
Study on the Adsorption Technology of Chitosan to the Protein in
Tofu Yellow Slurry Water
Cili Li
1a
and Jianbo Cheng
2b
1
College of food engineering, Harbin University of Commerce, Harbin 150028, China
2
Heilongjiang Feihe Dairy Co., Ltd., Qiqihar 161005, China
Keywords: Tofu Yellow Slurry Water, Chitosan, Protein, Adsorption.
Abstract: In this paper, the protein removal rate was used as an indicator to study the effects of the amount of chitosan
added, reaction time, reaction temperature, and pH on the process of chitosan's adsorption of protein in tofu
yellow slurry water. Orthogonal experiments were used to determine the optimal reaction conditions. The
results show that, optimum conditions for chitosan to adsorb protein in tofu yellow slurry water: chitosan
added 1.0g/L, pH 7, temperature 20℃, the response time is 3h, the removaling rate is 51.64%. The results
show that chitosan can be utilized to the process of the recycling of soybean protein and Tofu yellow slurry
water.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Soybean is one of the main food and oil crops in the
world. Processed products using soybeans as raw
materials are favored by consumers because
soybeans are rich in high-quality protein, calcium,
potassium, iron, copper, zinc and other trace
elements, vitamin B1 and B2, organic acids and
cellulose and other nutrients (Diao, 2015, Wang,
2019). The most popular food developed with
soybeans as a raw material by consumers is
traditional tofu. A large amount of yellow slurry
water is generated in the production of tofu. It is
estimated that 8-10 tons of wastewater will be
generated from processing 1 ton of soybeans (Du,
2008). Tofu yellow slurry water is produced in the
process of extracting tofu from soy milk and alkali-
dissolved supernatant. According to the current
research status (Che, 2017), yellow slurry water
contains a lot of organic matter, which contains
about 1700 mg/L of oil, 3800~4000mg/L of protein,
7000~20000 mg/L of total sugar, and 800~1700 mg
of total nitrogen (TN). /L, total phosphorus (TP)
100~200mg/L, BOD5 value is about
5000~10000mg, COD value is 20000~24000mg, it
is a kind of wastewater with high concentration and
high degree of biodegradability (Xie, 2009).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7519-7790
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2481-7985
Therefore, if the protein in the fermented tofu yellow
slurry water can be effectively recovered, not only
the utilization of raw materials will be improved, but
the sewage will be purified, and the pressure of
subsequent sewage treatment will be reduced,
thereby realizing the unification of environmental
and economic benefits.
Chitosan is a natural biopolymer of basic amino
polysaccharides, which is the product of
deacetylation of chitin. Chitosan has excellent
biocompatibility, non-toxicity and easy chemical
modification (Xie, 2013, Chen, 2001). Studies have
found that chitosan can be used as a flocculant for
water treatment. It has good effects in the treatment
of food wastewater, papermaking wastewater and
urban domestic wastewater. This paper studies the
flocculation conditions of chitosan to adsorb protein
in tofu yellow slurry water, which can provide a
certain theoretical basis for the treatment of tofu
yellow slurry wate.
64
Li, C. and Cheng, J.
Study on the Adsorption Technology of Chitosan to the Protein in Tofu Yellow Slurry Water.
DOI: 10.5220/0011180500003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 64-69
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials and Reagents
Soybeans, Northeast soybeans are commercially
available. Chemical reagents such as sodium
hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, and
methyl orange are all analytically pure. Chitosan,
Zhejiang Golden Shell Biochemical Co., Ltd.;
Bovine Serum Protein, Jilin Boshen Biotechnology
Co., Ltd..
2.2 Instruments and Equipment
Model 752 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer, Shanghai
Spectrometer Co., Ltd.; HZS-H Water Bath
Oscillator, Harbin Donglian Electronic Technology
Development Co., Ltd.; PHS-25 Digital Display pH
Meter, Shanghai Precision Scientific Instrument Co.,
Ltd.; ALC-2100 electronic balance, Shanghai
Precision Instrument Co., Ltd.; DHG-9123A electric
heating constant temperature blast drying oven,
Shanghai Yuejin Medical Equipment Factory; DK-
98-II electric heating constant temperature water
bath, Shanghai Yuejin Medical Equipment Factory;
JB-1 timing two-way Magnetic stirrer, Jiangsu
JintanRonghua Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd.;
80-2 centrifuge, Shanghai Anting Instrument
Factory; HZQ-C air bath oscillator Harbin Donglian
Electronic Technology Development Co., Ltd.,
DHP-9162 electric heating constant temperature
incubator Shanghai Yiheng Technology Co., Ltd..
2.3 Method
2.3.1 Preparation of Tofu Yellow Slurry
Water
Evenly take the tofu whey wastewater (yellow slurry
water) discharged when the traditional method is
used to produce tofu. 1 kg of raw soybeans produces
2.5 kg of tofu and discharges 8.95 kg of yellow
water.
2.3.2 Preparation of Chitosan Solution
The experiment uses glacial acetic acid to prepare
1% chitosan solution. Specific steps: (1) Configure
1% acetic acid solution. (2) Add an appropriate
amount of chitosan to 1% acetic acid solution, and
prepare 1% chitosan solution. A magnetic stirrer can
be used to help chitosan dissolve uniformly in acetic
acid.
2.3.3 Determination of the Degree of
Deacetylation of Chitosan
In the experiment, the degree of deacetylation of
chitosan was measured by acid-base titration. The
specific steps are as follows: accurately weigh
0.3~0.5g of chitosan dried to constant weight at
105℃, put it in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, add
30mL of 0.1mol/L hydrochloric acid standard
solution, and stir at 20℃~25℃ until it is completely
dissolved, Add 2~3 drops of methyl orange
indicator, titrate free hydrochloric acid with
0.1mol/L sodium hydroxide standard solution to the
end point (WU S H, 2009). Deacetylation degree
calculation formula:
Free amino content
(
−𝑁𝐻
)
%=
(
)
×.×%
Degree of deacetylation =
(
)%×%
.%
Where:
C1-Concentration of hydrochloric acid standard
solution, mol∕L
C2-Concentration of sodium hydroxide standard
solution, mol∕L
V1-The volume of hydrochloric acid standard
solution added, mL
V2-The volume of sodium hydroxide standard
solution consumed during titration, mL
G-Sample weight, g
0.016-The amount of amino group equivalent to
1mL 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution, g
9.94%-Theoretical amino content.
2.3.4 Single-factor Experiment of Protein
Adsorption in Tofu Yellow Slurry
Water
The Effect of Chitosan Addition on Protein
Removal Rate.
Take five 50mL colorimetric
tubes, and add 50mL tofu yellow slurry water,
labeled 1~5. Maintain the pH of the original
wastewater. Add 1% chitosan solution to No. 1~5
respectively, that is, the amount of chitosan added:
0.4g/L, 0.6g/L, 0.8g/L, 1.0g/L, 1.2g/L. The protein
removal rate is used as an indicator to determine the
optimal amount of chitosan added.
The Effect of pH on Protein Removal Rate.
Take eight 50mL colorimetric tubes, add 50mL of
tofu yellow slurry water, labeled 1~8, add chitosan
to 0.8 g/L, and adjust the pH to 3.08, 3.99, 5.04,
5.97, 6.14, 6.52, 7.07, 7.98, respectively. The protein
removal rate is an indicator to determine the optimal
pH.
Study on the Adsorption Technology of Chitosan to the Protein in Tofu Yellow Slurry Water
65
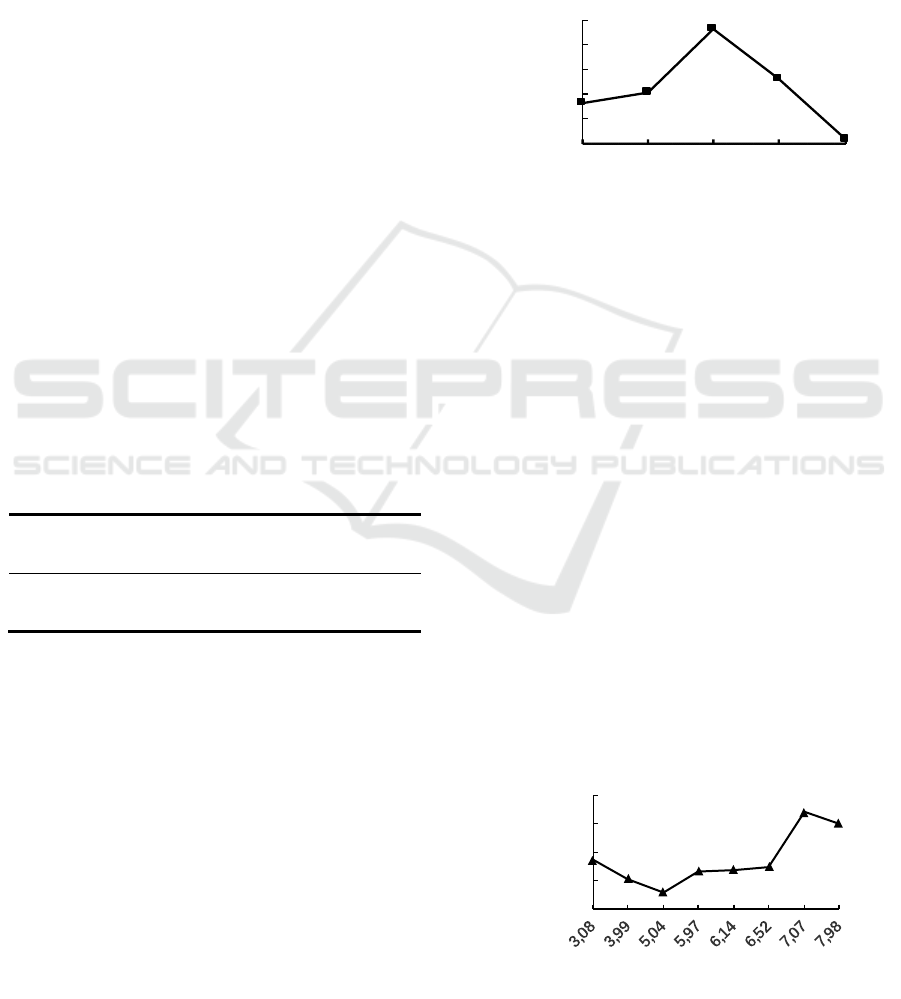
0
10
20
30
40
Protein removal rate/%
pH
0
5
10
15
20
25
0,4 0,6 0,8 1 1,
2
Protein removal rate/%
Chi tosan addition/g.L-1
The Effect of Temperature on Protein
Removal Rate.
Take five 50mL colorimetric
tubes, label 1~5 and add 50mL tofu yellow water.
The amount of chitosan added was 0.8 g/L, the pH
was 7.07, and the reaction temperature was
controlled at 5°C, 17°C, 25°C, 35°C, and 45°C. The
protein removal rate was used to determine the
optimal reaction temperature.
The Effect of Reaction Time on Protein
Removal Rate.
Take five 50mL colorimetric
tubes, and add 50mL tofu yellow slurry water,
labeled 1~5. The amount of chitosan added was 0.8
g/L, the pH was 7.07, the temperature was 25°C, the
reaction time was controlled to 1h, 2h, 3h, 4h, 5h,
and the protein removal rate was used to determine
the optimal reaction time.
2.3.5 Orthogonal Experiment on the
Absorption of Protein in Tofu Yellow
Slurry Water
According to the results of the single factor
experiment, the reaction time is controlled to 3h, and
the addition amount of chitosan, pH, and reaction
temperature are selected as factors for L9 (34)
orthogonal test. The protein removal rate is used as
an indicator to determine the best process
conditions. The experimental design is shown in
Table 1.
Table 1: Test factor level table.
Level
A
pH
B
the addition amount of
chitosan/g﹒L
-1
C
T/℃
1
2
3
6.5
7
7.5
0.6
0.8
1.0
20
25
30
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Determination of the Degree of
Deacetylation of Chitosan
The degree of deacetylation of chitosan was
determined according to 1.3.3, and the degree of
deacetylation of chitosan used in the test was 72.4%.
3.2 Single-factor Experiment of Protein
Adsorption in Tofu Yellow Slurry
Water
3.2.1 The Effect of Chitosan Addition on
Protein Removal Rate
The relationship between the amount of chitosan
added and the protein removal rate is shown in
Figure 1:
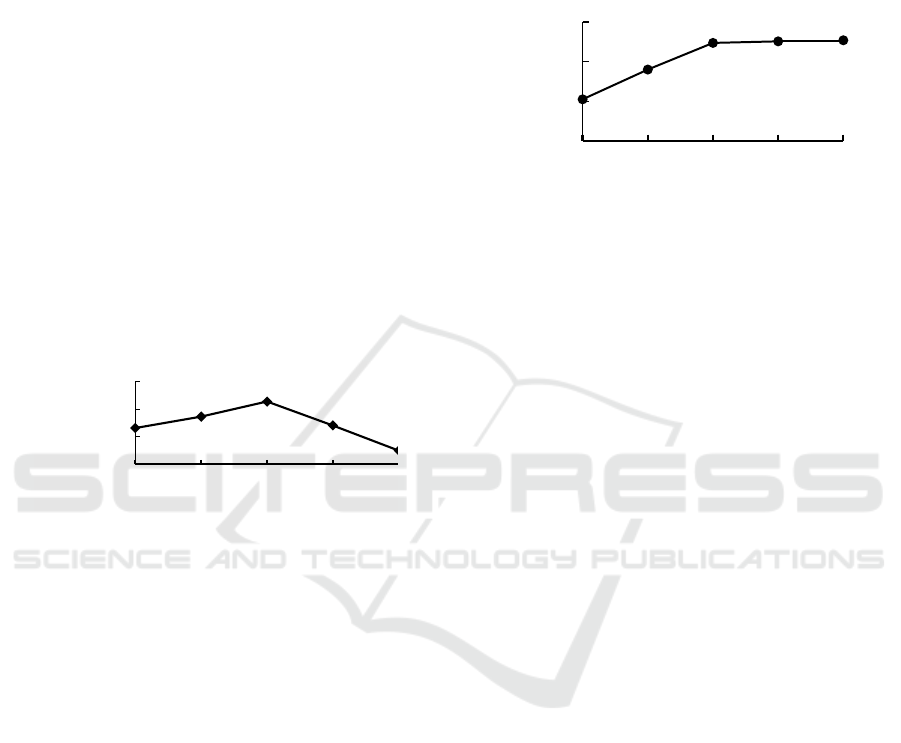
Figure 1: The effect of chitosan addition on protein
removal rate.
It can be seen from Figure 1 that as the amount
of chitosan added increases, the protein removal rate
shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing.
When the added amount reaches 0.8g/L, the protein
removal rate reaches the maximum, indicating that
the adsorption and separation effect of chitosan on
protein is the best at this time. The analysis believes
that when the amount of chitosan added is small, the
protein cannot fully bind to the chitosan, so it cannot
completely react to form a protein-chitosan
complex; when the amount of chitosan added is too
high, it will inhibit the formation of the protein-
chitosan complex, and the reaction consumes too
much chitosan, which is a waste of resources, so the
optimal addition amount of chitosan is 0.8g/L.
3.2.2 The Effect of pH on Protein Removal
Rate
The relationship between the pH of tofu yellow
slurry water and the protein removal rate is shown in
Figure 2:
Figure 2: The effect of pH on protein removal rate.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
66
It can be seen from Figure 2 that when the pH is
3~5, as the pH of the protein increases, the protein
removal rate decreases. This is because the protein is
positively charged at this time, and the chitosan is
also positively charged, and the two repel each
other, so when the pH is 5, the protein removal rate
reaches the lowest. When the pH is between 5 and 7,
the protein removal rate increases as the pH
increases. This is because when the pH of the
protein is greater than the isoelectric point, the
protein is negatively charged and attracts the
positive charge of chitosan to form a protein-
chitosan complex. When the pH is 7.04, the protein
removal rate reaches the maximum. Therefore, the
optimal pH value is 7.04.
3.2.3 The Effect of Temperature on Protein
Removal Rate
The relationship between temperature and protein
removal rate of tofu yellow slurry water is shown in
Figure 3:
0
10
20
30
5 1725354
Protein removal
rate/%
Temperature/℃
Figure 3: The effect of temperature on protein removal
rate.
It can be seen from Figure 3 that too high
temperature will inhibit the formation of chitosan-
protein complexes. As the reaction temperature
increases, the protein removal rate gradually
increases, which proves that the increase in
temperature is beneficial to the adsorption and
separation of proteins by chitosan. When the
temperature reaches 25°C, the protein removal rate
reaches the maximum, and chitosan has the best
effect on protein adsorption and separation. After
that, the protein removal rate decreases with the
increase of temperature. Excessive temperature
affects the adsorption and separation effect.
Therefore, the optimal reaction temperature is 25°C.
3.2.4 The Effect of Time on Protein
Removal Rate
The relationship between time and the protein
removal rate of fermented bean curd syrup is shown
in Figure 4:
0
10
20
30
12345
Protein removal rate/%
Time/h
Figure 4: The effect of time on protein removal rate.
It can be seen from Figure 4 that the prolonged
reaction time can promote the contact and reaction
between chitosan and protein. In 1~3h, the protein
removal rate increased obviously. In3~5h, the
increasing trend of protein removal rate was not
obvious, indicating that the adsorption and
separation of protein by chitosan was basically
completed at this time. Therefore, the optimal
reaction time is 3h.
3.3 Orthogonal Experiment on the
Adsorption of Protein in Tofu
Yellow Slurry Water
Table 2 shows the orthogonal experiment results of
chitosan adsorbing protein in tofu yellow slurry
wate.
Study on the Adsorption Technology of Chitosan to the Protein in Tofu Yellow Slurry Water
67

Table 2. Orthogonal test results.
Number
A
pH
B
Chitosan
addition/g.
L
-1
C
Temperature/
℃
D
Empty
column
Protein
removal
rate/%
1 1 1 1 1 32.74
2 1 2 2 2 20.29
3 1 3 3 3 24.96
4 2 2 3 1 27.51
5 2 3 1 2 49.87
6 2 1 2 3 24.18
7 3 3 2 1 38.97
8 3 1 3 2 24.96
9 3 2 1 3 21.84
K
1
77.99 81.88 104.45 99.22
K
2
101.56 69.64 83.44 95.12
K
3
85.77 113.80 77.73 70.98
k
1
25.997 27.293 34.817 33.073
k
2
33.853 23.213 27.813 31.707
k
3
28.590 37.933 25.910 23.660
R 23.57 44.16 26.72 28.24
Major factors→Secondary factors BCA
Optimal schemeA
2
B
3
C
1
From the range R value in Table 2, it can be seen
that the primary and secondary order of the three
factors affecting the protein removal rate is: B>C>A,
that is: chitosan added amount>reaction
temperature>pH, according to the orthogonal
experiment statistical calculations show that the
superior level is A
2
B
3
C
1
. Therefore, a verification
test was carried out, and the protein removal rate of
the combination A
2
B
3
C
1
was measured three times.
The results are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Protein removal rate of experimental combination A
2
B
3
C
1
Number 1 2 3 Average value
Protein removal rate/% 50.93 52.33 51.65 51.64
From Table 3, the optimal process conditions for
chitosan to adsorb protein in tofu yellow syrup were
determined: chitosan was added at 1.0 g/L, pH was
7, temperature was 20°C, reaction time was 3h, and
protein removal rate was 51.64%.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, tofu yellow slurry wate is used as the
raw material, The effect of chitosan on the protein
removal rate of tofu yellow syrup was investigated
through single factor experiment, and the optimal
process conditions for chitosan to adsorb protein in
tofu yellow slurry water were determined through
orthogonal experiment design. Get the following
conclusions: (1) The degree of deacetylation of
chitosan was determined by chemical analysis. The
degree of deacetylation of chitosan used in the test
was 72.4%. (2) Using chitosan as a flocculant, we
studied in detail the influence of pH, chitosan
addition, reaction temperature, and reaction time on
the protein removal rate in tofu yellow slurry wate.
(3) We adopted an orthogonal experiment design
and used the protein removal rate as an indicator to
determine the best conditions for chitosan to adsorb
protein in tofu yellow slurry water: pH is 7, the
addition amount of chitosan is 1.0g/L, reaction
temperature is 20℃, The reaction time is 3h. At this
time, the removal rate of protein in the tofu yellow
slurry water was 51.64%.
REFERENCES
Che Y J. (2017). Study on the production of single cell
protein by fermentation of yellow water D. Shangxi
Agricultural University, Jinzhong.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
68

Chen Liang. (2001). Research progress of chitosan
adsorption in wastewater treatment[J]. Sichuan
Environment, 20(3):19-23.
Diao N N. (2015). The utilization research of soybean
wastewater [J]. Food andFermentation Technology,
51(1): 20-24.
Du Ming. (2008). Research progress of soybean whey
protein[J]. Food industry technology, (2):302-305.
Wang Y. (2019). Sustainability of dairy and soy
processing: a review on wastewater recycling[J].
Journal of Cleaner Production, 237: 117821.
WU S H. (2009). Research of Common Indicator of
Degree of Deacetylation of Chitosan by
Alkalimetry[J]. Food Science and Technology. (4):
262-265,275.
Xie Guopai. (2009). Exploration on comprehensive
utilization of yellow pulp water[J], China brewing,
Chinabrewing, (04),129-130.
Xie Jiayi. (2013). Research Progress on characteristics and
application of Chitosan Flocculant[J]. Guangzhou
Chemical, 41(IS):45-47.
Study on the Adsorption Technology of Chitosan to the Protein in Tofu Yellow Slurry Water
69
