
Synthesis of Novel Environmentally Friendly
Dehydronor-Cantharidin Insecticides
Jianxin Sun
1a
, Mengjing Feng
1b
and Liangzhong Xu
1,2 c
1
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266042,
China
2
State Key Laboratory Base of Eco-chemcal Engineering, Qingdao 266042, China
Keywords:
Dehydronorcantharidin, Synhtesis, Biological Activity.
Abstract:
In order to find new environmentally friendly compounds with insecticidal activity, a series of
nornorcantharidin dihydrazide derivatives were synthesized by active substructure splicing method based on
the structure of norcantharidin and dihydrazide. the synthesized compounds were characterized by
1
H NMR,
13
C NMR and HRMS. The results of biological activity test showed that compound I
2
had the highest activity
(52% at the concentration of 1 mg/L against plutella xylostella and 70% at the concentration of 10 mg/L
against Tetranychus cinnabarinus).
1 INTRODUCTION
1
Insecticides from natural products are
environmentally compatible, so they are ideal sources
for developing environmentally friendly insecticides.
Cantharides (Zhang 2018) is a traditional Chinese
medicine, which comes from the dried bodies of
meloidae insects. It is mainly used in the treatment of
malignant tumors and tinea (Song 2020). It is difficult
to synthesize cantharidin artificially (Wang 2014), so
the main source of cantharidin is dry Mylabris
phalerata Pallas, so the main way to obtain
cantharidin is still natural extraction.
Cantharides
These factors seriously affect the development
and application of cantharidin. Norcantharidin (Zhou
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2070-2443
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6785-9245
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8391-2739
2020) is one of the important derivatives of
cantharidin. It can be obtained from maleic anhydride
and furan by two steps of Diels-alder reaction and
catalytic hydrogenation reaction (Chi 2019, Ogura
2021). The synthesis route is simple, the atom
economy is good and the synthesis cost is low. It can
be used in large-scale industrial production. In
addition, there are some similarities in biological
activities between the two compounds (Yang 2016).
This paper refers to dihydrazide pesticides as the
main reference structure, through the use of
dehydronorcantharidin (Jin 2015, Li 2014) part and
dihydrazide key active intermediate tert butyl
hydrazine condensation, dehydronorcantharidin (He
2020) derivatives were obtained, and then applied the
active substructure splicing theory to synthesize a
series of compounds.
Norcantharidin
Sun, J., Feng, M. and Xu, L.
Synthesis of Novel Environmentally Friendly Dehydronor-cantharidin Insecticides.
DOI: 10.5220/0011297200003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 833-837
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
833
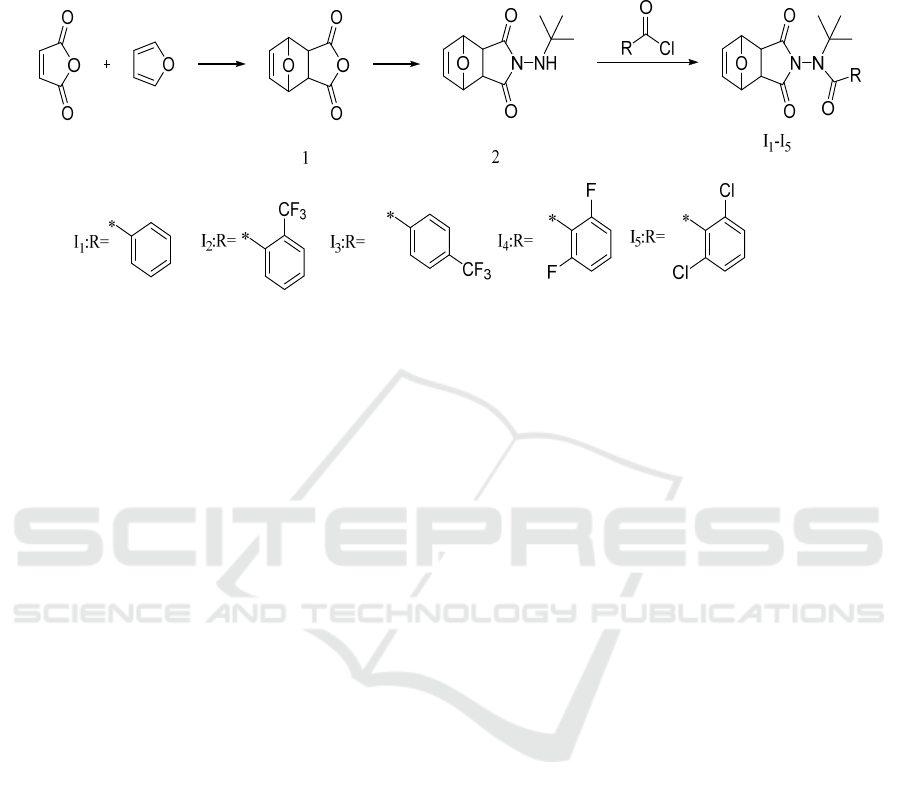
2 SYNTHESIS OF THE TARGET
COMPOUNDS
2.1 Synthesis of the Target Compounds
Figure 1: Synthetic route of target compounds I
1
-I
5
.
2.1.1 General Information for Synthesis
All reagents and solvents were used as received from
commercial sources. All reactions were carried out
under air atmosphere and monitored by thin-layer
chromatography (TLC) performed on 0.25 mm silica
gel plates (GF254) purchased from Haiyang
Chemical Industry Co., Ltd (Qingdao, China). The
TLC plates were visualized with a X-4 ultraviolet
analyser. Column chromatographic purifications
were carried out on silica gel (200-300 mesh) using
petroleum ether (PE) and ethyl acetate (EA) as
eluents. All
1
H NMR and
13
C NMR spectra were
recorded using a Bruker AV-500 instrument.
Chemical shifts (δ) were expressed in parts per
million (ppm) with TMS used as an internal standard.
High resolution electro-spray ionization mass spectra
(HRMS-ESI) were obtained using a Waters G2-XS
instrument.
2.1.2 Synthesis of Nornorcantharidin (1)
A 250 mL three-necked round bottom flask equipped
with mechanical stirrer, addition funnel and
thermometer, then added 9.8 g (0.1 mol) maleic
anhydride and 80 mL ethyl acetate respectively, keep
the room temperature, then 34.3 g (0.5 mol) furan was
added, while slowly rise to 40℃, continue stirring for
8 hours, during which A lot of white solid appeared.
The reaction mixture was filtered and dried to obtain
15.3 g (compound 1). as a white solid.
2.1.3 Synthesis of Compound 2
To a solution of 18.7 g tert butylhydrazine
hydrochloride in 80 mL ethanol, 15.2 g of
trimethylamine was added dropwise. while keeping
internal temperature between 35℃-40℃), 16.6 g
compound 1 was added in portions, continue stirring
for 4h, 80 mL of water was added in one portion, then
a lot of white solid appeared. The reaction mixture
was filtered and dried to obtain 21.3 g (compound
2).as a white solid.
2.1.4 Synthesis of Compound I
1
To a solution of 2.36 g compound 2 and 1.32 g
Potassium pyrophosphate in 40 mL acetonitrile added
1.5 g benzoyl chloride dropwise, then maintaining
gentle reflux, after compound 2 disappears, 40 g
water was added. The reaction mixture was filtered
and the filter cake was dried to give a crude product.
After purified by the flash chromatography, 2.8 g I
1
was obtained as a white solid. (compound I
2
-I
5
were
obtain by the same method).
2.2 Data of Compounds
Data for the I
1
:white solid, yield 88%, m.p.169-
170℃.
1
H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d
6
), δ(ppm),
7.85-7.89, (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.48-7.51(m, 3H, Ar-H),
6.15(s, 2H, CH), 4.76(s, 2H, CH), 2.97(s, 2H, CH),
1.40(s, 9H, CH3).
13
C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d
6
),
δ(ppm), 177.28, 177.28, 168.82, 139.46, 139.46,
139.44, 130.81, 128.12, 128.12, 128.00, 128.00,
80.21, 80.21, 58.14, 43.73, 43.73, 26.84, 26.84,
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
834

26.84. HRMS: Calcd for C
19
H
21
N
2
O
4
+
[M+H]
+
:
341.1511; Found: 340.1420.
Data for the I
2
: white solid, yield 67%, m.p.155-
157℃.
1
H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d
6
), δ(ppm),
7 .65-7.99(m, 4H, Ar-H), 6.15 (s, 2H, CH), 4.76 (s,
2H, CH), 2.97 (s, 2H, CH), 1.41 (s, 9H, CH3).
13
C
NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d
6
), δ(ppm), 176.50,
176.50, 171.10, 139.46, 139.46, 134.50, 132.06,
129.46, 129.00, 128.18, 127.08, 126.15, 80.21, 80.21,
59.65, 43.73, 43.73, 26.28, 26.28, 26.28. HRMS
Calcd for C
20
H
20
F
3
N
2
O
4
+
[M+H]
+
: 409.1375; Found:
409.1382.
Data for the I
3
: white solid, yield 89%, m.p.166-
168℃.
1
H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d
6
)δ (ppm) 8.27-
7.76 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 6.15(s, 2H, CH), 4.76 (s, 2H,
CH), 2.97 (s, 2H, CH), 1.40 (s, 9H, CH3).
13
C NMR
(125 MHz, DMSO-d
6
)δ 177.28, 177.28, 167.11,
142.85, 139.46, 139.46, 132.91, 130.83, 125.88,
125.88, 124.90, 80.20, 80.20, 58.14, 43.73, 43.73,
26.84, 26.84, 26.84. HRMS: Calcd for
C
20
H
20
F
3
N
2
O
4
+
[M+H]
+
: 409.1375; Found: 408.1370.
Data for the I
4
: white solid, yield 70%, m.p.138-
139℃.
1
H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d
6
), δ(ppm),
7.63-7.05(m, 3H, Ar-H), 6.15(s, 2H, CH), 4.76(s, 2H,
CH), 2.97(s, 2H, CH), 1.42(s, 9H, CH3).
13
C NMR
(125 MHz, DMSO-d
6
), δ(ppm), 176.86, 176.86,
163.94, 159.76, 159.76, 139.46, 139.46, 132.31,
114.90, 111.44, 111.44, 80.21, 80.21, 58.22, 43.73,
43.73, 26.48, 26.48, 26.48. HRMS Calcd for
C
19
H
19
F
2
N
2
O
4
+
[M+H]
+
: 371.1313; Found: 376.1307.
Data for the I
5
:white solid, yield 85% m.p.140-
142℃. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d
6
), δ(ppm),
7.91-7.52 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 6.15(s, 2H, CH), 4.76(s, 2H,
CH), 2.97(s, 2H, CH), 1.46(s, 9H, CH3). 13C NMR
(125 MHz, DMSO-d
6
), δ(ppm), 176.62, 176.62,
166.00, 139.46, 139.46, 137.61, 133.57, 133.57,
131.75, 127.57, 127.57, 80.21, 80.21, 57.34, 43.73,
43.73, 26.80, 26.80, 26.80. HRMS Calcd for
C
19
H
19
Cl
2
N
2
O
4
+
[M+H]
+
: 409.0722; Found:
408.0727.
3 INSECTICIDAL ACTIVITY
According to the methods from literatures, tested the
insecticidal activities against plutella xylostella and
Tetranychus cinnabarinus. The main contents of the
method were as follows: a certain concentration of
compound mother liquor was prepared with DMF,
and then diluted with 0.1% Tween-80 solution
according to different concentration gradients, so as
to prepare different concentrations of drug solutions.
Take out the fresh and clean cabbage leaves with a
punch with a diameter of 5 cm and uniform size and
shape. Place the cabbage leaves in different
concentrations of liquid medicine and soak them for
10-20 s. after that, put the dry cabbage leaves into a
Petri dish padded with two layers of filter paper. The
filter paper was wetted with clean water to ensure the
humidity in the Petri dish. 30 diamondback moth
larvae in the same growth state were cultured in a
Petri dish for 48 hours (temperature controlled at
25℃, photoperiod: L: D = 16:8, relative humidity
maintained at 60%). Checked and recorded the death
number of Plutella xylostella larvae and calculate the
mortality. During the experiment, clear water was set
as the blank control group, and each group was set
with three groups of repeated tests. The final
experimental results were the average of the three
groups of parallel tests.
Using spray method as test method, taking
Tetranychus cinnabarinus as test object. At first,
DMF was used to dilute the target compound into
different concentrations of liquid medicine, then
spray the leaves of the broad bean leaves with the
same number and growth form. Then the leaves were
placed in the observation room, and the condition of
Tetranychus cinnabaris was recorded after 48 h. The
death judgment method is to touch the mite body with
a brush, and if there is no response, it is regarded as
dead. Three groups of controls are set for each
concentration, and the average mortality of each three
parallel groups was taken as the mortality of this
concentration.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
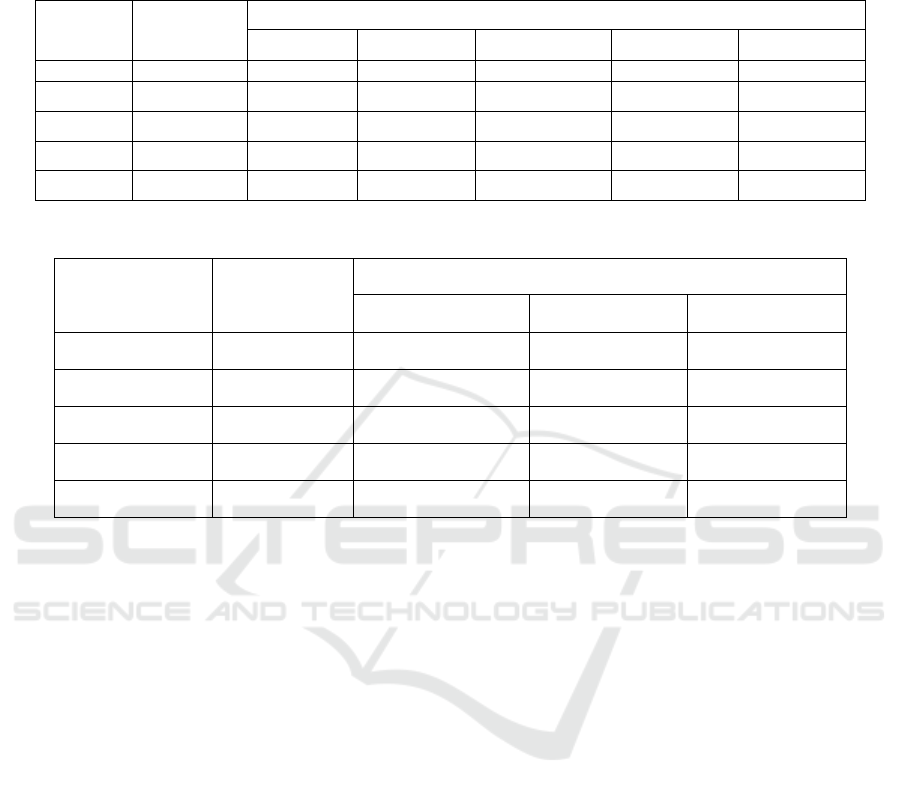
The data in Table 1 showed that all compounds had
certain insecticidal activities. When the concentration
of compound was 10 mg/L, the insecticidal activities
of compound I
1
, I
2
and I
3
were higher than 90%.
When the concentration was reduced to 1 mg/L, the
insecticidal activities against plutella xylostella of
compound I
2
were higher than 52%.
The data in Table 2 showed that at the
concentration of 100 mg / L, the acaricidal activities
of compounds I
1
, I
2
, I4 and I
5
reached 100%, and the
acaricidal activities of I
2
and I
5
were more than 80%.
When the concentration of compound continued to
decrease to 50 mg / L, the acaricidal activities of
compounds I
2
and I
5
were 87% and 81% respectively.
According to the relationship between structure and
activity, the activity of o-trifluoromethylphenyl
compound is higher than that of other compounds.
Therefore, it shows that fluorine-containing groups
can significantly improve the activity of compounds,
and the position of fluorine-containing group
Synthesis of Novel Environmentally Friendly Dehydronor-cantharidin Insecticides
835
substituents is very important for insecticidal and
acaricidal activity. When the concentration was
reduced to 10 mg / L, the activity of I
2
was 70%, and
it still had high activity.
Table 1: Insecticidal activities against plutella xylostella of target compounds.
No. compound
lethality rate against plutella xylostella(%)
50 mg/L 20 mg/L 10 mg/L 5 mg/L 1 mg/L
1 I
1
100 100 95 72 33
2 I
2
100 100 96 83 52
3 I
3
100 100 93 43 9
4 I
4
100 100 86 76 33
5 I
5
82 56 37 0 0
Table 2: The insecticidal activity against Tetranychus cinnabarinus results of target compounds.
No. Compound
lethality rate against Tetranychus cinnabarinus (%)
100 mg/L 50 mg/L 10 mg/L
1 I
1
100 78 33
2 I
2
100 87 70
3 I
3
79 56 37
4 I
4
100 76 55
5 I
5
100 81 65
5 CONCLUSIONS
In summary, 5 novel types of norcantharidin
derivatives were designed and synthesized, the
preliminary insecticidal activity against plutella
xylostella and Tetranychus cinnabarinus test showed
that all 5 target compounds had certain insecticidal
activities. Among them, the compound containing o-
trifluoromethylphenyl (I
2
) had the highest insecticidal
activity against plutella xylostella, and the
insecticidal activity was 52% at the concentration of
1 mg/L and the acaricidal activity against
Tetranychus cinnabarinus was 70%, at the
concentration was reduced to 10 mg / L. The
synthesis of these compounds had high atom
utilization rate, less waste and high insecticidal
activity. Besides, norcantharidin had good
biocompatibility and degraded easily in nature, so
norcantharidin derivatives were ideal environmental
protection insecticides. This work also revealed that
compound I
2
could be used as novel lead structures
for further research.
REFERENCES
Chi J et al. (2019) Synthesis and anti-metastasis activities
of norcantharidin-conjugated carboxymethyl chitosan
as a novel drug delivery system. Carbohyd Polym;
214:80-89.
He H et al. (2020). Equilibrium solubility of exo-5,6-
dehydronorcantharidin in thirteen pure solvents:
Determination, correlation, Hansen solubility
parameter and thermodynamic properties. J Mol Liq;
312: 113384.
Jin X, Tan X, Zhang X, Han M, Zhao Y. (2015) In vitro and
in vivo anticancer effects of singly protonated
dehydronorcantharidin silver coordination polymer in
CT-26 murine colon carcinoma model. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett; 25: 4477-4480.
Li S et al. (2014). Singly protonated dehydronorcantharidin
silver coordination polymer induces apoptosis of lung
cancer cells via reactive oxygen species-mediated
mitochondrial pathway. Eur J Med Chem; 86:1-11.
Ogura A, Ito T, Moriya K, Horigome H, Takao K. (2021)
Asymmetric Diels–Alder reaction between furans and
propiolates. Tetrahedron Lett:153075.
Song M et al. (2020) Cantharidin suppresses gastric cancer
cell migration/invasion by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway via CCAT1. Chem-Biol Interact;3
17: 108939.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
836

Wang M et al. (2014) Design, synthesis and bioactivity
evaluation of novel acylthiourea derivatives of
cantharidin. Ind Crop Prod;5 5: 11-18.
Yang P et al. (2016) Norcantharidin induces apoptosis in
human prostate cancer cells through both intrinsic and
extrinsic pathways. Pharmacol Rep; 68: 874-880.
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Zhang J, Guan C, Liu L. (2018)
Cantharides poisoning: A retrospective analysis from
1996 to 2016 in China. Regul Toxicol Pharm; 96:142-
145.
Zhou J et al. (2020) Norcantharidin: research advances in
pharmaceutical activities and derivatives in recent
years. Biomed Pharmacother; 131:110755.
Synthesis of Novel Environmentally Friendly Dehydronor-cantharidin Insecticides
837
