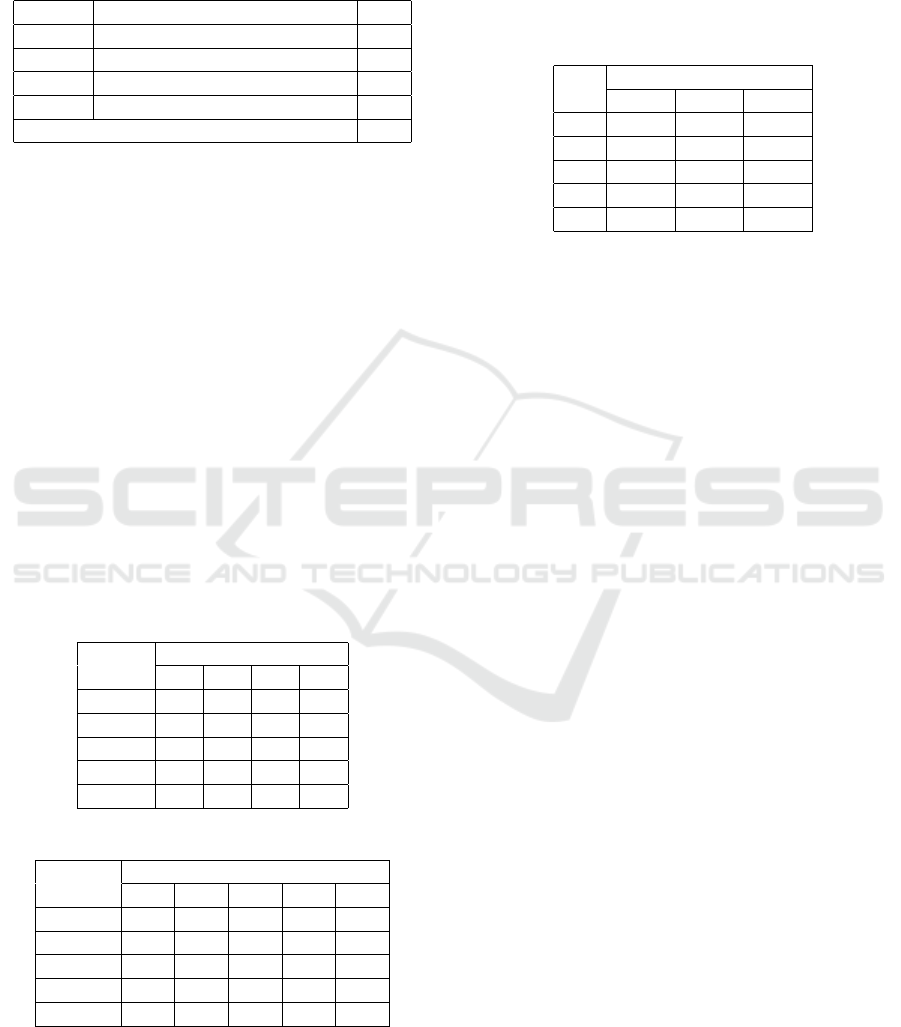
summarises the features used for each model.
For each model we make a feature selection with
Random Forest Feature Importance. For compari-
son purposes, we set to 100 the number of features
to keep. The single exception comes in Model 1, in
which only the 96 features from G1 are taken into ac-
count, and therefore no feature selection is applied.
The number of features selected per group can be ob-
served in table 6.
Table 5: Groups of features considered in each model.
Model
Group of features
G1 G2 G3 G4
M1 ×
M2 × ×
M3 × ×
M4 × ×
M5 × × × ×
Table 6: Number of features selected in each model.
Group
# of features selected in model
M1 M2 M3 M4 M5
G1 96 25 37 50 16
G2 0 75 0 0 41
G3 0 0 63 0 20
G4 0 0 0 50 23
TOTAL 96 100 100 100 100
The classifier used is a Random Forest and some
basic parameters are tuned, namely the number of
trees, the depth of the trees and the maximum number
of features selected in each node. The model is then
fitted on the train set, and outputs the probability for
each user in the test set to be in the target. Finally, we
proceed to computing precisions and recalls for every
probability threshold and compare the precisions as-
sociated to 3 recall benchmarks of each model. These
are summarised in table 7.
Table 7: Precisions for each model.
Recall
0.1 0.25 0.4
M1 0.385 0.368 0.268
M2 0.474 0.395 0.331
M3 0.468 0.405 0.342
M4 0.42 0.362 0.315
M5 0.544 0.434 0.346
4.3 Results Analysis
Model 1, which is the worst performing model over-
all, was intended to set a benchmark for comparison
purposes with the following models, so no big sur-
prises there.
Models 2 and 3 correspond to the models with fea-
tures created from the raw URL (in addition to the
domain and keyword features). These 2 models yield
close results, but Model 3 has a higher proportion
of features selected coming from the keywords and
domains. The features from group G1 being more
general, they complement probably better the clus-
ters created through TFIDF and NMF, which are more
specific.
Regarding content features used in Model 4, even
if they seem precise because based on the web pages,
we saw that the process was not practicable on every
URL. In particular, if the period considered is distant
from the moment data is scraped, many URL have
disappeared or their content is empty. The fact that
almost 70% of the logs have finally no distribution in
topics is a significant limit.
At last, Model 5 takes the best each group has to
offer and performs the best with a fairly large margin.
Overall, it improves the results by 30 to 40% depend-
ing on the recall threshold.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we reviewed different ways to exploit
URLs with the goal of creating meaningful features.
Some are more general than others, but as we have
seen, every group has its share of important, discrimi-
native features. Although the current results speak for
themselves, one might argue we should test the fea-
DATA 2022 - 11th International Conference on Data Science, Technology and Applications
234

tures with other classifiers and targets to make further
conclusions.
However, an improvement we could consider is
the use of the time spent on the web page, which is a
notion we have. A user could be weighted in a spe-
cific topic if they have spent more time on web pages
deeply associated to this topic. Moreover, we solely
focused on the URLs and their content in this paper,
but it should be noted that these features can be part
of a bigger project in which other information is used
in the feature engineering step, like the timestamps,
or the device used, which were not discussed here.
REFERENCES
Chen, E. (2011). Introduction to Latent Dirichlet Alloca-
tion. http://blog.echen.me/2011/08/22/introduction-
to-latent-dirichlet-allocation/.
David M. Blei, Andrew Y. Ng, M. I. J. (2003). Latent
Dirichlet Allocation. Journal of Machine Learning
Research 3.
McCormick, C. (2016). Word2Vec Tutorial - The Skip-
Gram Model. http://mccormickml.com/2016/04/
19/word2vec-tutorial-the-skip-gram-model/.
Mitchell, R. (2015). Web Scraping with Python.
Olivier Grisel, Lars Buitinck, C.-K. Y. (2017). Topic ex-
traction with Non-negative Matrix Factorization and
Latent Dirichlet Allocation. https://scikit-learn.org/st
able/auto examples/applications/plot topics extractio
n with nmf lda.html.
Prabhakaran, S. (2018). LDA in Python – How to grid
search best topic models? https://www.machinel
earningplus.com/nlp/topic-modeling-python-sklearn-
examples/#13compareldamodelperformancescores.
User Profiling: On the Road from URLs to Semantic Features
235
