
Cefaclor & Linezolid and Their Effectiveness against S. Aureus
Kaixuan Jin
Nanjing Foreign Language School, Nanjing, 210008, China
Keywords: Linezolid, Cefaclor, Antibacterial Drugs.
Abstract: Staphylococcus aureus is a common human pathogen that could cause skin and soft tissue infection.
Symptoms and severity of S. aureus SSTIs differ significantly, and complicated SSTI might require
antibacterial agents to treat. Both linezolid and cefaclor are effective against S. aureus infections. Linezolid
is an artificially synthesized antibacterial agent. It inhibits bacteria’s protein synthesis by binding to bacteria
ribosome and prohibiting the translation at an early stage. It could be delivered orally or intravenously.
Cefaclor is another human synthesized antibacterial agent. It could inhibit the synthesis of peptidoglycan by
binding to a type of penicillin binding protein, causing bacteria cell wall lysis. It is delivered orally. In this
work, the structures, mechanisms, limitations and economics of the two antibacterial agents would be briefly
discussed and the comparison between them would be shown clearly.
1 INTRODUCTION
The antibacterial properties of oxazolidinones were
first discovered in 1984. Years later, a research
program on oxazolidinone was performed. After
synthesis attempts and evaluations, scientists
discovered that linezolid had preferable
characteristics and further trials were done. Linezolid
was approved in the United States in 2000 and was
considered an effective drug against Gram-positive
bacteria (Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018,
Ford, Zurenko, Barbachyn 2001). Linezolid could
bind with bacteria ribosome and inhibit the
translation process at the early stage (Foti, Piperno,
Scala, Giuffrè 2021).
Cefaclor originated from a type of fungus and
belongs to the cephalosporin family. It is effective
against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive
bacteria. Cefaclor’s mechanism is similar to that of
penicillin’s (Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali 2017, Jeong, Jang,
Cho, Lee 2021).
Staphylococcus aureus is a common type of
bacteria (Wertheim, Melles, Vos, van Leeuwen, van
Belkum, Verbrugh, Nouwen 2005). Infections caused
by S. Aureus included skin and soft tissue infections.
Abscesses on the skin is an example of S. Aureus skin
and soft tissue infection (Foti, Piperno, Scala, Giuffrè
2021). Both linezolid and cefaclor are effective in
treating infections caused by S. aureus (Hashemian,
Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018, Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali
2017).
2 OVERVIEW OF DISEASE
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive bacterium.
It is spherical and its diameter is approximately 1 μm,
as shown in figure 1. It was first isolated by
Alexander Ogston from an infection in 1880 and in
1882 the term Staphylococcus was created by Ogston.
Further classifications were completed in the
following decades (Lakhundi, Zhang 2018).
Figure 1: S. aureus (Jensen, Koch, Aalbaek et al. 2017).
774
Jin, K.
Cefaclor Linezolid and Their Effectiveness against S. Aureus.
DOI: 10.5220/0011295000003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 774-779
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most
common types of bacteria. About 50% of total human
population are continuously or discontinuously
carrying S. aureus (Wertheim, Melles, Vos, van
Leeuwen, van Belkum, Verbrugh, Nouwen 2005). It
causes various infections, including different types of
skin and soft tissue infections (SSTI), the severity of
which could differ significantly (Tong, Davis,
Eichenberger, Holland, Fowler 2015).
Abscesses on the skin is a typical SSTI caused by
S. aureus (Tong, Davis, Eichenberger, Holland,
Fowler 2015). Impetigo is another example of S.
aureus SSTI, shown in figure 2. Among children,
impetigo is the most common SSTI caused by
bacteria (Bangert, Levy, Hebert 2012). Other types of
SSTI could also be caused by S. aureus, despite being
less common (Tong, Davis, Eichenberger, Holland,
Fowler 2015).
Figure 2: Impetigo complicating other infection (Tong,
Davis, Eichenberger, Holland, Fowler 2015).
It remains unclear whether uncomplicated S.
aureus SSTIs would require antibacterial agents in
treatments (Tong, Davis, Eichenberger, Holland,
Fowler 2015), but for the complicated SSTI-generally
defined as situations where an operation would be
needed to cure the infection, or when an extension of
the swollen, infected area into deeper structures
occur, or situations where serious underlying diseases
exist (Sunderkötter, Becker, Eckmann, Graninger,
Kujath, Schöfer 2020) -treatments using antibiotics
might be required (Tong, Davis, Eichenberger,
Holland, Fowler 2015).
3 ABOUT LINEZOLID
3.1 Chemical Structures
Figure 3: Chemical structure of linezolid.
The empirical formula of linezolid is C
16
H
20
FN
3
O
4
(molecular weight: 337.35 g/mol) (Hashemian,
Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018).
3.2 History
Oxazolidinones-the class linezolid belongs to-were
first used in 1978 due to their effectiveness against
plant diseases. In 1984, it was discovered that
oxazolidinones had antibacterial properties
(Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018). In the
1990s, with the increasing need for potential new
antibacterial agents, scientists from Pharmacia
Corporation began a biochemistry research program
on oxazolidinone. After massive synthesis attempts
and evaluations, improvements of antibacterial
activity for the chemicals were achieved. Among
various chemicals, linezolid showed preferable
characteristics and was selected for further clinical
test and evaluation. Consequently, the trials proved
linezolid’s effectiveness in treating various Gram-
positive infections (Ford., Zurenko, Barbachyn
2001). In 2000, linezolid was officially approved in
the United States (Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar
2018).
3.3 Mechanism
Linezolid inhibits protein synthesis by binding with
bacteria ribosome and prohibiting the translation
process. The A-site of 50S subunit of the ribosome
would form bonding with linezolid, and the 30S
subunit would not be affected. The initiator-tRNA
would then be prohibited from binding with the
ribosome, which prevents the translation process at
an early stage. To be more specific, the binding would
occur at the upper part of the peptidyl transferase
Cefaclor Linezolid and Their Effectiveness against S. Aureus
775
center and hydrogen bond would be formed
(Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018, Foti,
Piperno, Scala, Giuffrè 2021).
The mechanism of linezolid is unique as linezolid
inhibits the synthesis of protein at the early
translation stage. Linezolid is effective against not
only bacterial ribosome, but archaeal ribosome as
well. Human cells would not be inhibited by linezolid
(Foti, Piperno, Scala, Giuffrè 2021).
The 5-acylaminomethyl group binds with
ribosomes and is a pivotal structure for linezolid’s
activity. Electron-withdrawing group in the aryl ring
(the fluoride atom) could increase the activity of
linezolid. Changes with the extra substituents on the
proximal aromatic ring do not have direct effect on
the activity against bacteria but could alter various
characteristics of the chemical (Hashemian, Farhadi,
Ganjparvar 2018, (Chellat, Raguž, Riedl 2016).
3.4 Limitation
Drug resistance:
Although the unique mechanism of linezolid
makes it difficult for bacteria resistance to develop
(Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018, (Chellat,
Raguž, Riedl 2016), bacteria resistance might still be
a potential issue. A research which included data
from various regions of the world concluded that
linezolid had a 99.9% rate of effectiveness against
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
(Shariati, Dadashi, Chegini, van Belkum, Mirzaii,
Khoramrooz, Darban-Sarokhalil, 2020), but it is still
possible that the percentage of S. aureus resistant
against linezolid is higher in certain particular areas.
The mechanism of bacteria resistance against
Linezolid could be associated with mutation of 23S
rRNA as linezolid binds with the ribosome at the 23S
part (Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018).
Adverse effects:
Recorded side effects caused by linezolid include
the follows:
(a) Two patients were reported to develop
peripheral neuropathy (caused by damage to
neurological tissues outside of the brain and spinal
cord (Vital, Vital, Bouillot-Eimer, Brechenmacher,
Ferrer, Lagueny, 2004)) after a prolonged linezolid
treatment (Rho, Sia, Crum, Dekutoski, Trousdale,
2004).
(b) Anemia-a condition where blood haemoglobin
(a protein transporting oxygen) concentration is
relatively low for a person's age and gender (Sama,
Chiamo, Taiwe, Njume, Sumbele 2021) -could occur
due to linezolid’s direct effect on red cells
(Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018,) (Vinh,
Rubinstein 2009).
3.5 Drug Economics
A research has been carried out to determine the cost
for patients who acquired methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in hospitals in the
United States. The patients received intravenous
linezolid in the standard dose 600 mg every 12 hours,
2 doses/day. The patients received antibiotics for 10
days (20 doses). Among all costs generated during the
treatment, drug cost using linezolid was $2189.
Assuming that cost for intravenous linezolid did not
vary significantly due to different factors, a
conclusion could be made that the average cost per
standard dose (600 mg) of intravenous linezolid was
approximately $109.45 (Patel, Shorr, Chastre,
Niederman, Simor, Stephens, Charbonneau, Gao,
Nathwani 2014).
Linezolid could be changed from intravenous to
oral among patients who are clinically stable
(Hashemian, Farhadi, Ganjparvar 2018). The cost for
patients might therefore decrease.
4 ABOUT CEFACLOR
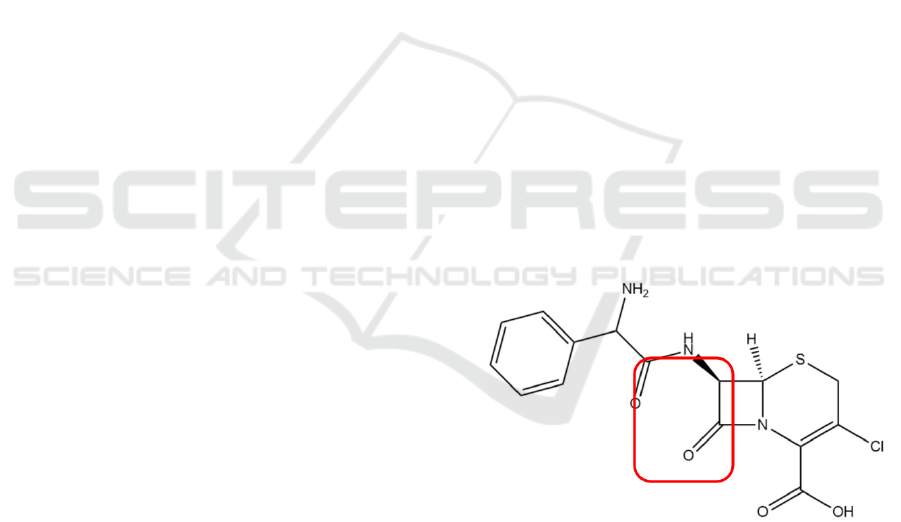
4.1 Chemical Structure
Figure 4: Chemical structure of cefaclor.
The empirical formula of cefaclor is
C
15
H
14
ClN
3
O
4
S (molecular weight: 368g/mol).
4.2 History
Cefaclor was originated from the fungus named
Acremonium (Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali 2017). Cefaclor
belongs to the second generation of the cephalosporin
family - antibacterial drugs that have β-lactam as their
activity center and resemble penicillin in mode of
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
776

action. Cefaclor is more effective against Gram-
negative bacteria and less effective against Gram-
positive bacteria compared to the first generation of
cephalosporins (Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali 2017, Jeong,
Jang, Cho, Lee 2021).
4.3 Mechanism
The β-lactam ring is responsible for cefaclor’s anti-
bacterial activity (Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali 2017).
Cefaclor’s mechanism is shown in figure 5.
Penicillin-binding proteins are proteins which are
responsible for the final steps of the synthesis of
peptidoglycan-a pivotal substance in the formation of
bacteria cell walls (Sharifzadeh, Dempwolff, Kearns,
Carlson 2020). Cefaclor would bind to a particular
type of penicillin binding protein, which
consequently lead to the prohibition of the synthesis
of peptidoglycan and the lysis of cell wall. The
mechanism is similar to that of penicillin’s (Jeong,
Jang, Cho, Lee 2021).
Peptidoglycans are pivotal substances for
bacterial cell walls while the substance is not found
in human cells. Cefaclor’s damage to human cells is
therefore minimized (Jeong, Jang, Cho, Lee 2021).
Figure 5: Mechanisms of cephalosporins, including cefaclor (Das, Madhavan, Selvi, Das 2019).
4.4 Limitation
Drug resistance:
Drug resistance among bacteria has always been
a significant globally issue. Resistant rate would vary
across different regions due to various factors
(Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali 2017). Percentage of resistance
against cefaclor among S. aureus recorded in the last
ten years is shown in the table below.
Table 1: Bacteria resistance against cefaclor (Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali 2017).
% Resistance Year Region Reference
14.0 2015 Pakistan (Ayub, Fatima, Naqvi, Sheikh, Ali, Ayub 2015)
15.0 2015 Serbia (Stojanovic-Radic, Dimitrijevic, Stankovic, Aleksic,
Pe
j
cic 2016
)
66.66 Before 2012 India (Shaifali, Gupta, Mahmood, Ahmed 2012)
21.0 2011 Pakistan (Arsalan, Naqvi, Sabah, Bano, Ali 2014)
The mechanism of resistance against cefaclor is
related to bacteria’s production of β-lactamase, a
substance that could break down the β-lactam ring in
cefaclor and decrease cefaclor’s effectiveness
(Arsalan, Ahmad, Ali 2017).
Damage to the environment:
Cefaclor belongs to cephalosporins.
Cephalosporin wastewater could pose threats to the
environment. The wastewater mainly contains toxic
organic chemicals, inorganic salts which could
Cefaclor Linezolid and Their Effectiveness against S. Aureus
777

potentially threat survival of organisms in natural
environment (Das, Madhavan, Selvi, Das 2019,
Yang, Zuo, Li, Wang, Yu, Zhang 2016, Guo, Chen
2015).
Adverse effects:
(a) Diarrhoea (approximately 5.6% of patients)
have been reported after use of cefaclor. The effect is
relatively minor (Turik, Johns 1998).
(b) Hypersensitivity cases have been observed but
the cases are not life-threatening (Arsalan, Ahmad,
Ali 2017, Murray, Singer, Singer, Veldman 1980).
4.5 Drug Economics
Cefaclor is an oral antibacterial drug. Cost for the
drug would vary depending on brands and types. A
250 mg capsule of cefaclor might cost $1.5 to $2.1.
5 DISCUSSION
Linezolid has oral and intravenous way of delivery,
while cefaclor is an oral antibacterial agent. Various
relatively serious adverse effects induced by linezolid
are reported, but it is possible that some side effects
could be reduced by appropriate control of time or
dose while using the drugs.
Linezolid has a relatively unique mechanism and
has a lower rate of resistance among S. aureus
compared to cefaclor. It is possible that future study
could make linezolid & cefaclor more effective
against resistant bacteria by altering part of their
structures. Other characteristics of the drugs, such as
solubility, might also be improved in future studies.
6 CONCLUSION
The review mainly compared the origins,
mechanisms, limitations and drug economics of
Linezolid and Cefaclor. Their effectiveness against
infections caused by S. aureus, a typical type of
pathogen, was also briefly discussed. There are
similar issues for antibacterial agents with different
mechanisms, such as the global spread of drug
resistant bacteria. In future studies, both drugs might
be improved to become more effective against drug-
resistant bacteria. Modifications of a drug’s structure,
for instance, might improve the drug’s reactivity or
stability.
REFERENCES
Arsalan A., Ahmad I., Ali S.A, 2017. Cefaclor: Clinical,
biochemical, analytical and stability aspects. Adv. Med.
Biol. 123:1–52.
Arsalan, A., Naqvi, S.B., Sabah, A., Bano, R. & Ali, S.I.,
2014. Resistance pattern of clinical isolates involved in
surgical site infections. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci., 27, 97-102
Ayub, S., Fatima, B., Naqvi, S.B.S., Sheikh, D., Ali, S.M.
& Ayub, F., 2015. Comparative study on resistance
pattern of staphylococcus aureus against amoxicillin,
cefaclor, levofloxacin and tetracycline. J. Pharm. Sci.
Bioscientific. Res., 5, 594-599.
Bangert S, Levy M, Hebert AA, 2012. Bacterial resistance
and impetigo treatment trends: a review. Pediatr
Dermatol 29:243-248. doi:10.1111/j.1525-
1470.2011.01700.x.
Chellat M.F., Raguž L., Riedl R., 2016. Targeting
Antibiotic Resistance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55:6600–
6626. doi: 10.1002/anie.201506818.
Das N., Madhavan J., Selvi A., Das D., 2019. An overview
of cephalosporin antibiotics as emerging contaminants:
A serious environmental concern. 3 Biotech. 9:1–14.
doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1766-9.
Ford C.W., Zurenko G.E., Barbachyn M.R., 2001. The
discovery of linezolid, the first oxazolidinone
antibacterial agent. 1(2):181-99. doi:
10.2174/1568005014606099.
Foti C., Piperno A., Scala A., Giuffrè O., 2021.
Oxazolidinone Antibiotics: Chemical, Biological and
Analytical Aspects. Molecules. 26(14): 4280. doi:
10.3390/molecules26144280
Guo R, Chen J, 2015. Application of alga-activated sludge
combined system (AASCS) as a novel treatment to
remove cephalosporins. Chem Eng J. 260:550–556.
Hashemian S.M., Farhadi T., Ganjparvar M., 2018.
Linezolid: A review of its properties, function, and use
in critical care. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 12:1759-1767.
doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S164515.
Jensen LK, Koch J, Aalbaek B, et al. 2017. Early implant-
associated osteomyelitis results in a peri-implanted
bacterial reservoir. APMIS. 125(1):38-45.
Jeong SH, Jang JH, Cho HY, Lee YB, 2021. Population
Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Cefaclor in Healthy
Korean Subjects. Pharmaceutics. 13(5): 754. doi:
10.3390/pharmaceutics13050754
Lakhundi S, Zhang K, 2018. Methicillin-Resistant
Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Characterization,
Evolution, and Epidemiology. Clinical microbiology
reviews. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00020-18
Murray, D.L., Singer, D.A., Singer, A.B. & Veldman, J.P.,
1980. Cefaclor- a cluster of adverse reactions. N. Engl.
J. Med., 303, 1003.
Patel DA, Shorr AF, Chastre J, Niederman M, Simor A,
Stephens JM, Charbonneau C, Gao X, Nathwani D,
2014. Modeling the economic impact of linezolid
versus vancomycin in confirmed nosocomial
pneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. Crit. Care. 18: R157. doi:
10.1186/cc13996.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
778

Rho JP, Sia IG, Crum BA, Dekutoski MB, Trousdale RT,
2004. Linezolid-associated peripheral neuropathy.
Mayo Clin Proc. 79(7):927–930.
Sama SO, Chiamo SN, Taiwe GS, Njume GE, Sumbele
IUN, 2021. Microcytic and Malarial Anaemia
Prevalence in Urban Children ≤15 Years in the Mount
Cameroon Area: A Cross-Sectional Study on Risk
Factors. Anemia. 2021: 5712309. doi:
10.1155/2021/5712309
Shaifali, I., Gupta, U., Mahmood, S.E. & Ahmed, J., 2012.
Antibiotic susceptibility patterns of urinary pathogens
in female outpatients. N. Am. J. Med. Sci., 4, 163-169.
Shariati A, Dadashi M, Chegini Z, van Belkum A, Mirzaii
M, Khoramrooz SS, Darban-Sarokhalil D., 2020. The
global prevalence of Daptomycin, Tigecycline,
Quinupristin/Dalfopristin, and Linezolid-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative
staphylococci strains: a systematic review and meta-
analysis. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 9(1):56. doi:
10.1186/s13756-020-00714-9.
Sharifzadeh S., Dempwolff F., Kearns D. B., Carlson E. E.,
2020. Harnessing β-lactam antibiotics for illumination
of the activity of penicillin-binding proteins. ACS
Chem. Biol. 15 1242–1251.
10.1021/acschembio.9b00977
Stojanovic-Radic, Z., Dimitrijevic, M., Stankovic, N.,
Aleksic, A. & Pejcic, M., 2016. Frequency of isolation
and antibiotic resistance patterns of bacterial isolates
from wound infections. Biologica Nyssana, 7, 151-158.
Sunderkötter C, Becker K, Eckmann C, Graninger W,
Kujath P, Schöfer H., 2020. Calculated initial
parenteral treatment of bacterial infections: Skin and
soft tissue infections. GMS Infect Dis. 8: Doc11.
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland TL, Fowler
VG., Jr. 2015. Staphylococcus aureus infections:
epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical
manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev.
28:603–661. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00134-14.
Turik, M.A. & Johns, D. Jr., 1998. Comparison of cefaclor
and cefuroxime axetil in the treatment of acute otitis
media with effusion in children who failed amoxicillin
therapy. J. Chemother., 10, 306-312.
Vinh DC, Rubinstein E, 2009. Linezolid: a review of safety
and tolerability. J Infect. 59(Suppl 1):S59-S74.
Vital C., Vital A., Bouillot-Eimer S., Brechenmacher C.,
Ferrer X., Lagueny A, 2004. Amyloid neuropathy: A
retrospective study of 35 peripheral nerve biopsies. J.
Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 9:232–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1085-
9489.2004.09405.x.
Wertheim HF, Melles DC, Vos MC, van Leeuwen W, van
Belkum A, Verbrugh HA, Nouwen JL. 2005. The role
of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections.
Lancet Infect Dis 5:751–762. doi:10.1016/S1473-
3099(05)70295-4.
Yang B, Zuo J, Li P, Wang K, Yu X, Zhang M, 2016.
Effective ultrasound electrochemical degradation of
biological toxicity and refractory cephalosporin
pharmaceutical wastewater. Chem Eng J. 287:30–37.
Cefaclor Linezolid and Their Effectiveness against S. Aureus
779
