
Teacher Professionalism Development in Constructive
Collaborative-Based Scientific Article Writing
Bambang Sumardjoko and Anam Sutopo
Pancasila and Civic Education Study Program of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of Surakarta Muhammadiyah
University, A.Yani Street, Tromol Pos 1, Pabelan, Kartasura, Surakarta
{bs131, Anam.Sutopo}@ums.ac.id
Keywords: Teacher Professionalism Development, constructive collaborative, and scientific article.
Abstract: This research aimed to describe the prior condition of teachers’ understanding and ability of writing scientific
article, the form of teacher need, and teacher professionalism development management model in constructive
collaborative-based scientific article writing. This research was conducted using research and development
design with educator-certified teachers in Muhammadiyah Secondary Schools in Sukoharjo, Central Java,
being the subject. Data was obtained through observation, interview, document analysis, questionnaire and
FGD. The results of research were as follows: firstly teachers’ understanding on scientific article was still low
and their ability of planning, organizing, and publishing scientific article should be improved. Secondly,
teachers had made some competency improvements either independently by attending workshop, seminar,
and providing new textbooks or by attending discussion activity of subject teacher. Thirdly, teachers highly
needed infrastructure and guidance in improving scientific article writing. Fourthly, the sustainable teacher
profession development model in constructive collaborative-based scientific article writing material started
with problem identification and then collaboration with group can motivate teachers in preparing scientific
article.
1 INTRODUCTION
Development model is intended to be a framework in
sustainable teacher profession development in
scientific article writing field. The matters discussed
include teachers’ understanding on scientific work
writing, activity forms, development need forms, and
sustainable teacher profession development model in
constructive collaborative-based scientific article
writing. Constructive collaborative is a strategy of
writing scientific article based on the problem found
themselves and then collaborating with group to find
the solution (Charlotte, 2005). The object of research
consisted of educator-certified teachers in senior high
schools in Muhammadiyah area of Sukoharjo, Central
Java.
Teachers is a professional educators with the main
duty of educating, teaching, guiding, leading,
training, assessing, and evaluating the students in
early age child education of formal education
channel, primary and secondary education. The
position of teachers as the professional serves to
improve the teachers’ dignity and role as the agent of
learning and to improve the national education quality
(Law No.14 of 2005). As the teaching staff, teacher is
required to have competency or pedagogic ability
thereby can transfer knowledge to the students. The
role of teacher becomes very strategic in preparing
high-quality human resource. Therefore, the
improvement of teacher professionalism should be
done continuously.
The development of teacher professionalism is
conducted based on institution’s need, teacher group,
and teacher itself. According to Danim (in
Syaefuddin Sa’ud, 2009), teacher development is
intended to stimulate, to maintain, and to improve the
quality of staff in solving organizational problems.
Although teacher development based on institution
need is important, the more important thing in teacher
professionalism development is based on teacher’s
individual need to realize professionalism (Payong,
2011). Therefore, teacher professionalism
development should be developed sustainably.
Speaking of sustainable teacher professionalism
development, it can be found that many teachers,
including those with Civil Servants status, are
hindered with the requirement to write scientific
article in their professionalism development.
Meanwhile, scientific article writing ability becomes
one indicator of teacher quality (Suhaenah, Kompas,
Sumardjoko, B. and Sutopo, A.
Teacher Professionalism Development in Constructive Collaborative-Based Scientific Article Writing.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education (ICSE 2017) - Volume 1, pages 143-149
ISBN: 978-989-758-316-2
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
143

22 April 2014), as through writing scientific work,
teachers can reflect their various experiences. In
Central Java Province, nearly 60% of Civil Servant
teachers having achieved the 4tha space grade cannot
be promoted to one higher level because they are
inhibited by scientific article writing problem. Data
shows that Secondary School teachers who have
occupied the 4tha grade are 50.88%, while those who
can be promoted to the 4thb and so forth are only
0.5% (Yunianto, 2007). Sumardjoko’s (2013) study
on the Model of Reinforcing the Certified Teachers
through Interpreting Professionalism in the teachers
of Public Senior High Schools in Sukoharjo, Central
Java showed that the dominant factor causing the
teachers’ less successful professionalism
improvement is their inadequate ability of conducting
classroom action research and writing scientific
article.
Furthermore, the next study conducted in
Muhammadiyah secondary schools in Sukoharjo
found that the development of sustainable teacher
professionalism shows no clearly and systematically
structured development. Therefore, considering the
phenomena above, a constructivist-collaborative-
based sustainable teacher professionalism model
should be developed to improve the teachers’ soft
skills-transferable skills in writing scientific article
writing.
Soft skill refers to interpersonal competency or
personality. Career Opportunities News publication
mentions that soft skills include positive skills to
support personality. Soft skills can be motivation,
respecting others, working in team, self-discipline,
self-confidence, adaptation to commonly prevailing
norms, and language or communication competency,
either spoken or written. Teachers having positive
soft skills are expected to master spoken and written
communication and to have high job motivation
thereby can work intensively under the pressure of
product target and deadline. An individual having
good soft skill is those that can be powerful in the
future because he/she can manage his/her personal
life, either internally into him/herself or externally in
establishing relation with others.
Soft skills can build a well-established teacher
personality. Considering the result of research on
effective lecturers, it can be found some general
phenomena that lecturers preferred by students are
those having positive personality. Gordon’s (1999)
study found that eight out of 18 teaching competency
statements are effective and the one having
significant and positive relationship is personality
type. The data indicates that 42.25% of competency
variation can be predicted from personality type.
Lecturer’s personality type dimension having high
score in the teaching effectiveness is whether or not
the lecturer’s presence is desirable, and whether or
not they can work as hard as possible to complete the
work fully and timely. The lecturer appreciating the
specified procedure and authority believe that they
will keep surviving as they have run their function
well.
Considering the description above, the research is
intended to describe the prior condition of teachers’
understanding and ability of writing scientific article,
the form of teacher need, and teacher professionalism
development management model in constructive
collaborative-based scientific article writing for
Muhammadiyah teachers.
2 METHOD
This study was research and development, starting
from preliminary study, development activity through
field study process, model designing, model design
tryout, to model validation. This research and
development was taken place in Sukoharjo, Central
Java Province. Data source included informant
(teachers, headmaster, chairperson of primary and
secondary education chamber [thereafter called
majlis dikdasmen]) place or event (senior high school,
vocational middle school, classroom, and learning
circumstance), and document based on snowball
sampling and purposive sampling. Data validation
was carried out using source triangulation and review
informant. Meanwhile, data analysis was conducted
using an interactive model of analysis (Miles and
Huberman, 1984).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Considering the data per June 25, 2015, teachers and
Muhammadiyah Secondary School can be described
as follows. There are 11 schools including SMA, MA,
and SMK with a total of 346 teachers. 116 teachers
have attended educator certification (34.39%) and the
rest of 227 (65.61%) have not. It indicates that the
number of teacher having not attended certification
program is larger than those having attended.
The 119 teachers having obtained educator
certificate, by their personnel status, are divided into
three categories: Civil Servant (PNS), Permanent
Foundation Teacher (GTY), and Non-Permanent
Teacher (GTT). There are 20 (16.81%) educator-
certificated teachers with Civil Servant status, 72
(60.50%) with GTY status, and 27 (22.69%) with
GTT status. This data of personnel status is
interesting because many teachers with non-PNS
status (83.19%) have obtained educator certificate,
compared with teachers with PNS status. Then, by
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
144

education level, they are divided into two categories:
master (postgraduate/S2) and graduate (S1). Ten
teachers (8.40%) with postgraduate degree have
obtained educator certification and 109 (91.60%)
with graduate degree have obtained it. The data of
education level shows that only few teachers with
postgraduate degree, so that the number of teachers
with graduate degree attending the higher level of
education should be improved. By sex, 81 (68.07%)
out of 119 Muhammadiyah Senior High School
teachers in Sukoharjo who have obtained educator
certification are males and 38 (31.93%) are females.
The data of sex shows that male teachers still become
the majority obtaining educator certification,
compared with the male ones.
3.1 Mapping and Teachers’ ability of
writing scientific work
Scientific work is essentially the result of a scientist’s
thinking product that wants to develop science,
technology, and art. This scientific thinking product
was acquired from library study, experience, previous
research, and others’ knowledge. Interview with BS
(June 5, 2015), related to scientific work concept,
suggested that “The mastery of research concept
inhibit me in Classroom Action Research (CAR).
Sometimes when I prepared, I was confused whether
or not it has been correct, so that finally I stopped to
prepare it”. SS, a history teacher, said “Actually
historical learning finds many problems. For
example, students’ motivation, the effective delivery
method, and relevant learning source. It can be the
theme of classroom action research. But I do not
master the concept of CAR completely. I am rather
confused in writing the correct proposal and
procedure. There is actually an example, but
regarding different discipline, so I remain to find
difficulty”.
Information obtained from ES, as the Pancasila
and Civic Education teachers on June 8, 2015,
revealed that “Conducting a research is perhaps one
of my weaknesses, because I did not write thesis
when I studied at university”. Meanwhile W stated:
“The difficulty in conducting CAR generally lies on
the development of research concept, from
determining an appropriate title, problem statement,
the theory used, to the method used. I would find
difficulty if no one guided me”.
The information from teachers of SMK
Muhammadiyah 1 and 2 Sukoharjo was crosschecked
with that from teachers of SMA Muhammadiyah 3,
and SMK Muhammadiyah Watukelir, all of which
concludes that there are still some constraints in
understanding scientific work concept. Teachers’
experience with scientific work writing is obtained
during Teacher Profession Practice Education
(thereafter called PLPG).
Considering the questionnaire distributed, it can
be found that the educator-certificated teachers’
understanding on scientific work concept can be
shown as follows: 15% understand, 55% understand
poorly, 30% do not understand. That condition is in
line with Sumardjoko’s (2012) study finding that the
constraints the teachers encounter in writing scientific
work are as follows. Firstly, reading interest is low.
Secondly, teacher has inadequate information about
latest development activity. Thirdly, there is
misperception. Teachers having inadequate
information about scientific work misperceive the
scientific work writing.
In addition, the poor understanding on scientific
work writing is due to internal factor of
corresponding teachers. Low motivation is one of
internal constraints consisting of teachers having no
reading habit, and having poor language ability.
Laziness in trying is one factor inhibiting the teachers
in starting to write scientific work.
3.2 Teacher Professionalism
Development so far
3.2.1 Teacher’s perspective
Basically any forms of self-development in educator-
certified teachers have been done, despite less
maximal. Teachers have conducted some self-
development to fulfill and to improve pedagogic,
professional, social, and personality competencies.
The evidence of teachers’ self-development activities
can be seen from the result of interview with some
informants. BS, as the Pancasila and Civil Education
teacher in SMK Muhammadiyah 1 Sukoharjo
(interview on June 5, 2015), stated that “I have read
many books, attended workshop, and outbond so far.
If those are done all, it think it is enough to improve
the competency”. This information is confirmed by a
history teacher, SS, stating that “in addition to reading
book, I also often browse in internet, because
historical events will be found more easily in internet.
I have ever attended seminar or workshop as well. It
can support my competency as History teacher”.
Information on teachers’ development activity
obtained from the two informants is similar to that
obtained from H.Sm, the certificated teacher
assuming entrepreneurship in SMK Muhammadiyah
1 Sukoharjo. ES, a Pancasila and Civic Education
teacher (Interview on June 8, 2015), has also
developed his competency and attended MGMP
activity and then, bought laptop for browsing in
internet, to search for recent information about civic
issues. This information is confirmed by W assuming
Teacher Professionalism Development in Constructive Collaborative-Based Scientific Article Writing
145

Physical Education and Health, and Sgn assuming
Indonesian language subjects.
Considering the description of data above, it can
be found that educator-certificated teachers have
conducted some activities so far to develop
competency after have been certified. The activities
conducted include attending workshop and seminar,
buying newest textbook, attending MGMP activity,
and discussing with fellow subject teachers. This
demand for realizing teacher professionalism is in
line with Hult and Edstrom’s (2016) research finding
that the improvement of teacher professionalism
should be supported by the presence of accountability
through significant evaluation and measures.
The attempts taken to improve teacher
professionalism can be seen in histogram below.
Table 1: Teachers’ Activities to Improve Professionalism.
Activity
Proportion %
Seminar
25 %
Workshop
20 %
MGMP
15 %
Discussion
10 %
Reading Book
10 %
Internet
5 %
Research
10 %
Social Activity
5 %
3.2.2 Headmaster’s Perspective
The headmasters as the leader are also responsible for
developing teacher professionalism in school. Many
attempts have been taken by headmaster to support
the certificated teacher in order to have better
competency. HM, as the headmaster of SMK 2
Muhammadiyah Sukoharjo, states that he supports
any teacher activities to develop competency. In the
interview on June 8, 2015, he stated that “When there
is an invitation for seminar or workshop, we will send
our teacher, and we provide the fund as well.
Teachers are given service trip document stamped by
the committee of seminar/workshop. Then, the
document is submitted to the school. MGMP activity
is also supported, and particularly the place is
provided, if necessary. Regarding teaching hour, we
adjust it with teachers’ need, particularly those
certificated ones in order to be consistent with their
teaching hour need. Many more activities can be
conducted to develop teachers’ competency”.
Information from HM was then crosschecked
with Mdj as the headmaster of SMK Muhammadiyah
1 Sukoharjo, and the result is similar. He said that the
school management supports completely the
development of teacher competency, despite some
constraints. Similarly, Skn, as the headmaster of
SMK Muhammadiyah Watukelir and SMA
Muhammadiyah Pontren Imam Syuhada always
support every teacher activity in developing
competency.
Considering the result of research, it can be found
that headmasters have attempted to support and to
facilitate the teachers in performing any activities in
order to improve their pedagogic, professional,
interpersonal and social competencies. The support
includes: (1) encouraging the teachers to attend the
seminar, (2) encouraging the teachers to attend
workshop, (3) facilitating the activity of discussion
with fellow subject teachers in respective school, (4)
supporting the MGMP activity, (5) motivating the
certificated old teachers to keep productive, (6)
supporting teacher to organize social activity in
religion holiday event, (7) supervising teacher
activities in school, (8) encouraging the teacher to
conduct research, and (8) participating in determining
policy when distributing teachers’ teaching hour.
Many attempts and activities the headmasters can
conduct to improve their professionalism sustainably,
including scientific work writing, can be seen in the
histogram below.
Table 2: Headmasters’ Attempts of Improving Teacher
Professionalism.
Activity
Proportion %
Seminar
25 %
Workshop
20 %
Discussion
15 %
MGMP
10 %
Motivation
8 %
Activity
7 %
Supervision
5 %
Research
5 %
Policy
5 %
3.2.3 Primary and Secondary Education
Chamber’s Perspective
The reality in the field represents that the Primary and
Secondary Education Chamber of Muhammadiyah
Sukoharjo tends to supervise, to support, and certified
teachers’ activity in developing their competencies.
The system developed is bottom-up. It is
characterized with any idea individual schools so that
the Primary and Secondary Education Chamber
supports only after the school takes action.
Limited role and function of teacher
empowerment by Primary and Secondary Education
Chamber of Muhammadiyah Sukoharjo and perhaps
in other areas seem to be affected by many factors.
The leadership of Primary and Secondary Education
Chamber is largely held by non-teacher figure and
retired teacher. As the private institution growing and
developing from the bottom and having social
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
146

religious vision, dakwah amar makruf nahi munkar,
some difficulties are found in realizing the
professional school management. Most of
Muhammadiyah schools manage the school by
applying efficiency and effectiveness principles
tightly. Therefore it is unsurprising that the Primary
and Secondary Education Chamber often finds
difficulties in funding the breakthrough and various
activities intended.
3.3 The need for Sustainable Teacher
Professionalism Development
Considering the result of document analysis and in-
depth interview, it can be explained that teachers have
attempted to develop their professionalism in some
way, using development model: “Individual Guided
Staff Development”. Teachers can assess their
learning need and learn actively and direct
themselves. They should be motivated when selecting
the learning objective based on personnel assessment
on their need. Independent professionalism
development the Muhammadiyah teachers have done
in Sukoharjo is consistent with the guidance of
Sustainable Professionalism Development activity
issued by government.
Meanwhile the constraints occurring in this
development are: time, funding, age, school
infrastructure, motivation, leader’s policy, and access
to internet network. Therefore, what is needed and
attempted continuously are firstly the measures of
simplifying anything related to learning
administrative activity and evaluation by the policy
makers in school; secondly, fund provision by
Primary and Secondary Education Chamber or other
sponsor in tapping to teacher activity. in this case, the
Primary and Secondary Education Chamber is
expected to be not only bottom-up but also up-down;
thirdly changing policy from the leader of Primary
and Secondary Education Chamber to make the
position promotion more selective thereby pertaining
to pedagogic, professional, interpersonal and social
domains; fourthly providing access to internet; fifthly
support from college in organizing workshop/seminar
and other activities; and sixthly, scholarship support
for advanced study.
3.4 Constructive Collaborative-Based
Teacher Professionalism
Development Management Model
Considering the result of preliminary study above, the
development model developed was based on the
teachers’ need for writing scientific article to improve
their professionalism. The model was developed
constructively, meaning that it based on the problems
found by the teachers themselves, while research
team gives reinforcement and facilitation. It is in line
with Moswela’s (2006) research finding that teacher
development program to achieve the intended
objective should improve teaching and learning
process and find out the need based on actual
problems in the class. Then, regarding facilitation
problem, it is in line with Raaen (2017) stating that
the placement of mentor will show the teacher how
research-based experience is relevant to teacher
professional job. It is collaborative, meaning that
teachers will collaborate with their group (a single
same school/same study area), to produce scientific
article. The attempts of finding solution
constructively and to be collaborative in writing
scientific article are the foundation to develop writing
ability more easily and meaningfully based on the
problems found by the teachers themselves. This
model grows self-confidence and motivation among
the teachers to write other scientific articles.
The measures of developing model are as follows.
Firstly, analyzing the teachers’ need for writing
scientific article. Secondly, preparing draft
constructivist-collaborative-based teacher
professionalism development model. Thirdly, focus
group discussion to solidify the model. Fourthly,
accomplishing the model set. Meanwhile, the
important components supporting the preparation of
sustainable teacher professionalism development
model in writing scientific article are as follows.
Firstly, the participation of all stakeholder. Secondly,
Majlis Dikdasmen Muhammadiyah constituting the
key component determining the model
implementation. Thirdly school providing
infrastructure for teacher. Fourthly, teacher
constituting the key component of model
implementation. Fifthly, LPTK (Team of Teacher
Training and Education Faculty) Surakarta
Muhammadiyah University as facilitator and
developer. Kempen and Steyn’s (2016) study found
that the constructivist-collaborative model becomes a
choice to improve model corresponding to teacher
need. This research serves as the example in which
valuable internal and external network is created for
the interests of all parties involved in this research the
constructive collaborative-based sustainable teacher
professionalism development model to improve soft
skills-transferable skills – in scientific article writing
for the educator-certified teachers in Muhammadiyah
Secondary School of Sukoharjo is shown in the figure
below.
Teacher Professionalism Development in Constructive Collaborative-Based Scientific Article Writing
147
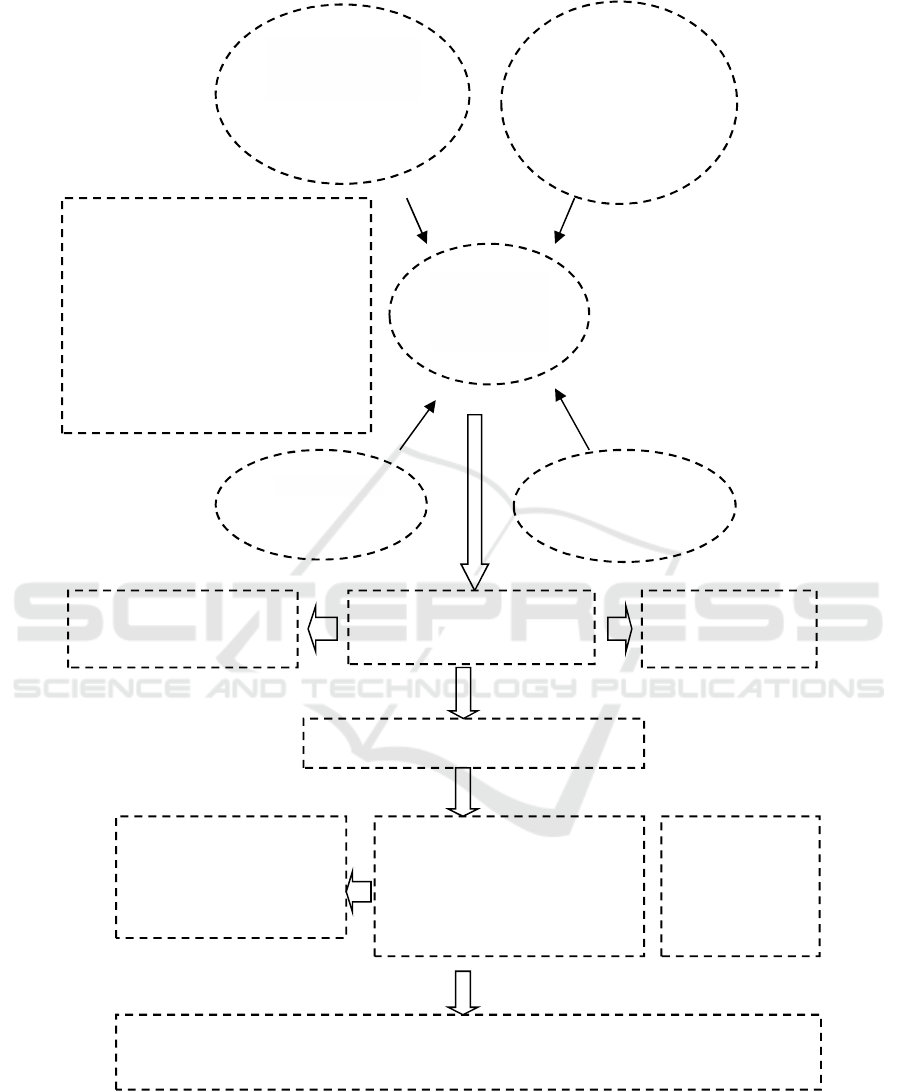
Figure 1: Sustainable Teacher Professionalism Development Model.
Sustainable Professionalism Development
attempt the teachers have done:
Attending seminar/workshop
Reading book/learning material
Utilizing internet
Active in MGMP activity
Active in societal activity
Comparative study along with MGMP
members
MAJLIS
DIKDASMEN
MUHAMMADIYAH
(Determinant of Model
implementation)
LPTK/ PT
(Facilitator and
developer)
TEACHER
(Actor/ Subject
of Development)
SCHOOL
(Provider of
infrastructure for
Teacher in improving
scientific work writing
ability
Teachers’ low ability of writing
scientific article
Training/Facilitation of
LPTK
Credit point Professionalism
Position
Ability of writing scientific article
Increased percentage of teacher
becoming presenter
Increased number of article
uploading in journal
The improvement
of Sustainable
Professionalism
Development
independently
TEACHERS’ INDEPENDENCY IN DEVELOPING PROFESSIONALISM & IMPROVING
LEARNING PROCESS QUALITY
Improved Soft Skill-Transferable Skill
Improved teacher performance
Improved teacher
Professionalism
Grade promotion runs
smoothly
STAKEHOLDER
ICSE 2017 - 2nd International Conference on Sociology Education
148

4 CONCLUSIONS
Firstly, teachers’ understanding on scientific article
writing has not been good entirely. Teachers’
experience with writing scientific article was mostly
done during teacher professionalism training (PLPG).
Secondly, teachers have done a variety of activities to
develop their competency independently by attending
workshop, seminar, buying the new lesson text,
attending Subject Teacher Discussion (MGMP)
activity, and discussing with fellow subject teachers.
Thirdly, to develop scientific article writing, the
educator-certified teachers still find constraints such
as time, fund, age, school infrastructure, motivation,
leader’s policy, and access to internet network.
Fourthly, the constructivist-collaborative-based
sustainable teacher professionalism development
model to improve teachers’ soft skills-transferable
skills in writing scientific article is integrated in
nature. In this development model, n writing
scientific constructively, teachers start with
identifying problem and then collaborating with their
group so that the constraint in developing scientific
article can be solved well.
REFERENCES
Charlotte Hua Liu and Robert Matthews. 2005. Vygotsky’s
philosophy: Constructivism and its criticisms examined.
International Education Journal. 6 (3). page: 386-399.
Gordon, Howard R.D. and Richard Yocke. 1999.
Relationship between Personality Characteristics and
Observable Teaching Effectiveness of Selected
Beginning Career and Technical Education Teachers.
DLA Ejournal Home. Volume 16, Number 1. Marshall
University.
Hult, A. and Edstrom, C. 2016. Teacher ambivalence
towards school evaluation: promoting and ruining
teacher professionalism. In Education Inquiry. Volume
7, 2016 - Issue 3. Special Issue: The Role of Evaluation
in Local School Governance in Sweden.
http://dx.doi.org/10.3402/edui.v7.30200
Kemendikbud RI. 2012. Tentang Kebijakan
Pengembangan Profesi Guru.
Kempen, M., Steyn, GM. 2016. “Proposing a Continuous
Professional Development Model to support and
Enhance Professional Learning of Teachers in Special
Schools in South Africa”. International Journal of
Special Education. Vol 31, No: 1, 2016.
Miles, M.B. and Huberman, A.M. 1984. Qualitative data
analysis: A sourcebook of new methods. Beverly Hills:
Sage Publication.
Moswela, B. 2006. Teacher professional development for
the new school improvement: Botswana. International
Journal of Lifelong Education. Volume 25, No 4.
Halaman 623-632.
Payong, Marselus R. 2011. Sertifikasi Profesi Guru;
Konsep Dasar, Problematika, dan Implementasinya.
Jakarta: PT Indeks Permata Puri Media.
Raaen, F.D. 2017. Placement mentors making sense of
research-based knowledge. An International Journal of
Teachers' Professional Development. Volume 21, 2017.
Issue 5. Pages 635-654.
Sa’ud, U. Syaefudin. 2009. Pengembangan Profesi Guru.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Sumardjoko, B. 2013. Model Penguatan Guru
Bersertifikasi melalui Pemaknaan Profesionalisme pada
Guru-guru SMA Negeri di Sukoharjo Jawa Tengah.
Laporan Penelitian. Surakarta: LPPM UMS.
Yunanto, Eris. 2007. Evaluasi Program bimbingan teknis
Penulisan artikel Ilmiah Pengembangan Profesi Guru
Sekolah Menengah di Propinsi Jawa Tengah. Tesis.
Semarang: Unnes.
.
Teacher Professionalism Development in Constructive Collaborative-Based Scientific Article Writing
149
