
Effect of Caffeine on Obesity and Its Application in the Treatment of
Obesity
Xinlu Yun
Institute of food, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Keywords: Caffeine, Obesity, Ephedrine, EGCG, Appetite.
Abstract: Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease, it is not only listed in the top ten chronic diseases by WHO, but also
is a risk factor in many other chronic diseases. At present, the treatment of obesity mainly includes lifestyle
intervention, drug therapy and surgery. Drug therapy was initially popular as a way to lose weight quickly
and has little trauma, but people gradually lost faith in it due to its endless negative news. Therefore it is
important to seek a natural substance with very low side effects as a source of drugs for obesity treatment.
Caffeine is a natural substance that is ubiquitous found in people's lives, making it more acceptable as a
treatment for obesity. Therefore, this paper aims to study the influence of caffeine on obesity, the
application of caffeine in the treatment of obesity and the prospect of caffeine as a weight loss drug,
expecting to provide new ideas for the development of natural weight loss drugs. Finally, through literature
analysis and case studies, it is concluded that caffeine can play a positive role in the treatment of obesity by
suppressing appetite and accelerating lipid metabolism, and that the combined use of caffeine with EGCG
or ephedrine has a more significant effect than caffeine alone.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to the development and progress of the Times, a
large number of delicious foods, especially the
mixture of sugar and oil, appear in people's life.
Meanwhile, due to the progress of science and
technology, people have less opportunity to put their
physical strength into some sports or activities,
resulting in the increase of obesity. Obesity is a
chronic metabolic disease, it will not only take a toll
on health, such as increasing the rate of
cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, osteoarthritis
and other diseases, but also it will has a great impact
on life, and even produce the psychological problems
such as depression. Thus, the prevention and
treatment of obesity has become today's global hot
spots (Seidell 2015). At present, the main treatment
methods of obesity include lifestyle intervention,
drug therapy and surgery. Among them, most of the
studies are related to drug therapy, such as lillutide,
which can suppress appetite, orlistat and inhibit
lipase activity in gastrointestinal tract. However,
there are also many drugs that have been phased out
due to the side effects. Therefore, weight-loss drugs
with "natural ingredients and low side effects" have
also become the focus of research in recent years.
Coffeeand tea have always been considered by many
people to have the effect of weight loss, but most of
the relevant studies on caffeine are about its main
ingredient or about its effects on apnea or
neurodevelopment treatment of premature infants,
and there are few relevant studies in whether it has an
impact on obesity treatment and the mechanism of
obesity. Thus, this paper will discuss how obesity is
produced, whether caffeine has an effect on obesity,
the specific application of caffeine in the treatment of
obesity and whether it can be widely used as a drug
in the treatment of obesity, expecting to provide a
safe and effective new idea for obesity treatment and
bring help to the obese people.
2 CAFFEINE AND OBESITY
In recent years, refreshing drinks such as coffee and
tea have become popular among young people and
those who need to stay up late at work. Caffeine has
also entered the public's field of vision. However,
Chinese and foreign scholars have different views on
whether caffeine has an effect on weight loss. On the
one hand, some people think that caffeine can
suppress appetite and improve metabolism so as to
450
Yun, X.
Effect of Caffeine on Obesity and Its Application in the Treatment of Obesity.
DOI: 10.5220/0011372000003438
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 450-455
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

play a role in weight loss, for example, Liu Hanyang
(LIU 2016) and Litong Liu (Liu 2018) believe that
caffeine can boost lipid metabolism or suppress
appetite. On the other hand, some people think that
the effect of caffeine on weight loss is not
obvious,for example, in the study of Schubert
(Schubert 2014) et al, the effects of coffee intake
(caffeinated and decaffeinated) on appetite
perception and energy intake were investigated and
no significant differences were found between the
two groups. So in this section whether caffeine could
alleviate obesity will be discussed.
2.1 The Emergence of Obesity
Obesity refers to overweight and obesity caused by
the accumulation of excessive fat in the body. The
pathogenesis of obesity is also very complex. In
addition to physiological factors, there are also
genetic and environmental factors, but the main
causes of obesity are excessive energy intake and
metabolic disorders.
Among those factors, energy intake is related to
food intake, and food intake is closely related to
appetite. Hunger signals due to insufficient energy
intake and proximity to delicious food can stimulate
appetite and promote eating behavior. And when the
body ingests too much, it will also cause the disorder
of ingestion control mechanism. For example, the
hypothalamus which regulates appetite and energy
balance is composed of multiple nuclei: arcuate
nucleus (ARC), paraventricular nucleus (PVN),
lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), ventromedial
nucleus (VMN)and dorsomedial nucleus (DMN).
The arcuate nucleus (ARC) located in the central
uplift of the hypothalamus, it is considered to be the
main region for sensing peripheral metabolic signals.
In ARC, two distinct but interrelated groups of
neurons are included, one stimulates appetite,
including agouti-related (AgR) released by
agouti-related peptide (AgRP)neurons and
neuropeptide Y (NPY), and the other one suppresses
appetite, including proopiomelanocortin (POMC)
and cocaine and amphetamine regulated transcript
(CART). In addition, some appetite regulation
factors such as appetite stimulating ghrelin and
appetite suppressing leptin, are also produced by the
nucleus of hypothalamus (Zhu 2013).
However, when energy intake is too high, AgRP
level can be increassed by reducing POMC and α
-melanocyte hormone (α-MSH) expression, thus
causing disturbance of feeding control mechanism
and energy imbalance, resulting in increased appetite
and further fat deposition (Zhu 2013).
Obesity is mostly caused by adipose tissue, it is
associated with energy metabolism, brown adipose
tissue (BAT) is used to produce heat and white
adiposetissue (WAT) is used to store fat, obese
patients have more WAT and less BAT but because
of the less amount of BAT group, leading to heat
production, which regulates metabolism, to break
down, causing excess energy to be converted to fat
(Liu 2003), It is also one of the causes of obesity.
However, from the perspective of genetics,
obesity can also be the result of a combination of
genetic and environmental factors. Obesity caused
by heredity is divided into single-gene obesity and
multi-gene obesity. The pathogenesis of single-gene
obesity is mostly caused by abnormal
LEP-melanocortin signaling pathway, which is
manifested as hyperfeeding and early onset of
obesity. While polygenic obesity is generally caused
by DNA variation produced by multiple genes,
which are significantly associated with BMI,waist
circumference, hip circumference and weight (Yu
2020).
To sum up, the causes of obesity are diverse and
are not the results of the action of any single factor,
so obesity treatment should also be "appropriate to
the case".
2.2 Influence of Caffeine on Obesity
Caffeine is a natural methyl xanthine, its chemical
name is 1, 3, 7-trimethylxanthine. Caffeine can be
found in many plants, such as coffee beans and tea.
Caffeine can stimulate the central nervous system,
usually dispel fatigue and refresh the brain, and is
often used in clinical treatment of neurasthenia and
coma resuscitation (Zhang 2021). So it is a popular
central nervous stimulant and widely used in food,
medicine and other fields. In addition, caffeine also
has a certain effect on obesity.
2.2.1 Caffeine’s Effect on Lipid Metabolism.
Caffeine can inhibit phosphodiesterase activity and
increase cyclic amp depends on protein kinase, and
it can induced the downstream of the sympathetic
nervous system and hormone sensitive lipase
reconciliation coupling protein increases, eventually
leading to the increase of energy consumption and
fat oxidation (LIU 2016). Because of caffeine’s
positive impact on the role of fat oxidation, it can
enhance the BAT heat production performance,
prevent the accumulation of body fat, and play a
positive role in the prevention and treatment of
obesity.
Effect of Caffeine on Obesity and Its Application in the Treatment of Obesity
451

2.2.2 Caffeine 's Effect on SNS(sympathetic
nervous system)
Caffeine can enhance the excitability of sympathetic
nervous system (SNS), and SNS plays an important
role in adjusting energy consumption and fat
metabolism. Norepinephrine (NE) is an important
mediator in determining SNS activity, so substance
that can stimulate or prolong the presence of NE can
increase energy expenditure and promote lipid
metabolism. Caffeine can affect activity by
inhibiting phosphodiesterase activity, an enayme
that can rapidly degrade adenosine
monophosphatidylate (cAMP)in cells and is also a
signal of reaction to NE (Yang 2019). Besides,
neuropharmacological studies have proved that
cateholamine like NE, dopamine (DA) and
serotonin(5-HT) neurotransmitter changes can
change feeding behavior, affect appetite, so the
excitement of SNS will have a negative effect on
appetite, thus reducing food intake, and because
appetite and obesity were positively related, the
reduction of appetite will have a positive impact on
obesity treatment (Wu 2000).
But the effect of caffeine on obesity depends on
the amount of caffeine used, individual differences
(age, sex, pregnancy or not), half-life (since caffeine
has a shorter half-life, the loner the time passes, the
less significant the effect), and whether it is used in
combination with other substances.
3 CAFFEINE IN THE
TREATMENT OF OBESITY
While many studies have shown that caffeine does
suppress appetite and improve metabolism, some
studies have shown that caffeine has no significant
effect on energy intake or appetite. So given that, it
would be more likely for caffeine to work in
combination with other substances.
3.1 Synergistic Application of EGCG
and Caffeine
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the main
component of green tea polyphenols. Like caffeine,
EGCG is also known for its anti-obesity effects. It
also regulates fat metabolism of obese patients, and
can stimulate the body to produce heat to accelerate
metabolism and reduce the body's absorption of
calories from food.
When EGCG is used alone, the possible
mechanism of its effect on obesity is that EGCG
affects the excitability of SNS, increases energy
consumption, and promotes fat oxidation, which in
turn drives other mechanisms including changing
appetite, up-regulating enzyme activity of liver lipid
metabolism, and reducing nutrient absorption. It can
be seen from the above that the activity of SNS
depends on NE, and EGCG can inhibit the activity
of catechol-o-methyl transferase (COMT), which
candegrade NE, thus prolonging the survival time of
NE. However, due to the low bioavailability of
EGCG (< 1%) and the serious side effects associated
with high doses of EGCG alone, EGCG in
combination with caffeine is a good choice. The
combination of EGCG and caffeine can solve the
problem that each of them can not be used alone
with large doses, and the worry that toxicity may be
produced(because they are from the same
substance). In addition, one of the reasons for the
limited effectiveness of EGCG is also due to the low
bioavailability of it, but effective experiments have
shown that EGCG with different proportions of
caffeine can improve the bioavailability of EGCG.
In the study of Yang Z (Yang 2019), all rats were
treated according to the experimental design in
Table 1: ND group rats had unchanged diet and were
given distilled water intragastrically. The other rats
were fed high-fat diet, and then randomly divided
into five subgroups: obesity group (OB), fed with
distilled water. Low EGCG group (LE), gavage
40mg/kgEGCG. High EGCG group (HE),
160mg/kgEGCG. Caffeine group (CF), 20mg/kg
caffeine intragastric administration. Low dose
EGCG+caffeine group (LE+CF), 40mg/kgEGCG
and 20mg/kg caffeine intragastric administration.
All the experiments were conducted in the morning,
and the volume of intragastic administration was
2ml for four consecutive weeks, and the results were
finally obtained as shown in Figure 1. OB group had
significant difference in weight gain over 4 weeks
compared with ND group. The weight gain of LE
group (57.1±8.9g) and CF group (46.2±7.6g) was
significantly slower than OB group (75.2±10.6g).
But in the HE group (20.3±7.3g) and the LE+CF
group (25.4±6.3g),the weight gain retardation effect
was more obvious, even lower than the ND group
(28.6±4.5g). Therefore, the HE group and LE+CF
group achieved the purpose of weight loss, and the
effect was better than the LE group and CF group.
However, due to the harm of high dose EGCG, it is
not suitable for the treatment of obesity, so the
combination of caffeine and low dose EGCG can be
a good choice for the treatment of obesity.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
452
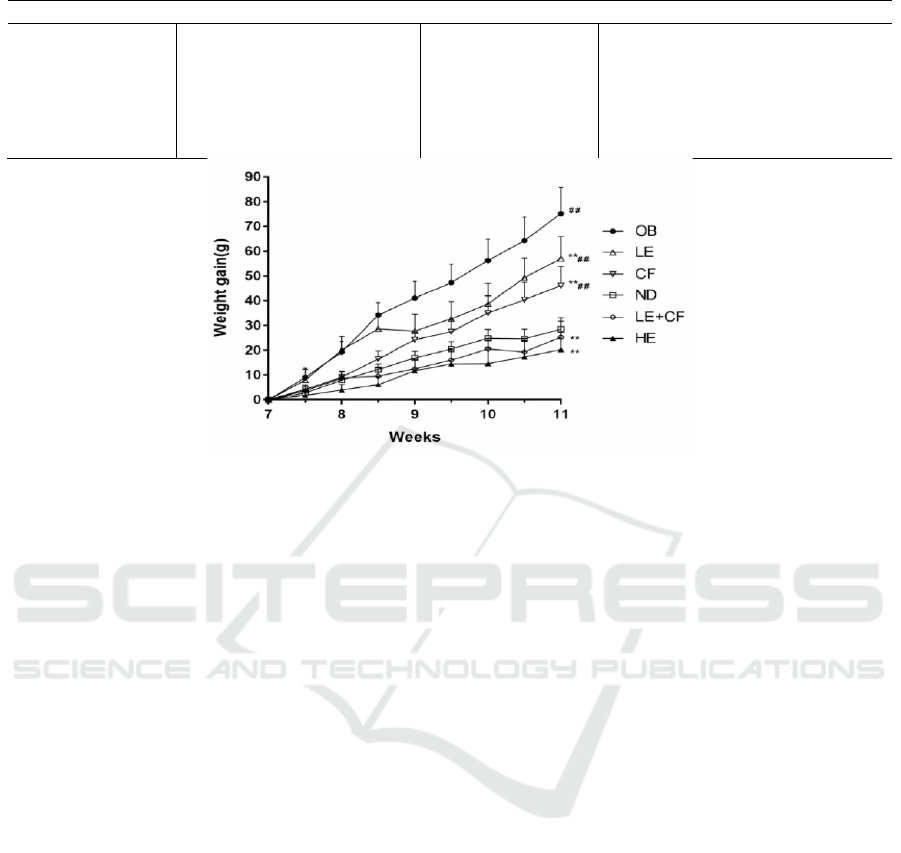
Table.1: Experimental design and process Quote.
Group name
Group name full name Feed Treatment dose
ND
OB
LE
HE
CF
LE+CF
Normal diet group
Obesity model group
Low EGCG group
High EGCG group
Caffeine group
Low EGCG+Caffeine group
Ordinary feed
High fat feed
High fat feed
High fat feed
High fat feed
High fat feed
Distilled water
Distilled water
40mg/kg EGCG
160mg/kg EGCG
20mg/kg Caffeine
40mg/kg EGCG+20mg/kg Caffeine
Figure1: Weight trend of rats
About how to mix EGCG with caffeine to get the
best results, Litong Liu (Liu 2018) etal discussed the
effects of the combined use of EGCG and caffeine
on anorexia and fat accumulation in mic in their
study, and 15 different concentrations of EGCG and
caffeine were used for 8-week experimental study in
mice, and the optimal ratio and mechanism of
EGCG and caffeine were finally determined. The
inhibitory effect of 0.1%EGCG+0.1% caffeine on
food intake was the strongest, and the decrease of fat
accumulation and body weight was the largest.
In these studies, it was found that the
combination of caffeine and EGCG had a more
significant effect on obesity and was more helpful in
inhibiting weight gain and fat accumulation than
using caffeine alone.
3.2 Synergistic Application of
Ephedrine and Caffeine
Because caffeine stimulates the sympathetic nerve
and thus plays a role in weight loss, it was wondered
whether the combination of ephedrine, which also
has a central stimulant effect, would make the
inhibition of obesity even more significant.
Ephedrine is a kind of epinephrine-like drug, and its
therapeutic effect is better than epinephrine. It is
often used in the treatment of bronchial diseases, etc.
For the combined use of ephedrine and caffeine in
the treatment of obesity, such auxiliary drugs have
been approved to use in foreign countries.
Ephedrine has a similar effect on obesity as
EGCG and caffeine, stimulating fat oxidation,
increasing energy expenditure and suppressing
appetite. Experimental studies indicate that
ephedrine can promote the release of catecholamine
(CA) transmitters, adrenergic receptors, and
promotethermogenesis. However, ephedrine is
affected by thenegative feedback regulation of
adenosine-prostaglandin and cAMP
phosphodiesterase system, they can reduces the
thermogenesis effect, but methyl yellow purine
compounds can affect the system again, so when the
caffeine and methamphetamine collaborative
application can enhance the effect of ephedrine,
Caffeine also contributes to weight loss by
antagonizing adenosine receptors and promoting fat
breakdown and thermogenesis (Wu 2000).
In the study of Greenway et al (Greenway 2008),
a case study was conducted on 3 patients with
hypothalamic obesity who continuously taking
caffeine plus ephedrine hydrochloride. The average
weight loss of these 3 patients was 13.9%, and two
of them maintained weight loss for several years.
Although the number of cases is too small to draw
definitive conclusions, it is not difficult to see the
significant effect of caffeine combined with
ephedrine. According to the study of Xiumei Wang
et al (Wang 2017), obese rats were divided into
control group, caffeine group, ephedrine group and
ephedrine combined with caffeine group for a period
of 21 days to observe the indexes, and the results in
Effect of Caffeine on Obesity and Its Application in the Treatment of Obesity
453

Table 2 were finally obtained. According to the
chart, the weight of the caffeine and ephedrine
groups showed little difference from that of the
normal control group, but the weight of the
ephedrine and caffeine combined group was
significantly lower than that of the obesity model
group. Therefore, caffeine and ephedrine alone had
little effect on weight loss. The combination of
ephedrine and caffeine resulted in significant weight
loss.
Table 2: Weight data of rats.
Group name 0 weeks weight 1 weeks weight 2 weeks weight 3 weeks weight
Normal Control group 188.23±10.81 251.01±8.55 308.37±20.23 358.03±24.56
Obesity model group 232.22±18.13 330.17±19.23 368.38±7.18 402.70±13.65
Caffeine group 224.42±12.24 243.09±19.03 301.03±22.51 340.36±20.03
Ephedrine group 228.41±18.13 256.31±17.01 310.37±18.53 351.14±17.18
Ephedrine and Caffeine
combined
g
rou
p
231.04±11.38 281.36±15.1 310.21±19.25 325.21±21.96
4 DISCUSSION
A large number of studies have confirmed the
positive effects of caffeine consumption in the
treatment of obesity, diabetes, etc. But whether
long-term consumption of caffeine will cause
damage to the body is not clear. And the effect of
suppressing appetite produced by caffeine has a
positive effect on weight loss, but it may cause
depression, anxiety and other psychological
conditions. In the next place, caffeine's half-life
(about 3-4 hours for a healthy adult) makes its
effects so short that it is not clear whether it has a
long-term lasting effect on obesity. Apart from that,
it remains to be seen whether long-term
consumption of large amounts of caffeine builds
tolerance and weakens weight loss, and whether it
leads to dependence.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the current research, it can be concluded that
caffeine does have a certain effect on appetite and
metabolism, and because of these effects, it has a
certain effect on obesity, so it can be applied in the
treatment of obesity. But caffeine alone did not
result in the same weight loss as caffeine combined
with EGCG or ephedrine. Thus, caffeine alone as a
weight loss drug for the treatment of obesity is not
easy to achieve, but the combination of caffeine with
EGCG or ephedrine and other substances for the
treatment of obesity has great prospects.
In addition, during the research process of this
paper, there are too few literature about the"
influence of caffeine on appetite", so the mechanism
of action is not clear.
Currently, there is no complete system of drugs
for obesity treatment, and caffeine as a kind of
natural substance appears in people's lives almost
every day, it certainly is a good choice of weight
loss. But there is still a long way to go for caffeine to
be widely used to treat obesity, future research is
likely to focus on whether there is dependence,
resistance, and how to extend the duration action
should be researched as well.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to thank Mr. Li Nuo and Mr. Wang
Xiaoying for their help and guidance in this study. I
would also like to thank my school shenyang
Agricultural University for the cultivation of me,
which has laid a solid foundation for me in the
professional field.
REFERENCES
Greenway Frank L, Bray George A.Treatment of
hypothalamic obesity with caffeine and
ephedrine.(2008),Endocrine practice : official journal
of the American College of Endocrinology and the
American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists,
14 (6) : 697-703.
Litong Liu, Kazutoshi Sayama. (2018)The combined
administration of EGCG and caffeine induces not only
suppression of fat accumulation but Effects of
anorexigenic action on the growth of mice. Journal
of Functional Foods,47:156-162.
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
454

Liu D, Liu H, Liu H, et al. Lipid metabolism and
metabolism of Obesity. (2003)Journal of Clinical
Medicine. (03):116-118.
LIU Hanyang, ZHOU Yan, GONG Yu, et al. (2016). J
med review, 22(5):928-932.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2016.05.027.
Schubert Matthew M, Grant Gary, Horner Kat, King Neil,
Leveritt Michael, Sabapathy Surendran, Desbrow Ben.
(2014)Coffee for morning hunger pangs. An
examination of coffee and caffeine on appetite, gastric
emptying, And energy intake. Journal of Appetite,
317-26.
Seidell Jacob C, Halberstadt Jutka. (2015)The global
burden of obesity and the challenges of
prevention.Annals of nutrition & Metabolism, 66
Suppl 2:7-12.
Shurui Yang, Yudian Zhou, Yayuan Wang, Wenyan
Wang, Fengxia Liang. (2021) Journal of Huazhong
University of Science and Technology (Medical
Edition).(04):544-547.
Wang Xiumei, Huang Lichun, Chen Mingying. Effects of
combination of ephedrine and caffeine on body weight
in rats,(2017)Journal of Pharmacy, (1):29-30.
Wu Ping, Hu Yongshi, Du Qingyun, Chen Hong.
Classification and mechanism of weight loss drugs.
(2000)Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacy,
(02):131-134.
Yang Z. The synergistic effect of EGCG and caffeine and
the effect of green tea on lipid reduction and weight
loss and its mechanism. (2019)Hunan Agricultural
University.(01).
Yu Baowen, ZHOU Hongwen. Research progress of
genetic obesity. (2020)Journal of Clinical Internal
Medicine, (09):611-615.
Zhang Jinyue, Yan Dongying, Gao Liang. Effect of
caffeine on central nervous system .(2021)Health
Vision, (12):33.
Zhu Yongxiang, Wang Qian, Wang Shuang, Yu Wei, Nan
Ying, Cao Jian. (2013)Journal of Jilin University
(Medical Edition).(05):1067-1071.
Effect of Caffeine on Obesity and Its Application in the Treatment of Obesity
455
