
Breathing Life into Models: The Next Generation of Enterprise Modeling
Peter Fettke
1,2 a
and Wolfgang Reisig
3 b
1
German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), Saarbr
¨
ucken, Germany
2
Saarland University, Saarbr
¨
ucken, Germany
3
Humboldt-Universit
¨
at zu Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Keywords:
Systems Composition, Data Modeling, Behaviour Modeling, Process Modeling, Composition Calculus,
Algebraic Specification, Systems Mining.
Abstract:
Edsger W. Dijkstra has frequently suggested building a “firewall” between the technology- and application-
side of computer science. His justification: The methods to attack the computer scientists’ formal, mathemati-
cal “correctness problem” differ fundamentally from the methods to attack the applicants’ informal “pleasant-
ness problem”. In this setting, a model is always confined to one side or the other of this wall. This keynote
shows that a seamless transition between both sides can be achieved by a framework with architecture, statics,
and dynamics as the three pillars of modeling computer-integrated systems. Selected examples justify this
framework. It allows to “breath life” into (static) models, and it implies a new understanding of the “pleasant-
ness” of computer-integrated systems, which is well-needed in the age of “digital first”.
1 INTRODUCTION: THE TWO
FACES OF COMPUTER
SCIENCE
Computer-integrated systems exhibit two faces: the
technological and the applied face. Edsger W. Dijk-
stra has frequently suggested to strictly separate both
sides and to build a “firewall” between them (Dijkstra,
1989). His justification: The methods to attack the
computer scientists’ formal, mathematical “correct-
ness problem” differ fundamentally from the methods
to attack the applicants’ informal “pleasantness prob-
lem”. In this setting, a model is always confined to
one side or the other of this wall.
In contrast to Dijkstra, we understand modeling
as an activity that should allow a seamless transition
between formally and informally given or asserted
facts of a computer-integrated system. Technology
and applications must be interlocked by shared mod-
els, based on the same foundations.
This keynote shows that our goal can be achieved
by the HERAKLIT framework with architecture, stat-
ics, and dynamics as the three pillars of model-
ing computer-integrated systems (Fettke and Reisig,
2021a; Fettke and Reisig, 2021b). Selected examples
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0624-4431
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7026-2810
justify this framework. It allows to “breathe life” into
previous static, logic-based models, and it implies a
new understanding of the “pleasantness” of computer-
integrated systems. This is a key to understanding
systems in the age of “digital first”.
This contribution consists of five sections. After
this introduction, Section 2 explains what is needed
for the foundations of computer-integrated systems
from the application perspective. Section 3 presents
our approach to digital modeling through a plain case
study. Main characteristics of HERAKLIT and related
work are discussed in Section 4 and 5, respectively.
The paper concludes with Section 6.
2 TOWARDS FOUNDATIONS FOR
THE APPLICATION SIDE OF
COMPUTER SCIENCE
In the last decades, computing-oriented disciplines
have developed several strong ideas for the founda-
tions of computer science. Typically, foundations
of computer science stem from technical foundations
such as abstractions of hardware, physical devices,
sensors, actuators, etc. Another approach stems from
theoretical computer science, starting with alphabets,
formal languages, computable functions, etc.
Fettke, P. and Reisig, W.
Breathing Life into Models: The Next Generation of Enterprise Modeling.
DOI: 10.5220/0011376600003266
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Software Technologies (ICSOFT 2022), pages 7-14
ISBN: 978-989-758-588-3; ISSN: 2184-2833
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
7

But what are the foundations from the application-
side of computer science? In this contribution, we
argue that such foundations must cope with three fun-
damental phenomena:
• Architecture: Computer-integrated systems in the
real or an imagined world are not monolithic,
amorphous, or unstructured, but can best be de-
scribed and understood as the composition of dif-
ferent sub-systems. Hence, composing a system is
inevitable for the proper understanding of a com-
plex system. In one sentence: composition mat-
ters!
• Statics: Computer-integrated systems process
data. However, the world we live in consists
not only of symbolic data objects but of many
more relevant objects, e.g. invoices, customers,
agreements, orders, and products. These objects
need to be understood and represented adequately.
Again, in one sentence: objects matter!
• Dynamics: The world is not static, but continu-
ously evolving. Events happen all over the world
in time and space. A system’s progress in time
induces an order of events; however, this order is
irrelevant for a proper understanding of the event
flow. On the contrary, it spoils the causal order of
events, which orders two events a and b by a < b
if and only if a is a prerequisite for b. Of course,
a < b implies each potential clock to timestamp
a before b. But a timestamped before b only im-
plies that b is not a prerequisite for a. Again, in
one sentence: causality matters!
To sum up, composition, objects, and causality
are important for understanding the application side
of computer science. In other words, the world we
are living in matters. In our contribution, we show
that HERAKLIT, an integrated modeling framework
to formally describe the aspects mentioned before, is
indeed feasible.
3 A PLAIN EXAMPLE
The following subsections illustrate the three HER-
AKLIT’s pillars by the plain example of a digital
stamp, a stamp that is augmented with a matrix code.
Fig. 1 depicts one exemplar of a digital stamp; each
digital stamp carries a unique matrix code for individ-
ual identification.
3.1 Architecture
The basic concept of architecture is modules. Inside a
module, HERAKLIT typically uses Petri nets in vari-
Figure 1: Digital stamp with matrix code (right).
ous forms. In general, a module M has two interfaces,
the left interface
∗
M, and the right interface M
∗
. An
interface can contain Petri net places as well as transi-
tions. Graphically, a module is represented as a rect-
angle, with the elements of the left interface on the
left or top edge of the rectangle and the elements of
the right interface on the right or bottom edge.
Fig. 2 shows a typical model for the transporta-
tion of conventional letters. There are three modules:
the sender, the postal service, and the receiver. The
left interface of the sender is empty, its right interface
contains a Petri net transition. The label of this tran-
sition, post, matches the labels of the transition of the
left interface of the postal service; transitions with the
same labels are merged later on when the two mod-
ules will be composed. Likewise, the right interface
of the postal service and the left interface of the re-
ceiver contain equally labeled transitions.
The labels of the interface elements indicate the
behavior and functionality of the modules: the sender
posts each letter to the postal service. The postal ser-
vice delivers each letter to the receiver. The receiver
finds the letter in its inbox.
Fig. 3 shows the composition of the three mod-
ules, namely:
sender • postal service • receiver (1)
with “•” being the universal composition opera-
tor. This bracket free notation is possible since the
composition operator is associative, i.e. for any three
models R, S, T holds (Reisig, 2019):
(R • S) • T = R • (S • T ). (2)
The greatest possible abstraction of the modules
is depicted in Fig. 4. Two activities of a postal ser-
vice are modeled: post and deliver a letter; techni-
cally as Petri net transitions in
∗
postal service and
postal service
∗
with the labels post and deliver, re-
spectively.
3.2 Statics
In each postal service, three sets of items play a cen-
tral role: letters, stamps, and matrix codes. In a
postal service, these quantities consists of different
elements: each postal service has different sets of let-
ters, stamps, and matrix codes.
ICSOFT 2022 - 17th International Conference on Software Technologies
8
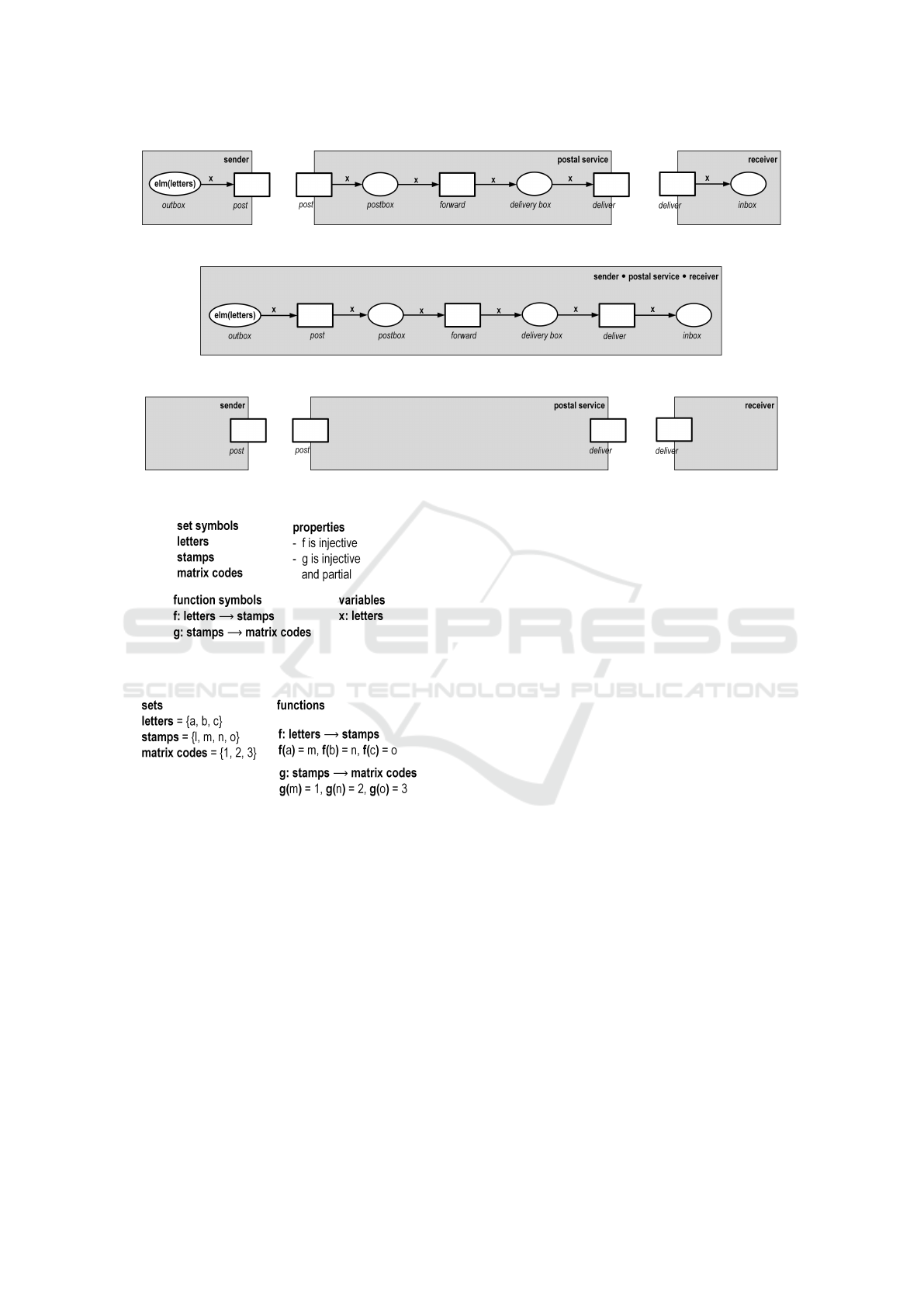
Figure 2: Three modules: sender, postal service, and receiver.
Figure 3: The composition sender • postal service • receiver.
Figure 4: The abstract form of the three modules sender, postal service, and receiver.
Figure 5: Signature Σ
0
.
Figure 6: Σ-structure S
0
.
Nevertheless, to formulate the processes for all
postal services in the same way, we use a signature,
Σ
0
, shown in Fig. 5, a technique to model a schema.
This technique allows to characterize concrete objects
from the real and imagined world as instantiations of
such a schema. Here, we adopt notions such as struc-
tures, signatures, and instantiations of signatures, that
are well-known from first-order logic (Suppes, 1957).
Technically, a signature is just a set of sorted sym-
bols for sets, constants, and functions. An instantia-
tion interprets these symbols consistently. We extend
signatures by requirements to exclude “unwanted” in-
stantiations.
In the example, the signature contains the three
symbols letters, stamps, and matrix codes for the
three sets described above, plus two symbols ( f and
g) for functions. The symbol f stands for a function
that assigns to each letter its stamp; g for a function
that assigns to each stamp its matrix code. Both func-
tions are injective. The function symbol g stands for
a function that is only partially defined since some
stamps do not carry a matrix code.
The signature Σ
0
can be instantiated in many
ways. Each concrete postal service is characterized
by such an instantiation of the signature. In the case
study, we discuss the instantiation S
0
of Fig. 6. This
instantiation consists of three letters (a, b, c), four
stamps (l, m, n, o), three matrix codes (1, 2, 3), and
a particular assignment between letters, stamps, and
matrix codes. For example, letter a is assigned to
stamp m; stamp m is assigned to matrix code 1.
3.3 The Behavior of the Three Modules
at the Schema Level
Signatures and their instantiations can naturally be
transferred to define Petri net schemata. Such a sche-
ma can be instantiated in different ways; each instan-
tiation results in a concrete Petri net.
We model the behavior of each of the three mod-
ules from Fig. 2. Fig. 3 shows the behavior of each
module at the schema level, i.e. based on the signature
Σ
0
, rather than a single instantiation. As a mathemat-
ical concept, a place represents a predicate that ap-
plies to a set of objects. This set can grow and shrink
through the entry of transitions.
The sender module in Fig. 2 describes the letters to
be sent. The question of an appropriate initial mark-
ing arises: for a given instantiation, i.e. a concrete
Breathing Life into Models: The Next Generation of Enterprise Modeling
9

postal service, the place outbox initially contains all
letters as tokens. In the example of the structure S
0
from Fig. 6, these are the three tokens a, b, and c.
On the schematic level, we only know the symbol let-
ters, for which each instantiation can freely choose an
assignment with a set of letters. However, the intu-
itively obvious idea of labeling the place outbox with
the symbol “letters” falls short: when instantiating
the symbol letters with a set, for example {a, b, c},
initially this set would emerge as a single token. How-
ever, we want the three elements of this set as individ-
ual tokens. This is noted as “elm(letters)”.
Mathematically, the idea behind this is that a place
represents a predicate that currently applies to the to-
kens on the place. The place outbox with the inscrip-
tion elm(letters) thus stands for the logical expression:
∀x ∈ letters : outbox(x). (3)
The instantiation S
0
thus generates in the ini-
tial marking the logical expression ∀x ∈ {a, b, c} :
outbox(x). Thus, initially, the three tokens a, b, c lie
on the place outbox.
In a given instantiation S
0
, the transition post can
occur in the sender or postal service module as soon
as a token is present on the place outbox. The assign-
ment of the variable x can freely be chosen from the
set with which the instantiation S
0
instantiates the set
symbol letters. In analogy, the postal service module
forwards one letter from the postbox to the delivery
box. Finally, the letter is delivered to the receiver.
3.4 The Instantiation S
0
and its
Behavior
Fig. 7 shows three instantiated modules; Fig. 8 shows
the module system S
0
, which is created from the mod-
ules of Fig. 2 in two steps: first, the three modules
from Fig. 2 are composed into a single module, and
second, the signature Σ
0
of Fig. 5 is instantiated with
the structure S
0
of Fig. 6. In particular, the place out-
box now contains three tokens.
In the instantiation S
0
, one can now document the
processing of individual postal services. In the ini-
tial state, for example, the transition post is activated.
After that, the letter can be posted by the sender, for-
warded to the delivery box, and be delivered to the
receiver.
HERAKLIT models a behavior as a distributed run;
formally conceived as a module. This makes it easy to
compose distributed runs. The current example also
shows that distributed runs show details of behavior
much more explicitly than is possible with sequential
runs. In particular, relationships between objects and
causality is explicitly modeled.
Fig. 9 shows what happens with the letter a: The
letter moves from the sender’s outbox to the postbox,
then to the delivery box and finally to the receiver’s
inbox. Technically, this is the run of letter a in the
system S
0
. Fig. 8 depicts two more letters, b and c,
yielding corresponding runs. Together, the three runs
of a, b, and c define the overall run of the system
S
0
, shown in Fig. 10. In the run of each single letter,
the events post, forward and deliver occur strictly or-
dered. As the letters proceed independently of each
other, the events of different letters occur indepen-
dently, namely their occurrences are not ordered in
the overall run of the system S
0
.
Fig. 10 exemplifies that events are not ordered
along a time axis; instead, order represents causal-
ity. For example, the event forward for letter a oc-
curs causally after the event post for letter a, but is
causally independent from all events of the letters b
and c. The run of Fig. 10 is the only run of the sys-
tem S
0
in Fig. 8. System S
0
is deterministic, as there
is never a decision to be taken; and S
0
is concurrent,
as some events occur unordered. One may neverthe-
less introduce global views into the run of Fig. 10.
A global view is a maximal set of unordered places.
Each of the three letters can be in exactly one of the
four boxes. In technical terms, each such set corre-
sponds to one of the 64 (= 4 ×4 ×4) reachable mark-
ings of the system in Fig. 8.
4 MAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF
HERAKLIT
The main characteristics of the HERAKLIT frame-
work were introduced by means of a plain exam-
ple. From a conceptual point of view, the HERAK-
LIT framework is based on three pillars (Fettke and
Reisig, 2021a; Fettke and Reisig, 2021b). Each pillar
focuses on different but integrated aspects of model-
ing (Fig. 11):
• Architecture: A HERAKLIT model consists of
modules. Each module has an arbitrarily designed
interior; in particular, the level of abstraction of
the representation is freely selectable. The inter-
face of a module contains labeled elements. The
composition of modules is technically simple and
always associative. The formal basis of this ar-
chitectural principle is the composition calculus
(Reisig, 2019).
• Statics: For dealing with data and data structures,
HERAKLIT employs abstract data types and al-
gebraic specifications, as they have turned out to
be useful in computer science from the begin-
ICSOFT 2022 - 17th International Conference on Software Technologies
10

Figure 7: Three instantiated modules.
Figure 8: System S
0
.
Figure 9: The run of letter a.
Figure 10: The run of S
0
.
ning and have long been used in specification lan-
guages such as V DM, Z, etc. (Sanella and Tar-
lecki, 2012). Symbolic representations (in terms
of a signature) are used as in predicate logic. Each
module has a signature, i.e. a set of symbols for
sets, constants, and functions, from which, to-
gether with variables, terms are then formed. A
signature, and thus its terms, can be instantiated
in quite different ways.
• Dynamics: A module for describing behavior
contains a Petri net inside of it. Here, each place
of the Petri net is a logical predicate, each arrow
is labeled with a term of the module’s signature,
and each transition with a condition. For a given
instantiation of the signature, the set of objects
to which the predicate applies can grow or shrink
due to the occurrence of an event. In detail, this
is described by terms at the arrows of the Petri
net. This allows behavior to be represented ab-
stractly on a schematic level, but also concretely
for a “meant” instantiation.
Figure 11: The three pillars of HERAKLIT.
Breathing Life into Models: The Next Generation of Enterprise Modeling
11

5 RELATED WORK
In the last decades, a plethora of modeling frame-
works emerged (Frank et al., 2014; Sandkuhl et al.,
2018; Vernadate, 2020; Wand and Weber, 2002).
In 1992 already, some colleagues coined the term
“methodology jungle” for characterizing the variety
and diversity of the research field (ter Hofstede and
van der Heide, 1992). Nowadays, this field is still
evolving and maturing. Relevant work can be ap-
proached from different angles, e.g. the problem ad-
dressed or the solution purported.
In the field of business informatics, typical frame-
works used are Architecture for Integrated Informa-
tion Systems (ARIS) (Scheer, 1999), Business Process
Model and Notation (BPMN) (Object Management
Group, 2014), Event-Driven Process Chains (EPC)
(Keller et al., 1992), MEMO (Frank, 2014), the St.
Gallen Approach to Business Engineering (
¨
Osterle,
1995; Winter, 2001), and Unified Modeling Language
(UML) (Object Management Group, 2017). Most
of them offer graphical representations to describe
behavior (e.g. BPMN, EPC), some have expressive
means for data structures (e.g. ARIS, MEMO), and in
some cases also for schemas (MEMO). Some known
frameworks use more or less formally defined com-
position operations. None of the frameworks are fully
formally defined but describe many aspects only intu-
itively. Thus, no other framework reaches the scope
of expressive means of HERAKLIT. This characteri-
zation is also true for frameworks stemming from the
information systems discipline, e.g. Bunge’s ontolog-
ical model (Wand and Weber, 1990) or work system
theory (Alter, 2013).
From a computer science perspective, several
modeling frameworks were proposed, e.g. Abstract
State Machines (ASM) (Gurevich, 2000), Aloy (Jack-
son, 1987), High-level Petri Nets (Genrich and Laut-
enbach, 1981; Jensen and Kristensen, 2009), event-
B (Abrial, 2005), FOCUS (Broy, 1997; Broy and
Stolen, 2001), Statecharts (Harel, 1987), TLA (Lam-
port, 2002), and Z (Spivey, 1992). The central
ideas and concepts of HERAKLIT combine three well-
proven, intuitively easy to understand, and mathe-
matically sound concepts that have been used for the
specification of systems in the past:
• Architecture: The composition calculus for struc-
turing large systems. This calculus with its widely
applicable associative composition operator is the
most recent contribution to the foundations of
HERAKLIT. The obvious idea, often discussed in
literature, of modeling composition as fusion of
equally labeled interface elements of modules is
supplemented by the distinction of left and right
interface elements, and composition A • B as fu-
sion of right interface elements of A with left
interface elements of B. According to (Reisig,
2019), this composition is associative (as opposed
to the naive fusion of interface elements); it also
has several other useful properties. In particu-
lar, the composition is compatible with refinement
and with single (distributed) runs.
• Statics: Abstract data types and algebraic spec-
ifications for the formulation of concrete and
abstract data: since the 1970s such specifica-
tions have been utilized, built into specification
languages, and often used for (domain-specific)
modeling. (Sanella and Tarlecki, 2012) presents
systematically the theoretical foundations and
some applications of algebraic specifications.
• Dynamics: Petri nets for formulating dynamic be-
havior: HERAKLIT uses the central ideas of Petri
nets (Petri, 1962; Reisig, 2013). A step of a sys-
tem, especially of a large system, has locally lim-
ited causes and effects (Petri, 1977). This allows
processes to be described without having to use
global states and globally effective steps. The
connection with algebraic specifications is estab-
lished by (Reisig, 1991).
These three theoretical principles harmonize to-
gether and generate further best-practice concepts that
contribute to a methodical approach of modeling with
HERAKLIT and which could only be touched upon in
this keynote. On the downside, industrially mature
tools for HERAKLIT are still under development.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The fundamental focus of our approach becomes clear
in comparison with the firewall propagated by Dijk-
skra: HERAKLIT follows the tradition of logic, inte-
grating formal arguments as part of the scientific pen-
etration of real-life facts. Logic has successfully been
doing this for 2000 years. HERAKLIT extends for-
mal logic by including dynamic aspects, and shapes a
connection between informal and formal concepts.
Like no other framework, HERAKLIT combines
the three pillars of architecture, statics, and dynam-
ics for modeling computer-integrated systems. For-
mulated in buzzword form on a technical level:
HERAKLIT =
modules + relational structures + local steps,
and on the level of calculi:
HERAKLIT =
composition calculus + logic + Petri nets.
ICSOFT 2022 - 17th International Conference on Software Technologies
12

With HERAKLIT, both sides of Dijskrta’s wall can
be grounded on the same foundations. It is obvious
that this approach has decisive advantages and will
achieve tremendous gains: It is seamlessly possible
to capture the main ideas of a natural and intuitive
understanding of the world we live in, enrich this
understanding with formal concepts, and use the de-
scription as a foundation for (forthcoming) supporting
software.
The technical HERAKLIT concepts described can
be used to model aspects of discrete systems in a way
that no other modeling technique can:
• Modules of different hierarchical levels can be
composed, e.g. a module may represent the be-
havior of a component at the finest, operational
level. At the same time, its neighboring modules
are given only by their names and their interface.
• Real-world and abstract objects are coequal ele-
ments of formal reasoning. HERAKLIT follows
predicate logic and conceives both, real-world and
formal objects, as interpretations of terms of a sig-
nature (an alphabet with typed symbols).
• Behavioral models can be parameterized. Each
interpretation of the symbolic labels of a
schematic HERAKLIT module generates a sepa-
rate system model. For example, a schematic
module describes the principles of business pro-
cesses of all branches of a commercial bank; each
interpretation describes a concrete branch.
• The size of models grows linearly with the size
of systems. This is especially true for model-
ing dynamic behavior. To achieve this, HERAK-
LIT works without globally effective constructs,
in particular without global states. The notion of
single runs, as well as the composition operator
for modules, are likewise locally confined.
• HERAKLIT adopts verification techniques. Petri
nets provide a variety of efficient computational
verification techniques. The most important ones,
in particular place- and transition invariants, also
work at the symbolic (signature) level and – more
expressively – for individual interpretations of a
signature. Verification based on model check-
ing is only possible for individual interpretations
of a signature; efficient procedures exist for this.
A large, still open research area is compositional
verification: properties of a composed system are
derived from properties of the composed modules.
• A single run can be distributed. In a run of a
system, events often occur independently. For
example, in a bank branch, employees interact
with individual customers largely independently;
they are only occasionally synchronized when ac-
cessing scarce resources, such as meeting rooms.
Many modeling frameworks model this kind of
independent events as “occurence in any order” .
This leads to exponentially many supposedly dif-
ferent “sequential” processes. HERAKLIT explic-
itly models independence of events, not only in
sequences but any other partial order. This yields
a clear notion of non-determinism and a theorem
according to which the runs of a composed system
are derivable from the runs of its components.
• HERAKLIT uses intuitively simple basic concepts:
predicate logic is familiar to many users from
other contexts anyway. Petri nets are also widely
used in computer science and its application areas.
The composition calculus is immediately conceiv-
able from small examples. The graphical means
of expression of Petri nets and the composition
calculus complement each other harmoniously.
It is plausible that HERAKLIT will help to har-
monize the plethora of different phenomena asso-
ciated with computer-integrated systems. In other
words, it will be possible to describe the essence
of different application types, and system structures
of applications, including real-time systems, reac-
tive systems, data-intensive systems, cyber-physical
systems, service-based systems, integrated business
systems for enterprise resource planning (“ERP sys-
tems”), supply chain management (“SCM systems”),
customer relationship (“CRM systems”, “ticket sys-
tems”), product lifecycle management (“PLM sys-
tems), and many more system types in the “digital
world”.
In the future, more work is needed to develop the
HERAKLIT framework into a universal modeling in-
frastructure:
1. More case studies and industrial applications are
required, to identify special classes of models,
shorthands, best practices, etc.
2. HERAKLIT specific analysis methods have to be
developed, respecting and employing the local
character of events and modules, to formulate and
to prove decisive properties of models.
3. Powerful software tools have to be created, sup-
porting the construction of models, their analysis,
the integration of databases, etc.
So far, HERAKLIT provides fundamental pillars
for systematically developed, theory-based models,
covering a broader spectrum of aspects than any other
modeling infrastructure. It is now time to “breathe
life” into models with HERAKLIT.
Breathing Life into Models: The Next Generation of Enterprise Modeling
13

REFERENCES
Abrial, J.-R. (2005). The B-Book – Assigning Programs to
Meanings. Cambridge University.
Alter, S. (2013). Work system theory: Overview of core
concepts, extensions, and challenges for the future.
Journal of the Association for Information Systems,
14(2).
Broy, M. (1997). Compositional refinement of interactive
systems. Journal of the ACM, 44(6):850–891.
Broy, M. and Stolen, K. (2001). Specification and Develop-
ment of Interactive Systems: Focus on Streams, Inter-
faces, and Refinement. Springer.
Dijkstra, E. W. (1989). Reply to comments. Commun. ACM,
32(12):1414.
Fettke, P. and Reisig, W. (2021a). Handbook of HERAKLIT.
HERAKLIT working paper, v1.1, September 20, 2021,
http://www.heraklit.org.
Fettke, P. and Reisig, W. (2021b). Modelling service-
oriented systems and cloud services with HERAK-
LIT. In Zirpins, C., Paraskakis, I., Andrikopoulos, V.,
Kratzke, N., Pahl, C., El Ioini, N., Andreou, A. S.,
Feuerlicht, G., Lamersdorf, W., Ortiz, G., Van den
Heuvel, W.-J., Soldani, J., Villari, M., Casale, G., and
Plebani, P., editors, Advances in Service-Oriented and
Cloud Computing, pages 77–89, Cham. Springer In-
ternational Publishing.
Frank, U. (2014). Multi-perspective enterprise modeling:
foundational concepts, prospects and future research
challenges. Journal of the Association for Information
Systems, 13(2):941–962.
Frank, U., Strecker, S., Fettke, P., vom Brocke, J., Becker,
J., and Sinz, E. J. (2014). The research field ”mod-
eling business information systems“ – current chal-
lenges and elements of a future research agenda. Busi-
ness & Information Systems Engineering, 6(1):39–43.
Genrich, H. J. and Lautenbach, K. (1981). System mod-
elling with high-level petri nets. Theoretical Com-
puter Science, 13:109–135.
Gurevich, Y. (2000). Sequential abstract-state machines
capture sequential algorithms. ACM Transactions on
Computational Logic, 1:77–111.
Harel, D. (1987). Statecharts: A visual formalism for com-
plex systems. Science of Computer Programming,
8(3):231–274.
Jackson, D. (1987). Alloy: A language and tool for explor-
ing software designs. Communications of the ACM,
62(9):66–76.
Jensen, K. and Kristensen, L. M. (2009). Coloured Petri
Nets: Modelling and Validation of Concurrent Sys-
tems. Springer.
Keller, G., N
¨
uttgens, M., and Scheer, A.-W. (1992).
Semantische Prozeßmodellierung auf der Grundlage
Ereignisgesteuerter Prozeßketten (EPK). Techni-
cal Report 89, Ver
¨
offentlichungen des Instituts f
¨
ur
Wirtschaftsinformatik (IWi) an der Universit
¨
at des
Saarlandes.
Lamport, L. (2002). Specifying Systems: The TLA+ Lan-
guage and Tools for Hardware and Software Engi-
neers. Adison-Wesley.
Object Management Group (2014). Business process model
and notation (bpmn): Version 2.0.2. Technical Report
formal/2013-12-09, Object Management Group.
Object Management Group (2017). Omg unified modeling
language (omg uml): Version 2.5.1. Technical Report
formal/2017-12-05, Object Management Group.
Petri, C. A. (1962). Kommunikation mit Automaten. PhD
thesis, Institut f
¨
ur instrumentelle Mathematik der Uni-
versit
¨
at Bonn.
Petri, C. A. (1977). Non-sequential processes. Techni-
cal Report ISF-77-5, Gesellschaft f
¨
ur Mathematik und
Datenverarbeitung, St. Augustin, Federal Republic of
Germany.
Reisig, W. (1991). Petri nets and algebraic specifications.
Theoretical Computer Science, 80:1–34.
Reisig, W. (2013). Understanding Petri Nets. Springer.
Reisig, W. (2019). Associative composition of compo-
nents with double-sided interfaces. Acta Informatica,
56(3):229–253.
Sandkuhl, K., Fill, H.-G., Hoppenbrouwers, S., Krogstie,
J., Leue, A., Matthes, F., Opdahl, A., Schwabe, G.,
Uludag, O., and Winter, R. (2018). From expert dis-
cipline to common practice: A vision and research
agenda for extending the reach of enterprise mod-
elling, business and information systems engineer-
ing. Business and Information Systems Engineering,
60(1):69–80.
Sanella, D. and Tarlecki, A. (2012). Foundations of Al-
gebraic Specification and Formal Software Develop-
ment. Springer.
Scheer, A.-W. (1999). ARIS – Business Process Frame-
works. Springer, 3 edition.
Spivey, J. M. (1992). The Z Notation: A reference manual.
Prentice Hall, 2 edition.
¨
Osterle, H. (1995). Business in the Information Age – Head-
ing for New Processes. Springer.
Suppes, P. (1957). Introduction to Logic. Van Nostrand
Reinhold.
ter Hofstede, A. H. M. and van der Heide, T. P. (1992). For-
malization of techniques: chopping down the method-
ology jungle. Information and Software Technology,
34(1):57–65.
Vernadate, F. (2020). Enterprise modelling: Research re-
view and outlook. Computers in Industry, 122:57–65.
Wand, Y. and Weber, R. (1990). An ontological model of
an information system. Transaction on Software En-
gineering, 16(11):1282–1292.
Wand, Y. and Weber, R. (2002). Research commen-
tary: Information systems and conceptual modeling–
a research agenda. Information Systems Research,
13(4):363–376.
Winter, R. (2001). Working for e-business – the business
engineering approach. International Journal of Busi-
ness Studies, 9(1):101–117.
ICSOFT 2022 - 17th International Conference on Software Technologies
14
