
Semi-automatic CT Image Segmentation using Random Forests
Learned from Partial Annotations
Old
ˇ
rich Kodym
1
and Michal
ˇ
Span
ˇ
el
2
1
Department of Computer Graphics and Multimedia, Brno University of Technology,
Bozetechova 2, 612 66, Brno, Czech Republic
2
3Dim Laboratory, s.r.o., Kamenice 34, 625 00, Brno, Czech Republic
Keywords:
Computed Tomography, Semi-automatic Segmentation, Random Forests, Graph-cut.
Abstract:
Human tissue segmentation is a critical step not only in the process of their visualization and diagnostics but
also for pre-operative planning and custom implants engineering. Manual segmentation of three-dimensional
data obtained through CT scanning is very time demanding task for clinical experts and therefore the auto-
mation of this process is required. Results of fully automatic approaches often lack the required precision in
cases of non-standard treatment, which is often the case when computer planning is important, and thus semi-
automatic approaches demanding a certain level of expert interaction are being designed. This work presents a
semi-automatic method of 3D segmentation applicable to arbitrary tissue that takes several manually annota-
ted slices as an input. These slices are used for training a random forest classifiers to predict the annotation for
the remaining part of the CT scan and final segmentation is obtained using the graph-cut method. Precision of
the proposed method is evaluated on various CT datasets using fully expert-annotated segmentations of these
tissues. Dice coefficient of overlap is 0.976±0.014 for hard tissue segmentation and 0.978 ± 0.008 for kidney
segmentation, achieving competitive results with other task-specific methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Three-dimensional segmentation of hard tissues in
medical Computed Tomography (CT) is a first step re-
quired not only for reliable 3D visualization for diag-
nostic purposes but also for precise presurgical plan-
ning of orthopedic surgeries (Jun and Choi, 2010;
Wu et al., 2014) or craniofacial surgery (Chim et al.,
2014; Parthasarathy, 2014). Recently, number of 3D-
printable patient-specific implants (Tetsworth et al.,
2017) has also started to grow. Since these applicati-
ons require very accurate anatomical models, the seg-
mentation is often performed by clinical experts slice-
by-slice. As this task is very time demanding and te-
dious considering the number of slices in CT data, the
automation of this process is highly desirable. Howe-
ver, obstacles such as low-contrast tissue boundaries
and scatter which are usually present in CT data make
the automatic segmentation very difficult. Also, met-
hods need to be robust against various pathologies and
anatomical variability.
Although fully automatic approaches often yield
acceptable results in standard cases where the patient
anatomy doesn’t strongly deviate from the norm, the
aforementioned applications often require precision
in cases of abnormalities such as fractures, lesions
etc. where these automatic methods very often fail.
Semi-automatic approaches allow the user to intro-
duce a priori case-specific information regarding the
desired result of the segmentation and alter the result
after the automatic segmentation, in case adjustment
is needed.
In this paper, we propose a new semi-automatic
method of 3D segmentation of arbitrary tissue in
medical CT scans based on Graph-Cut method and
Random Forests. The method searches for glo-
bally optimal binary segmentation of the volumetric
data with respect to probability fields acquired from
Random Forest classifiers trained online on several
expert-annotated slices. This method yields satis-
factory results while using as few as two orthogonal
user-annotated input slices as shown in Figure 1, al-
lowing for segmentation of objects with various de-
formities or pathologies. Additionally, we introduce
a novel way of encoding the voxel-wise classification
into both the region-term and boundary-term energies
of the graph-cut framework.
124
Kodym, O. and Špan
ˇ
el, M.
Semi-automatic CT Image Segmentation using Random Forests Learned from Partial Annotations.
DOI: 10.5220/0006588801240131
In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2018) - Volume 2: BIOIMAGING, pages 124-131
ISBN: 978-989-758-278-3
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Figure 1: An example of using the method. Input CT data
and two orthogonal user-annotated input slices (left) and the
segmentation result (right).
2 RELATED WORK
A number of methods of 3D medical data segmen-
tation is available in the literature up to date. The
most simple methods are segmentation of hard tis-
sues using adaptive thresholding of acquired Houns-
field units (HU), which was applied to segmentation
of long bones (Rathnayaka et al., 2011) as well as
cranial bones (Pakdel et al., 2012) and region gro-
wing (Xi et al., 2014). All these methods are often
used in medical research as well as practice for their
simplicity, user-friendliness and easy understanding
of the method so behavior of a method can easily
be predicted. However, these methods require opti-
mal setting of threshold values and even then they are
prone to failure in locations where object boundaries
are very thin and low-contrast, as is often the case in
CT data due to partial volume artifact.
The more sophisticated approaches based on
active contour models such as level-sets (Pinheiro and
Alves, 2015) are able to complete the segmented ob-
ject boundary in these low contrast areas by making
assumptions about smoothness and continuity of the
boundary, but also tend to fail in areas of low intensity
gradient and are strongly dependable on user initiali-
zation of the object shape.
Methods utilizing statistical shape models (Yo-
kota et al., 2013) or active shape models (He et al.,
2016) form another category of segmentation approa-
ches that include preliminary creation of model of the
segmented object based on a training dataset acquired
from previous examinations. Such model can then be
registered to the current patient data using manually
located landmarks (Virzi et al., 2017) or automatically
(Chen et al., 2010). Use of shape models however as-
sumes that enough training data of the object is avai-
lable to sufficiently cover the physiological variability
and it usually doesn’t anticipate notable deviations in
the patient data.
In recent years, graph-cut methods based on (Boy-
kov and Jolly, 2001) gained some popularity as the
method is able to reliably and efficiently find glo-
bally optimal segmentation of the object. While these
methods often require multiple iterations of user in-
teraction to achieve acceptable results (Shim et al.,
2009), another of their advantage is that they can ea-
sily utilize additional information such as output of
specialized edge detector (Kr
ˇ
cah et al., 2011) or shape
model (Keustermans et al., 2012).
Convolutional neural networks (Krizhevsky et al.,
2012) are currently one of the fastest developing met-
hods in area of image processing. With the advance-
ments in computational power and expansion of va-
rious image databases, they became the state of the
art in numerous areas such as semantic image seg-
mentation (Zheng et al., 2015) as well as volumetric
medical data segmentation (Prasoon et al., 2013). In
this area, however, the available datasets still lack the
sufficient scale and therefore the applications usually
rely heavily on synthetic dataset augmentation (Mil-
letari et al., 2016; Ronneberger et al., 2015). This
comes at cost of reduced robustness similar to the
model-based methods.
Classification random forests (Loh, 2011) is
an ensemble machine learning method which uses
random subsets of available training dataset to con-
struct a set of binary decision trees. Each of these
trees, given a vector of input data, then outputs his-
togram of class probabilities and finally either voting
or averaging strategy is used to extract the final clas-
sification of the ensemble of trees. The method has
been widely used in computer vision in recent years.
While random forests have lately been outperformed
by other machine-learning approaches such as con-
volutional neural networks in some image classifica-
tion and segmentation tasks, random forests usually
require a much smaller training dataset and shorter
training time.
In this paper, we show that random forests lear-
ned using a few user-annotated slices only, in matter
of minutes, can achieve classification accuracy suffi-
cient to provide local voxel-wise predictions of tissue
boundaries for final segmentation step based on glo-
bal graph-cut optimization.
3 GRAPH-CUT SEGMENTATION
WITH VOXEL-WISE
PROBABILITIES FROM
RANDOM FOREST
CLASSIFICATION
The segmentation method proposed in this paper first
requires the user to manually denote contour of the
Semi-automatic CT Image Segmentation using Random Forests Learned from Partial Annotations
125

object in several slices, for example 3 orthogonal sli-
ces through the middle of the data volume. Next,
three voxel-wise random forest classifiers are trained
on the user annotated slices. Applying these classi-
fiers to the whole data volume outputs the probabi-
lity for each voxel to be a part of the object, its inner
edge and its outer edge. These three probability fields
are then converted into a graph structure where mi-
nimum cut/maximum flow algorithm is employed to
find the optimal binary segmentation of the object and
its background while re-using the user-annotated sli-
ces as hard constraints.
3.1 Random Forest Classification
We formulate the segmentation as a binary classifica-
tion problem where each voxel is assigned probabili-
ties of belonging inside or outside the segmented ob-
ject based on HU values of its surrounding voxels. A
lot of work has been put into choosing image features
suitable as input into the methods based on random
forests in the available literature. Various features
such as first- and second-order statistics of the patch
surrounding the voxel (Cuingnet et al., 2012), entropy
metrics and Gabor features (Mahapatra, 2014) and
Haar-like features (Larios et al., 2010) have been used
for various segmentation tasks. However, our results
show that using only the intensity values from a small
volume patch surrounding the voxel yields sufficient
trade-off between the results and training complexity,
which is important for semi-automatic method.
As mentioned earlier, we train following three se-
parate random forest classifiers:
• Object detector trained using the user-annotated
input binary object mask as the training data.
• Outer edge detector trained using the difference
between the user-annotated mask and its corre-
sponding 2D binary dilatation as the training data.
• Inner edge detector trained using the difference
between the user-annotated mask and its corre-
sponding 2D binary erosion as the training data.
The examples of detector outputs are shown in Fi-
gure 2 (d). The reason for training three separate clas-
sifiers is explained in the following chapter.
3.2 Global Segmentation Refinement
using Graph-cut
In our method, graph-cut is used to refine the lo-
cal outputs of random forest classifiers into a com-
pact three-dimensional binary object. In the origi-
nal work by (Boykov and Jolly, 2001), the region-
and boundary-term energies used to find the opti-
mal boundary are conventionally derived from origi-
nal image data as follows:
R
p
(”ob j”) = −ln[Pr(I
p
|O)] (1)
R
p
(”bkg”) = −ln[Pr(I
p
|B)] (2)
B
{p,q}
= exp
−
(I
p
− I
q
)
2σ
2
!
·
1
dist(p, q)
, (3)
where Pr(I
p
|O) and Pr(I
p
|B) are probability values
corresponding to the intensity value of voxels extrac-
ted from histogram of user-annotated areas of image,
I
q
and I
p
are intensity values of the voxels and σ
is variance of intensity in data volume. Graph-cut
then finds the optimal segmentation by minimizing
the region-term energy over every individual voxel
and boundary-term energy over every combination of
neighboring voxels (6-neighborhood in 3D space).
Intuitively, we can replace the histogram-derived
probabilities in region term with the more task-
specific output of object detecting random forest clas-
sifier from the previous step as it is defined for every
individual voxel. The new region-term energy is then
defined as
R
p
(”ob j”) = −ln[RF
ob j
(p)] (4)
R
p
(”bkg”) = −ln[1 −RF
ob j
(p)], (5)
where RF
ob j
(p) is output of random forest object clas-
sifier for voxel p.
When defining the boundary-term energy for refi-
ning the output of voxel-wise classifier, most appro-
aches such as (Mahapatra, 2014) decide to keep the
intensity-derived energy values or simply replace the
intensity difference with the difference of classifier
output. This, however, discards the ability of the clas-
sifier to decide whether the object-background boun-
dary is likely between two given voxels. While it is
not practical to train and then evaluate a random fo-
rest classifier on each possible combination of neig-
hboring voxels, it is possible to train two voxel-wise
classifiers and then combine their outputs. Conside-
ring a pair of neighboring voxels p and q with cor-
responding inner edge detector outputs RF
in
(p) and
RF
in
(q) and outer edge detector outputs RF
out
(p) and
RF
out
(q), the probability that the object-background
boundary lies in between these voxels is:
P
edge
(p, q) = RF
in
(p) · RF
out
(q) + RF
out
(p) · RF
in
(q).
(6)
BIOIMAGING 2018 - 5th International Conference on Bioimaging
126

Figure 2: Overview of the segmentation framework. Original CT data (a) serve as an input along with several user-annotated
slices (b). Random forests (c) are then used to produce voxel-wise predictions of the object and its outer and inner edge (d).
These outputs are then integrated into a single graph structure (e) where min-cut/max-flow algorithm is employed to find final
segmentation (f).
Therefore, we can define the new boundary-term
energy in following way:
B
{p,q}
= −ln[RF
in
(p) · RF
out
(q) + RF
out
(p) · RF
in
(q)].
(7)
While this approach is similar to (Browet et al.,
2016) who also add ”border” class to the classifier be-
fore graph-cut, they derive the boundary-term energy
as maximum of the border penalization of the two
voxels while our method computes the penalization
for border between the two voxels specifically.
Similarly to the original method, we further use
the user-annotated slices as hard constraints by setting
the region-term energy of corresponding voxels to
R
p
(”ob j”) = 0 (8)
R
p
(”bkg”) = ∞ (9)
on voxels that user marked as object and to
R
p
(”ob j”) = ∞ (10)
R
p
(”bkg”) = 0 (11)
on the remaining voxels of the annotated slice. This
forces the final segmentation to correspond to the
user’s initial shape description as the voxels already
annotated as the object can never be assigned back-
ground label and analogically the remaining voxels in
the slice can never have the object label. Finally, all
segmented objects not directly connected to any user-
defined hard-constraints are discarded as false detecti-
ons.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
We conducted experiments on a medical CT data-
set that can be divided into three groups. The first
group (A) consisted of 5 standard longitudinal bone
scans with 1.27 mm voxel spacing and 0.5 mm slice
thickness. These scans were fully manually segmen-
ted by medical expert and could therefore be used for
quantitative analysis of our method. The dataset in-
cluded three tibia, one humerus with higher level of
noise and one radial bone with higher level of blur.
Second group (B) consisted of two high-resolution
mandible scans. First scan with 0.4 mm voxel spa-
cing and 0.4 mm slice thickness included a toothless
mandible and had expert segmentation made in 11 ax-
ial slices. The second mandible with 0.3 mm voxel
spacing and 0.2 mm slice thickness had expert seg-
mentation made for individual teeth in 3 orthogonal
slices for each tooth. Scans in this group could not be
used for quantitative analysis due to lack of ground
truth and only illustrate that the method can be used
Semi-automatic CT Image Segmentation using Random Forests Learned from Partial Annotations
127
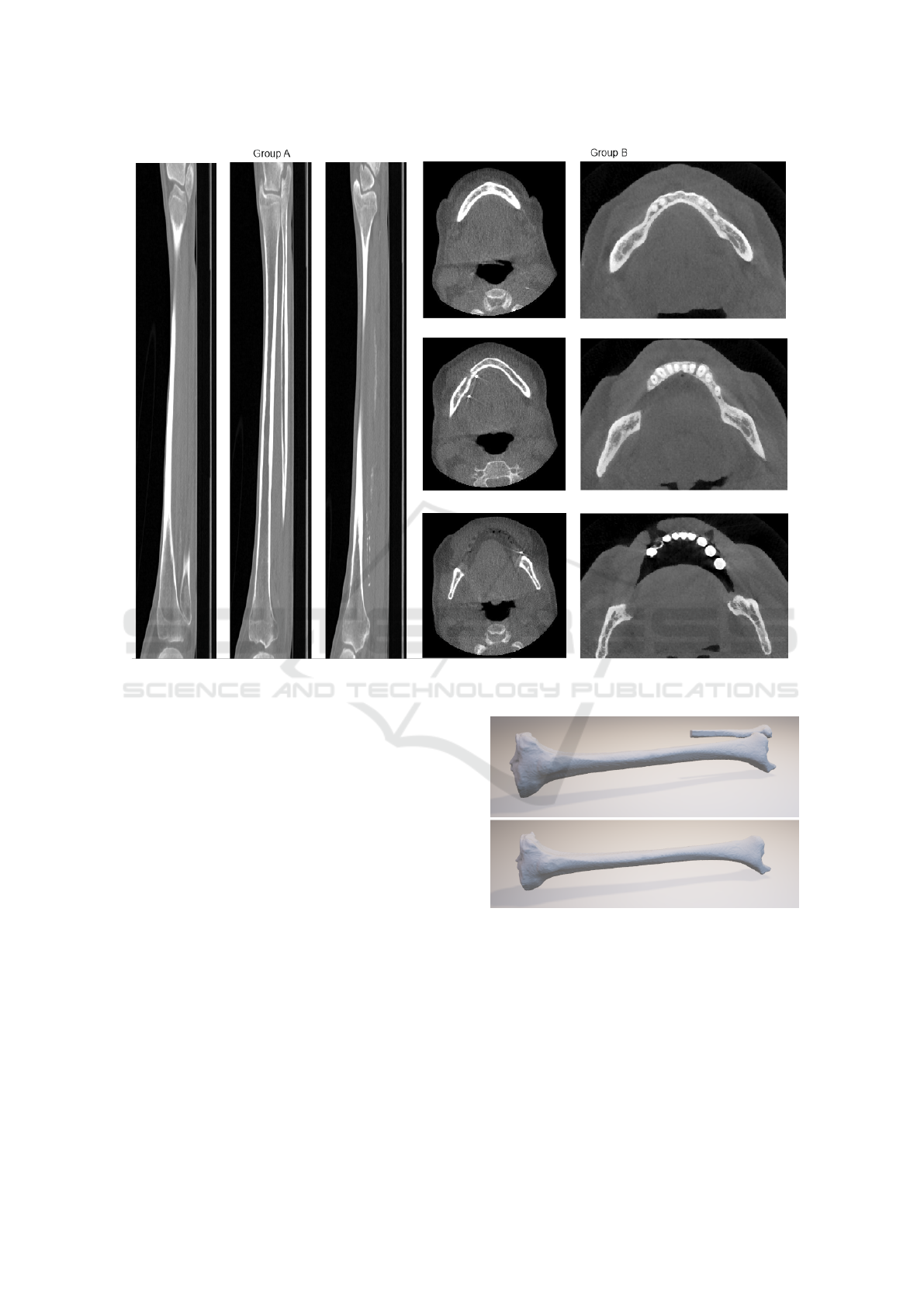
Figure 3: Example of CT scans on which the experiments were done. 3 lateral slices through a tibia in group A (left) and 3
axial slices of each mandible in group B (right).
to segment tissue of arbitrary shape. The third group
(C) consisted of 9 standard kidney scans with 0.7 mm
voxel spacing and 1.6 mm slice thickness. This da-
taset was also fully manually segmented to provide
ground truth. All scans were cropped around the ob-
jects of interest as an image pre-processing step. Ex-
amples of the scans in each group are shown in Fi-
gure 3.
The method was implemented in Python and Mat-
lab programming languages. Scikit-learn library
(Pedregosa et al., 2011) was used for implementa-
tion of the random forests and Visualization Toolkit
(Schroeder et al., ) for data vizualization. Matlab im-
plementation of the Maxflow algorithm (Boykov and
Kolmogorov, 2004) was used for the graph-cut opti-
mization. Tests were run on a laptop with 2.50GHz
i5-3210M processor and 8GB RAM. The required
computing time ranged from 4 minutes on smaller
data volumes such as single teeth scans to 15 minu-
tes on larger volumes such as shin bones.
For the scans in group A with full manual segmen-
tations available, Dice coefficient (Dice, 1945) was
used to quantitatively determine accuracy of the pro-
Figure 4: Example of false negative segmentation of part of
splint-bone during shin-bone segmentation with Dice coef-
ficient of 0.944 (upper) and correct shin-bone segmentation
after adding an additional input slice yielding Dice coeffi-
cient of 0.987 (lower).
posed method and to study dependency of its success
rate on the number of user-annotated slices used as
an input. The experiments showed a very high preci-
sion of the proposed method with Dice coefficient of
0.976 ± 0.016 when using 5 user-annotated slices as
input, specifically 3 orthogonal slices through middle
BIOIMAGING 2018 - 5th International Conference on Bioimaging
128
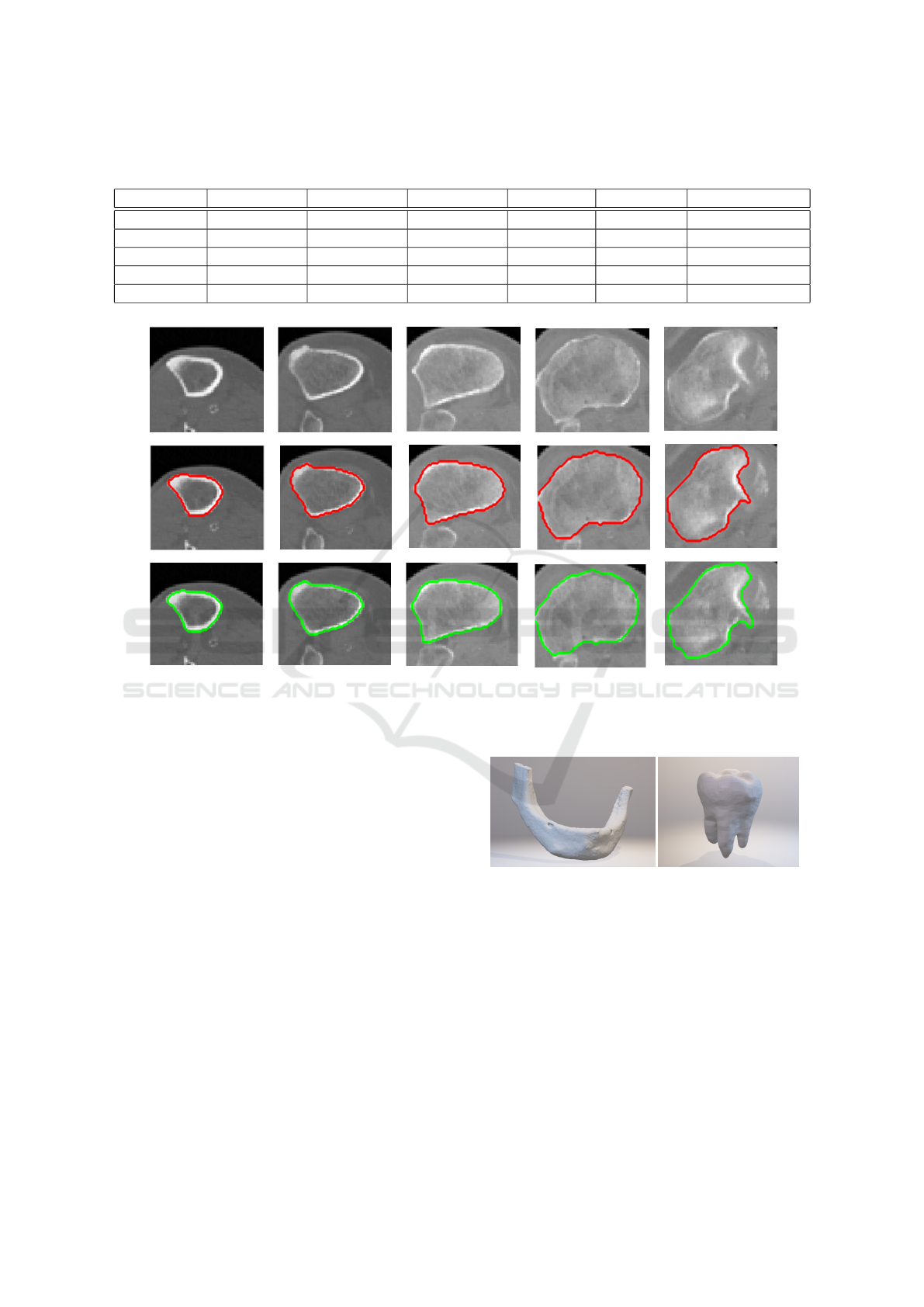
Table 1: Dice coefficients (DC) of final result and computation times of the classification step of the method for individual
objects of interest. Training times for cases where 5 input slices were used are presented.
DC (2 slices) DC (3 slices) DC (5 slices) Total slices Training (s) Classification (s)
Shin bone 1 0.983 0.983 0.984 770 95 423
Shin bone 2 0.959 0.968 0.991 530 182 764
Shin bone 3 0.944 0.944 0.987 540 134 386
Humerus 0.967 0.968 0.968 587 57 218
Radial bone 0.907 0.935 0.952 497 60 256
Figure 5: Example of result in 5 axial slices for the case where shin-bone was correctly segmented using only single frontal
and lateral slice as input. Red contour marks expert-annotated segmentation in these slices, green contour marks result of our
method.
of the bone and 2 additional axial slices through bone
proximities. When using more than 5 input slices, the
precision usually didn’t improve anymore. The spe-
cific results and computing times for each bone are
shown in Table 1. When using fewer user-annotated
slices, i.e. only one sagittal and one frontal slice, the
method still achieves high accuracy but can fail in se-
parating adjoining structures such as part of splint-
bone in case of shin-bone segmentation as shown in
Figure 4. This happens mostly when the adjoining
structure isn’t present in the annotated slices and can
be avoided by choosing the slices appropriately or by
allowing the user to interact with the graph-cut step of
the method. By marking only several voxels as being
false-positive detections, the graph-cut can be reeva-
luated in several seconds, incorporating the newly ad-
ded hard-constraints into the minimum cut search.
For the scans in group B, only several expert-
annotated slices were available and used as an input.
Although quantitative accuracy assessment is not pos-
Figure 6: Examples of the segmentation result for mandible
(left) and molar tooth (right). 11 axial slices were used as an
input for the mandible segmentation and 3 orthogonal slices
for the molar.
sible in these cases, the method yielded visually plau-
sible results in all cases when using the available user-
annotated slices as shown in Figure 6.
In experiments with the kidney scans in group
C, 3 orthogonal expert-annotated slices were used as
an input for each scan. The total number of ana-
lyzed slices per scan ranged from 59 to 83. The
mean Dice coefficient of the segmentation results was
0.978 ± 0.008 achieving competitive results with ot-
Semi-automatic CT Image Segmentation using Random Forests Learned from Partial Annotations
129
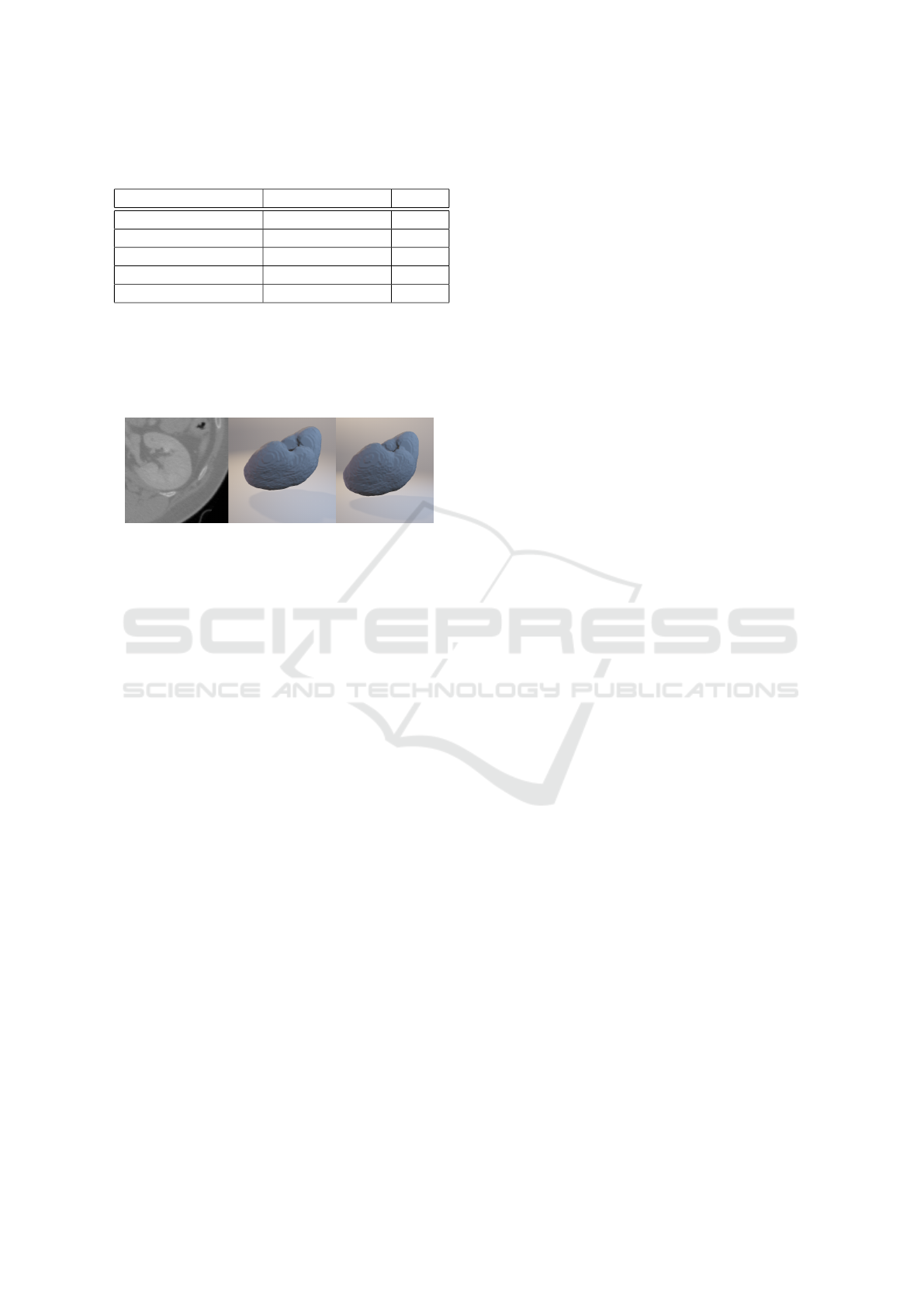
Table 2: Dice coefficients (DC) of various kidney segmen-
tation methods.
Method Input DC
(Glisson et al., 2011) Seed points 0.93
(Sharma et al., 2015) 1 annotated slice <0.9*
(Sharma et al., 2017) None 0.86*
(Khalifa et al., 2017) None 0.97
Our method 3 annotated slices 0.98
* Results on CT scans of kidneys with autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease
her automatic and semi-automatic kidney segmenta-
tion methods as shown in Table 2. The example result
of segmentation by our method is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7: Example of kidney segmentation. Original CT
data (left), manual segmentation (middle) and the output of
our method (right).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we proposed a method able to perform
segmentation of given tissue by first interpolating
the user-annotated slices using random forest clas-
sifiers and then refining their output with graph-cut.
We also introduce a new methodology of incorpora-
ting an output of voxel-wise classifier into boundary-
term energy of the graph structure generated from the
image in addition to the region-term energy.
The experiments show very good fit of the results
with manually segmented tissues. After using hard
tissue dataset to tune and analyze the algorithm per-
formance, we tested it on the kidney dataset to show
that the output of our universal method is comparable
with state-of-the-art methods designed for the specific
task.
Although it takes more user input, i.e. several ma-
nually segmented 2D slices, when compared to other
methods, it brings significant advantages. First, it al-
lows the user to segment an arbitrary tissue despite its
shape or intensity as the random forest classifier infers
the appropriate object and edge features on its own as
long as the variability is captured in the annotated sli-
ces. Second, it is possible for the user to correct any
faulty segmented regions by including them in the an-
notated slices and then either reevaluating the graph-
cut optimization step in several seconds, or running
the full process again in case of larger errors. While
this takes several minutes for every iteration, it still sa-
ves a lot of time and manual work when correcting the
segmentation result in every slice individually. Also,
the computational complexity could be further redu-
ced by parallelizing the random forest classification
step which takes majority of the computing time.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by the company
3Dim Laboratory and by the Technology Agency of
the Czech Republic project TE01020415 (V3C - Vi-
sual Computing Competence Center). We would also
like to thank 3Dim Laboratory for providing us anno-
tated CT data for experiments.
REFERENCES
Boykov, Y. and Kolmogorov, V. (2004). An experimen-
tal comparison of min-cut/max- flow algorithms for
energy minimization in vision. IEEE Transacti-
ons on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
26(9):1124–1137.
Boykov, Y. Y. and Jolly, M.-P. (2001). Interactive Graph
Cuts for Optimal Boundary & Region Segmentation
of Objects in N-D Images.
Browet, A., Vleeschouwer, C., Jacques, L., Mathiah, N.,
Saykali, B., and Migeotte, I. (2016). Cell segmenta-
tion with random ferns and graph-cuts.
Chen, A., Deeley, M. A., Niermann, K. J., Moretti, L., and
Dawant, B. M. (2010). Combining registration and
active shape models for the automatic segmentation of
the lymph node regions in head and neck CT images.
Chim, H., Wetjen, N., and Mardini, S. (2014). Virtual surgi-
cal planning in craniofacial surgery. Seminars in Plas-
tic Surgery, 28(3):150–157.
Cuingnet, R., Prevost, R., Lesage, D., Cohen, L. D., Mory,
B., and Ardon, R. (2012). LNCS 7512 - Automa-
tic Detection and Segmentation of Kidneys in 3D CT
Images Using Random Forests.
Dice, L. R. . (1945). Measures of the Amount of Ecologic
Association Between Species. Ecology, 26(3):297–
302.
Glisson, C. L., Altamar, H. O., Herrell, S. D., Clark, P., and
Galloway, R. L. (2011). Comparison and assessment
of semi-automatic image segmentation in computed
tomography scans for image-guided kidney surgery.
Medical Physics, 38(11):6265–6274.
He, B., Huang, C., Sharp, G., Zhou, S., Hu, Q., Fang, C.,
Fan, Y., and Jia, F. (2016). Fast automatic 3D liver
segmentation based on a three-level AdaBoost-guided
active shape model. Medical Physics, 43(5):2421–
2434.
BIOIMAGING 2018 - 5th International Conference on Bioimaging
130

Jun, Y. and Choi, K. (2010). Design of patient-specific hip
implants based on the 3D geometry of the human fe-
mur. Advances in Engineering Software, 41(4):537–
547.
Keustermans, J., Vandermeulen, D., and Suetens, P. (2012).
Integrating Statistical Shape Models into a Graph Cut
Framework for Tooth Segmentation. pages 242–249.
Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Khalifa, F., Soliman, A., Elmaghraby, A., Gimel’farb, G.,
and El-Baz, A. (2017). 3D Kidney Segmentation
from Abdominal Images Using Spatial-Appearance
Models. Computational and Mathematical Methods
in Medicine, 2017:1–10.
Kr
ˇ
cah, M., Sz
´
ekely, G., and Blanc, R. (2011). Fully auto-
matic and fast segmentation of the femur bone from
3D-CT images with no shape prior. Proceedings - In-
ternational Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pages
2087–2090.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012).
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional
Neural Networks.
Larios, N., Soran, B., Shapiro, L., Martinez-Munoz, G.,
Lin, J., and Dietterich, T. (2010). Haar Random Forest
Features and SVM Spatial Matching Kernel for Sto-
nefly Species Identification. In 2010 20th Internatio-
nal Conference on Pattern Recognition, pages 2624–
2627. IEEE.
Loh, W.-Y. (2011). Classification and regression trees.
Mahapatra, D. (2014). Analyzing Training Information
From Random Forests for Improved Image Segmen-
tation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,
23(4):1504–1512.
Milletari, F., Navab, N., and Ahmadi, S.-A. (2016). V-Net:
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric
Medical Image Segmentation. In 2016 Fourth Inter-
national Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pages 565–
571. IEEE.
Pakdel, A., Robert, N., Fialkov, J., Maloul, A., and Whyne,
C. (2012). Generalized method for computation
of true thickness and x-ray intensity information in
highly blurred sub-millimeter bone features in clini-
cal CT images. Physics in Medicine and Biology,
57(23):8099–8116.
Parthasarathy, J. (2014). 3D modeling, custom implants and
its future perspectives in craniofacial surgery. Annals
of Maxillofacial Surgery, 4(1):9.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer, P.,
Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos, A.,
Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., and Du-
chesnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning
in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
12:2825–2830.
Pinheiro, M. and Alves, J. L. (2015). A new level-set ba-
sed protocol for accurate bone segmentation from CT
imaging. IEEE Access, 3:1894–1906.
Prasoon, A., Petersen, K., Igel, C., Lauze, F., Dam, E., and
Nielsen, M. (2013). Deep Feature Learning for Knee
Cartilage Segmentation Using a Triplanar Convolutio-
nal Neural Network. pages 246–253. Springer, Berlin,
Heidelberg.
Rathnayaka, K., Sahama, T., Schuetz, M. A., and Schmutz,
B. (2011). Effects of CT image segmentation methods
on the accuracy of long bone 3D reconstructions. Me-
dical Engineering & Physics, 33(2):226–233.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T. (2015). U-Net:
Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Seg-
mentation.
Schroeder, W. J., Martin, K. M., and Lorensen, W. E. The
Design and Implementation Of An Object-Oriented
Toolkit For 3D Graphics And Visualization.
Sharma, K., Peter, L., Rupprecht, C., Caroli, A., Wang, L.,
Remuzzi, A., Baust, M., and Navab, N. (2015). Semi-
Automatic Segmentation of Autosomal Dominant Po-
lycystic Kidneys using Random Forests.
Sharma, K., Rupprecht, C., Caroli, A., Aparicio, M. C., Re-
muzzi, A., Baust, M., and Navab, N. (2017). Auto-
matic Segmentation of Kidneys using Deep Learning
for Total Kidney Volume Quantification in Autosomal
Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Scientific Re-
ports, 7(1):2049.
Shim, H., Chang, S., Tao, C., Wang, J.-H., Kwoh, C. K., and
Bae, K. T. (2009). Knee Cartilage: Efficient and Re-
producible Segmentation on High-Spatial-Resolution
MR Images with the Semiautomated Graph-Cut Algo-
rithm Method. Radiology, 251(2):548–556.
Tetsworth, K., Block, S., and Glatt, V. (2017). Putting 3D
modelling and 3D printing into practice: virtual sur-
gery and preoperative planning to reconstruct complex
post-traumatic skeletal deformities and defects. Sicot-
J, 3:16.
Virzi, A., Marret, J.-B., Muller, C., Berteloot, L., Boddaert,
N., Sarnacki, S., and Bloch, I. (2017). A new method
based on template registration and deformable models
for pelvic bones semi-automatic segmentation in pe-
diatric MRI. Proceedings - International Symposium
on Biomedical Imaging, pages 323–326.
Wu, D., Sofka, M., Birkbeck, N., and Zhou, S. K. (2014).
Segmentation of multiple knee bones from CT for ort-
hopedic knee surgery planning. Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in
Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinfor-
matics), 8673 LNCS(PART 1):372–380.
Xi, T., Schreurs, R., Heerink, W. J., Berg
´
e, S. J., and
Maal, T. J. J. (2014). A novel region-growing ba-
sed semi-automatic segmentation protocol for three-
dimensional condylar reconstruction using cone beam
computed tomography (CBCT). PLoS ONE, 9(11):9–
14.
Yokota, F., Okada, T., Takao, M., Sugano, N., Tada, Y.,
Tomiyama, N., and Sato, Y. (2013). Automated CT
Segmentation of Diseased Hip Using Hierarchical and
Conditional Statistical Shape Models. pages 190–197.
Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Zheng, S., Jayasumana, S., Romera-Paredes, B., Vineet, V.,
Su, Z., Du, D., Huang, C., and Torr, P. H. S. (2015).
Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Net-
works.
Semi-automatic CT Image Segmentation using Random Forests Learned from Partial Annotations
131
