
Soil Enzyme Activity and Physicochemical Properties of Tea Garden
Tianyu Li
a
, Lidan Mu
b
, Zhengjun Yang
c
, Chunhua Zhang
*d
and Ruifang Wang
*e
Pu’er University, Pu’er, Yunnan, 665000, China
*
Corresponding author
Keywords: Tea Garden, Soil Enzyme Activity, Fertilizer.
Abstract: Soil enzymes play an important role in material circulation and energy flow in ecosystems. In this study,
three tea plantations, without fertilizer, organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer were carried out to
determine the activity of soil hydrogen peroxide enzyme and sucrose enzyme, and the physical and
chemical properties of soil (soil weight, soil moisture content, soil pH and soil temperature). The results
showed that the soil enzyme activity of fertilizer applied was the highest, and the soil enzyme activity
without fertilizer was the lowest. Soil enzyme activity is closely related to soil physical and chemical
properties, which is of great significance to improve the yield and quality of tea leaves.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Soil microorganisms can have a significant effect on
enzyme activity. For example, cellulase, phosphatase
and urease are closely related to the content of
microorganisms. As the content of microorganisms
increases, their activities also increase. Nasegy used
root inoculation to change the genetic traits of
microorganisms, enhance the activities of
phosphatase and phosphonate esterase in soil, and
weaken the activities of enzymes such as glycosides
(Naseby 1998).
Soil moisture content, temperature (heat) and air
have significant effects on soil enzyme activity.
Enzyme activity is active in the case of relatively
high soil moisture but decreases when the soil is too
wet. The amount of pyrethroase in the mucous grain
with the temperature are negative correlation when
temperature at 25-60 ℃, soil temperature increased
to 70 ℃, enzyme activity increased, but the
temperature is higher than 70 ℃, the pyrethroase will
occur in a short period of time passivation
phenomenon. The enzyme becomes inactivated when
the temperature rises to 150 ℃ and heats up for a
day. Overrein found a correlation between enzyme
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2807-1172
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4334-698X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5867-3433
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9567-0987
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4715-6240
activity and oxygen elements of pyrethroenes, which
are affected by air directness (Min 1978).
Soil pH has a great effect on the rate of enzyme
chemical reaction. Urease is most active in the pH
range of 6.5 to 7.0. Some enzymes, such as
deoxygenase and hydrogen peroxide enzyme, are
completely inactivated when the pH is lowered
below 5.0. Soil pH also affects urease protein
structure and smaller molecules such as amino group,
which changes enzyme activity. The lower the
acidity, the more enzymes the clay can absorb.
Urease can be adsorbed much in weak acid medium
than that in weak base medium.
The organic matter in soil can directly affect the
physical and chemical properties of soil. The
enzymes will be attached to the surface of organic
matter, some in humus complex, still active. Urease,
invertase and acid phosphatase are directly affected
by organic matter, N and P elements (Liu 2003). Fan
Jun found that the activities of urease and protease
increased with the increment of organic matter
content (Fan 2003).
The diameter and stability of soil aggregates were
closely related to enzyme activities. The enzyme
activity was higher in the smaller aggregate diameter.
Urease of umber soil and black soil mostly
accumulates in micro-reunion, which are the same
size as soil clay (Zhou 1980). In the soil solution,
only a small amount of soil enzymes, more soil
enzymes gathered on the clay surface. Protease and
urease are the same, mostly concentrated in soil clay.
734
Li, T., Mu, L., Yang, Z., Zhang, C. and Wang, R.
Soil Enzyme Activity and Physicochemical Properties of Tea Garden.
DOI: 10.5220/0011281000003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 734-738
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Sprayed pesticides can enter the soil and affect
soil enzyme activity directly. Shen Biao found that
chlorobenzene, a substance in pesticides, can
stimulate urease activity. Dehydrogenase activity
decreased when chlorobenzene concentration was
increased (Shen 1997). Organochlorine pesticides,
the main component of which is HCH, can inhibit
hydrogen peroxide enzyme activity (Pang 2002). He
Wenxiang found that Insecticidal Dan inhibited
urease, oxidase activity and phosphatase (He 2002).
Different fertilization measures also effect
enzyme activity. The enzyme activity was more
active in the organic matter. Enzyme activity can be
enhanced with barnyard manure, but will be reduced
without fertilizer (He 2001). The application of
fertilizer can slightly enhance enzyme activity, and
the root metabolism accelerates, secretes more
substances, increases the growth rate of
microorganisms, enhances enzyme activity finally.
Soil fertility is a measure of the soil's ability to
provide a variety of nutrients needed for crop
growth. It is the comprehensive performance of
basic properties of soil, for agricultural production.
The application of different fertilizers affects the
level of soil enzyme activity, which plays a key role
in soil fertility and can reflect the soil productivity.
Therefore, the study on the soil enzyme activity in
tea garden is a basis for high quality and yield of tea
production, and provides theoretical guidance for tea
planting.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Soil Samples
In order to take out soil samples randomly, five
sampling points were randomly set in the tea garden,
and about 10g of soil was taken out at a soil depth of
10cm for reserve. The soil was placed in sterile
bottles and marked.
2.2 Hydrogen Peroxide Enzyme
Weigh 5 grams of air-dried soil and put it in a 150
ml triangular flask with 5 ml of 0.3% hydrogen
peroxide solution and 40 ml of distilled water. The
same reagent was taken without soil sample as the
control group. Then the bottle was plugged tightly
with a cork and placed on a shaker. The rotation
speed was adjusted to 120r/min and the oscillation
time was 30min. After 30min, the bottle was taken
out. After opening the cork, 5mL of 1.5mol/L
sulfuric acid was immediately injected and filtered
with dense filter paper.
After filtration, 25mL of filtrate was taken out
and titrated with potassium permanganate solution
with a concentration of 0.002mol/L to reddish color.
The catalase activity was then calculated as
0.002mol/L ml of potassium permanganate solution
per gram of soil weight, which was the difference
between the control group and the soil-taking group.
Its calculation formula is as follows:
Soil hydrogen peroxide enzyme activity (mL
KMnO
4
/ g air-dried soil) =V / DWT
(V: 0.002mol / L KMnO
4
solution in mg (mL);
DWT: Air dried soil weight (g)
2.3 Sucrose Enzyme
The activity of sucrose enzyme was determined by
3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetry. Using sucrose
as substrate, glucose is produced under the catalysis
of sucrose enzyme. 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid reacts
with glucose to form 3-amino-5-nitrosalicylic acid,
which has the maximum absorption value at 508 nm.
Configuration of glucose standard solution: add
an appropriate amount of distilled water to the
beaker, slowly add benzoic acid, and stir with a glass
rod until benzoic acid dissolves and a small amount
of crystals precipitate, to complete the preparation of
saturated benzoic acid solution. Then, 500 mg
glucose was weighed and dissolved in an appropriate
amount of benzoic acid solution, and 100 mL
volumetric flask was filled with benzoic acid
saturated solution for constant volume (5 mg/mL).
Weigh 0.45 g of air-dried soil into a 10 mL
centrifuge tube, add 1 mL phosphoric acid buffer
(pH=5.5) and 0.06 mL toluene, then add 3 mL 8%
sucrose solution, shake well, cover tightly, and place
in an incubator at 37 ℃ for one day. Then take out
the centrifuge tube, shake it well, centrifuge it for 5
min, and set the speed at 4000 r/min. After
centrifugation, remove 0.2 mL of the upper liquid
and add 20 mL to the glass tube. Injected 3,5-
dinitrocylic salicylic acid 0.5 mL in the glass tube,
immediately after the glass tube 5 min heated with
boiling water, after which the surface of the glass
tube with tap water washed 3 min, to achieve
cooling purposes. Then distilled water was used to
dilute the color liquid to 5 mL, and the
spectrophotometer was set at 508 nm for
colorimetry, and the light absorption value was
recorded.
Sucrose enzyme activity was expressed as mg of
glucose per unit of soil after one day
Glucose (mg) =100 × a
Soil Enzyme Activity and Physicochemical Properties of Tea Garden
735
(100 is the conversion unit; A: the number of mg of
glucose from the standard curve)
2.4 Soil Physical and Chemical
Properties
2.4.1 Soil Bulk Density
After measuring the quality of the ring knife, go to
the tea garden to take soil samples. Level the area
where the soil samples will be taken. After levelling,
vertically insert the ring knife into the soil, with one
end of the blade downward, until the soil column
reaches the upper end of the ring knife. Clean up the
soil around the ring knife with a shovel and then
remove the ring knife, remove the excess soil with a
soil cutting knife, cover the edge of the ring knife
with filter paper, and bring the bottom cover back to
the laboratory for future use. The soil bulk density
calculation formula is as follows:
Soil bulk density (g / cm
3
) = dry soil / ring knife
volume
Dry soil weight in ring knife (g) =100 wet soil
weight in ring knife /100 soil moisture content
2.4.2 Soil Moisture Content
Prepare aluminium boxes, and collect about 10 g of
soil samples. Open the lid of the box before putting
it into the oven. The oven temperature is set at 105
℃ and the drying time is 8 h. Then the aluminium
box was taken out and weighed, and then the
aluminium box was put into the oven to dry for 3 h
until the difference between the two weighing was
less than 0.05 g.
W % = (g1-g2) / (g2-g) ×100%
W: water content of soil (%), g: weight of
aluminium box (g), g1: weight of humidified soil in
aluminium box (g), g2: weight of aluminium box
plus dry soil (g)
2.4.3 Soil Ph
Weigh 20g of air-dried soil samples processed by
2mm aperture sieve and put them in a 50ml beaker,
add 20ml of distilled water, and stir the soil
suspension continuously for 5 minutes with a glass
rod. After the soil particles are fully dispersed, stand
for 30min for measurement. When measuring, the
pH meter is inserted into the beaker of the solution
to be measured, and the pH value of the soil sample
is recorded when the reading is stable. The pH meter
is removed, and the pH meter is washed with
distilled water to remove Carbon dioxide. Then, the
moisture can be dried with filter paper before the
measurement of the next soil sample.
2.4.4 Soil Temperature
Soil temperature was measured with a soil
thermometer every 2 h from 6:00 to 18:00, randomly
selected three points in the tea garden. Finally,
multiple values were analysed to obtain the soil
temperature of each tea field.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Enzyme Activity
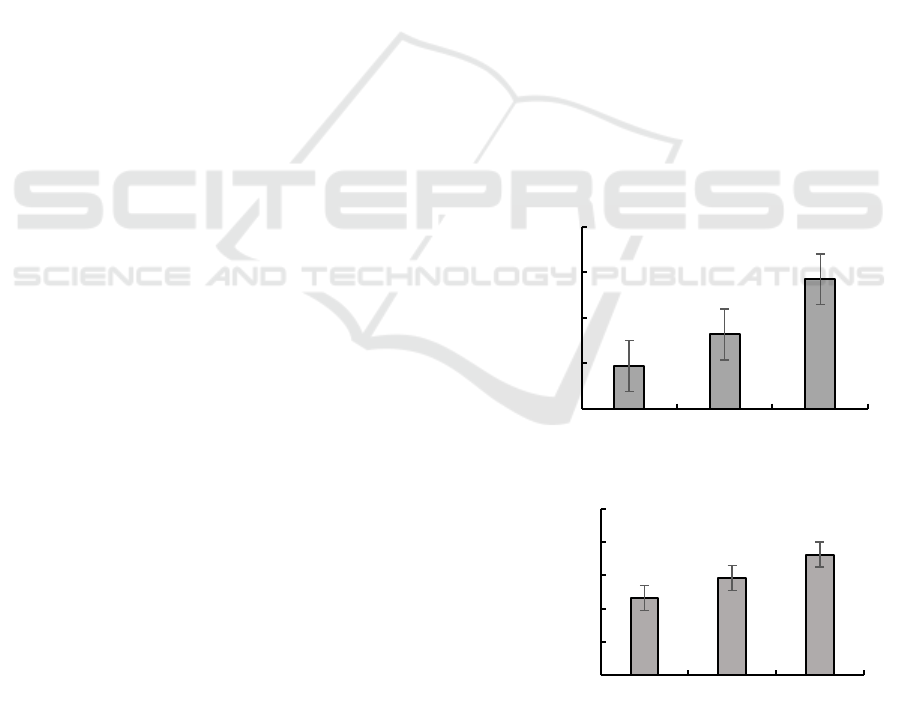
In Figure 1, hydrogen peroxide enzyme activities of
HS, SM and ZB were 1.89± 0.11, 3.27± 0.89 and
5.70± 1.77, respectively. It can be seen that
hydrogen peroxide enzyme activity of three types of
tea gardens have significant differences. The
hydrogen peroxide enzyme activity of the tea garden
with fertilizer was the strongest, while the enzyme
activity of the tea garden without any fertilizer was
the weakest, indicating that both fertilizer and
organic fertilizer could increase hydrogen peroxide
enzyme activity.
Figure 1: Hydrogen peroxide enzyme activity.
Figure 2: Sucrose enzyme activity.
Note: HS: tea fields treated without any fertilizer,
SM: tea fields treated with organic fertilizer, ZB: tea
1,89
3,27
5,7
0
2
4
6
8
HS SM ZB
Hydrogen peroxide
enzyme activity
1,16
1,46
1,81
0
0,5
1
1,5
2
2,5
HS SM ZB
Sucrose enzyme
activity
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
736

fields treated with chemical fertilizer; Data in the
figure were mean ± SD; N= 3; Different lowercase
letters indicate significant differences in soil enzyme
activity under different fertilizer application
conditions. Same as below for icon annotation).
In Figure 2, sucrose enzyme activity data were
0.49± 0.91, 0.75± 0.16 and 1.17± 0.07, respectively.
It can be seen both organic fertilizer and chemical
fertilizer can promote sucrose enzyme.
3.2 Soil Physicochemical Property
Table 1: Soi physicochemical properties of tea garden.
parameter HS SM ZB
Soil moisture (%) 17.3±3.05 31.3±1.53 26.67±3.22
Volume weight of soil (g/cm
3
) 4.66±0.20 3.86±0.16 4.23±0.11
Soil temperature℃ (0-10cm) 16.64±1.90 16.56±3.35 16.62±2.68
Soil temperature℃ (10-20cm) 17.23±2.02 17.07±2.73 16.68±2.38
Soil pH 5.41±0.15 5.74±0.09 5.06±0.18
It can be found that the highest soil water content
with organic fertilizer is 31.3 ± 1.53, and the lowest
soil water content with no fertilizer is 17.3 ± 3.05. In
terms of soil bulk density, the soil bulk density of
organic fertilizer treatment was significantly lower
than that of the other two treatments, which was 3.86
± 0.16. In terms of soil temperature, there was no
significant difference in soil temperature at the two
depths of the three plots, which were 16.64 ±
1.90℃, 16.56 ± 3.35℃ and 16.62 ± 2.68℃
respectively. From the point of view of soil pH
value, the weakest acidity of tea field without any
fertilizer was 5.74 ± 0.09, and the strongest acidity
was 5.06 ± 0.18 when fertilizer was applied.
4 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
Long-term application of organic fertilizer can
maintain and improve soil voidality, reduce soil bulk
density and increase soil surface water content. On
the contrary, long-term no fertilizer or only fertilizer
will cause poor soil voidality, soil bulk density
increases, resulting in soil compaction, reduce soil
water storage capacity. Long-term use of fertilizers
also acidifies the soil, reducing its pH. The results of
this experiment are similar to those of the above
studies. The soil bulk density of tea garden with
long-term application of organic fertilizer is
significantly lower than that of tea garden with long-
term application of chemical fertilizer and without
fertilizer, while the soil pH and soil water content
are significantly higher than those of the latter two
treatments.
It can be seen from the experimental data that the
activities of catalase and sucrase in the tea garden
with low soil bulk density are higher than those in
the back mountain without fertilizer. The activities
of catalase and sucrase were the strongest in the tea
field with chemical fertilizer, because the application
of chemical fertilizer had a significant effect on the
enzyme activity in the short term, but the long-term
application of chemical fertilizer had a negative
effect on the soil quality and enzyme activity. In the
experimental data, the enzyme activity was the
lowest in the plot with the highest temperature, and
increased in the plot with the lower temperature.
There were obvious differences in enzyme
activities in tea tree soil with different fertilizers, and
soil enzymes were closely related to soil fertility.
Chemical fertilizer can obtain more nutrients in the
short term and increase soil enzyme activity, so the
effect of chemical fertilizer treatment is the most
significant. However, long-term use of chemical
fertilizers is not conducive to the sustainable use of
soil.
Through the experimental data, it is concluded
that under the conditions of larger soil humidity,
moderate temperature, low soil bulk density and low
soil pH, it is conducive to the life and reproduction
of microorganisms, the increase of microbial
number, the increase of soil enzyme activity and the
growth of tea trees. The experiment was carried out
in the dry season and the plants were in a certain
water shortage condition. According to the
experimental data, the application of chemical
fertilizer or organic fertilizer can promote the
physiological activities of microorganisms and
increase the soil water content. So, in the dry season,
tea plants will not grow poorly because of the lack
of water or nutrients in the soil. Sufficient water
Soil Enzyme Activity and Physicochemical Properties of Tea Garden
737

retention capacity and active microorganism have
certain advantages for tea plant growth in dry
season, thus improving the yield and quality of tea in
spring next year.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the High-Level Talent
Introduction Project (k2015034) and Outstanding
Young Teacher Program (2020GGJS006) of Pu’ er
University.
REFERENCES
Fan Jun, Hao Mingde. Study on long-term localization of
crop rotation and fertilization in dryland of Loess
Plateau. ⅱ. Soil enzyme activity and soil fertility [J].
Plant nutrition and fertilizer science, 2003, 9(2): 146-
150.
He Wenxiang, Jiang Xin, Bian Yongrong, etc. Journal of
northwest a& f university (natural science edition),
2002, 30(1): 13-17.
He Wenxiang, Lai Haiyan, Wu Zhijun. Journal of
Zhejiang university (agriculture and life science
edition), 2001, 27(3): 265-268.
Liu Guangshen, Xu Dongmei, Xu Zhongjian, etc. Journal
of soil science, 2003, 40(5): 756-762.
Min Jiukang, Liu Jiling. Study on soil enzyme and its
significance.
Naseby D C, Lynch J M. Establishment and impact of
Pseudomonas fluorescens genetically modified for
lactose utilization and kanamycin resistance in the
rhizosphere of pea[J]. J Appl Microbial, 1998, 84:
169-175.
Pang Huancheng, Yan Huijun, Liu Jifang, etc. Soil And
Fertilizer,2002, (1): 30-33.
Shen Biao, Li Shunpeng, Zhao Shuowei, etc. Effects of
chlorobenzene and p-nitrophenol on soil biological
activity [J]. Acta pedologica sinica, 1997, 34(3): 309-
314.
Zhou Likai. Advances in soil science, 1980, 8(4): 9-15.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
738
