
Applications of HPLC in Pharmaceutical Engineering
Qing Ye
South China Agricultural University, Material and Energy College Guangzhou, 510630, China
Keywords: HPLC, Pharmaceutical, Purification, Drug Quality, Metabolites.
Abstract: The pursuit of high quality drugs leads to increasing demand for technique with high performance in mixture
separation. Pharmaceutical industry is a field requiring fine separation technology. High performance liquid
chromatography (HPLC) is commonly seen in pharmaceutical study and manufacture in separation processes
for diverse aims. In this paper, the related information from some databases are collected and summarized to
discuss three major applications including the purification of raw material, quality analysis of drug product
and assay of metabolites. Evidences show that HPLC has broad purpose by pharmaceutical engineering. This
paper is intended to offer an overview on applications of HPLC in pharmaceutical engineering and provide
ideas for improvements of technique with new methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chromatography has been developed a lot in the last
hundred years since the initial separating the plant
pigments. For the over decades, its analytical ability
have been greatly improved by the advance of
equipment. High performance liquid chromatography
(HPLC) is a rapid separation instrument commonly
used in pharmaceutical engineering, which is based
on the principle that different materials own different
distribution coefficients in a certain stationary phase
and mobile phase.
Pharmaceutical engineering is a field has high
requirement for separation. The fast running speed of
HPLC maks it one of the most applied tools in
substances separation and real-time detection in
several important segments pharmaceutical industry.
Connected with detective devices, it can help to
detect residual substances, determine the drug
content, analyse drug metabolism and so on (Ahuja
2017). HPLC plays an important role in the producing
process of those products with high purity
requirement. It is applied in the purification of
alkaloid and peptide which takes a quite low
proportion in the mixture (Wu et al. 2013). Besides,
it is also widely applied in drug metabolism analysis
for its high separation efficiency.
Recently, more and more specific HPLC methods
are developed for the research on certain drug or
preparation, which helps people to know better about
the drug’s properties and the improve its quality.
Therefore, the following paragraphs will focus on
three major applications of HPLC: purification,
quality analysis and metabolism analysis.
2 RELEVANT ANALYSIS ON
HPLC
2.1 HPLC for Drug Purification
A considerable part of the existing drugs come from
natural products of plants or microorganism.
Therefore, purification with high efficacy is an
indispensable stage during drug discovery and
manufacture. HPLC displays a good performance in
separating and purifying substances.
One of the problems in deriving natural product is
that the content of the active ingredient is very low
and the components are complicated, making
separation difficult. Fortunately, HPLC helps this
process easier. Liao X set up a method to determine
the active components of Osmanthus fragrans roots
by HPLC-MS/MS (Liao et al. 2021). In this
experiment, 36 compounds were detected in the
separation and one of them was newly found in the
work. Tandem mass spectrometer (MS/MS) helped to
measure the relative molecular mass of each
component segregated by HPLC, providing key
information for chemical structures. Hong Y and his
partners also used a similar method (HPLC-MS/MS)
962
Ye, Q.
Applications of HPLC in Pharmaceutical Engineering.
DOI: 10.5220/0011374700003443
In Proceedings of the 4th Inter national Conference on Biomedical Engineer ing and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 962-967
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

to determine the bioactive ingredients of Cercis
chinensis Bunge fruits (Hong et al. 2020). Gallic acid
was found to account for the largest proportion. This
has not been reported before, indicating some new
medicinal value of the fruits.
High throughput purification is demanded in
pharmaceutical industry. However, it’s not easy to
realize that in the production of antibody, cytokine
and other kinds of peptide drug. A large scale HPLC
system used for purifying IgGs was validated by
Schmitz S and his team (Schmitz et al. 2019). Three
running pumps were paralleled and work
simultaneously in this method to ensure the rapid
removal of aggregates and endotoxins. They also
used the autosampler to make the process automatic
and enable continuous manufacturing.
Besides changing the parameter of
chromatography, modifying the target product also
makes purification efficient. Tag-assisted technology
is quite useful in peptide drugs. The filler of column
binds the corresponding groups that can specifically
combine the tag of target protein. By this process,
separation with high resolution can be realized by
specific binding and elution. To simplify the
procedures, the self-cleavable tags have been
developed as well as the aggregating tags (Mmg et al.
2020). Such tags are intended to reduce the
pretreatment or post processing.
High purity and high production are two goals that
manufacturer wants to achieve. But these two
objectives are often contradictory due to the limit of
current manufacturing technique. Luca C. D. and her
team have established a multicolumn continuous
chromatography to solve the problem (Luca et al.
2020). Different from a classical forwardcurrent
chromatography, the method employed
countercurrent solvent to purify the products without
a solid filler column. An automatic internal recycling
was set in the system to increase production with
acceptable purity.
2.2 HPLC for Drug Quality
Drug quality inspection is a necessary step to ensure
the safety of preparations after production. Quality
and impurity determination are two general test items
for most preparations. HPLC is quite practical in
preparation analysis due to high resolution and
rapidity.
HPLC can be used for the determination of drugs
with similar chemical structures when a suitable
mobile phase and proper elution gradient are set.
Trifluoperazine and prochlorperazine are both
phenothiazine derivatives with only one different
group on benzene ring. According to Dhabab
(Dhabab et al. 2013), a determination method for
these two drugs was conducted by using reverse
phase HPLC (C18 column, acetonitrile as mobile
phase, chlorperazine hydrochloride as internal
standard), showing a good separation and acceptable
accuracy in quality (recovery percent is higher than
96%).
By applying a chiral stationary phase, HPLC can
be used to analyse the enantiomeric purity of certain
drugs. Sertaline is an antidepression drug with two
stereogenic centers. Ara B et al. have demonstrated a
reverse phase method for determining enantiomeric
purity of sertraline by using Chiralpak IG-3 column
with acetonitrile-water-DEA mixtures (75:25:0.1,
V/V/V) as mobile phase (Ara et al. 2020). The result
showed that it could recognize another two
stereoisomers of sertraline well within 15 min by a
single-run approach, reducing the time consumption
and expenditure of existing method.
HPLC is also applied in simultaneous estimation
for compound preparations containing more than one
active pharmaceutical ingredients. A simple, rapid
HPLC method for estimation of three antivirus drugs
(Lamivudine, Tenofovir, and Dolutegravir) is
developed by Rao N M et al (Rao et al. 2015). They
adopt a Inertsil ODS-3V C18 column with mobile
phase of mobile preparation A (mixture of potassium
dihydrogen orthophosphate buffer and methanol) and
B (mixture of orthophosphoric acid and acetonitrile).
These drugs can be separated within 14 mins and high
mean percent of recovery by different added amount
(all are over 99%), displaying a good applicability of
this method.
Test of drug degradation is a necessary step to
ensure its quality. HPLC can be applied to analyse the
degradation substances of the drug under certain
stress. Bisht R et al. have developed a reverse phase
HPLC method connected with UV detector for
determining the degradation of connexin43 mimetic
peptide (Bisht et al. 2017). It presented good linearity
between the concentration of 0.9-250 μg. The result
showed that the peptide, which helps to treat
inflammation, was sensitive to temperature and pH.
In addition, the analysis of excipient takes
advantage of some detection technology combined
with HPLC. Liposome is a good coating to improve
drug’s hydrophilicity. But one technical difficulty is
how to determine the uniformity of each liposme as
well as the drug inside it. Langer C and R Süss have
created an HPLC method applied in a range of
liposome drugs using diode array detector (DAD) for
qualitative detection and corona charged aerosol
detector (CAD) for quantitative detection (Langer et
Applications of HPLC in Pharmaceutical Engineering
963
al. 2021). The benefit of CAD is the non-reliance on
the structures of substance. Instead, it depends on the
number of charged atomized particles. Therefore, it
can detect both the drug and liposomes after they
were separated by HPLC. The method has been also
validated for cyclodextrin coated drugs.
2.3 HPLC for Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism analysis is an essential part during
the study of pharmacokinetics. One of the common
features of biological samples is the complex
composition. So the technique for detection in animal
experiment and clinical trial needs to be precise and
effective. HPLC plays an important role in this part.
Plasma is the most commonly used biological
sample. Sws A et al. have established an HPLC
method combined with fluorescence detector (FLD)
for determination of the metabolism of alpelisib in rat
plasma (Sws et al. 2020). FLD is suitable for
molecules which can emit fluorescence under certain
wavelength radiation. Alpelisib, an antibreastcancer
drug, has two aromatic rings which allow it to have a
significant response in test. The result presented that
the drug kept stable in blood for 24 hours.
Prodrug is an effective way to improve the
bioavailability. Finding out the metabolic pathway is
a significant step to ensure the safety of the drug.
Nobilis M and his team developed a method for
determination of the metabolites of new nabumetone
(a type of anti-inflammatory prodrugs) (Nobilis et al.
2013). They first used liquid-liquid-extraciton to
collect the compounds in liver microsomal fractions
(including human tissue and rat tissue), and then
employed HPLC with photo-diode array and tandem
mass spectrometer to analyse the metabolites. 3-
hydroxy nabumetone was found and it was inferred
to be the first metabolite of new nabumetone after a
further study on its biotransformation.
In order to make the detection comprehensive,
radioactive elements are used to track the distribution
and metabolism of drugs in the body. Accordingly,
the radio-HPLC is established for this kind of test.
Gaudin A et al. have developed a method to detect the
squalenoyl adenosine nanoparticles (radio-labeled
with 3H and 14C) in mice (Gaudin et al. 2015). In this
paper, the nucleoside is covalented to squalene to
extend its half-life. Mice plasma was used in the
stability determination of the drug in vitro and it was
separated by the HPLC and then detected by a
radioactive element detector. The result indicated that
the prodrug was able to persist for 1 hour and mainly
absorbed by the liver and spleen.
Multidimensional chromatography is a
technology that combines columns with different
selectivity or several types of chromatography
methods to improve the separation effect as much as
possible. Roberta K et al. have established a method
for the determination of albendazole metabolites in
microsomal fractions of mice liver (Kátia et al. 2013).
A chiral 2D-HPLC was employed in this work where
a bovine serum albumin column was for sample
clean-up and the other column for chiral resolution.
Result showed that sulfonylation to albendazole
occurred in liver tissue.
3 THE RESEARCH SITUATION
OF HPLC IN
PHARMACEUTICAL FIELD
Published papers in this field reflects the
development of the technqiue. By using the
visualized analysis of the database CNKI, the author
input key words “HPLC drug” and derived the overall
trend of the applications of HPLC in pharmaceutical
field in China of recent years.
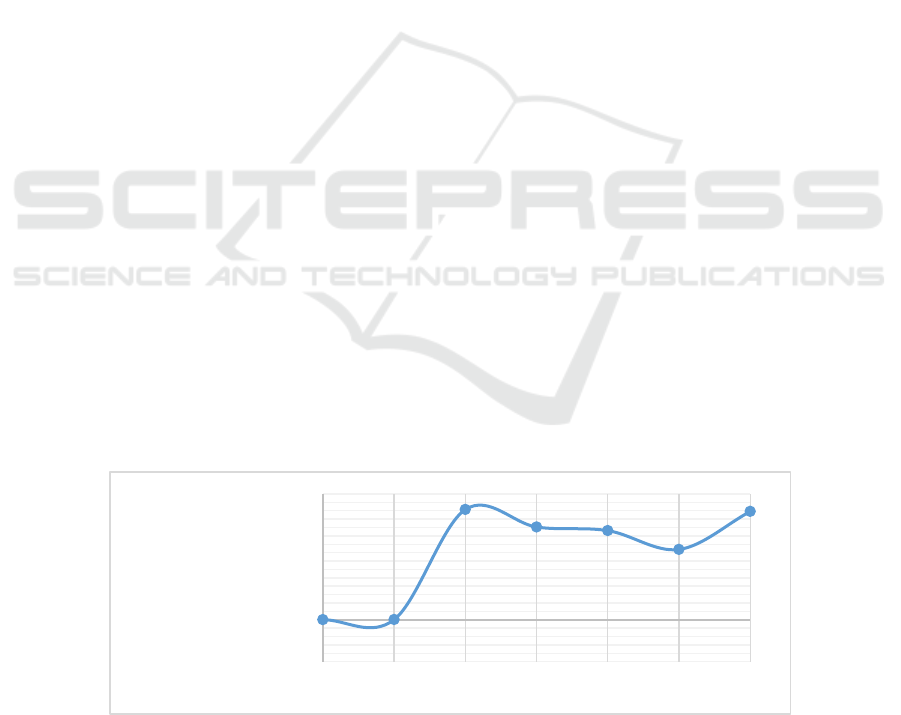
Figure 1: The annual published trend versus year
Figure 1 presents the change of the number
relevant published papers. A huge growth of the
number for over 1000 is seen from 2016 to 2017.
Then the quantity has dropped a bit in the following
-500
0
500
1000
1500
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021
The Number of
Published
Papers
Year
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
964
years but has increased again since 2020. This
indicates that more attention has been paid to the
study of HPLC in the field since 2016.
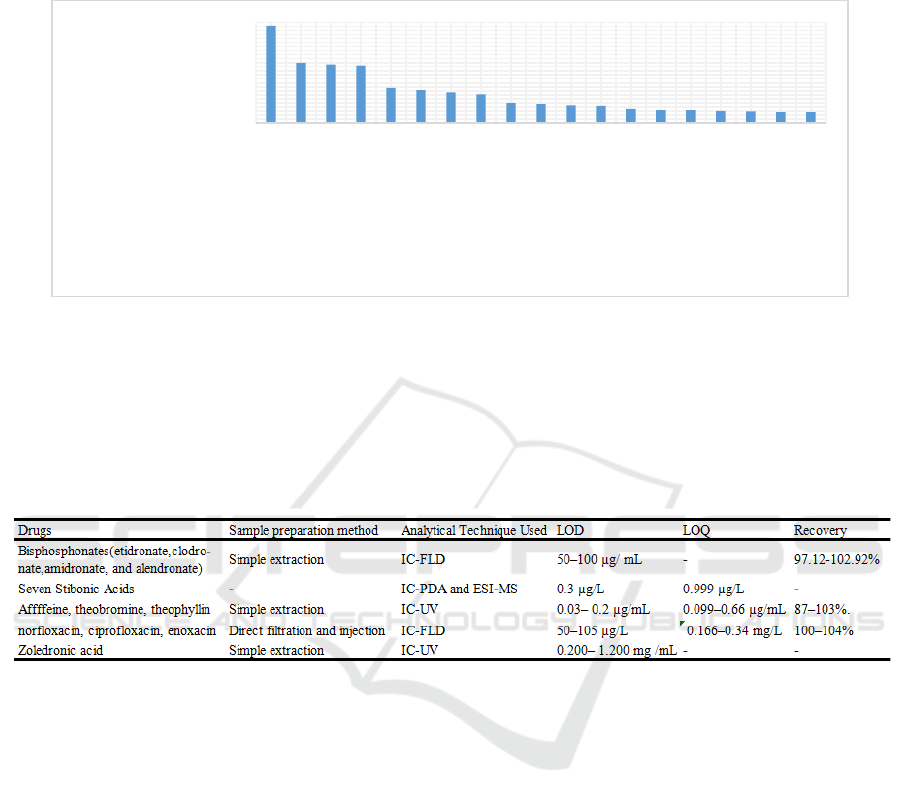
Figure 2: The distribution of major topics of the papers.
Figure 2 shows the different topics of the relevant
papers and their respective quantities. Study on
pharmacokinetics has taken up the highest number
with 242 articles in the recent 5 years, while the
HPLC method study ranked the second place with
close numbers of simultaneous determination and
chemical components. It can be inferred that HPLC
mainly serves in medicine analysis and the study on
purification for manufacture is rare.
Table 1: Application of IC-FLD/UV for the determination of different drugs.
Researches also concern about the comparison of
the application of HPLC by different drugs. Ion
chromatography (a type of HPLC with ion exchange
resin as solid phase) is used to analyse ionized
substance and table 1 gives figures of the
determination of several drugs applying IC
(Separovic et al. 2018). As it’s shown, FLD and UV
are commonly used as detectors, though the specific
condition of the chromatography could vary a lot. The
following data of each drug presented different
ranges of LOD and LOQ, indicating that the
performance of IC might be not universally
referential, while the same thing happened by
recovery with fluctuation of different degree. It might
be even doubtful whether HPLC is suitable for a
certain drug. Hence, a precise standard of HPLC
applicability for drugs should be defined to provide
more reference for quality analysis.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Overall, HPLC possesses good separation efficiency,
universal applications and easy operation, thus
making it practical in many fields of pharmaceutical
engineering. However, some disadvantages of HPLC
should not be neglected. Measurement uncertainty of
the equipment is a factor influencing the quality of
drug products. According to a study on HPLC
determination of amoxicillin tablets (Muhammad et
al. 2021), it has been found that the uncertainty of the
whole process exceeded the recommended value and
this has forced the manufacturer to take a higher risk.
This suggests that addictied measures should be taken
to check the accuracy during the process. Besides,
environmental burden and human health must be
considered since the organic solvents have a long-
term effect by accumulation. Recently, more and
more modified method using green solvents like
242
150
145
143
87
82
76
71
49
47
44
43
35
32 32
30
29
27 27
0
50
100
150
200
250
pharmacokin…
HPLC…
simultaneous…
chemical…
HPLC-MS/MS
fingerprint
biological…
drug…
primary…
liposome
quality…
impurity
in vitro and…
preparation…
antitumor…
nanoparticles
quality control
RP-HPLC
entrapment…
The Number of
Papers
Main topics of the papers
Applications of HPLC in Pharmaceutical Engineering
965

ethanol and acetic acid or even free solvent are being
proposed (Mya et al. 2020, Mikhail et al. 2021). It is
expected that more green and efficient methods will
be found and established.
Although some problems exist in the HPLC
method for pharmaceutical engineering, it still
remains the necessary technique in substance
purification, drug quality analysis and metabolism
assay. Wide range of application including chemical
drug, peptide drug, chiral drug and so on, makes it
adopted nearly throughout the whole process.
Overall, it is anticipated that more improved methods
will be put forward to overcome the shortcomings.
The findings above is aimed to provide some basic
facts of the applications of HPLC in pharmaceutical
engineering and more innovation of the method is
expected to be inspired.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The author thanks Professor Axel Zeitler for giving
lectures on introduction to pharmaceutical
engineering. The author also thanks the instructor
Cuihong Wang for her advice on this paper.
REFERENCES
Ahuja S. (2007). Overview of HPLC method development
for pharmaceuticals [J]. Separation Science &
Technology, 8:1-11.
Ara B, Rf A, Lz A, et al. (2020). Single-run reversed-phase
HPLC method for determining sertraline content,
enantiomeric purity, and related substances in drug
substance and finished product [J]. Journal of
Pharmaceutical Analysis, 10(6):610-616.
Bisht R, Rupenthal I D, Sreebhavan S, et al. (2017).
Development of a novel stability indicating RP-HPLC
method for quantification of Connexin43 mimetic
peptide and determination of its degradation kinetics in
biological fluids [J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical
Analysis, 7(6):365-373.
Dhabab J M, Al-Ameri S, Taufeeq A H. (2013). Separation
and determination of trifluoperazine and
prochlorperazine in pharmaceutical preparations by
HPLC [J]. Journal of the Association of Arab
Universities for Basic & Applied Sciences, 13(1):14-
18.
Gaudin A, Lepetre-Mouelhi S, Mougin J. (2015).
Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and metabolism of
squalenoyl adenosine nanoparticles in mice using dual
radio-labeling and radio-HPLC analysis [J]. Journal of
Controlled Release, 212:50-58.
Hong Y, Liao X, Chen Z. (2020). Determination of
bioactive components in the fruits of Cercis chinensis
Bunge by HPLC-MS/MS and quality evaluation by
principal components and hierarchical cluster analysis
[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis.
Kátia Roberta A. Belaz, Edenir Rodrigues Pereira-Filho,
Regina V. Oliveira. (2013). Development of achiral and
chiral 2D HPLC methods for analysis of albendazole
metabolites in microsomal fractions using multivariate
analysis for the in vitro metabolism [J]. Journal of
Chromatography B, 932:26-33.
Langer C, R Süss. (2021). HPLC-DAD-CAD-based
approach for the simultaneous analysis of hydrophobic
drugs and lipid compounds in liposomes and for
cyclodextrin/drug inclusion complexes [J]. Journal of
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 201:114120.
Liao X, Hong Y, Chen Z. (2021). Identification and
quantification of the bioactive components in
Osmanthus fragrans roots by HPLC-MS/MS [J].
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 11:299-307.
Luca C D, Felletti S, Lievore G, et al. (2020). Modern
trends in downstream processing of biotherapeutics
through continuous chromatography: The potential of
Multicolumn Countercurrent Solvent Gradient
Purification [J]. Trends in Analytical Chemistry,
132:116051.
Mikhail I E, Elmansi H, Belal F, et al. (2021). Green
micellar solvent-free HPLC and Spectrofluorimetric
determination of Favipiravir as one of COVID-19
antiviral regimens [J]. Microchemical Journal,
165:106189.
Mmg A, Sa A, Mf B, et al. (2020). Opportunities and
challenges of the tag-assisted protein purification
techniques: Applications in the pharmaceutical industry
[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 45:107653.
Muhammad N, Muhammad Z, Ali A. (2021). Ion
chromatography coupled with fluorescence/
UVdetector: A comprehensive review of its
applications in pesticides and pharmaceutical drug
analysis [J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,
14(3):102972
Mya B, Lf A, Tis B, et al. (2020). Development of a green
HPLC method for the analysis of artesunate and
amodiaquine impurities using Quality by Design [J].
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,
190:113507.
Nobilis M, Mikušek J, B Szotáková, et al. (2013).
Analytical power of LLE-HPLC-PDA-MS/MS in drug
metabolism studies: Identification of new nabumetone
metabolites [J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and
Biomedical Analysis, 80:164-172.
Rao N M, Sankar D G. (2015). Development and validation
of stability-indicating HPLC method for simeltaneous
determination of Lamivudine, Tenofovir, and
Dolutegravir in bulk and their tablet dosage form [J].
Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 1(2):73-77.
Schmitz S, Schnfeld D L, Freitag B, et al. (2019). Keeping
pace with the increasing demand for high quality drug
candidates in pharmaceutical research: Development of
a new two-step preparative tandem high performance
chromatographic system for the purification of
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
966

antibodies [J]. Journal of Chromatography B, 1104:18-
28.
Separovic L, Saviano A M, Loureno F R. (2018). Using
measurement uncertainty to assess the fitness for
purpose of an HPLC analytical method in the
pharmaceutical industry [J]. Measurement, 119:41-45.
Sws A, Jmk A, Dgh A, et al. (2020). A sensitive HPLC-
FLD method for the quantification of alpelisib, a novel
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in rat plasma:
Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic evaluation in
vitro and in vivo [J]. Journal of Chromatography B,
1163:122508.
Wu X, Deng Q, Xu Z, et al. (2013). The applications of
prepared HPLC in separation of natural product [J].
Electromechanical Information, 5:46-50.
Applications of HPLC in Pharmaceutical Engineering
967
