
The Relation between Gingipain, TREM-2 and the Condition of
Alzheimer’s Disease
Xiaolin Ding
Hangzhou NO. 14 Middle School,
Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310005, China
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease, Abeta, Gingipain, TREM-1, TREM-2.
Abstract: P. gingivalis is a kind of bacterial that causes Periodontitis, and will secrete gingipain, which can help the P.
gingivalis to colonize inside the host. It is proposed that the gingipain that is secreted by P. gingivalis will
activate TREM-1, which induces the inflammation inside the brain. The inflammation inside the brain will
cause the neurodegeneration and cognitive decline, which in a way worthen the AD. Thus, it can be concluded
that TREM-1 and gingipain have influences on AD. Beyond this, we found that TREM-2 shares homology
with TREM-1, and some studies shows that TREM-2 can help to against inflammatory. In this paper, we came
up with a hypothesis that the activation of TREM-2 reduces the level of inflammation and protects neurons
from degeneration, mainwhile, P. gingivalis colonizes in the brain and exacerbates features of AD via its
gingipains.
1 INTRODUCTION
P. gingivalis is what cause the periodontitis and
secrete gingipain. For gingipain, it is essential for P.
gingivalis survival and pathogenicity, and plays
critical roles in host colonization, inactivation of host
defenses, nutrient acquisition and tissue destruction.
TREM-1’s full name is The Triggering Receptor
Expressed on Myeloid cells 1. It is a surface receptor
on immune cells that amplifies inflammatory
processes, which means that once it is being
activated, it increases the level of inflammation. This
process can be activated by bacterial infection, and
studies have shown that it is regulated by gingipain of
P. Gingivalis, inducing chronic inflammation in the
brain, leading to neurodegeneration and cognitive
decline (Haditsch, Ursula, et al. 2020). TREM-2’s full
name is Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid
cells 2, it shares homology with TREM-1, encoding a
receptor expressed on immune cells such as
macrophageas and microglia (Dominy, Stephen, et al.
2019). In contrast, studies have shown that TREM-2
defends the liver against hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC), which is a chronic liver injury involving
inflammatory and hepatic regenerative processes
(Watts, Amber, et al. 2008). Once activated by its
ligand, TREM-2 reduces the level of inflammation in
the liver, and one of the ligands of TREM-2 is A-beta
protein (Esparza-Baquer, Labiano, et al. 2021).
Figure 1: (Matsushita, Kenji & Yamada-Furukawa, Masae & Kurosawa, Mie & Shikama, Yosuke. (2020). Periodontal Disease
and Periodontal Disease-Related Bacteria Involved in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of Inflammation
Research. Volume 13. 275-283. 10.2147/JIR. S255309.) It shows the process of how P. gingivalis cause the influences inside
the brain.
Ding, X.
The Relation between Gingipain, TREM-2 and the Condition of Alzheimer’s Disease.
DOI: 10.5220/0011238900003438
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 169-172
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
169
2 EXPERIMENTS
To prove our hypothesis, we designed experiments
follows, proven the function of gingipain, Co-
Immunoprecipitation, Gene knockout and Behavior
testing. By all these experiments, we are going to
prove that the TREM-2 can have a positive result in
AD, and it is gingipain that induces the AD (Singhrao,
Sim, and Ingar Olsen. 2019). In the first experiment
which is the proven of the function of gingipain, we
will use the following materials: Wild-type gingivalis
which normally exist in the nature, gingipain knock-
out mutant K1A which is deficient in Lys- gingipain
and E8 strains which is deficient in both Arg-
gingipain A and Arg-gingipain B (Bostanci, et al.
2016). We will first cultivate, collect, wash, and
suspend the bacterial to get enough copies for the
experiment, then, we will control environment for the
mouse and develop periodontitis inside mouse. After
five weeks, we will collect the brains of the mouse to
measure the data. We will measure the concentrations
of bacterial endotoxin in the brains and the
concentrations of A-beta protein (40 and 42) in the
brains so that we can find out whether the gingipain
works as expected (Ishida et al. 2017). In the second
experiment of Co-Immunoprecipitation, we are going
to determine the interactions between Aβ and
TREM2, the materials that will be use are the fresh
medium containing conditioning molecules and
microglia. First step of this experiment is the
preparation of cell lysates, we will cultivate bacterial
inside of a fresh medium, collect, wash, and suspend
the bacterial. After that, we will do the
immunoprecipitation, in this step, we will centrifuge
the supernatant, and aspirate the residue for use
(Maheshwari, Eslick 2015). Then, we will do the
western blot. In this step, we will run gel to get data
to prove that TREM-2 can be bound to Aβ as it will
show a similar result as Aβ is immunoprecipitated
with Aβ antibodies (Liu, Yu. 2019). In the third
experiment for gene knockout, we are going to prove
the function of TREM-1 and TREM-2. In this
experiment, we will use gingipain and mouse. The
first step is to set two LoxP sites so that it can be clear
which part of the gene is going to be knockout
(Singhrao, Sim, et al. 2015). After that, we are going
to knockout the TREM-1 gene and the TREM-2 gene
dividing by group 1 to 4 which with one only
knockout TREM-1, one only knockout TREM-2, one
knockout both and one does not knockout any gene.
Then, we will induce gingipain into the brains, and
measure the production of pro-inflammatory
cytokines by ELISA. By this experiment and the
research done by other scientists, we can conclude
that TREM-1 will increase the level of inflammation
while TREM-2 will decrease the level of
inflammation (Ishida et al. 2017).
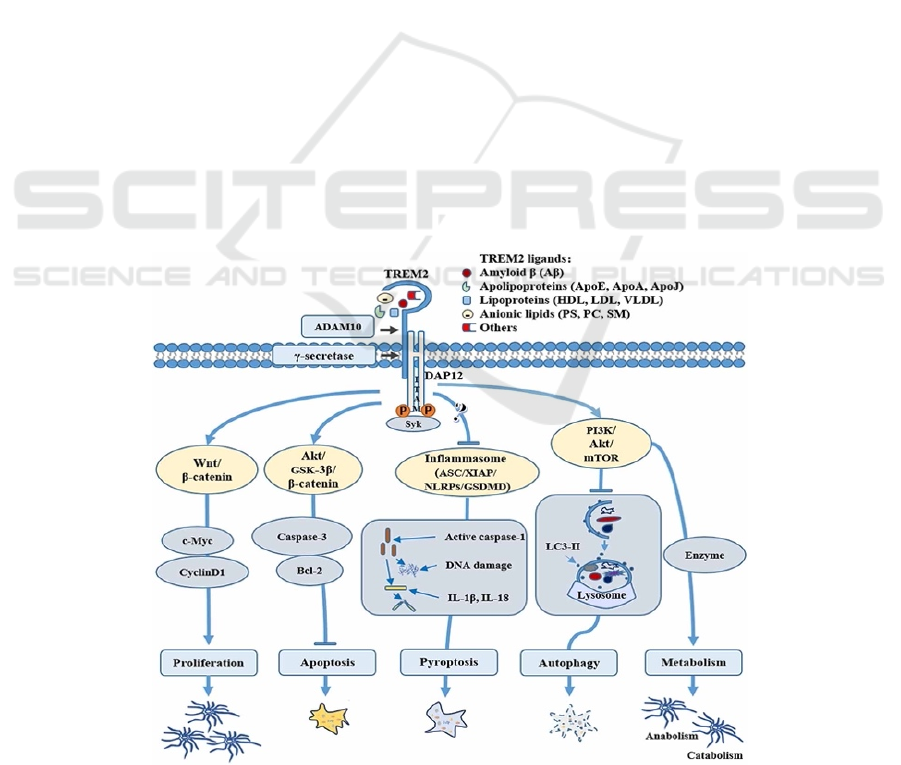
Figure 2: (from TREM2 in Alzheimer’s Disease: Microglial Survival and Energy Metabolism) shows the process of TREM-
2 and what it caused.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
170

3 BEHAVIOR TESTING
After all these experiments are done, we need to know
whether the TREM-1 and TREM-2 have influence on
AD, so we designed a behavior testing. We will first
divide mouse into 4 groups with group A for the
TREM-1 knock-out, group B for TREM-2 knock-out,
group C for both knock-out, group D for the one does
not do anything. Then, we design three testing to get
the result. In the first experiment, we will design a
maze with several turns that a normal mouse can walk
out. Put each group into the maze individually to
measure the time they need for the first time to find
way out. Do the same thing for 3 times and measure
the time each group need to get out. Compare the
change in the need of time between different groups
to conclude the result. In the second experiment, we
put each group into a box with road A and B that lead
to food, if the mice pass through road A, they will
receive an electron shock of 5V. Make the mouse
empty stomach for 5 hours and put each group into
the box so that they will go for the food. Do the same
thing for 10 times and measure the time they go for
road A and B. In the third experiment, a training for
all the mouse to open the box to find food will be done
before do the surgery. After the surgery, put two
sealed boxes in two directions with two different odor
that is not related with mouse in any areas, one of the
boxes contains food. Put each group in that area to
find food for 10 times. Measure the time it takes for
mouse to know the box with which odor contains
food. The results of these experiments are that ss the
experiments above, we can assume that TREM-1 will
exacerbate inflammation during acute inflammation,
while TREM-2 will prevent chronic inflammation.
According to Naoyuki Ishida, the inflammation is
correlated with AD that when inflammation
exacerbate, it will exacerbate the symptoms of
Alzheimer's Disease (Ishida et al. 2017). So that we
can expect that the knock-out of TREM-1 will
decrease the symptoms of AD, the knock-out of
TREM-2 will exacerbate the symptoms of AD, while
knock-out of both TREM-1 and TREM-2 will cause
the deterioration of AD afterward. As the assumption
we make, we can know that group A will present the
state that AD is weakened. In group B, the present of
AD will be exacerbated. In group C, the present of
AD will be exacerbated. In group D, it is same as
group C. For the behavior testing, if our hypothesis is
correct, the result will be that in experiment 1, group
A will show an obvious decrease in the time it takes
to pass the maze as the time of trying increases. Group
B will need almost the same time during each time of
trying. Group C shows a similar result as group B.
Group D shows a constant decrease in time as the time
it passes the maze increases. In experiment 2, as the
time of the experiment increases, group A shows an
obvious decrease in the chance it goes for road A.
Group B shows a chance of about 50% that it will go
for road A. Group C shows a similar result as group
B. Group C shows a decrease in the chance it goes for
road A as the time of experiment increases. In
experiment 3, group A will show a decrease in the
time it needed to find food as the time of experiment
increases and can be concluded that group A can link
a kind of odor to food. Group B shows a similar time
each time it needed to find food as the time of
experiment increases so that it can be concluded that
group B cannot link a kind of odor with food. Group
C shows a similar result as group B. Group D shows
a decrease in time as more experiment is done and can
be concluded that group D can link a kind of odor to
food. If the hypothesis is wrong, then the result will
be that in all the experiments, the behavior of all
groups of mice are similar and the improvement in
time is almost neglectable.
Figure 3: (from Predictably irrational: assaying cognitive inflexibility in mouse models of schizophrenia) It shows some types
of behavior testing, the A and C are used in this experiment.
The Relation between Gingipain, TREM-2 and the Condition of Alzheimer’s Disease
171

4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, it talks about the influence TREM-2
might have on Alzheimer’s Disease. After these
experiments, the hypothesis of TREM-2 and
gingipain can be proved. Though this article and the
hypothesis might be wrong, but TREM-2 and
gingipain have influences on AD by many factors in
different ways. As the Alzheimer’s disease is a very
serious disease that influence people in so many
ways, it is possible to say that the relation between
TREM-2 and Alzheimer’s disease is crucial to the
further research and the development of the treatment
in Alzheimer’s disease. This article is meant to show
a new way of seeing what influences Alzheimer’s
Disease and point out a factor that have not been
tested on. In the future, we will focus on the research
of what is the causation of Alzheimer’s Disease, what
are the factors that make it worse, and how the
symptoms Alzheimer’s Disease can be decreased.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Nicolas Chen, Priscilla Peng, Dan Wang.
REFERENCES
Bostanci, N, et al. (2016) Porphyromonas Gingivalis
Regulates TREM-1 in HUMAN Polymorphonuclear
Neutrophils via Its Gingipains.
qmro.qmul.ac.uk/xmlui/handle/123456789/12567.
Dominy, Stephen S., et al. (2019) Porphyromonas
Gingivalis in Alzheimer's Disease BRAINS: Evidence
for Disease Causation and Treatment WITH Small-
Molecule Inhibitors.
advances.sciencemag.org/content/5/1/eaau3333?intcm
p=trendmd-adv.
Esparza-Baquer A, Labiano I, et al. (2021) TREM-2
defends the liver against hepatocellular carcinoma
through multifactorial protective mechanisms.
gut.bmj.com/content/70/7/1345.
Haditsch, Ursula, et al. (2020) Alzheimer's Disease-like
Neurodegeneration in Porphyromonas Gingivalis
Infected Neurons with PERSISTENT Expression of
Active Gingipains.
content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-alzheimers-
disease/jad200393.
Ishida N, Ishihara Y, Ishida K, Tada H, Funaki-Kato Y,
Hagiwara M, et al. (2017) Periodontitis induced by
bacterial infection exacerbates features of Alzheimer’s
disease in transgenic mice.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41514-017-0015-x.
Liu, Changan, and Jun Yu. (2019) Genome-Wide
Association Studies for Cerebrospinal Fluid Soluble
TREM2 in Alzheimer's Disease.
www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2019.0029
7/full.
Maheshwari P, Eslick GD. (2015) Bacterial infection and
Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25182736/.
PMC2626915/.
Singhrao, Sim K, and Ingar Olsen. (2019) Assessing the
role of Porphyromonas gingivalis in periodontitis to
determine a causative relationship with Alzheimer's
disease.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6352933/.
Singhrao, Sim K., et al. (2015) Porphyromonas Gingivalis
PERIODONTAL Infection and Its PUTATIVE Links
with Alzheimer's Disease.
www.hindawi.com/journals/mi/2015/137357/.
Watts, Amber, et al. (2008) Inflammation as a potential
mediator for the association between periodontal
disease and Alzheimer's disease.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
172
