
Cross-context Analysis for Long-term View-point Invariant Person
Re-identification via Soft-biometrics using Depth Sensor
Athira Nambiar, Alexandre Bernardino and Jacinto C. Nascimento
Institute for Systems and Robotics, Instituto Superior T
´
ecnico, Av. Rovisco Pais, 1, 1049-001, Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords:
Person Re-identification, Context-aware, Cross-context, Anthropometrics, Gait, Kinect.
Abstract:
We propose a novel methodology for cross-context analysis in person re-identification using 3D features
acquired from consumer grade depth sensors. Such features, although theoretically invariant to perspective
changes, are nevertheless immersed in noise that depends on the view point, mainly due to the low depth re-
solution of these sensors and imperfections in skeleton reconstruction algorithms. Thus, the re-identification
of persons observed on different poses requires the analysis of the features that transfer well its characteristics
between view-points. Taking view-point as context, we propose a cross-context methodology to improve the
re-identification of persons on different view-points. On the contrary to 2D cross-view re-identification met-
hods, our approach is based on 3D features that do not require an explicit mapping between view-points, but
nevertheless take advantage of feature selection methods that improve the re-identification accuracy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Long-term person re-identification (Re-ID) is one of
the most interesting tools in the realm of intelligent
video-surveillance. It consists of identifying an indi-
vidual in different locations at significantly different
time instants, and assigning her/him the same iden-
tifier (Gong et al., 2014; Bedagkar-Gala and Shah,
2014). There are many fundamental challenges as-
sociated with the task of long-term re-identification,
wherein the surveillance period extends for many
days, weeks or more. Among the biggest challenges
are the change in appearance and view-points.
In this paper, we address the first challenge of ap-
pearance variation via leveraging soft biometric fea-
tures (like human gait and anthropometrics), which
are more stable over long periods than the appearance
cues. The recent availability of low-cost depth sen-
sors opens the possibility for improved surveillance
systems on indoor spaces. Exploiting the 3D ske-
leton tracking functions of these sensors, we extract
anthropometric and gait-based features from the tar-
get persons. The second challenge i.e., variation in
viewpoint, causes the features to vary among diffe-
rent poses. Albeit the skeleton coordinates provi-
ded by kinect data are, in principle, view-point in-
variant (can be normalized to a canonical view-point
by a roto-translation transformation), their computa-
tion (skeleton reconstruction) highly depends on the
view points and self-occlusions. In other words, even
though signal is the same, the noise level varies de-
pending on the view-points and self occlusions i.e.,
data quality highly depends on the view-point (Nam-
biar et al., 2017b). For instance lateral views of a per-
son are more subject to self-occlusion thus imposing
larger amounts of noise in the occluded parts of the
persons body. Frontal views, on the contrary, have
more noise in the arms and legs distances of walking
people. In order to tackle this view-point issue whilst
maintaining the quality of the feature data, the con-
cept of ‘Context’ was proposed in the work of (Nam-
biar et al., 2017a). Based on the concept that “the
characteristics of a person that best correlate to its
identity depend strongly on the view point ”, in that
work they associated context to the viewing direction
of walking people, and then selected the best featu-
res for each case. A method named Context-aware
ensemble fusion has been proposed in that work, by
choosing the relevant potential features in each view-
point and thus training individual classifiers for each
context. However, that method relies on the assump-
tion of the existence of samples of all subjects in all
view-points. This may not be possible to implement
in less controlled (on-the-wild) surveillance scenarios
where person samples are scarce and may not be pos-
sible to acquire in some view points. Thus, we extend
that work for the data-insufficient case, i.e. when it
can not be assured that all view points in the gallery
Nambiar, A., Bernardino, A. and Nascimento, J.
Cross-context Analysis for Long-term View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Soft-biometrics using Depth Sensor.
DOI: 10.5220/0006620601050113
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2018) - Volume 5: VISAPP, pages
105-113
ISBN: 978-989-758-290-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
105

have samples of all pedestrians, and denote it Cross-
context ensemble fusion. For instance, it is frequent
that some camera acquires a large sample set (e.g: ca-
mera facing to long corridor acquires long sequence)
whereas some other camera collects only a small sam-
ple set (e.g: Camera facing to a lift/ door may get only
short footage). This will be greatly reflected in the
number of training samples available in the gallery
for the Re-ID matching process. In order to tackle
such situations, we propose a novel idea called ‘cross-
context’ analysis. Since the best discriminating featu-
res will be different in different contexts, we propose
to employ a feature selection strategy a priori in order
to identify the features that represent well the identity
of the person in pairs of contexts. This data transfer
among contexts via feature selection is the crux of our
cross-context proposal.
Various experimental case studies on cross-
context analysis (viz., full cover, sparse cover and
single-cover) are carried out in order to verify the
clear impact of the amount of gallery samples in the
cross-context approach. In addition to that, we con-
ducted yet another improvement of the study in com-
parison with the work of (Nambiar et al., 2017a), na-
med as ‘switching of contexts’. Since they always
used straight line walkings for both testing and trai-
ning, it was not clear how well the system can re-
identify people while changing the walking direction
within a gait cycle. In order to analyze this criteria,
we analyze circular path movement as an instance of
such a context-switching scenario.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents the state-of-the-art research in the
field. Section 3 details our proposed approach follo-
wed by Section 4 that describes experimental results.
Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper, also by enu-
merating some future perspectives.
2 RELATED WORK
The concept of context has been incorporated in many
diverse fields including re-identification. Heterogene-
ous contextual information (e.g. activity, attributes,
clothing) have been used in (Zhang et al., 2014) to
fuse the notion of contexts by means of a a gene-
ric entity resolution framework called RelDC. Also,
some other works viz., (Leng et al., 2015; Garcia
et al., 2015) have used ‘context’ (information of k-
common nearest neighbors) wherein they used it in
addition to the content information. The use of view-
point as a context, has been reported in (Geng et al.,
2010; Nambiar et al., 2017a). In (Geng et al., 2010), it
is used a context-aware multi-biometric fusion, lever-
aging gait and face for human identification and by
considering two important context factors i.e., view
angle and subject-to-camera distance. However, in
(Nambiar et al., 2017a), the contexts were considered
as the view-points defined in the angular space. The
novelty of that work was the feature selection and the
individual classifier learning for different viewpoints.
However, the proposal was inadequate to deal with
the practical data deficient scenarios. In this work,
we build upon the proposal of (Nambiar et al., 2017a)
towards cross-context or cross-view analysis.
Only limited works have been reported on cross-
view analysis in the literature, and only in 2D. For
instance, in (Lisanti et al., 2017), they proposed a
method to overcome the drastic variability of appea-
rance in different camera views via Multi channel-
Kernel canonical correlation analysis (KCCA), where
a set of projection spaces are learned. In (Chen et al.,
2016) Cross-View Discriminant Component Analysis
(CVDCA) was proposed with the purpose to trans-
form the features of the different views points to a
common space where discriminative features are ex-
tracted for the Re-ID. In (Dai et al., 2017) a cross-
view semantic projection learning (CSPL) approach
was reported. Here the proposed methodology was
able to jointly learn both the semantic projection and
association functions that capture the relationship be-
tween the semantic representations of the same pe-
destrian from cross-views. Nevertheless, all of them
were addressing the short-term person Re-ID problem
in 2D. Also, the above methods require some sort
of projection mechanism for the feature transforma-
tion from different views to a common space, thus re-
quiring a mapping to model correlations in different
views. However in our proposal, no feature projection
is needed, and thus no feature mapping for correla-
tion is required. Instead, features have to be select,
to obtain the most relevant/discriminative features for
each context (i.e., view point). Also, in our work, we
envisage cross-view analysis towards long-term per-
son Re-ID task by exploiting more stable 3D biome-
tric features.
There have been some works proposed in the re-
identification paradigm, utilizing 3D data, mainly le-
veraging Kinect sensor. The main attempt of ex-
tracting Kinect-based soft biometric features, was
presented in (Barbosa et al., 2012). In that work, they
utilized static body information i.e., skeleton and sur-
face based features, in the frontal view. Based on that
work, many other works reported later other features
as well i.e., stride and arm kinematics (Gabel et al.,
2012), anthropometric and angles of lower joints (An-
dersson and de Ara
´
ujo, 2015) and static and dyna-
mic statistics (Gianaria et al., 2014; Nambiar et al.,
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
106
2017b). All of these works collected data in a con-
trolled predefined single direction say, either frontal
or lateral. The works of (Nambiar et al., 2017b; Nam-
biar et al., 2017a) were the first works explicitly ad-
dressing view-point invariant Re-ID scenario with 3D
data by collecting depth camera sequences of people
walking in different directions (each view-point na-
med as a ‘context’). Now, building upon these works
we extend them by proposing cross-view in 3D, to-
wards a realistic scenario of of sparse galleries, i.e.
where not all contexts contain samples from all per-
sons. Thus we try to answer the question of ‘how
to tackle the insufficiency of data samples?’. As we
mention in the forthcoming section, we propose the
concept of cross-context via feature selection in order
to transfer the information across different contexts.
To the best of our knowledge, this paper makes the
first work in cross-view analysis towards long term
Re-ID leveraging 3D data.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
In this section, we explain our proposed methodo-
logy of cross-context analysis, as the special case
of context-aware Re-ID scenario. In particular, in
Section 3.1, we first explain the basic methodology
associated with the baseline Context-aware ensem-
ble fusion technique as described in (Nambiar et al.,
2017a). Then, we particularize on our novel proposal
of Cross-context ensemble framework in Section 3.2.
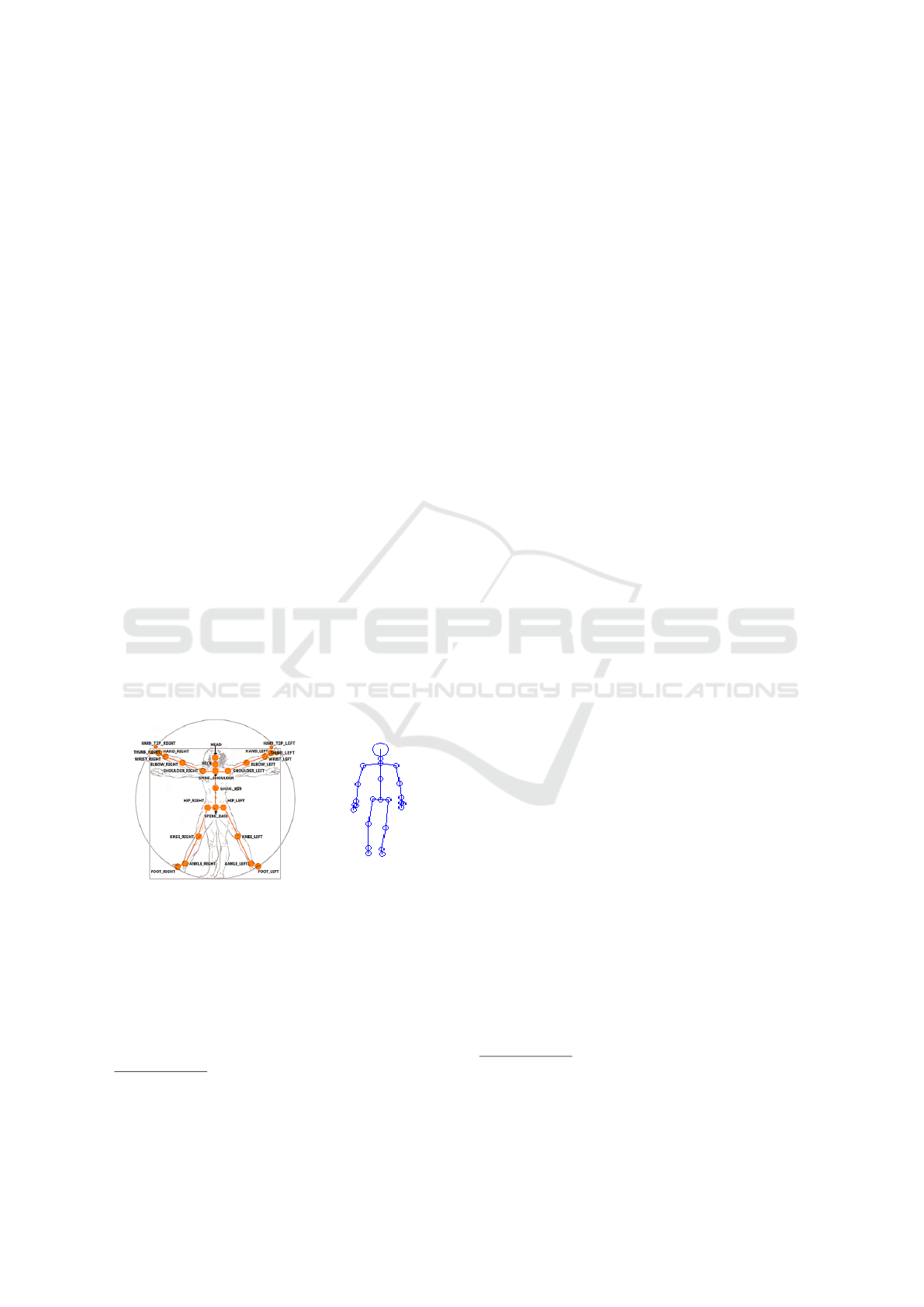
(a) (b)
Figure 1: (a) Skeleton positions relative to the human body
1
(b) A sample skeleton body visualization from our col-
lection.
3.1 Context-aware Ensemble Fusion
Framework
As we already mentioned in the Section 2, we built
upon the work of (Nambiar et al., 2017a) i.e., context-
1
For body joint types and enumeration, refer to the link:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/microsoft.kinect.
jointtype.aspx
aware ensemble fusion framework, to extend it to-
wards cross-context analysis. The essence of context-
aware fusion proposal was the arrangement of gal-
lery samples according to the context, and adaptive
selection of the potentially relevant features in order
to train context-specific individual classifiers.
Let the sample data be represented as X, which
is basically the raw data i.e., joint positions acquired
via Kinect depth sensor (see Fig.1), and the extrac-
ted features be denoted by F. Based on the dataset
characteristics of viewpoint l (l = 1, .., L), gait cycle
m (m = 1, .., M) and the person ID n (n = 1, .., N)
each individual sample data and the corresponding
extracted feature can be denoted as x
lmn
∈ R
j×z
and
f
lmn
∈ R
D
respectively
2
. In particular, we reimple-
mented 74 features similar to the (Nambiar et al.,
2017a), both anthropometric and gait features. Ba-
sically, two kinds of features were extracted: (i) An-
thropometric features are associated to the static phy-
sical features defining the body measurements (e.g.,
height, arm length, upper torso length, chest size etc.)
whereas Gait features are associated to the dynamic
features defining the kinematics in walking (e.g., an-
gles at various body joints,the distance between va-
rious right-left limbs, the relative position of body
joints, stride length etc.). Totally, the feature set con-
sists of 7 anthropometric features and 67 gait features
(See (Nambiar et al., 2017a) for the list of features
extracted).
One interesting characteristic of this proposal is
the partition of the data in different galleries, one for
each context (F
l
= { f
lmn
} where l = 1,... L, m = 1, ...
M, n = 1, ..., N). Thus for each person n, there will
be M × L examples in the gallery. Then, according to
context, the samples are grouped and feature selection
will be carried out to select the respective features.
Assume S
l
∈ {0, 1}
D
represents the binary vector enu-
merating the selected set of features for a particular
context l, with a 1 in the position of the selected featu-
res and zeros otherwise. Similarly to (Nambiar et al.,
2017a), we have used one of the most popular Feature
Selection (FS) techniques, the Sequential Forward Se-
lection (SFS) as an instance (Whitney, 1971). It works
iteratively by adding features to an initial subset, see-
king to improve the Re-ID measurement.
A context detector module analyses the walking
direction of the person and uses the Gallery with the
closest viewpoint or the two neighboring Galleries.
Hence, whenever the test context is known to the sy-
stem, it will direct the Re-ID process towards the cor-
2
Note that j refers to the number of joints in a skeleton
model where j=25; z represents the dimension of each joint
co-ordinate i.e., z=3 ; D if the total number of features in a
feature vector i.e., D=74.
Cross-context Analysis for Long-term View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Soft-biometrics using Depth Sensor
107
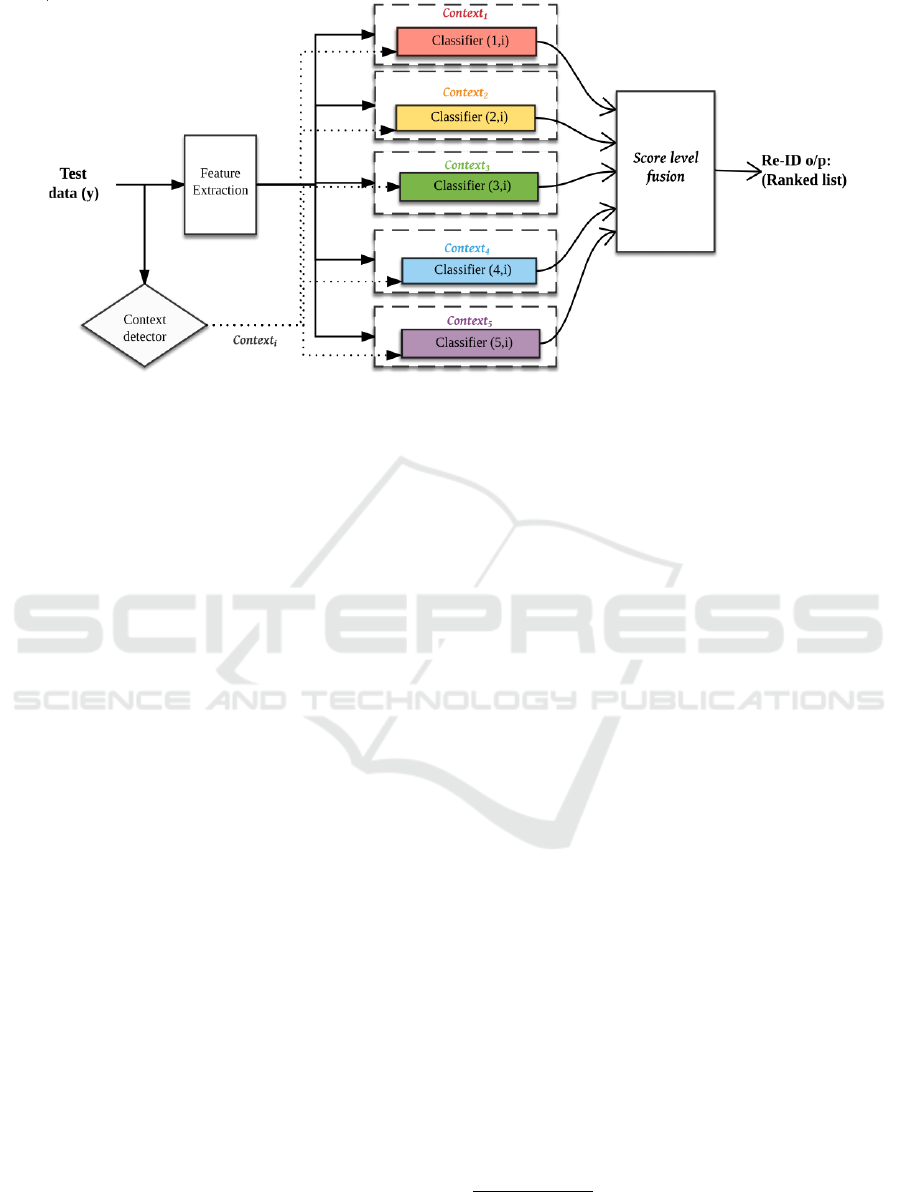
Figure 2: Cross-context ensemble fusion framework: A diagrammatic overview of cross-context analysis is given above.
Individual cross-context classifiers are trained based on the learned feature selection carried out between the probe context i,
and the gallery context of interest. Then, based on score level fusion overall Re-ID result is given as output.
responding gallery context in order to facilitate a fast
and accurate person matching. Based on these in-
dividual context feature selection, Nearest Neighbor
(NN) classifiers are designed according to the follo-
wing. Given a new test sample described by features f
with d being the index of the feature, the match score
C
lmn
(d)
(f) with the Gallery sample is computed as:
C
lmn
(d)
( f ) = | f
(d)
− f
lmn
(d)
|.S
l
(d)
(1)
Then, score-level fusion brings the overall score
of all the selected features:
C
lmn
( f ) =
∑
d
C
lmn
(d)
( f ) (2)
Then, the best matching score is computed by cal-
culating the minimum matching score (smaller the si-
milarity score, higher the matching ).
C
ln
( f ) = min
m
C
lmn
( f ) (3)
If more than one context is selected (two neighbo-
ring contexts), then linear interpolation technique will
be carried out in order to give adaptive weights to each
context Re-ID score which is described in (Nambiar
et al., 2017a) as ’Context-aware score level fusion’.
3.2 Cross-context Ensemble Fusion
Framework
The very basic concept behind our idea for cross-
context analysis is to solve the issue of data defi-
ciency in the gallery context corresponding to the cur-
rent context. Whereas in (Nambiar et al., 2017a), the
number of samples per person in each context l i.e.,
M was considered constant, in our case we consider
that the number can vary and can actually be zero in
some contexts. So, the number of samples per per
person in a certain context is denoted by M
ln
. This is
a much more realistic case in practical situations in-
the-wild where it is difficult to acquire gallery sam-
ples for each person in all contexts. We discuss our
approach in the light of Figure 2, which presents an
overview of the system architecture during run time.
Suppose the test data enters into the system. The first
module i.e., ‘Feature extraction module’ will extract
the soft-biometric (both anthropometric and gait fea-
tures) associated to the subject.
For the design of context detector, we adopt
the same methodology explained in (Nambiar et al.,
2017a), i.e., by calculating the direction of a stable
joint vector. Suppose the context of the test sample
is represented as i, (where 1 ≤ i ≤ 5)
3
. After kno-
wing the viewpoint of the test sample, the approach
of (Nambiar et al., 2017a) was to search for the gal-
lery samples in the very same Context viz., Context
i
where the intra-class variation will be minimal due to
the same viewpoint and noise level of the sensor in
that particular view. However, if Context
i
lacks the
data samples due to some reason, we can still ena-
ble the system to do the searching in the other views,
in a process that we denote cross-context analysis. As
per such an approach, we conduct searching across all
the contexts to leverage all gallery samples. Finally,
the matching scores from all contexts will be fused
3
The dataset is already organized in five views with ran-
ges (∼0
◦
,∼30
◦
,∼90
◦
,∼130
◦
,∼180
◦
), so we map each an-
gle to one of the views.
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
108
via score level fusion and given as the overall Re-ID
score and based on that the Re-ID ranked list will be
made.
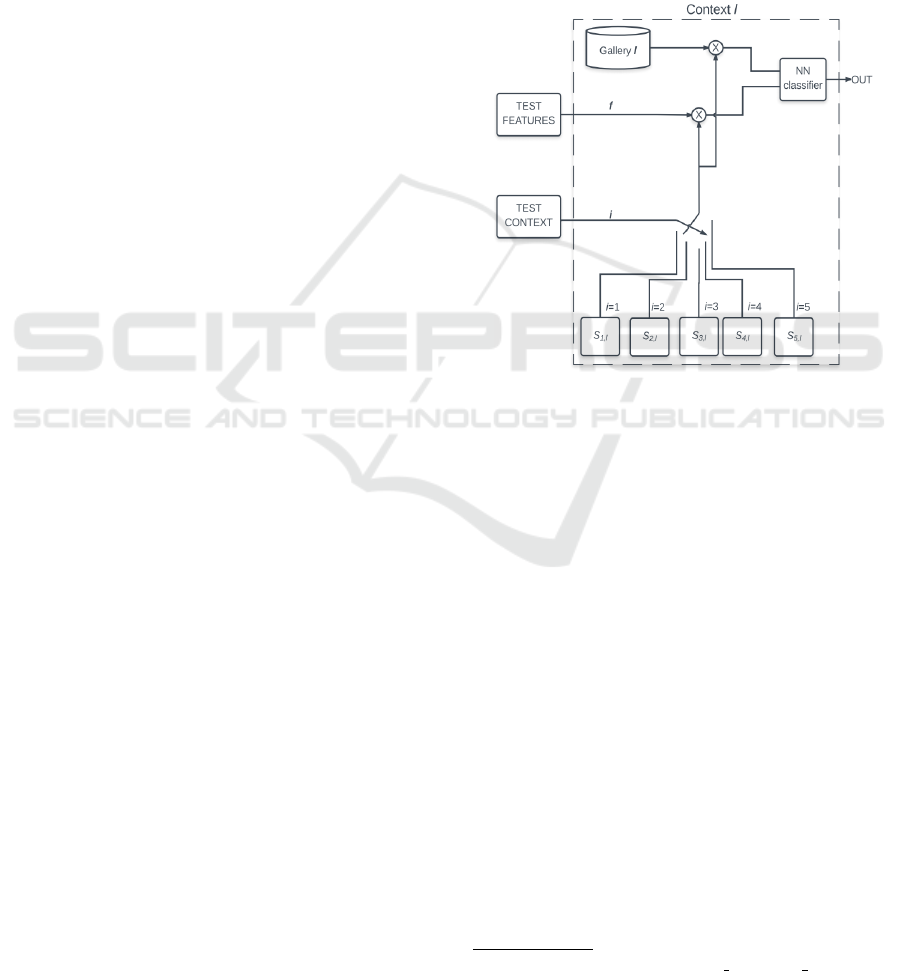
We detail the internal structure of an individual
context module in Figure3. Each contextual module
is pre-trained according to the feature selection con-
ducted for that particular context against all other con-
texts, including the same. In other words, it learns the
set of relevant features in a particular gallery context,
given the same/different context as the test context.
Based on this analysis we learn feature set S
i,l
a priori,
showing which are the features of interest in Context
l
,
given the test sample in Context
i
. Feature selection
among five contexts results in 25 possibilities (five fe-
ature subsets in each individual context).
A pictorial representation of the internal model
of each individual context is presented in Figure 3.
When the test context i is determined by the system,
it will select the appropriate feature set S
i,l
, for a par-
ticular context l. According to the feature selection
conducted among different contexts as a part of the
Cross-context analysis, feature subsets S
i,l
have been
pre-trained.
S
i,l
∈ {0, 1}
D
(4)
Then, the test feature vector (f ) will carry out a
multiplication with the selection vector S
i,l
, so that
only the relevant features will be chosen out of the
whole set of D features. Similarly, selection of the re-
levant features were also carried out at the gallery as
well, via multiplication of S
i,l
and Gallery feature vec-
tors ( f
lmn
). Afterwards, the matching of the selected
set of features in probe vs. gallery is carried out at
a nearest neighbor classifier, and the matching score
(C
lmn
) is given as the output from the context module.
Assuming that d is the index of the feature in a feature
set, let’s represent the overall feature matching (after
selected feature multiplication) as follows:
C
lmn
(d)
( f , i) = | f
(d)
− f
lmn
(d)
|.S
i,l
(d)
(5)
The score-level fusion brings the overall score of
all the selected features in for a particular gallery fea-
ture vector:
C
lmn
( f , i) =
∑
d
C
lmn
(d)
( f , i) (6)
Then, the best matching score is computed by cal-
culating the minimum matching score. Note here that
the best score out of 3 gait cycles (minimum score per
person) is selected as his individual score.
C
ln
( f , i) = min
m
C
lmn
( f , i) (7)
Similar evaluation would have been conducted in
each individual context. Then, at the score-level fu-
sion module, all of such results obtained from each
individual contexts will be fused according to the sum
rule of score-level fusion(Ross et al., 2006):
C
n
( f , i) =
∑
l
C
ln
( f , i) (8)
Based on these scores computed for all persons in
the dataset, the minimum matching score per person
(maximum similarity) will be found out by estimating
n*, the re-identified person ID, according to the follo-
wing.
n
*
= argmin
n
C
n
( f , i) (9)
Figure 3: The internal architecture and functioning of an
individual context is depicted above. Test features and the
test context enters into the context module and the matching
score will be given as the output. ⊗ refers to pointwise
multiplication.
4 EXPERIMENTS & RESULTS
In this section, we explain various experiments car-
ried out in order to understand the impact of cross-
context analysis upon Re-ID framework, and the re-
sults obtained. For the analysis, we used publicly
available KS20 Vislab Multi-view Kinect Skeleton da-
taset
4
. We first briefly explain the dataset. After-
wards, we explain the cross-context based system
analysis, wherein we hypothesize the practical scena-
rio of inadequate samples within the very same con-
texts of test and train. As a result, a naive strategy of
searching space reduction by searching onto the very
same context is not possible. Hence, in order to tackle
it, we formulate a cross-context approach, i.e., to se-
arch for the best match in all the contexts in order to
exploit ample number of gallery samples, upon which
4
http://vislab.isr.ist.utl.pt/vislab multiview ks20/
Cross-context Analysis for Long-term View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Soft-biometrics using Depth Sensor
109

we learn the relevant features apriori, via feature se-
lection across various contexts.
Two experiments are conducted in this regard.
First is the baseline case study where the contexts are
defined by straight paths. For its verification, we used
the straight line walkings acquired in the Vislab KS20
dataset. Here five various view directions are defi-
ned as contexts and hence cross-context analysis is
carried out via feature selection (FS) learned among
these five view-points. In the second experiment, we
exploit subjects walking in circular paths, which im-
plies that the contexts switch within each gait cycle.
In that case also, we cross analyze each gait cycle with
various contexts via feature selection.
4.1 Dataset
In this work, we exploited the Kinect
TM
based dataset
proposed by the authors (Nambiar et al., 2017a)
viz., KS20 VisLab Multi-View Kinect skeleton data-
set, consisting of different view-points specifically
designed towards view-point invariant long-term
Re-ID. In particular, it consists of multi-view Kinect
skeleton (KS) data sequences collected from 20
people, walking in five different directions i.e., Left
lateral (LL at ∼0
◦
), Left diagonal (LD at∼30
◦
),
Frontal (F at ∼90
◦
), Right diagonal (RD at ∼130
◦
)
and Right lateral (RL at ∼180
◦
). Altogether, 300
skeleton video sequences (3 sequences per person
along a direction) were collected. The five contexts
v
1
, ..., v
5
spread around their respective cluster
means µ = [1.67, 35.63, 92.83, 130.70, 180.17]
>
degrees with standard deviations σ =
[3.64, 4.90, 3.29, 5.34, 3.99]
>
degrees.
4.2 Experiment 1: Walking along
Straight Paths (Directional
Contexts)
As mentioned earlier, we first conducted a baseline
study of directional contexts upon subjects walking
along straight paths. Within the same study, we also
assume yet another realistic constraint that not all the
galleries contain equal number of samples. Due to
this latter assumption, it is not possible for the system
to reduce the search space to the very same context in
search of the matching person (because, sometimes
it may lack gallery samples), instead it has to search
for a different context which has sufficient amount of
training samples. This is the new paradigm we term
as cross-context analysis. According to this, among
various contexts, we learn a priori the relevant featu-
res via feature selection.
In order to better understand the proposed concept
of cross-context analysis, we conducted three diffe-
rent case studies, by changing the degree of availa-
bility of gallery samples in contexts. (i) Five-cross-
context case known as Full cover gallery (ii) Four-
cross-context case known as Sparse cover gallery and
(iii) One-cross-context case known as Single cover
gallery.
• Five-cross-context (Full cover gallery) is the
case where all contexts of every subject are re-
presented in the gallery. Or in other words, we
have the probe person available in all the five con-
text galleries. Hence, the test sample is compared
against all the remaining 299 data samples in all
the five contexts except the test sample.
• Four-cross-context (Sparse cover gallery) is the
case, where each subject is represented in other
contexts but not exactly the same context of the
test. In other words, we remove the test person
from the same context and thus only the matching
person data samples available in the gallery are
from other four different contexts. Here, each test
sample is compared against 297 data samples in
the gallery except the case that the test subject is
present in the very same context.
• One-cross-context (Single cover gallery) is the
case where each subject appears only in a single
context in the gallery, different from the probe i.e.,
we remove the test person samples from all the
contexts except a random context other than the
probe context. Hence, the test sample is matched
against 288 gallery samples, the case that the test
subject is present in only one random context, ot-
her than the very same context.
Within each of the aforementioned cases, con-
text unaware vs. context-aware matching techniques
are performed. Within the former (context-unaware),
(a) No FS and (b) Global FS are conducted. Met-
hod ‘no FS’ does not consider any Feature selection
and thus the matching will be the basic feature ma-
tching of 74D feature vectors in all the gallery con-
texts. The second method (Global FS) conducts fea-
ture selection globally upon the whole set of data irre-
spective of the context. Feature matching will be car-
ried out upon these globally selected set of features.
On contrary to these context-unaware paradigm, we
carried out context-aware case studies as well, where
the notion of the context is taken into consideration
as follows: (a) 1-context, (b) 2-context and (c) Cross-
context. The first two cases assume equal gallery dis-
tribution among the contexts and hence works only
for full cover case.
5
This was the baseline state-of-
5
For sparse and single cover, the original proposal of
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
110
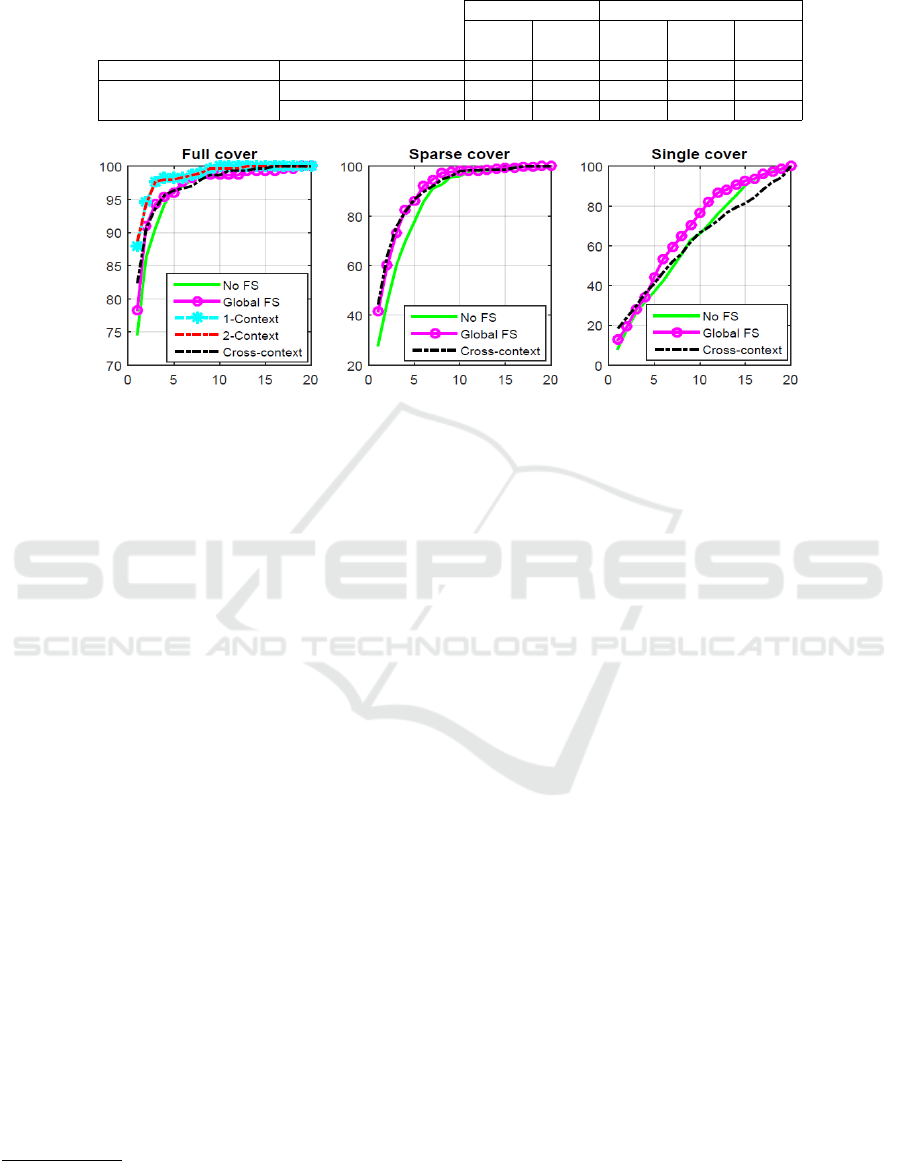
Table 1: Chart showing the Re-ID accuracy rates for Experiment 4.2.3. The accuracy rates shown in each cell represents
Rank-1 CMC rate.
Context-unaware Context-aware
No FS Global
FS
1-
context
2-
contexts
Cross-
context
Equal gallery samples (i) Full cover (5 contexts) 74.67% 78.33% 88.00% 88.67% 82.33%
Data deficiency of samples
(ii) Sparse cover (4 contexts) 28.00% 41.67% - - 44.33%
(iii) Single cover (1 context) 8.33% 12.67% - - 18.33%
Figure 4: Cumulative Matching Characteristic curves for rates for Experiment 4.2.3. 1-Context and 2-Context scenarios of
Context-aware cases are applicable only in Full cover case, where equal gallery samples are present.
the-art proposal in (Nambiar et al., 2017a). The last
method viz., Cross-contexts, execute feature selection
relying on the notion of context also by considering
the incomplete gallery scenario.
The Cumulative Matching Characteristic curves
and the Rank-1 Re-ID rates for the aforementioned
cases are shown in Figure 4 and Table 1 respectively.
The first observation drawn out is that the context-
aware case outperforms context-unaware cases. The
improvement in Re-ID performance by incorporating
feature selection scheme as well as context framework
is clearly observable. Within the context-unaware ca-
ses, we could observe that ‘Global FS’ improved the
results compared to the ‘no FS’.This clearly accentua-
tes the significance of Feature selection in Re-ID per-
formance. Second, by comparing the context-aware
cases, we can observe that the best results are reported
in the baseline 1-context/ 2-context scenarios, provi-
ded equal gallery samples are available (i.e., Full co-
ver). Nevertheless, in practical scenarios of sparse/
single cover, they are not applicable.
According to our new proposal of ’cross-context’,
we can observe that the rank 1 score of ‘Cross-
context’ outperforms both ‘no FS’ and ‘Global FS’, in
all the three gallery cover scenarios irrespective of the
gallery size in each context. Although in the Full co-
ver gallery case, this result is bit lower than the state-
of-the-art (Nambiar et al., 2017a) result, in the other
cases the results are highly promising and competi-
(Nambiar et al., 2017a) will not work due to the data defi-
ciency issue.
tive with respect to the classical context-unaware ca-
ses, showing the impact of cross-context analysis in
data deficiency practical situations. Thus, it is quite
informative to note that when the relevant features are
selected according the context by learning the feature
selection across various contexts, the Re-ID perfor-
mance can be improved. Since data deficiency in cer-
tain viewpoints are a big challenge in practical Re-ID
circumstances, cross-context customized FS approach
brings great significance into the paradigm.
The best Re-ID performance among the three gal-
lery settings was observed in the Full-cover gallery
context. This could be ascribed to the fact that there
are more and better examples to match to the test sam-
ple. Sparse cover produces worse results compared to
the former since there is no availability in the very
same context, instead it searches and finds the best
matching in four other different contexts. The worst
case is the Single cover scenario, where only a sin-
gle cover gallery (other than the test context) is pro-
vided, where always the matching is poor in terms of
the number of samples and quality of data, but still
outperforms the context-unaware case.
4.3 Experiment 2: Walking in Circular
Paths (Switching of Contexts)
We conducted another experiment as well, based on
the cross-context analysis. In this second case, we
experimented the complicated scenario of context
switching, which is basically change of view-points
within a gait cycle itself. As a simple instance of such
Cross-context Analysis for Long-term View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Soft-biometrics using Depth Sensor
111
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Re-identified kth rank
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
no cxt
#Test sample
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Re-identified kth rank
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
full
1 2 3 4 5 67
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
sparse
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
single
(a) Person#1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Re-identified kth rank
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
no cxt
#Test sample
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Re-identified kth rank
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
full
1 2 3 4 5 67
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
sparse
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
single
(b) Person#2
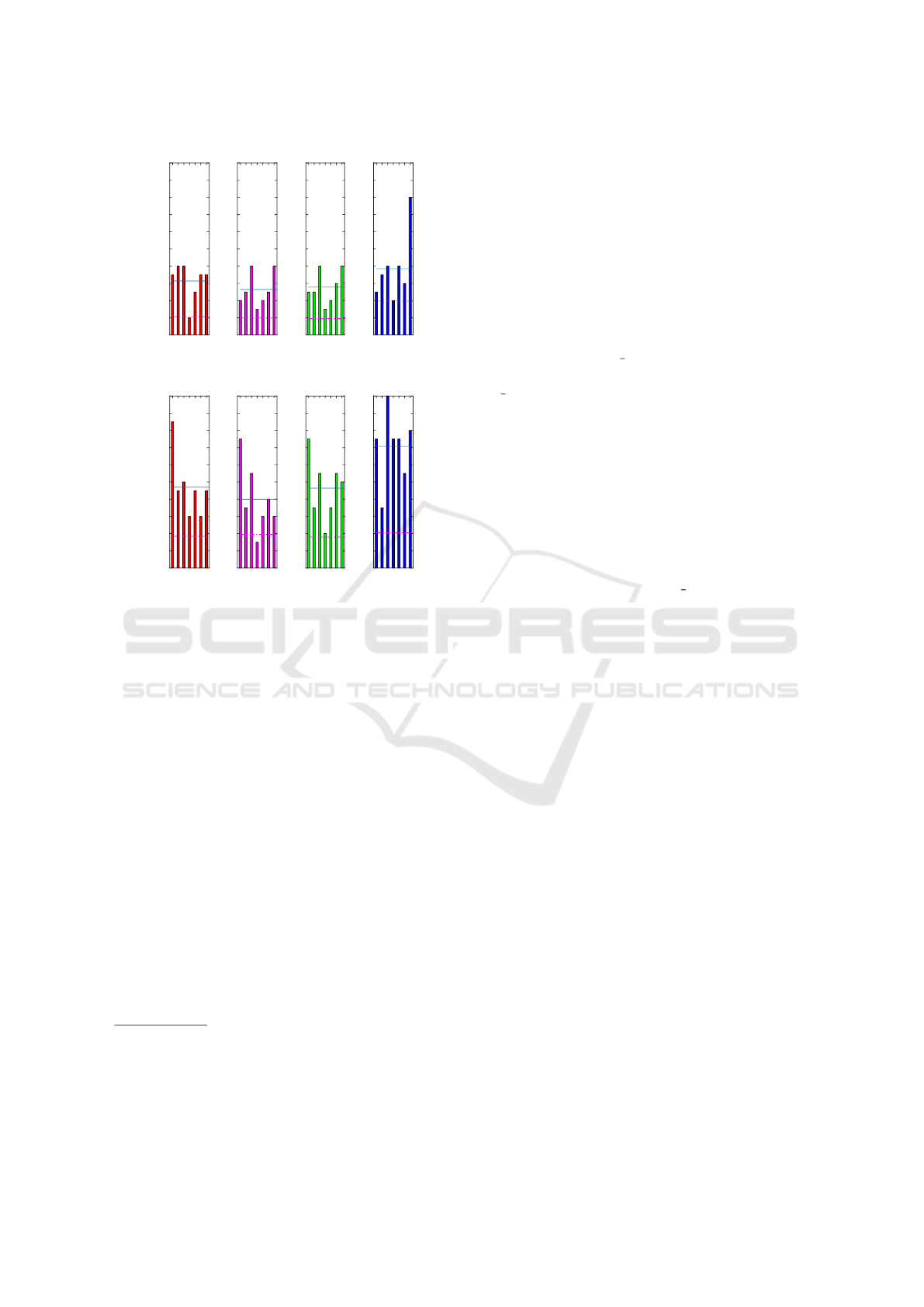
Figure 5: A case study of “switching the context”, carried
out upon two persons is depicted above. In each row, di-
agrams result from cross-contextual analysis (incomplete
gallery samples) in the order of no context, full, sparse and
single cross-context respectively. The mean and standard
deviation in each case is marked via the blue straight line
and magenta dash-dot line respectively. The best results are
associated with lower mean k-Rank.
a situation for our experiment, we used circular path
walkings of a subset of people who also have been a
part of the original Vislab KS20 dataset. For this pi-
lot study, we leveraged two people’s circular walking
sequences from the dataset.
Since the circular sequences of KS20 datasets
were acquired after a gap of one year, they clearly
ensured a long term Re-ID scenario, with drastic va-
riations in view-point. The circular walkings of two
people are used as the test sequences, and then ma-
tched against the linear training sequences of KS20
dataset
6
.
The results of the Re-ID performance of swit-
ching contexts incomplete gallery scenario via cross-
6
Regarding the circular path data, a full circle contains
five or six gait cycles, out of which only half of them were
considered, wherein the person walks towards the camera
(training set contains sequences towards the camera). Thus,
altogether seven gait cycles are extracted out of whole se-
quences of walking.
context are analysed in this experiment. Figure 5(a)
refers to the experimental results of Person #1 and Fi-
gure 5(b) refers to the experimental results of Person
#2. For a particular person, seven samples have been
obtained. Hence, we analyse the k-th rank at which
each sample of the person is correctly re-identified
(represented with individual bars). The mean (blue
straight line) and standard deviation(magenta dash-
dot line) are also depicted in the bar graph. Lower
the rank, better the performance.
We computed the Re-ID performances of context-
unaware scenario(‘no cxt’) (Context-unaware) vs.
full, sparse and single (Context-aware) scenarios.
‘no cxt’ scenario is the case where no notion of con-
text was incorporated, so that the system performs
as if the classical Re-ID models (with no splitting of
the data in the gallery). Among all the context-aware
Re-ID results, we can observe that the Re-ID perfor-
mance is in the descending order of Full, Sparse, and
Single respectively among the context-aware cases.
The gradual reduction in the performance is found to
be in accordance with the reduction in the number of
samples in the gallery. Hence, it clearly accentuates
the necessity for adequate number of training samples
in the gallery set. Regarding ‘no cxt’ scenario, it was
found to be underperforming compared to the full co-
ver case, which clearly underlines the significance of
the notion of context.
Person#1 and #2 are a woman and a man, respecti-
vely. Considering the relative population of women
and men in the dataset (16 men and 4 ladies), the over-
all Re-ID performance was found to be with lower k-
th rank Re-ID for Person#1, meaning that Re-ID of
the lady candidate was much easily done compared to
the man candidate.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we presented a novel method cal-
led ‘Cross-context ensemble fusion framework’-
a context-aware person Re-ID method- for re-
identifying people in a long term video surveillance
system. The key proposals of the architecture is to
facilitate cross-context analysis via feature selection
carried out across various contexts, and thus trying to
bypass the real-time Re-ID challenge of insufficient
data samples. In this regard, detailed analysis in terms
of different case studies viz., full, sparse and single
cover gallery were carried out. From the results, it
was observed that full gallery case performs the best
among the group, highlighting the importance of large
amount of training samples in Re-ID matching. Ho-
wever, in many practical cases the full gallery case is
VISAPP 2018 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
112

not-available. In these cases we have shown the ap-
plicability of the proposed cross-context analysis and
the advantages over the no-context case.
As a part of this study we carried out another
practical scenario of ‘Switching of contexts’ in in-
complete gallery samples, with the help of circu-
lar walking examples. Among the observations, we
could again observe the precedence of full cover case.
However, in both experiments, context-aware case
outperformed context-unaware case. Despite our tests
consider view-point as the contextual feature, we be-
lieve the method can be useful for the cross-context
analysis of other contextual features that are inhe-
rently pose invariant but suffer from heteroscedastic
noise sources, for instance distance, clutter or velo-
city. In future, we also envisage to learn contexts au-
tomatically (e.g., data clustering technique).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by the FCT
projects [UID/EEA/50009/2013], AHA CMUP-ERI/
HCI/0046/2013, doctoral grant [SFRH/BD/97258/
2013] and by European Commission project POETI-
CON++ (FP7-ICT-288382).
REFERENCES
Andersson, V. O. and de Ara
´
ujo, R. M. (2015). Person iden-
tification using anthropometric and gait data from ki-
nect sensor. In AAAI, pages 425–431.
Barbosa, I., Cristani, M., Del Bue, A., Bazzani, L., and Mu-
rino, V. (2012). Re-identification with rgb-d sensors.
In Computer Vision–ECCV 2012. Workshops and De-
monstrations, pages 433–442. Springer.
Bedagkar-Gala, A. and Shah, S. K. (2014). A survey of ap-
proaches and trends in person re-identification. Image
and Vision Computing, 32(4):270–286.
Chen, Y.-C., Zheng, W.-S., Lai, J.-H., and Yuen, P. (2016).
An asymmetric distance model for cross-view feature
mapping in person re-identification. IEEE Transacti-
ons on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology.
Dai, J., Zhang, Y., Lu, H., and Wang, H. (2017). Cross-
view semantic projection learning for person re-
identification. Pattern Recognition.
Gabel, M., Gilad-Bachrach, R., Renshaw, E., and Schuste,
A. (2012). Full body gait analysis with kinect. In An-
nual International Conference of the IEEE Engineer-
ing in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC).
Garcia, J., Martinel, N., Micheloni, C., and Gardel, A.
(2015). Person re-identification ranking optimisa-
tion by discriminant context information analysis. In
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on
Computer Vision, pages 1305–1313.
Geng, X., Smith-Miles, K., Wang, L., Li, M., and Wu, Q.
(2010). Context-aware fusion: A case study on fu-
sion of gait and face for human identification in video.
Pattern recognition, 43(10):3660–3673.
Gianaria, E., Grangetto, M., Lucenteforte, M., and Balos-
sino, N. (2014). Human classification using gait fe-
atures. In International Workshop on Biometric Au-
thentication, pages 16–27. Springer.
Gong, S., Cristani, M., Loy, C. C., and Hospedales, T. M.
(2014). The re-identification challenge. Person Re-
Identification, pages 1–20.
Leng, Q., Hu, R., Liang, C., Wang, Y., and Chen, J.
(2015). Person re-identification with content and con-
text re-ranking. Multimedia Tools and Applications,
74(17):6989–7014.
Lisanti, G., Karaman, S., and Masi, I. (2017). Multichannel-
kernel canonical correlation analysis for cross-view
person reidentification. ACM Transactions on Mul-
timedia Computing, Communications, and Applicati-
ons (TOMM), 13(2):13.
Nambiar, A., Bernardino, A., Nascimento, J. C., and Fred,
A. (2017a). Context-aware person re-identification in
the wild via fusion of gait and anthropometric featu-
res. In B-WILD Workshop at 12th IEEE International
Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recogni-
tion (FG).
Nambiar, A., Bernardino, A., Nascimento, J. C., and Fred,
A. (2017b). Towards view-point invariant person re-
identification via fusion of anthropometric and gait fe-
atures from kinect measurements.
Ross, A. A., Nandakumar, K., and Jain, A. (2006). Hand-
book of multibiometrics. 6.
Whitney, A. W. (1971). A direct method of nonparametric
measurement selection. IEEE Transactions on Com-
puters, 100(9):1100–1103.
Zhang, L., Kalashnikov, D. V., Mehrotra, S., and Vaisen-
berg, R. (2014). Context-based person identification
framework for smart video surveillance. Machine Vi-
sion and Applications, 25(7):1711–1725.
Cross-context Analysis for Long-term View-point Invariant Person Re-identification via Soft-biometrics using Depth Sensor
113
