
Mechanisms of the Toxicity of Chiral Pesticides Dinotefuran
Enantiomers on Esiena fetida Earthworm
Yaofang Zhang
1 a
, Youpu Cheng
1 b
, Yu Cheng
1,2, c
, Lijuan Lv
1 d
, Yanling Xu
1 e
and Chengling Gao
1 f
1
Tianjin Agricultural University, No. 22 Jinjing Road, Tianjin, China
2
Tianjin Institute of Agricultural Quality Standard and Testing Technology, Jinjing Road, Tianjin, China
Keywords:
Dinotefuran, Enantiomers, Eisenia foetida, Acute Toxicity, DNA Damage.
Abstract: As a promising insecticide, dinotefuran has been commercialized and widely used around the world. In this
study, the acute toxicity of Rac-dinotefuran and its two enantiomers on earthworm were estimated by
artificial soil method according to the OECD criteria at the individual-tissue-cell-molecule level. The
14d-LC50 values were 2.372 mg/kg for Rac-(±)-dinotefuran, 1.158 mg/kg for S-(+)-Dinotefuran and 6.002
mg/kg for R-(-)-Dinotefuran respectively. E. foetida was exposed to different concentrations of
Rac-dinotefuran and its two enantiomers and the enzyme activities, DNA damage and gene expression were
measured on 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days of post treatments, respectively. The results showed that
Rac-dinotefuran and its two enantiomers caused obvious modulations on DNA damage, enzyme activities
and gene expression. Additionally, the toxicity of Rac-dinotefuran and its two enantiomers behaved in time-
dose-dependent manner.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Neonicotinoid pesticides (NNs) are nitroguanidine
systemic insecticides that are commonly used to
protect seedling from leaf feeding by early season
pests (
Jeschke, 2008)
. Because of the high
selectivity, high efficiency and low toxicity to
mammals, neonicotinoid insecticides are now the
most widespread used pesticides around the world.
(Morrissey, 2015, Sparks, 2015). Neonicotinoid
insecticides including imidacloprid, clothianidin,
thiamethoxam, acetamiprid, and dinotefuran are
among the most effective insecticide recently
introduced to control pest with novel modes of
action (Lina, 2012). As the third generation
neonicotinoid insecticide, dinotefuran is deemed to
be a promising insecticide with emproved chemical
and biological properties, such as wide spectra of
targets, high insecticidal efficacies, and environment
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7677-9207
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0171-0165
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8607-9981
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3217-7535
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6190-9566
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5057-780X
safety (
Hem, 2012)
. Given the differences of chiral
pesticides enantiomers in the bio-activities,
toxicities, and environmental behavior, many
researchers have been vigilant to the security of
chiral pesticides (
Qi, 2015)
. However, dinotefuran
inevitably permeates into the natural environment
and sap the quality of soil. Although, the toxicity of
some pesticides can be partially and slowly
mitigated by some abiotic factors, such as
degradation, migration and transformation, the
contamination remains a long-lasting problem since
the pesticides including dinotefuran are notoriously
clumsy to be completely purged (
Morrissey, 2015)
.
Therefore, the acute toxicity of Rac-dinotefuran
and its two enantiomers on earthworems were
studied. Meanwhile, we compared the changes of
enzyme activities, DNA damage levels and the
modifications of gene expression of E.foetida with
and without the pesticides. The results provided
scientific basis for an evaluation of the
environmental safety on soil ecosystems.
Zhang, Y., Cheng, Y., Cheng, Y., Lv, L., Xu, Y. and Gao, C.
Mechanisms of the Toxicity of Chiral Pesticides Dinotefuran Enantiomers on Esiena fetida Earthworm.
DOI: 10.5220/0011232400003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 547-552
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
547

2 ATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials and Reagents
Earthworms (E. fetida) were purchased from an
earthworm cultivating farm (Tianjin, China).
Dinotefuran (98.0%) were provided by the ministry
of agriculture pesticide identification.
R-(-)-dinotefuran and S-(+)-dinotefuran were
prepared in our laboratory. The experimental soil
was artificial soil and prepared according to the
method described in the OECD guideline (
OECD,
2014)
.
2.2 Acute Toxicity Testing using
Earthworm E.fetida
The acute toxicity was conducted according to the
OECD standard method (
OECD, 2014)
. For the
media lethal concentrations (LC
50
) of
Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran and its enantiomers caculation,
seven test concentrations were used,
Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran (0.829, 1.077, 1.401, 1.821,
2.367, 3.077 and 4.000 mg/kg), S-(+)-Dinotefuran
(0.491, 0.638, 0.829, 1.077, 1.401 1.821 and 2.367
mg/kg) and R-(-)-Dinotefuran (2.072, 2.693, 3.501,
4.552, 5.917, 7.692 and 10.000 mg/kg). Each
concentration contained ten healthy earthworm and
with three replicates.
2.3 Experimental Design
Based on the acute toxicity experiment results, three
different concentrations (0.1, 0.5 and 1.0 mg/kg) and
three replicates for each concentration with artificial
soil were used in the present study. The control
groups were prepared similarly but without
insecticide. There are 0.5 g of dry cow dung was
added onto the artificial soil surface weekly from
days 1 to 28 and the same dose of artificial soils
were replaced on the days of 14. All the treatments
were cultured at 20±1 ℃ in 80 %-85 % relative
humidity for 16 h in light and 8 h in the dark, and
five exposure periods (3, 7, 14, 21 and 28 d) were
tested. Each earthworm was washed with distilled
water, gently dried with absorbent paper, and stored
at -80 ℃ before analysis.
2.4 Determination of Enzyme Activities
One Gut-cleaned earthworm was randomly selected
and homogenized in 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH
7.2). The supernatant was collected after
centrifuging at 10000 rpm for 30 min (at 4 ℃). SOD
activity was tested according with the method of
Song et al. (
Song, 2009)
. CAT activity was
determined by measuring the consumption of H
2
O
2
(
Xu, 1997)
. POD activity was determined using the
method of Kochba et al. (
Kochba, 1977)
.
2.5 Comet Assay
Earthworm coelomocytes were performed as
Eyambe et al. Described (
Eyambe, 1991)
. The
comet assay was described by the method of Mahsa
et al. (
Mahsa, 2014)
, which was used to determine
the degree of DNA damage. After electrophoresis,
each slide was neutralized with neutralizing buffer
every 5 min for 3 times, dehydrated with 95 %
ethanol and stained with SYBR green. At last, the
slides were observed under fluorescence microscope
(Olympus, BX51, Japan).
2.6 Real-time PCR Analysis
Total RNA was obtained using the Total RNA
extraction kit and reverse-transcribed to first-strand
cDNA was performed using the PrimeScript™ RT
reagent Kitr. The synthesized cDNA was stored at
-80 ℃ prior to use for real-time PCR. TransStart
Top Green qPCR SuperMix was used in real-time
PCR experiments, which was performed on a
real-time PCR system. The expression of five target
genes (SOD, MT, HSP70, TCTP) were compared to
the expression of the housekeeping gene (β-actin)
and presented as relative gene expression compared
to the control. The relative gene expression level
was calculated using the 2
-
△△
Ct
method (
Lukkari,
2004)
.
2.7 Statistical Analysis
Each treatment was analyzed with three replicates.
The data were analyzed with SPSS 17.0 statistical
software and the results were presented as
means
± standard deviation (SD). The comet images
were analyzed using CASP software. Olive tail
moment (OTM) value was used to determine the
degree of DAN damage.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
548

3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Acute Toxicity
After 14 days exposure, no mortality was observed
in control group. Dinotefuran and its enantiomers
showed different degree of toxicity on earthworms.
The values of 14d-LC
50
were Rac- (±)-Dinotefuran
2.372 mg/kg, S-(+)-Dinotefuran 1.158 mg/kg and
R-(-)-Dinotefuran 6.002 mg/kg. The results showed
that Rac-dinotefuran and its enantiomers are
moderately toxic to Eisenia foetida.
The data
showed that the mortality is both
concentration-dependent and application
time-dependent for all insecticides test. The acute
toxicity is
S-(+)-Dinotefuran>Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran>R-(-)-Dino
tefuran.
3.2 Enzyme Activities Assay
As antioxidant enzymes, SOD, CAT and POD, play
an important role in scavenging excess reactive
oxygen species (ROS) and promoting the growth of
healthy cells (
Ye, 2016)
. SOD plays a key role in
decomposing O
2
·-
to H
2
O
2
and O
2
, which is thought
to be the first line to prevent the harm of ROS
(
Liu,
2016)
. CAT can decompose H
2
O
2
to H
2
O and O
2
,
which is considered to play an important role in
detoxification of free radicals derived from oxygen.
As one type of redox enzyme, POD can eliminate
H
2
O
2
and other organic hydroperoxides to protect
the body from the damage posed by ROS (
Niu,
2013)
. The possible biochemical effects of
dinotefuran and its two enantiomers on the activities
of SOD, CAT and POD in E.foetida were measured
on the 3
th
, 7
th
, 14
th
, 21
th
, and 28
th
day respectively.
As is shown in Figure 1(A, B and C), After 7
days exposure, the SOD and CAT activities showed
the same trend of variation under high concentration
of S-(+)-Dinotefuran treatment groups which
showed significant pre-inhibiting and post-activating
effects. Their results suggested that a high
concentration of S-(+)-Dinotefuran may induce
excess toxicity which inhibited activities of SOD,
CAT and POD. At the same time, a high
concentration of S-(+)-Dinotefuran can induce
oxidative stress and induce the expression of
antioxidant enzymes to overcome the stress caused
by pollution. Finally, the SOD and CAT exhibited
higher activities, resulting in eliminating the
excessive ROS production. However, the POD
activities in the high concentration of
S-(+)-Dinotefuran treatment groups were inhibited
in the whole exposure time (P<0.001). Maybe the
toxicity is stronger to POD than to other antioxidant
enzymes. After 28 days of exposure, the SOD, CAT
and POD activities in 1 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg
S-(+)-Dinotefuran treatment groups changed more
significantly than the other groups and exhibited
dose-dependent elevate effect. The results showed
that the S-(+)-Dinotefuran is more toxic than
Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran and R-(-)-Dinotefuran.
Figure 1: The effect of dinotefuran and its enantiomers on
SOD (A), CAT (B) and POD (C) activity of Eisenia
foetida. Data are described as mean±SD (n=3). Statistical
significance compared with controls:
*
P<0.05,
**
P<0.01,
***
P<0.001.
3.3 DNA Damage Induced by
Dinotefuran and Its Enantiomers
The genotoxicity of dinotefuran and its enantiomers
to Eisenia foetida were evaluated by comet assay. As
is shown in Figure 2, after 3 d treatments, there were
no significant difference in OTM values, indicating
that after transit exposure did not cause DNA
damage. On the 7
th
day, the OTM values of the
S-(+)-Dinotefuran and 1 mg/kg Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran
treatment groups were significantly higher than
other treatment groups and control group (P<0.001,
P<0.05). After 14 d treatments, a significant
increase in the OTM values was observed for 1
mg/kg treatment groups and the OTM values
increased with the increase of dosage and exposure
time. The OTM values are
Mechanisms of the Toxicity of Chiral Pesticides Dinotefuran Enantiomers on Esiena fetida Earthworm
549
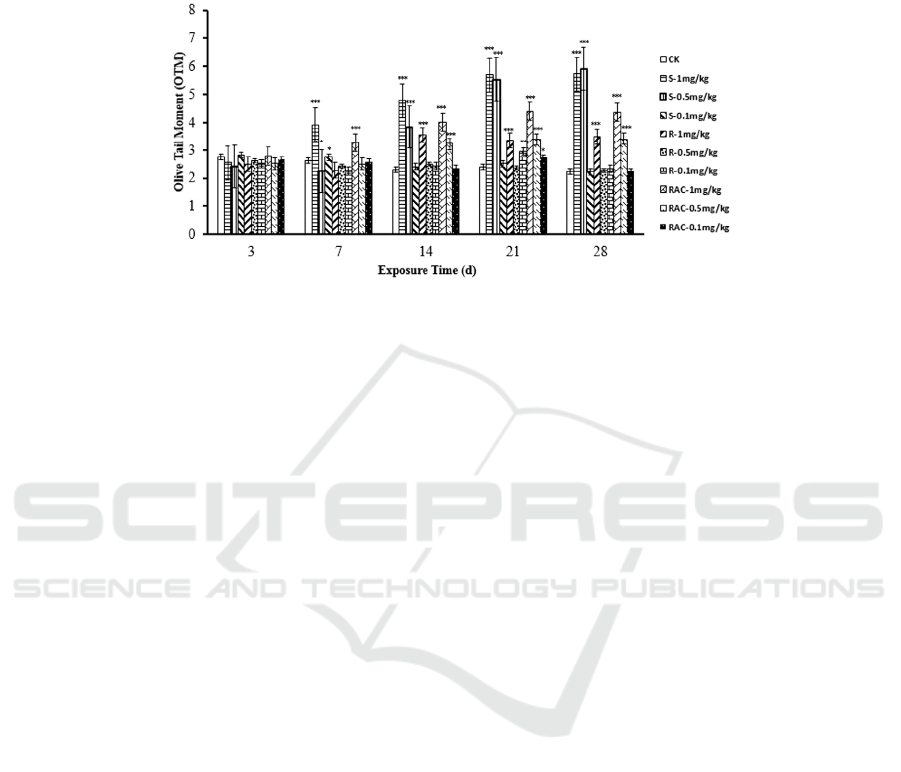
S-(+)-Dinotefuran>Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran>R-(-)-Dino
tefuran. However, the OTM did not change
significantly with the treatments of the low
concentration of dinotefuran and its enantiomers
compare the 21
th
day. The study indicated that the
DNA was damaged significantly by high
concentrations (1 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg) of exposure
to dinotefuran and its enantiomers and the toxicity
was S-(+)-Dinotefuran > Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran >
R-(-)-Dinotefuran.
Figure 2: The effect of dinotefuran and its enantiomers on DNA damage degree in earthworms. Data are described as
mean±SD (n=3). Statistical significance compared with controls:
*
P<0.05,
**
P<0.01,
***
P<0.001.
3.4 Real-time PCR Analysis of
Dinotefuran and Its Enantiomers
As is shown in Figure 3A, the relative expression of
SOD gene was significantly up-regulated on the 7
th
and 14
th
day (P<0.001). After 28 days treatments,
the expression levels of the SOD gene was more
significantly decreased by the treatment of the high
concentration of Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran and
S-(+)-Dinotefuran groups (1.0 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg)
than other treatment groups. The significant changes
of the SOD gene showed that dinotefuran and its
enantiomers caused toxic effects on earthworms and
had a positive correlation with the exposure time
and the dose.
The expression of MT gene is modulated by
environmental stress, so it has been used to assess
the eco-toxicity of contaminants (
Fisker, 2016)
. As
is shown in Figure 3B, after exposure for 7 days, a
significant up-regulation trend was observed and the
expression levels increased with an increase in the
dose and exposure time (P<0.001). However, on the
14
th
day, the up-regulation trend in high
concentration of S-(+)-Dinotefuran (1 mg/kg and 0.5
mg/kg) and 1mg/kg Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran, treatment
groups disappeared. Until being exposured for 28
days, the expression levels of the MT gene
down-regulated significantly on 1 mg/kg and 0.5
mg/kg treatments. Especially on the 28
th
day,
S-(+)-Dinotefuran (1 mg/kg and 0.1 mg/kg),
R-(-)-Dinotefuran (1 mg/kg) and
Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran (1 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg)
treatment groups were markedly lower than other
treatment groups.
Heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) play an essential
role in protecting cells from damages induced by
environment pressure
(
Wang, 2015)
. As is shown in
Figure 3C, after exposure for 3 days, a significant
increase of expression of HSP70 gene was observed
in the dinotefuran and its enantiomers treatment
groups (P<0.001). After 14 days treatments, the
relative expression levels of the HSP70 gene began
to wane. On the 28
th
day, the relative expression
levels of the HSP70 gene in all dinotefuran and its
enantiomers treatment groups were starkly lower
than the control group (P<0.001). The significant
changes in HSP70 expression indicated that
dinotefuran and its enantiomers caused stress in
earthworms.
TCTP plays an important role in preventing cell
apoptosis and causing tumor reversion (
Wang,
2015)
. As is shown in Figure 3D, a significant
up-regulation of the TCTP gene was observed in the
presence of S-(+)-Dinotefur, R-(-)-Dinotefuran (1
mg/kg) and Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran (1 mg/kg and 0.5
mg/kg) on the days of 7 and 14 (P<0.001). On the
days of 21 and 28, the relative expression levels of
the TCTP gene were markedly lower than the
control group except 0.1 mg/kg Rac-(±)-Dinotefuran
treatments (P<0.001). The up-regulation at first and
the following down-expression indicated that
dinotefuran and its enantiomers may influence cell
growth and lead to cell apoptosis at the final stage of
the exposure.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
550
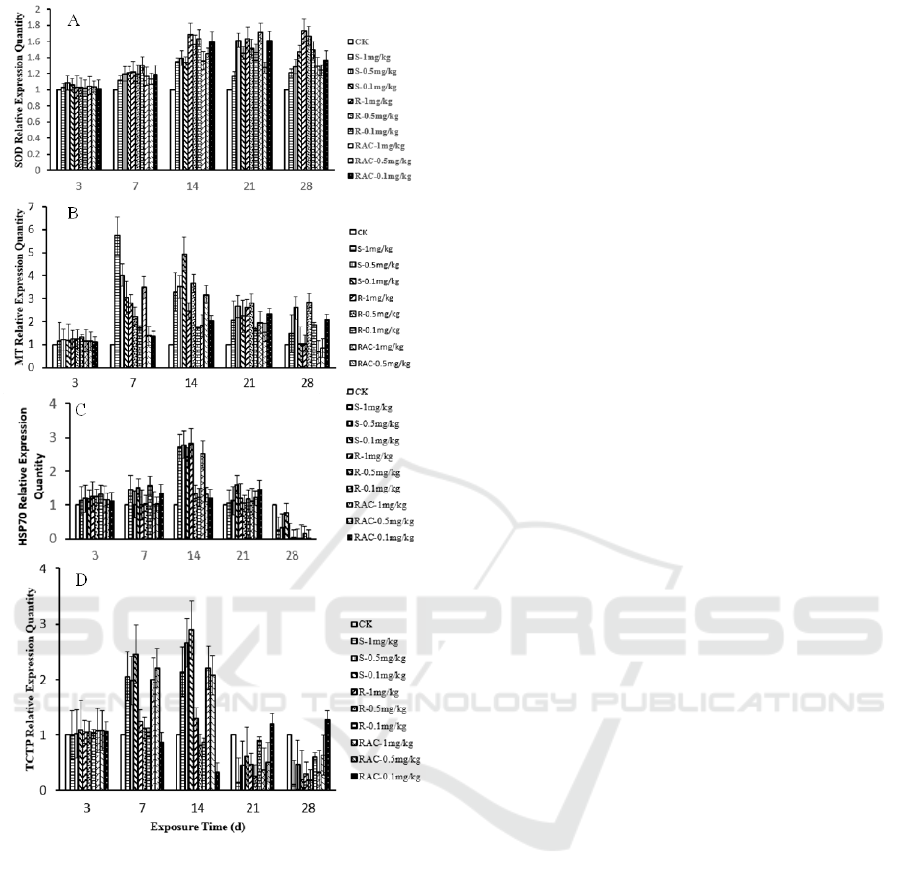
Figure 3: The effect of dinotefuran and its
enantiomers(S-(+)-Dinotefuran and R-(-)-Dinotefuran) on
the relative expression quantity of SOD (A), MT (B),
HSP70 (C) and TCTP (D). Data are described as
mean±SD (n=3). Statistical significance compared with
controls:
*
P<0.05,
**
P<0.01,
***
P<0.001.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, the biochemical and genetic toxicity of
dinotefuran and its enantiomers on Eisenia foetida
were evaluated from the individual, tissue, cell and
molecule levels. The results showed that,
dinotefuran and its enantiomers are moderately toxic
to Eisenia foetida and have negative impacts on the
earthworm at different levels. Both the exposure
dose and time had obvious impacts on the toxicity.
Moreover, increasing dose and time of dinotefuran
and its enantiomers could induce redundant
production of ROS, resulting in significant changes
in antioxidant enzyme activities, DNA damage and
the relative expression of functional genes.
This study explored the toxicity mechanisms
underlying the toxicity of dinotefuran and its
enantiomers on earthworms, and provided scientific
basis references for devising and developing new
environment-friendly pesticides.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge the financial support by
the National Natural Science of Foundation of China
(31572034) and (M2042003).
REFERENCES
Eyambe GS, Goven AJ, Fitzpatrick LC, et al. (1991) A
non-invasive technique for sequential collection of
earthworm (Lumbricus terrestris) leukocytes during
subchronic immunotoxicity studie Laboratory
Animals, 25(1): 61-67.
Fisker, K.V., Holmstrup, M., Sorensen, J.G. (2016)
Freezing of body fluids induces metallothionein gene
expression in earthworms (Dendrobaena octaedra).
Comp. Biochem. Phys. C., 179: 44-48.
Hem. L., Abd El-Aty, A.M., Park, J.-H., (2012).
Determination of dinotefuran in papper using liquid
chromatography: Contribution to safety evaluation. J.
Korean Soc. Appl. Bi.. 55: 765-768.
Jeschke, P., Nauen, R. (2008) Neonicotinoids—from zero
to hero in insecticide chemistry. Pest Manag. Sci, 64:
1084-1098.
Kochba, J, Lavee, S, SpiegelRoy, P. (1977) Differences in
peroxidase activity and isoenzymes in embryogenic
ane non-embryogenic ‘Shamouti’ orange ovular callus
lines. Plant & Cell Physiology, 18 (2):463-467.
Lina Hem, A. M. Abd El-Aty, Jong-Hyouk Park, Jae-Han
Shim, (2012). Determination of Dinotefuran in Pepper
Using Liquid Chromatography: Contribution to Safety
Evaluation. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 55,
765-768.
Liu, T., Zhu, L.S., Wang, J.H., Wang, J., Tan, M.Y. (2016)
Phytotoxicity of imidazolium-based ILs with different
anions in soil on Vicia faba seedlings and the
influence of anions on toxicity. Chemosphere, 145:
269-276.
Lukkari T, Taavitsainen M, Soimasuo M, et al. (2004)
Biomarker responses of the earthworm Aporrectodea
tuberculata, to copper and zinc exposure: differences
between populations with and without earlier metal
exposure. Environmental Pollution, 129(3): 377-386.
Mechanisms of the Toxicity of Chiral Pesticides Dinotefuran Enantiomers on Esiena fetida Earthworm
551

Mahsa Karbaschi, Marcus S. Cooke. (2014) Novel method
for the high-throughput processing of slides for the the
comet assay. Sci Rep. 4, 7200.
Morrissey, C.A., Mineau, P., Devries, J.H., Sanchez-Bayo,
F., Liess, M., Cavallaro, M.C., Liber, K. (2015).
Neonicotinoid contamination of global surface waters
and associated risk to aquatic invertebrates: a review.
Environ. Int., 74: 291-303.
Niu, X., Mi, L., Li, Y., Wei, A., Yang, Z., Wu, J., Zhang,
D., Song, X. (2013) Physiological and biochemical
responses of rice seeds to phosphine exposure during
germination. Chemosphere, 93(10):2239-2244.
OECD. (2014) Organization for Economic Co-operation
and Development. Test No. 222: Earthworm
reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/andrei). OECD
Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Paris,
France.
Qi Y.L., Liu D.H., Zhao W.T., Liu C., Zhou Z.Q., Wang P.
(2015) Enantioselective phytotoxicity and bioacitivity
of the enantiomers of the herbicide napropamide.
Pestic. Biochem, Physiol, 125, 38-44.
Song, Y., Zhu, L.S., Wang, J., Wang, J.H., Liu, W., Xie,
H. (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative
enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia fetida) induced by
atrazine. Soil Biol. Biochem, 41: 905-909.
Sparks, T.C., Nauen, R., (2015). IRAC: Mode of action
classification and insecticide resistance management.
Pestic. Biochem.Physiol. 121, 122-128.
Wang,J., Cao,X.,Sun,J., Chai,L., Huang,Y., Tang,X.
(2015).Transcriptional responses of earthworm
(Eisenia fetida)exposed to naphthenic acids in soil.
Environ. Pollut, 204: 264-270.
Xu, J.B., Yuan, X.F., Lang, P.Z. (1997) Determination of
catalase activity and catalase inhibition by ultraviolet
spectrophotometry. Chin. Environ. Chem,16: 73-76.
Ye, X.Q., Xiong, K., Liu, J. (2016) Comparative toxicity
and bioaccumulation of fenvalerate and esfenvalerate
to earthworm Eisenia fetida. J. Hazard. Mater, 310:
82-88.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
552
