
Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Hydrilla verticillata under
Cu and Zn Stress
Guiqing Gao
a
, Weihan Yang
b
, Bo Fang
c
and Qingwu Chen
d
School of Civil and Architecture Engineering, Nanchang Institute of Technology, Nanchang, China
Keywords: The Heavy Metal Stress, Hydrilla verticillata, Superoxide Dismutase, Peroxidase, Malondialdehyde.
Abstract: In order to understand the physiological and biochemical responses of Hydrilla verticillata under heavy
metal stress, single and combined Cu or Zn were used for stress cultivation. The results showed that the
activities of SOD, POD and MDA in the first treatment group (Cu<0.2 mg/L, Zn<1.6 mg/L, Cu+Zn<0.1
mg/L + 0.8mg/L) were slightly lower than those in a blank control group. SOD, POD and MDA increased
significantly with the increase of heavy metal concentration within 7 days. From the 7th day to the 21st day
of culture, they increased first, then decreased. The change range of enzyme activity was the largest under
combined stress. The inhibitory effects of heavy metals on H. Verticillata were: combined stress > Cu stress
> Zn stress.
1 INTRODUCTION
a
Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd are common heavy metal
pollutants in water (Xing, 2013). Heavy metals play
a key role in the balance of active oxygen
metabolism system in plants (Ji, 2017; Gao, 2019).
The types and sources of heavy metals are different,
which lead to the complexity of water pollution
(Shahid,2017). Therefore, heavy metal polluted
water also generally appears in the form of
combined stress. Cu and Zn are trace elements for
plant growth, which can promote its development
and growth at low concentration. However, high
concentrations of Cu and Zn will affect the
absorption of other nutrients by plants, break the
balance of cell metabolism, and seriously curb their
physiological growth (Jian, 2016).
Hydrilla verticillata is the dominant species in
most lakes in China. Because of its rapid growth,
wide distribution and good effect on the enrichment
of heavy metals, it has gradually become a pioneer
species to solve the problem of heavy metal
pollution (Wang, 2020). In this study, the
physiological and biochemical characteristics of
H.verticillata under Cu and Zn stress were discussed
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8468-3405
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5871-2543
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7352-8266
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3754-6993
in order to provide some basis for the ecological
restoration of heavy metal polluted water.
2 EXPERIMENT MATERIAL AND
METHOD
2.1 Material
H.verticillata and sediment were collected in Poyang
Lake. After removing sundries, the sediment with a
thickness of 8 cm was evenly laid in plastic square
boxes (34.0 cm long, 22.5 cm wide and 10 cm high).
The apical tips of H.verticillata with a height of 20
cm were planted in the plastic boxes after washing
off the surface attachments, with 6 tips in each box.
Then, the plastic boxes were placed into the glass jar
(40 cm long, 40 cm wide and 50 cm high). Air-dried
tap water was slowly added into the jars to the
height of 48 cm for preculture. After the plant
growth was stable, it was used in the later
experiment.
2.2 Experimental Design
The toxicity of Cu and Zn to H.verticillata was
about 8:1 from pre-experiment. Naturally, the
concentrations of Cu and Zn should be configured
according to 1: 8 in water body.
Gao, G., Yang, W., Fang, B. and Chen, Q.
Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Hydrilla verticillata under Cu and Zn Stress.
DOI: 10.5220/0011189000003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 111-115
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
111

Different concentrations of CuSO
4
and ZnSO
4
combined stress treatment, and 5 treatment groups
(T1, T2, T3, T4 and T5) were set respectively (Table
1). At the same time, a blank control group (CK)
was set, and 3 replicates were set in each treatment
group. The indexes of stress culture were measured
every 7 days, and the experimental period was 21
days.
Table 1: Concentration setting (mg/L).
Cu Zn Cu+Zn
C
K
0 0 0+0
T1 0.2 1.6 0.1+0.8
T2 0.4 3.2 0.2+1.6
T3 0.6 4.8 0.3+2.4
T4 0.8 6.4 0.4+3.2
T5 1.0 8.0 0.5+4.0
2.3 Method
Malondialdehyde (MDA) was determined by
thiobarbituric acid colorimetry. Superoxide
dismutase (SOD) was determined by nitrogen blue
tetrazole colorimetry. Peroxidase (POD) was
determined by guaiacol.
2.4 Data Analysis
The experimental results were expressed in the terms
of the mean and standard deviation more than three
parallel data. Excel 2017 was used for the processing
and mapping of the original test data. SPSS 19.0
software was used for one-way analysis of variance,
and SNK method was used for multiple comparative
analysis. P < 0.05 indicated significant difference.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Effects of Cu and Zn Stress on SOD
Single and combined stress of Cu and Zn had
significant effects on SOD of H.verticillata (P <
0.05). From T1 to T5, the SOD activity showed an
upward trend and reached the maximum at T5
(Figure 1).
There was no significant change in T1 and T2
compared with CK, and the activity of SOD at T1
was lower than that at CK. When the stress duration
was 14 days, the maximum of SOD under Cu single
stress and combined stress were 45.91 U/mg and
45.80 U/mg respectively, and appeared at T4. The
maximum of SOD under Zn single stress was 45.55
U/mg and appeared at T5.
Figure 1: Effects of different heavy metals stress on
SOD.
Under combined stress, the activity of SOD at T5
decreased below than that at CK. After 21 days’
stress culture, the maximum of SOD all appeared at
T3 under three stress modes, which increased
50.47%, 40.38% and 54.35% respectively compared
with CK, and then decreased gradually. On the
whole, the inhibition of Cu and Zn Stress on SOD
was as follows: combined stress > Cu Stress > Zn
stress.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
112
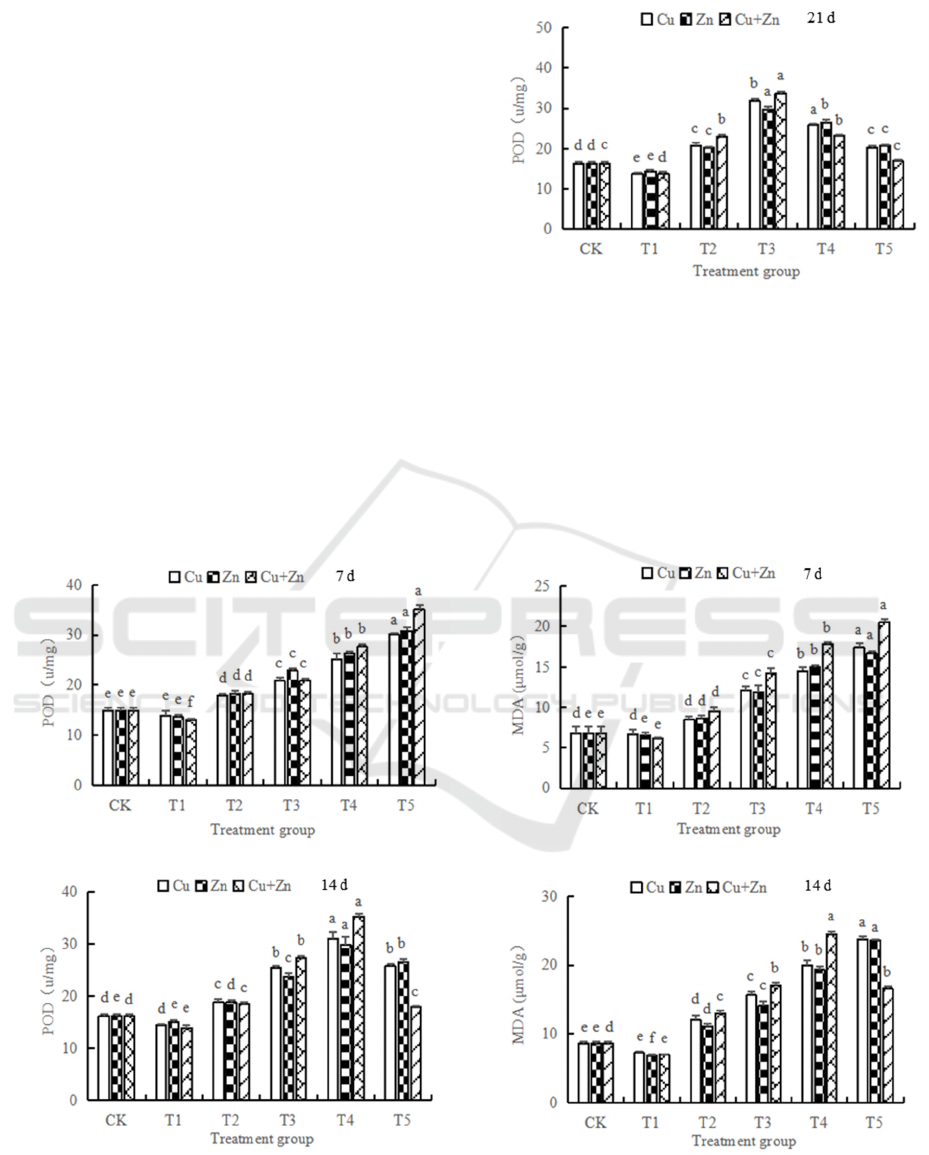
3.2 Effects of Cu and Zn Stress on
POD
After 7 days’ stress, the activity of POD gradually
increased with the increase of heavy metal
concentration (Figure 2).
The change of POD at T1 was not significant
compared with CK, which indicated that this
concentration range had a weaker effect on
H.verticillata. The values of POD at T5 reached the
maximum, which were 30.11 U/mg, 30.82 U/mg and
35.05 U/mg respectively. After 14 days’ stress
culture, the values of POD increased from T1 to T4,
then decreased at T5. The maximum values of POD
increased 91.12%, 84.05% and 117.28%
respectively compared with CK. When the culture
time reached 21 days, they reached the maximum at
T3 under three treatments, which were 31.87 U/mg,
29.66 U/mg and 33.64 U/mg respectively. The
values at T1 were smaller than those at CK under
three stress modes. On the whole, there were
significant differences in POD activity under heavy
metal stress.
Figure 2: Effects of different heavy metals stress on POD.
3.3 Effects of Cu and Zn stress on
MDA
Different concentrations of heavy metals had
significant effects on MDA (P < 0.05). After 7 days’
stress, the activity of MDA increased significantly
with the increase of heavy metal concentration
(Figure 3).
Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Hydrilla verticillata under Cu and Zn Stress
113

Figure 3: Effects of different heavy metals stress on MDA.
The maximum values of MDA were 17.41
μmol/g, 16.71μmol/g, 20.56 μmol/g respectively at
T5 under three stress modes. There was no
significant change at T1 compared with CK. After
14 days’ stress, the values of MDA still maintained
an upward trend under single stress of Cu and Zn,
and reached the maximum values at T5. However, it
reached the maximum of 24.51 μmol/g at T4
combined stress and began to decrease at T5. After
21 days’ stress, the maximum values of Cu and Zn
single stress were 20.58 μmol/g and 20.25 μmol/g
respectively at T4. The maximum value of combined
stress was 20.35 μmol/g at T3. In the three modes,
the change range of combined stress was greater
than that of single stress.
4 DISCUSSION
SOD plays an important role in improving plant
resistance to stress. In general, the toxicity of heavy
metals leads to excessive O
2
-
in plants. In order to
eliminate this effect, plants catalyze the conversion
of O
2
-
to H
2
O
2
by increasing SOD activity to protect
cells from damage (Parveen, 2017). Therefore, the
activity of SOD increased gradually with the
increase of heavy metals concentration. In this study,
the activity of SOD after 7 days’ stress culture
accorded with this characteristic. But the activities at
T5 on the 14th day, T4 and T5 on the 21st day
showed downward trends, which might be because
the stress of heavy metals has exceeded the tolerance
of H.verticillata and inhibited the enzyme activity of
the plant itself. Cu and Zn are elements required for
plant growth and can participate in their normal
physiological activities, and are conducive to the
exchange of cellular materials inside and outside the
cells. This is also the reason why the values of SOD
at T1 in the three treatments are slightly lower than
those of CK. In addition, the change range of SOD
under combined stress is greater than that under
single stress, which indicates that the existence of Zn
promotes the absorption of Cu by plant cells and
aggravates the toxicity of heavy metals.
POD catalyzes the decomposition of H
2
O
2
into
H
2
O and O
2
(Cao, 2004). The change law of POD is
very similar to that of SOD in this study. In the early
stage of the experiment, POD increased significantly
with the increase of heavy metals, but began to
decrease under the influence of high concentration
for a long time. On the 21st day, a significant
decrease of POD was observed in T4 and T5, which
indicated that high concentration of heavy metal
stress destroyed the normal function of enzyme,
weakened the ability of enzyme system to scavenge
reactive oxygen. It is similar to the reason for the
decrease of SOD.
The content of MDA represents the degree of
cell membrane oxidation (Tang, 2010), which is
used to reflect the damage degree of membrane lipid
in the process of plant stress or aging. The higher the
content of MDA, the more serious the inhibition of
plants (Wang, 2004). The content of MDA in
H.verticillata increased significantly with the
concentration of heavy metals and the duration of
poisoning, which indicated that the life activities of
plants were significantly inhibited by heavy metals.
On the 21st day of treatment, the value of MDA
reached the maximum under the single stress of Cu
or Zn at T4, but the combined stress reduced its
activity, which may be due to the increased toxicity
caused by the interaction between Cu and Zn, and
the toxic degree increased significantly, resulting in
the destruction of the enzyme protection system of
the plant itself. Therefore, the content of MDA
decreased significantly in T5 treatment group. The
change range of SOD, POD and MDA under
combined stress is the greatest, followed by Cu
single stress which may be that Cu is a very active
oxidative and reduced transition metal element, and
Cu can absorb or release an electron (Cu
2+
/Cu
+
) to
produce free radicals causing damage (Li, 1993),
while the chemical properties of Zn are much
weaker than that of Cu.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The activities of SOD, POD and MDA increased
significantly with the increase of heavy metal stress
in the early stage (within 7 days). From the 7th day
to the 21st day, the indexes in high concentration
treatment group showed a significant downward
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
114

trend. The inhibition on H.verticillata was the
largest under Cu and Zn combined stress, followed
by Cu stress. It is the smallest under Zn stress.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was financially supported by the
General Project of Jiangxi Science and Technology
Department (20212BAB204402), and the 18
th
“Challenge Cup” Science and Technology
Competition of of Nanchang Institute of
Technology.
REFERENCES
Cao, T., Ni, L.Y., Xie, P. (2004) Acute biochemical
responses of a submersed macrophyte, Potamogeton
crispus L., to high ammonium in an aquarium
experiment. J. Freshwater. Ecol. 19(2): 279-284.
Gao, G.Q., Zeng, K.H., Ji, Y., Li, W., Wang, Y. (2019)
Effects of lead stress on the chlorophyll content and
photosynthetic fluorescence characteristics of
Vallisneria natans. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 17(2): 4171-
4181.
Ji, Y., Zhang, J., Li, X.L. (2017) Biomarker responses of
rice plants growing in a potentially toxic element
polluted region: a case study in the Le’an region.
Chemosphere. 187: 97-105.
Jian, M.F., Wang, S.C., Yu, H.P., Li, L.Y., Jian, M.F.,
Yu, G.J. (2016) Influence of Cd
2+
or Cu
2+
stress on the
growth and photosynthetic fluorescence characteristics
of Hydrilla verticillata. Acta. Ecol. Sin. 36 (6): 1719-
1727.
Li, Y., Trush, M. A. (1993) DNA damage resulting from
the oxidation of hydroquinone by copper: role for a
Cu(Ⅱ)/Cu(Ⅰ) redox cycle and reactive oxygen
generation. Carcinogenes. 14(7): 1303-1311.
Parveen, M., Asaeda, T., Rashid, M. H. (2017) Hydrogen
sulfide induced growth, photosynthesis and
biochemical responses in three submerged
macrophytes. Flora. 230: 1-11.
Shahid, M., Dumat, C., Khalid, S., Schreck, E., Xiong, T.,
Niazi, N.K. (2017) Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity
and detoxification in plants: a comparison of foliar and
root metal uptake. J. Hazard. Mat. 325: 36-58.
Tang, K., Zhan, J.C., Yang, H. R., Huang, W.D. (2010)
Changes of resveratrol and antioxidant enzymes
during UV-induced plant defense response in peanut
seedlings. J. Plant. Physiol. 167(2): 95-102.
Wang, X., Shi, G.X., Xu, Q.S., Wang, C.T. (2004) Toxic
effects of Lanthanum, Cerium, Chromium and Zinc on
Potamoqeton malaianus. J. Chin. Rare. Earth. Soc.
22(5): 682-686.
Wang, Y., Gao, G.Q., Lv, S.H., Guan, K. (2020)
Remediation effect of Cu an Pb contaminated
sediments on submerged plants under different
planting patterns. Chin. J. NIT. 39(01): 48-52+59.
Xing, W., Wu, H.P., Hao, B.B., Huang, W.M., Liu, G.H.
(2013). Bioaccumulation of heavy metal by
submerged macrophytes: looking for
hyperaccumulators in eutrophic lakes. Environ. Sci.
Technol. 47 (9): 4695-4703.
Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Hydrilla verticillata under Cu and Zn Stress
115
