
UVA Induced Quality Deterioration of Ponkan Mandarin Juice
Guijie Li
1,2 a
, Yujiao Cheng
2b
, Jun Wang
2c
and Tenghui Zhang
3d
1
Chongqing Collaborative Innovation Center for Functional Food, Chongqing University of Education, Xuefu Rd., Nan’an,
Chongqing, China
2
Citrus Research Institute, Southwest University, Xiema, Beibei, Chongqing, China
3
Chengdu Centre Testing International Group Co., Ltd., Xinsheng Rd., Wuhou, Chengdu, China
Keywords: UVA, Ponkan, Juice Quality, Volatile, Off-Flavor.
Abstract: Ponkan mandarin is a promising variety of citrus fruit for juice production. However, there is little knowledge
in shelf-stability of Ponkan juice under normal sun lighting. In this study, Ponkan juice was investigated for
the changes of quality under the most common powerful irradiation of sunlight, ultraviolet A (UVA).
Properties related to taste, color, nutritive values, characteristic mandarin aroma, and volatile sulfuric off-
flavor were analyzed to make a comprehensive evaluation. The results showed that after 50 days UVA
radiation through PET bottles at 25°C, juice acidity, total soluble solid content, chromaticity values, vitamin
C and B2 content decreased significantly, and the characteristic mandarin aroma weakened. In addition, 10
more volatile sulfur compounds introducing distinctly off-putting smell were detected than the fresh juice.
UVA is responsible for the accelerated deterioration of Ponkan juice quality and should be properly shielded.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco) is a verity of
citrus whose fruits are thin-skinned and easy-peeling.
The most popular cultivars include Ponkan, Satsuma,
Tangerine and Clementine. According to a report
from the United States department of agriculture, the
global production of mandarin will reach 30 million
tons per year (USDA 2019). Almost all mandarin
production is sold as fresh fruit. Due to the saturation
of the fresh fruit market and the changes in consumer
preferences, an increase in mandarin juice production
is to be anticipated.
Food products placed on outdoor market shelves
are exposed to sun light. It is known that light,
especially ultraviolet, can accelerate the oxidation of
fat, degradation of ascorbic acid, browning of color,
and formation of off-flavor
(Conrad 2005, Zhang
2015, Hashizume 2006). Riboflavin-promoted
formation of reactive oxygen species, such as
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9701-4796
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7130-3143
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2887-6429
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0311-775X
superoxide anion, single oxygen, hydroxyl radical
and hydrogen peroxide, can result in the degradation
of amino acids, lipids, carbohydrates, and vitamin
(Grant 2017). In the presence of light and oxygen, off-
flavor can be formed in the orange juice due to the
lipid peroxidation (Fan 2004). Light also increases
the off-flavored volatiles in cloudy apple juice such
as 1-octen-3-one pentanal, 2-methyl-1-penten-3-one,
hexanal, (E)-2-heptenal, 6-methyl-5-hepten-2-one,
and (E)-2-octenal (Hashizume 2006).
Volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) are known to
be responsible for heated juice off-flavor (Cheng
2020). They introduce a variety of odor
characteristics: rotten eggs, potato, cabbage, meat,
coffee, and onion (I-Min 2011). VSCs are
degradation products of amino acid precursors like
methionine, S-methyl methionine, cysteine and so on
(Gonda 2013, Lee 2014). In white wines, UV-visible
light can increase the amount of volatile methanethiol
and dimethyl disulfide, too, resulting in the sunlight
flavor (Grant 2017).
Juice quality is a comprehensive combination of
color, flavor, nutritive value, and other physical-
Li, G., Cheng, Y., Wang, J. and Zhang, T.
UVA Induced Quality Deterioration of Ponkan Mandarin Juice.
DOI: 10.5220/0011213600003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 411-415
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
411

chemical properties. Mandarin juice had been less
studied for its quality. The objective of this study was
to investigate changes of several commercially
important properties of Ponkan mandarin juice such
as chromaticity, vitamin C and B2, volatile organic
and sulfur compounds after an ultraviolet-A (UVA)
radiated shelf-life, and evaluate the resulting
deteriorative effect on the juice quality.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Sample Preparation
Fresh mature Ponakan fruits were purchased from a
local market in Chongqing, China. Fruits were hand-
squeezed and the released juice was pasteurized for
30s at 98℃ and hot-filled into sterile 200 mL
polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles. Bottles
were sealed and cooled immediately using an ice bath
to reach the ambient temperature. Bottles were
exposed separately in the dark (control) or under
UVA (360nm, 25μW/cm
2
) radiation at 25℃ for a 50-
day shelf-life study.
2.2 Vitamin C Determination
A 2,6-dichloro indophenol method was used to
determine the content of ascorbic acid (Harris 1942).
2.3 Measurement of Chromaticity
L*, A* and B* were measured respectively by using
a Juice chromometer, where L* value indicates
whiteness, A* for red/green color, and B* for
yellow/blue color (Min 2002).
2.4 Extraction and HPLC Analysis of
Riboflavin
A C18 solid-phase extraction procedure was adopted
with modifications from Blanco-Gomis (Gomis
1994). Fifteen milliliters of juice were acidified with
2 mL of 1M H
2
SO
4
at 100℃ for 30 min. It was cooled
down and adjusted to pH5-6. A 15 mL mixture was
centrifuged at 13362 g for 15 min. The supernatant
passed through a C18 cartridge that had been
previously conditioned by 5 mL methanol and
washed with 10 mL of water. Riboflavin was eluted
using 5 mL of methanol. Solvent was evaporated
under nitrogen at 35℃. The extract was then
redissolved in 0.4ml of aqueous methanol solution
(50/50, v/v) and membrane filtered before an HPLC
injection.
An Agilent C18 column (150×4.6 mm, 5μm)
connected to a 1260 LC system was used to analyze
riboflavin. Separation was based on an isocratic
method using methanol-water (35:65, v/v) as the
solvent. The flow rate was 0.7 mL/min, and the
injection volume was 5 μL. Fluorescence detection
was monitored at an emission wavelength of 522 nm.
2.5 Static Headspace Solid-phase
Micro-extraction
A 20 mL vial containing 5 mL of juice was
equilibrated at 40℃ for 20 min. A 2 cm-long fiber
coated with divinylbenzene/carboxen/polydimethyl-
siloxane (DVB/CAR/PDMS) was exposed in the
headspace for 30min. The extracted juice volatiles
were desorbed for 5 min at 200℃ in GC inlet port.
2.6 Gas Chromatography-Mass
Spectrometry/Pulsed Flame
Photometric Detection
(GC-MS/PFPD)
Volatiles were analyzed using an Agilent-7890B GC
equipped with a 5977B MS detector coupled to a
5380 PFPD (OI Analytical). Separation was on an
RTX-Wax column (60 m×0.25 mm id×0.25 μm). The
temperature program was set as the following
gradient: 35℃ for 6min; linearly elevated to 203℃ at
a rate of 7℃/min and held for 10 min. Electron impact
(EI) voltage was set at 70 ev, and the m/z range was
set between 44 and 300 amu. For VSCs detection, the
temperature of PFPD was set at 250℃. Identification
of compounds was confirmed by matching the TIC
spectra to the mass spectral library (W10N14),
comparing with authentic standards, and/or checking
their linear retention index (LRI). Quantitation of
characteristic volatiles was applied by using a
cyclohexanone internal standard method.
2.7 Sensory Evaluation
Ten well-trained assessors (6 females and 4 males,
ages between 22 and 40 years) participated in sensory
analysis of Ponkan juice. Sensory evaluation was
conducted at room temperature under clean air
conditions. Evaluation criteria are shown in Table 1
as below.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
412

Table 1: Sensory evaluation criteria for Ponkan juice.
Item Score Criteria
Appearance
and Defects 20 No stratification, flocculation &
obvious defects, 20 points; a small
amount of flocculation,
stratification & impurities, 12-19
points; serious flocculation,
stratification & impurities, 0-11
points.
Flavor 50 Showing citrus characteristic
aroma, without any bitterness,
astringency, and off-flavor, 50
points; insufficient aroma, slightly
more sour or sweeter, no bitter,
astringent, but with a hint of
cooked smell, 35-49 points; poor
aroma, too sour or sweet, with a
slight bitterness and cooked smell,
18-34 points; no characteristic
aroma, very sour, bitter and
serious smelly, 0-17 points.
Color 30 Typical bright mandarin color,
stable and homogenous, 18-30
points; dim and uniform, 14-17
points; dark and less uniform, 10-
13 points; colorless and
nonuniform, 0-9 points.
2.8 Data Analysis
All analyses were performed in triplicate. Analysis of
variance were performed using SPSS 22.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Changes in Physical and Chemical
Indices
After 50 days UVA radiation, results of the essential
physical and chemical properties relating to Ponkan
juice quality are shown in Figure 1. Juice stored in
dark condition is compared as a control. Data with
significant differences are labelled with different
letters. The figure shows that juice acidity, total
soluble solid content, color (including brightness L*,
redness a*, and yellow b*), vitamin C content, and
vitamin B2 content were all significantly lower in
UVA radiated juice than those in dark stored and
fresh juices. Particularly, over 98% of riboflavin
(VB2) had been lost. They were likely to participate
in the formation of reactive oxygen species and
responsible for the degradation of VC which
decreased by about 70%.
Figure 1: Comparison of major physical and chemical
properties among three juice samples.
Notes: TSS, total soluble solids; L*, a*, b*, three
dimensions of chromaticity; a-c, significant differences.
3.2 Characteristic Volatile Flavor
Components
In addition to taste, color and nutritional properties,
characteristic mandarin aroma is another important
trait of Ponkan juice. The characteristic aroma
compounds in fresh juice and juices that had been
stored for 50 days in dark condition and under UVA
lighting were analyzed using GC-MS. The odor
activity value (OAV), which is a quotient of the
sample concentration divided by the threshold
concentration, were calculated to describe the
aroma/flavor intensity of each compound. The results
of compound identification, odor description and
OAVs of the three samples are shown in Table 2.
There were significant differences of the intensities of
various aroma attributes among samples. For
example, OAVs of off-flavor compounds such as α-
pinene (piny), β-myrcene (moldy), perillaldehyde
(solvency), terpinen-4-ol (woody), thymol
(medicinal), and carvone (caraway) have greatly
increased after 50 d UVA irradiation. Accumulation
of these compounds would destruct the aroma balance
of the Ponkan juice. Only slight increases were
detected in the juice sample stored in dark. In
addition, some typically good aroma attributes such
as citrusy, green, lemony, floral, mint, and fruity have
decreased considering their total aroma intensity.
UVA Induced Quality Deterioration of Ponkan Mandarin Juice
413
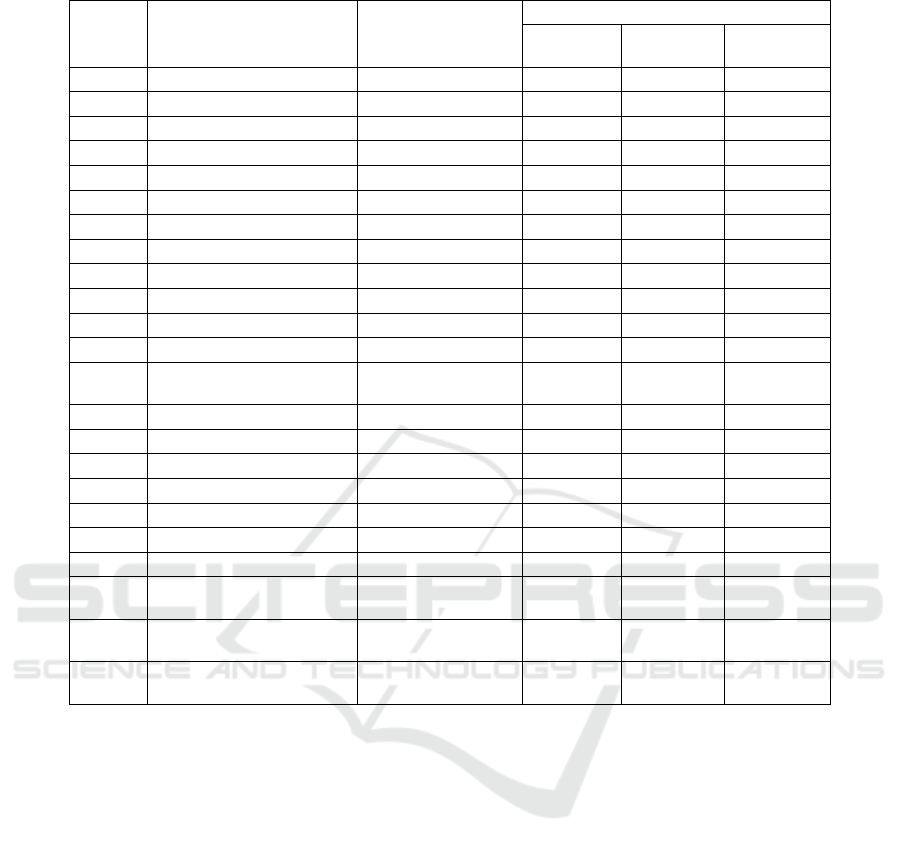
Table 2: Characteristic aroma identification and flavor intensity among three Ponkan juice samples.
No. Compounds Odor
OAV
0 d
50 d
dar
k
50 d
UV
1 α-pinene piny 59 100 124
2 camphene camphor 16 2 2
3 β-myrcene moldy 45 63 82
4 d-limonene citrusy 1430 860 1060
5 p-cymene citrusy 51 71 173
6 γ-terpinene citrusy 43 34 23
7 terpinolene piny 26 21 17
8 hexanal green 16 7 6
9 nonanal lemony 6 4 2
10 perillaldehyde solvency 4 5 7
11 1-octanol citrusy 1 1 -
12 linalool floral 860 370 330
13
cis-p-2-
menthen-1-ol
mint 16 2 2
14 fenchol unpleasant - - 2
15 terpinen-4-ol woody 2 5 5
16 α-terpineol floral 4 15 23
17 citronellol fruity 9 19 24
18 carveol caraway 0 0 1
19 thymol medicinal 2 2 8
20 carvone caraway 2 4 120
21
ethyl 2-methyl
p
ropanoate
fruity 30 36 43
22
butanoic acid,
ehtyl este
r
fruity 8 2 2
23
ethyl 2-methyl
b
utanoate
fruity 1720 1790 340
Notes: OAV, odor activity value.
3.3 Volatile Sulfur Compounds
Volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) are known to be
responsible for a variety of bad smell characteristics.
In this study we found both the number of compounds
and their concentrations were increased after 50 d
storage. As shown in Figure 2, fresh Ponkan juice
only contain small amount of hydrogen sulfide (H
2
S),
methanethiol (MeSH), dimethyl sulfide (DMS), and
ethyl (methylthio)acetate (EMA). Additional VSCs
were found in the 50 days stored juice, such as S-
Methyl thioacetate, (MTA), dimethyl disulfide,
(DMDS), 2-methylthiophene (2-MT), 3-
methylthiophene (3-MT), dimethyl trisulfide
(DMTS), and methional. The content of DMS
increased, too. After 50 days storage under UVA
radiation, more amount of DMS, DMDS, 2-MT, 3-
MT, DMTS and methional were observed. Carbon
disulfide (CS
2
) and three unknown VSCs were newly
detected. The odors of DMS, DMDS, DMTS,
methional, and CS
2
have been described as cabbage,
onion, garlic, cooked potato, and solvency,
respectively. Increases of these specific sulfur off-
flavors in addition with other unknown VSCs would
definitely undermine the comprehensive flavor of
Ponkan juice.
3.4 Deterioration of Juice Overall
Quality
The overall apparent sensory quality scoring by
assessors showed a consent to above analytical
results. In the item of Appearance and Defects, scores
for fresh juice, 50 days in dark and 50 days under UV
were 18, 17 and 15. Scores of Flavor were 40, 37 and
30, respectively. Color scores were 18, 18 and 17,
respectively. The total scores were 76 (fresh), 72
(dark) and 62 (UVA).
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
414

4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study we have shown that the overall quality
of Ponkan mandarin juice deteriorated after being
placed on shelf under UVA radiation at an ambient
temperature (25°C) for 50 days. The control, same
juice placed in dark, showed a much better quality
close to the fresh juice. These results demonstrate that
UVA, the major UV irradiation in our everyday life,
should be screened so that to protect juices from
quality deterioration.
Figure 2: VSCs chromatogram detected using PFPD.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was financially supported by the Scientific
and Technological Research Program of Chongqing
Municipal Education Commission (KJQN201801613
and KJQN202100209).
REFERENCES
Cheng, Y. J., et al. (2020) Methanethiol, an off-flavor
produced from the thermal treatment of mandarin
juices: a study of citrus sulfur volatiles. J. Agric. Food
Chem., 68(4): 1030-1037.
Citrus: World markets and trade. https://apps.fas.usda.gov/
psdonline/circulars/citrus.pdf (accessed Sep 2019).
Conrad, K. R., et al. (2005) Influence of PET and PET/PEN
blend packaging on ascorbic acid and color in juices
exposed to fluorescent and UV light. J. Food Sci.,
70(1): 19-25.
Fan, X. (2004) Involvement of volatile sulfur compounds in
ionizing radiation-induced off-odor of fresh orange
juice. J. Food Sci., 69(8): 593-598.
Gomis, D. B., et al. (1994). High-performance liquid
chromatographic determination of cymiazole in honey
with UV and electrochemical detection.
Chromatographia, 39(9): 602-606.
Gonda, I., et al. (2013) Catabolism of L-methionine in the
formation of sulfur and other volatiles in melon
(Cucumis melo L.) fruit. Plant J., 74(3): 458-472.
Grant, P. P., et al. (2017) Light-induced changes in bottled
white wine and underlying photochemical mechanisms.
Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutri., 57(4): 743-754.
Harris, L. J. & Olliver, R. J. (1942) Vitamin methods 3. The
reliability of the method for estimating vitamin C by
titration against 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol. 1.
Control tests with plant tissues. Biochem. J., 36: 155-
182.
Hashizume, M., et al. (2006) Light-induced off-flavour in
cloudy apple juice. Dev. Food Sci., 43(06): 273-276.
I-Min, T. & Mina, R.M. (2011) Volatile Sulfur Compounds
in Food. In Understanding Aroma Impact of Four
Important Volatile Sulfur Compounds in Oregon Pinot
Noir Wine, Qian, M.C., Fan, X., and Mahattanatawee,
K. (Eds.), Am. Chem. Soc., Washington. pp. 279-312.
Lee, H. R., et al. (2014) Digestive recovery of sulfur-
methyl-L-methionine and its bioaccessibility in Kimchi
cabbages using a simulated in vitro digestion model
system. J. Sci. Food Agric., 94(1): 109-112.
Min, J. S., et al. (2002) Real Effect of pH on CIE L*, a* and
b* of Loins during 24 h Chilling of Beef Carcasses.
Asian Austral. J. Anim., 15: 2.
Zhang, L. C.et al. (2015) Regulation of ascorbic acid
metabolism by blue LED light irradiation in citrus juice
sacs. Plant Sci., 233: 134-142.
UVA Induced Quality Deterioration of Ponkan Mandarin Juice
415
