
Study on Microbial Population Difference for the Treatment of
Domestic Sewage between Micro-Pressure Swirl Reactor (MPSR) and
SBR
Hua Kang
1,2 a
, Fan Wang
1,2 b
, Wenai Liu
1,2 c
, Xichao Wang
2,3 d
, Lubo Shao
1,2 e
and Dejun Bian
1,2,* f
1
School of Water Conservancy and Environmental Engineering, Changchun Institute of Technology, 395 Kuanping Road,
Changchun, China
2
Key Laboratory of Urban Sewage Treatment of Jilin Province, Changchun, China
3
Changchun Municipal Engineering & Research Institute Co., Ltd., 855 Kunshan Road, Changchun, China
*Corresponding Author
Keywords: Micro-Pressure Swirl Reactor (MPSR), Microbial Community Structure, High-Throughput Sequencing.
Abstract: The comparative study on the microbial community structure of activated sludge from micro-pressure swirl
reactor (MPSR) and SBR under stable operation was conducted by the 16S rRNA third-generation high-
throughput sequencing, which was sampled from simulated domestic sewage. The experimental results
indicated that the two reactors had great differences in the microbial community structure of activated sludge
due to the different circulating flow patterns under the same water quality and intermittent operation mode.
Compared with SBR, MPSR had more dominant bacteria phyla and some functional bacteria of higher relative
abundance such as Flavobacterium and Thiotrix, and simultaneously strictly anaerobic, strictly aerobic and
facultative anaerobic microbial species existed so as to produce higher species diversity and population
richness, which is accord with the polyphase theory of the reactor.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
In the urban sewage treatment system, activated
sludge is very important for the removal of pollutants,
and the microbial community structure will directly
affect the stability and treatment efficiency of sewage
biological treatment. Therefore, the diversity of
community structure and dominant bacteria are one
of the main indicators to evaluate the structure and
function of sewage treatment system (Tian 2020).
Many scholars pointed out that the activated sludge
of sewage treatment plant had high species diversity
and community richness, and the influent quality,
process composition and operating conditions have a
certain impact on the microbial community structure
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1093-3168
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8688-6102
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2182-1604
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5198-8037
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9908-0335
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6188-6560
of activated sludge (Ma 2021, Chang 2021, Li 2021).
However, there are few comparative studies on the
microbial community structure of activated sludge
with different process types.
MPSR is a new sewage treatment device with
anaerobic, anoxic and aerobic environments
coexisted, which has good organic matter removal,
nitrogen and phosphorus removal effects (Bian 2020,
Bian 2020). In this study, high-throughput
sequencing technology was used to study the
microbial community structure of MPSR and SBR in
order to provide a theoretical basis for the
optimization of Activated Sludge Method wastewater
treatment process performance and provide reference
for subsequent research.
Kang, H., Wang, F., Liu, W., Wang, X., Shao, L. and Bian, D.
Study on Microbial Population Difference for the Treatment of Domestic Sewage between Micro-pressure Swirl Reactor (MPSR) and SBR.
DOI: 10.5220/0011177100003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 31-35
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
31
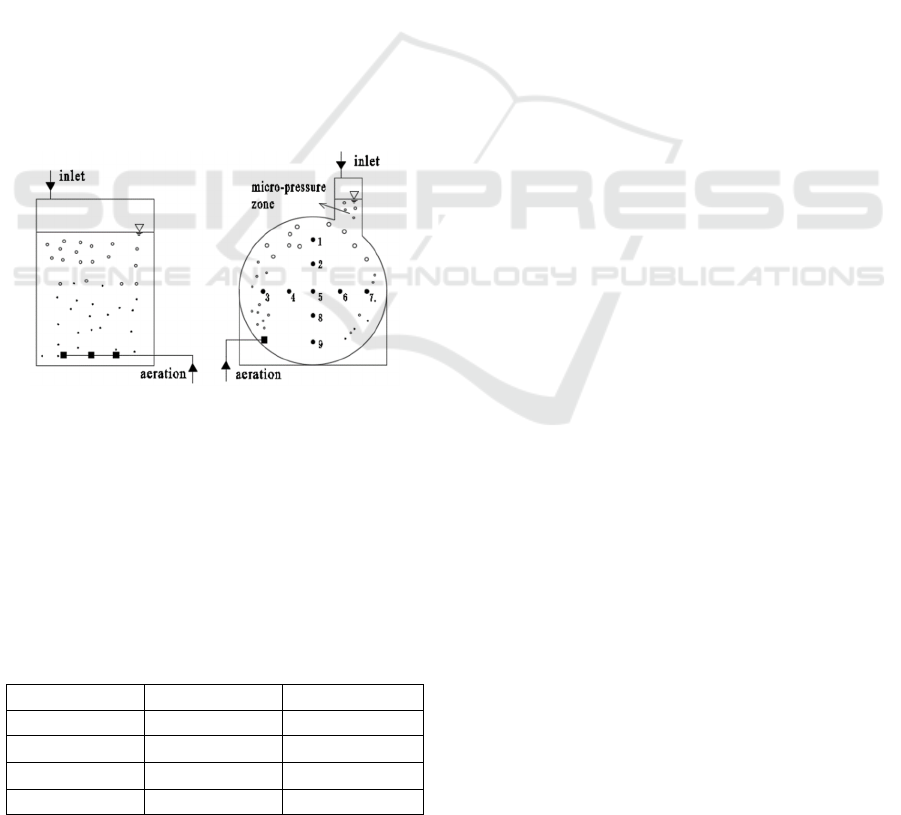
2 MATERIAL AND METHOD
2.1 Test Devices
The test device was shown in Figure 1. The effective
volumes of reactors were both 36L. The size of the
SBR was 300mm long, 300mm wide and 500mm
high. MPSR included two parts, the main reaction
zone and micro-pressure zone. The main reaction
zone was a diameter of 900mm and 90mm wide, and
the micro pressure zone was 130mm long, 90mm
wide and 400mm high. The flow rate of MPSR
gradually decreased from outside to inside, and the
concentration of DO also showed an obvious gradient
change from outside (2.02mg/L) to inside (lower than
0.05mg/L) (Bian 2020). SBR sludge was sampled
about 200mm below the liquid level, and MPSR
sludge was sampled from the mixed liquid at the nine
points in Figure 1. The inoculated sludge was taken
from an aeration tank of a sewage treatment plant at
Changchun, and the initial sludge concentration of the
mixed liquid was 2000mg/L. After aeration culture,
the sludge was evenly divided into two reactors
(abbreviated as R).
(a)SBR (b)MPSR
Figure 1: Test devices
2.2 Experiment Water Quality
The synthetic wastewater was used to simulate
domestic sewage, which including nutrients and trace
elements required by microorganisms from beef
extract, peptone, starch and etc. The concentration of
main water quality indexes was shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Influent water quality.
Index Range Average
COD/mg·L
-1
305.2~386.0 338.1
NH
4
+
-N/mg·L
-1
29.8~36.4 31.4
TN/mg·L
-1
32.1~38.6 34.2
TP/mg·L
-1
2.5~4.5 3.2
2.3 Operating Condition
The two reactors were operated for two cycles every
day, with cycle time of 12h including 8h of aeration
(initial 5min of feeding), 3h of sedimentation, 10min
of drainage and 50min of free time. The aeration
capacity was 1.5L/min, and the operating temperature
was (20±1) ℃. The sludge residence time (SRT) was
22d, and the drainage ratio was 0.5. The two systems
operated stably for 30 days. During the operation, the
average removal rates of COD, NH
4
+
-N, TN and TP
of SBR were 92.0%, 98.8%, 66.3% and 95.8%
respectively, while 94.0%, 98.8%, 75.6% and 98.6%
in MPSR.
2.4 High-throughput Sequencing
Total genomic DNA samples were extracted using the
OMEGA Soil DNA Kit (M5635-02) (Omega Bio-
Tek, Norcross, GA, USA), following the
manufacturer’s instructions, and stored at -20°C prior
to further analysis. The quantity and quality of
extracted DNAs were measured using a NanoDrop
NC2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and agarose gel
electrophoresis, respectively.
The extracted DNA was amplified with two-step
PCR, with sample-specific 16-bp barcodes were
incorporated into the forward and reverse primers for
multiplex sequencing in the second PCR step. A total
of PCR amplicons were purified with Agencourt
AMPure Beads (Beckman Coulter, Indianapolis, IN)
and quantified using the PicoGreen dsDNA Assay Kit
(Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). After the
individual quantification step, amplicons were pooled
in equal amounts, and Single Molecule Real Time
(SMRT) sequencing technology was performed using
the PacBio Sequel platform at Shanghai Personal
Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Microbial Alpha Diversity Analysis
The statistical results of the samples were shown in
Table 2. It showed Chao1 of MPSR was the largest,
followed by R and SBR, indicating that the
population abundance in MPSR is the highest. The
order of Shannon and Simpson value was R > MPSR
> SBR, indicating that the community diversity of
MPSR was better than SBR. The good's coverage
values of the three samples all reached 0.94, which
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
32

indicated that the high-throughput sequencing results
of the samples were in good agreement with the real
situation and could represent the real situation of the
samples.
Table 2: Statistics of activated sludge population abundance
and diversity index.
Index
Sample
R MPSR SBR
Chao1 458.43
484.48 418.42
Simpson 0.98
0.92
0.85
Shannon 7.20
6.02
4.91
Good's
coverage
0.94 0.93 0.94
3.2 Species Community Differences
The number of OTU clusters of R, MPSR and SBR
samples were represented by Venn diagram. As
shown in Figure 2, the OTU numbers of R, MPSR and
SBR were 387, 316 and 263 respectively, and the
species numbers of both reactors decreased after 30
days. The number of unique species in the three
samples was 159, 86 and 92, respectively, and owned
number of OTU was 79 (12.91%), which meant quite
different species communities. After the activated
sludge was cultured in their respective reactors, the
microbial environmental conditions changed, and
different dominant bacteria was formed in the system
due to the different internal structures of MPSR and
SBR.
Figure 2: Wayne diagram of OTU distribution of sludge
sample.
Species number and relative abundance were
counted from top20 phylum levels of the average
abundance of the sample. The results showed that
there were 2114, 3708 and 4712 species inside R,
MPSR and SBR, respectively. The number of species
in MPSR and SBR increased by 75.4% and 122.9%
respectively, indicating that the two processes
provided a good living environment for
microorganisms and improved species diversity.
Proteobacteia were major group in all the sludge
systems, followed by Bacteroidetes, Chloroflexi and
Actinobacteria. However, the abundance of sludge
samples varied significantly (Figure 3a).
3.3 Species Abundance Composition
As can be seen from Figure 3a, the dominant bacteria
phyla in SBR were Proteobactia (60.2%), Chloroflexi
(14.7%) and Bacteroidetes (11.9%), of which
Proteobactia was the most dominant phyla involved
in nitrogen and phosphorus removal and organic
matter degradation (Zhang 2015). The dominant
phyla of MPSR were Proteobacteia (29.7%),
Bacteroidetes (15.0%), Chloroflexi (7.6%),
Actinobacteria (6.9%), Firmicutes (3.4%) and other
phyla greater than 1% including Nitrospirae,
Plantomycetes and Verrucomicrobia, while another
32% of the species were not clear. Compared with
SBR, MPSR had more dominant bacteria phyla and
richer species.
As can be seen from Figure 3b, Thauera was the
main dominant bacteria of R, while its abundances
were reduced in both reactors, substitute for more
suitable for their own environment. Thiotrix occupied
a relatively high abundance in SBR. It belongs to
chemoautotrophic flora and plays a major role in
nitrification of the denitrification process. In MPSR,
nitrification and denitrification were in progress
simultaneously, and the dominant flora were various
functional flora such as Flavobacterium dominated by
heterotrophic denitrification and Thiotrix dominated
by nitrification (Zhang 2019).
(a) phylum
Study on Microbial Population Difference for the Treatment of Domestic Sewage between Micro-pressure Swirl Reactor (MPSR) and SBR
33
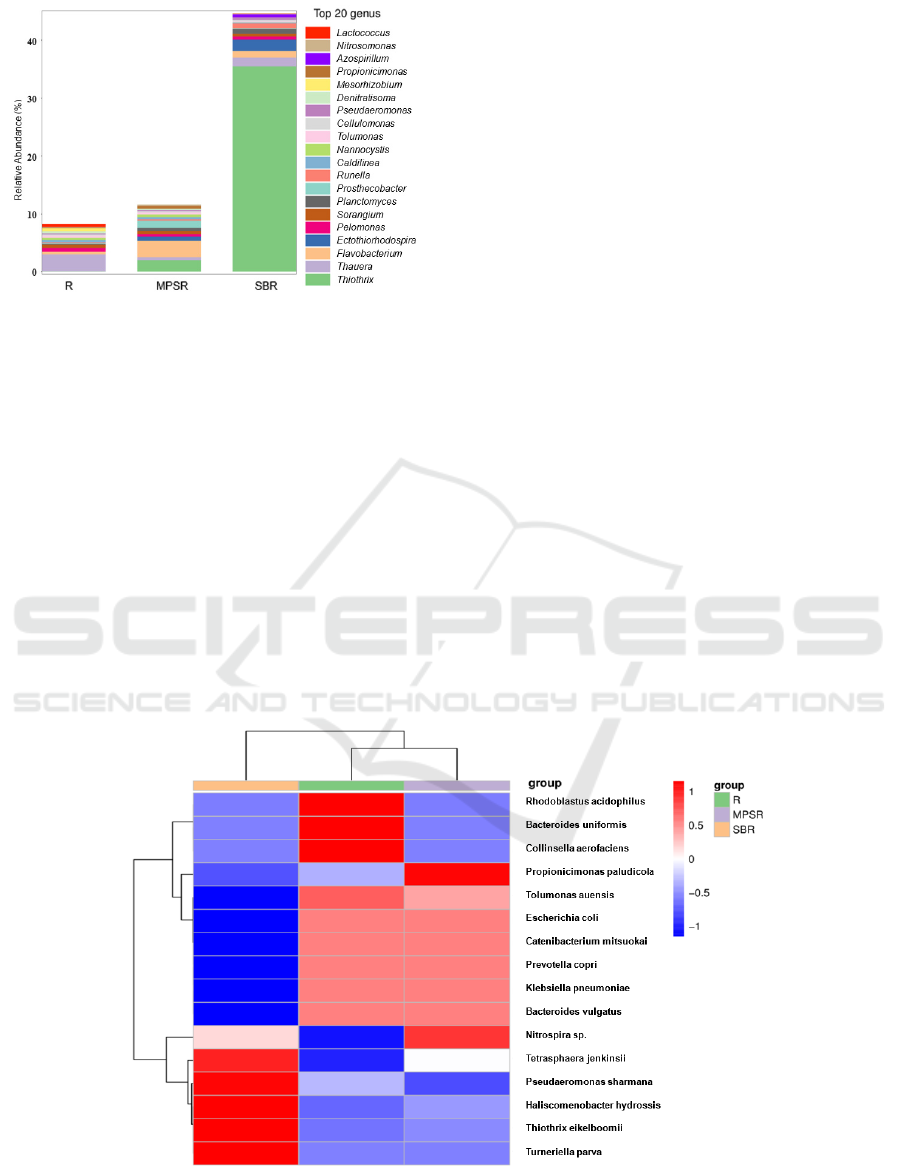
(b)genus
Figure 3: Species abundance of different sludge samples.
3.4 Species Composition Heat Map
In order to further compare the species composition
differences between samples, the abundance data of
top50 species in the average abundance were used to
draw a heat map for species composition analysis. In
the Figure 4, the red color block indicates that the
abundance of this species in this sample is higher than
that in other samples, and the blue color block
indicates that the abundance of this species in this
sample is lower than that in other samples.
The bacterial clustering results of three sludge
samples R, MPSR and SBR showed that there were
significant differences in microbial abundance
between the two reactors, which was due to the
effects of different circulating flow patterns and
oxygen environment on microbial flora. In MPSR
samples, the abundances of Propionicimonas
paludicola, Nitrospira sp. and Prevotella Copri were
larger, and in SBR samples, the dominant bacteria
were Thiothrix eikelboomii, Haliscomenobacter
hydrossis and etc.
Propionicimonas paludicola was a Gram-positive
bacterium, belonging to Actinobacteria. It was
facultative anaerobic and chemotrophic
heterotrophic, which could ferment and metabolize
glucose and other carbohydrates into a large amount
of acetic acid and propionic acid. Nitrospira sp. was a
gram-negative bacterium, belonging to Nitrospirae. It
was strictly aerobic and could oxidize nitrite into
nitrate to obtain energy which was the main nitrite
bacteria in the sewage treatment system (Siripong
2007). Prevotella Copri was a polymorphous
bacterium and did not produce spores. It was strictly
anaerobic and chemotrophic heterotrophic which
could use organic matter for anaerobic fermentation.
Therefore, compared with aerobic bacteria in SBR,
there were dominant microbial species of strict
anaerobic, strict aerobic and facultative anaerobic
inside MPSR. From the perspective of
microorganisms, the multiphase theory of MPSR was
proved and the function of simultaneous nitrification
and denitrification in multi-oxygen environment was
realized.
SBR R MPSR
Figure 4: Species level species composition heat map based on double clustering.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
34

4 CONCLUSIONS
Although water quality and intermittent operation
mode were the same, the two reactors had significant
differences in microbial community structure due to
different circulating flow patterns. Compared with
SBR, MPSR had more dominant bacteria phyla and
some functional bacteria of higher relative abundance
such as Flavobacterium and Thiotrix, and there
existed strictly anaerobic, strictly aerobic and
facultative anaerobic microbial species
simultaneously so as to produce higher species
diversity and population richness, which is accord
with the polyphase theory of the reactor.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research was funded by the Project of science and
technology development plan of Jilin Province
(20210101079JC), Project of ecology and
environment department of Jilin Province (2021-14),
Project of science and technology fund of school
(320200030).
REFERENCES
Bian, D. J., Wang, X. C., Ai, S. S., Wang, F., Liu, S. L. &
Zhu, S. Y. (2020). Comparison of pollutants removal
and sludge characteristics between micro-pressure swirl
reactor and sequencing batch reactor. J. Environmental
Pollution and Control. 42, 11:1315-1318.
Bian, D. J., Nie, Z. B., Wang, F., Ai, S. S., Zhu, S. Y. &
Guo, H. Y. (2020). Micro-pressure swirl reactor
(MPSR) for efficient COD and nitrogen removal of
high-concentration wastewater. J. Water Science &
Technology. 82, 9: 1795-1807.
Chang, M. & Ma, H. R. (2021). High-throughput
sequencing analysis of sludge microbial communities
under different anaerobic treatment processes. J.
Leather Science and Engineering. 31, 4:17-21.
Li, Y., Chen, W., Zheng, X. Y., Liu, Q., Wei, X., Qu, J. X.
& Yang, C. F. (2021). Microbial community structure
analysis in a hybrid membrane bioreactor via high-
throughput sequencing. J. Chemosphere. 282, 130989.
Ma, Q. Q., Yuan, L. J., Niu, Z. D., Zhao, J. & Huang, C.
(2021). Microbial community structure of activated
sludge and its response to environmental factors. J.
Environmental Science. 42, 8: 3886-3893.
Siripong, S. & Rittmann, B. E. (2007). Diversity study of
nitrifying bacteria in full-scale municipal wastewater
treatment plants. J. Water Research. 41, 5: 1110-1120.
Tian, L. & Wang, L. (2020). A meta-analysis of microbial
community structures and associated metabolic
potential of municipal wastewater treatment plants in
global scope. J. Environ. Pollut. 263, 114598.
Zhang, Z. & Tang, B. (2015). Research progress in the
microbial community and its functional characteristics
in activated sludge systems. J. Industrial Water
Treatment. 35, 3: 5-8.
Zhang, X. H., Jiang, B., Zhang, W. W., Chen, L. M. & Guo,
H. L. (2019). Microbial community diversity of
activated sludge from municipal wastewater treatment
plants in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Microbiology
China. 46, 8: 1896-1906.
Study on Microbial Population Difference for the Treatment of Domestic Sewage between Micro-pressure Swirl Reactor (MPSR) and SBR
35
