
Predictive Model of Septic Shock Staging Base on Continuing
Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring
Ruowen Liao
Department of Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, Ontario, Canada
Keywords: Septic Shock, Hemodynamic, Deep Active Learning, Multi-Classification, Predictive Model.
Abstract: Septic shock is a major public health concern across the world, also is a typical cause for patients being
admitted to the intensive care unit. It is easier to be misdiagnosed, yet the situation is getting worse. Septic
shock can be classified into three stages: irreversible (early stage), compensated, and decompensated. Sepsis
has long been misdiagnosed, but it develops and worsens at an alarming rate, often reaching irreversible
levels within hours. This work has expanded the proportion of invasive hemodynamics to septic shock for
the development of understanding of the phases of septic shock. This article aims to construct and develop a
real-time prediction model of septic shock staging based on continuous invasive hemodynamic monitoring.
The ultimate model of the article is a multi-classification prediction model.
In this experiment, the eICU collaborative research database was employed, and four characteristics from
the dataset were scored to indicate the stage of septic shock. Need to point out that deep active learning, a
new approach that combines deep and active learning, was chosen as the research's major learning approach.
Margin sampling is the main query strategy used in the active learning approach, with the random selection
strategy serving as a control strategy. There are two groups of query strategies, compare the two groups to
see which one is more effective: random selection or active learning. As a result, the query strategy of active
learning is considerably most stable than random selection in deep active learning. Although septic shock
cannot be diagnosed purely based on hemodynamic characteristics, the model can nevertheless assist
clinicians in making an early diagnosis or warning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Septic shock is a common reason for patients to be
admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), and it is
also a significant cause of mortality among severely
sick patients in the ICU. In 2017, there were 48.9
million instances of sepsis and 11 million fatalities
due to sepsis, accounting for roughly 20% of all
deaths worldwide (Genga 2017). It is worth noting
that COVID-19, from its emergence in 2019 and
continues to this day, has been linked to sepsis.
Health care personnel pay particular attention to the
development of sepsis after a COVID-19 patient is
brought to the ICU (Bediako 2021). This was
demonstrated in many studies that shock could be
divided into three stages: irreversible, compensated,
and decompensated shock. Sepsis is very easy to be
misdiagnosed, but it deteriorates very quickly in
hours. The staging of shock assists medical
personnel in determining the severity of the
condition and appropriately intervening in treatment
and medicines to enhance patient survival rates.
There is thereby a need for classification, but it is
still a significant challenge to define clearly what
stage of shock the patient is at based on the clinical
presentation. Thus, to have better knowledge of the
phases of septic shock, this research has increased
the proportion of invasive hemodynamics in septic
shock.
The ultimate objective of this study is to provide
some help in using a machine learning approach to
determine the stage of shock in patients with sepsis
in the ICU, improve efficiency and reduce fatality.
There are many excellent reviews in literature
dealing with the basic concepts of machine learning
and sepsis. Continuing to learn about septic shock
using machine learning is also a significant step
forward in medicine. Notably, hemodynamic
monitoring is critical for the diagnosis and
intervention of septic shock patients. The eICU
Collaborative Research Database (eICU-CRD)
Demo was utilized as a source of clinical study data
518
Liao, R.
Predictive Model of Septic Shock Staging Base on Continuing Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring.
DOI: 10.5220/0011373200003438
In Proceedings of the 1st Inter national Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare (ICHIH 2022), pages 518-523
ISBN: 978-989-758-596-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

in this study, which comprised 24 hours of
continuous vital sign monitoring of systemic
circulation (Badawi 2018). The author recruited
patients previously diagnosed with sepsis from the
eICU-CRD Demo for observation and research. The
use of machine learning for invasive continuous
hemodynamic monitoring of eICU sepsis patients is
expected to further improve the understanding of the
shock stage.
2 METHODS
2.1 The eICU-CRD Dataset
Between 2014 and 2015, researchers from the MIT
Computational Physiology Laboratory, Philips
Healthcare, and PhysioNet's colleagues collected
data from over 200,000 ICU patients for the ICU-
CRD database (Badawi 2018). It should be pointed
out that this database is an electronic version that
provides a new model of care in ICU: remote
monitoring. The e-recording allows clinicians to
instantly retrieve a patient's vital signs, saving time
and preventing the loss of paper data. This research
utilized the eICU-CRD demo as the experimental
database because the researcher intends to see if it
can generate predictions with a smaller amount of
electronic data. The eICU-CRD demo includes
2,500 patients in the ICU department from 20 large
hospitals in the United States. These patients are
divided into a training set and test set according to
the radio of 8:2. The file in the eICU-CRD called
'vitalPeriodic.csv' is particularly attractive as the
main dataset, due to the study is based on the
characteristic of hemodynamic to make a prediction
model. The VitalPeriodic table includes the
continuous invasive hemodynamic monitoring
features which are need in this research: heart rate,
oxygen saturation (SaO
2
), central venous pressure
(CVP), systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood
pressure.
2.2 Features and Score Setting
Four features were collected to determine the stage
of septic shock: heart rate, CVP, mean arterial
pressure (MAP), SaO2.
2.2.1 Heart Rate
When cardiovascular decomposition occurs, the
heart is the first compensation mechanism. At this
time, the heart rate will increase to ensure sufficient
cardiac output. According to the definition and
diagnostic criteria of sepsis and septic shock, a heart
rate of more than 90 beats per minute or two
standard deviations greater than the normal value of
the same age can be confirmed or suspected of
infection(CCM1993).
2.2.2 CVP
It is generally believed that CVP at 8 to 12mmHg is
a treatment target for severe infections and septic
shock. In recent years, CVP has been challenged as
a pressure indicator to evaluate volume load. It is
now believed that CVP can be used to determine the
type of shock. However, unless in the extreme range
of the variables, such as in the case of a history of
bleeding, and the CVP value is 0mmHg, it should
always be interpreted together with other variables
(Antonelli 2014).
2.2.3 MAP
Invasive blood pressure (IBP) is a commonly used
technique in the ICU. Continuous monitoring as one
of the advantages of IBP could provide patients
status in real-time. In our research, MAP is selected
as a variable shown the IBP’s feedback of patients.
2.2.4 SaO2
As an important monitoring indicator of severe
infection and septic shock recovery, SaO2, also
selected as one of the scoring indicators in this
article. SaO2 value is from 60% to 80% in patients
with severe infection and septic shock in normal
circumstances. It must also be mentioned that a
significant increase in mortality when the SaO2
value is less than 70%.
2.2.5 Scoring Design
The designer created a simplified score sheet based
on the given information and the MAP data in the
APACHE II score, as shown in table 1.
Table 1: Criteria for scores calculated based on invasive
hemodynamic data patients.
Predictive Model of Septic Shock Staging Base on Continuing Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring
519

Parameters Points
+4 +3 +2 +1
Heart Rate
(BPM)
- - - ≥90
CVP
(mmHg)
- - -
<8 &
>12
MAP
(mmHg)
≥160 or
≤49
130~159
≥110 or
≤ 69
-
SaO2 (%) 60~70 70~80 - -
In addition, the scores are divided as follows
based on the aforementioned features and scores to
identify the phases of septic shock: 1) a score of 0 to
4 is judged to be a non-septic patient. The patient’s
septic shock phase is assessed to be more severe as
the score rises. 2) with the score of 4, it is in
irreversible stage, 3) it is belonging to a
compensated stage when the score is 5 to 7, 4) and
the patient will be classified as in the
decompensated phase with the score of 8 to 10. This
shown as below figure. This is the multi-
classification standard of this experiment.
Table 2: Stratification criteria for multi-classification scores.
Score
Non-sepsis
Irreversible
Compensated
Decompensated
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2.3 Model Development
The eICU-CRD is collected patients’physiological
data every few minutes. As mentioned previously,
the patients are randomly separated into two parts:
80% for model training (2000 patients), 20% as the
test set. Convolution neural networks (CNN) also is
a multi-layer neural network, were utilized in this
research to create a prediction model of which phase
of the septic shock the patient will be in. CNN has
the ability to extract features automatically, the
convolution layer is in charge of extracting features
and convolution is used to extract the needed
information (Asafuddoula 2016).
One of our goals is to develop a prediction
model with as minimal data as feasible; the model
also uses deep active learning (DAL), a hybrid of
deep and active learning(Chang 2020). The flow of
the model is shown in Figure 1 below. DAL
framework can be roughly divided into two parts:
the active learning query strategy on the unlabeled
data set and the training method of the deep learning
model(Chang 2020). There are hundreds, if not
thousands, of records for each of the 2,500 patients.
Unlike most traditional active learning algorithms,
which query one by one, batch model deep active
learning (BMDAL) picks an entire batch of
unlabeled data based on certain selection criteria
(Agarwal 2019). The amount of information and
diversity of the samples are considered at the same
time as the batch selection of samples (Agarwal
2019). The DAL code is built on a Github library
called "deep active learning" and is publicly
available. It is worth pointing is that the optimizer of
the DAL used Adam. The benefit of DAL code is
that it has a rapid gradient to huge data, which is
ideal for our needs in eICU-CRD, where we need to
analyze enormous volumes of data. Another
significant advantage of the DAL is that it does not
boost the budget of recognition and classification
(Chang 2014).
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
520
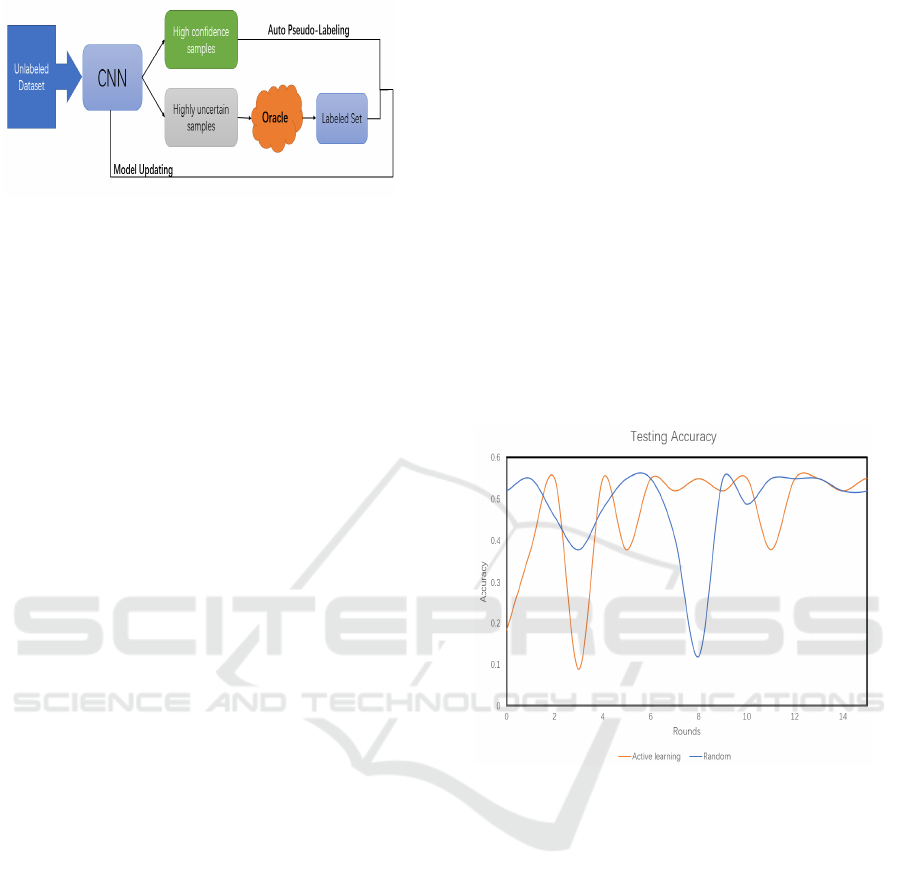
Figure1: The framework of the deep active learning
process.
2.4 Query Strategy
The most important things in active learning are
how to select samples for labeling and the selection
of query strategy. There are two main principles for
how to select samples for labeling: uncertainty
principle and difference principle. Margin sampling
as one of the uncertainty samplings was chosen in
the active learning. The concept of active labeling
by margin sampling is to give the sample the
smallest separation between the top two class
predictions, as seen in the equation:
(y
x
y
x
)
(1)
where y 1 and y 2 are the deep learning network's
first and second most probable class labels,
respectively (Agarwal 2019). The Random sampling
strategy, is mainly as a control strategy. This
strategy randomly select a certain proportion of
samples from the unlabeled samples and submit
them to the labeler for labeling. It also has been used
in this article. In the processing, there are two
groups:
One uses a combination of margin sampling and
the Random sampling, referred to as active learning
by learning strategy. Another does not use a margin
sampling strategy.
To determine which strategy is more successful,
the two groups will be compared in the next and the
more effective strategy will be found between
random selection and active learning.
3 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
According to information derived from the eICU-
CRD sub-database ‘diagnose’, the proportion of
people diagnosed with septic shock during their ICU
stay was 7.33 percent of the total number of people
in the database. The percentage of positive to
negative occurrences was 3:38. These are patients
who were diagnosed with sepsis and shock by
clinicians, but who were not classified as being in
the septic shock phases by the doctors.
After 15 rounds with 1000 batch sizes and 1000
queries per round, the ultimate accuracy of the
active learning by learning approach is 55.017
percentage, whereas the accuracy of random
selection is 51.958 percent. Regardless of the fact
that there may not be much of a difference in the
accuracy, Figure 2 illustrates that the accuracy of
random selection outperforms that of active learning
initially. As shown in the diagram, the initial
random selection approach has significantly higher
accuracy and stability than the active learning
technique. However, when additional input data and
data are labeled, the stability of random selection
tends to deteriorate, compared to active learning.
Figure 2: Active accuracy of two query strategies.
Conversely, since more data is added to the
model, the accuracy of active learning gradually
overcomes the measurement rate of random
selection, and the active learning model is more
stable than random selection. This article also makes
use of deep learning. Deep neural networks (DNN)
were constructed, and the batch-based sample query
approach was used. The following graphs of
accuracy and loss are obtained using the case of a
batch size of 64. Deep learning is better than active
learning if readers look objectively at the accuracy
and loss of the final model in this experiment, as is
demonstrated in figures 3 and 4.
Predictive Model of Septic Shock Staging Base on Continuing Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring
521

Figure 3. Deep learning accuracy.
Figure 4. Deep learning loss.
4 DISCUSSION
The most direct charm of active learning is that it
can significantly reduce the cost of labeling samples.
Researchers have discovered that accuracy is quite
low and about 0.55 based on of Figure 2, which
represents accuracy in both query techniques,
random selection and active learning. for this, the
authors have come up with the following hypothesis.
Firstly, it can no longer learn from the data, although
it is an active learning model. Our deep learning
model, on the other hand, appears to contradict this
notion. Furthermore, the authors discovered that the
percentage of individuals with septic shock in the
eICU-CRD demo is extremely tiny. The percentage
of scores below 4 that indicate a non-sepsis state is
approximately 0.99, and the distribution is
extremely unbalanced. As a result, it's thought that
this data set isn't appropriate for the test model, and
the accuracy rate is poor. Even though the testing
accuracy is indeed very high for this type of
database, it really has no effect on the model. A
further option is that a deep active learning library
setting was not properly debugged in the
experiment, preventing the DAL model from
learning anything.
Another thing worth mentioning is that because
of the interdependence of the sympathetic and
parasympathetic nervous systems, shock should not
be judged simply based on "normal" hemodynamic
measurements. Regardless of the fact that the model
can predict a patient's sepsis stage based on current
eICU datasets, it still has to be validated and
adjusted before it can be utilized in real life. Since
this complex septic shock phase is solely assessed
by invasive hemodynamics, the model is still
immature. Nevertheless, most ICU patients who
underwent intubation medication are adept at
gathering invasive hemodynamics parameters. As a
consequence, the model can still be used as a guide
to assist clinicians in promptly diagnosing or
warning of the onset of more severe shock.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on hemodynamic data and the features of
most intubation treatments in ICU patients, this
paper provides a technique for predicting and
staging septic shock in the article. For multi-class
prediction, deep active learning and deep learning
active learning are used to study. Deep learning
validates the model’s feasibility and correctness.
The query strategy of active learning is considerably
most stable than random selection in deep active
learning. The fraction of patients with sepsis is too
small since the data is concentrated, resulting in the
low accuracy of the active learning model. The low
accuracy and instability of the DAL model are
caused.
However, this paper also has the deficiency that
the author's knowledge of the DAL source code is
incomplete and inaccurate, a representative database
should be chosen to debug the model and code. And
even though it cannot fully diagnose and forecast
septic shock with invasive and continuous
hemodynamic monitoring of patients, this
experiment is likely to increase the understanding of
the shock stage and aid clinicians in quick diagnosis
and real-time prediction. Even if invasive
hemodynamics cannot properly detect and
discriminate the stages of septic shock after
successful debugging of the future model, it will
ICHIH 2022 - International Conference on Health Big Data and Intelligent Healthcare
522

offer a new research avenue for the study of the
stages of septic shock. Septic shock may be
immediately interfered with and the mortality
incidence of septic shock can be reduced by
accurately evaluating the stage of septic shock and
offering assistance to medical personnel.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Professor Robert F. Murphy of Carnegie Mellon
University and Assistant Teacher Jinzhe Zhang of
the University of Tokyo are gratefully received for
their support and suggestions. Thanks for providing
the PhysioNet eICU-CRD data and the deep active
learning source code supplier. Simultaneously, I
express gratitude to the Western University for its
nurturing and the content related to this article was
learned in the department of medical biophysics.
Appreciate also the Editor and reviewers for your
valuable suggestions, which helped the author
enhances the work.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, A., Ash, J. T., Krishnamurthy, A., Langford, J.,
& Zhang, C, (2019). Deep batch active learning by
diverse, uncertain gradient lower bounds. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1906.03671.
Antonelli, M., Beale, R., Bakker, J., Cecconi, M., De
Backer, D., Hofer, C., Jaeschke, R., Mebazaa, A.,
Pinsky, M. R., Rhodes, A., Teboul, J. L., Vincent, J.
L., (2014). Consensus on circulatory shock and
hemodynamic monitoring. Task force of the European
Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive care
medicine, 40(12), 1795–1815.
Asafuddoula, M., Shaheen, F. & Verma, B., (2016).
Impact of automatic feature extraction in deep
learning architecture. In 2016 International conference
on digital image computing: techniques and
applications (DICTA)(pp. 1-8). IEEE.
Badawi, O., Celi, L. A., Johnson, A. E., Mark, R. G.,
Pollard, T. J., & Raffa, J. D., (2018). The eicu
collaborative research database, a freely available
multi-center database for critical care research.
Scientific Data, 5(1).
https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.178
Bediako, Y., Djomkam Zune, A. L., Duodu, S, Nganyewo,
N. N., Olwal, C. O., Owoicho, O., &Tapela, K.,
(2021). Parallels in sepsis and covid-19 conditions:
Implications for managing severe covid-19. Frontiers
in Immunology, 12.
Chang, X., Chen, X., Huang, P.-Y., Li, Z., Ren, P., Wang,
X, & Xiao, Y., (2020). A survey of deep active
learning. arXiv.org.
Data: Badawi, O., Johnson, A., Johnson, A., & Raffa, J.,
(2021). eICU Collaborative Research Database Demo
(version 2.0.1). PhysioNet.
https://doi.org/10.13026/4mxk-na84.
Ej0Cl6/Deep-Active-Learning: Deep active learning.
GitHub. (n.d.). https://github.com/ej0cl6/deep-active-
learning.
Genga, K. R. & Russell, J. A., (2017). Update of sepsis in
the intensive care unit. Journal of Innate Immunity,
9(5), 441–455.
Sepsis and organ failure definitions and guidelines,
(1993). Critical Care Medicine, 21(10), 1612.
Shang, Y., & Wang, D., (2014). A new active labeling
method for deep learning. (2014) International Joint
Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN).
Predictive Model of Septic Shock Staging Base on Continuing Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring
523
