
Co-occurrence Background Model with Hypothesis on Degradation
Modification for Robust Object Detection
Wenjun Zhou
1
, Shun’ichi Kaneko
1
, Manabu Hashimoto
2
, Yutaka Satoh
3
and Dong Liang
4
1
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Hokkaido University, Japan
2
Chukyo University, Japan
3
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan
4
Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China
Keywords:
Background Model, Co-occurrence Pi xel-Block Pairs (CPB), Object Detection, Correlation Depended
Decision Function, Severe Scenes, Hypothesis on Degradation (HoD).
Abstract:
This paper presents a prospective background model for robust object detection in severe scenes. This back-
ground model using a novel algorithm, Co-occurrence Pixel-block Pairs (CPB), that extracts the spatiotem-
poral information of pixels from background and identifies the state of pixels at current frame. First, CPB
realizes a robust background model for each pixel with spatiotemporal information based on a “pixel to block”
structure. And then, CPB employs an efficient evaluation strategy to detect foreground sensitively, which is
named as correlation dependent decision function. On the basis of this, a Hypothesis on Degradation Modifi-
cation (HoD) for CP B is introduced to adapt dynamic changes in scenes and reinforce robustness of CPB to
against “noise” in real conditions. This proposed model is robust to extract foreground against changes, such
as illumination changes and background motion. Experimental results in different challenging datasets prove
that our model has good effect for object detection.
1 INTRODUC TION
Object detection is one ac tive area of research in th e
field of visual surveillance (Hu et al., 2004), where
backgr ound subtraction has be e n widely used in va-
rious problems(Yilmaz e t al., 2006; Moeslund et al.,
2006; Cheung and Kamath, 2005). However, imple-
menting backg round subtraction for real scenes with
severe backgrou nds is beset with challenges(Vacavan t
et al., 2012), not least of which are those related to
il-
lumination changes
, e.g. variable sunlight outdo ors
or lights being switched on and off indo ors, and then
background motions
, e.g. swaying trees or moving
waves on the water.
To overcom e such challenges, two types of design
schema have been proposed. First is the
pixel-wise
model, in which the intensity of each pixel is inde-
pendently analyzed in the temporal domain and then
the current frame is subtracted. An example of this
approa c h is Pfinder(Wren et al., 1997), a real-time
method for analyzing the color information (Y/U/V)
of each pixel and then building a pixel-wise mo-
del by the Gaussian mixture model (GMM)(Stauffer
and Grimson, 1999), which is a well-k nown way to
deal with multiple background objects. Elgamma l et
al.(Elgammal et al., 2002) proposed a non-parametric
method that can be used to detect object in severe sce-
nes by the using of kernel density estimation (KDE).
The second scheme is the
spatial-based
mo-
del, in which a background model is built by ma-
king decisions regarding the spatial correlations be-
tween pixels o r blo c ks. Seki(Seki et al., 2003)
proposed such a meth od that involved estimating
the co-occurrence correlation between neighboring
blocks. Subsense(St-Charle s et al., 2015), a re-
cently algorithm following ViBe’s strategy(Barnich
and Van Dro ogenbroeck, 2011) that pre sented one
pixel-level segmentation method that relies on spati-
otemporal binary features combined with color infor-
mation to detect foreground.
The first design schema can not deal well with
illumination changes in the a bsence of contextual
spatial inf ormation and most of the second design
schema pay much attention to the lo c al spatial infor-
mation of ne ighboring pixels or blocks and ignore the
global spatial information.
To counter these overlooked issues, we propose an
effective method of co-occurre nce pixel-block pairs
266
Zhou, W., Kaneko, S., Hashimoto, M., Satoh, Y. and Liang, D.
Co-occurrence Background Model with Hypothesis on Degradation Modification for Robust Object Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0006613202660273
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2018) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
266-273
ISBN: 978-989-758-290-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(CPB) for detecting objects robustly in severe scenes.
This is based on our earlier works(Iwata et al., 2009;
Zhao e t al., 2011; Liang et al., 2015) with the inno-
vations: 1) a “pixel to block” struc ture that can pro-
vide a fast statistical training solution, thereby allo-
wing an on-lin e approach; 2) a novel evaluation stra-
tegy named correlation depended decision function
for accurate object detection. Based on CPB, we
propose a Hypothesis on Degradation Modification
(HoD) for CPB to adapt dynamic ch a nges in scenes
and reinforce robustness of CPB to against “noise”
in real conditions. More details are described in f ol-
lowing sections and we also compare the proposed
method with other advanced techniques to prove the
efficiency of our method under various challenging
datasets. This paper is organiz ed as fo llows. Secti-
ons 2 introduces how CPB method works in details.
Section 3 g ives one introduction of Hyp othesis on
Degradation Modification (HoD) for CPB. Section 4
reports experimental results to compare the perfor-
mance of the p roposed method with other advanced
approa c hes. Sectio n 5 conclude s the paper along with
future work.
2 CPB BACKGROU ND MODEL
Figure 1: Overview of working mechanism of CPB.
2.1 Overv iew
In general, the proposed CPB includes two pro cesses:
training process and detecting process. Fig. 1 shows
the overview of working mechanism of CPB.
2.2 Model Building
As an extension from the “pixel to pixel ” structure
that works SRF(Iwata et al., 2009), GAP(Zhao et al.,
2011) and CP3(L iang et al., 2015) to estimate th e tar-
get pixel p with other pixels on e by one and then
to select the suitable supporting pixels for the tar-
get pixel p, in CPB we compare the target pixel p
with the Q
B
as block, and define {Q
B
k
}
k=1,2,...,K
=
{Q
B
1
, Q
B
2
, ..., Q
B
K
} to denote a supporting block set for
the target pixel p. As an instance, we first divide each
frame (the size is U×V ) into the blocks {Q
B
}, the
size of each block is m×n and the number of blocks
is M×N (
U
m
= M,
V
n
= N). In the ory, sinc e a large
part of computation cost can be reduce d in the trai-
ning process , CPB is expected mn times faster in the
training than CP3(Liang et al., 2015).
For each pixel p, it is expected to own one or more
blocks Q
B
that maintain a stable relatio n in the diffe-
rence I
p
−
¯
I
Q
throughout the whole training frames as
shown in Fig.2, where
¯
I
Q
is the average intensity of
block Q
B
. The relation shown in Fig.2(b) is called as
“Co-occurrence between intensity,” and we can utilize
this knowledge to design the statistical model for the
characteristics in background pixels. Since the main
purpose of this study is to design a robust detector
of any foreground events, such as walking peoples,
animals or cars on the r oads or grasses without any
detection of the m eaningless events, such as moving
clouds or shaking gr asses, w e utilize multiple relati-
onship of the co-occurrence mentioned above to build
the background model.
(a) Co-occurrence pixel- block pair
structure.
(b) Pairwise statistical model of pixel-
block pair (p, Q
B
1
).
Figure 2: Basic structure of co-occurrence pixel to block
pair.
2.2.1 Selection of Supporting Blocks
A set of supporting blocks {Q
B
k
} is defined f or
each pixel p in scene by utilizing Pearson’s pro duct-
moment correlation c oefficient:
γ(p, Q
B
k
) =
C
p,
¯
Q
k
σ
p
· σ
¯
Q
k
, (1)
where C
p,
¯
Q
k
is the intensity covariance between target
pixel p and its k-th suppor ting block Q
B
k
from a set of
training frames, σ
p
and σ
¯
Q
k
are the standard deviati-
ons in the pixel and the bloc k, respec tively.
In general, we can expect that if the pixel-block
pair (p, Q
B
k
) keeps a high correlation coe fficient, then
Co-occurrence Background Model with Hypothesis on Degradation Modification for Robust Object Detection
267

Figure 3: Example l ayouts of pixel-block pairs for different position pixels p
1
(168, 334), p
2
(384, 325), p
3
(439, 131) and
p
4
(223, 50), respectively, where K = 5 and the si ze of each block is 5×5.
the supporting block Q
k
can provid e some reliabi-
lity to estima te the current sate of the target pixel
p. According this a pproach, we pro pose a set
of supporting blocks{Q
B
k
}
k=1,2,...,K
= {Q
B
|γ(p, Q
B
)
is the K highest} fo r each pixel p. Fig.3 shows
example layo uts of the supporting blocks using
PET S2001 − dataset3 and the target pixels are se-
lected from the four repre sentative regions: “Grass,”
“Road,” “Building,” “Sky,” respectively.
2.2.2 Statistical Modeling of Pairwise Intensity
Co-occurrence
For the selected K pixel-block pairs, we build a statis-
tical model using the single Gaussian distribution as
defined in the following expression:
∆
k
∼ N(b
k
, σ
2
k
) ∆
k
= I
p
−
¯
I
Q
k
, (2)
where I
p
is the intensity of the pixel p at t frame and
¯
I
Q
k
is the average intensity of the block Q
B
k
at t frame.
We assume th a t the d ifference in intensities between
any co-o ccurrenc e pairs follows a normalized d istri-
butions N(b, σ
2
)(Liang et al., 2015), and then we use
the single Gaussian model to build the background
model for each co-occurrence pair. The variance esti-
mation σ
2
k
cis defined as follows:
σ
2
k
=
1
T
T
∑
t=1
(∆
k
− b
k
)
2
, (3)
and b
k
is the differential increment
b
k
=
1
T
T
∑
t=1
∆
k
, (4)
where T is the sequence of frames. Through the
training process, the parameters σ
k
and b
k
are re-
corded as a model description for the next detecting
stage and then the background model is built as a list
consisting of [u
k
, v
k
, b
k
, σ
k
] for supporting block set
{Q
B
k
}
k=1,2,...,K
, where (u
k
, v
k
) is the coordinate of sup-
porting block.
2.3 Object Detection
We contain a competitive binary classification p rocess
for the object detection(Elhabian et al., 2008) in our
CPB by evaluating each pa ir (p, Q
B
k
) of every pixel in
turn. It includes two procedures: 1) to estimate the
steady or unsteady state of each pair, and the n 2) to
distinguish a target pixel is belongs to foreground or
backgr ound.
2.3.1 State Classification of Pixel-Block Pairs
To identify whether a pixel p is belongs to foreground
or backgr ound , it is necessary to design a framework
which can distinguish the difference between these
two states at the dete cting process. The state F (un -
steady) mea ns p may be occluded by any foreground
object, while the state B (steady) means that p may be
exposed to the camera as it has been in the statistical
training frames. In or der to obta in any difference be t-
ween these two states, for eac h pixel p, we introduce
an index value as a “penalty” for v iolating the rela ti-
onships authorized at the statistical training process.
In other words, if the state F is associate d with pixel p
and the pixel value may also be changed, therefore we
can utilize statistical tests in which the d ifference may
belong to the registered distribution or be rejected as a
value outside of the distribution. This idea can be rea-
lized as the following expression for identifying pixel
p is foreground or b a ckground as shown in Fig. 4.
In CPB, we can define this statistical structure in
each relation between any pixel and its supporting
block set as the collection of Gaussian distributions
learned in the training process. In the detecting pro-
cess, we utilize these knowledges to find any fore-
ground pixels which may violate the knowledge due
to a different intensity from its background pixel. For
each pa ir (p, Q
B
k
), a binary function for identifying its
steady or unsteady state can be defined as follows:
ω
k
=
(
1 if
(p − Q
B
k
) − b
k
≥ η· σ
k
0 otherwise
, (5)
where
(p − Q
B
k
) − b
k
represents a bias in the inten-
sity difference between the real value and the modeled
parameter b to estimate the steady or unsteady state
of each pair (p, Q
B
k
), where η is a constant for setting
some significant level in this statistical test procedure .
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
268

Figure 4: Relationship in the intensity changes between target pixel p and supporting block Q
B
.
In this function, ω
k
correspo nds a logical value to re-
present the steady state with 0 or the unsteady state
with 1 for each pair, respectively.
2.3.2 Correlation Depended Decision Function
In order to define an efficient decision function for
target pixel, with considering the K supporting blocks
around it, h ere we introduce γ
k
of the k-th eleme ntal
pair (p, Q
B
k
) as a weight in the weighted summation
of the products ω
k
· γ
k
based on the previous decisio n
proposed in (Liang et al., 2015; Elhabian et al., 2008).
The lager γ
k
may be stronger or more reliable on the
state decision of target pixel p. Th e definition is rea-
lized as Γ as follows.
Γ =
K
∑
k=1
ω
k
· γ
k
. (6)
Γ has th e following two significa nces: first, Γ c an
count up the unsteady p airs, second, Γ has its own
ideal value, the maximum value of Γ is possibly obtai-
ned in the case that all of K elemental pairs are in the
unsteady state and it is also a r elative value with re-
spect to the target pixel. Furthermore, Γ would not
miss to c ount any high γ
k
in the summation to lead a
wrong decision. To realize relative decision making
on Γ, we can have the following possible maximum
value of it.
Γ
all
=
K
∑
k=1
γ
k
. (7)
With the consideration of mentioned above, by use
of Γ
all
, we can define the following evaluation cri-
terion to classify the ta rget pixel into the foreground
class as:
if Γ > λ· Γ
all
, then
p is foreground
else
p is background.
λ is a threshold para meter. A s shown in Fig. 5, It is
natural to evaluate the state of pixel p through a com-
parative ana lysis between Γ and Γ
all
, if the value of Γ
is high, it is high ly likely that pixel p is a foreground
pixel.
Figure 5: Relationship between Γ and Γ
all
.
3 HoD MODIFIC ATION
We have introduced the basic algorithms for robust
backgr ound subtraction so far, however, in the real
world we have on ly a set of limited data for training
model over some limited tim e range. We may have
some mechanism to modify the model to fix some er-
rors which may be observed in any new target frames
out of the training set. In th is section, we inte nd to
introdu ce a simple mechanism named H ypothesis on
Degradation Modification (HoD) extended from CPB
to adapt dynamic changes in scenes and reinforce ro-
bustness of CPB to against “ noise” in real conditions.
3.1 Hypothesis on Degradation
By use of the basic algorithm in learning and de-
tecting structure of CPB, we can extract p articular
Co-occurrence Background Model with Hypothesis on Degradation Modification for Robust Object Detection
269

Figure 6: Overview of HoD Modification.
events, such as pedestrians or vehicles in scene. Af-
ter a long utilization of initial CPB bac kgrou nd mo-
del for real data, we may encounter some strange o r
unknown situations which do not belong to the ini-
tial training dataset, and then our initial CPB model
may g radually or suddenly decrease its performance
by reason of the chang e of observation in scene.
In practice, we propose an assumption that some
“noise” may arise in detecting process due to some
trouble in CPB structure over tim e. However, we
could not know the true of these troubles without
any ground truth data, and it is not p ossible to rea-
lize groun d truth of future frames in real condition.
Hence, we need an effective modification to adapt
the possible changes in real condition and consolidate
the performance of pro posed CPB over time. In this
study, we call this above assumption as “Hypothesis
on Degradation” and name the “noise ” in detecting
process as “hypothetical noise.”
Based on mentioned above, we propose a Hypot-
hesis on Degrada tion Modification ( H oD) for CPB to
against the hypothetical noise by modify ing the ini-
tial structure to a new one. Fig. 6 describes an over-
view of the proposed HoD. Here in Fig. 6, it is clear
that HoD is no t one post-processing technique, in this
study, HoD is an u pdate approa c h of model structure
to reinforc e the robustness of CPB and is also a feasi-
ble on-line mode for CPB.
To estimate which Pixel-Block structure sho uld be
modified, we first define two type s of hypothetical
noise: 1) the hole surrounded by the detected fore-
ground pixels, which is estimated as the backgroun d
and we named it ‘NaB’; 2) the dot surro unded by the
non-detected pixels, which is estimated as the event
and we named it ‘NaE’. Fig. 7 shows an example of
the hypo thetical noise using AIST − Indoor-dataset
provided by the National Institute of Advanced Indus-
trial Science and Technology in Japan.
For such pixels as mentioned above, we detect
Figure 7: Example of hypothesized noise. (a) Raw data. (b)
Description of hypothesized noise.
them as noise and do modification for the Pixel-Block
structure of them.
3.2 Detection of Possible Wrong
Pixel-Block Pairs
For any detec ted noise pixels, we need to define
wrong or broken elementa l p airs in the Pixel-Block
structure . As introduction in Section 2.3, we adopt
the strategy that any Pixel-Block pair, which has the
lager γ must hold the higher weight in the traine d
structures and suc h pair is more likely to affect the
state of NaE and Na B. We propose a weight-based
decision rule to detect the wrong pair:
if γ
m
≥
¯
γ, then (p, Q
B
m
) is wrong (8)
where (p, Q
B
m
) is the ‘wr ong’ pair, which is in unste-
ady state of NaE or steady state of NaB. Depending on
the no ise is NaE or NaB, the threshold
¯
γ has the diffe-
rent definition. In the case o f NaE, it is defined by use
of the total num ber of unsteady pairs M =
∑
K
k=1
ω
k
as
follows:
¯
γ =
1
M
K
∑
k=1
γ
k
· ω
k
=
1
M
Γ. (9)
While in the case of NaB, it is defined as follows:
¯
γ =
1
K − M
K
∑
k=1
γ
k
· (1 − ω
k
) =
1
K − M
(Γ
all
− Γ).
(10)
We can see a sligh t difference in the above defini-
tions. The calculations contain the e le mental correla-
tion coefficient, the supporting blo c k set and the total
number of Pixel-Block pairs {(p, Q
B
m
)}, and then we
record these “broken pairs” as shown in Fig. 8.
3.3 Remova l of Wrong Structure
We try to exchange the wrong pair by new one which
is kept as a spare pair in the training process. Fig. 8
shows its schema for exchange to keep K pairs in any
supporting block sets.
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
270
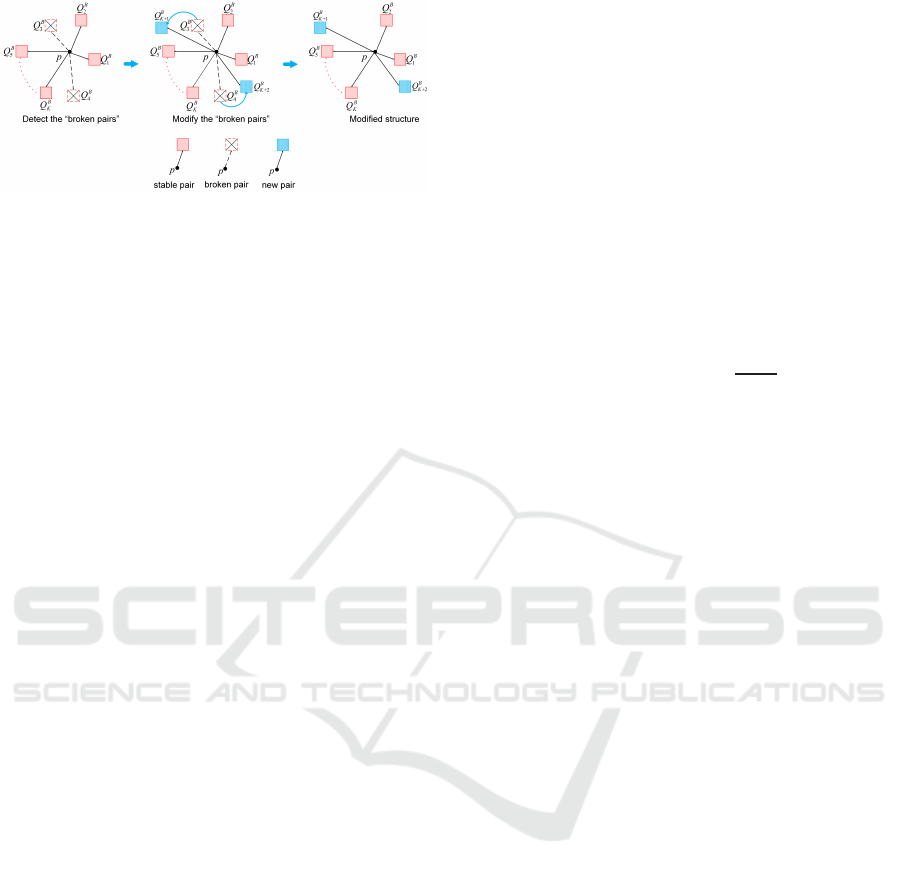
Figure 8: Modification process.
4 EXPERIMENTS
4.1 Experimental Setup
At first, considering the several challenges of vi-
deo sur veillance for background subtrac tion algo-
rithm(Brutze r et al., 2011). We consider the following
challenges for evaluation:
• Gradual Illumination Changes: the light in-
tensity typically varies during day. We consider
PET S2001 − camera1 as the testing data for eva-
luation with the illumination change during day.
• Sudden Illumination Changes: for example the
sudden switch of light, strongly affects the obser-
vation of object to lead a fault for detection . We
consider the d ataset AIST − Indoor with strong
sudden light chan ges when the auto-door ope ning,
in such momen t it is difficult to detec t true fore-
ground from the scene.
• Dynamic Background: some movement in
scene should be regarded as back groun d e.g.
swaying tree, waving water. We select one
challengin g seque nce advertisementBoard from
SceneBackgroundModeling.NET(SBMnet) data-
set for testing, and this sequence contains an ever-
changin g advertising board in the scene.
• Intermittent Object Motion: this category is one
difficult challenge for object detection with back-
ground objects moving away, aband oned obje c ts
and objects stopping for a short while and th en
moving away. In this category, it is difficult to
detect correct foreground objects. The so f a se-
quence from Change − detection dataset(Goyette
et al., 2012 ) is selected for testing.
• Camera Jitter: in video surveillance, camera
jitter is one issue that need to be solved for
backgr ound subtraction. In our experiment,
we consider sidewalk from Change − detection
dataset(Goyette et al., 2012) to test the perf or-
mance of proposed CPB and CPB+HoD in such
extreme category.
4.2 Evaluation Measurement
To analyze the quality of our method, we utilize three
common analysis measurements: Precision, Recall,
and F-measure. These metrics are widely used to
estimate the quality of background subtraction met-
hods (Brutzer et al., 2011; Vacavant et al., 2012). For
further evaluating our CPB and CPB+HoD, we in-
troduce the peak signal-to-n oise ratio (PSNR) as our
metric(Huynh-Thu and Ghanbari, 2008), which can
be used to measure the q uality of the estimated resul-
ted com pared with the background truth(Huynh-The
et al., 2016). The definition of PSNR is calculated as
follows:
PSNR = 10 · log
10
255
2
MSE
, (11)
where MSE is the mean square erro r.
4.3 Result Evaluation
In this section, we compare the prop osed CPB and
CPB+HoD with four different foreground detection
methods: GMM(Stauffer and Grimson, 1999) and
KDE(Elgammal et al., 2002), which a re two well-
known traditional algorithms, and two state of the
art techniques IMBS(Bloisi and Iocchi, 2012) and
SuBSENSE(St-Charles et al., 2015), especially SuB-
SENSE is one of the top-ranked metho ds in Change −
detection dataset at pr esent. In contrast to methods
with c omplex strategies(Bloisi and Iocchi, 2012; St-
Charles et al., 2015), CPB is a low-complexity al-
gorithm th at is more easily r ealized. The parame-
ters f or GMM, KDE, IMBS and SuBSENSE were set
by using the tool bgslibrary(Sobral, 2013). In experi-
ments, we set each bloc k as 8×8 pixels, λ = 0.5 and
η = 2.5 for CPB.
Fig. 9 shows examples of foreground detection for
a typical fra me from eac h dataset sequence. Table 1
lists the results of the perf ormance measurements of
CPB and CPB+HoD with other m ethods from all th e
categories, r espectively. Compared with above fo-
reground detection results, the proposed algorithms
outperform the me thods GMM, KDE , IMBS and
SuBSENSE in most testing sequences. Meanwhile,
CPB+HoD is quite efficient in extracting foreground
from sequences that suffers from sudden illumination
changes and dynamic background. Furthermore, it is
should be noted that CPB and CPB+HoD can lead
high Precision and PSNR in m ost testing sequ ences
as the results shown in Table 1, that means our algo -
rithm is robust again st noise for detectin g foreground
in severe scen e s.
Co-occurrence Background Model with Hypothesis on Degradation Modification for Robust Object Detection
271

Figure 9: Foreground detection results in different challenging sequences.
Table 1: Comparison in different challenging categories.
Method Measure Category
Gradual illumination Sudden illumination Dynamic Intermittent object Camera
changes changes background motion jitter
GMM Precision 0.6465 0.6523 0.5151 0.8462 0.4150
Recall 0.9508 0.9207 0.5196 0.6876 0.4811
F-measure 0.7697 0.7636 0.5174 0.7587 0.4456
PSNR 39.46 40.57 26.92 36.11 31.79
KDE Precision 0.5181 0.5896 0.4962 0.7361 0.5640
Recall 0.8836 0.6944 0.4856 0.7820 0.5167
F-measure 0.6532 0.6377 0.4909 0.7583 0.5393
PSNR 17.77 38.16 21.67 25.99 33.68
IMBS Precision 0.51 62 0.5760 0.5095 0.8353 0.4457
Recall 0.8841 0.6923 0.5118 0.7298 0.4879
F-measure 0.6518 0.6288 0.5107 0.7790 0.4658
PSNR 16.20 36.36 30.09 28.21 32.10
SuBSENSE Precision 0.9008 0.5864 0.5018 0.9556 0.5966
Recall 0.8840 0.7047 0.5033 0.7803 0.5079
F-measure
0.8923 0.6401 0.5025 0.8591 0.5487
PSNR 54.11 37.14 27.62 32.29 34.92
CPB Precision 0.9566 0.8651 0.7653 0.8928 0.6365
Recall 0.7517 0.8181 0.5118 0.8691 0.5051
F-measure 0.8418
0.8409 0.6133 0.8808 0.5633
PSNR 56.05 53.14 36.64 32.04 34.22
CPB+HoD Precision 0.9652 0.8668 0.7973 0.9079 0.6384
Recall 0.7562 0.8227 0.5214 0.8750 0.5055
F-measure
0.8480 0.8442 0.6305 0.8912 0.5642
PSNR 56.39 53.31 37.39 32.69 34.28
∗
Note that
red entries indicate the best in F − measure, and blue entries indicate the second best.
Based on co-occurrence pixel-block pa irs, CPB
can build one p rospective background model from a
scene, such background model con ta ins spatial and
temporal information of each pixel in sequence, and
then CPB can analy ze th e current sate of ea ch pixel
effectively with these information. In other words,
at training process, CPB can learn the information of
scene, whether the scene is dynamic or static, our mo-
del can acquire the regularity of scene. Then, at de -
tecting p rocess, when any object enters into the scene
and the inf ormation o f this object is out of range of
our model, so we can extract the object from the scene
efficiently.
For that reason, CPB does well in above scenes.
On the basis of this, w e introduce a HoD into CPB to
adapt dynamic changes in scenes and reinforce robus-
tness in real conditio ns. T hrough the results of above
experiments, CPB+HoD leads a good performance in
various scenes.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have proposed a robust and efficient object de-
tection approach named CPB in severe scen e s. It
was designed to reduce the computing cost in trai-
ning process and also to keep the robustness against
scene change s in reality. Furth ermore, we rea lized
a novel modification approach name d hypothesis-on-
degradation modification (HoD) for CPB to defend
the possible d egradation in practice and it is also a
feasible on-line mode for the proposed CPB. The ex-
perimental results show the good performance of the
proposed approa ch. In future, we would like to im-
prove our CPB to be an on-line approach by hypothe-
sis on degradation modification (HoD).
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
272

REFERENCES
Barnich, O. and Van Droogenbroeck, M. (2011). Vibe: A
universal background subtraction algorithm for video
sequences. IEEE Transactions on Image processing,
20(6):1709–1724.
Bloisi, D. and Iocchi, L. (2012). Independent multi modal
background subtraction. In CompIMAGE, pages 39–
44.
Brutzer, S., H¨oferlin, B., and Heidemann, G. (2011). Eva-
luation of background subtraction techniques for vi-
deo surveillance. In Computer Vision and Pattern Re-
cognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on, pages
1937–1944. IEEE.
Cheung, S.-C. S. and Kamath, C. (2005). Robust back-
ground subtraction wit h foreground validation for ur-
ban traffic video. EURASIP Journal on Advances in
Signal Processing, 2005(14):726261.
Elgammal, A. , Duraiswami, R., Harwood, D., and Da-
vis, L. S. (2002). Background and foreground mo-
deling using nonparametric kernel density estimation
for visual surveillance. Proceedings of the IEEE,
90(7):1151–1163.
Elhabian, S. Y., El-Sayed, K. M., and Ahmed, S. H. (2008).
Moving object detection in spatial domain using back-
ground removal techniques-state-of-art. Recent pa-
tents on computer science, 1(1):32–54.
Goyette, N., Jodoin, P.-M., Porikli, F., Konrad, J. , and
Ishwar, P. (2012). Changedetection. net: A new
change detection benchmark dataset. In Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW),
2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, pages
1–8. IEEE.
Hu, W., Tan, T., Wang, L. , and Maybank, S. (2004). A
survey on visual surveillance of object motion and
behaviors. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man,
and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews),
34(3):334–352.
Huynh-The, T., Banos, O., Lee, S., Kang, B. H., Kim, E.-
S., and Le-Tien, T. (2016). Nic: a robust background
extraction algorithm for foreground detection in dyna-
mic scenes. IEEE transactions on circuits and systems
for video technology.
Huynh-Thu, Q. and Ghanbari, M. (2008). Scope of validity
of psnr in i mage/video quality assessment. Electronics
letters, 44(13):800–801.
Iwata, K., Satoh, Y., Ozaki, R., and Sakaue, K. ( 2009). Ro-
bust background subtraction based on statistical reach
feature method. IEICE Trans. on Information and Sy-
stems, 92:1251–1259.
Liang, Dong Kaneko, S., Hashimoto, M., Iwata, K., and
Zhao, X. (2015). Co-occurrence probability-based
pixel pairs background model for robust object de-
tection in dynamic scenes. Pattern Recognition,
48(4):1374–1390.
Moeslund, T. B., Hilton, A., and Kr¨uger, V. (2006). A sur-
vey of advances in vision-based human motion cap-
ture and analysis. Computer vision and image under-
standing, 104(2):90–126.
Seki, M., Wada, T., Fujiwara, H., and Sumi, K. (2003).
Background subtraction based on cooccurrence of
image variations. I n Computer Vision and Pattern Re-
cognition, 2003. Proceedings. 2003 IEEE Computer
Society Conference on, volume 2, pages II–II. IEEE.
Sobral, A. (2013). Bgslibrary: An opencv c++ background
subtraction library. In IX Workshop de Visao Compu-
tacional (WVC2013), volume 7.
St-Charles, P.-L., Bilodeau, G.-A., and Bergevin, R. (2015).
Subsense: A universal change detection method with
local adaptive sensitivity. IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing, 24(1):359–373.
Stauffer, C. and Grimson, W. E. L. (1999). Adaptive
background mixture models for real-t ime tracking.
In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1999.
IEEE Computer Society Conference on., volume 2, pa-
ges 246–252. IEEE.
Vacavant, A., Chateau, T., Wilhelm, A., and Lequi`evre,
L. (2012). A benchmark dataset for outdoor fore-
ground/background extraction. In Asian Conference
on Computer Vision, pages 291–300. Springer.
Wren, C. R., Azarbayejani, A., Darrell, T., and Pentland,
A. P. (1997). Pfinder: Real-time tracking of the hu-
man body. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and
machine intelligence, 19(7):780–785.
Yilmaz, A., Javed, O., and Shah, M. (2006). Object
tracking: A survey. Acm computing surveys (CSUR),
38(4):13.
Zhao, X., Satoh, Y., Takauji, H., Kaneko, S., Iwata, K., and
Ozaki, R. (2011). Object detection based on a robust
and accurate statistical multi-point-pair model. Pat-
tern Recognition, 44(6):1296–1311.
Co-occurrence Background Model with Hypothesis on Degradation Modification for Robust Object Detection
273
