
Improving Students’ Interest to Learn Mandarin with Mandamonik
Game in Three Languages
Yi Ying ¹, Putri Mustika Susilo ¹, Fu Ruomei ¹, Theresia¹
¹Chinese Department, Faculty of Humanities,
Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia 11480
Keyword: Impove, students’ interest, mandarin, mandamonik game
Abstract: Foreign language education has begun to incorporate conventional education with mobile learning or "M-
Learning." M-Learning offers a modern way to support the learning process through mobile devices, such as
handheld computers and tablets, MP3 players, smartphones and mobile phones. This study explains the
learning of Chinese through M-learning with a smartphone. With the development of technology, the use of
smartphones among elementary school students is also increasing especially for games. Students' interest to
play games, especially on smartphones becomes the background for researchers to design the Chinese
learning by emphasizing on game-based learning. Researchers before designing the smartphone games first
surveyed 129 elementary school students grade 1-6 in two private elementary schools in Jakarta about the
use of smartphones and the interest of students to play educational games. From the survey, researchers
designed a game application called "Mandamonik." This application consists of three types of games,
namely memory game, puzzle game and word crosshairs game. The authors asked 33 students to play the
game. From the students’ feedback, it is known that 85% of students consider the game Chinese Character
helps Chinese learning especially mastery of vocabulary.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chinese learning in Indonesia starts from
kindergarten to university level. By distributing
questionnaires to 594 respondents consisting of
elementary students to university students and
Chinese teachers, also interviews to 8 Chinese
experts in Indonesia for the research on the
condition of Chinese teaching in Indonesia can be
concluded two things, namely 1) there is a need for
interesting and illustrated mandarin teaching
materials; 2) The learning application as a tool of
teaching materials and textbooks for independent
study is also very much needed by Indonesian
students (Zhang SL, Ying Y, 2012).In the process of
learning Chinese language, most learners find it
difficult especially in learning Chinese Character. To
help elementary school students learn Chinese,
especially Chinese Character along with their
meanings, the researchers use technology which is
via mobile games. Chinese learning through games
becomes a better solution for children than the
traditional learning. Researchers introduce the
Mandamonik method of combining vocabulary
learning with educational play (Ying Y, Rawendy D
and Arifin Y, 2016).The use of gamification and
mnemonic methods into the game content is a
strategy to improve memory in various ways. The
gamification and mnemonic methods show positive
results in the learning environment. This game refers
to the elementary school, where students are aged 6-
12 years. Based on the pre-test and post-test results,
this game can improve students' learning outcomes
(Rawendy D, Ying Y and Arifin Y, 2017).
2 RESEARCH METHODS
This research uses survey method and experiment
method. The authors first surveyed 129 elementary
school students from Immanuel School and Sang
Timur Christian Primary School. After the student
feedback is obtained, then authors design the game
containing the vocabulary taken from the Mandarin
book for elementary students grade 1-6 which is
arranged in three languages namely Indonesia,
Chinese and English. The book is arranged by the
authors. After the survey data was processed, the
Ying, Y., Susilo, P., Ruomei, F. and Theresia, .
Improving Students’ Interest to Learn Mandarin with Mandamonik Game in Three Languages.
DOI: 10.5220/0010003200002917
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Social Sciences, Laws, Arts and Humanities (BINUS-JIC 2018), pages 99-103
ISBN: 978-989-758-515-9
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
99

authors design the game called Mandamonik. This
game consists of 3 parts: 1. Puzzle Games, 2.
Memory Game; 3. Word Crosshairs Game. Due to
time limitations, this game is only played by 32
students consisting of 15 students from Harapan
Kasih and 18 students from Immanuel. The study
was conducted from September 2016 until April
2017.
3 MOBILE LEARNING
3.1 Mobile Learning
The phenomenon of iPhone or Android phone users
is increasingly widespread, and it is not surprising
among educators. This has spawned mobile learning
(often called "M-Learning"). Language educators are
interested in the process of learning a language using
an application on a mobile phone (Jones RG, 2011).
The use of mobile phones in vocabulary learning
(abbreviated as VL) is more acceptable for language
learning. Several studies have been conducted on the
effects of Mobile-assisted language learning
(MALL) on vocabulary learning. The teaching
process has grown rapidly, and many scientists have
the same opinion on the role of mobile phones in
VL. Technology, in general, has a positive effect on
VL (Afzali P, Shabani S, Basir Z and Ramazani M,
2017). Research on the advantages and
disadvantages of students using the tablet devices
(iPad 2 only) in the assignments of English video
product was also done in Japan. The study also
examines students' perceptions when they use tablet
devices to see if they can make it a tool for learning
(Brown M, 2012). Research on the benefits,
challenges, and hindrances of mobile learning to
support teaching and learning was also done.
The study shows that M-Learning as distance
learning brings great benefits to society including
the learning that can be done anytime and anywhere
(Mehdipour Y, Zerehkafi H, 2013). Mobile-based
learning is one of the learning alternatives that can
be implemented for smart students who need a
unique approach (Ying Y, Mursitama TN, Oktriono
K and Abbas BS, 2017). Learning will be more
comprehensive if accompanied by game learning
because learning through the game makes the
learning process more enjoyable for the students.
Game-based learning models have been developed
and become the solutions (Ying Y, Mursitama TN,
Lin X and Yetty, 2017). The function of the phone
as a language learning tool and the students'
opinions after the mobile learning experience of 24
adult learners show the phone as an alternative
source for adult learners to learn vocabulary and to
meet the special needs of adult learners who need
more flexible time and place in learning (Hu Z N,
2013). The use of iPads for the English learners in
Japan shows some benefits such as speed in viewing
English video (Brown M, Castellano J, Hughes E
and Worth A, 2012). Mobile phone usage in creating
an out-of-class learning experience makes students
interested in learning by the method that explores
the mobile learning experience with their own
mobile devices (Kim D, Rueckert D, Kim DJ and
Seo D, 2013 ).
3.2 Game based Learning
Game-based learning is a trend that has been
implemented in many ways including workplace
training, education, and social media (Pho A,
Dinscore A, 2015). Research on the effectiveness of
Digital Game Basic Learning (DGBL) shows that
the game design should contain more specific game
elements to be more interesting. (AnissaA, Elena P,
Nuñez C and Jan V L, 2016). Learning through
experience is often more efficient than learning in
class. The trick is to provide the learning experience
needed to respond to the current challenges, i.e. to
use games in education. Innovative education, such
as learning-based games, is considered the most
appropriate (Pivec M, Dziabenko O, 2004). Using
mobile games in education by combining places and
active learning is great fun. The effect of a mobile
city game called Frequency 1550, developed by The
Waag Society to help students in the first year of
secondary education to study the history of
Amsterdam in the Middle Ages. After being
observed, the students who played the game got
more knowledge about the Amsterdam in the Middle
Ages. This shows that the location-based technology
and game-based learning have an impact on students'
knowledge and motivation (Jantina H, Admiral W,
Akmerman S and Dam GT, 2009).
4 MANDAMONIK APPLICATION
4.1 Survey Results before
Mandamonik Application Design
Before designing a Mandarin learning game called
"Mandamonik", first the survey of smartphone usage
was conducted towards 129 students in grade 1-6
elementary school in Jakarta. From the survey
BINUS-JIC 2018 - BINUS Joint International Conference
100
results can be seen that 91 students have a
smartphone. There are 91 students using android
apps. A total of 48 students said that they like to
play educational games using smartphones. A total
of 46 students said they had played Mandarin-
language educational games. A total of 99 students
said game-based learning could be helpful in
learning Chinese vocabulary and they are interested
if there is a game designed to help them memorize
the Chinese vocabulary. Therefore, the researchers
designed the game containing the vocabulary in
Chinese textbooks. The vocabulary in this design is
taken from a Chinese study textbook compiled by
the author. The vocabulary in this book consists of
11 categories namely fruits, numbers, studental
pronoun, family members, animals, school tools,
food and beverages, objects, vegetables, wind
direction and places.
4.2 Mandamonik Design
Mandamonik is a game application to memorize
Chinese vocabulary. The application is designed in
both Chinese and Indonesian languages. The
application design as follows:
Figure 1: App Front View.
Figure 2: Types of Game.
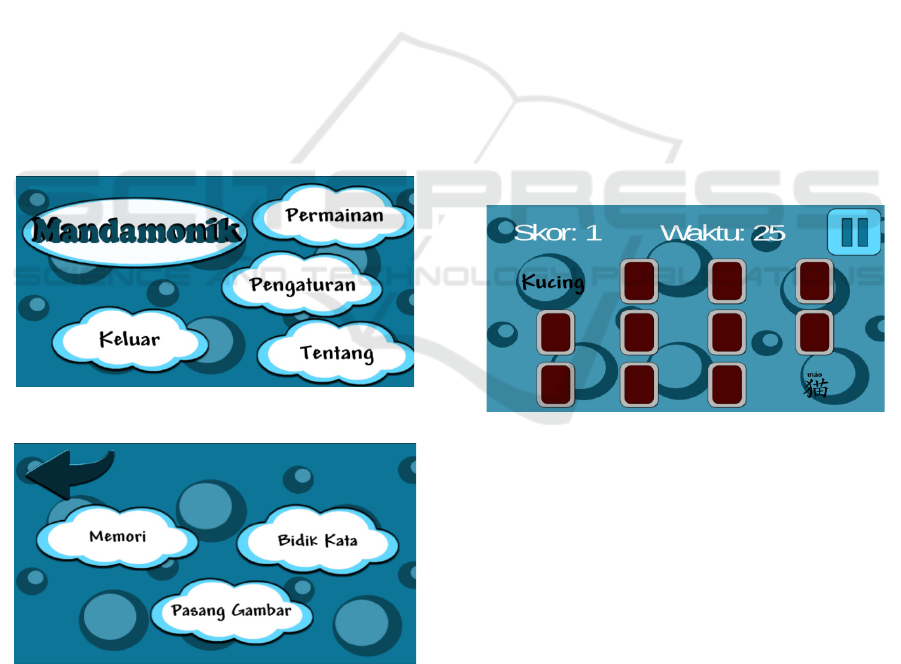
"Mandamonik" is the name of the application to
learn Chinese language. Learners need to touch the
screen with words or pictures. "Permainan" means
game, when the screen is touched it will display
three types of games. "Pengaturan" means setting
that contains information about the origin of the
game background sound. "Tentang" explains the
name of the student who designed the game.
"Keluar" means out, and the function is to exit the
game app.
Three types of game in this application are
Memory game (Memori), Puzzle game
(PasangGambar), Word Crosshairs game (Bidik
Kata).
4.2.1
Mandamonik Game
Applications.TheMandamonik Game App is
designed to help students memorize everyday
vocabulary. The vocabulary is equipped with
Chinese Character and Hanyu Pinyin in addition to
helping students memorize Chinese Character and
how to read it. This app contains three types of
game. Each type of game comes with game duration
(Waktu). The faster the game is completed, the
shorter the time is. This game comes with a score
(Skor). If you want to stop or change to another
game, then you can press the "pause" п.
Memory Game.
Figure 3: Memory Game.
This game consists of some closed cards and
players should look for a pair of cards that consists
of meaning and Chinese character along with Pin
Yin (how to read it). The player touches one of the
cards first and tries to guess its pair on a closed card.
If the player has discovered the pair, then both cards
will open. If have not met, the player continues to
look for a pair while remembering the Chinese
characters and words that have been opened before.
Repetition of the game will change the layout of the
card from the previous game so that the time
achieved from the previous game may not be faster
because it relies on the player's memory.
Improving Students’ Interest to Learn Mandarin with Mandamonik Game in Three Languages
101

Puzzle Game.The game is sorting the pieces of the
image and forming the whole picture as in the right-
hand corner image.
Figure 4: Puzzle Game 1
Figure 5: Puzzle Game 2
To sort the image is by merely touching the piece
and put it in the desired place.Figure 5 is an example
of a puzzle which is almost completed. If the image
is in accordance with the instructions, then the image
will automatically change into another image
.
Word Crosshairs Game.The game puts a + sign in
a word which meaning is corresponding to the
Chinese Characters in the left-hand corner. The +
sign will shift if moving the mobile phone.
Figure 6: Word Crosshairs Game.
If the + hint has been placed in the correct word
corresponding to the Chinese Characters in the
instruction, then the player immediately presses the
+ sign in the word in question. Thus, the addition of
scores and time calculations stalled when the answer
is right
.
5 STUDENTS’ VIEW OF
MANDAMONIK
After the application was designed, then it was
tested to 33 elementary school students. Here is the
student's response to the Mandamonik Game. Only 1
respondent answers uncertain, while 6 respondents
agree and 26 respondents say strongly agree that
“Mandamonik” game isi fun. There are 4
respondents answer uncertain, while 12 respondents
agree and 17 respondents strongly agreethat
“Mandamonik” Game makes learning Chinese
interesting. There are 7 respondents are still in
doubt, while 12 respondents agree and 14
respondents strongly agree that“Mandamonik”
Games are not hard to play. Two respondents answer
undecided, while 13 respondents answer agree and
18 respondents answer strongly agree that game
design of “Mandamonik” is not boring. There are 4
respondents answer undecided, while 17 respondents
answer agree and 11 respondents answer strongly
agree that memory game is fun to play while
learning Mandarin. Only one students who answers
undecided, while 11 respondents answer agree and
21 respondents answer strongly agree that Puzzle
Game id fun to play while learning Mandarin. Only
nnestudent disagrees or dislikes the word crosshairs
game, while 5 respondents are undecided and 12
respondents agree and 15 respondents answer
strongly agree that word crosshairs is fun to play
while learning Mandarin.A total of 2 respondents
answer disagree and undecided, while 14
respondents answer agree and 17 respondents
answer strongly agree that Chinese writing on the
“Mandamonik”.Game is readable. There are 3
respondents who are undecided. While 15
respondents answer agree and 15 respondents
answer strongly agree that “Mandamonik” Game
make them more interested in learning Mandarin.
One respondent does not agree if the game is easy to
understand, while 3 other respondents hesitate and
16 respondents agree as well as 13 respondents
strongly agree.A total of 7 respondents say they do
not agree if Mandamonik game is easy to play, while
12 respondents agree that the game is easy to play
and 14 strongly agree if the game is easy to play.
BINUS-JIC 2018 - BINUS Joint International Conference
102

6 CONCLUSIONS
Chinese learning through games can motivate
elementary school students to learn Chinese. In
addition to learning Chinese Character, students also
learn how to read (Pinyin) and tone (Shengdiao).
Students also learn to memorize Chinese characters
through memory. This game can sharpen students'
memory if the memory game is played periodically.
In addition, the speed in memorizing Chinese
character and its meaning can also be increased
because, with the independent learning, students can
learn anytime and anywhere. The more often to play
this game the more duration of play will be reduced
and then it will be quicker to complete the game.
The drawback of this game is the absence of sound
when the player has found the word pairs for the
game. Besides, the puzzle game also has no sound
when the finished picture is prepared. Similarly, the
word crosshairs game also has no sound when the
right words are shot. Subsequent research should
improve this application for better utilization.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The study is a result of the initial implementation of
a research project supported by Bina Nusantara
(BINUS) University Research Grant 2018. The
subsequent study will represent the result of
application trial that has been designed.
REFERENCES
Zhang SL, Ying Y 2012The condition of mandarin
language learning in indonesia Lingua Cultura6(1)
95-107
Ying Y, Rawendy D and Arifin Y 2016 Game education
for learn Chinese language with mnemonic
methodProceeding Information Management and
Technology (ICIMTech), International Conference on
Game education for learning Chinese language with
mnemonic method 10.1109/ICIMTech.2016.7930324
Rawendy D, Ying Y and Arifin Y 2017 Design and
development game chinese language learning with
gamification and using mnemonic methodProcedia
Computer Science11661-67
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.10.009
Jones RG 2011 Emerging technologies mobile apps for
language learningLanguage Learning &
Technology15(2) 2-11
Afzali P, Shabani S, Basir Z and Ramazani M 2017
Mobile-assisted vocabulary learning: A review
studyAdvances in Language and Literary
Studies8(2)190-195
Brown M 2012 Tablet computing to cultivate Japanese
EFL digital literacy: A study on video production in
the classroomThe medium mattersedColpaert J, Aerts
A, Vivian WC and Joni CYC Proceeding of the
Proceedings 15th International CALL Conference 48
Mehdipour Y, Zerehkafi H 2013 Mobile learning for
education: Benefits and challengesInternational
Journal of Computational Engineering
Research3(6)93-101
Ying Y, Mursitama TN, Oktriono K and Abbas BS
2017Proceeding of the 2017 3rd International
Conference on Information Management (Chengdu,
China, April 21-23, 2017).
Onlinehttp://www.icim.org/ICIM2017-
Proceedings.zip
Ying Y, Mursitama TN, Lin X and Yetty 2017 Mobile
learning based of mandarin for college students: A
case study of international department’
sophomoresProceeding of the 2017 11th International
Conference on Information & Communication
Technology and System (Surabaya, Indonesia, October
31, 2017 Online
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8265684/
Hu Z N2013 Vocabulary learning assisted by mobile
phones:Perceptions of Chinese adultLearners Journal
of Cambridge Studies8(1) 139-154
Brown M, Castellano J, Hughes E and Worth A 2012
Integration of ipads in a Japanese university’s
freshman curriculumProceedings of the JALT CALL
ConferenceOnlinehttp://journal.jaltcall.org
Kim D, Rueckert D, Kim DJ and Seo D 2013 Students'
perceptions and experiences of mobile
learningLanguage Learning & Technology17(3) 52-73
Pho A, Dinscore A 2015 Game-based learning, association
of college and research libraries and american library
asociationDOI=http://acrl.ala.org/IS/wp-
content/uploads/2014/05/spring2015.pdf
AnissaA, Elena P, Nuñez C and Jan V L 2016 Assessing
the effectiveness of digital game-based learning: Best
practicesComputers & Education92–9390-103
Pivec M, Dziabenko O 2004 Game-based learning in
universities and lifelong learning: “UniGame: Social
skills and knowledge training” Game ConceptJournal
of Universal Computer Science10(1) 14-26
Jantina H, Admiral W, Akmerman S and Dam GT 2009
Mobile game-based learning in secondary education:
Engagement, motivation and learning in a mobile city
game Journal of Computer Assisted Learning25(4)
332–344
Improving Students’ Interest to Learn Mandarin with Mandamonik Game in Three Languages
103
