
Metabonomics Study on the Mechanism of the Effect of Low Salt on
the Liver of Qinghai Lake Naked Carp
Yanfei Wu
1,2
, Jiang Qi Qu
2
, Yi Liu
2
, Yuxiang Cui
2
, Hongfang Qi
3
, Hong Zhang
3
, Yang Wang
3
and Qingjing Zhang
2,3,*
1
Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, 316022, China
2
Beijing Key Laboratory of fishery Biotechnology, Fisheries Research Institute, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and
Forestry Sciences, Beijing 100068, China
3
Qinghai Key Laboratory of Qinghai-Lake Naked Carps Breeding and Conservation, Rescue and Rehabilitation Center of
Naked Carps of Qinghai Lake, Xining 810016, China
Keywords: Low-Carbon Agriculture, Naked Carp Liver, Biology.
Abstract:
In order to explore the metabonomics study of the mechanism of low salt on the liver of Qinghai Lake
naked carp, this study investigated the liver enzyme activity, tissue structure and related immune genes
during the salinity change of Qinghai Lake naked carp. The role of naked carp in immunity can provide a
theoretical basis for the research on the adaptability of Qinghai Lake naked carp to changes in salinity. Two
experimental groups of Qinghai Lake naked carp with different salinities were established in the Emergency
Center (JH) and Qinghai Lake (QH). The rescue center is Freshwater, and the salinity of Qinghai Lake is
1.24‰. This experiment uses ultra-high performance liquid chromatography non-targeted metabonomics
technology, and the differential metabolites were screened according to the variable weight value (VIP) and
independent sample T test, and the KEGG pathway enrichment and annotation analysis were performed.
The results showed that compared with the JH group, in this study, 221 metabolites among the 1,525
differential metabolites identified received 90 KEGG annotations. We performed KEGG enrichment
analysis on the 65 differential proteins obtained, and the results showed that the differentially expressed
proteins mainly come from primary bile acid biosynthesis: M (Primary bile acid biosynthesis: M),
Parkinson's disease: (Parkinson disease: HD), Linoleic acid metabolism: M (Linoleic acid metabolism: M),
protein digestion and absorption: OS (Protein digestion and absorption: OS), cancer choline metabolism:
HD (Choline metabolism in cancer: HD) , This study clarified the metabonomics of the liver metabolism
mechanism of Qinghai Lake naked carp with different salinities, and the study of Qinghai Lake naked carp
liver function has a good guiding significance for molecular biology.
1 INTRODUCTION
Qinghai Lake naked carps belong to the genus
Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae, Schizoma subfamily,
and naked carps, commonly known as Huangyu. It
is the only commercial fish in Qinghai Lake and
occupies a very important position in the Qinghai
Lake ecosystem. (
CAO, WU, SHAO, 2010)
. Due to
its historical and natural reasons, Qinghai Lake
naked carp resources were once greatly destroyed.
In order to accelerate its resource recovery in
Qinghai Lake, the Qinghai Lake Naked Carp Rescue
Center has carried out artificial breeding and
breeding of Qinghai Lake naked carp resources in
the past 20 years, especially in recent years through
the establishment of a factory circulating water
breeding system to develop Qinghai Lake naked
carp Great progress has been made in breeding.
Qinghai Lake naked carp has the habit of
reproductive migration, has a strong adaptability to
changes in salinity, and can live in fresh water,
brackish water, and alkaline water (Walker, Dunn,
Edwards, Petr, Yang, 1995). Wang Ping et al.
(WANG, LAI, YAO, 2015) Metabonomics studies
and studies on the mechanism of the intestine of
Qinghai Lake naked carp under different salinity
environments have shown that there are gene
expression in many tissues such as Qinghai Lake
naked carp intestine and liver.
Salinity is one of the important factors affecting
the survival and growth of fish. Especially for
Wu, Y., Qu, J., Liu, Y., Cui, Y., Qi, H., Zhang, H., Wang, Y. and Zhang, Q.
Metabonomics Study on the Mechanism of the Effect of Low Salt on the Liver of Qinghai Lake Naked Carp.
DOI: 10.5220/0011196600003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 225-230
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
225

euryhalinic fish, the salinity changes in the water
environment in which they live will cause the
adaptation of enzyme activities, tissue structure and
gene expression in the fish. Sexual changes (Yong
Zhong); (Wang, 2018); (Zhang, Wen, Zhang, 2018),
studying the growth, survival, metabolism and other
physiological activities of fish under low-salt
conditions (Lian, 2012) can help understand the
anti-low-salt mechanism of fish and guide the
healthy breeding of fish. Although predecessors
performed correlation analyses on liver tissues at
different salinities to explain the differences in gene
transcription level expression of Qinghai Lake
naked carp, but due to the regulation of gene
expression and translation level, Qinghai Lake
naked carp cannot perform liver transcriptomics
research without saline environment. Fully explain
the types of products involved in the synthesis of
liver metabolites.
Non-targeted metabolomics can perform
qualitative and relative quantitative analysis of small
molecular metabolites in biological systems for
specific physiological conditions, and reflect the
total metabolite information to the greatest extent
(Wen, 2019); (Yang, 2020). Non-targeted
metabolomics can provide the maximum amount of
information about the metabolism of the central
carbon cycle, reflecting the body's metabolism after
being subjected to environmental stress through
biological processes such as gene expression,
transcription, post-transcriptional regulation, protein
translation and modification, etc. Changes in the
final product. In this part of the research, we used
the naked carp of Qinghai Lake (JH) and Qinghai
Lake (QH) as the research object, and used
non-targeted metabolomics to study the metabolic
changes of Qinghai Lake naked carp in response to
low-salt stress, hoping to reveal Qinghai Lake naked
carp. Carp provides metabolite data and basic
information on the regulation mechanism of low-salt
stress.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
The test materials were naked carps in the rescue
center (JH) and Qinghai Lake (QH) in September
2020. All naked carps were fresh and live fish
species identified by the staff of Qinghai Lake
Naked Carp Rescue Center. 10 samples of each were
collected. The collected naked carp was washed and
deplaned, and the liver was collected, and
immediately subjected to biological reaction
inactivation treatment (liquid nitrogen freezing), and
stored in a refrigerator at -80°C.
2.2 Sample Pretreatment
The pretreatment method of the liver tissue sample
was prepared according to the method of He et al.
(He, An, Huang, 2019). Accurately weigh 50 mg of
the liver tissue sample and transfer it to a 1.5 mL EP
tube; add 400 µl of extraction solution (methanol:
water=4:1) to the sample at low temperature ,
High-throughput tissue disrupter (-20°C, 50HZ,
6min); vortex (30s) to mix, then low-temperature
ultrasonic extraction for 30min (5°C, 40KHz); place
the sample at -20°C, 30min; centrifuge Centrifuge
the sample at 13000 rpm and 4°C for 15 minutes,
aspirate the supernatant, and transfer it to an LC-MS
vial for analysis. The quality control sample (QC) is
prepared by mixing equal volumes of all sample
extracts, each The QC volume is the same as the
sample. All extraction reagents are pre-cooled at -20
℃ before use.
2.3 LC-MS Detection
The instrument platform for this LC-MS analysis is
the UPLC-TripleTOF system of AB SCIEX. The
chromatographic conditions are: The
chromatographic column is a BEH C18 column (100
mm × 2.1 mm id, 1.7 µm; Waters, Milford, USA);
the mobile phase A is water (containing 0.1% formic
acid), and the mobile phase B is
acetonitrile/isopropanol (1/1) (containing 0.1%
formic acid); the mobile phase elution gradient
program is as follows: 0 min, 5% B; 3 min, 20% B;
9 min, 95% B; 13.0 min, 95% B; 13.1 min, 5% B;
16min, 5%B. The flow rate is 0.40mL/min, the
injection volume is 10μL, and the column
temperature is 40°C.
The sample mass spectrum signal acquisition
adopts positive and negative ion scanning mode and
ion spray voltage. The mass spectrometry
parameters are as follows: spray gas 50V; auxiliary
heating gas 50V; curtain gas 30V; ion source
heating temperature 500℃; ionization voltage
(positive) 5000V, ionization voltage (negative)
-4000V; interface heating on; declustering voltage
80V, The collision energy is 20-60(rolling)V.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
226

2.4 Quality Control
Quality control samples (QC) are prepared by
mixing the extracts of all samples in equal volumes.
The volume of each QC is the same as that of the
sample. It is processed and tested in the same way as
the analysis sample. In the process of instrument
analysis, every 10 analysis Insert a QC sample into
the sample to examine the repeatability of the entire
analysis process.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis is used for pattern
recognition analysis of multivariate variables.
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a statistic
that converts a set of observed possibly related data
into linear uncorrelated data (ie principal
components) through orthogonal
transformationmethod. As an unsupervised analysis
method, it can automatically analyze the income
without default grouping arrangement. Model
construction of sample metabolism data, using a
small amount of principal components to reduce
data dimensions, represent data information, and
reveal The internal structure of the data. Among
them, 35.5% of the data in Figure 1aPCA
participated in the model construction; in the P-LCA
model established in Figure 1b, 35.3% of the data
participated in the model construction. The closer
R2Y and Q2 are to 1, the more stable and reliable
the model is. Generally, the model with Q2 greater
than 0.5 is stable and reliable. As shown in the table,
the tested model is reliable regardless of the cation
or anion mode. The metabolites identified on this
basis are Believed to be reliable.
a.PCAScore graph
b.PLS-DAScore graph
Figure 1: Principal component analysis diagram.
3.2 Screening of Differential
Metabolites
Obtain more accurate labeled compounds, and
further conduct biomarker mining and functional
analysis of compounds with complete secondary
information detected in the positive and negative ion
mode. The differential metabolite identification
standard used in this study was P<0.05 by paired
t-test, and it also satisfies log 2 Fold change<-1 or
log 2 Fold change>1. See the volcano map for the
screening results of differential metabolites (Figure
2). Each point in the volcano map represents a
metabolite, the abscissa represents the fold change of
each compound compared to the Qinghai Lake naked
carp and the rescue center control (take the logarithm
to the base 2), and the ordinate represents the P value
of the paired t test (Take the negative logarithm to
the base 10). The scattered colors represent the final
screening results. There are a total of 901 differential
metabolisms, of which 124 are up-regulated and 97
are down-regulated.
Figure 2: Volcano map of differential metabolites.
Metabonomics Study on the Mechanism of the Effect of Low Salt on the Liver of Qinghai Lake Naked Carp
227
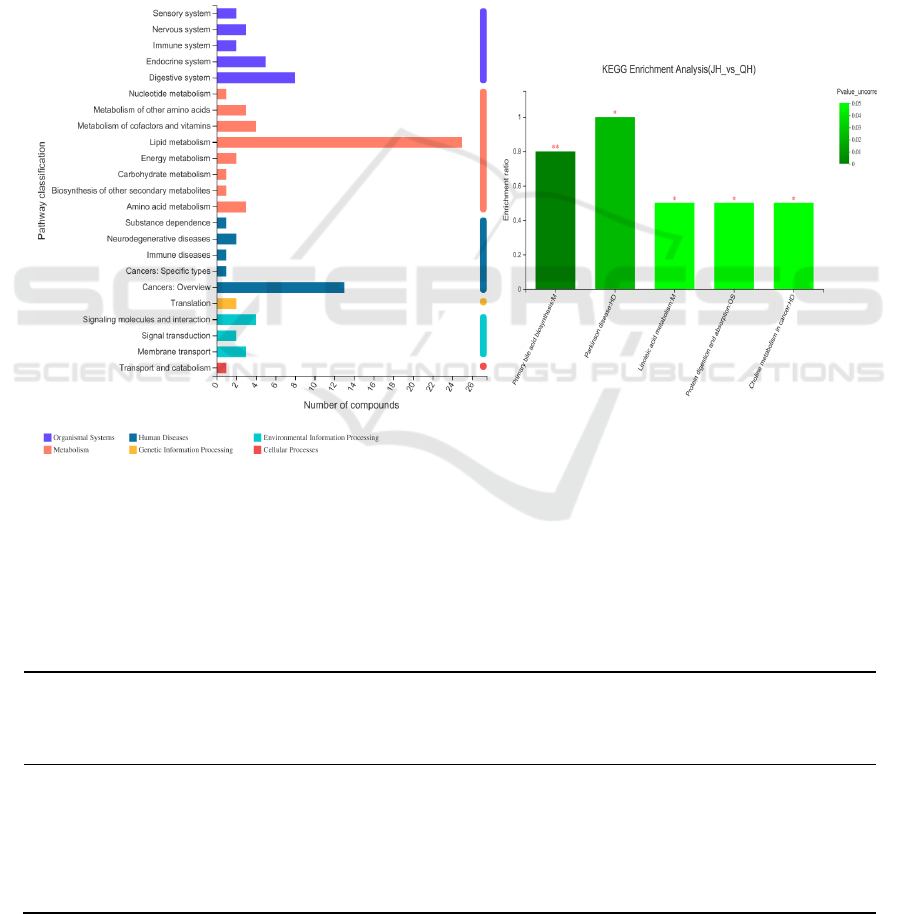
3.3 KEGG Pathway Annotation and
Enrichment Analysis
In this study, out of the 1,525 differential
metabolites identified, 221 metabolites received 90
KEGG annotations. In order to further reveal the
overall pathway enrichment characteristics of all
differential metabolites, we performed an
enrichment analysis on the KEGG annotation results
of the differential metabolites. The KEGG
annotation analysis of the differential proteins is
shown in Figure 3a. The results showed that under
high altitude stress conditions, the liver metabolites
of Qinghai Lake naked carp were significantly
enriched in the sensory system, Nervous system,
Immune system, Endocrine system, and digestive
system. Digestive system, Nucleotide metabolism,
Metabolism of other amino acids, Metabolism of
cofactors and vitamins, Lipid metabolism, Energy
metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism (Biosynthesis
of other secondary metabolism), amino acid
metabolism (substance dependence),
neurodegenerative diseases, cancer: specific types,
cancer: overview, transport (Translation), signaling
molecules and interactions (Signaling molecules and
interaction), signal transduction, membrane
transport and catabolism.
a.KEGG annotation analysis of differentialproteins b.KEGG enrichment analysis of differential proteins
Figure 3: Annotation diagram of KEGG pathway enrichment of differential proteins.
We performed KEGG enrichment analysis on the
65 differential proteins obtained. The analysis
results are shown in Figure 3band table 1. The
results indicate that the differentially expressed
proteins mainly come from Primary bile acid
biosynthesis: M, Parkinson disease: HD, Linoleic
acid metabolism: M, Protein digestion and
absorption: OS, cancer choline metabolism: HD.
Table 1: Enrichment analysis of KEGG pathway in the liver of Qinghai Lake naked carp.
Metabolite Metab ID Formula
VIP_pred_OP
LS-DA
FC(JH/Q
H)
P_valu
e
mode
Taurine metab_7226
C2H7NO
3S
2.727 2.869 <0.001 neg
3a,7a,12a-Trihydroxy-5b-cholestan-26-al metab_106
C27H46O
4
7.024 0.127 0.0165 pos
Taurocholic acid metab_610
C26H45N
O7S
1.290 0.013 <0.001 pos
5b-Cyprinol sulfate metab_2325
C27H48O
8S
7.908 0.110 0.025 pos
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
228

9,10-DiHOME metab_6109
C18H34O
4
1.628 10.651 <0.001
neg
PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/1
8:2(9Z,12Z))
metab_9591
C48H80N
O8P
5.434 7.685 <0.001 neg
PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/2
2:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z))
metab_9633
C52H80N
O8P
1.479 1.704 0.008 neg
9-OxoODE metab_2646
C18H30O
3
2.090 0.108 <0.001 pos
L-Isoleucine metab_5783
C6H13N
O2
4.023 0.447 <0.001 pos
Piperidine metab_1437 C5H11N 1.843 0.422 <0.001 pos
L-Tyrosine metab_1454
C9H11N
O3
1.047 0.528 <0.001 pos
4 DISCUSSION
Salinity is one of the important environmental
factors that affect the survival of fish. Changes in
salinity will cause changes in enzyme activities,
tissue structure and gene expression levels in fish.
The liver is an important metabolism-based organ in
the fish body. It plays a vital role in the synthesis
and catabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Therefore, the strength of the liver can be used as
the ability of fish to resist external environmental
stress. An important indicator of size. We mainly
focus on Primary bile acid biosynthesis: M, Linoleic
acid metabolism: M, Protein digestion and
absorption: OS, several major The differential
metabolism of the KEGG pathway was analyzed.
The liver occupies an important position in the
metabolism of bile acids, which is closely related to
the synthesis, secretion, and conversion of bile
acids. The changes of bile acids are also known as
metabonomic markers of liver injury (Liu, Jiang,
Shen, 2016), the primary bile acid is directly
synthesized by hepatocytes using cholesterol as a
raw material. It is secreted from the liver and enters
the intestinal lumen, where it becomes a secondary
bile acid under the metabolism of some enzymes
and bacteria (MA, XIE, WANG, 2019). Li Xiulong
et al. (LI, HU, LI, 2020) found that the acute liver
injury induced by acetaminophen in rats may be
related to glycerophospholipid metabolism,
sphingolipid metabolism, and primary bile acid
biosynthesis and other metabolic pathways. related.
Jin Wenjie (Jin, Li, Ran, 2021) et al. conducted a
transcriptome analysis of copper toxicology in
naked carp, and the results showed that several
genes involved in oxidative stress in the gill and
liver were up-regulated. Up-regulation of these
genes indicates that copper treatment causes
oxidative stress, which may cause ribosome damage.
The metabolism of linoleic acid is the main
component of the cell membrane. The increase and
decrease of its content may be related to the necrosis
and apoptosis of hematopoietic stem cells. Liu Teng
et al. (LIU, XU, LU, 2020) studied the intervention
effect of Astragalus injection on leukopenia model
mice based on LC-MS metabonomics and found that
Astragalus injection can increase the white blood
cells, lymphocytes and neutral of leukopenia model
mice. Granulocyte and monocyte count; its effect of
increasing white blood cells may be related to the
metabolism of linoleic acid, the biosynthesis of
phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan, and the
metabolism of phenylalanine. Protein digestion and
absorption: OSis a component of the animal body
and participates in various life activities of the
Qinghai Lake naked carp (Deng, 2020), Li et al. (Li,
Wang, Xu, 2015) used transcriptomics to study hens
before and after laying eggs In liver tissue, a large
number of differential genes were found to
participate in amino acid metabolism pathways.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, a non-targeted metabolomics study
was conducted on 30 cases of naked carp liver tissue
samples using LC-MS analysis method. The main
conclusions can be summarized as follows: (1)
Obtain the metabolite list and data matrix, combine
the T test and VIP(OPLS-DA) to screen out the
different metabolites, (2) Among the 1,525
differential metabolites identified, there are 221 90
KEGG annotations were obtained for metabolites
(3) The 65 differentially expressed proteins
identified were mainly derived from primary bile
acid biosynthesis: M, linoleic acid metabolism: M,
protein digestion and absorption: OS. In future
work, Progenesis QI (Waters Corporation, Milford,
USA) software is used for metabolite annotation,
data preprocessing, etc., to carry out metabonomics
research on the mechanism of low-salt impact on the
Metabonomics Study on the Mechanism of the Effect of Low Salt on the Liver of Qinghai Lake Naked Carp
229

liver of Qinghai Lake naked carp, and to improve
the use of pathway analysis, Advanced analysis,
such as association analysis and cluster analysis,
mine the biological information of differential
metabolism.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was funded by funds from the
National Key R&D Program of China
(2020YFD0900103); Beijing Academy of
Agriculture and Forestry Sciences young scholar
fund (QNJJ202020); Beijing modern agricultural
industrial technology system project.
REFERENCES
CAO Yi-Bin, WU Lan-Qin1, SHAO Lin-Xiang1, et al.
EXPRESSION AND PURIFICATION OF
RECOMBINANT INSULIN-LIKE GROWTH
FACTOR-II OF NAKED CARP (GYMNOCYPRIS
PRZEWALSKII) IN LAKE QINGHAI [J]. Acta
Hydrobiologica Sinica (Acta Hydrobiol Sin, 2010,
34(2): 459-462.
Deng LiIing. Effect and Mechanism of Mulberry Leaf and
Konjac Compound Powder on the Digestion and
Metabolism of Animal Derived High Protein Diet of
Old Mice [D]. Southwest University, 2020.
He H, An F, Huang Q, et al. Metabolic effect of AOS-iron
in rats with iron deficiency anemia using LC-MS/MS
based metabolomics[J]. Food Research International,
2019, 130:108913.
Jin W, Li Z, Ran F, et al. Transcriptome analysis provides
insights into copper toxicology in piebald naked carp
(Gymnocypris eckloni)[J]. BMC Genomics, 2021,
22(1).
Lian hua Feng. Effects of Low Salinity on Growth and
Physiology of Juvenile Orange-spotted Grouper
(Epinephelus Coioides) [D]. Guangdong Ocean
University, 2012.
Liu L, Jiang H Z, Shen B. Influence of Gandouling on
Liver Metabolites in Rats with Liver Injury Induced
by Copper Overload[J]. Journal of Anhui University
of Chinese Medicine, 2016.
LIXiu-long, HU Cheng, LI Yun-heet al. Mechanism study
of acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in rats
based on metabolomics [J]. Chinese Pharmacological
Bulletin, 2020, 36(08): 1068-1075.
LIU Teng, XU Jinfang, LU Xiaolin, et al. Study on the
Intervention Effects of Huangqi Injection on
Leukopenia Model Mice Based on LC-MS
Metabolomics [J]. China Pharmacy, 2020, 31(21):
2627-2633.
Li H, Wang T, Xu C, et al. Transcriptome profile of liver
at different physiological stages reveals potential
mode for lipid metabolism in laying hens[J]. BMC
Genomics, 2015.
MA Rong,XIE Qian,W ANG Jian, et al. Metabolomics
study on effects of compatibility of alcohol extracts of
Magnolia officinalis and Polygala tenuifolia on urine
metabolites in rats [J]. Chinese Pharmacological
Bulletin, 2019, 35(06): 870-877.
Walker K. F.,Dunn I. G.,Edwards D., Petr T., Yang H. Z..
A fishery in a changing lake environment: The naked
carpGymnocypris przewalskii (Kessler) (Cyprinidae:
schizothoracinae) in Qinghai Hu, China[J].
International Journal of Salt Lake Research,
1995,4(3).169-222
WANG Ping, LAI Qi-fang, YAO Zong-li, et al.
Differential expressions of genes related to HCO3-
secretion in the intestine of Gymnocypris przewalskiii
during saline-alkaline water transfer [J]. MARINE
FISHERIES, 2015(04):341.
Wang Jun. Effects of environmental factors on the ability
of Takifugu obscurus to tolerate salinity and its
differences at the level of transcriptomics [D]. Nanjing
Normal University, 2018.
Wen Xin. Study on the Physiological Response and
Molecular Mechanism of Takifugu fasciatus to Low
Temperature Stress [D]. Nanjing Normal University,
2019.
Yong Zhong. Effects of salinity on growth and osmotic
gene expression in spotted scat (Scatophagus argus)
[D]. Shanghai Ocean University.
Yang lei. Correlation between sarcopenia and
metabolicsyndrome in middle-aged and elderly people
and metabonomics research [D]. Xinjiang Medical
University,2020.
Zhang Xiaoyan, Wen Haishen, Zhang Kaiqiang, et al.
Analysis of the isotonic point and effects of seawater
desalination on the Na+/K+/Cl- concentration,
Na+-K+-ATPase activity and relative gene
expressions in Lateolabrax maculatus [J]. Journal of
Fisheries of China, 2018, v.42(08):34-43.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
230
