
PEEK
An LSTM Recurrent Network for Motion Classification from Sparse Data
Rafael Rego Drumond
1
, Bruno A. Dorta Marques
2
, Cristina Nader Vasconcelos
2
and Esteban Clua
2
1
Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab, University of Hildesheim, Hildesheim, Germany
2
Instituto de Computac¸
˜
ao, Universidade Federal Fluminense, Niter
´
oi, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords:
Motion Classifier, IMU Device, Deep Learning, Recurrent Neural Networks, Sparse Data, Machine Learning.
Abstract:
Games and other applications are exploring many different modes of interaction in order to create intuitive
interfaces, such as touch screens, motion controllers, recognition of gesture or body movements among many
others. In that direction, human motion is being captured by different sensors, such as accelerometers, gyro-
scopes, heat sensors and cameras. However, there is still room for investigation the analysis of motion data
captured from low-cost sensors. This article explores the extent to which a full body motion classification
can be achieved by observing only sparse data captured by two separate inherent wereable measurement unit
(IMU) sensors. For that, we developed a novel Recurrent Neural Network topology based on Long Short-Term
Memory cells (LSTMs) that are able to classify motions sequences of different sizes. Using cross-validation
tests, our model achieves an overall accuracy of 96% which is quite significant considering that the raw data
used was obtained using only 2 simple and accessible IMU sensors capturing arms movements. We also built
and made public a motion database constructed by capturing sparse data from 11 actors performing five dif-
ferent actions. For comparison with existent methods, other deep learning approaches for sequence evaluation
(more specifically, based on convolutional neural networks), were adapted to our problem and evaluated.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advances of virtual-reality technologies and
context-awareness give rise to new possibilities of
game genres. Among these, we can highlight the
pervasiveness, requiring the usage of body move-
ments and gestures as interface, in order to achieve
a correspondent immersion and self-presence sensa-
tion (Rautaray and Agrawal, 2015; Silva et al., 2015)
Head-mounted Displays (HMDs) are receiving a huge
attention from the industry, with hundreds of solu-
tions being offered by assemblers. However, most
of the interfaces for game control are still based on
the Desktop/console/mobile paradigm of interaction,
where the user must push buttons on a keyboard
and/or hold controllers, breaking the immersion feel-
ing that the visual experience of HMDs may produce.
Traditional interfaces, such as the PlayStation
Move or HTC motion (psm, 2017a; psm, 2017b) con-
troller do not provide a natural way of interaction,
such as touch or pick elements in real environments,
since they still use a joystick to represent human mo-
tion. In this scenario, the usage of body movements
and gestures are important for maintaining the immer-
sion and self-presence sensation in VR experiences,
being the next big challenge for the upcoming years
(Wachs et al., 2011; Rautaray and Agrawal, 2015).
In this context, our goal is to develop a robust
body motion classifier working over sequences of
sparse data (or, in other words, without all the data
from the body) captured over continuous body mo-
tions produced by the use of common and low-cost
sensors classified as IMUs. The IMUs devices are
usually composed of one accelerometer, gyroscope
and one magnetometer sensors. We remark that the
sensors responsible to produce the data source for
classification are preferably wearable, such as smart-
phones, armbands (myo, 2015), smart watches and
others simpler devices in order to keep the user expe-
rience as natural and intuitive as possible (Prathivadi
et al., 2014; Kuni et al., 2015; Yuan and Chen, 2014;
Chen, 2013).
Our work aims to fulfill the need of a motion
classifier using only two Inertial Measurement Unit
(IMU) devices in the scope of a pervasive virtual
reality game system that is accessible to the user.
Most classification systems require four or more ac-
celerometers, cameras or other peripherals. However,
the excessive amount of accessories needed makes the
system unfeasible or expensive, and monitoring the
Drumond, R., Marques, B., Vasconcelos, C. and Clua, E.
PEEK - An LSTM Recurrent Network for Motion Classification from Sparse Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0006585202150222
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2018) - Volume 1: GRAPP, pages
215-222
ISBN: 978-989-758-287-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
215

user through cameras has many limitations such as
the occlusion of the body and complex setups. The
possibility of capturing and classifying movements
with only two sensors makes this task possible in al-
most any situation, by using popular devices such as
a smartwatch, smartphone or motion armbands.
Inspired by the current success of deep learning
based approaches in several areas, our main contribu-
tion is a topology, called Peek, of a Recurrent Neu-
ral Network constructed based on Long Short-Term
Memory (LSTM) cells (Hochreiter and Schmidhuber,
1997; Goodfellow et al., 2016), that is able to clas-
sify motion observing sequences of sparse data cap-
ture from IMU devices.
The proposed LSTM based solution is able to dif-
ferentiate a set of whole-body motions by just observ-
ing the movements of the user’s arms captured by 2
simple IMU sensors. We strongly believe that Peek
may be an important solution for Pervasive Virtual
Reality applications, games, and other areas that can
be benefited by a low budget motion classification.
2 RELATED WORKS
Several studies have been working on motion clas-
sification, motion reconstruction, and actions recog-
nition. The analysis of dense data (from video) has
been explored by computer vision for decades (Wein-
land et al., 2011). Dense motion classification is not
the focus of our work, thus, in this section, we briefly
present most relevant works related to our proposal
that focus on sparse data analysis based on deep learn-
ing classifiers.
Zhang et al. in (Zhang and Li, 2015) describes
a method called DBCNN (DataBand Convolutional
Neural Network) for classifying 20 different types
of gestures using acceleration and angular speed se-
quences (both including x,y,z axis). The data is pro-
duced using sensors able to track the user’s arm mo-
tions. The authors created their own database by
recording over 20 different gestures and interpolated
them to generate new samples. Each motion sequence
is coded inside a structure called Databand, a 96x6
matrix where each of the 6 rows represents the an-
gle and acceleration coordinates over 96 instances of
time. The Databands are used to train a convolutional
neural network and achieved an accuracy of 98,66%.
While this approach is limited by classifying single
finite gestures from hand movement, our proposal re-
quires only two IMU units in order to classify contin-
uous body-motion activities.
The work implemented by Kruger et al (Kr
¨
uger
et al., 2010) that aims to create an animation recon-
struction model approach that uses a large number
of motion clips as a knowledge database, achieved
from a marker-based motion capture. This knowl-
edge database is used to estimate the poses of a person
wearing four accelerometers (one on each wrist, and
one on each ankle). At each new step, a new pose is
estimated by comparing the last four captured motion
frames with the sequences from the original database.
This database is preprocessed in order to be compara-
ble to the accelerometer-based data.
As a follow-up work from Kruger et al (Kr
¨
uger
et al., 2010), Tautges et al. (Tautges et al., 2011) used
a server to perform the calculations online. The server
has access to the preprocessed database, which is also
pre-indexed in a KD-Tree. At each new frame, it com-
putes the nearest neighbor search in the database to
find out which is the closest pose to the user’s. This
is done by comparing wrists and ankle positions from
the devices with the ones in their database. The pose
is reconstructed by considering not only the last four
frames, and the last reconstructed poses. This work
does not try to classify motion, instead, it tries to re-
construct the motion itself. It also requires four ac-
celerometers, while our system requires only two de-
vices.
M. Baccouche et al. (Baccouche et al., 2011) de-
signed a deep learning network combining convolu-
tional and recurrent layers that processed images se-
quences to classify the kind of human action that was
performed. In order to do so, they extend 2D convolu-
tions to 3D. They built a network with convolutional
layers followed by a fully connected LSTM (Long
Short-Term Memory) hidden layer. The authors used
a data set called KTH Dataset (Schuldt et al., 2004)
in order to test it. This dataset contained videos of
humans performing sequences of six kinds of actions.
The authors achieved a 94.39% accuracy, being the
highest at the time of their publication. While their
work is relevant to the field, since it presents a recur-
rent neural network that classifies sequences, it does
not work with IMU units.
Berger et al. (Berger et al., 2011) describes a mo-
tion detection system that was developed using mul-
tiple Kinects. This combination brings up some in-
terferences and inaccuracies mainly due to the need
to gather information of depth images extracted from
different angles. Despite this, the developed applica-
tion presents good tracking results. Another proposal,
described by Wei et al. (Wei et al., 2012) is based on
the reconstruction of movements using images pro-
duced by a single depth camera. Having 90% of ac-
curacy as a result of its lowest test case.
When comparing with our work, we remark that
their work is capable of pose estimation, but not ac-
GRAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
216

tion classification. In addition, the cost to process
images, filter the noises and produce useful data is
considerably large. Besides that, it requires proper
care for the accuracy and efficiency so that the mo-
tion tracking is not compromised. On the other hand,
the IMU sensors are low-cost sensors and the data it
produces requires little or no processing. Our work
is focused on Motion Classification and not Motion
Reconstruction. We also aim to classify motion data
from two accelerometers in each arm of the user, but
we seek to infer complete body action. We also aim
to be able to classify without the need of an image
resource. That being said combined with the new mo-
tion database, our work becomes a novel approach to
the motion classification problem.
3 SPARSE MOTION DATA
CLASSIFICATION USING
LONG SHORT-TERM MEMORY
NETWORKS
This section presents our solution based on a novel
RNN constructed using LSTM cells. Next, we present
the properties of the LSTM Networks, how the mo-
tion raw data from IMU sensors is structured as input
for the network and the proposed topology.
3.1 Recurrent Neural Networks
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are a class of neu-
ral network models that have a self-connected hidden
layer. Such recurrent connection creates an internal
state of the network, allowing it to record internal
states such as for usage of past context.
As expected, understanding context is a crucial
ability for tasks such as sequence recognition and
classification tasks (Goodfellow et al., 2016). In order
to evaluate a sequence of any size, an RNN is repli-
cated throughout time flowing the contextual informa-
tion learned to update the corresponding weights that
represent its internal states.
Depending on the problem, the output of each
time step will have a different meaning. An RNN can
either be used to classify a whole sequence with a sin-
gle class, to generate a new sequence as output (e.g.
Translating a text), but also for creating a sequence
from a single input (e.g. for automatically captioning
an image).
Our approach can be seen as a sequence to one
approach, as the input represents the data describing
motion sequences while the output is one single ac-
tion label (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Motion sequence analysis: each time step of the
motion sequence is evaluated by a RNN. The t-th step se-
lects what information is relevant and updates contextual
information using the network weights that represent its in-
ternal states and pass it forward to the next step. The output
layer is associated with the possible classes, and is com-
puted after every step.
It is well known that standard RNNs have a lim-
ited contextual information range, thus it is hard to
learn long-term contextual dependencies. The prob-
lem is caused by the amount of influence that a given
input is subjected in the hidden layer. The recurrent
connection causes the input’s influence to either decay
or blow up exponentially, which is referred as the van-
ishing gradient problem (Graves et al., 2009). This is
especially important to our application as it is not pos-
sible to know a priori the size of our sequences, that
is, the time elapsed performing a certain action is not
limited.
The Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) (Good-
fellow et al., 2016) is an RNN architecture that ad-
dresses the vanishing gradient problem. The LSTM
hidden layer is composed of memory blocks, which
are self-connected subnetworks containing multiple
internal cells. Through multiplicative gates, the cell
is capable to store and access information over a long
period of time (Graves et al., 2009). In other words,
LSTM carries data from various steps through all
steps and each cell step is capable of including and
removing information from this data while process-
ing sequential input.
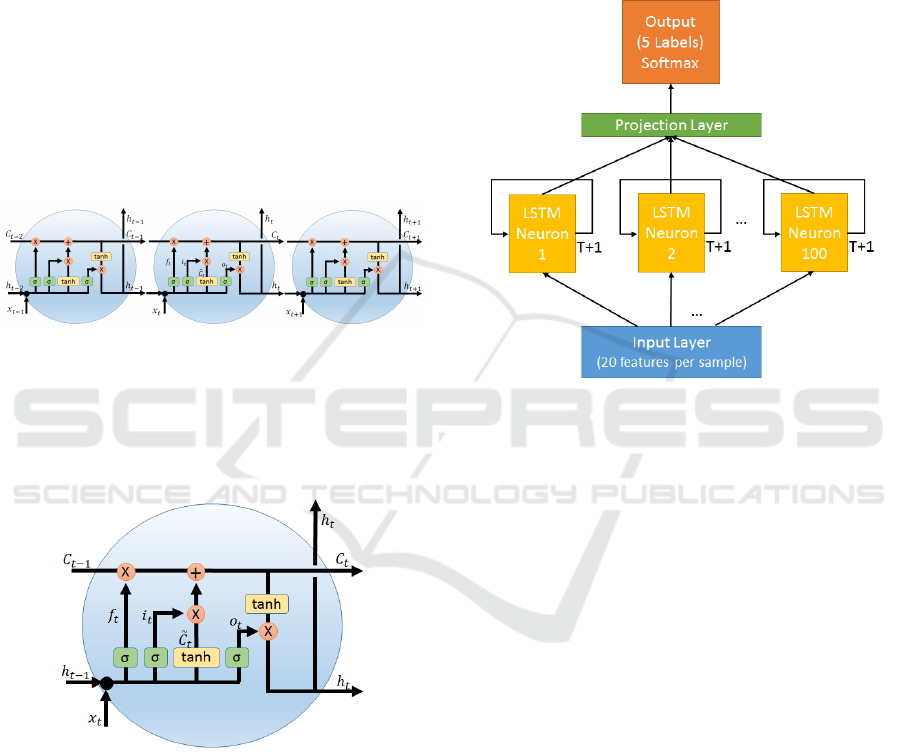
Each t-th LSTM cell step (Figure 3) from an
LSTM network (Figure 2) represents the t-th step of a
sequence and receives previous Cell State C
t−1
repre-
senting the information being carried so far until the
previous t − 1-th step and h
t−1
as the output of pre-
vious t − 1-th step. Each cell receives x
t
as the t-th
sample of a sequence, and will output an updated Cell
State C
t
and some output value h
t
. LSTM cells have
layers called “gates” which will allow information
to be “forgotten” or “perpetuated” to next steps/cells
(Goodfellow et al., 2016; Olah, 2015).
There is a forget gate f
t
to forget information no
longer necessary:
f
t
= σ(W
f
· [h
t−1
, x
t
] + b
f
)
PEEK - An LSTM Recurrent Network for Motion Classification from Sparse Data
217
An input gate i
t
to save new information (com-
puted as
e
C
t
from the current step x
t
and previous out-
put h
t−1
) that will be necessary:
i
t
= σ(W
i
· [h
t−1
, x
t
] + b
i
)
And an output gate o
t
To control the output of the
cell:
o
t
= σ(W
o
· [h
t−1
, x
t
] + b
o
)
The new t-th values are updated using these equa-
tions:
C
t
= f
t
∗C
t−1
+ i
t
∗
e
C
t
W here :
e
C
t
= tanh(W
C
· [h
t−1
, x
t
] + b
C
)
h
t
= o
t
∗tanh(C
t
)
Where W and b represent network parameters:
Weights and Biases.
Figure 2: Representation of an LSTM Cell over time. Each
cell step receives a sample from the sequence x from the in-
put layer, and sends out an updated cell state and the output
value h to the next step. Each time-step also sends the value
h to the output layer. (LSTM example by C. Olah (Olah,
2015)).
Figure 3: Representation of an LSTM Cell. Where C
t−1
represents the previous t −1-th step Cell State, h
t−1
the out-
put of previous t − 1-th step, x
t
represents the t-th sample of
a sequence, C
t
represents the updated Cell State and h
t
as
the output. We also have represented the gates: forget gate
f
t
, input gate i
t
and the output gate o
t
. (Picture by C. Olah
(Olah, 2015)).
3.2 Proposed Network Architecture
Our architecture is mainly composed of an Input
Layer with a 20-feature size (20 values composing
one input). This layer is followed by a Hidden Layer
composed of 100 LSTM neurons. The neurons (or
cells) from the hidden layer connects to a Projection
Layer which connects to the Output Layer. The Out-
put Layer has the size of an X-label vector (being X
the size of possible outputs). Each value of this vec-
tor represents the probability of the processed MW
to correspond to a certain action. This architecture is
represented in Figure Figure 4.
Figure 4: Network Architecture Topology. The input layer
sends the motion frames (one at a time) to each step of an
LSTM Neuron. Neurons will output a value each step to the
next step. Each neuron outputs the final value to the projec-
tion layer. The projection layer output the classification val-
ues from the neurons as a final classification to the output
layer using a softmax algorithm. The blue block represents
the input layer, which sends each frame of a sequence to
the neurons. The yellow blocks represent the LSTM neu-
rons. The Orange block represents the final output value,
computed after the projection layer (green block).
We propose an architecture where the input layer
is fed with sliding windows called Motion Windows
(MWs) of any length carrying 20 features in each
sample. At each step, each neuron will receive a new
frame of the MW from the output layer and its previ-
ous output. It will process the new output and send
it to the next step. The final step will output the re-
sult to the projection layer. This layer will encode on
the results of the neurons into a single output vector
of actions to the output layer. The final output is a
vector where each position represents one kind of ac-
tion, encoding a representation of what action most
approximates to the sequence.
3.3 Network Input/Output
In order to feed our network, we gather data from real
human subjects doing a set of body actions, where
GRAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
218
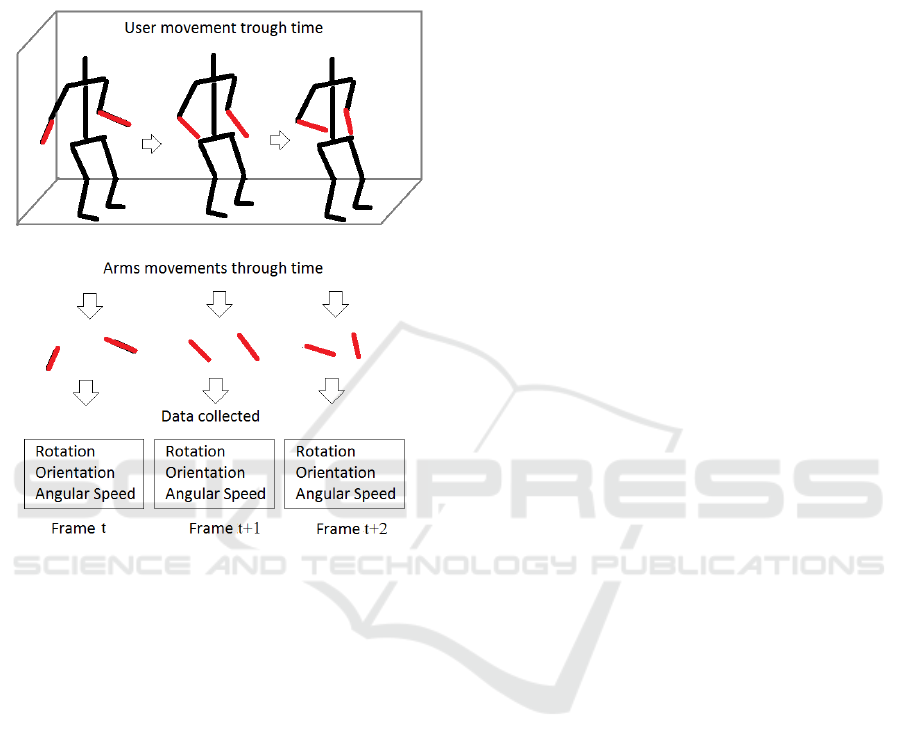
each subject wear an IMU sensor on each arm.
Each type of action should be done separately, that
is, each time frame is associated with a single action.
We call a frame, the recording of the state of both
of the IMU sensors at a certain time-stamp (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Body sparse data retrieval process. Red limbs
represent the arms being tracked by the IMU sensor and the
data collected from it.
Each frame contains 20 features (10 from each
sensor): {v, i, j, k}: that represent the axis of the
quaternion; {α, β, γ}: corresponding to three Euler
angles for representing rotation and orientation of the
arms; and finally, {ax, ay, az}: the angular accelera-
tion of both arms described in the world coordinate
system of both devices.
Supposing X as the size of the MWs, the first X
consecutive frames of a motion sequence are read and
written as one MW, followed by the next MW that
contains the same frames excluding the first frame and
including the frame that comes after the X-th frame.
In other words, we create MWs by sliding a frame
window of different sizes over our original motion
database.
It is important to note that the LSTM structure
does not impose a fixed size input, neither does
the proposed solution. Differing from text analysis,
where a natural segmentation is presented (e.g. text
punctuation), in motion analysis, one action is nat-
urally followed by another, and a minimum number
of frames may be elapsed before the new action can
be recognized as such. Exploring MWs allowed us
to investigate how many frames are sufficient to the
LSTM so that it could classify the action, that is, the
time elapsed of a certain movement so that the net-
work can already distinguish it.
These MWs will be used as input for our network.
Each MW has a label encoded as a one-hot vector in-
dicating what kind of activity the subject is perform-
ing.
4 DATABASE CONSTRUCTION
We built one database, composed of 11 subjects that
recorded 5 different kinds of activities for a certain
period of time equally distributed among them.
The actions consisted of: Standing idle, Walk-
ing, Running, Crouching (which includes staying
crouched) and Swinging a Weapon (attacking). Each
subject was instructed to do the actions in a variety
of forms (i.e. direction, speed) they, however, did not
know the purpose of the recordings in order to help
them perform the actions as natural as possible.
The actions were recorded using two Myo arm-
bands (myo, 2015) in each arm of the subjects (Fig-
ure 7). The recording used a fixed frame-rate of 50
frames per second. We had around 550.000 motion
frames allowing us to generate over 500.000 Motion
Windows.
The Motion Windows used for training, valida-
tion, and testing were 100-frames long. We also cre-
ated Motion Windows (from the same test sequence)
with lengths of 60, 50, 30, 25 and 10 frames to test
the trained network with different input sizes.
This database is available at: https://github.
com/RafaelDrumond/PeekDB.
5 RESULTS
We trained our model using a training set with Motion
Windows of 100 Frames using the Cognitive Toolkit
from Microsoft (McCaffrey, 2017) (CNTK). We used
Stochastic Gradient Descent as our optimizer, cross-
entropy as our loss function. We initialized our neu-
rons with zero values. Our model was trained using
5 epochs, we experimented increasing the number of
epochs, but there was no difference in performance
as it converged in the fourth epoch. The training
took around 6 hours to finish. Other training speci-
fications are available in Table IV. For the tests, we
used data from an actor that was not present in the
PEEK - An LSTM Recurrent Network for Motion Classification from Sparse Data
219
Training or Validation Sets. The testing used differ-
ent Motion Windows sizes (10, 25, 30, 50, 60 and
100 frames). All the Motion Windows were extracted
from the same data set and each size was used in a
different test case. The results are shown in Table I.
We also included results from tests using two different
techniques described by X. Zhang et al.(Zhang et al.,
2015)(text classification based on character sequence
based on convolutional networks) and by R. Zhang
et al.(Zhang and Li, 2015)(gesture classification us-
ing convolutional networks) in Table II. Since these
techniques were meant for other purposes, we adapted
their topology in order to test with our database. The
details of these two experiments are available in Sec-
tion 6 of this paper.
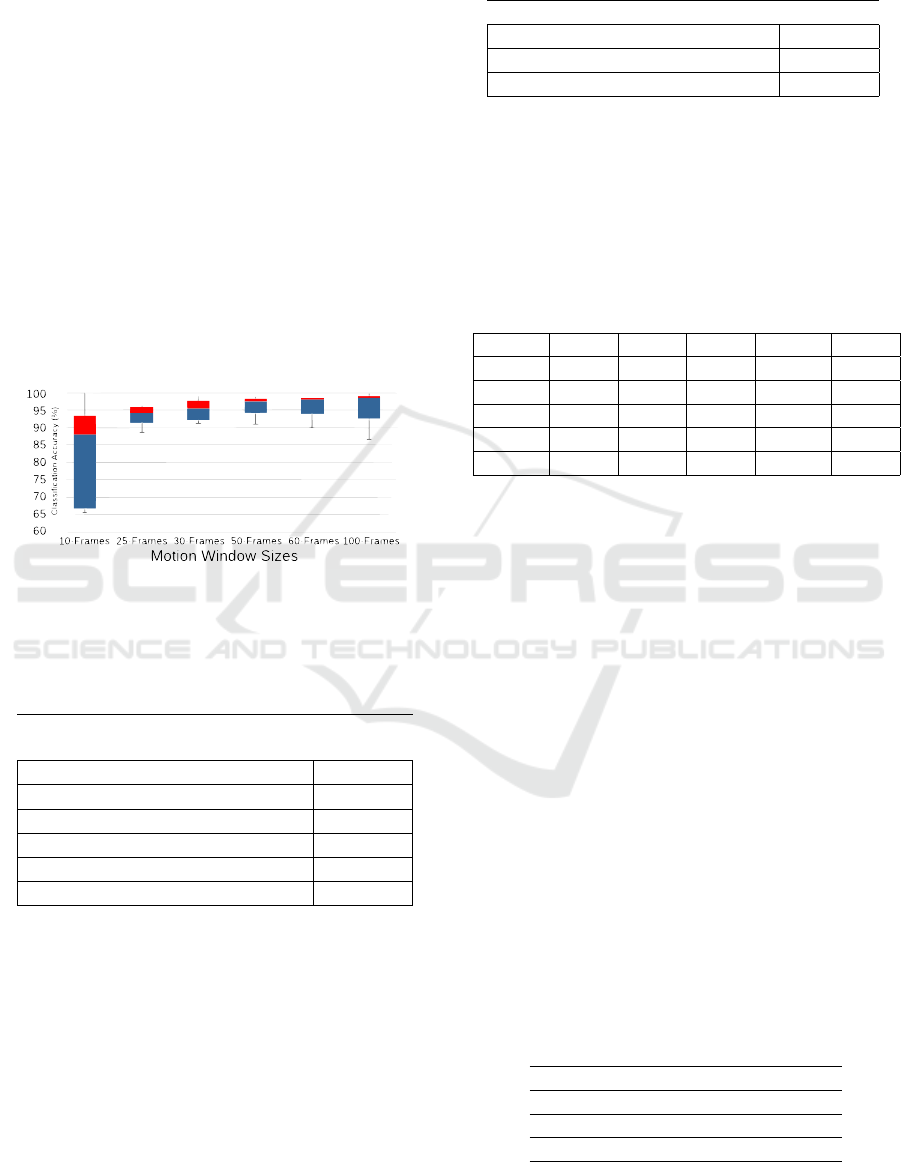
Figure 6 depicts the results of each experiment in
a box-plot chart using the per-class accuracy for each
test using our model.
Figure 6: Test Accuracy for each Experiment using the per-
class accuracy for each test
Table 1: Comparative percentual results of the tests with
the same test-set using different Motion Window Sizes. The
best results are boldfaced.
Model Overall
Accuracy
RNN Layer (100 frames window)
96.40%
RNN Layer (60 frames window)
96.63%
RNN Layer (50 frames window)
96.48%
RNN Layer (30 frames window)
95.09%
RNN Layer (25 frames window)
93.85%
RNN Layer (10 frames window)
81.69%
From the presented results, we can notice that us-
ing 60-Frame Windows return the best classification
accuracy but increasing this size does not guarantee
better results. Using 50-frames also gives an accu-
racy above the 96% mark. 30-Frames Windows can
give an accuracy almost as reliable as the 60-frame.
In order to further analyze these results, we built a
Confusion Matrix of the 60-frame experiment (Table
III). From it, we can see that all classes achieved the
mark o 98% except for “Idle”. This happened prob-
ably because the “Crouch” motion sequences include
not just the actors staying crouched, but also the tran-
Table 2: Comparative Results of our best Window Frame
size with two other different techniques.
Model Accuracy
Our Model (60 frames window)
96.63%
(Zhang and Li, 2015) 75.11%
(Zhang et al., 2015) 87.5%
sition from standing to crouching. We strongly be-
lieve that if we fix the labeling of some of the crouch-
ing frames where the actor is not yet (fully) crouched,
this problem would be solved. Still, the current results
are still acceptable.
Table 3: Confusion Matrix of the 60 Frames Window Ex-
periment. Rows represent the ground-truth classification
and columns represent the trained model results. Cro stands
for Crouch or Crouching.
Walk Idle Run Swing Cro
Walk 98.06 0 0.57 0.21 1.15
Idle 0.27 90.08 0 0 9.65
Run 0 0 98.59 1.37 0.04
Swing 0.86 0.0 0.71 98.31 0.11
Cro 1.69 0.06 0.0 0.14 98.11
We also tried different configurations for the net-
work. By using fewer neurons our network was un-
able to achieve high accuracy, staying below the 70%
overall accuracy during tests, causing under-fitting.
We experimented using 5, 20, 50, and 100 neurons,
where using 100 neurons improved greatly the re-
sults. By adding more hidden layers, the accuracy
dropped. The network only achieved an accuracy be-
low the 80% mark, by adding one extra layer, causing
over-fitting.
This network was validated using 5-Fold Cross-
Validation. This validation consists of separating the
actors into 5 groups randomly and performing the ac-
tions. After diving into groups (folds) we used the
first three folds as the training set, the fourth one as
the validation set and the fifth as the test set. We per-
formed the experiments with this configuration and
repeated four times, rotating the folds positions in
each stage. The highest mark and the lowest had 8%
of overall accuracy difference and their results had a
standard deviation of 2.87. This shows that our net-
work is efficient in generalizing cases that were not
recorded previously.
Table 4: Peek training specifications for CNTK.
Minibatch Size 512
Epochs 5
Momentum per MiniBatch 0.9
Learning Rate per MiniBatch 0.1
It is also necessary to remind that Peek accepts
GRAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
220

different sizes and not just the ones mentioned in the
experiments. Peek accepts Motion Windows of dif-
ferent sizes, for both training, validation and testing.
During training, the Motion Windows used were ran-
domly ordered (but not the frames inside their se-
quences).
6 EXPERIMENTS DESCRIPTION
All the experiments were performed using a GPU
GTX TITAN X, with 12GB of global memory and
with Nvidia Digits (NVIDIA, 2017). We used the
same actors for validation, testing and training by
generating images of 20x64, which corresponds to the
values of each frame and the instant of time, respec-
tively. Each pixel corresponds to a value, that was
mapped to a normalized number between 1 and 255.
We used 64 instants since it is the power of 2 closest
to the number of frames used in the best-case clas-
sification scenario achieved by Peek. The validation
interval corresponds to one quarter of an epoch. A
fixed learning rate of 0.0001 was used. Both have a
transform layer for the number of classes followed by
a softmax layer.
Databand Motion Classifier. This experiment
reached convergence with 12 training epochs. The
convolution networks are described in Table 5. We
instantiated this network using Caffe (Vision, 2017).
Except for the size of the input, this experiment fol-
lowed the settings of the best experiment listed on
(Zhang and Li, 2015).
Table 5: Layer configuration for the Databand Classifica-
tion(Zhang and Li, 2015).
Layer Size
1 Convolution
Output: 30
Kernel: Height 20 x Width 6
Stride: 1
2 Max-Pooling
Height 1 x Width 3
3 Convolution
Output: 40
Kernel: Height 1 x Width 5
Stride: 1
4 Max-Pooling
Height 1 x Width 2
5 Internal Product Size 500
Character Based Classifier. This experiment
reached convergence with 22 training times. The
convolution network is described in Table 6. To
instantiate the network, the authors used the language
Lua together with the library Torch (tor, 2017). As
the original work (Zhang et al., 2015) used strings
where each character was represented by one one-
hot-vector, the new input followed a similar format,
maintaining the width to reference the time in the se-
quence and the columns to represent the current state
instead of a character. This caused a drastic change
in the size of the input, which required readjusting
the size of the convolution and max-pooling layers.
Table 6: Layer configuration for the character based classi-
fication(Zhang et al., 2015) experiment.
Layer Size
1 Temporal Convolution Input: 20x64x1
Kernel: 3x3x256 (size)
2 Max-Pooling Height 3 x Width 3
3 Temporal Convolution Kernel: 1x1 256
4 Max-Pooling Height 3 x Width 3
5 Temporal Convolution Kernel: 1x1x256 (size)
6 Temporal Convolution Kernel: 1x1x256 (size)
7 Temporal Convolution Kernel: 1x1x256 (size)
8 Temporal Convolution Kernel: 1x1x256 (size)
9 Max Pooling Height 3 x Width 3
10 Re-Size size: 512
11 Linear Transformation 512 to 1024
12 Dropout Layer 0.5
13 Linear Transformation 1024 to 2014
14 Dropout Layer 0.5
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presented a recurrent neural network using
LSTM that is capable of learning and classifying Mo-
tion data coming from two sparse sensors. The pre-
sented model only requires two IMU sensors (on for
each arm) and does not require any additional periph-
erals such as cameras or extra gadgets. Depending on
the context of the application, the database can be eas-
ily built in order to create a different dictionary since
it also requires only two IMU devices. The fact that
only two IMU devices are required, provide accessi-
bility to final users, as well as fewer inconveniences
by having many peripherals attached to their body.
The arms were chosen due to the variety of acces-
sories available to users designed to this body part.
Each sequence contained samples of 20 features.
The network contained a single hidden layer of 100
neurons to process the input. The output corre-
sponded to a vector indicating the resulting classifi-
cation.
We also remark that Peek does not restrict or limit
the sizes of the Motion Windows, it accepts any size.
However, the sizes of the MWs may affect the effi-
ciency of the network. In our experiments, Motion
PEEK - An LSTM Recurrent Network for Motion Classification from Sparse Data
221

Windows with length around 60 frames were ideal for
achieving the best classification results.
It is not known by the authors of this paper any
other public database containing mocap data anno-
tated for actions corresponding to whole body motion
obtained from IMU sensors (including acceleration or
speed data).
As future work, there many are possible research
lines such as Attempting to reconstructing motion
from upper-limbs sparse data. Another future work
is to build an application integrating this model with
a real virtual reality-based game.
REFERENCES
(2015). Myo gesture control armband - wearable technol-
ogy by thalmic labs.
(2017a). Playstation (ps) move motion controller ps3 mo-
tion controller.
(2017). Torch: A scientific computing framework for luajit.
(2017b). Vive.
Baccouche, M., Mamalet, F., Wolf, C., Garcia, C., and
Baskurt, A. (2011). Sequential deep learning for hu-
man action recognition. In International Workshop
on Human Behavior Understanding, pages 29–39.
Springer.
Berger, K., Ruhl, K., Schroeder, Y., Bruemmer, C., Scholz,
A., and Magnor, M. A. (2011). Markerless motion
capture using multiple color-depth sensors. In VMV,
pages 317–324.
Chen, X. (2013). Human motion analysis with wearable
inertial sensors.
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., and Courville, A. (2016).
Deep Learning. MIT Press. http://www.
deeplearningbook.org.
Graves, A., Liwicki, M., Fern
´
andez, S., Bertolami, R.,
Bunke, H., and Schmidhuber, J. (2009). A novel
connectionist system for unconstrained handwriting
recognition. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis
and machine intelligence, 31(5):855–868.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Kr
¨
uger, B., Tautges, J., Weber, A., and Zinke, A. (2010).
Fast local and global similarity searches in large mo-
tion capture databases. In Proceedings of the 2010
ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Com-
puter Animation, pages 1–10. Eurographics Associa-
tion.
Kuni, R., Prathivadi, Y., Wu, J., Bennett, T. R., and Jafari,
R. (2015). Exploration of interactions detectable by
wearable imu sensors. In 2015 IEEE 12th Interna-
tional Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body
Sensor Networks (BSN), pages 1–6. IEEE.
McCaffrey, J. (2017). Machine learning - exploring the mi-
crosoft cntk machine learning tool. volume 32. MSDN
Magazine Blog.
NVIDIA (2017). Nvidia digits - interactive deep learning
gpu training system.
Olah, C. (2015). Understanding lstm networks.
Prathivadi, Y., Wu, J., Bennett, T. R., and Jafari, R. (2014).
Robust activity recognition using wearable imu sen-
sors. In IEEE SENSORS 2014 Proceedings, pages
486–489. IEEE.
Rautaray, S. S. and Agrawal, A. (2015). Vision based hand
gesture recognition for human computer interaction: a
survey. Artificial Intelligence Review, 43(1):1–54.
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., and Caputo, B. (2004). Recogniz-
ing human actions: a local svm approach. In Pat-
tern Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004. Proceedings of
the 17th International Conference on, volume 3, pages
32–36. IEEE.
Silva, A. R., Valente, L., Clua, E., and Feij
´
o, B. (2015). An
indoor navigation system for live-action virtual reality
games. In Computer Games and Digital Entertain-
ment (SBGames), 2015 14th Brazilian Symposium on,
pages 1–10. IEEE.
Tautges, J., Zinke, A., Kr
¨
uger, B., Baumann, J., Weber,
A., Helten, T., M
¨
uller, M., Seidel, H.-P., and Eber-
hardt, B. (2011). Motion reconstruction using sparse
accelerometer data. ACM Transactions on Graphics
(TOG), 30(3):18.
Vision, B. (2017). Caffe: Deep learning framework.
Wachs, J. P., K
¨
olsch, M., Stern, H., and Edan, Y. (2011).
Vision-based hand-gesture applications. Communica-
tions of the ACM, 54(2):60–71.
Wei, X., Zhang, P., and Chai, J. (2012). Accurate realtime
full-body motion capture using a single depth camera.
ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 31(6):188.
Weinland, D., Ronfard, R., and Boyer, E. (2011). A sur-
vey of vision-based methods for action representation,
segmentation and recognition. Comput. Vis. Image
Underst., 115(2):224–241.
Yuan, Q. and Chen, I.-M. (2014). Localization and velocity
tracking of human via 3 imu sensors. Sensors and
Actuators A: Physical, 212:25–33.
Zhang, R. and Li, C. (2015). Motion sequence recogni-
tion with multi-sensors using deep convolutional neu-
ral network. In Intelligent Data Analysis and Applica-
tions, pages 13–23. Springer.
Zhang, X., Zhao, J., and LeCun, Y. (2015). Character-
level convolutional networks for text classification. In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
pages 649–657.
GRAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
222
