
The Implementation of Classroom Management Concept Towards
Joyful Learning on Learning Activity
Yayah Rahyasih
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia
yayahrahyasih@upi.edu
Keywords: Classroom Management, Joyful Learning, Learning Model.
Abstract: Joyful learning is really influencing the condition and situation of learning. Therefore, the teacher is
demanded to be able to implement the concept that can create fun situation inside the classroom so that the
student feel comfortable during teaching and learning activity. This research implemented a descriptive and
qualitative method. While the objectives of joyful learning itself are encourage the learning ability of the
student make the teaching learning process is fun and satisfy for the student and to give charity fully
towards happiness, intelligent, competency, and success. A joyful learning process can be done by: first, by
arranging a comfortable room design by fulfilling health, second, by a living and varied learning
management that is implementing pattern and model of learning, a relevant media and learning sources and
also teacher movements that can increase students’ learning motivation. From the result and discussion, it
can be concluded that most of students (67%) do not feel a fun learning situation, and the rest (33%)
mention they are happy. It is the situation that should be handling immediately because learning should be
fun, for that it needs another effort for creating joyful learning completely.
1 INTRODUCTION
The quality of learning depends on teachers’
professionalism level. Therefore, a qualified teacher,
a teacher able to create a qualified and encouraging
learning ambience, is urgently needed. Teachers
who are mastering lots of learning models will
prevent students to feel bored or lose interest in
learning. They, in the other hand, will create a kind
of learning that is enthusiastic, joyful, and prompting
students’ achievement.
A joyful learning will be strongly influenced by
the students’ learning condition and ambience.
Therefore, it requires the teachers to be creative and
innovative in creating a joyful learning in a
classroom so that students will be comfortable and
enjoying the learning process itself. Teachers’
attractive and innovative skill will enable them to
create a joyful learning.
How the teacher is able to create such a joyful
learning is influenced by knowledge of the joyful
learning itself and skill of classroom management
that teachers are able to change the atmosphere into
a playful one. Thus, teachers have to implement a
learning method suitable with pupils’ characteristics.
Each class may have their own special learning
methods which are different with the others.
Classroom management based on behavioral
modification principles is a set of teacher activities
applied to develop desired student behavior and
reduce or eliminate undesirable behavior. Briefly,
teachers help students learn appropriate behavior
through the application of principles derived from
the reinforcement theory.
Classroom management is the process of creating
a positive socio-emotional climate in the classroom.
This view has a statute that learning activities will
develop optimally in a positive climate classroom,
which is the atmosphere of good interpersonal
relationships between teachers and students and
students with students. To create such atmosphere,
teachers play a key role. The role of teachers is to
develop a positive socio-emotional classroom
climate through the growth of healthy interpersonal
relationships. Thus, classroom management is a set
of teacher activities used to develop good
interpersonal relationships and a positive socio-
emotional classroom climate.
Rahyasih, Y.
The Implementation of Classroom Management Concept Towards Joyful Learning on Learning Activity.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences (ICES 2017) - Volume 2, pages 139-143
ISBN: 978-989-758-314-8
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
139

It is a type of classroom management that departs
from the assumption that the class is a social system
with group process as its core. In this connection the
basic presumption is that teaching takes place in
relation to a group. Thus, classroom life as a group
is seen as having a significant effect on learning
activities, although learning is considered as an
individual process. The role of teachers is to
encourage the development and effectiveness of
effective classroom systems. Therefore, classroom
management is a set of teacher activities to cultivate
and maintain effective classroom organization
(Depdikbud, 1982).
The term joyful learning derives from the word
“joyful” which means having fun while learning.
Dave Meier states that joyful learning is a learning
system that seeks to arouse interest, fully engage
students, and create meaning, understanding, and
value on students.
Joyful learning is a learning that has no pressure,
both physically and psychological. Because, any
kind of pressure will only dwarf the mind of the
students, while any freedom of its form will be able
to encourage the creation of a conducive learning
climate. Joyful learning is making the class fun,
avoiding it to become monotonous. Meanwhile,
according to Yanu Armanto, joyful learning is an
approach that can make students motivated to
continue to find out and keep learning.
Accordingly, joyful learning is the approach used
by teachers to make students more able to accept the
material delivered which is due to a pleasant
atmosphere and without tension in creating a sense
of pleasure. The creation of a sense of joy in this
matter is not a learning process that creates a noisy
and festive atmosphere. Also, feeling fun or excited
in classroom learning does not mean creating a
melee atmosphere but arousing interest, fully engage
students as well as creating meaning, understanding
materials and values that students are happy with.
2 METHODS
The object of research is the application of
Classroom Management concepts conducted by
elementary school teachers in implementing
Teaching and Learning Activities in Primary School
in Bandung.
The method used in this research is qualitative
descriptive research that describe and explain a
problem as it is, so is the disclosure of a fact by
collecting information relating to the object under
study. Through qualitative descriptive research, the
researcher seeks to find facts and deep
understanding of the reality from the perspective of
the person who in this case is the primary school
teacher. By using qualitative methods, the data
obtained will be more complete, more in-depth,
credible so that the research objectives will be
achieved.
Unicef say that Joyful learning has emerged as a
powerful concept to change the way we manage
schools and classrooms. Central to the success of the
programme is teacher empowerment. Teachers use
songs and games as well as a variety of locally
available materials, such as leaves, stones and trees,
as teaching tools. A joyful classroom is an active,
bright and cheerful place.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
From the Classroom Management variable, with the
number of respondents as many as 50 people came
from 10 schools. Through the total score of
responses to 10 proposed statements about the
implementation of the concept of Classroom
Management variable, it can be seen that some of
the variables have understood the concept of
classroom management (64%) and only a few have
applied the concept of Classroom Management.
From the phenomenon, it can be interpreted that
some other (34%) teachers have not implemented
and have not applied the concept of classroom
management in learning activities.
3.1 Joyful Learning Aspect
As for the variable of Joyful Learning, it is
conducted to elementary students in low and high
class, with the number of respondents as many as
100 students coming from 3 schools.
Based on the answers to 10 proposed statements
about the variables of Joyful Learning, it can be seen
that the variable of concept implementation is
already happy (43.3%), some just feeling happy
sometimes (48.3%) and a small part of them (8,4%)
feel uncomfortable. From the phenomenon it can be
interpreted that most have been happy and there are
still some perceived by students as not joyful
enough.
In detail the respondent's answers about the items
questions relating to joyful that 45 students (45%)
said that the teachers like to ask them singing, 9
students said no, and 46 students said sometimes. It
can be interpreted that the teachers do not always
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
140
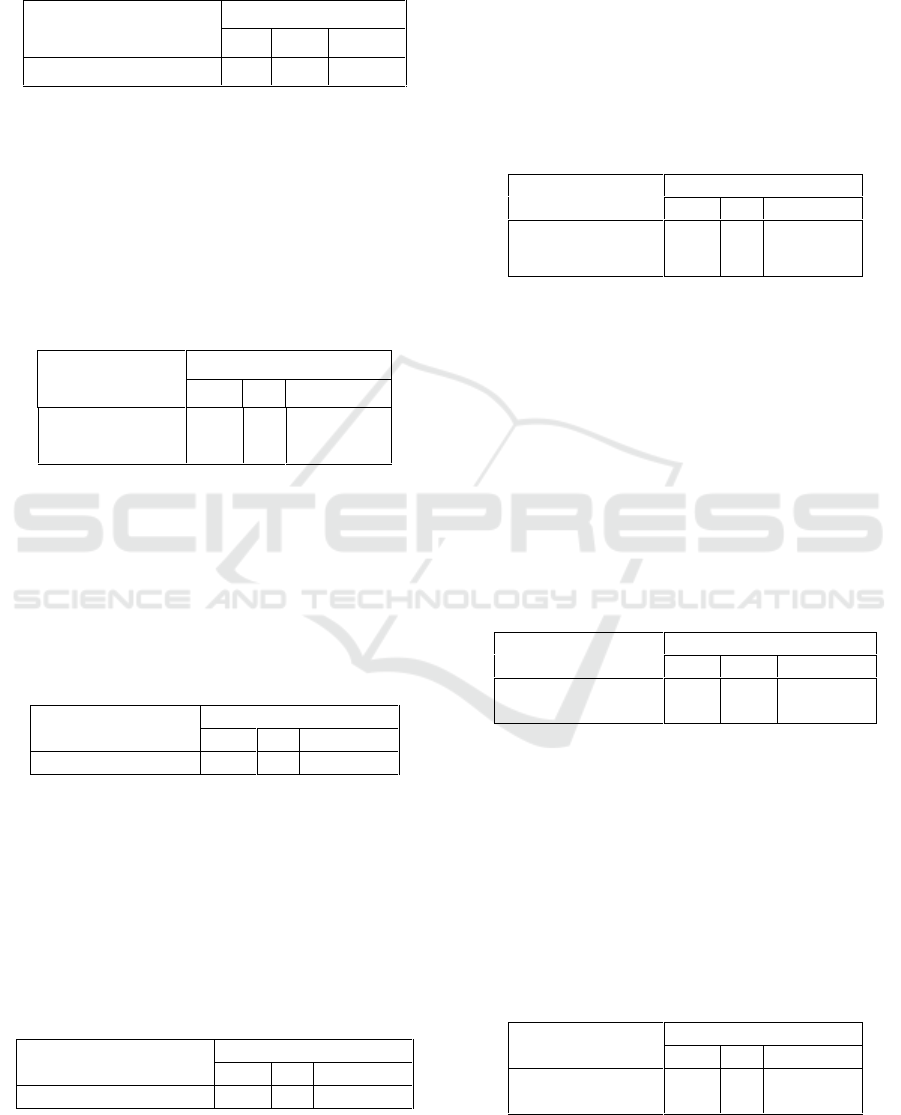
invite students to have fun by doing singing
activities.
Table 1: Teachers like to tell stories.
Questions
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Teachers like to tell stories
57
3
40
Table 1 describes how most of students (57
students) answered that their teachers like to tell
stories. It can be assumed that students find it
enjoyable to listen to stories. By singing teachers
provide a fun experience for children, it is in
accordance with Wei et al (2011) research that
Joyful Learning provides a learning experience that
makes learners feel pleasure in the learning process.
Table 2: Teachers like to make students laugh.
Question
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Teachers like to
make students
laugh
18
3
79
Table 2 shows that about 79 students answered
that sometimes teachers make them laugh.
Moreover, teachers conduct the learning process in a
serious manner. Laughter is interpreted as a pleasure
so that teachers should be able to create a child to
laugh freely because when the fun stops, learning
often stops too (Willis, 2007).
Table 3: Teachers are friendly.
Question
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Teachers are friendly
9
3
88
Table 3 shows that 88 students feel the teacher to
be sometimes friendly, 9 students answered that
teachers are friendly and the rest answered that the
teachers are not friendly at all. Psychological studies
conducted by Christianson (1992) provide clinical
evidence of stress, boredom, emotion, low
motivation, and anxiety can be done individually,
and more in combination, lessons learned.
Table 4: Teachers often give reward.
Questions
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Teachers often give reward
-
73
27
Table 4 with the question of whether the teachers
likes to give rewards, the students answered
sometimes as many as 27 (27%) and 73 students
(73%) said no. It means that teachers almost never
give rewards, something that should be done even
only with a small reward. According to Vygotsky
(1994) through play, all aspects of child
development can be improved. Students are seen
more zeal in applying the learning activities as
learning activities can be done while playing.
Table 5: Students are sad when teachers do not come.
Question
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Students are sad
when teachers do
not come
-
24
76
Table 5 illustrates elementary students only
occasionally feel sad or disappointed when teachers
are absent with them, i.e. 76 people or 76%. Even 24
students or 24% of them said they did not feel sad or
disappointed. This illustrates the emotional
relationship between teacher and student is almost
non-existent, so the students do not feel lost if the
teachers are not attending the class. Teachers should
be able to teach their students to explore.
Exploration by Wolk (2001) can crawl into students
who can be a place of curiosity, inspire them to ask
questions, and help them find joy in learning.
Table 6: Students are happy being in the classroom.
Questions
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Students are happy
being in the classroom
76
1
23
Table 6 shows that 76 people said that they are
happy being in classroom. While a 23 students state
that they are hesitate to feel the atmosphere of a
joyful class. Roulston (2010) said that teachers
should be able to use the strategies learned from the
education they get to provide a learning experience
that is enjoyable for students.
Ariawan et al (2017) say that the joyful learning
might be one of the strategies that a teacher can
choose in raising the students’ learning motivation.
Table 7: Teachers often assign difficult tasks.
Questions
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Teachers often
assign difficult tasks
45
9
46
The Implementation of Classroom Management Concept Towards Joyful Learning on Learning Activity
141

Table 7 with the question of whether teachers
often give difficult tasks, about 45% or 45 students
answered yes and 46 students responded sometimes.
This illustrates that the teacher gives the task in
sufficient portion. Triastuti et al (2013) stated that
the percentage of active students in the
implementation of learning based on Joyfull
Learning is higher than the percentage of students'
activities on expository learning, and teacher activity
in managing learning based on Joyfull Learning
achieves excellent criteria.
Table 8: Teachers usually get angry when students do not
finish assignments.
Questions
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Teachers usually get
angry when students do
not finish assignments
66
3
31
Table 8 with the question of whether the teacher
usually get angry if the students do not do the
assignment shows that most of them justify with the
answer "yes" as many as 66 students or 66%, and
only a few said no, that is 31% or 31 people. This
illustrates that the atmosphere of learning process is
more authorized, and less persuasive approach that
provides comfort to students. Wolk (2001) joyfull
learning can provide students with experience in a
way, students seek fun while studying, rewarding,
encouraging students to do many things, exhibiting
student work, playing while learning, comfortable
classrooms, and occasional play in outside.
Hasan et al (2015) say that joyful learning shows
that it is able to improve the students’ capability to
achieve the desired learning objective more
effectively and efficiently.
Table 9: Teachers often give suggestions as for the
students to be more respectful to parents through
stories/tales.
Questions
Answers
Yes
No
Sometimes
Teachers often give
suggestions as for the
students to be more
respectful to parents
through stories/tales.
50
-
50
Table 9 illustrates that some 50 students (50%)
answered that teachers do not always take advantage
of story-telling time by giving advice to respect for
parents, while the rest of the students answered that
teachers always provide a moral message to students
to honor their parents. Chopra et al (2013) say that
as educators, teacher have the responsibility to
educate and inspire the whole child - mind, heart,
and soul and put more joy into students’ experience
of going to school and get more joy out of working
inside one, joyful learning can flourish in school if
teacher give joy a chance.
Enjoyable learning should be supported by
security the environment, the relevance of teaching
materials and the assurance that learning in a manner
emotional will have a positive impact. Joyful
Learning learning model can spur students to build
your own concept through the task the teacher gave
at the beginning learning.
Overall, the learning atmosphere established
within the classroom has not been entirely enjoyable
and does not make students feel at home or
motivated to learn. There are some things that are
not in accordance with the concept of joyful learning
in teachers; for example, there are teachers who
focus more on the classroom as a place of learning,
and provide few opportunities for playing, there are
still teachers who are reluctant in giving rewards or
praises, and encourage students to achieve high
achievement. This shows that the teacher's
understanding of the concept of joyful learning is
still very low.
From the results of research and discussion about
the application of the concept of Classroom
Management implemented by elementary school
teachers and learning atmosphere perceived by
students, it is concluded that only some teachers
have tried to apply the concept of Classroom
Management in accordance with the classroom
management principles, in order to create a
supportive learning atmosphere. However, there are
still some teachers who do not pay attention to the
principles of classroom management which resulted
in the inappropriate learning atmosphere.
Based on the data found, there are still teachers
who have not fully understood the concept of
classroom management, so they could not apply the
concept of Classroom Management as a whole. it is
probably because some teachers are more
concentrated on other things that require a lot of
attention, al: (1) learning material, (2) learning
model, (3) curriculum, (4) RPP, (5) learning media
and other administrative activities which consumes
teacher’s mind and energy.
4 CONCLUSIONS
From the results of research and discussion, it can be
concluded that there are still many students who do
not feel happy in learning activities, some 43% other
enjoy the learning activities. This is a condition that
ICES 2017 - 1st International Conference on Educational Sciences
142

must be fixed immediately. To achieve a fun
learning condition, the need for extra effort is an
absolute requirement so a supportive and fun
learning environment can be created.
A consolidation effort needs to be made on the
understanding and mastering Classroom
Management concepts for teachers. It can be done
through several ways, and those are; (1)
socialization and consolidation of the concept, (2)
workshops which is related to the principles of
Classroom Management.
As consolidating the understanding of classroom
management concept, in creating a fun learning
environment, teachers get a briefing in the form of
guidance or specific programs that can improve
teachers' understanding and skills in creating a fun
learning environment.
Improving the quality of teachers personally and
professionally should be done continuously by
involving various parties. one that can be done is by
providing education and training on the pedagogic
competence of teachers in learning as well as the
introduction of new methods more contemporary
which requires teachers more creative.
REFERENCES
Ariawan, Vina, A. N., Pratiwi, I. M., 2017. Implementing
Joyful Learning Strategy Using Treasure Clue Game
Method in Order to Improve Reading Comprehension
Skill. Jurnal Prima Edukasia. 5 (2), 203-210.
Chopra, Vanita and Chabra S., 2013. Digantar In India: A
Case Study for Joyful Learning, Journal of
Unschooling and Alternative Learning. Volume 7,
Issue 13.
Christianson, S. A., 1992. Emotional stress and eyewitness
memory: A critical review. Psychological Bulletin,
112 (2), 284–309.
Depdikbud, 1982. Pengelolaan Kelas, Direktorat Jenderal
Pendidikan Tinggi. Jakarta.
Hasan, A., Othman, Z., Majzub, R. M., 2015. Using
Active, Creative, Effective and Joyful (ACEJ)
Learning Strategies toward English Achievement and
their Behavioural Changes among Primary School
Students. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences
MCSER Publishing, Rome-Italy. Volume 6 No 6 pg.
455-459.
Roulston, K., 2010. There is no end to learning’: Lifelong
education and the joyful learner. International journal
of Music education. Volume 28 Issue 4, pages 341-
352.
Triastuti R., Asikin M., Wijayanti K., 2013. The
Effectiveness of Joyful Learning-based CIRC Model
to Mathematical Reasoning Ability Kreano Junior
High School Students. Journal of Creative-Innovative
Mathematics. Volume 4 Issue 2 pp. 182-188.
Unicef. Joyful Learning.
http://unicef.in/PressReleases/336/Joyful-Learning
Vygotsky, L. S., 1994. Mind in Society: The Development
of Higher Psychological Processes, Cambridge:
Harvard University.
Wei, C., Hung, I., Lee, L., Chen, N., 2011. The Turkish
Online Journal of Educational Technology. 10 (2) 11-
23.
Willis, J., 2007. The Neuroscience of Joyful Education.
Association for Supervision and Curriculum
Development. Engaging the Whole Child (online
only). Summer 2007, Volume 64.
Wolk, S., 2001. The benefits of exploratory time.
Educational Leadership, 59(2), 56–59.
The Implementation of Classroom Management Concept Towards Joyful Learning on Learning Activity
143
