
Evaluating Method Design Options for Action Classification
based on Bags of Visual Words
Victoria Manousaki
1,2
, Konstantinos Papoutsakis
1,2
and Antonis Argyros
1,2
1
Computer Science Department, University of Crete, Greece
2
Institute of Computer Science, FORTH, Greece
Keywords:
Action Classification, K Nearest Neighbours, Support Vector Machines, Radial Basis Function Neural
Network, Bag of Visual Words, Motion Boundary Histograms.
Abstract:
The Bags of Visual Words (BoVWs) framework has been applied successfully to several computer vision tasks.
In this work we are particularly interested on its application to the problem of action recognition/classification.
The key design decisions for a method that follows the BoVWs framework are (a) the visual features to be
employed, (b) the size of the codebook to be used for representing a certain action and (c) the classifier applied
to the developed representation to solve the classification task. We perform several experiments to investigate
a variety of options regarding all the aforementioned design parameters. We also propose a new feature type
and we suggest a method that determines automatically the size of the codebook. The experimental results
show that our proposals produce results that are competitive to the outcomes of state of the art methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, human motion analysis and action re-
cognition have attracted a lot of attention due to the
significance of their solution in domains such as as-
sisted living, surveillance, human-computer/robot in-
teraction (Moeslund et al., 2006), etc. Despite several
breakthroughs, human action recognition remains a
challenging problem that is unsolved in its generality.
In this work, we are interested in action classifi-
cation based on motion capture/skeletal data and we
rely on the Bags of Visual Words (BoVWs) method
that has been a quite successful framework for sol-
ving this problem. As it is illustrated in Fig. 1, we
follow a framework consisting of three main steps:
(a) feature extraction, (b) representation/encoding ba-
sed on a BoVWs codebook and (c) classification of
the resulting action representations. In this study, our
goal is to provide an experimental evaluation of vari-
ous options regarding the selection of the components
of this framework that, when instantiated, give rise to
a specific recognition method.
In that direction, the contributions of this work
are many-fold. First, we investigate the performance
of three existing types of features. We also propose
a new feature for representing human pose data that
is inspired by the work on Motion Boundary Histo-
grams (MBH) (Wang et al., 2013). The use of the
proposed feature is shown to produce results that are
competitive to the state of the art. We also investigate
three different classification methods (K-NNs, SVMs,
RBFNNs). We also investigate the size of the code-
book used to represent actions, which is a major de-
sign issue in BoVWs-based methods. To achieve this,
We perform an empirical, almost exhaustive study to
determine the best codebook size for each feature type
and classifier. All previous works define a specific
codebook size without providing details on how this
has been decided. Given these individual results, we
explore methods that determine automatically the co-
debook size. This investigation shows that Affinity
Propagation (Frey and Dueck, 2007), an unsupervised
clustering technique that determines automatically the
number of clusters in a dataset, can be used effecti-
vely as a replacement of the k-Means algorithm which
is used in most of the BoVWs-based recognition met-
hods. All the experiments have been carried out on the
standard, extensive and ground truth-annotated Ber-
keley MHAD dataset (Ofli et al., 2013).
2 RELATED WORK
Action classification is a research topic in computer
vision that has been investigated extensively (Poppe,
Manousaki, V., Papoutsakis, K. and Argyros, A.
Evaluating Method Design Options for Action Classification based on Bags of Visual Words.
DOI: 10.5220/0006544201850192
In Proceedings of the 13th Inter national Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theor y and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2018) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
185-192
ISBN: 978-989-758-290-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
185

3D Joint Angles
3D Euler Angles
3D Pairwise
Joint Distances
MBH
KNN
SVM
RBFNN
Action
Classification
Feature extraction Feature encoding
Action classifiers
BoVWs
Input
action video
Figure 1: Illustration of the employed action recognition pipeline and the options that were considered for each of the stages.
2010). Most notable challenges concern the large
number of actions categories, the large variability in
action execution style among different people, as well
as the ambiguity in the interpretation of actions that
have similar appearance but different meaning de-
pending on the action execution context. We review
methods that follow the conventional pipeline that in-
volves hand-crafted feature extraction, feature repre-
sentation/encoding and classification as well as deep-
learning based methods that perform automatic fea-
ture extraction for action classification.
The approaches for action classification can be ca-
tegorized based on whether they employ features ex-
tracted from video or from skeletal data (Weinland
et al., 2011). In this work, we are interested in using
3D skeletal data of human motion extracted from mo-
tion capture systems or pose estimation methods. The
class of such methods can be subdivided into met-
hods that use joint-based or dynamics-based descrip-
tors (Presti and Cascia, 2016). Joint-based representa-
tions may comprise of spatial, geometric, or key-pose
based descriptors. Spatial descriptors (e.g., (Niebles
and Fei-Fei, 2007; Zhu et al., 2013)) compute the
pairwise distances of 3D joints. Geometric descrip-
tors rely on the geometric relations of body parts as
in (M
¨
uller et al., 2005). Key-pose based descriptors
represent an action based on a codebook of key po-
ses (Baysal et al., 2010). Dynamics-based descrip-
tors treat motion data as 3D trajectories of joints and
model the dynamics of such time series (Gowayyed
et al., 2013). In this work, we propose such a descrip-
tor based on the idea of Motion Boundary Histograms
(MBH) (Wang et al., 2013) to represent the evolution
of the 3D angles of body joints during the execution
of an action.
In a next step, the extracted features need to be
encoded before being fed into a classification met-
hod. For this task, Bag-of-Visual-Words (BoVWs)
is one of the most widely-used techniques. Several
works adopt this encoding (e.g., (De Campos et al.,
2011)) which is presented in detail in (Peng et al.,
2016). BoVWs have been used with both video (Nie-
bles and Fei-Fei, 2007) and skeletal data (Chaaraoui
et al., 2013; Han et al., 2017; Ofli et al., 2013).
Regarding classification algorithms, K-Nearest-
Neighbors (K-NN) is one of the most widely used and
simple non-parametric classification methods (Efros
et al., 2003). Besides K-NN, Support Vector Machi-
nes (SVMs) is a popular, supervised method for vi-
deo classification. Human actions can be detected in
videos by using a linear SVM on shape and appea-
rance features (Niebles and Fei-Fei, 2007). Schuldt
et al. (Schuldt et al., 2004) proposed that local space-
time features can be used to recognize complex mo-
tion patterns like human actions using SVM classi-
fication. In (Scovanner et al., 2007), a scheme re-
lying on 3D SIFT descriptors extracted from video
data, BoVWs encoding and SVM classification is pro-
posed for action recognition. Laptev et al. (Laptev
et al., 2008) used local space-time features, space-
time pyramids and multichannel non-linear SVMs for
accurate video classification. In (Evangelidis et al.,
2014), a linear SVM is used to classify local ske-
leton descriptors that encode the relative position of
joint quadruples producing view-invariant skeletal fe-
atures. As another example, the work in (Vemulapalli
and Chellapa, 2016) combines rolling maps based on
3D skeletal data and SVM classification for recogni-
zing human actions.
The availability of large video databases and the
leap progress made in learning methods and architec-
tures for neural networks over the last decade has led
to an explosion of relevant methods for action clas-
sification. Another type of neural nets is the Deep
Belief Neural Networks that are used to automati-
cally built high level representations of human motion
data (Foggia et al., 2014). Other important methods
employing deep neural networks and skeletal data for
the action classification refer to hierarchical recurrent
neural networks (HRNNs) used in (Du et al., 2015b)
and convolutional neural network (CNNs) (Du et al.,
2015a; Karpathy et al., 2014). Moreover, the work
in (Tao and Vidal, 2015) introduces a type of skele-
tal features called Moving Poselets that are used for
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
186

Figure 2: The employed human body model of the 3D joint
angles feature. Each body part (red arrows on the skeletal
model) is represented by a 3D vector (pink arrow) and its
3 angles (φ, θ, ω) w.r.t. a body centered reference frame (in
yellow). (Image originally taken and modified from (Theo-
dorakopoulos et al., 2014)).
action classification based on a novel two layer CNN-
like classifier.
The following methods are the most relevant to
our work. In (Vantigodi and Babu, 2013), skele-
tal data from the MHAD dataset were employed to
extract features based on the 3D joint angles of the
body with respect to a fixed point on the skeleton al-
ong with the temporal variance of the skeletal joints.
The temporal information is embedded for improving
the discrimination of similar actions. For classifi-
cation an SVM classifier is used. In a subsequent
work (Vantigodi and Radhakrishnan, 2014), a new
method is introduced using the same type of featu-
res but employing a BoWs encoding of features and a
meta-cognitive RBFNN as classifier. A Projection-
Based Learning algorithm is used to estimate the
optimal network output parameters. Chaudhry et
al. (Chaudhry et al., 2013) proposed a novel, hier-
archical scheme of bio-inspired dynamic 3D skeletal
features. They extend neural static shape encoding
features to represent human actions by using a set of
Linear Dynamical Systems (LDS), each one modeling
the dynamics of a level in their hierarchical structure
of features. For the classification part, they use Sim-
pleMKL to learn a set of optimal weights and train
a full kernel SVM classifier using a weighted kernel
in a supervised manner. The proposed scheme achie-
ves remarkable results in three well-known datasets,
including the Berkeley MHAD dataset. Finally, Kap-
souras et al. (Kapsouras and Nikolaidis, 2014) use the
joints orientation angles and the forward differences
of these angles in different temporal scales as featu-
res for action classification. BoVWs encoding is then
used to feed the KNN and SVM classifiers.
3 ACTION RECOGNITION
Figure 1 illustrates the action recognition pipeline we
employ, which comprises of (a) selecting features, (b)
encoding them with BoVWs, and (c) classifying the
resulting representations. In total, we consider four
different types of skeletal features. Three of them
already appear in the literature (3D joint angles, 3D
Euler angles, 3D pair-wise joint distances). We also
propose a new type of feature that is inspired by Mo-
tion Boundary Histograms. Each of them is combined
with the BoVWs encoding and three different classi-
fiers (K-Nearest Neighbor, SVM, RBFNN).
3.1 Feature Extraction
Several representations of skeletal data have been pro-
posed in the literature (Kovar and Gleicher, 2004;
Moeslund et al., 2006). Given such representati-
ons, human actions can be represented as multi-
dimensional time-series.
3D Joint Angles: We employ a variant of the repre-
sentation proposed in (Rius et al., 2009), also em-
ployed in (Papoutsakis et al., 2017) (see Fig. 2(a)).
According to this, a human pose is represented as a 30
+ 30 + 4 = 64D vector. The first 30 dimensions encode
angles of selected body parts with respect to a body-
centered coordinate system. The next 30 dimensions
encode the same angles in a camera-centered coordi-
nate system. The representation is augmented with
the 4 angles between the fore- and the back-arms as
well as the angles between the upper- and lower legs.
3D Euler Angles: We use the raw 3D Euler angles
for 16 3D joints of the human skeleton. These joints
are the endpoints of the body parts involved in the
representation of 3D joint angles. Thus, we end up
with a 16 × 3 = 48D vector representing each frame.
3D Pair-wise Joint Distances: We consider a set of
Euclidean distances of pairs of body joints. In or-
der to be invariant to the somatometrics of the sub-
jects, the computed distances are normalized by the
height of each subject. We take into account the follo-
wing pairs of joints: body center-ground center, body
center-left wrist, body center-left ankle, body center-
right wrist, body center-right ankle, left wrist-left
ankle, right wrist-right ankle, left wrist-right wrist,
left ankle-right ankle, left shoulder-left wrist, right
shoulder-right wrist.
3.1.1 MBH on the Evolution of 3D Angles
We propose the use of a variant of the Motion Boun-
dary Histograms (MBH) representation introduced by
Dalal et al. (Dalal et al., 2006). Originally, MBH was
used to represent human motion based on 2D optical
Evaluating Method Design Options for Action Classification based on Bags of Visual Words
187

Figure 3: Illustration of median action recognition accuracy as a function of the codebook size k. (a) Scores per classifier over
all feature types. (b) Scores achieved per type of features over all classifiers.
Figure 4: Left: 3D trajectories for a subset of body joints
during the execution of an action. Right: The MBH tra-
jectory descriptor (Wang et al., 2013) based on 2D motion
information. We extend this in 3D to encode the spatio-
temporal dynamics of each body joint.
flow and spatio-temporal interest points. We extended
this idea in 3D by building an MBH of the evolution
of the 3D angles of the skeletal body joints during the
execution of an action as seen in Fig. 4. We use the
3D joint angles representation described earlier and
compute their temporal evolution on each of the X, Y
and Z dimensions, individually. We differentiate the
obtained quantities once more in each dimension, as
described also in (Dalal et al., 2006). We then cal-
culate the magnitude and orientation of the projection
of these vectors on the XY , Y Z and ZX planes. Orien-
tations are quantized into histograms using the mag-
nitude as the weight of each vote. A histogram of 8
orientation bins is computed separately per plane. Fi-
nally, the three histograms are concatenated to get a
single feature vector per sequence.
3.2 Feature Encoding
We investigate the Bag-of-Visual-Words (BoVWs)
encoding for each type of features of Sec. 3.1 to build
a visual vocabulary (codebook) using k-Means. The
BoVWs encoding assigns each feature vector (frame)
to its nearest cluster center. An action is then repre-
sented as the normalized histogram of all codewords
over all the frames of an action sequence. We run
k-Means 5 times and keep the cluster centers of the
run that gave rise to the best performance. Also, we
investigate techniques that automate the selection of
the codebook size.
3.3 Action Classification
For the action classification step we employ three dif-
ferent popular classifiers. The first is K-NN, a classifi-
cation method mostly employed when there is little or
no prior knowledge regarding the distribution of the
training data. Each feature point in N-dimensional
space is classified based on the majority of class-
related votes of its K nearest neighbours, using the
χ
2
distance. In our case we use K = 1.
Support Vector Machines (SVM) is a supervised
classifier, widely used for action classification. SVM
is a kernel-based, margin classifier that separates the
data into categories using a hyperplane. The optimal
hyperplane is the one that maximizes the margin bet-
ween the categories (Schuldt et al., 2004).
As a third classifier, we employ a Radial Basis
Function Neural Network (RBFNN), a multi-layer,
feed-forward artificial neural network that uses radial
basis activation functions. The output of the network
is a linear combination of radial basis functions of the
inputs that is dependent on the neuron parameters.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
We use the Berkeley Multi-modal Human Action Da-
tabase (MHAD) (Ofli et al., 2013). This consists of
660 motion sequences of 11 actions, each performed 5
times (repetitions) by each of 12 subjects. From these
12 subjects, 7 are male and 5 are female. All are in
the age range of 23 − 30 years, except for one elderly
subject. The action categories represented in the da-
tabase are: jumping in place, jumping jacks, bending,
punching, waving two hands, waving right hand, clap-
ping throwing a ball, sit down and stand up, sit down,
and stand up. The subjects perform the actions with
different styles and speeds.
The database provides video sequences of RGB
and depth frames. It also includes motion capture
data containing the 3D positions of 43 LED markers,
which have been processed to obtain 3D skeletal data
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
188
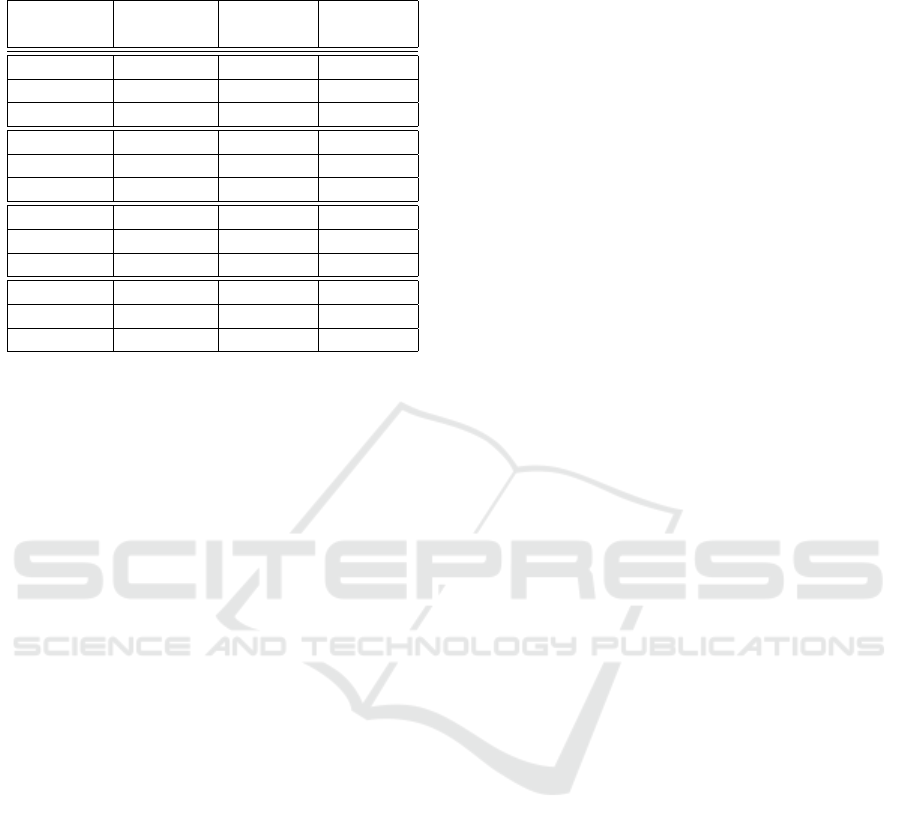
Table 1: Top performing combinations of features, classi-
fiers and codebook sizes.
Feature Codebook Classifier Accuracy
Type size k (%)
Joint ang. 40 KNN 98.51
Joint ang. 75 SVM 99.12
Joint ang. 245 RBFNN 98.51
Euler ang. 345 KNN 91.40
Euler ang. 330 SVM 90.69
Euler ang. 125 RBFNN 89.42
Distances 9 KNN 96.42
Distances 50 SVM 95.59
Distances 75 RBFNN 95.48
MBH 115 KNN 98.07
MBH 75 SVM 97.25
MBH 20 RBFNN 98.07
of 30 joints that are represented by 3D Euler angles.
We use the motion capture data of all actions and re-
petitions of the first 6 subjects as training samples,
and those of the last 6 subjects for testing.
4.1 Parameter Settings
The parameters for the SVM and RBFNN classifiers
have been chosen using 6-fold cross validation on the
training data (first 6 subjects of the MHAD dataset, all
repetitions). For the experiments regarding the SVM
classifier, we used the one-versus-all multi-class ap-
proach. For the selection of the appropriate kernel (li-
near or RBF) we conducted a set of experiments for
the selection of the best parameters for each one of
the kernels. Then, we compared them by using the
same training and test sets and chose the one with the
best performance. The SVM classifier uses a linear
kernel for the 3D Euler Angles with the cost C para-
meter equal to 8. For the other types of features, an
RBF kernel has been employed. More specifically, for
the 3D pair-wise distances and the MBH features the
RBF kernel is used with parameters C = 8 and γ = 1.
For the 3D angles, C and γ were set equal to 8 and 2,
respectively. For the RBFNN classifier several values
of the spread parameter have been evaluated. The op-
timal values for the 3D angles, 3D Euler angles, 3D
pair-wise Distances and MBH features was set equal
to 0.4, 0.5, 12 and 0.21, respectively.
4.2 Evaluating BoVWs Codebook Sizes
An important decision in BoVWs-based classification
is the size k of the optimal visual vocabulary. In most
of the related works, k is decided empirically. Co-
dewords are estimated by employing the k-Means al-
gorithm with k equal to the selected codebook size.
In this work we aim at investigating the impact of k
depending on the features and the classifiers. Additi-
onally, we investigate whether it is possible to identify
k automatically and in a way that guarantees satisfac-
tory classification results, regardless of the employed
features and/or classification methods.
Empirical Investigation of Codebook Sizes: We
executed an experiment that considered a wide range
of codebook sizes k. More specifically, we tested va-
lues for k in the range 1 to 30 with step 1 and in the
range 30 to 350 with step 5. Codebooks were then
determined by running k-Means. We then measured
the performance of the 1-NN action classification for
all different choices of k.
An overview on the obtained scores for this series
of experiments is illustrated in Fig. 3. The two graphs
present the median accuracy performance (a) per clas-
sifier and (b) per feature type with respect to the code-
book size k. Median accuracy per classifier is calcula-
ted as the median of the classification scores of every
classifier over all feature types. Median accuracy per
feature type is set as the median of the classification
scores of every feature type over all the classifiers.
Overall, the 1-NN and SVM classifiers outperform
RBFNN up to k = 200. For k > 200, RBFNN achie-
ves a slightly higher performance in terms of median
accuracy. For the per feature type performance, the
3D angle-based skeletal representation outperforms
all other types of features. The proposed MBH repre-
sentation achieves the next highest performance for
all codebook sizes.
As it can be verified in Fig. 3, a fairly small value
of k = 30 brings action classification accuracy above
94%. A notable exception is case of the 3D Euler
angles-based features, whose performance tends to
stabilize the overall median accuracy for K > 250.
Table 1 shows the top performing combinations
of features, codebook sizes and classifiers, out of the
exhaustive list of combinations that were evaluated.
We note that each feature-classifier combination uses
its individually-optimized BoVWs codebook size. It
can be verified that the performance of each classifier
is maximized for a different codebook size.
Automatic Estimation of Codebook Sizes: We in-
vestigated techniques that estimate automatically the
codebook size k of the BovWs framework. Based on
the training data of the MHAD dataset (see Sec. 4.1),
we assessed the following techniques: Sparse Mo-
deling Representative Selection (SMRS) (Elhamifar
et al., 2012), Affinity Propagation (AP) (Frey and
Dueck, 2007), Elbow, Gap (Tibshirani et al., 2001),
Calinski-Harabasz (Cali
´
nski and Harabasz, 1974) and
Davies-Bouldin (Davies and Bouldin, 1979). We em-
Evaluating Method Design Options for Action Classification based on Bags of Visual Words
189
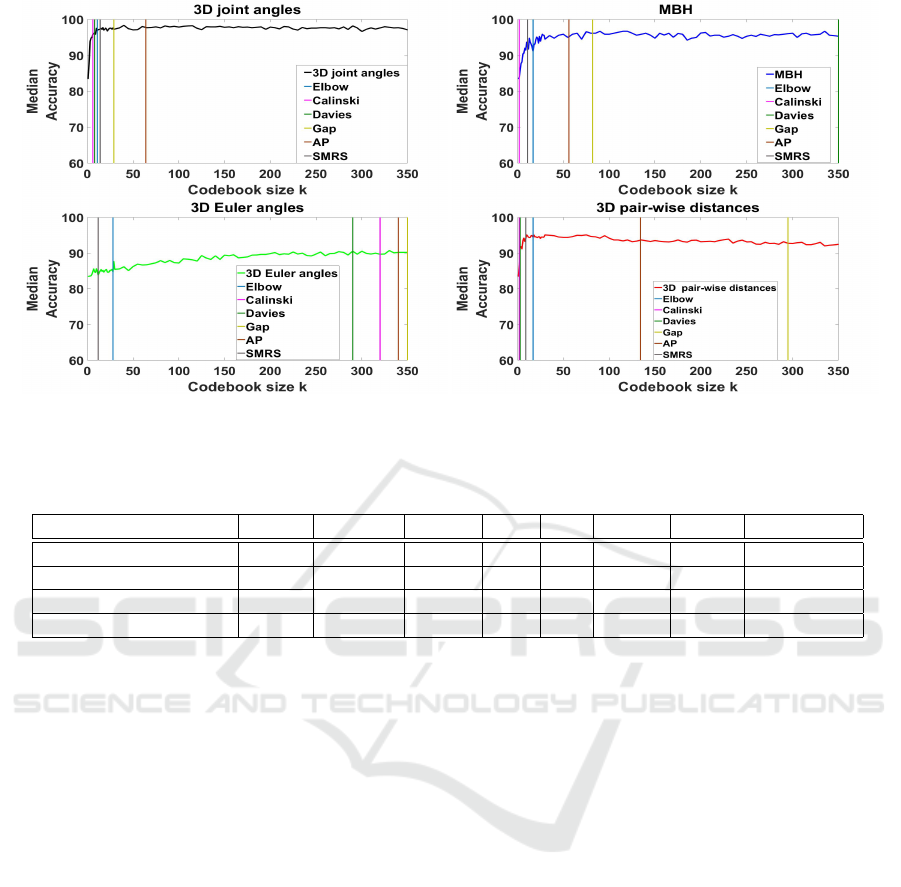
Figure 5: Automatic selection of codebook size k based on various methods, for all four feature types. Each figure plots the
median accuracy among the three classification methods, as a function of the codebook size.
Table 2: Automatic selection of codebook sizes k per feature type. We also report the best k as computed based on the
exhaustive search as well as the value of k (threshold) above which the median accuracy remains almost constant.
Features Elbow Calinski Davies Gap AP SMRS Best k Threshold k
3D angles 11 6 8 29 64 14 75 30
MBH 17 2 350 82 56 11 20 20
3D Euler angles 28 320 290 350 340 12 345 250
3D Pair-wise distances 17 2 3 295 134 10 9 [9-100]
ployed these criteria and methods for each feature
type and got suggested codebook sizes k. Those va-
lues are illustrated in Fig. 5 by projecting them to
the median accuracy performance graphs per type of
feature in order to also compare them qualitatively
with the codebook size that was chosen based on the
exhaustive search. The obtained results are also lis-
ted in Table 2, in comparison with the best codebook
size identified based on the exhaustive search. Over-
all, Affinity Propagation (AP) best approximates the
number of centers resulting from the exhaustive se-
arch for the majority of feature types. AP is an unsu-
pervised clustering method that determines automati-
cally the number of data clusters. Thus, it could be
used as an alternative to k-Means.
Table 3 summarizes the achieved accuracy per fea-
ture type for every criterion. The classifier that achie-
ved the corresponding accuracy is also indicated. This
experiment is based on the cluster centers that have re-
sulted from each corresponding criterion. We observe
that the accuracy achieved using the automated cri-
teria is comparable to the one achieved with k -means.
Thus, when the suggested number of clusters from the
criteria falls near or above the suggested threshold the
resulting accuracy is near optimal.
4.3 Action Classification Performance
Choosing the Best Feature Type: In order to assess
the performance of the types of features presented in
this work, we compute the median accuracy for the
classification scores of every feature type for all three
classification methods. As shown in Fig. 3(b), the 3D
joint angle-based and the MBH representations are
preferable compared to the 3D Euler angles and 3D
pairwise joint distances.
Choosing the Best Classifier: The median accuracy
for every classifier over all feature types is illustrated
in Fig. 3(a). In general, KNN and SVM provide a sta-
ble behavior in all experiments and for the combinati-
ons of features that have been carried out. RBFNN is
quite unstable for different values of k.
Comparison to the State of the Art: We compare
the best performing action recognition method in our
framework with existing methods and summarize the
results in Table 4. We employ all repetitions of acti-
ons performed by the first 6 subjects of the dataset for
training and those of the rest 6 subjects for testing.
All other evaluated methods use 7 subjects for trai-
ning and 5 subjects for testing or use leave-one-out
cross-validation on the set of all subjects.
The method in (Ofli et al., 2013) has an accu-
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
190
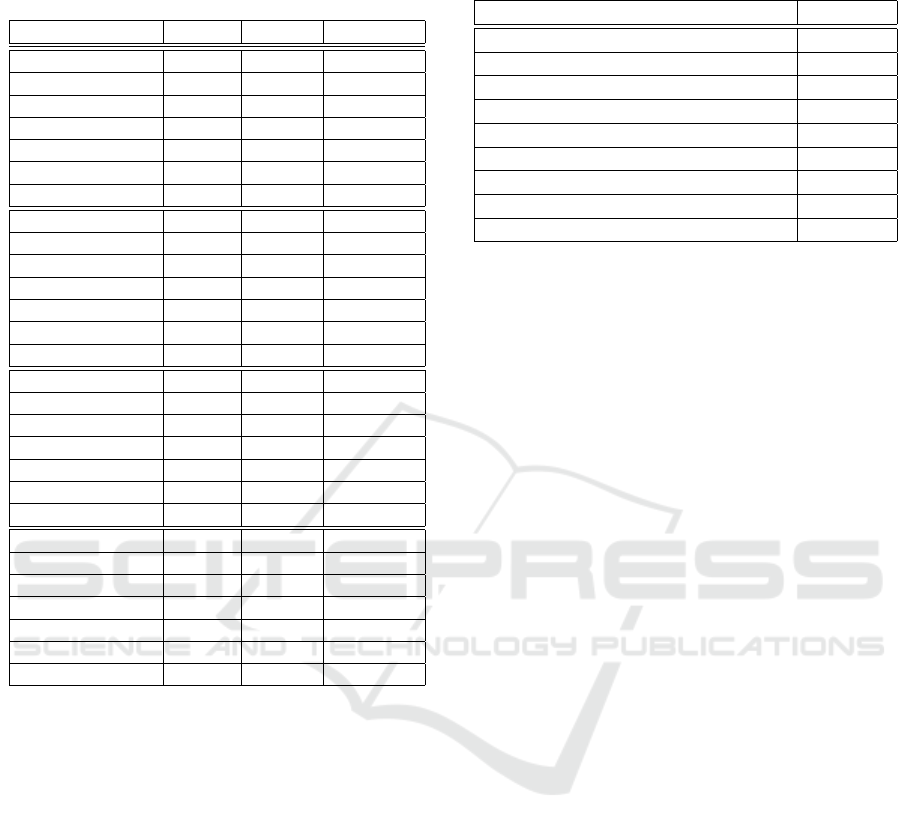
Table 3: Accuracy values per feature type for all the criteria
based on their codebook sets. We also report the best accu-
racy value that we achieved using the k-means algorithm.
Feature Type Criterion Classifier Accuracy %
3D joint angles Elbow RBFNN 98.13
3D joint angles Calinski SVM 96.14
3D joint angles Davies RBFNN 96.42
3D joint angles Gap RBFNN 97.02
3D joint angles AP KNN 98.20
3D joint angles SMRS RBFNN 96.75
3D joint angles Best k SVM 99.12
3D Euler angles Elbow KNN 86.63
3D Euler angles Calinski SVM 90.66
3D Euler angles Davies RBFNN 89.72
3D Euler angles Gap SVM 90.85
3D Euler angles AP SVM 90.95
3D Euler angles SMRS KNN 89.31
3D Euler angles Best k KNN 91.40
Pair-wise distances Elbow KNN 95.98
Pair-wise distances Calinski RBFNN 85.95
Pair-wise distances Davies SVM 89.26
Pair-wise distances Gap KNN 92.12
Pair-wise distances AP RBFNN 93.58
Pair-wise distances SMRS SVM 93.44
Pair-wise distances Best k KNN 96.42
MBH Elbow SVM 94.05
MBH Calinski KNN 83.75
MBH Davies RBFNN 94.99
MBH Gap RBFNN 95.26
MBH AP RBFNN 96.35
MBH SMRS KNN 92.89
MBH Best k RBFNN 98.07
racy of 79.93%. This is improved in a subsequent
work (Ofli et al., 2014) to 94.91% by using a more
elaborate human pose representation of the most in-
formative joints (SMIJ). The method in (Vantigodi
and Babu, 2013) achieved 96.06% using temporal
information and an SVM classifier. Temporal in-
formation helps in disambiguating actions that in-
volve the same poses in different order (e.g., sit
down and stand up). In a relevant work (Vantigodi
and Radhakrishnan, 2014), temporal information with
an RBFNN classifier improves accuracy to 97.58%.
Kapsouras et al. (Kapsouras and Nikolaidis, 2014)
achieved 98.18% without considering temporal in-
formation. Chaudhry et al. (Chaudhry et al., 2013)
achieve 100% accuracy by using bio-inspired 3D ske-
letal features. Other methods that achieve 100% accu-
racy on the MHAD dataset are based on deep neu-
ral networks such as H-RNNs (Du et al., 2015b) and
CNNs (Du et al., 2015a; Tao and Vidal, 2015).
Table 4: Comparative evaluation of existing action classifi-
cation methods on the MHAD dataset.
Method Accuracy
(Foggia et al., 2014) 85.8
(Ofli et al., 2014) 94.91
(Vantigodi and Radhakrishnan, 2014) 97.58
(Kapsouras and Nikolaidis, 2014) 98.18
Proposed 99.12
(Chaudhry et al., 2013) 100
(Du et al., 2015b) 100
(Du et al., 2015a) 100
(Tao and Vidal, 2015) 100
5 SUMMARY
We investigated several design options for using Bags
of Visual Words (BoVWs) for action classification ba-
sed on 3D motion capture data. We experimented
with three existing human pose representations and
we proposed a fourth one that is inspired by Motion
Boundary Histograms. We considered three classi-
fication methods (K-NNs, SVMs, RBFNNs) and a
broad range of codebook sizes. Additionally, we in-
vestigated the effectiveness of several techniques that
can be used to automate the selection of the codebook
size. The obtained results suggest that Affinity Propa-
gation can be used as an alternative to the widely used
k-Means. Then, we evaluated all possible combina-
tions with respect to their classification accuracy on
the Berkeley MHAD dataset and compared the best
performing action classification technique to existing
methods. The investigation has shown that the pro-
posed approach achieves competitive action classifi-
cation results.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partially supported by the EU H2020
projects Co4Robots and ACANTO.
REFERENCES
Baysal, S., Kurt, M. C., and Duygulu, P. (2010). Recogni-
zing human actions using key poses. In ICPR.
Cali
´
nski, T. and Harabasz, J. (1974). A dendrite method for
cluster analysis. Communications in Statistics-theory
and Methods.
Chaaraoui, A., Padilla-Lopez, J., and Fl
´
orez-Revuelta, F.
(2013). Fusion of skeletal and silhouette-based featu-
res for human action recognition with rgb-d devices.
In ICCVW.
Evaluating Method Design Options for Action Classification based on Bags of Visual Words
191

Chaudhry, R., Ofli, F., Kurillo, G., Bajcsy, R., and Vidal, R.
(2013). Bio-inspired dynamic 3d discriminative skele-
tal features for human action recognition. In CVPRW.
Dalal, N., Triggs, B., and Schmid, C. (2006). Human de-
tection using oriented histograms of flow and appea-
rance. In ECCV.
Davies, D. L. and Bouldin, D. W. (1979). A cluster separa-
tion measure. PAMI.
De Campos, T., Barnard, M., Mikolajczyk, K., Kittler, J.,
Yan, F., Christmas, W., and Windridge, D. (2011).
An evaluation of bags-of-words and spatio-temporal
shapes for action recognition. In WACV.
Du, Y., Fu, Y., and Wang, L. (2015a). Skeleton based
action recognition with convolutional neural network.
In ACPR.
Du, Y., Wang, W., and Wang, L. (2015b). Hierarchical re-
current neural network for skeleton based action re-
cognition. In CVPR.
Efros, A. A., Berg, A. C., Mori, G., Malik, J., et al. (2003).
Recognizing action at a distance. In ICCV.
Elhamifar, E., Sapiro, G., and Vidal, R. (2012). See all by
looking at a few: Sparse modeling for finding repre-
sentative objects. In CVPR.
Evangelidis, G., Singh, G., and Horaud, R. (2014). Skeletal
quads: Human action recognition using joint quadru-
ples. In ICPR.
Foggia, P., Saggese, A., Strisciuglio, N., and Vento, M.
(2014). Exploiting the deep learning paradigm for re-
cognizing human actions. In AVSS.
Frey, B. J. and Dueck, D. (2007). Clustering by passing
messages between data points. American Association
for the Advancement of Science.
Gavrila, D. (1999). The visual analysis of human mo-
vement. CVIU.
Gowayyed, M. A., Torki, M., Hussein, M. E., and El-
Saban, M. (2013). Histogram of oriented displace-
ments (hod): Describing trajectories of human joints
for action recognition. In IJCAI.
Han, F., Reily, B., Hoff, W., and Zhang, H. (2017). Space-
time representation of people based on 3d skeletal
data: A review. CVIU.
Huang, B., Tian, G., and Zhou, F. (2012). Human typical
action recognition using gray scale image of silhouette
sequence. Computers & Electrical Engineering.
Kapsouras, I. and Nikolaidis, N. (2014). Action recognition
on motion capture data using a dynemes and forward
differences representation. Journal of Visual Commu-
nication and Image Representation.
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Sukthan-
kar, R., and Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Large-scale video
classification with convolutional neural networks. In
CVPR.
Kovar, L. and Gleicher, M. (2004). Automated extraction
and parameterization of motions in large data sets. In
ACM SIGGRAPH.
Laptev, I., Marszalek, M., Schmid, C., and Rozenfeld, B.
(2008). Learning realistic human actions from mo-
vies. In CVPR.
Moeslund, T. B., Hilton, A., and Kr
¨
uger, V. (2006). A sur-
vey of advances in vision-based human motion cap-
ture and analysis. CVIU.
M
¨
uller, M., R
¨
oder, T., and Clausen, M. (2005). Efficient
content-based retrieval of motion capture data. In
ACM Trans. on Graphics.
Niebles, J. C. and Fei-Fei, L. (2007). A hierarchical model
of shape and appearance for human action classifica-
tion. In CVPR.
Ofli, F., Chaudhry, R., Kurillo, G., Vidal, R., and Bajcsy, R.
(2013). Berkeley mhad: A comprehensive multimodal
human action database. In WACV.
Ofli, F., Chaudhry, R., Kurillo, G., Vidal, R., and Baj-
csy, R. (2014). Sequence of the most informative
joints (smij): A new representation for human skeletal
action recognition. Journal of Visual Communication
and Image Representation.
Papoutsakis, K., Panagiotakis, C., and Argyros, A. A.
(2017). Temporal action co-segmentation in 3d mo-
tion capture data and videos. In CVPR.
Peng, X., Wang, L., Wang, X., and Qiao, Y. (2016). Bag of
visual words and fusion methods for action recogni-
tion: Comprehensive study and good practice. CVIU.
Poppe, R. (2010). A survey on vision-based human action
recognition. Image and Vision Computing.
Presti, L. L. and Cascia, M. L. (2016). 3d skeleton-based
human action classification: A survey. Pattern Recog-
nition.
Rius, I., Gonz
`
alez, J., Varona, J., and Roca, F. X. (2009).
Action-specific motion prior for efficient bayesian 3d
human body tracking. Pattern Recognition.
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., and Caputo, B. (2004). Recognizing
human actions: A local svm approach. In ICPR. IEEE.
Scovanner, P., Ali, S., and Shah, M. (2007). A 3-
dimensional sift descriptor and its application to
action recognition. In Proc. ACM Int. Conference on
Multimedia.
Tao, L. and Vidal, R. (2015). Moving poselets: A discrimi-
native and interpretable skeletal motion representation
for action recognition. In ICCVW.
Theodorakopoulos, I., Kastaniotis, D., Economou, G., and
Fotopoulos, S. (2014). Pose-based human action re-
cognition via sparse representation in dissimilarity
space. Journal of Visual Communication and Image
Representation.
Tibshirani, R., Walther, G., and Hastie, T. (2001). Estima-
ting the number of clusters in a data set via the gap
statistic. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Se-
ries B.
Vantigodi, S. and Babu, R. V. (2013). Real-time hu-
man action recognition from motion capture data. In
NCVPRIPG.
Vantigodi, S. and Radhakrishnan, V. B. (2014). Action
recognition from motion capture data using meta-
cognitive rbf network classifier. In ISSNIP.
Vemulapalli, R. and Chellapa, R. (2016). Rolling rotations
for recognizing human actions from 3d skeletal data.
In CVPR.
Vijay, P. K., Suhas, N. N., Chandrashekhar, C. S., and Dha-
nanjay, D. K. (2012). Recent developments in sign
language recognition: A review. Int. J. Adv. Comput.
Eng. Commun. Technol.
Wang, H., Kl
¨
aser, A., Schmid, C., and Liu, C.-L. (2013).
Dense trajectories and motion boundary descriptors
for action recognition. IJCV.
Weinland, D., Ronfard, R., and Boyer, E. (2011). A sur-
vey of vision-based methods for action representation,
segmentation and recognition. CVIU.
Zhu, Y., Chen, W., and Guo, G. (2013). Fusing spatiotem-
poral features and joints for 3d action recognition. In
CVPRW.
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
192
