
Comparison between Auditory and Kinesthetic Learning Style of
Student Atheletes in Achieving Grade Point Average
Ucu Hidayat, Sopyan Rizki Haryadi, RohmatRohmat, Rio Akbar Bahari and Berliana Berliana
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi No. 229, Bandung 40154, Indonesia
ucuhidayat88@gmail.com
Keywords: Comparison, Learning Style Auditory and Kinaesthetic.
Abstract: The purpose of this study was to determine the learning style which is more influential between auditory and
kinesthetic towards achieving cumulative grade on the student athletes. Method used that is descriptive
method with case study approach. Samples in this study amounted to 50 student’s athletes consisting of
various sports in Sport Education program. The instrument used to measure the student's learning style
teaching style questionnaire athletes use student athletes who have tested the validity and reliability to
student’s athlete Pelatda PON West Java, 2016. Furthermore, to measure learning outcomes seen from the
achievement of the GPA shows that the value of F count equal to 2,818 with significant value 0.083 greater
than the probability of 0:05 it is proven that there is significant influence between auditory and kinesthetic
towards GPA. Further correlation coefficient product moment (rx1x2y) between auditory learning styles (x1)
with GPA. The product moment correlation coefficient (rx1x2y) between kinesthetic (x2) and Ipk (y) is 0.419
with p 0.05 indicating that there is a significant correlation between kinetetic learning styles with GPA.
1 INTRODUCTION
Being an athlete is a pride. In addition to success in
the world of sports athletes want to succeed in the
world of education to get a bright future and
promising future. However, in real life there are many
athletes who have to fall out of education because of
things that can not balance the world of sports and
education.
To gain success in the world of education, athletes
must learn. According to Spears in Thobroni (2013,
pp. 21) "Learning to observe, read, imitate, try
something, hear, and follow a certain direction.
Two individuals who grow in the same
environment and are given the same treatment do not
necessarily have the same view, understanding and
thought to the world around. Each has its own way of
every event seen and experienced. One such way of
view is known as the learning style, so each
individual has a different learning style to capture all
stimuli and process in different ways. Various styles
of learning according Thobroni and Mustafa (2013,
pp. 262-266) "man has a wide range of learning
styles, namely: visual, auditory and kinesthetic."
This study is intended to answer some questions
1) How big is the academic achievement and
graduation student athletes learn shortly NOTICE
auditory learning style? 2) How big is academic
achievement and graduation student athletes who
learn to use kinesthetic learning style?
2 METHOD
In this study, the authors used descriptive method
because they want to know how to describe the
learning style of athlete students in the Ministry of
Education coaching. As Hartoto explained in
Nasution (2008, p.69) that "descriptive research is a
method of research that seeks to describe and
interpret objects as they are." So in this study the
results obtained in accordance with the conditions at
the time of the study conducted without changing the
slightest result which is obtained. Furthermore clear
about the descriptive method described by Furchan in
Lutan (2014, p.27) regarding its characteristics as
follows:
The characteristics of descriptive method are: (1)
Descriptive research tends to describe a phenomenon
30
Hidayat, U., Haryadi, S., Rohmat, R., Bahari, R. and Berliana, B.
Comparison between Auditory and Kinesthetic Learning Style of Student Atheletes in Achieving Grade Point Average.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2017) - Volume 2, pages 30-33
ISBN: 978-989-758-317-9
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

as it is by studying a phenomenon as it is by regularly
reviewing it, using objectivity and done carefully; (2)
Absence of any given or controlled treatment; (3)
Absence of hypothesis test.
For a best viewing experience the used font must
be Times New Roman, on a Macintosh use the font
named times, except on special occasions, such as
program code (Section 2.3.7).
In the study entitled Athlete Student Learning
Styles on Achievement of Academic Achievement
and Graduation, the research location on the title was
held at Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia (UPI),
Faculty of Sport and Health Education (FPOK) at the
athlete students of the Education Department of
Coaching precisely in the 4th floor Auditorium room.
The reason for choosing the location is because the
studying places all the research samples are on
Campus FPOK precisely in the Ministry of Education
coaching, so that the location close to college student
athletes can simplify the research process to be more
effective and efficient.
2.1 Population and Sample
2.1.1 Population
To obtain data in this study required data sources that
are generally called population and sample research.
According to Arikunto (2010, pp. 173) "the
population is the whole subject of the research." The
population referred to in this study is an athlete
student of the Ministry of Education at the Faculty of
Sport and Health Education (FPOK) at the University
of Education Indonesia (UPI) totalling 162 athletes,
consisting of 31 martial art sports of athlete students,
87 sports of athlete students, 36 measured sports of
athlete students, and 8 precision sports of athlete
students. This population was chosen because the
students of the Ministry of Education have many
athlete students with achievements at provincial,
national and international levels from various sports.
Besides student athletes have some concerns
regarding the low GPA (IP) and a grade point average
(GPA), which resulted in student athlete graduation
rate exceeds the normal time (4 years / 8 semesters)
as shown in appendix 4. Low Grade (IP) in the
previous semester resulted in at least SKS that can be
a student contract for athletes in the next semester in
SIAK so as to cause some courses can not be
contracted on time, even to repeat some courses so
that student graduation is delayed or exceeds normal
time (4 years / 8 semesters).
2.1.2 Sample
According to Lutan, Berliana, and Surnandi (2014,
pp. 80) "the sample is the group used in the study
where the data / information is obtained, while the
population is the larger group in which the results are
generalized."
Samples to be used in this study amounted to 50
students athletes. The selection of samples using the
Simple Random Sampling method, according to
Sunaryadi (2014, pp. 5.7) explains that "simple
random samples are one method in which every
member of the population has the same opportunity
to choose." Based on that opinion, it means that every
athlete student has the same and independent
possibilities to choose from.
The sample selection will be randomly
randomized with a 30% percentage of the total of
each force in each sport category. For more details
can be seen in Table 3.2 as follows.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Test F-test
F test is used to determine whether the independent
variables simultaneously have a significant effect on
the dependent variable. The degree of trust used is
0.05. If the value of F calculation results greater than
the value of F according to the table then the
alternative hypothesis, which states that all
independent variables simultaneously have a
significant effect on the dependent variable. The
output is as follows:
Table 1: Test F test ANOVA.
MODEL
sum
df
f
Sig
Regresion
Residual
total
445
9,1
9,6
1
48
9,6
49
a. Dependent Variable: IPK1
b. Predictors: (Constant), Learning Styles
Comparison between Auditory and Kinesthetic Learning Style of Student Atheletes in Achieving Grade Point Average
31
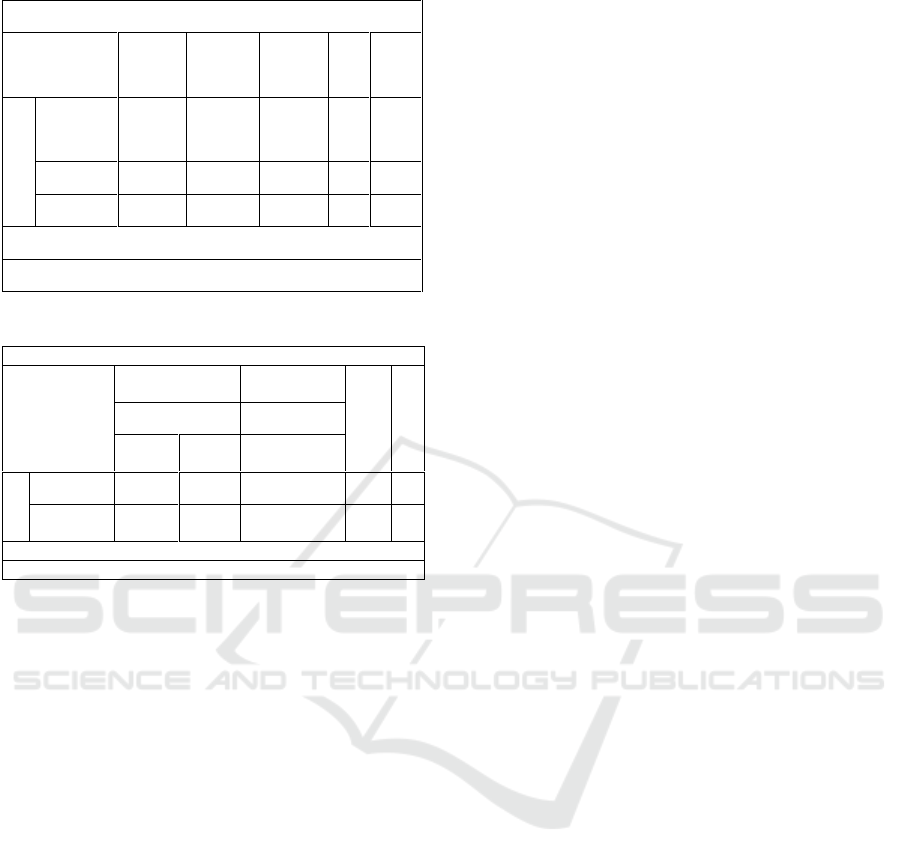
Table 2: Test Anova a.
Table 3: coefficients a.
Test F 'shows that F count equal to 2,323 with
level (sig) 0,134 or can significance value 0,134
greater than probability value 0.05. "It proves that
there is a significant relationship between Learning
Styles of GPA".
F test is used to determine whether the
independent variables simultaneously have a
significant effect on the dependent variable. The
degree of trust used is 0.05. If the value of F
calculation results greater than the value of F
according to the table then the alternative hypothesis,
which states that all independent variables
simultaneously have a significant effect on the
dependent variable. The output is as follows:
Test F 'shows that F count equal to 2,818 with
level (sig) 0,083 or can significance value 0,083
greater than probability value 0.05. "It proves that
there is a significant influence between auditory and
kinesthetic against GPA".
3.2 Test T-test
The t test is used to find out whether the independent
variables are partially significant or not to the
dependent variable. The degree of significance used
is 0.05. If the significant value is less than the degree
of trust then we accept the alternative hypothesis,
which states that an independent variable partially
affects the dependent variable. The output is as
follows:
Based on these results, it is known product
moment correlation coefficient (rx 1 x 2 y) between
Learning Styles (x) with GPA. (Y). Learning Style
Correlation (x) with GPA (Y) of = 0,134 with p =
0,05. It turns out that p is greater than the specified
alpha (level of significance) of 5%. So it can be
concluded that there is a significant relationship
between Learning Styles with GPA.
The t test is used to determine whether the
independent variables are partially significant or not
to the dependent variable. The degree of significance
used is 0.05. If the significant value is less than the
degree of trust then we accept the alternative
hypothesis, which states that an independent variable
partially affects the dependent variable.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on this research, calculations, data analysis avg
se, the writer can draw conclusions about the student's
learning style against achievement athlete academic
achievement and graduation:
The percentage of students' learning styles
athletes Coaching Education Department are:
26% auditory learning styles, and 66%
kinesthetic learning style.
Students of athletes of the Department of
Coaching Education with an auditory learning
style have an average GPA of 3.09 and the
average graduation ranges from 8 semesters to 9
semesters.
Students of athletes of the Ministry of Education
with a kinesthetic learning style have an average
GPA of 3.27 and the average graduation ranges
from 8 semesters to 9 semesters.
Percentage of student learning style athletes
Department of Education coaching based on
sports category that is: Martial Art Sports
(auditory 44.44%, 55.56% kinesthetic),
Measured Sports (auditory 30%, kinesthetic
70%), Game Sports (auditory 21:43%,
kinesthetic 71.43%), Precision Sports (auditory
0%, kinesthetic 33.33%).
REFERENCES
Agustama, Y. 2013. Identification of Learning Styles
Mathematics Student Class VII SMP Negeri 14 Malang.
ANOVA
a
Model
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.
1
Regression
, 354
2
, 177
2,8
18
, 083
b
Residual
1,255
20
, 063
Total
1.609
22
a. Dependent Variable: IPK2
b. Predictors: (Constant), Kinesthetic, Auditory
coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
T
Sig.
B
Std.
Error
Beta
1
(Constant)
2,344
, 559
4,193
, 000
Learning
Styles
, 009
, 006
, 215
1.524
, 134
a. Dependent Variable: IPK1
b. Predictors: (Constant), Learning Styles
ICSSHPE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sports Science, Health and Physical Education
32

Essay Bachelor on University Negeri Malang: no
published.
Anonymous. 2011. UPI curriculum. Bandung: University
Indonesian education.
Anonymous. 2012. Guidelines Academic. Bandung:
University Indonesia Education
Arikunto, S. 2010. Procedure Research, Jakarta: PT Rineka
Copyright.
Gerung, N. J. 2007. Conceptual Learning and Learning
Style. Volume 2 No. 1.
Hasrul. 2009. Understanding about Learning Styles.
Journal Medtek: Volume 1 No. 2.
Ibrahim Rusli. 2014. Psychology Kependidikan. Bandung:
Redpoint.
Jensen, E. 2011. Learning Based Brain. Jakarta: PT. Index.
Jumardi. 2014. Influence Approach Learning and Learning
Styles To Results Learn History Students. Journal
Education History: Volume 3. No. 1.
Komalasari, F. 2013. Paper Problem Learn and Birds
[Online]. Available:
https://ferakomalasari.wordpress.com/2013/03/11
paper-problem-learning and mitigation / [8 August
2015].
Lutan, R. et al. 2014. Module Research Education in
Training Sports. Bandung: University Indonesian
education.
Luxas. 2008. Oxford dictionaries [Online]. Available:
http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/
graduated [2 July 2015].
Nasution. 2008. Research Methods, Jakarta: Earth Script.
Nasution. 2008. Various Approach In the Learning Process
and Teaching. Bandung: Earth Script.
Nurhasan et al. 2008. Module eye Lecture Statistics.
Bandung: University Indonesian education.
Nurhasan et al. 2015. Test and Measurement. Bandung:
University Indonesian education.
Rachmat, J. 2007. Learn Intelligent. Bandung: MLC.
Riduwan. 2012. Basics Statistics. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Riyana, C. 2002. Components Learning. Bandung: LPPM
UPI.
Smith, B. 2012. Role and Function Students [Online].
Available:
http://pamuncar.blogspot.com/2012/06/definisi-peran-
dan-fungsi-mahasiswa.html [7 August 2015].
Sarwanto. 2010. Learning and Education Character.
Journal Research Education: Volume 14 No. 2.
Slameto. 2003. Learn and Factors Affecting. Jakarta:
Rineka Copyright.
Sugiyono. 2012. Method Research Educational Approach
Quantitative, Qualitative, and R & D. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Sugiyanto. 2012. Effect of Experiential Learning in the
Learning Styles Enhancement Achievement Academic
and Its application In Learning. Essay Bachelor in FIP
UNY: no published.
Sunaryadi, Y. 2014. Method Research. Bandung: CV
Conscience.
Suryabrata. 1982. Development Individuals. Jakarta: PT
Rajawali.
Susilowati, U. 2010. Influence of Learning Styles and
Motivation Learn to Achievement Learn College
student Academy Midwifery Bhakti Nusantara Salatiga.
Thesis Post Graduate Program Bachelor on University
Eleven Maret: no published.
Tanta. 2010. Influence of Learning Styles to Results Learn
College student On Course Biology General. Journal
Education Basis: Volume 1. No. 1.
Thobroni, M., Mustafa Arif. 2013. Learn and Learning.
Yogyakarta: AR-RUZZ MEDIA.
Wandini, K. 2008. Influence Pattern Foster Learning,
Environment Learning, Motivation Learning, and
Potency Academic to Achievement Academic Student
School Basic. Essay Bachelor on IPB students: no
published.
Comparison between Auditory and Kinesthetic Learning Style of Student Atheletes in Achieving Grade Point Average
33
