
Exploration of Potential Drug Targets for Parkinson’s via Text
Mining and Data Analysis
Zihao Yang
1,# a
and Sixian Wang
2,* b
1
East China University of Political Science and Law,Shanghai 200042, China
2
Department of Transfusion, Minhang Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 201199, China
*Corresponding Author: Sixian Wang, Email: 2021110083@ecupl.edu.cn
Keywords: Text Mining, Differentially Expressed Genes (Degs), Genetic Diagnosis, Drug Discovery.
Abstract: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disease of the central nerve system around the world.
However, the current therapeutic regimens were not always effective. We found gene targets of existing drug
and give indications of the potential value of new drugs by text mining and microarray data analysis. We
firstly used text mining (“Parkinson's disease” and “parkinson”) and microarray data analysis (GSE22491) to
screen the genes that we want. Then, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
(KEGG) analysis, as well as the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were used to analysis the genes.
Gene-drug interaction analysis was finally applied to the significant genes to provide insight into potential
drug. As a result, we got 1,116 text mining genes (TMGs) and 4,437 differentially expressed genes (DEGs)
through text mining and microarray data analysis. 258 genes were up-regulated genes and 31 genes were
down regulated among the genes overlapped between TMGs and DEGs. There are six genes are significantand
target 16 existing drugs. In summary, in this study, these six genes (Bax, Apaf-1, BCL2L11, Bcl-2, BCL2L1
and CYCS), associated with apoptosis, are the targets of 16 existing drugs. The finding may shed light on the
indication of the drugs indications to Parkinson's disease.
1 INTRODUCTION
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic
neurodegenerative disease that affects the central
nerve system and affects more than 6 million people
worldwide. Among them, PD typically occurs in
people over 60-year-old, with about 1% of the older
suffering from the disease. Furthermore, males are
more likely to suffer from PD than females (Scholpa
et al. 2018). PD is less common in young adults under
the age of 40, most cases are sporadic, and only
around 10% are familial. Degeneration of dopamine
(DA) neurons in the substantia nigra are one of the
most common pathological features of PD, and the
precise etiology of this pathological change remains
unknown. Degeneration of dopamine neurons may be
caused by genetic factors, aging, environmental
factors, oxidative stress, and possibly other elements
(Chen et al. 2017). Due to the slow progression of PD,
the most obvious symptoms in the early phases are
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0351-3501
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0777-3204
tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability,
and there may also be cognitive and behavioral
problems. Although some treatments including
medication, surgery and physical therapy have been
used to relieve symptoms, such as dopamine receptor
agonists and monoamine oxidase inhibitors to
improve motor function, there is still no effective
treatment for PD (Ganguly et al. 2018). Thus, there is
an urgent need to discover new therapeutic drugs and
effective strategies to effectively prevent the
progression of PD to improve the therapeutic effect.
In short, drugs that may be applied to prevent and
treat PD can be obtained from text mining and data
analysis strategies, providing new ideas for drug
research and development and new applications.
In this study, we firstly used bioinformatics tools
such as text mining and microarray data analysis to
obtain common and unique genes. Significant
differences between PD patients and control groups
were depicted, while correlations between these
Yang, Z. and Wang, S.
Exploration of Potential Drug Targets for Parkinson’s via Text Mining and Data Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0011231400003438
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 83-91
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
83

genes existed. Secondly, these genes were screened
for module genes and associated pathways using
protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis.
Finally, drug-gene interaction of module genes was
performed in the drug gene interaction database
(DGIdb), with the goal of discovering some current
drugs to provide new ideas for the prevention and
treatment of Parkinson's disease. Figure 1 depicts the
framework of this study.
Figure 1: An overview of the workflow. Text mining for TMGs, Microarray data analysis for DEGs.
2 METHODS
2.1 Text Mining Analysis
We used GENCLIP3
(http://ci.smu.edu.cn/genclip3/analysis.php) to
perform text mining. We entered the keyword, and
the GENCLIP3 website can retrieve and extract all
gene markers associated with the keyword from
PubMed published articles (Wang et al. 2019). We
entered the keyword "Parkinson's disease" and
"parkinson" into GENCLIP3 and then extracted all
non-repeat genes, and these gene sets formed the Text
Mining Genes (TMGs).
2.2 Microarray Data Analysis
The microarray datasets of PD patients were searched
from the publicly available GEO database (gene
expression omnibus dataset). We screened the
literature against inclusion and exclusion criteria and
cross-checked it. Inclusion criteria: the approval of
the Ethics Committee was indicated within the
research; diagnosis of PD by clinical and
neuropathology; raw microarray gene data can be
obtained; raw GeneChip data had high quality.
Exclusion criteria: the approval of the Ethics
Committee was not indicated within the research;
diagnosis of PD was not demonstrated by clinic and
neuropathology; raw microarray gene data cannot be
obtained; raw GeneChip data had poor quality.
Following selection, GSE22491 files were obtained
and downloaded.
GSE22491 expression files (.txt format files) and
meta clinical information data (.soft format file)
downloaded from GEO website, which was executed
on the GPL6480 platform (Ron Edgar 2002, Barrett
et al. 2009). The GSE22491 dataset comprises 18
blood samples from 10 Parkinson's disease (PD)
patients and 8 healthy controls (Control) (Barrett et
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
84

al. 2007, Mutez et al. 2011). The probe identification
numbers were converted into official gene symbols
according to the annotation information of the
GPL6480 platform. Afterwards, we counted
duplicate genes, retained mRNA probes, deleted non-
mRNA probes, and retained probes showing
significant gene expression values for multiple probes
of the same gene. Finally,
we followed previous methods, and through
manipulated the R language limma package to detect
gene expression matrix, processed by Affy, AffyPLM
packages, and obtain differentially expressed genes
(DEGs) in Parkinson's disease samples and normal
controls (Gautier et al. 2004, Larriba et al. 2019). As
the threshold standards were utilized for the follow-
up research, DEGs with the |log2 fold change (FC)|
≥1 and adjust P value <0.01, corrected by the
Benjamini–Hochberg (BH) method (Wan et al.
2020). Crossing of DEGs and TMGs was then used
as a starting point for further analysis.
2.3 Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG
Analysis of Overlapping genes
We adopted a research path similar to Zhao B et al.,
and briefly describe as follows (Zhao et al. 2020).
Gene ontology (GO) is a common and useful note
approach for annotating their functional features and
gene products. Then, the GO terms were divided into
three categories: biological process (BP), cellular
component (CC), and molecular function (MF). The
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)
is an open database resource for discovering
biological functions and features of organic systems,
especially in the datasets of gene chips and high-
throughput experiments. (Kanehisa et al. 2017).
Overlapping genes were analyzed by DAVID, a
functional note bioinformatics microarray analysis
website. Significance was assumed for P < 0.05.
2.4 Potential Protein-protein
Interaction (PPI) Network
Construction for Overlapping
Genes
Potential protein-protein interaction of selected genes
was generated using the STRING database
(http://string-db.org) (Szklarczyk et al. 2019). As in a
previous study by Wan Z et al., we also apply a
similar principle (Wan et al. 2020). In this study, we
used the STRING to construct the PPI network of
overlapping genes, with a combined score > 0.4
considered statistically significant. We downloaded
the TSV format file of protein-protein interaction
(PPI), and PPI networks were created by Cytoscape
software. Important gene modules (clusters) were
classified by Molecular Complex Detection
(MCODE) and STRING appin Cytoscape. These
important gene modules are highly interconnected.
Execute MCODE with default parameters. Drug-gene
interaction analysis was applied to the genes in the
gene module.
2.5 Drug-gene Interaction and
Function Analysis of Potential
Genes
To explore the possible application of new drug
indications for the treatment of Parkinson's disease in
humans, the drug gene interaction database (DGIdb)
was handled to search for interactions between
selected genes and existing drugs. The DGIdb
database (http://www.dgidb.org) is an open access
information website, which contains 41,102 genes,
14,449 drugs and 54,591 drug-gene interactions
(Freshour et al. 2021). In the present study, we used
the DGIdb database to search and filter information
on the interactions between selected genes and
existing drugs, screen potential matches with these
drugs, and carry out functional enrichment analysis
(Zhao et al. 2020).
2.6 Statistics Analysis
According to the experience of many academic
circles(Kirk et al. 2018, Pan et al. 2018, Zhang et al.
2019, Wan et al. 2020, Zhao et al. 2020, Zhao et al.
2020), we used a moderated t-test to identify DEGs.
We used fisher’s Exact Test to analyzed GO and
KEGG annotation enrichments (Fisher 1922). All
statistical analysis was performed with the R version
3.5.3 software.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Screening of TMGs and DEGs
As shown in Figure 1, We got 1,116 TMGs and 4,437
DEGs through text mining and microarray data
analysis. As shown in Table I, there were 289
overlapping genes between TMGs and DEGs, and
258 genes were up-regulated and 31 genes were
down-regulated.
Exploration of Potential Drug Targets for Parkinson’s via Text Mining and Data Analysis
85

Table 1: The 289 overlapped genes between TMGs and DEGs.
Overlapped
g
enes
Gene Symbol
Up-regulated
genes
DYRK1A,PPP3CA,SKP1,EP300,TAF9,DLD,HBB,*CYCS,UBE2K,YWHAE,NDUFS1,HMGB1,HPRT1,GLUL,A
IFM1,SMS,CLINT1,TCP1,HSPA9,MTHFR,REL,CARD8,OPA1,GLO1,FBXO7,MTR,NDUFA5,GSTO1,SON,GT
F2I,YWHAZ,CDC42,CREB1,ATF6,ITM2B,UCHL3,ATG5,DR1,CHMP2B,DECR1,ADRBK2,FMR1,RAN,MUTE
D,BNIP3L,MAP2K3,UBE2L3,ALDH2,TFAM,BCL10,PDCD2,PARK7,DNM1L,PPM1A,FECH,PDHB,EGLN1,P
DP1,RBX1,MAP2K4,APPL1,PTEN,GSK3B,TXN,SSR1,SFPQ,SLC2A1,FAS,MEF2A,MXI1,ARPP19,SERPINI1,
YY1,NUCB2,DEK,TP53INP1,BAG5,MAPK14,YWHAQ,C1orf9,LARS,FKBP1A,ZCRB1,MYO5A,ABHD5,PANK
2,PCNA,ARHGDIB,NEDD8,TAF1,GCLC,CD55,RB1,NOC2L,IRF2,BCKDHB,FLOT1,RNF41,DPYSL2,ABAT,
USP24,MTIF3,SRI,GLB1,*BCL2L11,LAMP2,GTPBP4,POLG,PSMC1,GNE,AGPS,PDIA3,MAP3K5,PSMD9,A
NXA1,ASPSCR1,DLG4,ATXN3,NDUFB6,UBE2A,HSD17B4,TFCP2,CNDP2,*APAF1,MSN,PGK1,CBS,MTFM
T,AOC3,MAPK1,*BCL2L1,KIAA1267,FXN,TUBB,GNPTAB,HSPA4,GPI,GLUD1,UBB,HSPA8,MEA1,PSMA6,
EIF2AK2,PPP4C,EIF2AK3,DPYD,BCL2L2,B2M,BAP1,LMNA,S100A6,HSP90AB1,TARDBP,HSF1,MRPS7,M
AP3K7,SMG1,FOXO4,MBP,LIAS,GCH1,LPP,FANCB,SHMT1,TFB2M,IKBKAP,MDM2,SSNA1,PRRG4,NDUF
S4,EIF2C2,MTSS1,SNCA,IMMT,RTN4,ACTB,COPS2,AHR,HSPA5,PRKAA1,YWHAH,SMN2,ADCY7,ACO2,HS
PD1,PTPRC,CAST,RAF1,GSN,PAWR,SLC6A8,NMT1,PAF1,PPP3CC,HNMT,TBP,LIMS1,UPP1,NONO,CTNN
BL1,HSPA1A,PES1,LMOD1,IQCB1,HDAC9,PDLIM7,CHM,VIM,TOR1B,UBR5,ATP1A3,HIF1A,BRCA1,SDP
R,SMARCB1,TSPO,AGFG1,ERGIC2,DHDDS,CSNK2A1,TKT,CD44,PARP1,GALC,RAI1,GALNS,PDPK1,TUB
A1A,MAP3K1,CASP1,ENO1,UROD,PPARA,KIF11,MAP2K1,CANX,RB1CC1,TNFRSF1A,FES,IGF2R,DLX4,U
CHL1,GATA1,KIAA0101,HLAE,TUBB3,AES,CA1,PTPN11,IDE,SOD1,PON2,ITGAM,PINK1,ANXA5,NOD2,H
L
A-
A
,HLA-
B
Down-regulated
genes
BEST1,SOX1,FHIT,PRNP,CKB,TPSG1,THY1,GRIN1,EN2,SYN1,ZFPM1,TH,*BCL2,CD4,GDNF,BBC3,SLC17
A7,AVP,CHRNA4,ATN1,FGF3,*BAX,DRD4,ALDOA,ACAP3,TBX1,OXT,DRD2,GGT1,MYC,GFRA3
*, the final six genes
3.2 GO and Pathway Enrichment
Analysis
To better understand the functions of overlapping
genes, GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses
were analyzed using an online tool DAVID. Figure 2
showed that the top six significant enrichment terms
for biological process (BP), cellular component (CC),
molecular function (MF) and KEGG of overlapping
genes. In BP annotation, it was significantly involved
in the cell death, apoptotic process, and regulation of
programmed cell death, which are all related to
neuronal cell death as the major event in PD. In the
CC category, it was mainly involved in the cytosol,
mitochondrion, myelin sheath. In the MF category,
genes were primarily enriched in “ubiquitin-like
protein ligase binding”, “enzyme binding” and
“protein kinase binding”. KEGG analysis showed that
the overlapping genes were mainly involved in
Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and
apoptosis.
Figure 2. The top six significant GO terms and KEGG pathways of common genes. The bar charts represent the counts of
genes classified in the BP, CC, MF and KEGG respectively; the yellow line chart represents the significance of enrichment
terms. GO, gene ontology; BP, biological process; CC, cellular component; MF, molecular function; KEGG, Kyoto
Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
86

3.3 Protein Interaction and Module
Analysis
The 289 overlapping genes were entered into the
STRING database and then statistically analyzed
using the STRING APP within Cytoscape software.
The results are shown in Figure 3A. A total of 199
genes/nodes with 556 edges participated in the
construction of the PPI networks, and 5 genes haven’t
fallen into the PPI networks. The 6 significant genes
were screened as potential targets for drug-gene
interaction analysis using MCODE application built
in Cytoscape software. The significant gene module
consists 6 genes/nodes with 13 edges/interactions,
which exhibit 4 up-regulated genes (CYCS,
BCL2L11, APAF1 and BCL2L1) and 2 down-
regulated genes (BCL2, BAX) (Fig. 3B).
Figure 3. The PPI networks construction and significant
gene module analysis. (A) The entire PPI networks of
common genes. (B) The significant gene module, including
6 genes.
3.4 Drug-gene Interaction and
Functional Analysis
The 6 genes clustered in the significant gene module
were eventually screened as potential targets for drug-
gene interaction analysis using MCODE application
built in Cytoscape software. Six key genes target to
16 drugs. It was divided into 7 types, with their drug
indications (Figure 4A, Table II). Furthermore, as
shown in Figure 4B, the six target genes are mainly
involved in the intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway,
the positive regulation of the apoptotic process and
the positive regulation of programmed cell death. In
the CC category, it was mainly involved in the Bcl-2
family protein complex, mitochondrial outer
membrane, organelle outer membrane. In the MF
category, genes were primarily enriched in “BH3
domain binding”, “death domain binding” and “BH
domain binding”.
Exploration of Potential Drug Targets for Parkinson’s via Text Mining and Data Analysis
87
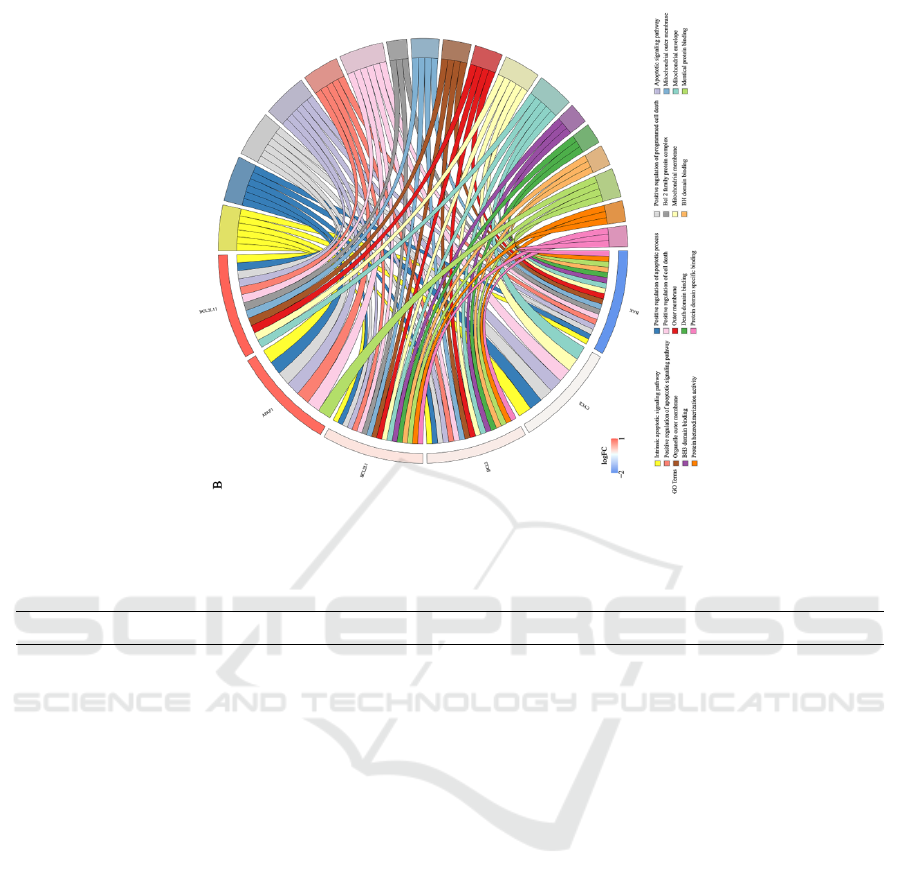
Figure 4. The drugs targeted to genes and its functional enrichment analysis. (A) Chord plot for the connection between 6
drugs and 16 genes. (B) Chord plot for functional enrichments of 6 genes.
Table 2: The specified information of drugs and its target genes.
Number Gene Drug Interaction Drug class*
1 BCL2 IBUPROFEN Modulator
Anti-inflammatory agents, nephrotoxic agents,
other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents,
causing angioedema agents, causing
hyperkalemia agents, produce hypertension
a
g
ents
2 BCL2 NAVITOCLAX Antagonist,Inhibitor Anti-inflammatory agents
3 BCL2 OBATOCLAX Inhibitor Antineoplastic agent
4 BCL2 VENETOCLAX Antagonist,Inhibitor
Antineoplastic agent, apoptosis regulator Bcl-
2 inhibitor,antineoplastic and
immunomodulating agents
5 BCL2 ABT 737 Antagonist Not available
6 BCL2 BORTEZOMIB Inhibitor
Antineoplastic agent,cardiotoxic
antineo
p
lastic
7 BCL2 OBLIMERSEN
Antisense
oli
g
onucleotide
agents,hepatotoxic agents,immunosuppressive
a
g
ents,
p
otential
q
tc-
p
rolon
g
in
g
a
g
ents
8 BCL2 OBATOCLAX Inhibitor Antineoplastic agent
9 BCL2 RASAGILINE Activator Not available
10 BCL2 PACLITAXEL Inhibitor
Antiparkinson agent,antidepressive agents,
serotonin agents
11 BCL2 DEXIBUPROFEN
Inhibitor,negative
modulato
r
Antineoplastic agent,antiinflammatory
agent,causing
12 BCL2L1 ABT 737 Antagonist
muscle toxicity agents,cardiotoxic
antineoplastic agents,neurotoxic agents
13 BCL2L1 NAVITOCLAX Antagonist,Inhibitor Anti-inflammatory agents,nephrotoxic agents
14 BCL2L1 OBATOCLAX Inhibitor Not available
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
88

15 BCL2L1 VENETOCLAX Antagonist
Antineoplastic agent, apoptosis regulator Bcl-
2 inhibitor,antineoplastic and
immunomodulating agents
16 CYCS MINOCYCLINE
Inhibitor,negative
modulato
r
Photosensitizing agents,causing muscle
toxicity agents
17 CYCS ARTENIMOL Ligand Antiparasitic agents,anti-infective agents
18 BCL2L11 IMATINIB Inhibitor
Antineoplastic agent,antineoplastic
agents,cardiotoxic antineoplastic agents,qtc
p
rolonging agents,photosensitizing agents
19 APAF1 MYOCET Inhibitor Not available
20 BAX PROCARBAZINE Inhibitor
Antineoplastic agent, antidepressive
agents,serotonin agents
21 BAX CIPROFLOXACIN Inhibitor
Antineoplastic agent,photosensitizing
agents,qtc prolonging agents
*, the drug indications have been approved by FDA
4 DISCUSSION
Parkinson's disease is a common neurodegenerative
disorder caused by the degeneration and apoptosis of
dopaminergic neurons. In this study, the aim was to
find potential therapeutic drugs for PD based on text
mining and data analysis, and to provide fresh ideas
for research into new applications of conventional
drugs. As shown in Figure 4, we finally identified 6
potential genes and 16 existing drugs for PD, which
could be utilized as targets and drugs for the study of
PD.
Based on a search of the published literature, we
found these six genes are tightly associated with PD.
Four genes (Bax, Apaf-1, BCL2L11 and CYCS) show
a promotive effect, while the other two (Bcl-2 and
BCL2L1) sustain an inhibitory effect on PD. The
family of Bcl includes the anti-apoptosis genes (Bcl-
2, Bcl-xL, etc.) and the pro-apoptosis genes (Bax,
BCL2L11, etc.). It inhibits or promotes the release of
cytochrome C (CYCS) into the cytoplasm, which
binds to Apaf-1 (apoptosis protease activating factor-
1) , thus induces apoptosis. This process is involved
in the degeneration and apoptosis of dopaminergic
neurons in PD (Xu et al. 2007, Liu et al. 2020).
According to Wolter et al., BCL2-Associated X (Bax)
is the main pro-apoptotic gene in the Bcl-2 gene
family(Reljic et al. 2016). Under normal conditions,
Bax is present as a monomer in the outer
mitochondrial membrane or cytoplasm, but upon
induction of apoptosis, Bax is specifically
translocated to the mitochondria.
The B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), an important
anti-apoptosis gene, is correlated with cell apoptosis.
In general, the Bcl-2 and Bax genes regulate
apoptosis, and Bcl-2 binds to Bax, further inhibiting
Bax and promoting cell survival (Wolter et al. 1997).
CYCS encodes a protein that binds to the inner
membrane of mitochondria, where it receives
electrons from cytochrome B and transfers them to
the cytochrome oxidase complex, thus participating
in the initiation of apoptosis (Reljic et al. 2016). It is
well known that CYCS release, activation of cellular
caspases and subsequent apoptosis are thought to be
among the important factors leading to neuronal cell
death (Lederer et al. 2007). Reljic et al. elucidated
that BCL2L1 belongs to the Bcl-2 protein family of
anti-apoptotic or pro-apoptotic regulators (Nicosia et
al. 2020). The protein encoded by this gene contains
a BCL-2 homologous structural domain 3 (BH3). Its
interaction with other members of the BCL-2 protein
family and role as an apoptotic activator is verified.
Chen, et al. clarified that the BCL2-like protein 1
(BCL2L1) gene encodes a mitochondrial protein
thought to prevent apoptosis in normal cells (Chen et
al. 2019). BCL2L1 may regulate the opening of
channels in the outer mitochondrial membrane and
control the release of cytochrome c. Apaf-1 is a key
molecule in the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis
(Nicosia et al. 2020).
As evidenced by numerous literatures, the main
characteristic of PD is the degeneration and death of
dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain. Apoptosis,
also known as programmed cell death, is one of the
key mechanisms leading to degeneration and death of
dopaminergic neurons in PD patients (Xu et al. 2007,
Wilczynski et al. 2017, Liu et al. 2020). The extrinsic
and the intrinsic apoptosis pathway are the two main
signaling pathways for apoptosis. The extrinsic
apoptosis pathway is activated in PD pathology, but
the underlying mechanisms are yet to be further
investigatied (Mao et al. 2016, Zhang et al. 2020).
The mitochondrial mediated cell apoptosis intrinsic
pathway is stimulated by positive factors (eg. toxins,
radiation and hypoxia) or negative factors (eg. the
absence of hormones and growth factors in the cell)
Exploration of Potential Drug Targets for Parkinson’s via Text Mining and Data Analysis
89

Pro-apoptotic genes such as BAX are then up-
regulated, while anti-apoptotic genes such as BCL-2
and BCL2L1 are repressed. This arouses change in
the permeability of mitochondrial cell membrane,
resulting in the opening of the mitochondrial
permeability transition pore (mPTP) (Wang et al.
2020). Pro-apoptotic proteins such as cytochrome C
are released from the mitochondria into the cytosol
and bind to Apaf-1 to form apoptosomes, which
activate the caspase cascade. In particular, the
apoptosome activates caspase-9, which in turn
activates caspase-3 and other downstream caspases,
leading to apoptosis (Xu et al. 2007).
The drug interactions between the 6 genes within
16 existing drugs we identified can be divided into
four types, namely modulator, agonist, binder,
antagonist and inhibitor (Table II). These drugs can
be classified into several categories, including anti-
parkinson agents, anti-inflammatory agents, anti-
depressive agents, immunomodulating and anti-
neoplastic agents. The types of drugs identified in this
study were broader and more focused on addressing
PD symptoms that may be caused by apoptotic factors
than those as potential treatments for PD in previous
literature (Xu et al. 2018, Raasmaja et al. 2019,
Elbeddini et al. 2020). The combined use of drugs
may have synergistic therapeutic effects, for example
reducing side effects and improving selectivity.
While these existing drugs offer a new perspective on
the study of PD, their new functions and indications
need to be confirmed in further clinical trials.
5 CONCLUSIONS
According to the text mining conception (keyword:
Parkinson's disease and parkinson) and microarray
data analysis (dataset: GSE22491), we found 16
existing drugs, approved by FDA, target to six genes,
which involved in the intrinsic apoptotic signaling
pathway. These genes might be used for Parkinson's
disease, as well as its original drug indications.
ACKNOWLEDEGMENTS
Thanks to Zhao’s Team of Xiamen University for
suggestions on the manuscript.
REFERENCES
Barrett, T., et al. (2007). "NCBI GEO: mining tens of
millions of expression profiles--database and tools
update." Nucleic Acids Res 35(Database issue): D760-
765.
Barrett, T., et al. (2009). "NCBI GEO: archive for high-
throughput functional genomic data." Nucleic Acids
Res 37(Database issue): D885-890.
Chen, C., et al. (2019). "Role of long non-coding RNA
TP73-AS1 in cancer." 39(10).
Chen, Y., et al. (2017). "The expression and significance of
tyrosine hydroxylase in the brain tissue of Parkinsons
disease rats." Exp Ther Med 14(5): 4813-4816.
Elbeddini, A., et al. (2020). "Potential impact and
challenges associated with Parkinson's disease patient
care amidst the COVID-19 global pandemic." J Clin
Mov Disord 7: 7.
Fisher, R. A. (1922). "On the Interpretation of
χ<sup>2</sup> from Contingency Tables, and the
Calculation of P." Journal of the Royal Statistical
Society 85(1): 87-94.
Freshour, S. L., et al. (2021). "Integration of the Drug–Gene
Interaction Database (DGIdb 4.0) with open
crowdsource efforts." Nucleic Acids Research 49(D1):
D1144-D1151.
Ganguly, U., et al. (2018). "Alpha-synuclein, Proteotoxicity
and Parkinson's Disease: Search for Neuroprotective
Therapy." Curr Neuropharmacol 16(7): 1086-1097.
Gautier, L., et al. (2004). "affy--analysis of Affymetrix
GeneChip data at the probe level." Bioinformatics
20(3): 307-315.
Kanehisa, M., et al. (2017). "KEGG: new perspectives on
genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs." Nucleic Acids
Res 45(D1): D353-D361.
Kirk, J., et al. (2018). "Text mining-based in silico drug
discovery in oral mucositis caused by high-dose cancer
therapy." Support Care Cancer 26(8): 2695-2705.
Larriba, Y., et al. (2019). Microarray Data Normalization
and Robust Detection of Rhythmic Features.
Microarray Bioinformatics: 207-225.
Lederer, C. W., et al. (2007). "Pathways and genes
differentially expressed in the motor cortex of patients
with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis." BMC
Genomics 8: 26.
Liu, Y., et al. (2020). "Preparation and Neuroprotective
Activity of Glucuronomannan Oligosaccharides in an
MPTP-Induced Parkinson's Model." Mar Drugs 18(9).
Mao, Y., et al. (2016). "Regulation of cell apoptosis and
proliferation in pancreatic cancer through PI3K/Akt
pathway via Polo-like kinase 1." 36(1): 49-56.
Mutez, E., et al. (2011). "Transcriptional profile of
Parkinson blood mononuclear cells with LRRK2
mutation." Neurobiol Aging 32(10): 1839-1848.
Nicosia, A., et al. (2020). "Carbon Nanodots for On
Demand Chemophotothermal Therapy Combination to
Elicit Necroptosis: Overcoming Apoptosis Resistance
in Breast Cancer Cell Lines." Cancers (Basel) 12(11).
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
90

Pan, Y., et al. (2018). "Text miningbased drug discovery in
cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma." Oncol Rep 40(6):
3830-3842.
Raasmaja, A., et al. (2019). "The Water Extract of Juniperus
communis L. Induces Cell Death and Sensitizes Cancer
Cells to Cytostatic Drugs through p53 and PI3K/Akt
Pathways." Int J Mol Sci 20(9).
Reljic, B., et al. (2016). "BAX-BAK1-independent LC3B
lipidation by BH3 mimetics is unrelated to BH3
mimetic activity and has only minimal effects on
autophagic flux." Autophagy 12(7): 1083-1093.
Ron Edgar, M. D. a. A. E. L. (2002). "Gene Expression
Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization
array data repository." Published by Oxford University
Press Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, Vol. 30, No. 1
207–210.
Scholpa, N. E., et al. (2018). "5-HT1Freceptor-mediated
mitochondrial biogenesis for the treatment of
Parkinson's disease." British Journal of Pharmacology
175(2): 348-358.
Szklarczyk, D., et al. (2019). "STRING v11: protein-protein
association networks with increased coverage,
supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets." Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):
D607-D613.
Wan, Z., et al. (2020). "Drug discovery in cardiovascular
disease identified by text mining and data analysis."
Ann Palliat Med 9(5): 3089-3099.
Wang, J. H., et al. (2019). "GenCLiP 3: mining human
genes' functions and regulatory networks from PubMed
based on co-occurrences and natural language
processing." Bioinformatics.
Wang, Y., et al. (2020). "Ma xing shi gan decoction
eliminates PM2.5-induced lung injury by reducing
pulmonary cell apoptosis through Akt/mTOR/p70S6K
pathway in rats." Biosci Rep 40(7).
Wilczynski, J., et al. (2017). "Body Posture, Postural
Stability, and Metabolic Age in Patients with
Parkinson's Disease." Biomed Res Int 2017: 3975417.
Wolter, K., et al. (1997). "Movement of Bax from the
cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis." 139(5):
1281-1292.
Xu, C., et al. (2018). "Potential Therapeutic Drugs for
Parkinson's Disease Based on Data Mining and
Bioinformatics Analysis." Parkinsons Dis 2018:
3464578.
Xu, J., et al. (2007). "Rifampicin protects PC12 cells against
MPP+-induced apoptosis and inhibits the expression of
an alpha-Synuclein multimer." Brain Res 1139: 220-
225.
Zhang, N., et al. (2019). "Computational Drug Discovery in
Chemotherapy-induced Alopecia via Text Mining and
Biomedical Databases." Clin Ther 41(5): 972-980 e978.
Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). "Small molecule CDS-3078
induces G2/M phase arrest and mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis in HeLa cells." Exp Ther Med 20(6): 284.
Zhao, B., et al. (2020). "Comprehensive analysis reveals a
six-gene signature and associated drugs in mimic
inguinal hernia model." Hernia 24(6): 1211-1219.
Zhao, B., et al. (2020). "Six-Gene Signature Associated
with Immune Cells in the Progression of
Atherosclerosis Discovered by Comprehensive
Bioinformatics Analyses." Cardiovasc Ther 2020:
1230513.
Exploration of Potential Drug Targets for Parkinson’s via Text Mining and Data Analysis
91
