
Effect of Helianthus Tuberosus Straw and Sheep Manure Ratio on
Growth and Fruit Quality of Pepper
Xiangyun Lou
a
, Xiaoqiang Wei
b
, Guangnan Zhang
c
, Yi Li
d
and Qiwen Zhong
*e
Qinghai University Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Key Laboratory of Vegetable Genetics and Physiology of
Qinghai Province, Xining, Qinghai, China
Keywords: Fermented, Erusalem Artichoke Straw, Substrate Cultivation, Pepper, Quality and Yield.
Abstract:
Helianthus tuberosus is an emerging economic crop that has developed rapidly in Northwest China in recent
years. Its straw biomass is large, but its utilization rate is still low at present. To solve the problem of combined
utilization, this paper carried out a study on the appropriate ratio of Helianthus tuberosus fermented stalks and
sheep manure in the substrate cultivation of different varieties of pepper. The results showed that when the
ratio of Helianthus tuberosus stalks to sheep manure is 1:3, the physical and chemical properties of two
different pepper varieties, such as pH and aeration porosity, are better than the seedling substrate treatment
within a reasonable range after 100 days of cultivation; the soluble sugar and vitamin C content of the two
pepper fruits are significantly higher than the seedling substrate treatment, reaching 71.59mg/g and 102.95
mg/g, respectively; compared with the seedling substrate treatment, the yield of the two peppers increased by
3% and 5% respectively. Therefore, the suitable substrate ratio for pepper cultivation is: V
Helianthus tuberosus straw
:
V
sheep manure
: V
substrate soil
: V
perlite
: V
vermiculite
=1: 3: 3: 1: 1.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Helianthus tuberosus (Helianthus tuberosus L.), a
perennial herb with strong adaptability, has the
characteristics of cold and drought resistance, barren
tolerance, and strong stress resistance. It is an
extensive plant (Wu, 2013; Xue, 2017). The above-
ground stems and leaves of Helianthus tuberosus
have high protein, sugar and other nutrients, and the
biomass accounts for 40%-50% of the total plant (Li,
2011). Each hectare of Helianthus tuberosus tubers
can produce 2~3t, and the yield of stems and leaves
is8.7t (Xiang, 2019). At present, the research and
development of Helianthus tuberosus is mainly
concentrated on desertification of saline-alkali land
(Lu, 2007), inulin content (Liu, 2016), biotechnology
(Wang, 2004), feed value of stems and leaves (Yan,
2018), bioenergy (Liu, 2012), etc. It is the research on
the underground tubers of Helianthus tuberosus, and
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9609-953X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3811-9528
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6123-5987
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6171-2349
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2118-7401
there are few studies on the utilization of the above-
ground stems and leaves (Ji, 2017).
Organic ecological soilless cultivation is a new
type of crop cultivation mode that has developed
rapidly in recent years. The use of solid fertilizer
instead of nutrient solution greatly reduces the
investment cost and has the characteristics of
simplicity, practicality, and effectiveness. The
substrate is mainly agricultural waste such as straw
and animal manure, and the recycling of agricultural
waste is also an important way to achieve sustainable
agricultural development. Previous studies have
concluded that the application of Helianthus
tuberosus leaves into the soil has a certain inhibitory
effect on the growth of weeds (Wang, 2018)
and
Helianthus tuberosus stalks are conducive to the
growth of continuous cropping tomatoes and have a
certain effect on root-knot nematode control (Song,
2013). Regarding the substrateization of crop stalks,
Song’s research (Tong, 2012) showed that the growth
of tomatoes grown on a composite substrate of 100%
514
Lou, X., Wei, X., Zhang, G., Li, Y. and Zhong, Q.
Effect of Helianthus Tuberosus Straw and Sheep Manure Ratio on Growth and Fruit Quality of Pepper.
DOI: 10.5220/0011224800003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 514-522
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

rice straw, rice straw: rice husk=75V:25V performed
better, and indicators such as stem thickness and
number of leaves were significantly better than the
control. And the yield has increased by 30%~33%; it
shows that substrate cultivation can indeed increase
the yield of peppers, tomatoes and other vegetables.
The experiment of Tong (Fu, 2010) proved that the
volume ratio 4:6 is the best among the different ratios
of coal gangue and decomposed rape straw, and the
plant height, fresh weight and number of leaves of
vegetables such as cabbage and lettuce are all
significant. Better than soil cultivation; Fu’s (Liu,
2017)
experiments proved that adding fermented corn
stalks can improve the risk resistance of greenhouse
pepper overwintering cultivation to a certain extent,
and at the same time improve the quality of pepper to
a certain extent, promote early maturity of pepper,
and increase total output; Liu et al. found that the
substitution amount of Helianthus tuberosus
fermented straw for peat is best when adding 20%-
40% to the substrate of peat and vermiculite (Li,
2003); Ji further refined the research on this basis and
concluded When the addition of Helianthus tuberosus
straw was 20%-30%, the vitamin C, soluble sugar
content and sugar-acid ratio were significantly higher
than the control. When the addition of Helianthus
tuberosus straw was 20%, the yield increased by 14%
(Ji, 2017). At present, there are many researches on
Helianthus tuberosus stalks used in tomato planting,
and there are few researches on pepper planting.
However, through the above research, it can be seen
that Helianthus tuberosus stalks have the potential to
be used as a pepper cultivation substrate.
Animal manure is rich in organic matter and
various nutrient elements required by crops, which is
an important substrate component for organic
ecological soilless cultivation. Sheep manure is a
common material for substrate compounding. It has
features such as large yield, easy availability and low
cost in Qinghai. Therefore, in this experiment,
Helianthus tuberosus straw was used as the research
material, the fully fermented Helianthus tuberosus
straw and sheep manure were mixed in different
proportions, and V
substrate soil
: V
vermiculite
: V
perlite
=3:1:1
was added to each treatment, then used as a pepper
cultivation substrate. The trough-type soilless
cultivation method is used to monitor the physical
and chemical properties of the substrate and the
growth of peppers, analyze and determine the
physical and chemical properties of the composite
substrate and the growth, quality, and yield of
peppers, compare the differences between different
ratios, and find suitable Qinghai The cultivation
substrate for provincial pepper cultivation combines
the resource utilization of agricultural waste with
soilless cultivation, improves the utilization rate of
Helianthus tuberosus stalks, promotes the
development of Helianthus tuberosus and pepper
industry, and provides a theoretical basis for
promoting the development of circular agriculture.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
Helianthus tuberosus straw comes from the
Horticultural Innovation Base of Qinghai Academy
of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences. It was
harvested on October 20, 2018 and crushed into small
pieces of about 1 cm; the straw fermentation
inoculum was selected from the straw degradation
agent 008-J produced by Zhengzhou Yifuyuan
Biotechnology Co., Ltd.; the inoculum was used
Propagating at room temperature for 5-7 days,
stirring every day; fermentation adopts indoor static
high temperature and aerobic method, turning the pile
and sprinkling water every 5 days to keep the
moisture content at about 60%; the average indoor
temperature is 6.3℃; the tested pepper varieties were
Qinghai local variety “Ledu long pepper” and main
variety “Hangjiao No. 8”. The LED plant sterilization
fill light used in the experiment was provided by
Zhejiang Xiaoyang Agricultural High-tech Co., Ltd.
2.2 Experimental Design
The experiment was carried out in the plastic
greenhouse of the Horticulture Innovation Base of the
Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences of
Qinghai University. It adopted a completely
randomized block design with a total of 5 treatments
(see Table 1), among which the seedling substrate (V
Substrate Soil
: V
Perlite
: V
Vermiculite
= 3:1:1) as control group
(CK), 3 repetitions, 2 test pepper varieties (P1 is
“Ledu long pepper”, P2 is “Hangjiao No.8”), a total
of 30 plots with a plot area of 2.1m
2
. The digging
groove was used for cultivation, with a length of 300
cm, a width of 70 cm, a depth of 35 cm, and a groove
spacing of 50 cm. The cultivation substrate was
isolated by a plastic shed film. Double-row planting,
single-stem pruning, plant spacing 30cm, and
planting 20 plants per groove were adopted. On
February 25, 2019, the pepper seeds were soaked and
disinfected with 72-hole plastic plugs for sowing. The
seedling substrate ratio was V
Substrate soil
: V
Perlite
: V
Vermiculite
= 3:1:1. When the pepper seedlings grow to
8 leaves of each core, and the seedling age is 55 days,
Effect of Helianthus Tuberosus Straw and Sheep Manure Ratio on Growth and Fruit Quality of Pepper
515

healthy and healthy seedlings were chosen to be
planted on April 20, and the integrated irrigation
method of water and fertilizer was used for watering
management, and irrigate the special nutrient solution
for pepper prepared , then place an LED plant
sterilization fill light 1m away from the top of the
plant, 1 lamp / 10m
2
by the Academy of Agriculture
and Forestry Sciences of Qinghai University. The
physical properties of the substrate were measured at
the time of planting and 100d after planting; the
growth and quality indexes of pepper were measured
at 60 days, 90 days and 120 days after planting.
During the growth period of pepper, all other
conditions were set as the same.
Table 1: The ratio of Helianthus tuberosus straw substrate (volume ratio).
Treated
Helianthus
tuberosus straw
Sheep
manure
Matrix soil Perlite Vermiculite
C
K
- - 3 1 1
Q1 2 2 3 1 1
Q2 3 1 3 1 1
Q3 1 3 3 1 1
Q4 - 2 3 1 1
2.3 Index Measurement and Method
2.3.1 Physical Properties of the Substrate
Refer to the method of Li (Guo, 2005), the physical
and chemical properties of the decomposed straw
were determined, including bulk density, total
porosity, aeration porosity, water pore porosity, air-
water ratio, pH, EC value, etc. A beaker with a known
volume (650 mL) and weigh (W1) was used; adding
the dried straw to the beaker and weighing as W2;
sealing the beaker with two layers of wet gauze and
soaking it in water overnight (i.e., the water should
cover the top of the container), taking out the
weighing as W3, and weighing the wet gauze as W4.
Sealing the beaker again with wet gauze and turning
it upside down, making the water in the cup drain
freely until no water flows out, and weigh as W5. The
indicators were calculated as the following formula:
Bulk density (BD)/(g·cm
-3
)=(W2-W1)/V;
Total porosity (TP)/%=(W3-W2-W4)/V×100;
Aeration porosity (AFP)/%=(W3-W5)/V×100;
Water pore porosity (WPP)/%=total porosity-
aeration porosity;
Air-water ratio = aeration porosity/ water pore
porosity.
Drying he pile material and smashing it, mixing it
with the volume ratio of 1:10 of pile material and
distilled water, placing it in a shaker (200 r·min
-1
, 30
min), after shaking the supernatant was taken for later
use. ORION STAR A211 pH meter was used to
measure pH and FiveEasy conductivity meter was
used to measure EC value.
2.3.2 Growth and Quality Index of Pepper
The ground part and fruit of pepper was sampled, and
a ruler was used to measure the plant height, leaf area
and plant width; a vernier caliper was used to measure
the stem thickness of the pepper; when the pepper
fruit matures, the yield per plant and the total yield
were directly harvested and weighed.
According to the “Guide to physiological testing
of plants”, the soluble protein content of pepper
leaves and fruits was determined by the Coomassie
brilliant blue colorimetric method; the vitamin C
content of pepper fruit was determined by the
molybdenum blue colorimetric method; the soluble
sugar contents of pepper fruits and above-ground
parts were determined by the Anthrone colorimetry;
the dry matter contents of the ground part and fruit of
the pepper were determined as the dry mass per
plant/fresh weight per plant.
2.4 Data Analysis
The data was processed and analyzed using Excel
2007 and SPSS16.0 data analysis software.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 The Physical and Chemical
Properties of the Matrix with
Different Proportions
By measuring the physical and chemical properties of
the cultivation substrates of the two pepper varieties
on the 1st and 100th days, it was found that the pH,
EC and bulk density increased to different degrees in
different treatments, the aeration porosity decreased
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
516
and the water pore porosity increased. The air-to-
water ratio drops accordingly. It shows that through
the irrigation of nutrient solution, secondary
fermentation and further decomposition of humus, the
matrix is loose and air-permeable, which effectively
improves the physical and chemical properties of the
matrix. It can be seen from the treatment of the
cultivation substrates of the two pepper varieties that
the pH and bulk density of the Q3 treatment were the
highest at 100 days, reaching 6.8, 0.19 and 6.82, 0.18,
respectively, and other indicators were better than the
control group (Table 2).
Table 2: The physical and chemical properties of different Helianthus tuberosus straw composite substrates.
treated
Bulk
density(g·cm
-3
)
Aeration
porosity (%)
Water pore
porosity (%)
Air-water
ratio (%)
pH EC (ms/cm)
1d 100d 1d 100d 1d 100d 1d 100d 1d 100d 1d 100d
P1
CK 0.16 0.18 14.26 9.64 50.58 57.87 0.28 0.17 5.76 6.75 9.12 10.72
Q1 0.15 0.18 14.17 12.27 49.36 53.02 0.29 0.24 5.53 6.62 9.31 11.28
Q2 0.15 0.17 17.92 17.15 48.12 50.84 0.37 0.34 5.86 7.33 9.54 11.73
Q3 0.16 0.19 18.91 16.54 52.31 59.34 0.36 0.28 5.97 6.80 9.28 11.90
Q4 0.16 0.18 15.16 11.29 52.89 58.47 0.29 0.19 5.42 6.16 9.49 11.10
P2
CK 0.16 0.18 14.26 10.23 50.58 59.21 0.28 0.17 5.76 6.63 9.12 10.51
Q1 0.15 0.18 14.17 12.37 49.36 53.81 0.29 0.23 5.53 6.71 9.31 11.32
Q2 0.15 0.18 17.92 15.21 48.12 52.34 0.37 0.30 5.86 6.97 9.54 10.95
Q3 0.16 0.18 18.91 16.37 52.31 58.21 0.36 0.29 5.97 6.82 9.28 11.28
Q4 0.16 0.18 15.16 11.08 52.89 57.12 0.29 0.19 5.42 6.24 9.49 11.14
[Note] P1 is “Ledu long Pepper”, P2 is “Hangjiao No.8”, the same below.
Different lowercase letters after the numbers in the same column indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level, the same
below.
3.2 The Effect of Different Substrates
on the Growth and Development of
Pepper
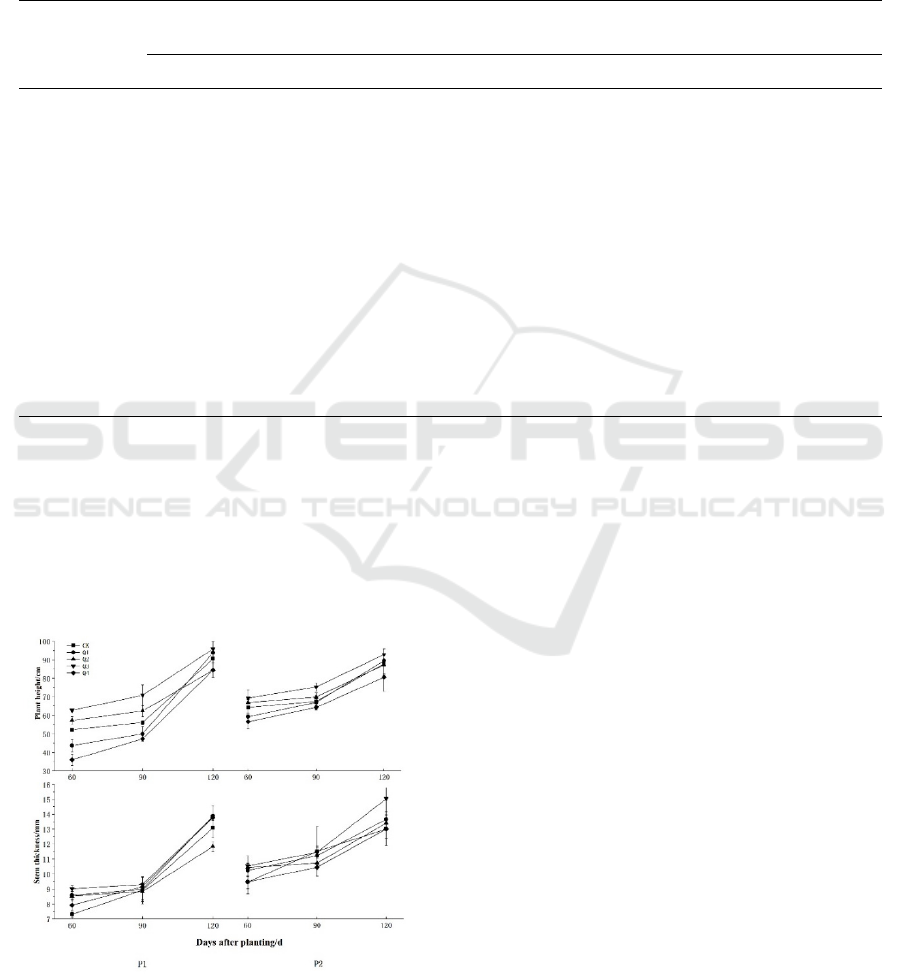
1. Plant height; 2. Stem thickness; 3. Days after planting.
Figure 1: The effect of different substrates on pepper plant
height and stem thickness.
After 60 days of planting, it was measured that the
stem thickness of Q3 treatment was larger in both
cultivars, 9.02 mm and 10.62 mm, which were
significantly larger than other treatments. The
treatment with Helianthus tuberosus straw added to
the two cultivars was larger than the control group;
after planting 90 days, Q3 and Q4 were larger in P1,
Q1 and Q2 were smaller, and CK and Q3 were larger
in P2, but the difference between the treatments was
not significant; after 120 days of colonization, Q1 and
Q3 were larger in P1 and significantly higher than
those in Q2, the difference was significant by the
analysis of variance. In P2, the Q3 treatment was
larger, which was 15.23 mm, but there was no
significant difference between the treatments (Figure
1). The performance of each treatment in the different
periods of the two varieties shows that Q2 treatment
has a certain promotion effect on pepper growth
during the peak and early fruit period of pepper, but
the promotion effect gradually decreases in the later
stage of fruiting, and Q3 treatment can promote the
growth of pepper stems during the entire growth
period of pepper.
Effect of Helianthus Tuberosus Straw and Sheep Manure Ratio on Growth and Fruit Quality of Pepper
517

After 60 days of planting, it was measured that the
plant heights of the two varieties were 52.25cm and
64.22cm in the CK treatment, respectively, which
were significantly different from other treatments. In
P1, there were also greater differences between the
treatments with straw addition. However, there was
no difference in P2; after planting 90 days, the plant
height of the CK treatment in P1 was larger, 56.09cm,
and it was significantly different from other
treatments. In the treatment with straw addition, the
plant height of the Q1 and Q3 treatments was greater
than that of Q2, and the Q3 treatment had larger
significant difference. In P2, the plant height of CK,
Q1, Q2, and Q3 treatments was larger, and the
difference between the treatments was not
significant; after 120 days of planting, the plant
height of Q1 treatment was larger in P1 and P2
treatments, which were 93.87cm and 89.78cm, but
the difference between the treatments was not
significant (Figure 1). It shows that adding straw can
promote the growth of pepper plants, and the
performance between two different pepper varieties
is basically the same. Among them, the promotion
effect of Q1 treatment is better.
After 60 days of planting, it was measured that the
two cultivars treated with CK and Q3 had larger plant
widths, which were 41.54 cm, 42.08 cm, 54.43 cm,
and 53.13 cm, respectively, and they were
ignificantly different from other treatments. After 90
days of planting, CK and Q3 were significantly
different in P1. Q1, Q2, and Q3 treatments have
larger plant sizes, no significant difference between
treatments, and significantly larger than Q4
treatments. In P2, CK and Q3 treatments have larger
plant sizes and significant differences from each
treatment; after 120 days of colonization, the Q1 and
Q3 in P1 and P2 treatments treatments were larger
and significantly larger than the other treatments,
which were 68.98 cm, 69.58 cm and 75.78 cm, 76.92
cm, respectively (Figure 2).
After 60 days of colonization, the dry matter
content of Q3 in P1 was higher and significantly
greater than that of other treatments. In P2, Q3 and
Q4 treatments had no significant difference and were
significantly greater than other treatments; after 90
days of colonization, Q3 treatment in P1 was
significantly greater than other treatments. In P2, the
dry matter content of Q2, Q3, and Q4 treatments was
significantly greater than that of other treatments;
after 120 days of planting, the dry matter contents of
Q1 and Q3 treatments in P1 were significantly greater
than that of other treatments. In P2, Q3 and Q4
treatments were significantly greater than other
treatments (Figure 2). It indicated that the two
varieties performed the same in terms of dry matter
accumulation, and Q3 and Q4 treatments were better.
1. Plant width; 2. Dry matter weight; 3. Days after planting.
Figure 2: Effects of different substrates on pepper plant width and dry matter quality.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
518

3.3 The Effect of Different Substrates
on the Quality of Pepper Fruit
1. Soluble sugar content; 2. Vitamin C content; 3. Days
after planting.
Figure 3: Effects of different matrix ratios on the soluble
sugar and vitamin C content of pepper fruit.
The soluble sugar content of the fruit was measured
90 days after planting. In P1, the total soluble sugar
content of Q1 and Q3 treatments was significantly
higher than that of the other treatments, and the
difference between the two treatments was not
significant. In P2, the Q3 treatment was significantly
larger than the other treatments, which was 50.32
mg/g, the treatment with Helianthus tuberosus straw
added was significantly greater than that of the
control; at 120 days of colonization, the soluble sugar
content of the Q1 and Q3 treatments in P1 was
significantly greater than the other treatments, and the
content of the Q3 treatment reached 71.59 mg/g. In
P2, the soluble sugar content of the Q3 treatment was
significantly greater than that of other treatments, and
the content of the treatment with Helianthus
tuberosus straw was significantly greater than that of
the control group (Figure 3). The two varieties
showed similar differences in soluble sugar content,
indicating that adding Helianthus tuberosus straw to
the cultivation substrate can increase the soluble
sugar content of pepper fruits, while Q3 treatment can
better increase the soluble sugar content of fruits.
The vitamin C content of the fruit was measured
90 days after planting. In P1, the vitamin C content of
the Q3 treatment was greater than that of the other
treatments, but the difference between the treatments
was not significant. In P2, the Q1 and Q3 treatments
were significantly greater than the other treatments,
66.98 mg/ g and 73.40mg/g; at 120 days of
colonization, the vitamin C content of Q1 and Q3
treatments in P1 was significantly greater than that of
the other treatments, both exceeded 95mg/g, and the
content of Q3 treatment reached 102.95mg/g. In P2,
vitamin C contents of CK, Q1, Q2, and Q3 treatments
were significantly larger than Q4 treatment. The Q3
treatment had the largest value of 71.50 mg/g. The
treatment content with straw addition was
significantly greater than the control group with
sheep manure (Figure 3). The two cultivars showed
similar differences in vitamin C content. The vitamin
C content of the treatment with Helianthus tuberosus
straw was better than the control group, and the Q3
treatment performed best among them.
1. Soluble protein content; 2. Fruit dry matter content; 3.
Days after planting.
Figure 4: Effects of different matrix ratios on the soluble
protein and dry matter content of pepper fruit.
The soluble protein content of the fruit was
measured 90 days after planting. In P1, the soluble
protein content of Q1 treatment was greater than
other treatments, but the numerical difference was not
big and the content was small. In P2, Q2 treatment
was greater than other treatments but there was no
significant difference between treatments; when the
planting for 120 days, the soluble protein content of
both cultivars under Q3 treatment was higher, but the
values between treatments were smaller and there
was no significant difference (Figure 4), indicating
that adding Helianthus tuberosus straw has no
obvious effect on fruit resistance.
The dry matter content of the fruit was measured
after 90 days of planting. In P1, the dry matter content
of Q1 and Q3 treatments was significantly higher
than that of other treatments, and the content of
Helianthus tuberosus straw added treatment was
greater than that of the control group. In P2, the dry
matter content of Q3 treatment was greater than other
treatments. However, there was no significant
difference among the treatments; in P1, the dry matter
content of the CK, Q1, and Q3 treatments was greater
than that of the other treatments and there was no
significant difference between the three treatments. In
P2, the dry matter content of the Q3 treatment was
significantly greater than other treatments, and the
Effect of Helianthus Tuberosus Straw and Sheep Manure Ratio on Growth and Fruit Quality of Pepper
519

content of treatment with Helianthus tuberosus straw
added was greater than that of the control group
(Figure 4).
3.4 The Effect of Different Substrates
on the Yield of Pepper
The addition of Helianthus tuberosus stalks had an
effect on the number of fruits per plant, the yield per
plant and the total yield of the two pepper varieties,
but the effect was greater in P2 than in P1. In P1, there
was no significant difference in the number of fruits
per plant, yield per plant and total yield of each
treatment. The number of fruits per plant of CK
treatment was slightly higher than that of other
treatments. The yield of each plant and total yield of
Q3 treatment were higher than those of other
varieties; in P2, the number of fruits per plant in Q3
treatment was the highest and was significantly larger
than that in other treatments, which was 32.80. The
yield of each plant and total yield were also the largest
in Q3 treatment, reaching 1.37 kg and 4738.87 kg
(Table 3). It shows that adding Helianthus tuberosus
stalks to the cultivation substrate can effectively
increase the yield of pepper, and the Q3 treatment of
Helianthus tuberosus stalks has the best yield increase
effect.
Table 3: The yield of peppers with different ratios of substrates.
Treated
P1 P2
Number of
fruits on
per plant
Yield
per
plant
(kg)
Early
production
(kg)
Total
output
(kg)
Number of
fruits on
per plant
Yield
per
plant
(kg)
Early
production
(kg)
Total
output
(kg)
CK
23.87±
0.89a
1.09±
0.04a
1175.8±
93.32a
3792.94±
155.54a
29.40±
1.33a
1.28±
0.01ab
1510.06±
70.60ab
4441.35±
50.82ab
Q1
22.13±
1.38a
1.13±
0.09a
1288±
213.76a
3904.98±
328.01a
31.87±
2.49a
1.34±
0.06a
1481.33±
129.59a
4629.15±
196.35a
Q2
20.47±
1.11a
1.03±
0.10a
1070±
189.43a
3568.88±
339.56a
28.63±
5.49a
1.26±
0.13ab
1523.59±
269.80ab
4353.11±
449.67ab
Q3
23.13±
0.58a
1.16±
0.03a
1321.80±
78.60a
4005.46±
106.26a
32.80±
2.53a
1.37±
0.03a
1611.22±
56.33a
4738.87±
90.86a
Q4
20.60±
4.27a
0.96±
0.13a
1031.16±
261.29a
3326.33±
450.44a
24.32±
3.39a
1.02±
0.17b
1170.56±
340.35b
3547.16±
576.87b
4 DISCUSSION
The soilless culture substrate needs to have suitable
physical and chemical properties. Generally
speaking, the bulk density of the substrate is in the
range of 0.1~0.8g·cm
-3
(Zhang, 2015), the aeration
porosity is more than 15%, and the water pore
porosity are more than 60%. Studies have shown that
the addition of Helianthus tuberosus straw can make
the aeration porosity of the composite matrix more
approach the aeration porosity requirements of the
ideal matrix (Li, 2003). According to the test data in
this paper, pH and EC have different degrees of
increase in different treatments; the bulk density and
water pore porosity are low, which does not meet the
requirements of ideal matrix bulk density and water
pore porosity. The reason may be caused by the
degree of straw crushing. As the bulk density is
directly related to the texture of the straw and the size
of the particles, it affects the compactness of the
straw, as well as the water-holding and air-permeable
capacity (Liu, 2007). The Q2 and Q3 treatments have
larger aeration porosity, which meets the
requirement that the ideal matrix aeration porosity
should be greater than 15%, and is in line with the
results of previous studies (Li, 2003). Aeration
porosity, pH and other indicators of Q3 treatment are
significantly better than other groups, and the stem
thickness, soluble sugar content, vitamin C content
and yield of pepper are also increased in Q3
treatment. The reason may be that relatively suitable
water pore porosity and aeration porosity make the
substrate support and water retention capacity strong,
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
520

which is conducive to the growth and development
of plant roots (Fu, 2010).
Previous studies have shown that the use of
organic substrates can increase crop growth (Jiang,
1996). The treatments adding Helianthus tuberosus
stalks have a relatively obvious promotion effect on
the synthesis of pepper biomass during the entire
growth period of pepper, which is specifically
reflected in the promotion of growth indicators such
as plant height, stem thickness and plant width in
different degrees. However, the different ratio of
Helianthus tuberosus stalks and sheep manure has
different promotion effect on the growth indicators
of pepper. The treatment with Helianthus tuberosus
stalks has not obvious promotion effect in the early
stage of pepper growth and the difference between
treatments is not significant, but it significantly
increases the plant width and other indicators in the
later stage of pepper growth, indicating that the
treatment of adding Helianthus tuberosus straw and
sheep manure has insufficient short-term fertilizer
capacity but has a long and stable fertilizer effect,
which promotes the growth and development of
pepper in the later period
[14]
, and the promotion
effect on stem thickness and plant width is the most
obvious when the ratio of Helianthus tuberosus straw
to sheep manure is 1:3.
Research has shown that the nutrient
transformation and release of the substrate itself
plays a very important role in the fertilizer supply of
tomato plants. The substrate has biological activity
(Sun, 2019), and its feeding mechanism is different
from the nutrient solution. Organic wastes such as
straws can be used as substrates after being
decomposed by composting and fermentation. They
contain large amounts of elements and trace elements
required for plant growth. In addition, during the
cultivation process, the substrates themselves will
continue to ferment and release nutrients
continuously to promote the growth and
development of plants (Wang, 2004). In this
experiment, the addition of Helianthus tuberosus
stalks can indeed promote the synthesis of soluble
sugar and vitamin C in peppers, promote the
accumulation of fruit dry matter, enhance disease
resistance and increase yield, but the promotion
effect is very large with the addition of Helianthus
tuberosus stalks and sheep manure. relation. Studies
have shown that the co-decomposition of crop stalks
and sheep manure can reduce the C/N in the compost
to a certain extent, and can also alleviate the
competition between microorganisms and crops for
nitrogen sources after being applied to the soil
(Wang, 2011). Therefore, the reason may be that the
change of sheep manure content leads to the change
of substrate carbon-nitrogen ratio and nutrients,
which affects the growth of pepper. It can be seen
from the various data that the Helianthus tuberosus
straw and sheep manure are treated at a ratio of 1:3,
that is, the Q3 treatment is better than the other two
treatments with added straw in all indicators, but the
more Helianthus tuberosus straw is added, All
indicators are declining.
The strong ecological adaptability of Helianthus
tuberosus and its huge application potential as an
energy plant, as well as the important position of the
research and development of cultivation substrates in
agriculture, make the substrateization of Helianthus
tuberosus stalks have broad application space and
prospects.
5 CONCLUSION
The Helianthus tuberosus straw and sheep manure
are used in the pepper cultivation substrate in
different proportions, which can improve the
physical and chemical properties of the cultivation
substrate. When the cultivation substrate ratio is V
Helianthus tuberosus straw
: V
sheep manure
: V
substrate soil
: V
perlite
: V
vermiculite
=1: 3: 3: 1: 1, the pepper biomass will
increase, which will promote the growth of pepper
plants, increase the fruit quality and the yield of
pepper.
FUND PROJECT
This article is the National Natural Science
Foundation of Qinghai Province (2021-ZJ-921),
Qinghai Province Science and Technology
Achievement Transformation Special Project (2020-
NK-121), Qinghai Province Agriculture and Forestry
Science Innovation Fund (2019-NKY-02), Qinghai
Province Science and Technology Department Key
Laboratory Project (2020-ZJ- Y02) One of the
phased results.
REFERENCES
Fu Naixu. Effects of straw bio-fermentation on the
overwintering cultivation of pepper in solar
greenhouse [D]. Chinese Academy of Agricultural
Sciences, 2010.
Guo Shirong. Research on development status and trend of
solid cultivation substrates[J]. Transactions of the
Effect of Helianthus Tuberosus Straw and Sheep Manure Ratio on Growth and Fruit Quality of Pepper
521

Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,
2005(S2): 1-4.
Ji Yanhai, Zhao Mengliang, Wu Zhanhui, et al. Study on
the suitable ratio of Helianthus tuberosus fermented
stalks in tomato cultivation medium [J]. Acta Hort.
Sin., 2017, 44(08): 1599-1608.
Jiang Weijie, Zheng Guanghua, Wang Hao, et al. Organic
ecological soilless culture technology and its
nutritional and physiological basis[J]. Acta
Horticulture, 1996(02): 139-144.
Li Qiansheng. Basic research on the application of reed
powder substrate and discussion on the quality
standard of horticultural substrate [D]. Nanjing
Agricultural University, 2003.
Li, Sun Xuemei. Analysis on the development of
Helianthus tuberosus industry on Qinghai-Tibet
Plateau [J]. China Seed Industry, 2011(9): 22-24.
Liu Bin. Preparation of Helianthus tuberosus inulin and its
degradation to produce oligofructose [D]. Wuxi:
Jiangnan University, 2016.
Liu Mingchi, Ji Yanhai, Zhao Mengliang, et al. Effects of
composite matrix of Helianthus tuberosus
fermentation straw on growth and development of
tomato [J]. Acta Agricultural Science, 2017, 7(01): 63-
68.
Liu Yanpeng, Yu Hongjun, Jiang Weijie, et al. Effects of
different organic fertilizers on growth and quality of
soilless tomato [J]. Northern Horticulture, 2007(07): 1-
3.
Liu Zuxin, Xie Guanghui. Research progress of Helianthus
tuberosus as an energy plant. Journal of China
Agricultural University, 2012, 17(6): 122-32.
Lu Tiange, Zhou Jingyu, Ma Yi, etc. An excellent sand
control plant-Helianthus tuberosus [J]. Liaoning
Forestry Science and Technology, 2007(2): 58-59.
Song Zhigang. Research on different crop stalks used as
substrate for soilless cultivation of tomato Chinese
Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013.
Sun Xiaohua, Liu Jiecai, Sun Jing, et al. Study on the
optimal ratio of corn stalk and sheep manure
compost[J]. Henan Agriculture, 2019(20): 27-29.
Tong Guanhe, Zhang Kegui, Liu Tianjiao, et al. The effect
of a new type of soilless culture substrate ratio on the
growth, development and yield of four leafy
vegetables——Taking the culture substrate composed
of coal gangue and rape straw as an example [J].
Research of Agricultural Modernization, 2012, 33(06):
762-765.
Wang Pengdong, Yang Xinyuan, Zhang Jie. Application of
Helianthus tuberosus in sunflower breeding [J].
Shaanxi Agricultural Sciences, 2004(4): 38-39.
Wang Shaojie, Meng Yuyin, Sun Shiqing, et al. Research
progress of Helianthus tuberosus [J]. Shandong
Sciences, 2011, 24(06): 62-66.
Wang Shiwen. Effects of Helianthus tuberosus stalks on
root-knot nematodes, continuous cropping tomatoes
and soil microorganisms [D]. Northeast Agricultural
University, 2018.
Wu Rina, Zhu Tiexia, Yu Yongqi, et al. Research status
and development potential of Helianthus tuberosus [J].
Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(08): 1295-1300.
Xiang Linlin. High-quality and high-yield cultivation
techniques of Helianthus tuberosus in semi-arid
areas[J]. Modern Agriculture, 2019(07): 41-42.
Xue Yanlin, Sun Lin, Yin Guomei, et al. Effects of
biological additives and filling density on silage
quality of Helianthus tuberosus [J]. Animal Husbandry
and Feed Science, 2017, 38(01): 39-43.
Yan Qi, Zhang Shiting, Zhao Changming, et al. Feeding
value of stem and leaf silage of different Helianthus
tuberosus varieties in alpine pastoral area [J].
Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(6): 1568-1573.
Zhang Ting. Effects of different fermentation treatments
on physicochemical properties of corn straw [J].
Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(12):
200-202.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
522
