
Attention for Inference Compilation
William Harvey
1
, Andreas Munk
1
, Atılım G
¨
unes¸ Baydin
2
, Alexander Bergholm
1
and Frank Wood
1,3
1
Department of Computer Science, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
2
Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, U.K.
3
Mila - Quebec Anguilla Institute and Inverted AI, Canada
Keywords:
Attention, Bayesian Inference, Probabilistic Programming, Inference Compilation.
Abstract:
We present a neural network architecture for automatic amortized inference in universal probabilistic programs
which improves on the performance of current architectures. Our approach extends inference compilation (IC),
a technique which uses deep neural networks to approximate a posterior distribution over latent variables in
a probabilistic program. A challenge with existing IC network architectures is that they can fail to capture
long-range dependencies between latent variables. To address this, we introduce an attention mechanism
that attends to the most salient variables previously sampled in the execution of a probabilistic program. We
demonstrate that the addition of attention allows the proposal distributions to better match the true posterior,
enhancing inference about latent variables in simulators.
1 INTRODUCTION
Probabilistic programming languages (van de Meent
et al., 2018; Mansinghka et al., 2014; Milch et al.,
2005; Wood et al., 2014; Minka et al., 2018; Good-
man et al., 2008; Bingham et al., 2018; Tran et al.,
2016) allow for automatic inference about random
variables in generative models written as programs.
Conditions on these random variables are imposed
through observe statements, while the sample state-
ments define latent variables we seek to draw infer-
ence about. Common to the different languages is the
existence of an inference backend, which implements
one or more general inference methods.
Recent research has addressed the task of making
repeated inference less computationally expensive, by
using up-front computation to reduce the cost of later
executions, an approach known as amortized infer-
ence (Gershman and Goodman, 2014). One method
called inference compilation (IC) (Le et al., 2017) en-
ables fast inference on arbitrarily complex and non-
differentiable generative models. The approximate
posterior distribution it learns can be combined with
importance sampling at inference time, so that infer-
ence is asymptotically correct. It has been success-
fully used for Captcha solving (Le et al., 2017), in-
ference in particle physics simulators (Baydin et al.,
2019), and inference in heat-transfer finite element
analysis simulators (Munk et al., 2019).
The neural network used in IC is trained to ap-
proximate the joint posterior given the observed vari-
ables by sequentially proposing a distribution for each
latent variable generated during an execution of a pro-
gram. As such, capturing the possible dependencies
on previously sampled variables is essential to achiev-
ing good performance. IC uses a Long Short Term
Memory (LSTM)-based architecture (Hochreiter and
Schmidhuber, 1997) to encapsulate these dependen-
cies. However, this architecture fails to learn the
dependency between highly dependent random vari-
ables when they are sampled far apart (with several
other variables sampled in-between). This motivates
allowing the neural network which parameterizes the
proposal distribution for each latent variable to explic-
itly access any previously sampled variable. Inspired
by the promising results of attention for tasks involv-
ing long-range dependencies (Jaderberg et al., 2015;
Vaswani et al., 2017; Seo et al., 2016), we imple-
mented an attention mechanism over previously sam-
pled values. This enables the network to selectively
attend to any combination of previously sampled val-
ues, regardless of their order and the trace length.
We show that our approach significantly improves the
approximation of the posterior, and hence facilitates
faster inference.
80
Harvey, W., Munk, A., Baydin, A., Bergholm, A. and Wood, F.
Attention for Inference Compilation.
DOI: 10.5220/0011277700003274
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications (SIMULTECH 2022), pages 80-91
ISBN: 978-989-758-578-4; ISSN: 2184-2841
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Probabilistic Programming
Probabilistic programming languages (PPLs) allow
the specification of probabilistic generative models
(and therefore probability distributions) as computer
programs. Universal PPLs, which are based on Tur-
ing complete languages, may express models with
an unbounded number of random variables. To
this end, they combine traditional programming lan-
guages with the ability to sample a latent random vari-
able (using syntax which we denote as a sample state-
ment) and to condition these latent variables on the
values of other, observed, random variables (using an
observe statement). More formally, following (Le
et al., 2017), we will operate on higher-order proba-
bilistic programs in which we discuss the joint distri-
bution of variables in an execution “trace” (x
t
,a
t
,i
t
),
where t = 1,...,T , with T being the trace length
(which may vary between executions). x
t
denotes the
value sampled at the tth sample statement encoun-
tered, a
t
is the address of this sample statement and
i
t
represents the instance count: the number of times
the same address has been encountered previously, i.e.
i
t
=
∑
t
j=i
1(a
t
= a
j
). We shall assume that there is a
fixed number of observations, N, and these are de-
noted by y = (y
1
,...,y
N
), and we denote the latent
variables as x = (x
1
,...,x
T
). Using this formalism,
we express the joint distribution of a trace and obser-
vations as,
p(x,y) =
T
∏
t=1
f
a
t
(x
t
|x
1:t−1
)
N
∏
n=1
g
n
(y
n
|x
1:τ(n)
), (1)
where f
a
t
is the probability distribution specified by
the sample statement at address a
t
, and g
n
is the prob-
ability distribution specified by the nth observe state-
ment. τ denotes a mapping from the index, n, of the
observe statement to the index of the most recent
sample statement before the nth observe statement.
As an example, consider the simple circuit as well
as the probabilistic program shown in Figure 2, which
expresses the joint distribution over the battery volt-
age, V , whether the resistor is faulty, F, the resis-
tance of the resistor, R, and the measured current, I,
as p(V,F,R,I) = p(I|V, R)p(R|F)p(F)p(V ).
Traces will have the form (x
t
,a
t
,i
t
)
T =3
t=1
where
there are two trace “types,” one corresponding to the
sequence of addresses of random variables generated
if the resistor is faulty, and the other the opposite. In
other words a
1
is the address where V is sampled, a
2
is the address where F is sampled, and a
3
is the ad-
dress from which R is sampled, which depends on F.
The instance counts in this program are always i
1
=
i
2
= i
3
= 1, and the observation, measured current
∼ N(I,0.001), with N = 1.
This generative model allows posterior inference
to be performed over the joint distribution of the in-
put voltage V , current I, and “faulty” variable F given
the observed measured current. Estimates of the
marginal posterior distribution over F make it possi-
ble to directly answer questions such as whether the
resistor is faulty or not. We will return to a more com-
plex version of this problem in Section 4.3.
Generally, PPLs are designed to infer posterior
distributions over the latent variables given the obser-
vations. Inference in probabilistic programs is car-
ried out with algorithms such as Sequential Impor-
tance Sampling (SIS) (Arulampalam et al., 2002),
Lightweight Metropolis-Hastings (Wingate et al.,
2011), and Sequential Monte Carlo (Del Moral et al.,
2006). However, these algorithms are too computa-
tionally expensive for use in real-time applications.
Therefore, recent research (Le et al., 2017; Kulkarni
et al., 2015) has considered amortizing the computa-
tional cost by performing up-front computation (for a
given model) to allow faster inference later (given this
model and any observed values).
2.2 Inference Compilation
Inference compilation, or IC (Le et al., 2017), is
a method for performing amortized inference in the
framework of universal probabilistic programming.
IC involves training neural networks, which we de-
scribe as “inference networks,” whose outputs pa-
rameterize proposal distributions used for Sequen-
tial Importance Sampling (SIS) (Arulampalam et al.,
2002). IC attempts to match the proposal distribu-
tion, q(x|y; φ) =
∏
T
t=1
q
a
t
,i
t
(x
t
|η
t
(x
1:t−1
,y,φ)) close to
the true posterior, p(x|y) using the Kullback-Leibler
divergence, D
KL
(p(x|y)||q(x|y;φ)), as a measure of
“closeness”. In order to ensure closeness for any ob-
served y, an expectation of this divergence is taken
with respect to p(y),
L (φ) =E
p(y)
[D
KL
(p(x|y)||q(x|y;φ))]
=E
p(x,y)
[−log q(x|y,φ)] + const. (2)
The parameters, φ, are updated by gradient descent
with the following gradient estimate of (2),
∇
φ
L (φ) ≈
1
M
M
∑
m=1
−∇
φ
logq(x
m
|y
m
,φ), (3)
where (x
m
,y
m
) ∼ p(x,y) for m = {1,...,M}. Note
that the loss used, and the estimates of the gradi-
ents, are identical to those in the sleep-phase of wake-
sleep (Hinton et al., 1995).
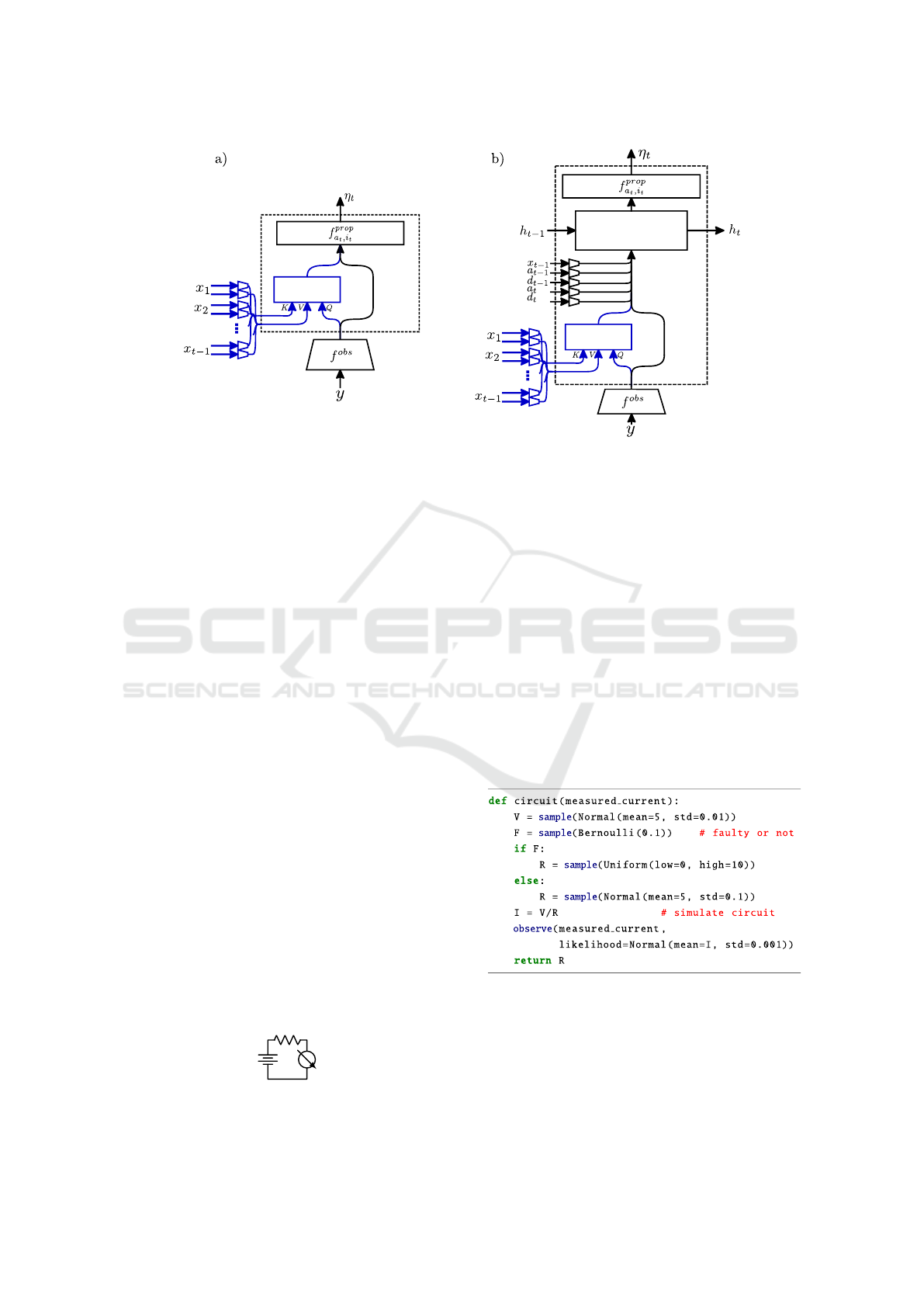
The architecture used in IC (Baydin et al., 2019;
Le et al., 2017) consists of the black components
Attention for Inference Compilation
81
dot-product
attention
LSTM
...
dot-product
attention
...
Figure 1: Feedforward and LSTM neural network architectures with attention mechanisms. The components inside the dashed
line are run once at each sample statement in a program trace, while the parts outside this line are run only once per trace.
The added attention mechanism is shown in blue.
shown in Figure 1b. Before performing inference,
observations y are embedded by a learned observe
embedder, f
obs
. At each sample statement encoun-
tered as the program runs, the correspondingly LSTM
runs for one time step. It receives an input con-
sisting of the concatenation of the embedding of the
observed values, f
obs
(y), an embedding of x
t−1
, the
value sampled at the previous sample statement, em-
beddings of the current and previous address, instance
and distribution-type. The embedder used for x
t−1
is
specific to (a
t−1
,i
t−1
), the address and instance from
which x
t−1
was sampled. The output of the LSTM
is fed into a proposal layer, which is specific to the
address and instance (a
t
and i
t
). The proposal layer
outputs the parameters, η
t
, of a proposal distribution
for the variable at this sample statement.
2.3 Dot-product Attention
Attention has proven useful in a number of tasks, in-
cluding image captioning, machine translation, and
image generation (Xu et al., 2015; Bahdanau et al.,
2014; Gregor et al., 2015). The two broad types of at-
tention are hard and soft attention. Hard attention (Ba
et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2015) selects a single “loca-
tion” to attend to, and thus requires only this location
to be embedded. However, it is non-differentiable. In
contrast, soft attention mechanisms (Vaswani et al.,
V
R
A
Figure 2: The electronic circuit modelled by the probabilis-
tic program in Figure 3.
2017; Xu et al., 2015) are fully differentiable and here
we focus especially on dot-product attention (Luong
et al., 2015; Vaswani et al., 2017).
The dot-product attention module (Luong et al.,
2015; Vaswani et al., 2017), shown in Figure 5, re-
ceives three inputs: one or more query vectors (which
describe the desired properties of the locations to at-
tend to), a key vector for each location, and a value
vector for each location; these are represented as the
matrices Q ∈ R
q×k
, K ∈ R
k×l
, and V ∈ R
l×v
respec-
tively. Note that in our context a location corresponds
to a previously sampled value. Here, l is the number
of locations, k is the length of each query and key em-
bedding, v is the length of each value embedding, and
q is the number of queries. For each query, attention
Figure 3: Probabilistic program modeling the circuit in Fig-
ure 2 with a possibly faulty resistor. First the voltage, V ,
of the battery is sampled from a Gaussian prior centered on
5V. We then sample whether or not the resistor is faulty. If
it is, its value is sampled from a broad uniform distribution.
Otherwise, its value is sampled from a tightly peaked Gaus-
sian. A noisy measurement of the current is then sampled
from a Gaussian prior centered on the true value.
SIMULTECH 2022 - 12th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
82
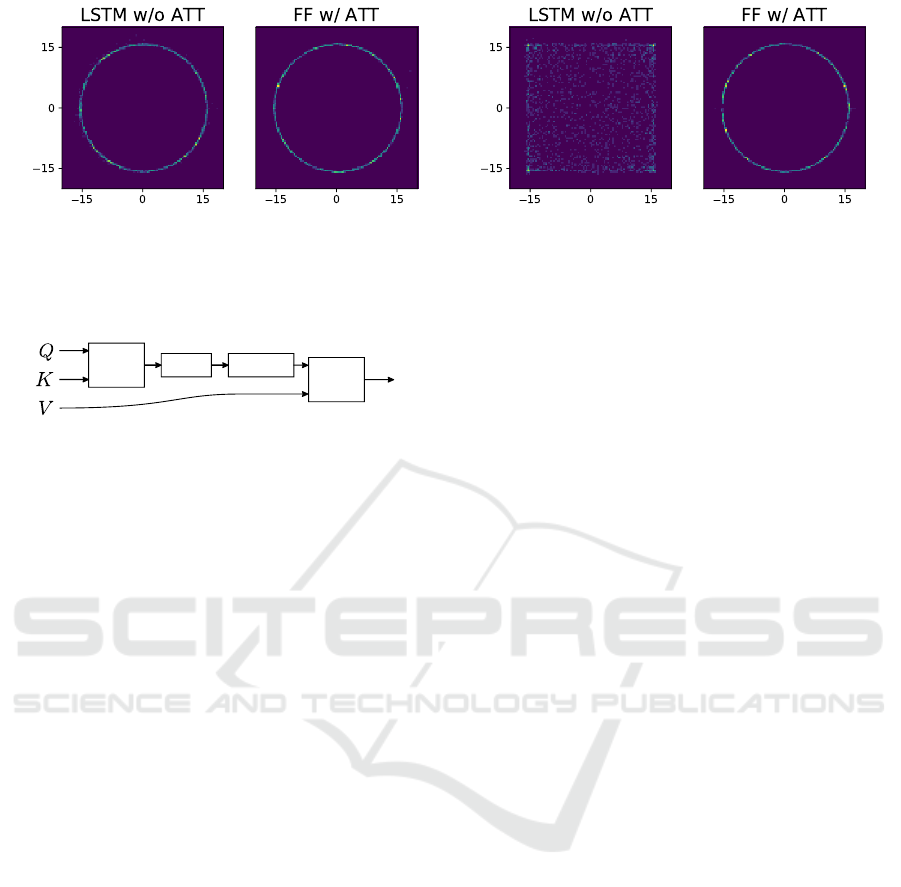
(a) Model with 20 nuisance variables. (b) Model with 50 nuisance variables.
Figure 4: 2000 samples from the proposal distributions of each of an LSTM-based inference network and an attention-based
network. The LSTM is able to learn the dependence of y on x when they are separated by 20 nuisance variables, but fails
when this is increased to 50. The attention mechanism can handle either case.
SoftMax
MatMul
MatMul
Scale
Figure 5: A scaled dot-product attention mechanism. Figure
adapted from (Vaswani et al., 2017).
weights are computed for every location by taking the
dot-product of the query vector and the relevant key.
3 METHOD
We augment both the LSTM and feedforward archi-
tectures with dot-product attention over all previously
sampled variables, as shown in Figure 1. Although
soft attention is, in many cases, vastly more computa-
tionally expensive than hard attention, this is not the
case for our application; since the embedding of each
sampled value can be used at every later time step, the
cost of calculating these embeddings scales only lin-
early with trace length. This is no worse than the rate
that hard attention achieves. We therefore use soft at-
tention for the ease of training.
During training we build a data structure, d
k,v,q
,
with associative mappings linking address/instance
pairs (a,i) to key, value and query embedders. The
embedders in d
k,v,q
are constructed dynamically for
each new address and instance pair (a
t
,i
t
) encoun-
tered. During inference, the queries, keys, and values
fed to the attention mechanism at each sample state-
ment are calculated as follows: for the first sample
statement, identified by (a
1
,i
1
), no previously sam-
pled variables exist and so the attention module out-
puts a vector of zeros. Using the associated key and
value embedders in d
k,v,q
, the variable sampled, x
1
,
is embedded to yield a key and a value, k
1
and v
1
.
(k
1
,v
1
) are kept in memory throughout the trace, al-
lowing fast access for subsequent sample statements.
The second sample statement can attend to the first
sampled variable via (k
1
,v
1
) using a query. The em-
bedder used for finding the query takes as input the
observe embedding, f
obs
(y), and is specific to the
current address and instance (a
2
,i
2
). As with the
key/value embedders, the query embedder is found in
d
k,v,q
. The output of the attention module is then fed
to the LSTM or proposal layer (see Figure 1). As for
x
1
, x
2
is sampled and embedded using the embedders
stored in d
k,v,q
, yielding the key, value pair (k
2
,v
2
).
This procedure is repeated until the end of the trace,
as defined by the probabilistic program. In the con-
text of higher-order programs, an address and instance
pair may be encountered during inference that has not
been seen during training. In this case the proposal
layers have not been trained, and so the standard IC
approach is to use the prior as a proposal distribution.
For the same reason, the key/value embedders do not
exist and so no keys or values are created for this
(a
t
,i
t
). This prevents later sample statements from
attending to the variable sampled at (a
t
,i
t
).
4 EXPERIMENTS
We consider feedforward and LSTM architectures
both with and without attention, which we de-
note FF w/o ATT, FF w/ ATT, LSTM w/o ATT and
LSTM w/ ATT. We compare them through experi-
ments with inference in three probabilistic programs:
a pedagogical example to illustrate a failure case of
the LSTM architecture; a model of gene expression
in plants; and finally an electronic circuit simulator.
We implement our proposed architecture in, and per-
form the experiments using, pyprob (Le et al., 2017;
Baydin and Le, 2018), a probabilistic programming
language designed for IC. All experiments use the
same attention mechanism hyperparameters: q = 4,
k = 16 and v = 8. We also use pyprob’s default neu-
ral network layer sizes, optimizer (Adam (Kingma
and Ba, 2014)) and associated hyperparameters, batch
Attention for Inference Compilation
83

Figure 6: Fifth-order band-pass Butterworth filter with resistors, capacitors and inductors denoted by R, C, and L respectively.
The dashed lines represent possible short circuits. The existence of these short circuits and whether or not each component
is faulty (represented by a noisy component value) or disconnected is sampled according to the generative model. Given
observations of V
out
for various input frequencies, the task is to infer a distribution over possible faults such as short circuits
and poorly connected or incorrectly valued components.
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
AC Voltage (V)
ESS =1.2±0.27
M
FF w/o ATT
ESS =1.9±0.47
M
LSTM w/o ATT
ESS =3.3±1.19
M
FF w/ ATT
Proposal
ESS =2.3±0.73
M
LSTM w/ ATT
980 1000 1020
f (Hz)
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
AC Voltage (V)
980 1000 1020
f (Hz)
980 1000 1020
f (Hz)
980 1000 1020
f (Hz)
Estimated Posterior
Observations Samples
Figure 7: Reconstruction of the output voltage using samples from each proposal distribution. In the architectures with
attention, the sampled voltages are almost all close to the observations (green ‘x’s) whereas, without attention, the proposals
place high probability in regions which do not fit the observations. These better proposal distributions lead the higher effective
sample sizes shown in each figure (mean and standard deviation, calculated with 5 estimates). The proposal distribution is
shown using 100 samples from each architecture.
FF w/o ATT LSTM w/o ATT FF w/ ATT LSTM w/ ATT Ground truth
None
C4 short
C2 short
Multiple
Figure 8: A visualisation of the proposal distributions given some observation sampled from the model. The pie charts show
the probability of different possibilities: that there are no faults, multiple faults, or one of multiple specific types of fault. For
each architecture, 1000 unweighted samples are shown. A ‘ground truth’ posterior, created with 10 000 importance-weighted
sampled from LSTM w/o ATT, is shown to the right. Since it is probable that exactly one of the faults ‘C2 short’ or ‘C4 short’
has occured, there is a dependence between these two variables. Either an LSTM or an attention mechanism (or both) can be
seen to be sufficient to capture this dependence (thus reducing the error of the weighted posterior approximation). The error
is calculated by embedding the samples as a vector where each element corresponds to a possible fault and is 1 if this fault is
present, or 0 otherwise. The L2-Wasserstein distance from the ground truth is then measured.
size (64) and learning rate (10
−3
). The only exception
to this is that a learning rate of 10
−4
was used to sta-
bilise training of the gene expression model.
4.1 Magnitude of Random Vector
Our first program samples two latent variables, x
and y, from identical and independent normal dis-
tributions, N(0,σ
p
). An observation of x
2
+ y
2
is
then made with Gaussian noise, and denoted ˆr
2
∼
N(ˆr
2
|x
2
+ y
2
,σ
l
). We wish to infer the posterior over
x and y conditioned on this. We use σ
p
= 10 and
σ
l
= 0.5, giving a peaked posterior exhibiting circular
symmetry, and so a strong dependence between x and
y. To test the inference network’s ability to capture
long-term dependencies, we sample “nuisance” vari-
ables between sampling x and y. These are not used
elsewhere in the program, serving only to increase the
“distance” between x and y. We provide pseudocode
for this program in the appendix.
All inference networks for this model are trained
for 2000 000 traces. Figure 4 shows samples of x
and y from learned proposal distributions for two pro-
grams with different numbers of nuisance variables
(which are marginalized out). The inference network
with an attention mechanism can be seen to learn the
dependency even with 50 nuisance variables, while
the LSTM cannot.
SIMULTECH 2022 - 12th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
84

4.2 Plant Gene Expression
We consider a model of gene expression for Ara-
bidopsis thaliana, a small plant. This was presented
by (Opgen-Rhein and Strimmer, 2007) as a Bayesian
network, and we write it as a probabilistic program.
Although this model has simple link functions (each
node is normally distributed with mean given by an
affine function of the values of parent nodes), it tests
the ability of each architecture to learn a dependency
structure from a real-world simulator. The network
contains 107 nodes and 150 edges. We randomly se-
lect 40 of the 67 leaf nodes to be observable, and at-
tempt to infer the values of all other nodes given these.
We train inference networks for 4 000 000 traces for
this model. Visualizations of the attention weights for
this model and the magnitude model are in the ap-
pendix.
4.3 Electronic Circuit Fault Diagnosis
The final probabilistic program we consider is a
model of an electronic circuit (specifically, a band-
pass Butterworth filter). The model samples many
random variables describing the components values
and the existence of possible faults (such as short-
circuits or missing components). A pre-existing cir-
cuit simuator (Venturini et al., 2017) then generates
the complex-valued output voltage (i.e. voltage mag-
nitude and phase) at 40 different input frequencies.
Given an observation of this (under Gaussian noise),
we infer what faults, if any, exist. An illustration of
the Butterworth filter can be found in Fig. 6. The in-
ference networks are trained for 3000 000 traces.
To perform inference we write a probabilistic pro-
gram (see appendix) that iterates through each com-
ponent of the circuit and samples in the following or-
der: first, whether or not it is correctly connected to
the rest of the circuit. Second, the component value
is sampled from a mixture of a broad uniform distri-
bution and a tightly peaked Gaussian, both centered
on the nominal value. The value is sampled from
the tightly peaked Gaussian with 98% probability and
from the uniform distribution with 2% probability.
Conceptually, one can interpret the tightly peaked
Gaussian as the distribution given that the component
has been correctly made. The broad uniform distri-
bution represents the distribution for components that
are faulty.
To test each inference network, we generate 100
different observations by running the probabilistic
program, and attempt to infer the posterior using
each different network architecture. For each in-
ference network architecture, we estimate the pos-
terior distribution 5 times using importance sam-
pling with 20 traces each time. Across the 5 es-
timates, we compute the average ESS, and average
these over all 100 observations. The averaged results
were 1.40 for FF w/o ATT, 7.26 for LSTM w/o ATT,
8.46 for FF w/ ATT and 8.35 for LSTM w/ ATT. The
attention-based architecture has an 16.5% higher av-
erage ESS than the LSTM core, showing that the use
of attention leads to quantitatively better proposal dis-
tributions.
We further find that whenever the observed signal
appears to originate from a correctly working Butter-
worth filter, all architectures seem to produce reason-
able predictive posterior distributions - i.e. the dis-
tribution of the voltage signal generated by the sam-
pled latent variables. However, the attention-based
architectures yield a higher average ESS with only
a few exceptions. When the observed signal clearly
originates from an erroneous filter, M
FF w/o ATT
pro-
duces predictive posterior distributions which poorly
fit the observed data. The LSTM-based architecture
produces better predictive posterior distributions but
these are still significantly worse than the distribu-
tions produced by the attention-based architecture in
almost all cases where the filter is broken.
Figure 7 shows inference performance for one
such observation originating from a filter in which
the component is faulty. We plot voltages gener-
ated according to the sampled latent variables from
the predictive proposal distributions using each ar-
chitecture. The proposals from FF w/ ATT and
LSTM w/ ATT are clustered near to the observations,
whereas FF w/o ATT and LSTM w/o ATT produce
many proposals that do not fit the observations.
We suspect that these outliers occur due to the in-
ability of M
FF w/o ATT
and M
LSTM w/o ATT
to learn long-
range dependencies. For example, an output volt-
age of zero could be explained by a number of dif-
ferent faults (e.g. a short-circuit across C
2
or across
C
4
). If the resulting dependency between these can be
learned, the proposals could consistently predict that
only one is broken (predicting more would be unlikely
due to the strong prior on parts working). However, if
the dependency is not captured, the proposals would
be prone to predicting that zero or multiple compo-
nents are broken. This interpretation is supported by
Figure 7, where both architectures without attention
are seen to sometimes propose an output voltage cor-
responding closely to a working circuit.
Figure 8 shows an example of the posterior dis-
tributions inferred over possible faults by each archi-
tecture. For this purpose, a component is considered
faulty when its value is outside of a 0.3% tolerance
of its nominal value. The architectures with attention
Attention for Inference Compilation
85
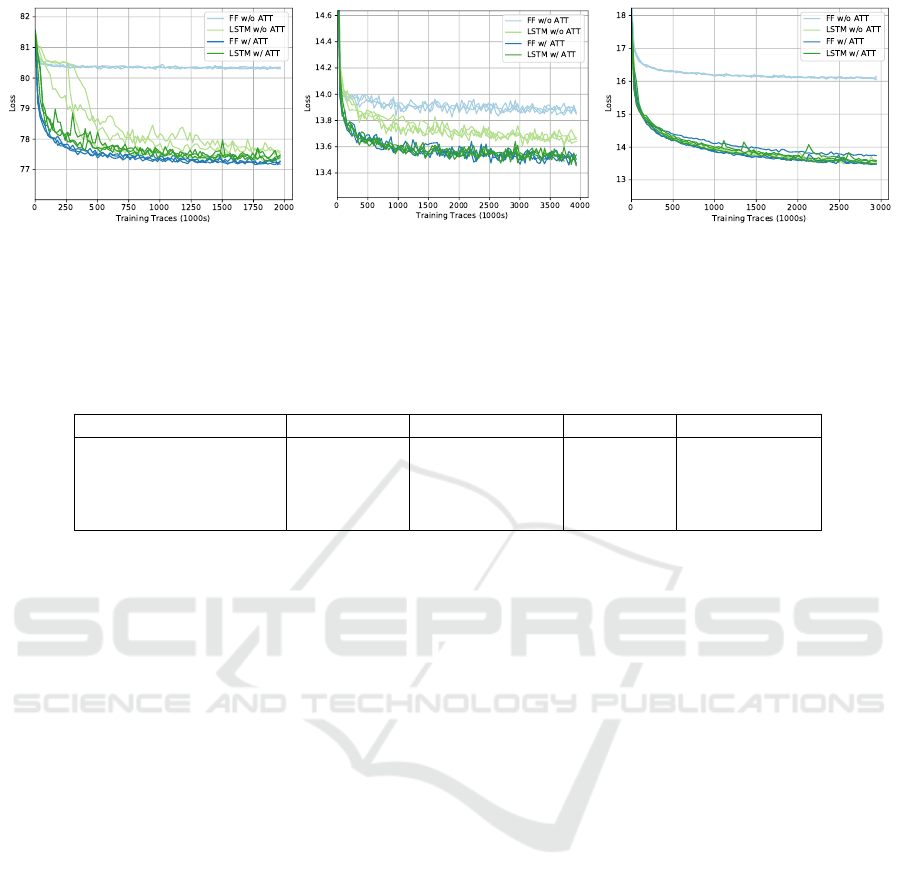
(a) Magnitude (20 nuisance var.).
(b) Plant gene expression model.
(c) Electronic circuit fault model.
Figure 9: Loss, E
p(x,y)
[−log q(x|y,φ)], throughout training for each model and architecture. To reduce noise, the losses are
averages over batches of 468 training steps. Runs with 3 different random seeds are shown. Due to space constraints, the plot
for the magnitude model with 50 nuisance variables is in the appendix.
Table 1: Milliseconds per inference trace for each model and architecture, using a node with 8 CPU cores. Measurements are
averaged over 10 runs of inference, with each drawing 100 samples.
FF w/o ATT LSTM w/o ATT FF w/ ATT LSTM w/ ATT
Magnitude of r.v. 20 74.1 86.5 89.6 104
Magnitude of r.v. 50 161 200 198 236
Plant gene expression 233 282 282 324
Electronic circuit faults 121 140 145 173
manage to most closely fit the ground truth posterior.
4.4 Analysis
Fig. 9 shows the loss of each network throughout
training. In every case, the feedforward network with
attention performs at least as well as the LSTM-based
architecture without attention. In particular, the at-
tention model achieves a significantly better final loss
for the plane gene expression model. The plot for
the magnitude model with 50 nuisance variables, in
which attention also gives an improved final loss, is
in the appendix. When only 20 nuisance variables are
used, the architecture with attention trains faster but
to a similar final loss. We also observe that, in our ex-
periments, using an LSTM and attention in conjunc-
tion never provides a significant improvement over
using attention alone, while being more computation-
ally costly.
Table 1 shows the time taken to run each archi-
tecture. Magnitudes 20 and 50 have 22 and 52 la-
tent variables respectively, the plant gene simulator
has 67, and the circuit simulator typically encounters
43. Since each variable is proposed sequentially, in-
ference takes time proportional to the number of la-
tent variables. The computational cost of the attention
mechanism is similar to that of the LSTM. Also, al-
though the cost of calculating attention weights, and
thus the runtime of the attention mechanism, theoreti-
cally scales as the square of the trace length while the
LSTM’s runtime scales linearly, their runtimes scale
similarly in these experiments.
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSION
We have demonstrated that the standard LSTM core
used in IC can fail to capture long-range dependen-
cies between latent variables. To address this, we
have proposed an attention mechanism which attends
to the most salient previously sampled variables in an
execution trace. We show that this architecture can
speed-up training and sometimes improve the quality
of the learned proposal distributions (measured by the
KL divergence loss), while we never observe it harm-
ing them. These advantages come at negligible com-
putational cost. We believe this makes the attention-
based architecture a sensible default choice for new
inference problems. Future work could consider ex-
tending the usage of such an attention mechanism to
also attend to observed variables. The inference com-
pilation framework is only applicable to models with
a fixed number of observations, but such an attention
mechanism may allow this requirement to be relaxed.
REFERENCES
Arulampalam, M., Maskell, S., Gordon, N., and Clapp,
T. (2002). A tutorial on particle filters for online
SIMULTECH 2022 - 12th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
86

nonlinear/non-gaussian bayesian tracking. Ieee Trans-
actions on Signal Processing, 50(2):174–188.
Ba, J., Mnih, V., and Kavukcuoglu, K. (2014). Multiple ob-
ject recognition with visual attention. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.7755.
Bahdanau, D., Cho, K., and Bengio, Y. (2014). Neural ma-
chine translation by jointly learning to align and trans-
late. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473.
Baydin, A. G. and Le, T. A. (2018). pyprob.
Baydin, A. G., Shao, L., Bhimji, W., Heinrich, L., Naderi-
parizi, S., Munk, A., Liu, J., Gram-Hansen, B.,
Louppe, G., Meadows, L., et al. (2019). Efficient
probabilistic inference in the quest for physics beyond
the standard model. In Advances in Neural Informa-
tion Processing Systems, pages 5460–5473.
Bingham, E., Chen, J. P., Jankowiak, M., Obermeyer, F.,
Pradhan, N., Karaletsos, T., Singh, R., Szerlip, P.,
Horsfall, P., and Goodman, N. D. (2018). Pyro: Deep
Universal Probabilistic Programming. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.09538.
Del Moral, P., Doucet, A., and Jasra, A. (2006). Sequen-
tial monte carlo samplers. Journal of the Royal Sta-
tistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology),
68(3):411–436.
Gershman, S. and Goodman, N. (2014). Amortized infer-
ence in probabilistic reasoning. In Proceedings of the
Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, vol-
ume 36.
Goodman, N. D., Mansinghka, V. K., Roy, D., Bonawitz,
K., and Tenenbaum, J. B. (2008). Church: A language
for generative models. Proceedings of the 24th Con-
ference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Uai
2008, pages 220–229.
Gregor, K., Danihelka, I., Graves, A., Rezende, D. J.,
and Wierstra, D. (2015). Draw: A recurrent neu-
ral network for image generation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1502.04623.
Hinton, G. E., Dayan, P., Frey, B. J., and Neal, R. M. (1995).
The” wake-sleep” algorithm for unsupervised neural
networks. Science, 268(5214):1158–1161.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Jaderberg, M., Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A., et al. (2015).
Spatial transformer networks. In Advances in neural
information processing systems, pages 2017–2025.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A
method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Kulkarni, T. D., Kohli, P., Tenenbaum, J. B., and Mans-
inghka, V. (2015). Picture: A probabilistic program-
ming language for scene perception. In Proceedings
of the ieee conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 4390–4399.
Le, T. A., Baydin, A. G., and Wood, F. (2017). Inference
compilation and universal probabilistic programming.
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference
on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, volume 54
of Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pages
1338–1348, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA. PMLR.
Luong, M.-T., Pham, H., and Manning, C. D. (2015). Ef-
fective approaches to attention-based neural machine
translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.04025.
Mansinghka, V., Selsam, D., and Perov, Y. (2014). Ven-
ture: a higher-order probabilistic programming plat-
form with programmable inference. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1404.0099.
Milch, B., Marthi, B., Russell, S., Sontag, D., Ong, D. L.,
and Kolobov, A. (2005). Blog: Probabilistic models
with unknown objects. Ijcai International Joint Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence, pages 1352–1359.
Minka, T., Winn, J., Guiver, J., Zaykov, Y., Fabian, D., and
Bronskill, J. (2018). /Infer.NET 0.3. Microsoft Re-
search Cambridge. http://dotnet.github.io/infer.
Munk, A.,
´
Scibior, A., Baydin, A. G., Stewart, A., Fern-
lund, G., Poursartip, A., and Wood, F. (2019). Deep
probabilistic surrogate networks for universal simula-
tor approximation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.11950.
Opgen-Rhein, R. and Strimmer, K. (2007). From cor-
relation to causation networks: a simple approxi-
mate learning algorithm and its application to high-
dimensional plant gene expression data. BMC systems
biology, 1(1):37.
Seo, M., Kembhavi, A., Farhadi, A., and Hajishirzi, H.
(2016). Bidirectional attention flow for machine com-
prehension. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.01603.
Tran, D., Kucukelbir, A., Dieng, A. B., Rudolph, M., Liang,
D., and Blei, D. M. (2016). Edward: A library for
probabilistic modeling, inference, and criticism. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1610.09787.
van de Meent, J.-W., Paige, B., Yang, H., and Wood, F.
(2018). An introduction to probabilistic programming.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10756.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones,
L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł., and Polosukhin, I.
(2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 5998–
6008.
Venturini, G., Daniher, I., Crowther, R., and KOLANICH
(2017). ahkab.
Wingate, D., Andreas Stuhlm
¨
uller, A., and Goodman, N. D.
(2011). Lightweight implementations of probabilis-
tic programming languages via transformational com-
pilation. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
15:770–778.
Wood, F., Meent, J. W., and Mansinghka, V. (2014). A
new approach to probabilistic programming inference.
In Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pages 1024–
1032.
Xu, K., Ba, J., Kiros, R., Cho, K., Courville, A., Salakhudi-
nov, R., Zemel, R., and Bengio, Y. (2015). Show, at-
tend and tell: Neural image caption generation with
visual attention. In International Conference on Ma-
chine Learning, pages 2048–2057.
Attention for Inference Compilation
87

APPENDIX
Magnitude of Random Vector
Psuedocode
Program 1: Generative model for the magnitude of a ran-
dom vector with M nuisance random variables.
def magnitude (obs, M):
x = sample(Normal (0, 10))
for in range(M):
# nuisance variables to extend trace
= sample(Normal (0,10))
y = sample(Normal (0,10))
observe(obs
2
,
Likelihood = Normal(x
2
+ y
2
, 0.1))
return x, y
Additional Training Plot
Figure 10: Loss curve for various inference networks for the
“Magnitude of random variable” model with 50 nuisance
variables.
Attention Weights
x
z
0
z
1
z
2
z
3
z
4
z
5
z
6
z
7
z
8
z
9
Variable Attended to When Sampling y
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
Weight
ˆ
E(w
1
)
ˆ
E(w
2
)
ˆ
E(w
3
)
ˆ
E(w
4
)
Figure 11: Attention weights used on each previously sam-
pled variable when creating a proposal distribution for y in a
version of the magnitude model with 10 nuisance variables.
Each color represents one of the four queries. The weights
are averaged over 100 traces. Queries 1 and 4 attend solely
to x, explaining how the attention mechanism enables the
inference network to capture the long-term dependency, and
ignore the nuisance variables.
SIMULTECH 2022 - 12th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
88

Plant Gene Expression Model
Attention Weights
Figure 12: Attention weights used by an FF w/ ATT inference network on the plant gene expression model. The cells in each
row i correspond to the weight given to previously sampled variable when variable i is being sampled. The node numbers
correspond to (Opgen-Rhein and Strimmer, 2007).
Electronic Circuit Fault Diagnosis
Program 2: Generative model for the Butterworth filter.
class Butterworth ( Model ):
@staticmethod
def sample componen t ( name , mean ,
std =None , p broken =0.02):
if std is None:
std = 0.001
*
mean
broken = pyprob.sample(
dist.Categorical (
torch.tensor ([1−p broken , p broke n ])
)). item()
if broken:
r = pyprob.sample(
dist.Uniform ( torch . tensor ([0.]) ,
torch.tensor ([2.]))). item()
val = r
*
torch.tensor ([ mean])
else:
r = pyprob.sample(
Attention for Inference Compilation
89

dist.Normal(torch.tensor (0) ,
torch.tensor (1))). item()
val = mean + r
*
std
return max(val , 1e −16)
@staticmethod
def sample erro r ( name , p =0.005):
return bool(
pyprob.sample(
dist.Categorical (
torch.tensor ([1−p , p]))). item ())
def forward ( self):
cir = Circuit (’Butterworth 1kHz band −pass filter ’)
R1 = self.sample componen t (’R1’, mean=50.)
R1 open = self.sample error(’R1open ’)
L1 = self.sample componen t (’L1’, mean =0.245894)
L1 open = self.sample error(’L1open ’)
C1 = self.sample componen t (’C1’, mean=1.03013 e−07)
L2 = self.sample componen t (’L2’, mean=9.83652 e−05)
L2 open = self.sample error(’L2open ’)
C2 = self.sample componen t (’C2’, mean =0.000257513)
C1 open = self.sample error(’C1open ’)
if self .sample e rro r ( ’C1short ’):
cir . add resis tor (’Rshort2 ’, ’n3 ’, ’n4’, 0.001)
C2 open = self.sample error(’C2open ’)
if self .sample e rro r ( ’C2short ’):
cir . add resis tor (’Rshort2 ’, ’n4 ’, cir .gnd , 0.001)
C3 open = self.sample error(’C3open ’)
C4 open = self.sample error(’C4open ’)
L3 = self.sample componen t (’L3’, mean =0.795775)
L3 open = self.sample error(’L3open ’)
C3 = self.sample componen t (’C3’, mean=3.1831e−08)
Vin broke n = self.sample erro r ( ’ Vin broken ’)
if self .sample e rro r ( ’C3short ’):
cir . add resis tor (’Rshort3 ’, ’n5 ’, ’n6’, 0.001)
C5 open = self.sample error(’C5open ’)
L4 = self.sample componen t (’L4’, mean=9.83652 e−05)
L4 open = self.sample error(’L4open ’)
C4 = self.sample componen t (’C4’, mean =0.000257513)
if self .sample e rro r ( ’C4 ’):
cir . add resis tor (’Rshort4 ’, ’n6 ’, cir .gnd , 0.001)
C5 = self.sample componen t (’C5’, mean=1.03013 e−07)
C5 open = self.sample error(’C5open ’)
if self .sample e rro r ( ’C5 ’):
cir . add resis tor (’Rshort5 ’, ’n7 ’, ’n8’, 0.001)
L5 open = self.sample error(’L5open ’)
R2 open = self.sample error(’R2open ’)
L5 = self.sample componen t (’L5’, mean =0.245894)
R2 = self.sample componen t (’R2’, mean=50.)
if not Vin bro ken :
cir . add vsource (’V1 ’, ’n1 ’, cir.gnd , dc v alu e =0. , ac va lue =1.)
if not R1 op en :
cir . add resis tor (’R1 ’, ’n1 ’, ’n2’, R1)
if not L1 op en :
cir . add induc tor (’L1 ’, ’n2 ’, ’n3’, L1)
if not C1 op en :
cir . add capacitor(’C1 ’, ’n3 ’, ’n4’, C1)
if not L2 op en :
cir . add induc tor (’L2 ’, ’n4 ’, cir.gnd , L2)
if not C2 op en :
cir . add capacitor(’C2 ’, ’n4 ’, cir.gnd , C2)
SIMULTECH 2022 - 12th International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications
90

if not L3 op en :
cir . add induc tor (’L3 ’, ’n4 ’, ’n5’, L3)
if not C3 op en :
cir . add capacitor(’C3 ’, ’n5 ’, ’n6’, C3)
if not L4 op en :
cir . add induc tor (’L4 ’, ’n6 ’, cir.gnd , L4)
if not C4 op en :
cir . add capacitor(’C4 ’, ’n6 ’, cir.gnd , C4)
if not C5 op en :
cir . add capacitor(’C5 ’, ’n7 ’, ’n8’, C5)
if not L5 op en :
cir . add induc tor (’L5 ’, ’n6 ’, ’n7’, L5)
if not R2 op en :
cir . add resis tor (’R2 ’, ’n8 ’, cir.gnd , R2)
else:
cir . add resis tor (’R2 ’, ’n8 ’, cir.gnd , R2
*
1000)
# analysis
ac1 = new ac (.97e3 , 1.03e3 , 40 , x0 =None)
res = run (cir , ac 1 )[’ac’]
vouts = res [’Vn8’]
rs = abs( vouts )
thetas = np.angle(vouts)
# observations
pyprob.observe( dist.Normal ( torch . tensor(rs ), torch. tensor (0.03)),
name=’ | Vout | ’)
pyprob.observe( dist.Normal ( torch . tensor(thetas), torch . tensor(0.05)) ,
name=’ theta o ut ’)
Attention for Inference Compilation
91
