
Expression Analysis of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Pathway Genes in
Indosasa hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’
Chunsheng Zhang
1a
, Guisha Peng
2b
and Rui Shi
3,* c
1
Office of Academic Affairs, Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, 650221, Kunming, Yunnan, China
2
Key Laboratory for Forest Disaster Warning and Control in Yunnan Province, Southwest Forestry University, 650224,
Kunming, Yunnan, China
3
Key Laboratory for Forest Resources Conservation and Utilization in the Southwest Mountains of China, Ministry of
Education, Southwest Landscape Architecture Engineering Research Center of National Forestry and Grassland
Administration, Southwest Forestry University, 650224, Kunming, Yunnan, China
Keywords: Indosasa Hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’, Anthocyanin Biosynthesis, Gene Expression.
Abstract: Anthocyanins existed in diverse plants have many health beneficial functions such as anti-inflammatory, anti-
oxidation and antihypertensive. Studies have demonstrated that anthocyanin accumulation in plant organs is
related to gene expression in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway. In order to probe which gene or genes have
correlation with the anthocyanin biosynthesis in bamboo species, the expression level of some genes involved
in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway was determined by real time PCR semi-quantitatively at seven different
growth stages of Indosasa hispida cv. ‘Rainbow’. Results showed that all of the genes studied were expressed
with similar patterns in most tissues, and which also showed a positive correlation between the level of CHS,
F3H, DFR, UFGT gene expression and anthocyanin accumulation.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Anthocyanins are accumulated in cell vacuoles and
produce a diverse pigmentation from orange to red,
purple and blue in flowers, fruits and vegetables
(Oancea, Oprean, 2011, Horbowicz et al, 2008). Anti-
oxidant effects, protecting DNA and the
photosynthetic machinery from high radiation fluxes,
resistance to cold and drought stress, anti-aging and
anti-cancer properties and recruitment of pollinators
are some well-known roles of anthocyanins (Oancea,
Oprean, 2011, Horbowicz et al, 2008). Studies have
demonstrated that anthocyanin biosynthesis is
mediated by the anthocyanin pathway some
genes/transcription factors (Li et al, 2021).
Indosasa hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’ (Y. M.
Yang et J. Wang) with high ornamental value, a new
variety of Indosasa hispida, exhibits different degree
of purplish red at different stages of its growth, and
the purplish red material was ascertained as
anthocyanin after isolation and analysis (Wang et al,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8542-8676
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7018-1965
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2593-7302
2012, Miao et al, 2014, Wang et al, 2014). Although
the anthocyanin pathway has been thoroughly
characterized and the correlation between gene
expression level and anthocyanin accumulation in
many plants having been identified (Yonekura-
Sakakibara et al, 2019, Boss et al, 1996, Jenog et al,
2004), the question about how their biosynthesis is
regulated in bamboo species is rarely known at
present. In this study, ten structural genes related to
anthocyanin biosynthesis of I. hispida MeClure cv.
‘Rainbow’ were determined by real time PCR semi-
quantitatively at seven different growth stages to
interpret a correlation between anthocyanin
biosynthesis and gene expression level.
184
Zhang, C., Peng, G. and Shi, R.
Expression Analysis of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Pathway Genes in Indosasa hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’.
DOI: 10.5220/0011194200003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 184-188
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Plant Materials
I. hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’ was obtained from
greenhouse of Yunnan Academy of Forestry, and
which was divided into seven growth stages
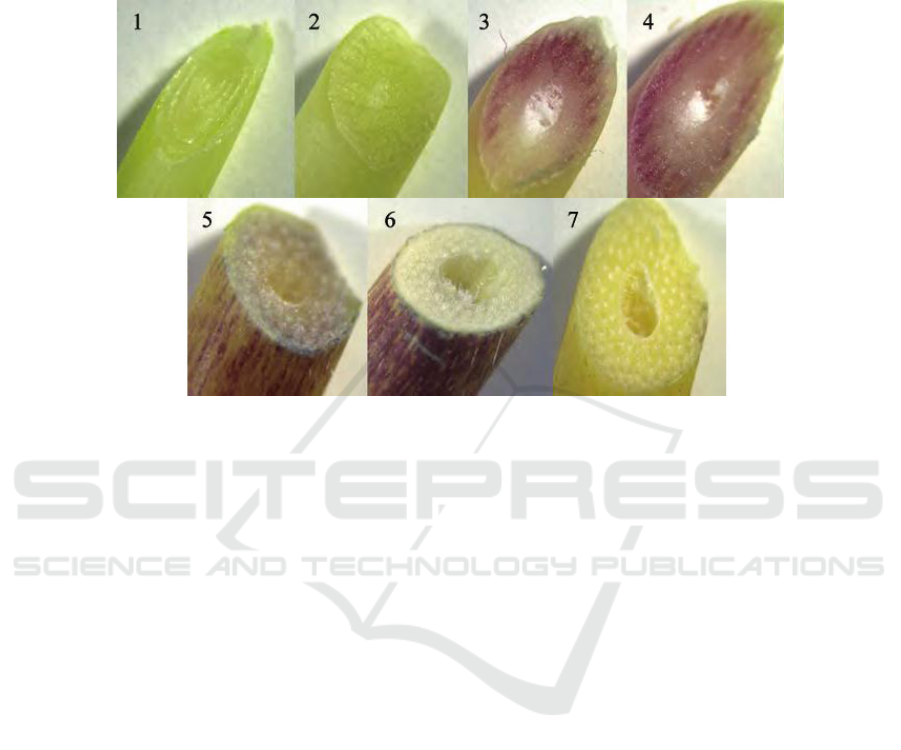
according to colour differences (Figure 1). The culm
tissues for RNA isolation were collected directly into
liquid nitrogen and were stored at -80℃ until used.
Description of the growth stages: 1, 2: Tender apex without visible anthocyanin pigments; 3: Intermediate stem with purplish
red tissues and colourless skin; 4: Intermediate stem with purplish red tissues and skin; 5: Intermediate stem with little purplish
red tissues and purplish red skin; 6: Mature stem with colourless tissues and purplish red skin; 7: Mature stem without visible
anthocyanin pigments.
Figure 1: The cross profile of I. hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’ at different growth stages.
2.2 Main Reagents
DEPC-treated Water; UltraPower Nucleic Acid Stain;
75% ethanol; isopropyl alcohol; chloroform; Takara
RT-PCR Kit; PCR mix Kit; TRNzol® Reagent.
2.3 RNA Extraction and cDNA
Synthesis
Total RNA was isolated from culm tissues using
TRNzol® Reagent (TIANGEN Biotech (Beijing)
Co., Ltd.). Purity and concentration of isolated RNA
was determined by protein nucleic acid analyzer, and
integrity of which was verified by electrophoresis on
1.2% agarose gel, respectively. RNA was reverse
transcribed to cDNA with the first strand cDNA
synthesis kit (TaKaRa Biotechnology (Dalian) Co.,
Ltd.) according to the manufacture’s protocols. The
reverse transcription system and conditions are as
follows: Oligo (dT) Primer 1 Μl, dNTP Mixture 1 μL,
Total RNA 3 μL, RNase-free dH2O up to 10 μL; 65℃,
5 min annealing response, ice chill; 5×PrimeScript®
Buffer 4 μL, RNase Inhibitor 0.5 μL, PrimeScript®
RTase 1μL, RNase Free dH2O 4.5 μL; 30℃ 10 min,
42℃ 60 min, 95℃ 5min.
2.4 PCR Cloning and Analysis of the
Products
Primers were designed on the basis of transcriptome
data acquired by our group earlier, and the designed
primers for amplifying gene are as follows (Tab. 1).
Conditions for PCR of genes involved are as follows:
95℃ for 5 min followed by 35 cycles at 95℃ for 45s,
at annealing temperature listed below for 30 s, and at
72℃ for 5 min, with a final extension at 72℃ for 8
min. The PCR products were assessed by agarose gel
electrophoresis, taking actin primer as a reference
gene.
Expression Analysis of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Pathway Genes in Indosasa hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’
185
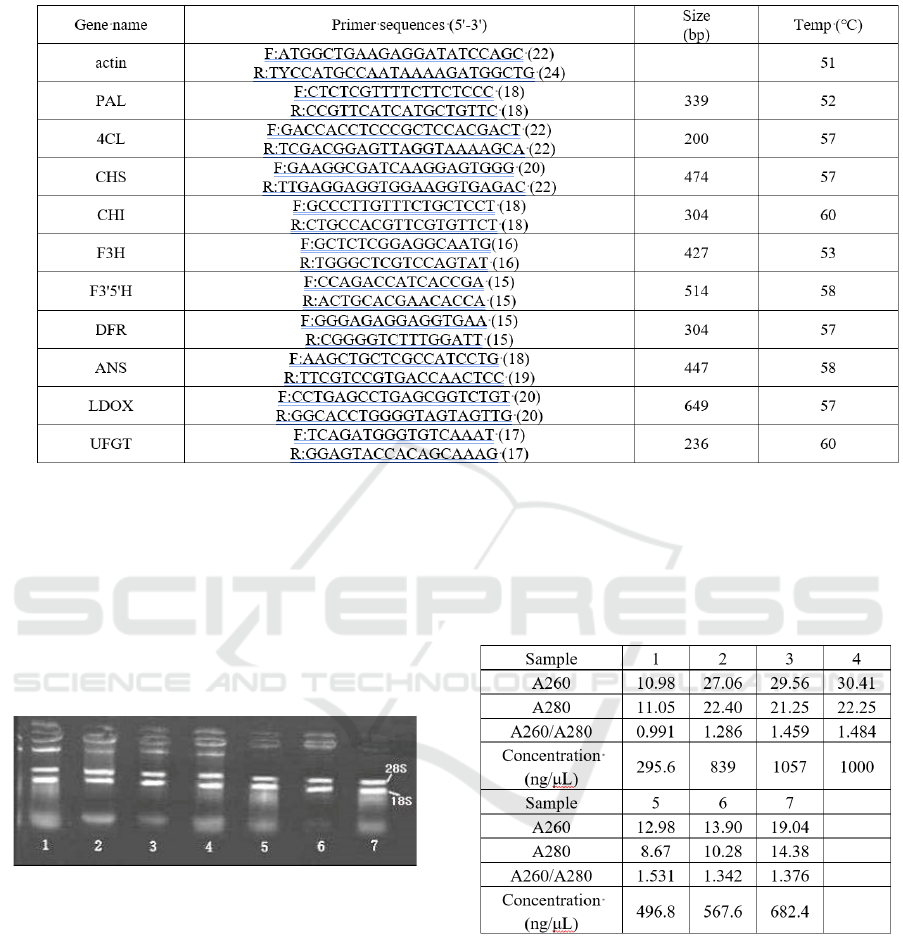
Table 1: PCR primer and reaction condition for PCR.
Abbreviations: PAL, phenylalanine ammonia lyase; 4CL, coenzyme A ligase; CHS, chalcone synthase; CHI, chalcone
isomerase; F3H, flavanone-3-hydroxylase; F3'5'H, flavonoid-3’,5’-hydroxylase; LDOX, leucoanthocyan-idin dioxygenase;
DFR, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; ANS, Anthocyanidin Synthase; UFGT, UDP glucose-flavonoid 3-O-glucosyl transferase.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Analytical Results of Isolated Total
RNA
Figure 2: Electrophoresis Image of total RNA at different
stages.
The agarose gel electrophoresis of total RNA at
different stages was shown in figure 2. The data of
A260/A280 ratio and concentration of total RNA
listed Tab. 2 shows that total RNA isolated for study
can be used for cDNA synthesis.
Table 2: Purity and concentration of total RNA from culm
tissues.
3.2 Expression of the Anthocyanin
Biosynthesis Pathway Genes
As depicted in figure 3, the target genes with the
exception of F3H, DFR and UFGT were all expressed
with different levels at the first two stages. No
anthocyanin pigments were seen in young tissues,
presumably because UFGT is missing. In the
pigmented tissues, the expression levels of several
genes increased dramatically, but the expression
levels were gradually decreased toward the end of
ripening. Half of genes were not expressed in the
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
186

ripening tissues without visible anthocyanin pigments
compared with the first two stages, in which 4CL and
CHI still showed higher levels.
Figure 3: Electrophoresis Image of PCR products at
different growth stages.
4 DISCUSSION
It was evident that anthocyanin accumulation in plant
is associated with gene expression in anthocyanin
biosynthesis pathway (Rouholamin et al, 2015). Ten
structure genes related to anthocyanin biosynthesis
pathway were investigated at seven different stages of
a new variety of Indosasa hispida. Similar expression
patterns of PAL and 4CL were observed at the whole
growth stages, and the difference between them is that
there was no expression of PAL in the unpigmented
ripening tissue. The results indicated that they are not
only the precursor genes of anthocyanin biosynthesis
pathway, but also related to the accumulation of
anthocyanin.
Only weak expression of CHS and CHI was
detected at the first two stages while the expression of
the two genes increased dramatically to a very high
level subsequently. Notably, the high levels of
expression of CHI lasted to the unpigmented ripening
stage. Therefore, there is a significant positive
correlation between the accumulation of anthocyanin
and the expression of CHS and CHI, especially CHS
gene.
Previous study showed that the colour of grape
skins is blue or red was determined by the ratio of
F3’5’H/F3H (Simone, Gabriele, 2007). In the study,
both F3’5’H and F3H were expressed in culm tissues
contained visible anthocyanin pigments, where levels
of F3’5’H was higher. It can be deduced that F3’5H
and F3H might commonly regulate anthocyanin
biosynthesis of I. hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’ to
account for the fact of purplish red.
The expression of LDOX and ANS showed same
trends, both of them had no expression in the
unpigmented ripening tissue. DFR and UFGT were
only expressed obviously in the pigmented tissues,
which demonstrate that DFR and UFGT are two key
encoding enzyme genes to regulate anthocyanin
biosynthesis of I. hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’,
and DFR expression was consistent to the study on
other species (Hasegawa, 2001).
5 CONCLUSIONS
For preliminary study the expression of genes
involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway of I.
hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’, ten genes was
determined at seven different growth stages. It can be
seen from the results that the appearance of
anthocyanin at the onset of ripening coincides with
increased expression of each of the genes encoding
biosynthetic enzymes in this pathway, and which
suggested that the induction of anthocyanin synthesis
is triggered by regulatory genes in I. hispida MeClure
cv. ‘Rainbow’. Further, the content analysis of
anthocyanin in various tissues is currently being
undertaken by our group to understand the deeper
correlation between anthocyanin biosynthesis and
gene expression level.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by China Agriculture
Research System (CARS-21), Yunnan Provincial
Key Programs (202102AE090042, 2019ZG00901,
202002AA10007), High-end Foreign Experts
Program of Yunnan (202105AQ130011, 2019013),
and Yunnan Provincial Financial Forestry Science
and Technology Promotion Demonstration Special
Project (2020, No: TS09).
REFERENCES
Boss, P. K., Davies, C., Robinson, S. P. (1996). Expression
of anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway genes in red and
Expression Analysis of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis Pathway Genes in Indosasa hispida MeClure cv. ‘Rainbow’
187

white grapes. Plant Mol. Bio., 32, 565-569.
Hasegawa, H., Fukasawa-Akada, T., Okuno, T., et al.
(2001). Anthocyanin accumulation and Related gene
expression in Japanese parsley (Oenanthe stolonifera
DC.) induced by low temperature. Plant Physiol., 158,
71-78.
Horbowicz, M., Kosson, R., et al. (2008). Anthocyanins of
fruits and vegetables-Their occurrence, analysis and
role in human nutrition. J. Fruit and Ornamental Plant
Res., 68(1), 5–22.
Jeong, S.T., Goto-Yamamoto, N., Kobayashi, S., et al.
(2004). Effects of plant hormones and shading on the
accumulation of anthocyanins and the expression of
anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in grape berry skins.
Plant Sci., 167, 247–252.
Li, T. S., Yamane, H. & Tao, R. (2021). Preharvest long-
term exposure to UV-B radiation promotes fruit
ripening and modifies stage-specific anthocyanin
metabolism in highbush blueberry. Horticu. Res., 8, 67-
89.
Miao, F. J., Chen J., Sun H., et al. (2014). Cloning and
expression analysis of dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase
Gene IhDFR1 from Indosasa hispida cv. ‘Rainbow’.
Plant Physiol. J., 50(4), 447-452.
Oancea, S. and Oprean, L. (2011). Anthocyanins, from
biosynthesis in plants to human health benefits. Acta
Univ. Cibiniensis Ser. E: Food Technol., 15 (1), 1–16.
Rouholamin, S., Zahedi, B., F Nazarian-Firouzabadi, &
Saei, A. (2015). Expression analysis of anthocyanin
biosynthesis key regulatory genes involved in
pomegranate (punica granatum l.). Scientia
Horticulturae, 186, 84-88.
Simone, D. C. and Gabriele, D. G. (2007). Transcriptional
control of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in extreme
phenotypes for berry pigmentation of naturally
occurring grapevines. BMC plant boil., 7, 46-53.
Wang, C. C., Bi, W., Wang, J., et al. (2014). Cloning and
expression analysis of IhCHI1 from Indosasa hispida
cv. ‘Rainbow’. J. West China Forestry Sci., 43(2), 85-
90.
Wang, J., Sun, H., Peng, G. S., et al. (2012). Phylogenetic
study on anthocyanin produced mutant of Indosasa
hispida based on rDNA ITS sequences. J. West China
Forestry Sci., 41(1), 1-6.
Yonekura-Sakakibara, K., Higashi, Y. & Nakabayashi, R.
(2019). The origin and evolution of plant flavonoid
metabolism. Front. Plant Sci., 10, 943.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
188
