
The Metabolic Mechanism of Satiety Signal and Adiposity Signal on
Food Intake Regulation
Bochen Li
The School of Food Science and Nutrition University of Leeds,
Leeds, U.K.
Keywords: Food Intake, Satiety Signals, Adiposity Signals, Neuron Pathways.
Abstract: Obesity rates rose sharply in past 40 years, owing to the availability of appetizing food and work-related
sedentary habits. Obesity is caused by a long-term positive energy balance, but by reducing food intake
significant weight loss can be achieved. Food intake is simultaneously regulated by biochemical signals
(homeostasis) and social factors (non-homeostasis). As two important homeostasis factors, satiety and
adiposity signals have been well studied, but it is relatively fragmented. Therefore, this study looks at satiety
and adiposity signals to understand the metabolic mechanism of human food related metabolic pathways from
the perspective of homeostasis factor. Satiety and adiposity signals are critical for reducing obesity, because
they play such a large role in appetite control to reduce food intake. This research analyses literature about
satiety and adiposity signals, such as references related to CCK, GLP-1, ghrelin, leptin and insulin, and
combines the research of exogenous injection satiety and adiposity signals for calorie restriction to better
illustrate the metabolic pathways of these hormones.Through the analysis of these factors, it is concluded
that satiety and adiposity signals are expressed on two neuron pathways via NTS and ARC to
synergeticly control food intake by regulating appetite, but it seems that the method of injecting exogenous
hormones to treat obesity is currently difficult to achieve.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the past 40 years, the global obesity level
exorbitantly rose by three times, according to WHO
report, the percentage of overweight and obesity for
18 years old and elder adults was 39% and 13% in
2016, respectively (Website:
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-
sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight). Obesity is
characterized as having a BMI of 30kg/m2 or above
and it has become one of the most important global
public health issues which affects human well-being
and lifetime. Thus, it is very important to find an
effective way to lose weight.
Increasing activities and dietary restriction are the
only two methods that have been proved effective in
improving obesity from the energy balance view.
Comparing these two methods, dietary restriction is a
more effective way for weight loss than moderate
energy expenditure without calorie restriction (Swift,
McGee, Earnest, Carlisle, Nygard, Johannsen 2018;
Varady 2011).
Food consumption is coordinately regulated by
homeostasis and non-homeostasis factors. Non-
homeostasis factors include all external social factors,
such as food availability, eating patterns, food
delectability and previous experience, so it is
unpredictable and hard to control for improving
obesity. However, homeostasis factors play an
important role in controlling food intake by
biochemical signals (hormones) and understanding
the fundamentals of food intake control is critical to
understanding the etiology of eating disorders and
obesity. Homeostasis factors have been extensively
explored in human physiology to assist people in
understanding the cause of obesity and develop
therapeutic targets to cure obesity.
Depending on energy requirements, the
physiological regulation of calorie intake is exerted
on the meal's conclusion through a subtle
modification of meal size and sensation of fullness.
Thus, satiety and adiposity signal as the homeostasis
factors are important in appetite regulation because
the amount of food consumed in each meal is mostly
determined by the gut secreted hormones (satiety
144
Li, B.
The Metabolic Mechanism of Satiety Signal and Adiposity Signal on Food Intake Regulation.
DOI: 10.5220/0011234400003438
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 144-150
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
signal) and adipose related hormones (adiposity
signal) (Brunerová, Anděl 2013), lots of exogenous
injection of satiety and adiposity signal has been put
forward to reinforce specific neurons by changing
hormone level for treating obesity. And it’s important
to combs out the metabolic mechanism of satiety and
adiposity signals to let more people know the
mechanism in a clearer way.
However, there is relatively few article that combs
out these two signals and their effect in human’s
brain, thus, this study aims to evaluate the impacts of
two key hormonal signals (adiposity signal and
obesity signal) in the metabolic pathways on food
intake and discuss the feasibility for administration of
the exogenous key hormonal signals for weight loss.
Through this paper, relevant researchers can get a
clear idea of the internal mechanisms of obesity. And
for those who are relatively fat, knowing the related
concepts and mechanism about dietary restriction will
also help them lose weight and find a healthier life
style in a more scientific way.
2 FOOD IN TAKE RELATED
METABOLIC PATHWAY
As homeostasis regulation, key hormone signals
control dietary calorie intake via meal size, satiety,
and feeding interval, these controlling are based on
the action of these hormones to the brain to regulate
food intake, such as cephalic insulin (Ahrén, Holst
2001). To understand the effect of these hormones, it
is essential to understand their metabolic pathways.
As two important food intake related hormones,
satiety and adiposity signals regulate appetite through
reaching the signal integration site, the arcuate
nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC) and the nucleus
tractus solitarius (NTS).
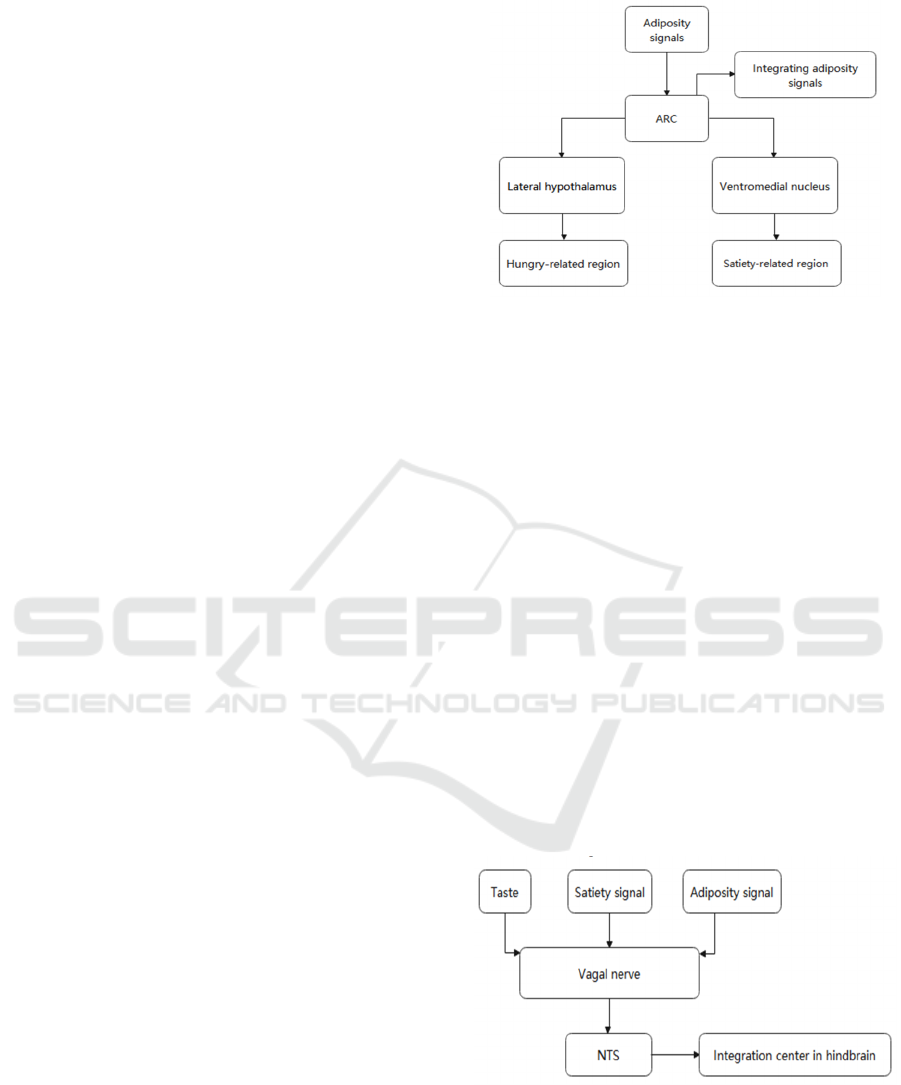
Hypothalamus as the body's most important brain
tissue to regulate of food intake has several regions,
as shown in Fig.1, the lateral hypothalamus and
ventromedial nucleus are associated with hunger and
satiety, which has been proved in animal experiments.
As the main region for integrating food intake related
signals to controlling food intake in hypothalamus,
ARC is close to the third ventricle. ARC is engaged
in two well-studied interconnected neural pathways
that are crucial for controlling food intake. The effects
of the two neuronal groups on food intake are
diametrically opposed, where the synergy of pro-
opiomelanocortin (POMC) and cocaine- and
amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) are
responsible for satiety to reduce
Figure 1: The metabolic pathways of food related signals in
hypothalamus.
food intake and the coordinated expression of
neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti related peptide
(AgRP) is related with inhibiting of satiety by
releasing AgRP neuron on melanocortin 4 receptor
(MC4R) to antagonize with POMC pathway neuron
(αMSH) (Zhan 2018). Notably, some signal
hormones like ghrelin govern hunger by stimulating
one of the two neuron routes, whereas some specific
signaling hormones like leptin and insulin can control
food intake by simultaneously affecting both neuron
pathways.
Like the hypothalamus, NTS, as shown in Fig.2,
is the integration site in the hindbrain for taste-
relative information and vagal and circulating signals,
NTS offer physicochemical property information and
quantity about food to the POMC and AgRP neurons
to rapidly promote satiety after meal digestion (Sohn
2015). Additionally, the NTS also express taste-
relative information which is non-homeostasis factor
to the ARC to control feeding behavior (Valassi,
Scacchi, Cavagnini 2007).
Figure 2: The metabolic pathways of food related signals in
nucleus tractus so-litarius (hindbrain).
Although satiety and adiposity signals share the
same neuron pathway, their biochemistry and
duration of action are different. Satiety signals are
short-term signals of negative feedback of the body's
The Metabolic Mechanism of Satiety Signal and Adiposity Signal on Food Intake Regulation
145

rapid response, satiety signals control hunger
sensation, satiety and feeding interval, it changes
constantly with the start of eating (ghrelin excepted),
while the adiposity signal is a long-term signal
targeted at maintaining the body's energy balance, it
does not change dramatically due to the beginning of
eating behaviors ,but they constantly control the
appetite through negative feedback of the amount of
adipose tissue. The satiety signal that is transmitted to
the NTS via the vagal and spinal nerves, is eventually
transmitted to the neuron routes in the hypothalamus,
while the adiposity signal, which express to the ARC
via the median eminence or by crossing the blood-
brain barrier (BBB) to enter the two specific neuron
pathways (Abdalla 2017).
3 THE SATIETY
SIGNAL- SHORT-TERM
Satiety signals are produced in the GI tract from one
hour before the start of the meal to the completion of
the meal as a signal to regulate food intake. Satiety
signal production is linked to eating anticipation, such
as the usual eating surroundings, daily habitual eating
time and the aroma and beauty of food. The brain
receives sensory stimulus or biological clock
regulation, the external stimulus and internal
regulation instruct the GI tract to create satiety signals
and transmits them down the vagal and spinal nerves
to the NTS (except ghrelin), then they express onto
neuron pathways and causing hunger or satiety.
Cholecystokinin (CCK), glucagon, glucagon-like
peptide-1 (GLP-1), ghrelin (hunger signal), and
peptide YY (PYY) are the most prominent satiety
signals which have been studied. To improve obesity,
significant pharmaceutical research has been
conducted based on this information.
Interestingly, a national survey has found that fast
eaters eat significantly more (for the same weight)
than slow eaters (Zeng, Cai, Ma, et al 2018), owing to
the fact that the slow eaters' satiety signal hasn't yet
reached the POMC pathway to increase satiety and
stop eating, whereas heavy eaters feel fuller after
meals due to more satiety signals reaching MC4R
receptors and increasing satiety. On the flip side of the
capacity to regulate food intake quickly, most satiety
signals have short half-lives, which will be discussed
further in the particular satiety signals section.
3.1 Cholecystokinin (CCK)
CCK as the first satiety signal to be identified and
investigated has been widely studied. CCK is
produced in the duodenum and jejunum and acts on
the CCK 1 receptor via the vagal afferent nerve to
inhibit food intake by activating the POMC pathway.
In a human trial of exogenous CCK injection, it was
discovered that exogenous CCK decreased food
intake in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore,
food intake in mice treated with a CCK 1 receptor
antagonist was significantly greater (when compared
to the placebo group), demonstrating the satiety-
enhancing impact of endogenous CCK(Beglinger,
Degen, Matzinger, D'Amato, Drewe Loxiglumide
2001).
Exogenous CCK injection, on the other hand, has
been shown to have some limitations in rat
experiments. The administration of exogenous CCK
more than 15 minutes before feeding seemed to have
no effect on the amount of food consumed by mice,
whereas the treatment of CCK immediately before
feeding significantly reduced the amount consumed
by mice(Begg, Woods 2013). This also proved that
CCK has a short half-life in human metabolism and
that the injection time must be carefully regulated to
get the desired effect of lowering consumption.
Additionally, when mice were continuously
injected with CCK over a long period of time, the
drop in food intake was shown to vanish after a very
short amount of time. According to the findings of
E.A. Duncan et al., rat consumption was significantly
reduced in the first three days after receiving
consecutive CCK injections compared to the saline
group (control group), but there was no significant
difference in consumption between the two groups
from day 4 to the end of the experiment (day 11). On
the other hand, from day one until the completion of
the experiment (day 28), the intermittent group
(exogenous CCK injections every three days)
consumed significantly less sucrose than the control
group (saline).
On the test of final day sucrose intake level, the
consecutive CCK group (110.0 ± 6.2% of baseline)
consumed significantly more sucrose than the
intermittent CCK group (98.6 ± 2.5% of baseline), t
(16) = 1.72, p≤0.05, and the saline group (97.4 ±
3.5% baseline), t (17) = 1.83, p<0.05 (Duncan,
Davita, Woods 2005). This state (consecutive CCK no
effect) could be caused by behavioral tolerance or
extinction of the learned respond (for endogenous
CCK) of CCK receptors. Accordingly, the results of
these rat trials are helpful in determining the
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
146

administration time and interval for exogenous CCK
injection in clinical practice.
3.2 GLP-1
GLP-1, another key intestinal hormone, stimulates
insulin synthesis and secretion triggered by glucose
while inhibits glucagon secretion. The injection of
exogenous GLP-1 was linked to a reduction in food
intake (which was dose-dependent) and weight loss in
mice, but it was shown that after a long-term infusion,
the obese group's post-meal GLP-1 release gradually
declined, providing a reference for clinical use
(Kanoski, Hayes, Skibicka 2016). GLP-1's clinical
application is additionally hampered by its short half-
life, as GLP-1 can be rapidly inactivated in the body
by an enzyme called Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV
(DPPIV) (Maselli, Camilleri 2020).
GlP-1 levels typically peak approximately an hour
before a meal, perhaps to promote insulin production
by islet B cells to digest incoming nutrients (glucose).
This is because insulin, as a long-term adiposity
signal, needs to take a long time to reach ARC and
induce satiety.
Long-acting GLP-1 agonists and DPPIV
inhibitors based on GLP-1 mechanisms have been
demonstrated to lower food intake in mice trials,
although most of these medications (for humans) are
still in development.
3.3 Ghrelin
Ghrelin, as the only hormone produced by GI tract
that promotes appetite among satiety signals,
expresses on ARC. Ghrelin stimulates the NPY and
AgRP pathways to boost appetite, and the NPY
pathway's activation also inhibits the POMC pathway
to be further hunger(Abizaid, Liu 2006). Ghrelin
levels spiked in the hour leading up to feeding and
then plummeted back to baseline once feeding began
(Begg, Woods 2013). This wide range of ghrelin
levels also suggests that ghrelin, as a satiety signal,
has a rapid and short-term potential to control eating
behavior.
Ghrelin has also been linked to body weight self-
control. According to the experimental outcomes,
ghrelin levels are higher in anorexia patients and
lower in obese patients (Begg, Woods 2013),
implying that ghrelin is engaged in the negative
feedback regulation of body weight change. The
findings may also shed light on why people who lose
weight struggle to manage their appetites. But chronic
ghrelin administration for anorexia patients will limit
fat utilization as a source of energy, it may be an
unhealthy method for gaining weight. In addition,
ghrelin has been linked to reproduction, glucose and
lipid metabolism, gastric motility, acid secretion,
sleep, and antiproliferative activity.
4 THE ADIPOSITY
SIGNAL- LONG-TERM
Adiposity signal is a long-term hormone that informs
the brain about the state of the body (the number of
fat cells) and aids the body in changing its diet to
maintain health. With the exception of insulin, other
obesity signals are produced by adipose tissue as the
signals to feedback information to the brain. The
adiposity signals are named because these hormones
are proportionate to body fat content. The two most
well-studied adiposity signals, insulin and leptin, are
proportional to the degree of obesity(Bagdade ,
Bierman, Porte 1967; Lönnqvist, Arner, Nordfors,
Schalling 1995), and insulin and leptin promote
catabolism while blocking anabolism and they
activate or inhibit the appropriate neuron pathways to
lower food intake by expressing on their respective
receptors on the ARC via active transport to the
blood-brain barrier (BBB).
4.1 Leptin
Leptin, the first adipocytokine that is identified, is the
primary regulator of the "brain gut axis," with the
bulk of leptin generated by white adipose tissue. To
lower meal size and extend time intervals, leptin
enters particular neuron pathways via activating
leptin receptors on the ARC, stimulating the POMC
pathway and inhibiting the NPY route. Leptin also
has a long-term control on obesity through regulating
energy metabolism by altering the energy utilization
ratio of glucose and fat.
Both congenital leptin and leptin receptor
deficiency contribute to obesity (which is very rare in
humans), and it has been demonstrated that leptin and
leptin receptor deficiency obesity patients treated
with recombinant human leptin and leptin
dramatically lowered their weight and food intake
(Valassi, Scacchi, Cavagnini 2007).
However, the experiment discovered that persons
with obesity who did not have a congenital deficit had
much greater blood leptin levels, indicating that
obesity is linked to leptin resistance. The molecular
mechanism behind resistance is unclear now.
The Metabolic Mechanism of Satiety Signal and Adiposity Signal on Food Intake Regulation
147

4.2 Insulin
Obesity can disrupt the body's energy metabolism and
is the major cause of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D), it is
mostly caused by insulin resistance induced by a lipid
metabolism disorder. Insulin and leptin function in
various ways. Insulin enters the ARC and activates
the POMC Neuron, but it does not inhibit the AgRP
and NPY pathways. Interestingly, insulin stimulated
AgRP production while inhibiting NPY (Vettor,
Fabris, Pagano, Federspil 2002). According to a
randomized crossover trial for oral insulin in healthy
male subject, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, it
can be seen that the total exposure [AUCIns338,0-∞]
and maximum concentration [Cmax,Ins338] of
insulin 338 were both significantly lower for 0 versus
360 minutes post-dose fasting (ratio [95 percent
confidence interval (CI)]: 0.36 [0.26-0.49], p <
0.001, and 0.35 [0.25-0.49], p < 0.001, respectively)
(Halberg et al 2019). This trial suggests insulin can
reduce food intake by increasing satiation and so
control body weight in terms of results.
Figure 3:Post-dose fasting period (Halberg et al 2019).
\
Figure 4: Post-dose fasting period (Halberg et al 2019).
The study of H.A. Halem et al. have shown that
central insulin injections can significantly reduce
intake in animal models (Halem, Taylor, Dong, Shen,
Datta, Abizaid, Diano, Horvath, Culler 2005), but the
major effect of insulin is to lower blood glucose
through glycogen synthesis and accelerate glucose
absorption in cells, which will let patients consume
more food due to hypoglycemia, that is why it is
impossible to use significant amounts of insulin to
treat obesity in clinical treatment.
5 SIGNALS INTERACTION AND
SENSITIVITY
As previously stated, adiposity and satiety signals are
expressed in the same weight-control neuron
pathways. Surprisingly, these hormones can alter the
sensitivity of each other's receptors, for enhancing the
appetite-controlling effect and this can be interpreted
as a mechanism for the body to maintain weight
effectively. For example, obese persons will have
higher amounts of leptin which boosts insulin
receptor sensitivity to improve production and lower
blood sugar to preserve health. However, insulin and
leptin, as long-term adiposity signals, can also
influence the sensitivity of satiety signal represented
by CCK (Begg, Woods 2013). For instance, patients
who were losing weight had lower levels of insulin
and leptin which affected a reduction in CCK 1
receptor sensitivity to prevent satiety, it is thought to
be the body's regulation to maintain weight stability.
These studies also suggest another reason why
exogenous insulin and leptin injections might help
people lose weight: increasing insulin and leptin can
help people lose weight by modifying CCK and GLP-
1 sensitivity.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In sum, satiety signal and adiposity signal are
expressed via different integration centers (NTS and
ARC) to the POMC and AgRP neurons that
coordinate regulate food intake to keep the body
weight, these biochemical pathways are essential for
researchers to understand the underlying processes of
obesity, such as changes in associated hormone levels
and neuron pathway reinforcement, calorie restriction
therapy also requires a deep understanding of the
fundamental mechanism of obesity. A clinically
significant weight loss benefit is not easy to occur
without side effects from recognized satiety and
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
148

adiposity signals and pathways. Food intake
homeostasis is a complicated system governed by
numerous hormones, and the precise mechanism by
which insulin and leptin influence satiety signal
sensitivity need to be investigated further, the
regulation of satiety signal sensitivity is a potential
target for improving obesity clinically. This paper
only discusses some important satiety and adiposity
signal, but not include some novel studied signals
such as GLP-2 and adiponectin. However, the future
clinical treatment of obesity should also be focused
on dietary control (mild case) and bariatric surgery
(severe case), because of the complexity of human
metabolic pathways and the side effects (resistance)
caused by exogenous hormones injection.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Some basic biochemical knowledge was provided by
the School of Food science and nutrition- University
of Leeds. Thanks for inspiration from Xiaoying Wang
in King’s College London. This work was supervised
by Professor Andrew Murray in University of
Cambridge.
REFERENCES
Abdalla MM. Central and peripheral control of food intake.
Endocr Regul. 2017 Jan 1;51(1):52-70. doi:
10.1515/enr-2017-0006. PMID: 28222022.
Abizaid A, Liu ZW, Andrews ZB, Shanabrough M, Borok
E, Elsworth JD, Roth RH, Sleeman MW, Picciotto MR,
Tschop MH, Gao
Ahrén B, Holst JJ. The cephalic insulin response to meal
ingestion in humans is dependent on both cholinergic
and noncholinergic mechanisms and is important for
postprandial glycemia. Diabetes. 2001
May;50(5):1030-8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.5.1030.
PMID: 11334405.
Bagdade JD, Bierman EL, Porte D Jr. The significance of
basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin
response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic
subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549-57. doi:
10.1172/JCI105646. PMID: 6061732; PMCID:
PMC292903.
Begg DP, Woods SC. The endocrinology of food intake. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 2013 Oct;9(10):584-97. doi:
10.1038/nrendo.2013.136. Epub 2013 Jul 23. PMID:
23877425.
Beglinger C, Degen L, Matzinger D, D'Amato M, Drewe J.
Loxiglumide, a CCK-A receptor antagonist, stimulates
calorie intake and hunger feelings in humans. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001
Apr;280(4):R1149-54. doi:
10.1152/ajpregu.2001.280.4.R1149. PMID: 11247838.
Bouret SB, Levin BE, Ozanne SE. Gene-environment
interactions controlling energy and glucose
homeostasis and the developmental origins of obesity.
Physiol Rev. 2015;95:47–82.
Brunerová L, Anděl M. Regulace příjmu potravy - I. část
[Food intake regulation - 1st part]. Vnitr Lek. 2013
Sep;59(9):808-17. Czech. PMID: 24073953.
Clin Invest 116: 3229 –3239, 2006.
Damon L. Swift, Joshua E. McGee, Conrad P. Earnest,
Erica Carlisle, Madison Nygard, Neil M. Johannsen ,
The Effects of Exercise and Physical Activity on
Weight Loss and Maintenance. Ypcad (2018),
doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2018.07.014
Duncan EA, Davita G, Woods SC. Changes in the satiating
effect of cholecystokinin over repeated trials. Physiol
Behav. 2005 Jul 21;85(4):387-93. doi:
10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.04.023. PMID: 15978640.
Halberg IB, Lyby K, Wassermann K, Heise T, Plum-
Mörschel L, Zijlstra E. The Effect of Food Intake on the
Pharmacokinetics of Oral Basal Insulin: A Randomised
Crossover Trial in Healthy Male Subjects. Clin
Pharmacokinet. 2019 Nov;58(11):1497-1504. doi:
10.1007/s40262-019-00772-2. PMID: 31093929;
PMCID: PMC6856260.
Halem HA, Taylor JE, Dong JZ, Shen Y, Datta R, Abizaid
A, Diano S, Horvath TL, Culler MD. A novel growth
hormone secretagogue-1a receptor antagonist that
blocks ghrelin-induced growth hormone secretion but
induces increased body weight gain.
Neuroendocrinology. 2005;81(5):339-49. doi:
10.1159/000088796. Epub 2005 Oct 5. PMID:
16210868.
Kanoski SE, Hayes MR, Skibicka KP. GLP-1 and weight
loss: unraveling the diverse neural circuitry. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2016 May
15;310(10):R885-95. doi:
10.1152/ajpregu.00520.2015. Epub 2016 Mar 30.
PMID: 27030669; PMCID: PMC4888559.
Lönnqvist F, Arner P, Nordfors L, Schalling M.
Overexpression of the obese (ob) gene in adipose tissue
of human obese subjects. Nat Med. 1995 Sep;1(9):950-
3. doi: 10.1038/nm0995-950. PMID: 7585223.
Maselli DB, Camilleri M. Effects of GLP-1 and Its Analogs
on Gastric Physiology in Diabetes Mellitus and
Obesity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1307:171-192. doi:
10.1007/5584_2020_496. PMID: 32077010.
organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while
promoting appetite. J
Sohn JW. Network of hypothalamic neurons that control
appetite. BMB Rep. 2015 Apr;48(4):229-33. doi:
10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.4.272. PMID: 25560696;
PMCID: PMC4436859.
Valassi E, Scacchi M, Cavagnini F. Neuroendocrine control
of food intake. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008
Feb;18(2):158-68. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2007.06.004.
Epub 2007 Dec 3. PMID: 18061414.
Varady KA. Intermittent versus daily calorie restriction:
which diet regimen is more effective for weight loss?
The Metabolic Mechanism of Satiety Signal and Adiposity Signal on Food Intake Regulation
149

Obes Rev. 2011 Jul;12(7):e593-601. doi:
10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00873.x. Epub 2011 Mar
17. PMID: 21410865.
Vettor R, Fabris R, Pagano C, Federspil G. Neuroendocrine
regulation of eating behaviour. J Endocrinol Invest
2002; 25:836e54.
Website: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-
sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
Wren AM, Seal LJ, Cohen MA, Brynes AE, Frost GS,
Murphy KG, Dhillo WS, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR.
Ghrelin enhances appetite and increases food intake in
humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001
Dec;86(12):5992. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.12.8111.
PMID: 11739476.
XB, Horvath TL. Ghrelin modulates the activity and
synaptic input
Zeng, X., Cai, L., Ma, J. et al. Eating fast is positively
associated with general and abdominal obesity among
Chinese children: A national survey. Sci Rep 8, 14362
(2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32498-9
Zhan C. POMC Neurons: Feeding, Energy Metabolism, and
Beyond. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1090:17-29. doi:
10.1007/978-981-13-1286-1_2. PMID: 30390283.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
150
