
Workflow Optimization through Business Reengineering
for Tele-cardiac System
Farkhanda Rasheed and Shoab Ahmad Khan
Department of Computer Engineering, College of EME, National University of Sciences and Technology (NUST),
H-12, Islamabad, Pakistan
Keywords: Healthcare, Business Process Re-engineering, Workflow, Cardiology Department, Workflow Reengineering
Methodology (WRM).
Abstract: Today’s third largest industry is healthcare sector. This care sector is in trouble in many ways such as
“extra-long waiting time, high expenses on medical and delivery error removal cost and insufficient access
of client to important information”. Business process re-engineering helps manager in health department to
discover best ways to produce better results without having any effect on quality. Business process
reengineering recovers the procedures of the business process including its improvement. Workflow
Reengineering Methodology is a form of Business Process Reengineering which has upgrading capability
starting from need identification to execution. It also has ability of maintenance of workflow. It means that
much benefit can be attained by consolidating existing task rather than focusing on previous task. It is
optimized that how to re-engineer task by using workflow reengineering methodology in order to reduce
time and cost for best quality. Here we present a case study of cardiology hospital, which is a tertiary care
corporate hospital of Rawalpindi “Armed Forces Institute of Cardiology and National Institute of Heart
Diseases” (AFIC-NIHD). We will show how workflow can be optimized through re-engineering
methodology in Tele Cardiac system.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 BPR towards Healthcare Sector
Today’s third largest industry is healthcare sector.
This care sector is in trouble in many ways such as
“extra-long waiting time, high expenses on medical
etc. When there increase in cost for providing
healthcare then health managers try to improve
greater performance by reducing cost (Romanow,
2002) The reforming and exploration of workflow,
for making it more practical is called Business
process reengineering. Dramatic growth in the price
of delivery of health related services, worth race,
changing markets are the important influences that
are motivating hospitals to observe their business
processes and to modify them by the way that help
to keep the prices sensible and provide best quality
to patients. BPR is problem-solving methodology
that highlights fundamental redesigns of process to
attain intense improvements in present-day measures
of performance for example quality, cost, speed and
service. A Delphi study has been conducted that
shows BPR is ranked at the top in research priorities
for health informatics. According to this record
electronic patient records and operating systems are
put at higher priorities. (Brender, 2000). BPR
elements are to be forced by entire provision
practice and also focus on whole service to patients
across several functional zones in hospital. In the
healthcare, the most active change is technology. By
every change, the methodology of service delivery
changes. Business process reengineering has greater
power for improving all parameters like cost,
quality, time and efficiency (Soudabeh, 2013).
1.2 Workflow Reengineering Method
Workflow Reengineering Methodology (WRM) is
the technique that for Business Process
Reengineering in which workflow controlling
automation is used as permitting skill. Workflow
Reengineering Methodology is created from the
BPR and by all other techniques as discussed in the
BPR principles of (Linden, 1993), and (Hammer and
Champy, 1993). This methodology empowers BPR
33
Rasheed F. and Ahmad Khan S..
Workflow Optimization through Business Reengineering for Tele-cardiac System.
DOI: 10.5220/0005435100330038
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering (ENASE-2015), pages 33-38
ISBN: 978-989-758-100-7
Copyright
c
2015 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

by using workflow automation. WRM is which need
for change is identified and also improved workflow
maintenance and ultimate implementation is covered
(Jamaiah H. Yahaya and Syafrani Fithri, 2012).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Healthcare especially cardiology department is
rising rapidly in developing and also in established
countries. Patients’ increase in waiting time is
identified as the “growth of length of time when
patient move in hospitals and when patient leaves
hospitals”. The time required for registering,
appointment, emergency cure, lab testing,
procedures, and distribution of the results for tests.
(Romanow, 2002). Electronic histories of patient
and associated inter-operating systems are also topic
of interest according to this study. BPR performs
many improvements which are possible by
automated patient records, and inter-operating
systems.(Juha, 2007)
Many adverse events are triggered because of
incorrect resource allocations, and complicated or
poorly presented rules and procedures (Blais, 2008).
Methods should be developed for decreasing load in
all departments focusing in operating rooms.
(Cleary, 2004). High amount of saved money and
resources are necessary because eighty precent of
money are used for patient care (Kumar, 2004). In
BPR method, clinical process are mapped and
decomposed into activities that are involved in the
process. These mapped process is termed “as-is”
process. Avoidable steps are identified in this
procedure. We also identify all non-value added
activities, delays and bottlenecks (Patwardhan,
2008). After that, the new clinical process are named
as “to-be” process (Netjes, 12 2010). In some issues,
modification of the process is not enough and may
needed to be redesigned or even remove wasteful
activity completely (Brock ,1997).
3 CASE STUDY
3.1 Cardiology Hospital Profile
The case discussed over here is a cardiology hospital
named “Rawalpindi Armed Forces Institute of
Cardiology and National Institute of Heart Diseases
“(AFIC-NIHD) which is operational from thirty five
years. This modern cardiac hospital has two hundred
and fifty beds. It is situated in the heart of
Rawalpindi. This cardiac hospital provides facility
of being treated to citizens of Rawalpindi Islamabad,
Peshawar and Kashmir.
3.2 Current Workflow Description
In cardiology hospital doctor advise the patient for
admission and /or cath lab process, Patient or
patient’s families go to admission counter.
Admission officer confirms availability of beds
according to availability. Allotting of bed and case
observation is done by Admission officer. And in
ward, duty medical officer check the case sheet. He
checks the patient and asks nurse for treatment.
Nurse gives treatment to patient.
Cath lab treatments like balloon angioplasty,
closure, stenting and pacemaker are needed for
treatment. After examination, patient gets admitted
in ward. Blood and urine Samples are transported to
laboratory for examination. And result Report is
made. Before starting treatment, Patient is kept in
special unit for at least six hours. After treatment
process, ICCU a bed is prepared for patient. At the
time of discharge, discharge summary is prepared
by duty medical officer. Then this is transferred to
doctor for consultation and confirmation. After this
procedure discharge summary is sent for keying.
Billing department receive case sheet by transport.
Billing department make up bill. Patient relatives
pay bill at billing counter. They fill up feedback
form if they consider it necessary.
3.3 Operational Analysis of Current
Method
First of all complexity appears due to structure of
hospitals, because in hospitals there are many
primary wards and secondary units away from one
another. Patient journey covers almost all the units
for getting treatment. Many other complications
occur during treatment are discussed here.
In emergencies situations and also in morning
timing an interruption appears in admission
procedure when patient enters into the hospital
because there is availability of LAN by which
obtainability of the beds can be easily checked.
Transportation process of patient is delayed
because of the problems in transport staffs. So
there is a need of maximum staff for taking up
patient to any section and sub section easily for
treatment.
Research samples are directed to laboratory by
workers or by the help of couriers. Due to which
handoff delays appear.
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
34

Delay also appears in diagnostic tests passed
before cath lab processes as a consequence of
shared Echo machines in primary section and
sub section:
Duty Medical Officers are fewer in number as
related to Doctors which cause a big problems:
Number of Duty Medical Officers should be in
ratio with Doctors
In case of emergency lifesaving medicines like
urokinese, streptokinase etc. are in shortage
because of expensiveness cause major delay
during treatment.
In case of discharge a separate billing procedure
is not present in hospital. That is also a cause of
delay.
4 ARCHITECTURE
Bonita soft architecture is presented over here to in
figure 1 show overall methodology (Bonita Soft,
2014)
Figure 1: Bonita Soft Architecture.
5 IMPLEMENTATION
For overcoming of previously mentioned problems,
there is need to replace old paper based system with
paperless and automated system. Bonita Soft is a
tool used for implementation. It is workflow
optimization tool having capability of
communications, and identifying chances for
refining the supply of healthcare services by the
reduction of costs and maximizing revenue. It
provides surety in delivery of information to relevant
person in a given time by focusing on 4 important
points patient-centered communications, increased
throughput, proficiency and complete data.
We consider all 32 steps of workflow
reengineering methodology to attain our related
goals. First of all an objective is set and then starts
changing in existing workflow in order to attain all
performance goals in cardiology hospital, For this
purpose task are prioritised and we make form
according to administration and customer/patient.
And operational of business cycle component are
prioritised.
After the identification and recording of all the
processes of a business, single process is selected for
implementation by the team. Team uses Weighted
Selection Approach to rate each process. The scales
from 1 to 5 are used for the factors of changeability,
performance, and business and customer impact
(Harrington, 1991). For determination of value of
every element following questions are important.
5.1 Reengineer Process for Workflow
First of all efficiency of existing system is measured.
On the basis of these identification new goals are
specified. Reengineering process includes following
steps:
• Transformation and Elimination of
Unimportant Tasks:
Workflow tasks are of three kinds (Harrington,
1991)
The tasks those are important to the
customer.
The tasks that important for business but not
for customer.
The tasks that are totally unimportant
In cardiology department there are many
unimportant tasks that are the major cause of delay
like that are shown in following flow charts.
• Arrangement of Tasks:
In normal routine, tasks are arranged in serial
sequence. This arrangement unreasonably increases
the length of cycle of process. The tasks should be
performed in parallel sequence because parallel
processed task are performed automatically in short
timer. For example when patient reached to his bed
all of requirement of his treatment should be
processed initially. All the tasks in cardiology
hospital are arranged in natural order like first of all
patient checkups then admission is processed etc.
• Positioning of Object:
Transfer of object from one place to another around
the department is very much expensive and time
consuming. It causes overhead in tracking all the
process associated with each other. (Hammer and
Champy, 1993). Each and every task in cardiology
department has to be observed to understand for
WorkflowOptimizationthroughBusinessReengineeringforTele-cardiacSystem
35

their functional expertise that is already assigned or
it can be accomplished with the help of other
workflow participant.
• Combination of Similar Tasks:
In cardiology hospital all the hand-off in admission,
lab procedure, in patient checkup should be removed
by the help of tool used in order to increase
efficiency, cycle time and cost reduction and
improve quality. By using tool like Bonita soft all
the paper work is removed and similar tasks are
combined.
• Transfer of Decision Power to Smaller Level:
In hospital to increase the speed of tasks of
processes, decision power should be distributed even
at smaller level. Because at every level approval
confirmation causes delays which is risk to patient
life
• Reduce Checks and Controls:
Spontaneous checks and control should be stopped.
Because they cause delays in hospital operations and
procedures. Bonita soft is very much dynamic tool
that can easily provide status information. With the
help of this there is no need to stop of procedures
running in the hospital.
• Reduction of Task Completion Time:
The cost of product is directly affected by the task
completion time. If we reduce this time quality and
efficiency of product increases. Bonita soft is an
automated tool that performs this work efficiently.
By using this sub tasks are dynamically created that
reduce burden
• Removal of Blockages and Resource Shortages:
When workflow processes are slow down at a point,
blockages occur. Transfer of object from one place
to another also become slowly. Due to which many
processes are lined up in queue. Such slow process
binds resources needed at other point. Many
problems occur because every patient needs full
treatment resources. He cannot wait for even a single
resource. It is duty of team to identify all blockages
and remove them. Number of employees and
resources should be according to requirement of
hospital.
• Making Multiple Versions of the Process:
In backup and recovery many version of processes
should be produced. Tool mentioned over here has
an ability to store all backup process for future. In
hospital it is very mush necessary in case of
treatment, billing etc. because record of every
patient is essential for future consideration (Hammer
and Champy 1993).
6 RESULTS
The proposed framework uses the most recent
standards and technologies for modeling and
implementing workflow system. It uses BPMN
Bonita soft tool to model the as-is and to-be
workflow system. The choice of BPMN is due to its
capacity and richness to represent different
workflow patterns and different business process.
Bonita soft is very much efficient tool where
machines movement of patient through hospital can
be shown easily. This tool has an efficient graphical
user interface. Using that tool following automated
workflow is produced that will covers all the
problems in cardiology hospital. When we run that
workflow task screen appears at every desktop of
doctor, admission desk, lab completing available
tasks we can attain our officer and billing
department. Following figure shows flow overall
process. After implementation automated workflow
is shown in figure 3.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Patient health is very much important in cardiology
hospital. Efficiency and high quality are critical
missions that every hospital wants to attain. The
paper targets at a framework enabling the re-
engineering of business processes in order to
improve clinical procedures. Thereby, a case study
has been conducted to reveal insights on real-world
processes in the given context. The presented
framework is applied to the investigated processes
and results are shown with respect to the improved
processes. Moreover, architecture of the framework
is presented.
The proposed future work is that we will
calculate the performance of all reengineered tasks
using four parameters like cost, quality, time and
flexibility with the help of devil’s quadrangle.
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
36
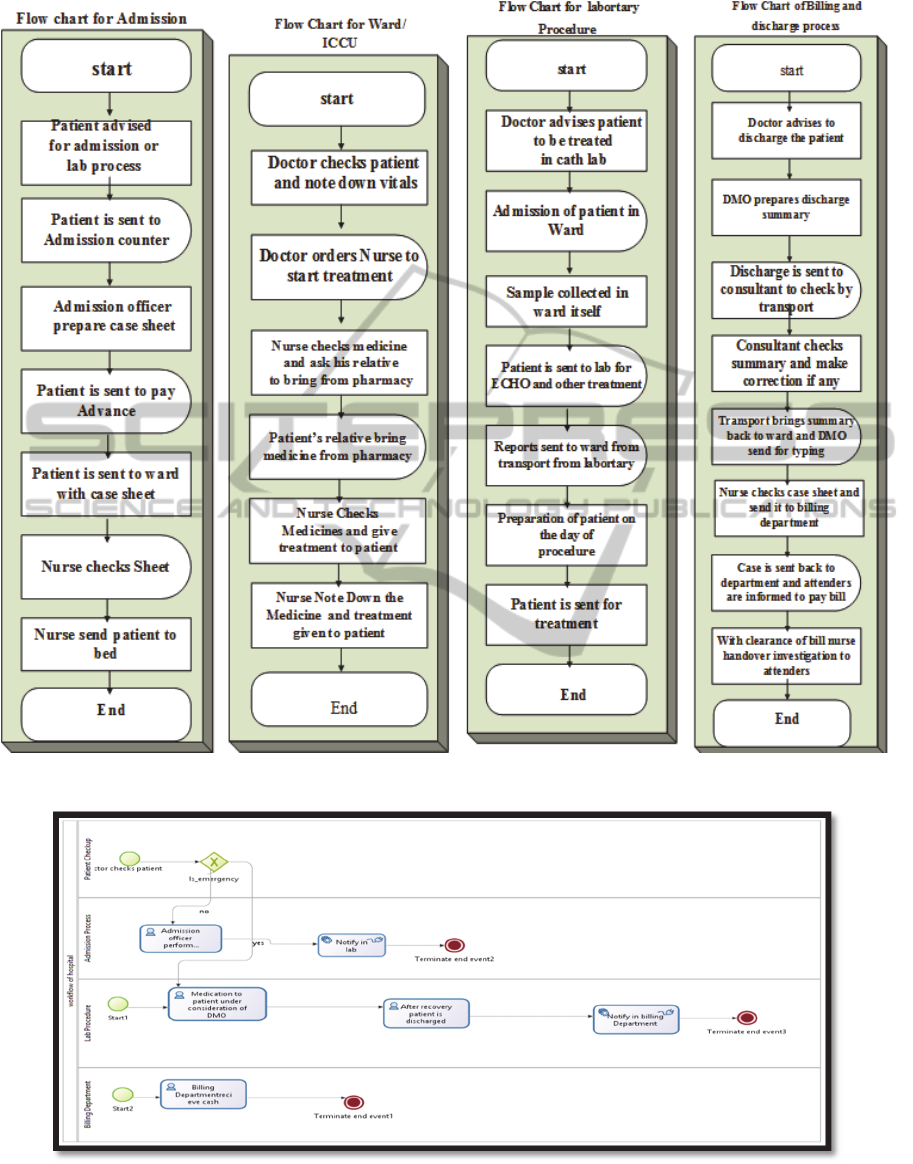
Figure 2: Flow Chart of System.
Figure 3: Automated workflow.
WorkflowOptimizationthroughBusinessReengineeringforTele-cardiacSystem
37

REFERENCES
Romanow, R.J. (2002) Building on Values: The Future of
Healthcare in Canada, Commission on the Future of
Healthcare in Canada, May 12, http://www.
healthcarecommission.ca/pdf/HCC_Fin al_Report.pdf.
Brender, J., Nohr, C. and McNair, P. (2000) ‘Research
needs and priorities in health informatics’,
International Journal of Medical Informatics, Vol. 58,
pp.257–289
Soudabeh Khodambashi 2013 Business Process Re-
Engineering Application in Healthcare in a relation to
Health Information Systems CENTERIS - Conference
on ENTERprise Information Systems / PRojMAN
2013 -International Conference on Project
MANagement / HCIST 2013 - International
Conference onHealth and Social Care Information
Systems and Technologies
R. Linden, 1993 “Business Process Reengineering:Newest
Fad, or Revolution in Government?”
PublicManagement, vol. 75, no. 11.
M. Hammer and J. Champy, 1993 Reengineering
theCorporation, New York: Harper Business,
Juha Kontio 2007: Business Process Re-engineering: A
Case Study At Turku University of Applied Sciences,
Proc. of European and Mediterranean Conference on
Information Systems 2007 (EMCIS2007) June 24-26,
Polytechnic University of Valencia, Spain
www.emcis.org (2007).
Blais, R. (2008), “Patient safety: Scope of the problem and
possible solutions”, Qmentum Quarterly: Quality in
healthcare, Vol. 1 No. 1, pp.8-11.
Cleary, K., Chung, H. Y., Mun, S. K. (2004), “OR2020
workshop overview: operating room of the
future”,Proceedings of the 18th International Congress
and Exhibition Computer Assisted Radiology and
Surgery (CARS’04), Vol. 1268, pp.847-852.
Kumar A., and Ozdamar, L. (2004), “Business process
reengineering at the hospitals: a case study at
Singapore Hospital”, Proceeding of the 18th European
Simulation Muti conference, Magdeburg, Germany,
pp. 308-317.
Patwardhan, A. and D. Patwardhan, 2008. Business
process re-engineering–saviour or just another fad? -
One UK health careperspective. International Journal
of Health Care Quality Assurance 21(3): p. 289-296.
Netjes, M., et al. 2010 BPR Best Practices for the
Healthcare Domain. Springer.
Hammer, M. and J. Champy, Reengineering the
corporation: A manifesto for business revolution.
1993.
Brock Jr, J. L., J. P. Finedore, and D. A. Davis, 1997
Business Process Reengineering Assessment Guide:
DIANE Publishing.
M. Hammer and J. Champy, 1993 Reengineering
theCorporation, New York: Harper Business,.
H. J. Harrington, 1991 Business Process
Improvement,New York: McGraw-Hill,.
Jamaiah H. Yahaya and Syafrani Fithri, 2012 “An
Enhanced Workflow Reengineering Methodology for
SMEs, International Journal of Digital Information
and Wireless Communications (IJDIWC) 2(1): 51-65
http://br.bonitasoft.com/produtos/visao-geral/bonita-bpm-
engine.
ENASE2015-10thInternationalConferenceonEvaluationofNovelSoftwareApproachestoSoftwareEngineering
38
