
Study on Gelatinization Behavior of Aging Rice Starch Granules at
High Temperature
Rui Song
a
School of Biological and Food Engineering, Anhui Polytechnic University, Wuhu, China
Keywords:
Rice Aging, Starch Granules, Gelatinization Behavior, Quality Deterioration.
Abstract:
Rice starch is one of the most important nutrition sources worldwide. In the current study, we prepared,
characterized and evaluated gelatinized glutinous rice starch. The main purpose of this study was to
investigate the effect of 95℃ slurry on the separation and functional properties of rice endosperm cells
granules aged for 12 months. Our results showed that during high temperature treatment, particle size
analysis observed that the degree of separation for endosperm cells granules decreased, morphology
examination suggested that the protein distribution was uneven, and starch granules was more difficult to
swelling. Morever, The texture of cooked aged rice was higher hardness, chewiness and gumminess while
lower adhesiveness, also higher setback value whereas lower breakdown value. Thus, different methods
have been proposed to classify that why the n vitro weight loss rate diminished for aged rice starch granules
at at high temperatures. These results provide a new basis for understanding aging mechanisms from the
pasting behavior of rice flour particles at high temperatures.
1 INTRODUCTION
1
More than half of the world’s population consumes
rice and rice products, rich in starch, as their main
staple food (Lamberts, De, Vandeputte, 2007). To
product flour for various food items, the quality of
aging rice needs to be increased. Aging is the most
common phenomenon in rice storage, but its
mechanism is still not fully understood. Starch is the
main ingredient of rice, since it is its most important
component. Rice products are mainly processed by
starch entities such as cooking, gelatinization, and
retrogradation properties, which are important
factors to consider when commercializing rice
products (Likitwattanasade, Hongsprabhas, 2010)
At present, most rice products, such as rice
cakes, baby food, and instant rice milk, are made
from rice noodles. Thus, there are many domestic
and overseas countries to improve the quality of rice
products through heat-moisture treatment, like the
superheated steam modifying wheat flour (Hu, Guo,
Liu, 2018), food crop starches (L, Y, X, 2019) and
potato starches (Hu, Guo, Liu, 2018), add functional
polysaccharides and enzyme preparations, etc (Heo,
Jeon, Lee, 2014). And China mainly from the
a
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0002-1911-5292
improvement of production process, delaying aging,
improving nutrition and other aspects of rice flour
(Advances on fermentation in rice noodle
production, 2013). During the storage process, the
microcrystal bundle structure of starch strengthens,
the molecular weight decreases, the content of
insoluble amylose increases. Due to these changes,
water molecules are contained in the cell so that
water absorption expansion force is too weak for the
aging starch granules to disperse, reducing the
amount of dissolved starch molecules and
consequently the texture. The current study
investigates the influence of high temperature on its
morphology and functional properties to validate the
theory and observations.
The aim of this paper is to clarify the separation
of high temperature starch granules by using inner
rice flour for endosperm cells aggregates. The
purpose is to study the gelatinization behavior under
the effect of high temperature gelatinization
treatment on the separation of new and aged rice
starch granules as well as the changes in functional
properties of aging rice, for understanding the
mechanism of rice aging and improve the process of
commercial manufactures of rice products.
Song, R.
Study on Gelatinization Behavior of Aging Rice Starch Granules at High Temperature.
DOI: 10.5220/0011375500003443
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics (ICBEB 2022), pages 1007-1012
ISBN: 978-989-758-595-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1007

2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
This study used freshly milled non-waxy japonica
rice harvested in Jiangsu Province, China with an
initial water content of 14.30±0.01%. All chemicals
and reagents used in the study were of analytical
grade.
2.2 Preparation of Endosperm Cell
The rice was first divided into two samples and
sealed in a bottle, with one sample stored at 4℃ as a
control and the other in a 37℃ incubator for 12
months to obtain the aged rice sample for further
testing (Zhou, Robards, Helliwell, 2010). The rice
samples were then milled using a fine rice machine.
Rice flours of both new and aged rice grains were
obtained by grinding the inner layer of rice grains,
which accounted for 15% in the whole rice grains.
20 g of kernel rice was crushed in the shredder for
20s The crushed powder further went through a 150-
mesh sieve, and then passed a120-mesh sieve. The
sieved powder (approximately with sizes finer than
100-125μm) were stored in a self-sealed pocket at
4℃ for later use.
2.3 Particle Size Analysis
Using a laser light scattering particle size analyzer,
we determined the particle size distribution of rice
flour particles. Then 0.2 g of samples was added to
the tube, followed by 10 mL of distilled water
vortexing for 1 minute to prevent the sticky wall
from dispersing the samples, which then pasted in a
95℃-water bath for 5 min. The sample was removed
and placed in a bath for 50℃ to prevent aging.
Particle size analysis was performed 5 times and
averaged using an ultrasound dispersion using water
as the dispersant at 1800 r/min, and the shading
between 10%-20% (Odeku, Itiola, 2007).
2.4 Light Microscope Observation
After completely dispersed using a vortex for 1 min,
rice flour particles were dispersed in distilled water
and heated in a water bath at 95 °C for 5 min. Then
the sample was kept in 50 °C before further testing.
After removed from water bath, the samples were
briefly vortexed for 1 min, dripped on slides with
0.02% iodine fluid, and covered with cover glass.
The particles were then observed and imaged under
a light microscope to observe its morphological
properties.
2.5 Scanning Electron Microscope
Observation
Following the same sample preparation method as
above, the sample was vortexed for 20s and set still
for 2 min. Supernatant was removed using a pipette
and the residues were washed three times through a
5 mm filter film using 10 mL of 50℃ distilled
water. The filter residue on the filter membrane was
dispersed into a petri dish. After the sample freeze-
dried, it was grinded and bagged, followed by
mounting to a circular aluminum stub with double-
sided sticky tape. After coating with gold to form a
thickness of 10 nm, the sample was examined and
photographed using a cold field emission scanning
electron microscope at an accelerating voltage of 15
kV.
2.6 Determination of the Textural
Properties
We implemented similar textual analysis method
similar to Huo et al., etc (Huo, Yuan, Tang, 2019)
methods with slight modifications. 2,000 g samples
were taken with 8 mL distilled water supplemented
to form a rice slurry suspension of 20%. The mixture
was stirred evenly in a 40 mm diameter small
aluminum box, heated at a constant temperature to
95℃ water bath for 15 min, and then cooled to room
temperature and stored in an upper 4℃ refrigerator
for 12 h. Each starch gel sample in the canister was
pressed to form distances of 30 mm (trigger force =
5.0 g) with a cylinder probe with 0.5 inch in
diameter at the speed of 1.0 mm/s during two
replication. The bite speed, pre-speed and post-speed
were all set at 1.0 mm/s, compressing the original
sample to 50% and residence time of 4s.
2.7 Determination of the Pasting
Properties
A 0.5g sample of rice flour was added to 4mL of
distilled water and stirred ten times quickly to
prevent sticking to the wall, and the starch pasting
viscosity measurement instrument (FDV-E) was
used to set the programmed temperature control: 50-
50℃, 5min; 50-95℃, 6min; 95-95℃, 4min; 95-
51℃, 6min; 51-51℃, 5min. peak viscosity (PV),
final viscosity (FV), Holding strength (HS) and
pasting temperature (PaT).
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1008
2.8 Determination of the in Vitro Mass
Loss Rate
We following the produced according to Li et al
(LI, YANG, XU, 2019) with slight modifications.
200 ± 0.1mg rice paste sample was added to 10ml of
distilled water in centrifuge tubes, heated up to 95℃
for 5min, added 6mL of artificial gastric juice, and
then digested at a constant temperature of 37℃ for 4
hours. After 10 min- centrifugation at 10,000 r/min,
the supernatant was discarded, and the precipitation
was washed three times with anhydrous ethanol. The
precipitation was dried at 105℃, and the the mass
loss rate of artificial gastric juice was calculated as
W1:
𝑊1 =
×100%
The above digested samples were combined with
6mL of artificial intestinal fluid and digested at a
constant temperature for 5h. Then the mixer was
centrifuged at 10,000 r/min for 10min, and the
supernatant was discarded, washed three times with
anhydrous ethanol and dried at 105℃. The mass loss
rate of artificial intestinal fluid, W2, was measured
and calculated as the following:
𝑊2 =
×100%
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Starch Particle Size Analysis
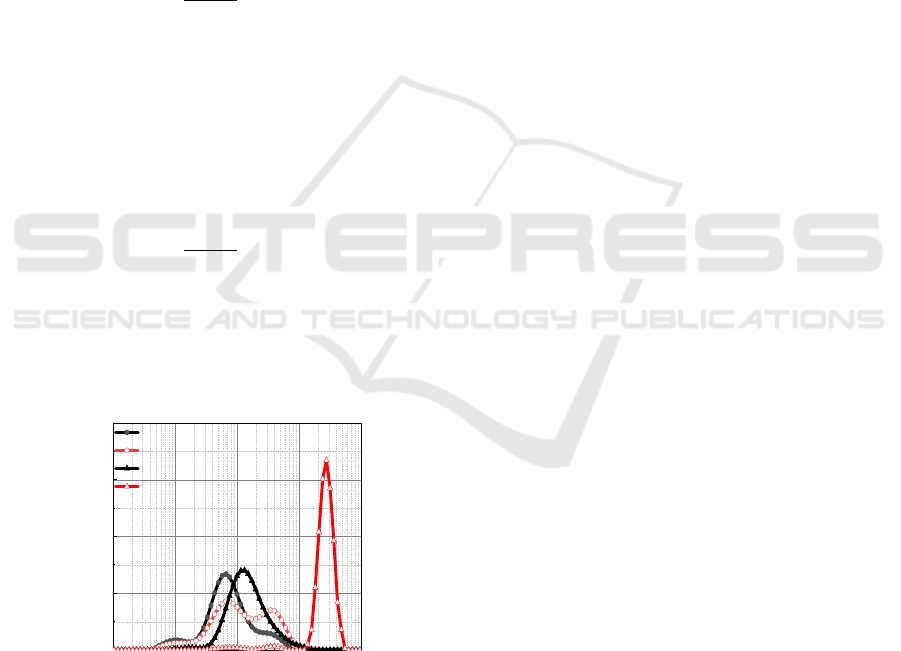
Figure 1: Starch granule particle size distribution of native
and gelatinized starch at 25℃and 95℃. (Black curve:
fresh rice; red dashed curve: aging rice).
It is obvious from the above figure that the new
rice particle distribution after 95℃ compared that
with room temperature. Three particle size peaks are
shown in the figure. The peak of middle particles
with most of it concentrating near 7 um, which
belongs to the range of single starch (JANE,
KASEMSUWAN, LEAS, 2010). The peaks of small
particle sizes are concentrated around 1 um and fall
within the range of protein bodies. (COFFMAN,
JULIANO, 1987) Large particle size peaks are
concentrated in the range of 40 um and found in
endosperm cells (PAN, ZHAO, LIN, 2017). At room
temperature, in addition to the easy dissociation
between the endosperm cells, the starch granules
also disaggregated easily between the fresh rice;
while the aged rice only dissociated easily between
the endosperm cells, but it was difficult to
disaggregate between starch granules, which was
reflected by the higher peak of the endosperm cells
than the starch granules in the aged rice, indicating
that aging had little effect on the dissociation
between the cells, but mainly affected the tightness
of the bond between the starch granules. When aged
rice is pasted at 95℃, the small particle size peak
decreases to a certain extent, while the large particle
size peak increases. Moreover, fresh rice peak
position shifted to the right. It appears that even the
native rice has difficulties in endosperm cells, and
endosperm cells between starch granules separate
more completely,
Rice flour granules can be sorted into small
starch granules, swelling, and unbroken rice flour
particles. Aged rice becomes difficult to separate
between starch granules within endosperm cells,
which decreases the volume fraction of small
particle size peaks. In aged rice, gelatinization at
high temperatures inhibits the depolymerization of
starch granules while promoting slightly their
swelling. Due to uneven water absorption and
swelling of rice noodle particles, the edge of larger
particles scatters and falls off, and then the internal
particles absorb water and dissolve. Water is more
easily absorbed and swollen by thinner particles.
Consequently, the amount of small and middle
particle granules decrease while glued at 95℃, and
the amount of larger particle gradually increases.
3.2 Light Microscope
The new rice disaggregated more smaller particles at
95°C than the old rice. There is less cracking on the
aged rice starch granules, because the edges of the
rice flour particles, are dissociated, and there are
fewer granules in the cell wall. There is high edge
dissociation in rice flour particles, a small swelling
of starch granules, and the boundaries between the
cell walls is. The degree of fresh rice flour is
0.1 1 10 100 1000
0
6
12
18
24
Volume(%)
Particle diameter (μm)
Fresh rice flour at 25℃
Aging rice flour at 25℃
Fresh rice flour at 95℃
Aging rice flour at 95℃
Study on Gelatinization Behavior of Aging Rice Starch Granules at High Temperature
1009
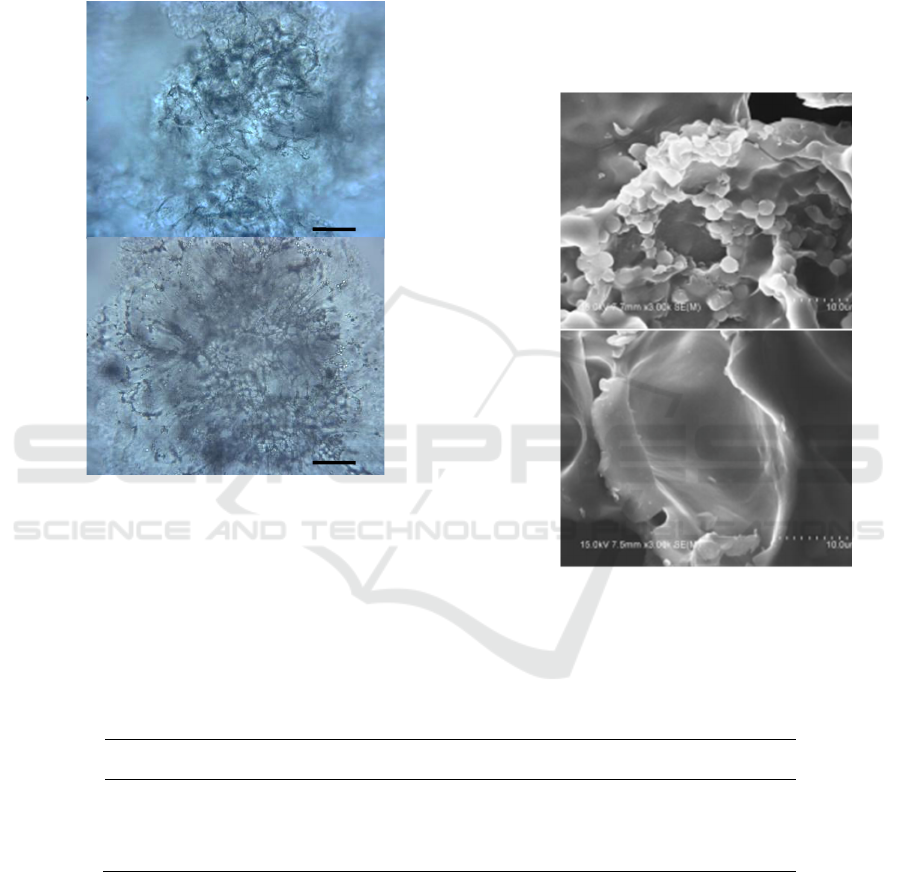
uniform, most of which is higher than that of old
rice. the starch granules are larger and the cell wall
boundary is clear and thick. The aging rice shows
more protein body in the grain rim, meaning that the
body has expanded; the protein body in the new rice
is evenly distributed throughout the rice flour
particles, indicating that it is more likely to dissolve.
Figure 2: Light microscope images of fresh (A) vs. aged
rice particles (B) at 400× resolution.
3.3 Scanning Electron Microscope
In scanning electron microscope (SEM)
observations, fresh rice flour after swelling has a
loose structure, the particles are small, and aging
rice has a small swelling degree. as Along with the
overall swelling, compact structure, which is
consistent with those of the particle distribution
analysis for fresh rice paste starch compound or cell
loss left diameter larger pit. Moreover, it can be seen
that the starch shed inner wall has a smaller and
shedding pit, and the protein body is more
concentrated in the edge and more exposed. Despite
this, the starch particle shedding pit is small and
shallow, its diameter is large, the inner wall is
smooth, not as thick, and partially buried in the
starch.
Figure 3: Electron microscope images of fresh (A)vs. aged
rice granules (B) at 3000× resolutions.
3.4 Gel Texture
Table 1: Measured hardness, adhesiveness, chewiness, and gumminess of fresh and aged rice flour.
Type Hardness/N Adhesiveness/N chewiness/N
gumminess/N
Fresh 1.507±0.0084 0.373±0.031 1.326±0.081 1.328±0.081
Aging 1.840±0.016 0.548±0.064 2.101±0.218 1.537±0.070
Rice is often been characterized by the texture of
it (such as hardness, chewiness and adhesiveness).
Changes in starch gel hardness are related to the
starch colloid structure. According to studies, rice
hardness is positively related to rice protein content
(Zhu, Wu, Cheng, 2020). It can be seen that when
under 95℃ the four texture parameters of aged rice
flours are significantly higher than that of native rice
flours, higher hardness and chewing are the typical
characteristics of aging. (Table 1). It is possible that
the central part of fresh starch granules becomes
fully gelatinized during cooking because increased
soluble solids, resulting in a softer texture (low
hardness). Aged rice slurry has significantly
improved hardness and chewiness compared with
new rice. their because fresh endosperm cells are
50μm
A
50μm
B
A
B
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1010
relatively brittle, easy to rupture and form a sticky
state. When aged rice undergoes oxidation, the rice
protein located around the starch granules becomes
cross-linked, preventing them from absorbing water
and swelling, resulting in insufficient gelatinization.
Additionally, the disulfide bond increases during
heating, and the stronger binding effect of protein
and starch promotes the formation of gel network
structures. Aged rice becomes harder, gummier, and
chewier as the gel strength and force needed to grow
stronger when chewing. For rice grains, the hardness
is increased after the aging, but its adhesiveness is
reduced; and for rice glue, the hardness and
adhesiveness of the aged increase (Wu, Li, Bai,
2019), maybe since the aged rice particles in glue
are large and the clearance space is small, the
surface solids of the unit particles are relatively
large, or the small amount of aged starch particles
dissociated are more likely to rupture.
3.5 Determination of the Pasting
Properties
Table 2: Measured PaT, PV, HS, and FV of fresh and aged
rice flour.
Type Fresh rice flour Aging rice flour
PaT/℃ 71.467±0.702 72.667±1.457
PV/cP 1424.167±37.942 1080.833±27.651
HS/cP 639.167±5.774 685.000±17.321
FV/cP 1395.000±70.134 1415.833±13.769
From Table 2, it can be seen that aging increases
the FV, the PV decreases significantly, and the HS
does not change much and increases slowly a little.
The breakdown (BD) value decreases and the
setback(SB) value increases. BD value is the most
sensitive indicator in pasting properties, the decrease
in BD value indicates that the less starch particles
are released in heating. The smaller the decreases,
the smaller the taste (Zhang, Xu, Jiang, 2021) The
SB value represents the stability and aging trend of
starch cold paste, the larger value, the more prone to
aging, the worse the quality of eating. Moreover, the
increase of pasting temperature indicates that the
pasting ability of starch is inhibited, the degree of
water absorption and dissociation and dispersion of
starch gradually decreases, and the energy required
for gelatinization increases. It can be seen that aging
increases the degree of swelling of rice flour but it is
difficult to break the granules, the number of
remaining starch granules is smaller, the viscosity
and the eating quality decreases.
3.6 Determination of the in Vitro
Weight Loss Rate
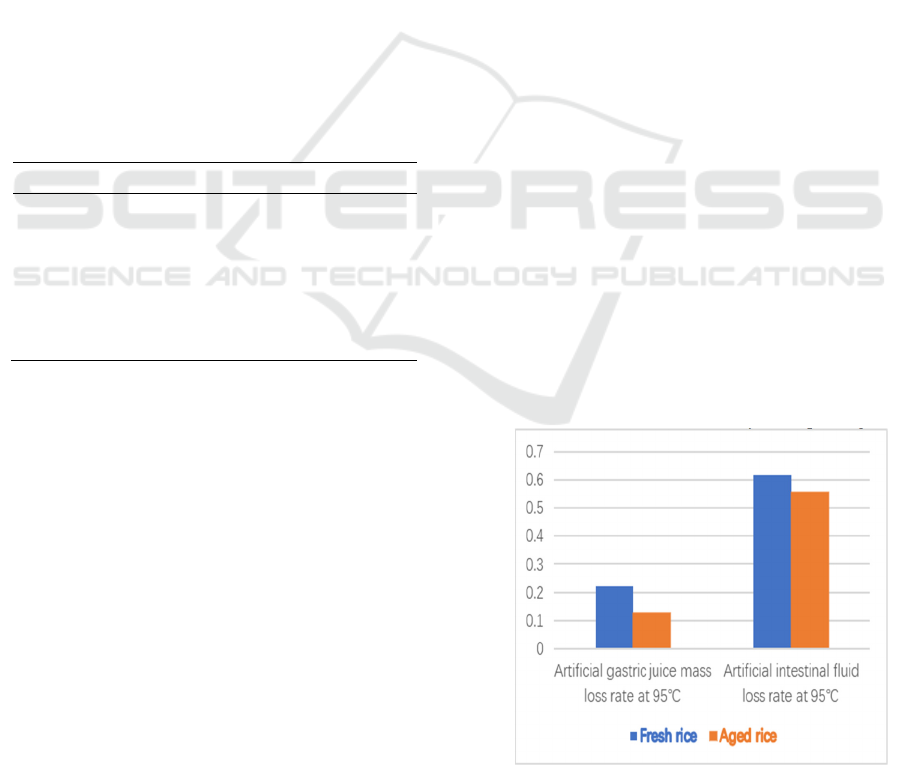
Studies reveal that the degree of gelatinization of
rice flour is closely related to its in vitro digestibility
(Molecular disassembly of rice and lotus starches
during thermal processing and its effect on starch
digestibility, 2016). Investigate the influence of rice
flour particle size on the degree of gelatinization
using in vitro digestibility studies. In Figure 5,
which simulates in vitro digestion of artificial gastric
juice and artificial intestinal juice. It is shown that
gelatinized rice at high temperatures is also
digestible in artificial gastric juice and artificial
intestinal juice, and new rice noodles can be digested
at higher temperatures than old rice noodles.
Therefore, after high-temperature gelatinization, rice
starch granules are more prone to absorbing water,
swelling and can be more easily hydrolyzed by
digestive enzymes. Leading to the increase of the
rate of the digestibility in aged rice starch granules
expand with temperature. The higher the aged rice
paste, the greater the degree of gelatinization of aged
rice noodles, the greater the degree of swelling in
aging rice flour. Moreover, compared with new rice
starch, the old losses less weight in vitro.is still
decline. It is possible that aged rice flour particles
are difficult to dissolve and highly gelatinized under
high temperatures, which impedes enzymes from
entering the particles and slow digestion. Therefore,
the digestion rate of new rice noodles is affected by
both rate dispersion and rate of gelatinization.
furthermore, aging rice slurry are mainly affected by
gelatinization due to their difficulty in dispersing.
Figure 3. Calculated simulated gastric juice mass loss rate
and artificial intestinal fluid loss rate of fresh vs. aged rice.
Study on Gelatinization Behavior of Aging Rice Starch Granules at High Temperature
1011

4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, we investigated the effect of high
temperature on the gelatinization behavior and
functional properties of fresh and aged rice in non-
waxy rice flour. After gelatinization at 95 ℃. Aging
endosperm cells are harder to separate into
individual starch and protein bodies. Aged rice
starch particles has difficulty swelling and
dissociation, and dispersion outside the particles.
Morphological observation showed aged rice starch
granules contain more tightly bound protein and
starch. TPA indicated higher hardness, chewiness
and gumminess, while lower adhesiveness. FDV
revealed higher SB whereas lower BD. These can
lead to starch-protein complexes forming, which
may be difficult to disperse due to insufficient
friction between granules or surface polymerization
force, and low gelation and low degree of digestion.
The quality deterioration after high temperature
gelatinization of aging rice starch granules can be
explained by owing to the increasing gel strength of
starch-protein complexes, as well as decline of low
water absorption ability swelling, and permeability,
contributing to starch granules difficult to
dissociation, which interfere with the absorption of
internal starch. This will provide a basis for
discovering the mechanism of rice aging, and then
regulating its edible quality.
REFERENCES
Advances on fermentation in rice noodle production[J].
Food and Machinery, 2013, 29(5): 223-225.
Chengmei L, Xiaoyan Y, Xingfeng X, et al. Changes in
Granular Swelling and Rheological Properties of Food
Crop Starches Modified by Superheated Steam [J].
Starch - Starke, 2019, 71(3-4): 1800132.
Coffman W R, Juliano B O. Rice: Nutritional Quality of
Cereal Grains: Genetic and Agronomic Improvement
[M]. Nutritional Quality of Cereal Grains: Genetic and
Agronomic Improvement, 1987.
Hu X, Guo B, Liu C, et al. Modification of potato starch
by using superheated steam [J]. Carbohydrate
Polymers, 2018, 198(19-20): 375-384.
Heo S, Jeon S, Lee S. Utilization of Lentinus edodes
mushroom β-glucan to enhance the functional
properties of gluten-free rice noodles [J]. LWT - Food
Science and Technology, 2014, 55(2): 627-631.
Huo Y Q, Yuan B H, Tang S W, et al. Effect of rice gluten
on gelatinization and gel properties of rice starch[J].
Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,
2019, 34(6):1-5
Jane J L, Kasemsuwan T, Leas S, et al. Anthology of
Starch Granule Morphology by Scanning Electron
Microscopy [J]. Starch ‐ Strke, 2010, 46(4): 121-129.
Lamberts L, De Bie E, Vandeputte G E, et al. Effect of
milling on colour and nutritional properties of rice [J].
Food Chemistry, 2007, 100(4): 1496-1503.
Likitwattanasade T, Hongsprabhas P. Effect of storage
proteins on pasting properties and microstructure of
Thai rice [J]. Food Research International, 2010,
43(5): 1402-1409.
Li Shanshan, Yang Ping, Xu Xin, et al. Preparation and in
Vitro Digestibility of Potato ResistantStarch [J]. Farm
Products Processing, 2019, 472(2): 18-22.
Molecular disassembly of rice and lotus starches during
thermal processing and its effect on starch digestibility
[J]. Food & Function, 2016, 7(2): 1188-1195.
Odeku O A, Itiola O A. Compaction Properties of Three
Types of Starch [J]. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical
Research, 2007, 6(1): 17-23.
Pan T, Zhao L, Lin L, et al. Changes in kernel morphology
and starch properties of high-amylose brown rice
during the cooking process [J]. Food Hydrocolloids,
2017, 66(3): 227-236.
Wu P, Li C, Bai Y, et al. A starch molecular basis for
aging-induced changes in pasting and textural
properties of waxy rice [J]. Food Chemistry, 2019,
284(11-12): 270-278.
Zhou Z, Robards K, Helliwell S, et al. Effect of storage
temperature on rice thermal properties [J]. Food
Research International, 2010, 43(3): 709-715.
Zhu L, Wu G, Cheng L, et al. Investigation on molecular
and morphology changes of protein and starch in rice
kernel during cooking [J]. Food Chemistry, 2020,
316(11-12): 126262.
Zhang D, Xu H, Jiang B, et al. Effects of ultrahigh
pressure on the morphological and physicochemical
properties of lily starch [J]. Food Science & Nutrition,
2021, 9(2): 952-962.
ICBEB 2022 - The International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Bioinformatics
1012
