
The Direction and Mechanism of Temporal and Regional Progression
of Amyloid Beta Plaques in Mice’s Brains
Xintong Xu
Wuhan Britain-China School, Wuhan, Hubei, 430034, China
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease, Transgenic Mice, Hippocampus, Amyloid Beta, APP E693Q.
Abstract: The amyloid beta (Aβ) is one of the major characteristics of Alzheimer’s Disease, the neurodegenerative
disease. This paper hypothesized that the progression of amyloid beta is by diffusion from the hippocampus
to the cortex. To test this idea, this work is firstly designed to compare brain slices of C57BL/6J wild type
mice with human FAD gene in all brain area and C57BL/6J wild type mice without human FAD gene in the
hippocampus at 2, 6, 9, 12 months of age. If the result shows that there are no amyloid beta plaques present
in both hippocampus and cortex after FAD gene knockout in the hippocampus, this indicates amyloid beta
plaques are originally produced in the hippocampus. Then, the work is designed to compare brain slices of
C57BL/6J wild type mice with wild-type FAD expression in the brain and C57BL/6J wild type mice with
E693Q mutation FAD expression only in the hippocampus at 2, 6, 9, 12 months of age. If E693Q mutated
FAD gene is present in the amyloid beta from the cortex, this indicates amyloid beta diffuses from the
hippocampus to the cortex. This paper only provides theoretical experiment design and possible results about
the direction and mechanism of temporal and regional progression of amyloid beta, which needs further
research in the pathology of Alzheimer’s Disease.
1 INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease is considered a
neurodegenerative disease (Alzheimer’s Association
2016), meaning it causes the degeneration, or loss, of
neurons in the brain. This leads to the symptom
characteristic of dementia. Alzheimer’s disease is
progressive, meaning the patients will gradually
suffer from memory loss and other cognitive
inabilities throughout the rest of their life.
Although the causes of Alzheimer’s disease
remain mysterious, one of the major characteristics of
it is amyloid beta (Aβ) (Billings, Oddo, Green,
McGaugh, LaFerla 2005). The transmembrane
protein, amyloid precursor protein, or APP, is
responsible to produce amyloid beta protein.
In the Alzheimer’s case, APP is cut by β and γ
secretase instead of α and γ in the normal situation
The peptide remained is insoluble and creates a
monomer: amyloid beta (Aβ). These monomers are
more chemically sticky, bond together extracellularly,
and form amyloid beta plaques.
These plaques can potentially block the neurons,
which inhibits neuron-to-neuron signaling. It is also
thought that these plaques can start-up an immune
response and cause inflammation which might
damage surrounding neurons.
As shown in Figure 1, the amyloid beta plaques
labeled by brown-dye antibodies have a progression
pathway that starts from the entorhinal cortex and
spread to the hippocampus, and finally spread
throughout the cortex in the mice’s brains as the mice
grow up.
The spread of amyloid beta is possibly caused by
diffusion, meaning the amyloid beta is produced in
the hippocampus and diffuse to the cortex through
membranes. Thus, a hypothesis of “The accumulation
of amyloid beta plaque is initiated from the
hippocampus and Aβ plaques diffuse to the entire
cortex.” is established.
2 HYPOTHESIS
The accumulation of amyloid beta plaque is initiated
from the hippocampus and Aβ plaques diffuse to the
entire cortex.
Xu, X.
The Direction and Mechanism of Temporal and Regional Progression of Amyloid Beta Plaques in Mice’s Brains.
DOI: 10.5220/0011371700003438
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 429-436
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
429

Figure 1: Representative -amyloid (A) immunohistochemistry in 2 (A, B), 5 (C, D) and 13 (E, F) month old 5XFAD mice.
(Macdonald, DeBay, Reid, O’Leary, Jollymore, Mawko et al. 2014).
Figure 2: First experiment design for the hypothesis.
3 METHODS AND MATERIALS
3.1 Amyloid Beta Progression Pathway
To testify this hypothesis, the following experiments
are designed. There are two subsets in this
investigation.
Firstly, to determine whether the amyloid beta is
originated from the hippocampus, the amyloid
production in the hippocampus is designed to be
suppressed and the presence of amyloid beta plaques
is detected in the cortex, as shown in Figure 2.
3.1.1 Animals
60 mice wild-type (C57BL/6J), 30 female and 30
male. (Manocha et al. 2019)
3.1.2 Transgenic Material
Human FAD (Familial Alzheimer’s disease) gene
3.1.3 Transgenic Method
Virus-mediated gene delivery: Import the FAD gene
into the mice's brains at the embryo stage.
3.1.4 Cre-loxP System
The Cre-loxP recombination is a special type of site-
specific recombination, which can remove a certain
gene in a certain area. To stop amyloid beta
production in the hippocampus, the FAD gene in the
hippocampus is removed immediately after
transgene. The transgenic line in which Cre
recombinase expression is restricted in the
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
430

hippocampus is used, so the specific promoter can
activate loxP sites in the same direction in the
hippocampus and the FAD gene is deleted, as shown
in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Excision cis placement of loxP sites in same directional orientation causes a gene deletion (Ju 2020) .
3.1.5 Procedure
Experimental group
Transgenic mice with FAD gene expression in all
brain cells
Transgenic mice without FAD gene expression in
the hippocampus
Firstly, the FAD gene is imported using virus-
mediated gene delivery into all 60 mice’s brains at the
embryo stage. After one day, the FAD gene is
removed in the hippocampus region of 30 mice (15
female and 15 male) using the Cre-loxP system.
By 2, 6, 9, 12 months of age, six strong, healthy
mice (three males and three females) were taken from
each group. The brain of each mouse is taken and
cutting slices of each mouse’s hippocampus and
cortex are made. Brown-dye antibody is added to the
cutting slices and observes under the microscope.
3.2 Mechanism of Amyloid Beta
Progression
Figure 4: Second experiment design for the hypothesis.
Once the pathway of progression is confirmed that
it is from the hippocampus to the cortex, the
mechanism of amyloid beta spreading requires a
second experiment to testify, as shown in Figure 4.
3.2.1 Animals
60 mice wild-type (C57BL/6J), 30 female and 30
male. (Manocha et al. 2019)
3.2.2 Transgenic Material
Human FAD (Familial Alzheimer’s disease) gene:
Familial AD, which represents a minority of AD
cases, is due to mutations in one of three genes,
presenilin (PS) 1 and 2 and the amyloid precursor
protein. (Van Cauwenberghe, Van Broeckhoven,
Sleegers 2015)
E693Q mutated FAD gene:
To determine whether the amyloid beta plaques
present in the cortex are produced in the hippocampus
and diffuse out, a method to distinguish the amyloid
beta in the hippocampus and the cortex is required. In
this experiment, the Dutch mutation, E693Q on the
amyloid precursor protein is used.
The Direction and Mechanism of Temporal and Regional Progression of Amyloid Beta Plaques in Mice’s Brains
431

Figure 5: Partial amino acid sequence of APP containing multiple secretases' cutting sites (APP E693Q (Dutch) 2021).
As shown in Figure 5, the amyloid beta which
forms plaques and causes neurodegeneration in
Alzheimer’s disease is cut by β and γ secretase at
specific cutting sites.
Figure 6: Amino acid sequence of amyloid beta and Dutch mutation (APP E693Q (Dutch) 2021).
The Dutch mutation is on the 693
rd
amino acid of
the APP, which is the 22
nd
amino acid on the amyloid
beta, as shown in Figure 6. The Dutch mutation
changes the glutamic acid into glutamine. Since “the
mutated gene may also undergo accelerated
aggregation and accumulation” (Knight et al. 2014),
so the function of E693Q is similar to the wild-type
FAD gene.
3.2.3 Transgenic Method
Virus mediated gene delivery: Import the strand
containing the FAD gene into the mice’s brains at the
embryo stage, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7: Simplified structure of imported gene strand.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
432

3.2.4
Cre-loxP System
The Cre-loxP recombination is a special type of site-
specific recombination, which can remove a certain
gene in a certain area, as shown in Figure 3. In the
imported gene strand, as shown in Figure 7, a wild-
type FAD gene and a terminator are added between
two loxP sites in the same direction and an E693Q
mutated FAD gene after the loxP sites. After virus-
mediated gene delivery, the gene can be expressed
throughout the brain. During transcription, the only
gene before the terminator, stop codon, can be
expressed successfully, which is the wild-type FAD
gene. After that, the transgenic line in which Cre
recombinase expression is restricted to the
hippocampus is used, so the specific promotor
activates two loxP sites in the same direction in the
hippocampus. The gene between the two loxP sites is
deleted, including the terminator, snd only the E693Q
mutated FAD gene is remained and is expressed in the
hippocampus.
3.2.5
IP – immunoprecipitation
To testify the presence of the E693Q mutated FAD
gene in the cortex, firstly, the amyloid beta plaques in
the cortex of mice’s brains should be extracted. IP,
immunoprecipitation, is a technique of precipitating a
protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that
specifically binds to the amyloid beta. In this
experiment, the brown-dye antibody is used. IP can be
used to isolate and concentrate the amyloid beta from
a sample of cortex mixture, as shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8: Process of IP ( MBL Life Sience -ASIA-. Mblbio.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021).
3.2.6
Elution
To extract out amyloid beta from the antibody-
amyloid eta complex, a process called elution is used.
As shown in Figure 9, by washing the extraction with
a solvent, as in the washing of loaded ion-exchange
resins to remove captured ions, the pure amyloid beta
molecule can be extracted.
Figure 9: Process of elution (Solid Phase Extraction/SPE Guide | Waters. Waters.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021).
The Direction and Mechanism of Temporal and Regional Progression of Amyloid Beta Plaques in Mice’s Brains
433
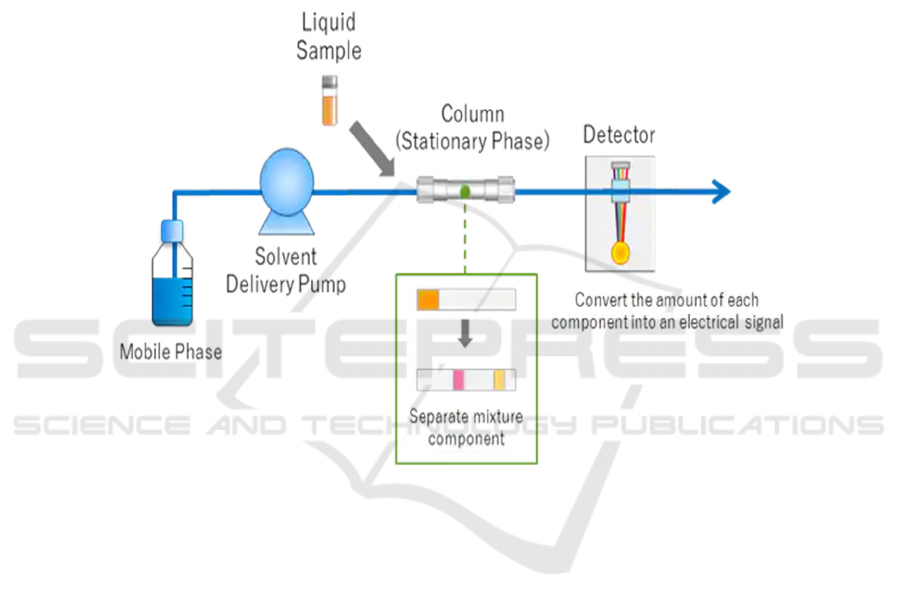
3.2.7
E693Q Mutated FAD Gene Testing
HPLC-High performance liquid chromatography
After extraction of the pure amyloid beta
molecule, HPLC is used to testify the presence of the
E693Q mutated FAD gene on amyloid beta. As shown
in Figure 6, the E693Q mutated amyloid beta
molecule has one glutamine instead of glutamic acid
compared to the wild-type amyloid beta. As shown in
Figure 10, the solvent is forced through a metal tube
under high pressure. The particle size of the stationary
phase is much smaller, which leads to better
separation of the components. The two amyloid beta
samples (wild-type and E693Q mutated type) are
injected into the column. Finally, the components are
detected after passing the column, by their polarity.
Then the retention times of two different amyloid beta
forms are compared. Firstly, samples of HPLC on
both E693Q mutated type and wild-type amyloid beta
are made, and results are recorded. When testing the
amyloid beta form from the cortex of the transgenic
mice’s brains, its result can be compared with the two
recorded results to see which result matches with it,
thus determine the type of amyloid beta.
Figure 10:Process of HPLC (Shimadzu.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021).
3.2.8
Procedure
Experimental group
Transgenic mice with wild-type FAD expression
in the brain
Transgenic mice with E693Q mutation FAD
expression only in the hippocampus
Firstly, gene strand is imported using virus-
mediated gene delivery into all 60 mice’s brains at the
embryo stage. After one day, the wild-type FAD gene
and terminator are removed in the hippocampus of 30
mice (15 female and 15 male) using the Cre-loxP
system.
By 2, 6, 9, 12 months of age, six strong, healthy
mice (three males and three females) were taken from
each group. The brain of each mouse is taken and
cutting slices of each mouse’s hippocampus and
cortex are made. Brown-dye antibody is added to the
cutting slices and observes under the microscope. The
amyloid beta plaques in the cortex region of mice
with E693Q mutated FAD expression only in the
hippocampus are extracted using IP and elution. The
presence of the E693Q mutated FAD gene is tested
using HPLC.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Amyloid Beta Progression Pathway
There are three possible results for the first
experiment. Firstly, neither the hippocampus nor
cortex has plaques present. Secondly, plaques are not
present in the hippocampus but present in the cortex.
Lastly, both hippocampus and cortex have plaques
present.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
434

4.2 Mechanism of Amyloid Beta
Progression
There are two possible results for the first experiment.
Firstly, E693Q mutated FAD gene is present in the
amyloid beta from the cortex. Secondly, E693Q
mutated FAD gene is not present in the amyloid beta
from the cortex
Discussion
For the first experiment, it is designed to determine
whether amyloid beta originates from the
hippocampus, and there is one result that corresponds
to the hypothesis. If the result shows that there are no
amyloid beta plaques present in both hippocampus
and cortex after FAD gene knockout in the
hippocampus, this indicates amyloid beta plaques are
originally produced in the hippocampus.
The other two results are not consistent with the
hypothesis, and both indicate that amyloid beta
originates from the cortex. One of the results is that
amyloid beta is present in the cortex but cannot be
seen in the hippocampus. The other result is that
amyloid beta is present in both areas, which shows
that amyloid beta is initiated from other parts of the
brain and spread to the hippocampus region.
For the second experiment, it is designed to testify
whether amyloid beta diffuses from the hippocampus
to the cortices. This corresponds to the result that the
same Dutch mutated gene in the amyloid beta from
the cortex is found as that in the hippocampus, which
is consistent with the gene imported into the
hippocampus. This implies that amyloid beta is
produced in the hippocampus and diffuses out to the
cortex from the hippocampus.
The second result is that the wild-type amyloid
beta is present in the cortex, which differs from the
mutated amyloid beta in the hippocampus. This
indicates that signals were sent to the cortex to
activate the β and γ secretase and thus the production
of amyloid beta. Hence, this does not match what
have speculated.
5 EVALUATION
This work tried to design an experiment of RNA
sequencing previously to testify the second possible
result of the second experiment, which is assumed to
be signaling from the hippocampus. But it was
weeded out because no effective and pragmatic way
was found to do it. It is hard to determine the signal
in one simple experiment because the possible signal
can vary from Herpes Virus to small proteins.
Therefore, it has been ruled out as details were
considered to practice it.
The Cre-loxP system used in both experiments
allows us to knock out specific genes between two
loxP sites. It is very useful and reliable to cut the
specific site wanted and precede as is expect.
However, only genes in the hippocampus region are
designed to be knocked out in both experiments. This
work has been checked whether there is a specific
promoter that only activates the Cre line in the
hippocampus region and it turns out there are only
promoters that work in subunits in the hippocampus.
To perform the experiments, a specific promoter is
assumed that activates the Cre line in the whole
hippocampus region, which may not exist.
In the second experiment, Dutch mutation is used
for us to track and distinguish the origin of amyloid
beta proteins. This mutation changes the 693
rd
amino
acid on APP from glutamic acid to glutamine. Dutch
mutation are specifically chosen because it does not
affect the function of APP, and the mutation site is on
the amyloid beta section. Therefore, different amyloid
beta can be produced, which indicates no
inconsistency with our experimental design.
Our hypothesis will determine the direction and
mechanism of amyloid beta spreading, which can
provide clues for limiting the area amyloid beta
spread, and possibly control dementia. If the first half
of the hypothesis is consolidated, the next step will be
to control the amount of amyloid beta plaques and
clear them in the hippocampus. If amyloid beta
diffuses to the cortex, restricting amyloid beta
diffusion to control dementia would be important.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper provides two designed experiments on
transgenic C57BL/6J wild type mice to investigate
the pathway and mechanism of amyloid beta
progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cre-LoxP
system were used to introduce or remove gene
segment of Human FAD gene and APP E693Q into
the mice’s brains and specifically the hippocampus
region. The research significance lies on the
pathology and possible treatment of Alzheimer’s
Disease. If the amyloid beta progression can be
controlled or eliminated, we are one step closer to the
cure of Alzheimer’s Disease.
The Direction and Mechanism of Temporal and Regional Progression of Amyloid Beta Plaques in Mice’s Brains
435

REFERENCES
Alzheimer’s Association (2016). 2016 Alzheimer’s disease
facts and figures. Alzheimer's and Dementia: the
Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, 12(4), 459–50
APP E693Q (Dutch) | ALZFORUM. Alzforum.org.
Retrieved 21 September 2021, from
https://www.alzforum.org/mutations/app-e693q-dutch.
Billings, L., Oddo, S., Green, K., McGaugh, J., & LaFerla,
F. (2005). Intraneuronal Aβ Causes the Onset of Early
Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Cognitive Deficits in
Transgenic Mice. Neuron, 45(5), 675-688.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.040
Ju, W. (2020). 3.5 Cre-Lox, Driver Lines, and Next Order
Specificity. Ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub. Retrieved
21 September 2021, from
https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/neurosciencecd
n2/chapter/3-5-cre-lox-driver-lines-and-next-order-
specificity/.
Knight, E., Williams, H., Stevens, A., Kim, S., Kottwitz, J.,
& Morant, A. et al. (2014). Evidence that small
molecule enhancement of β-hexosaminidase activity
corrects the behavioral phenotype in Dutch APPE693Q
mice through reduction of ganglioside-bound Aβ.
Molecular Psychiatry, 20(1), 109-117. doi:
10.1038/mp.2014.135
Macdonald, I., DeBay, D., Reid, G., O’Leary, T., Jollymore,
C., & Mawko, G. et al. (2014). Early Detection of
Cerebral Glucose Uptake Changes in the 5XFAD
Mouse. Current Alzheimer Research, 11(5), 450-460.
doi: 10.2174/1567205011666140505111354
Manocha, G., Floden, A., Miller, N., Smith, A., Nagamoto-
Combs, K., & Saito, T. et al. (2019). Temporal
progression of Alzheimer's disease in brains and
intestines of transgenic mice. Neurobiology Of Aging,
81, 166-176.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.05.025
Solid Phase Extraction/SPE Guide | Waters. Waters.com.
Retrieved 21 September 2021, from
https://www.waters.com/waters/en_US/Solid-Phase-
Extraction-SPE-
Guide/nav.htm?cid=134721476&locale=en_US.
The principle and method of immunoprecipitation (IP) |
MBL Life Sience -ASIA-. Mblbio.com. Retrieved 21
September 2021, from
https://www.mblbio.com/bio/g/support/method/immun
oprecipitation.html.
Van Cauwenberghe, C., Van Broeckhoven, C., & Sleegers,
K. (2015). The genetic landscape of Alzheimer disease:
clinical implications and perspectives. Genetics In
Medicine, 18(5), 421-430.
https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.117
What is HPLC (High Performance Liquid
Chromatography) ?. Shimadzu.com. Retrieved 21
September 2021, from
https://www.shimadzu.com/an/service-
support/technical-support/analysis-
basics/basic/what_is_hplc.html.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
436
